D1.2 Protein synthesis
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is transcription?
It is the process in which an RNA strand is created from a DNA template
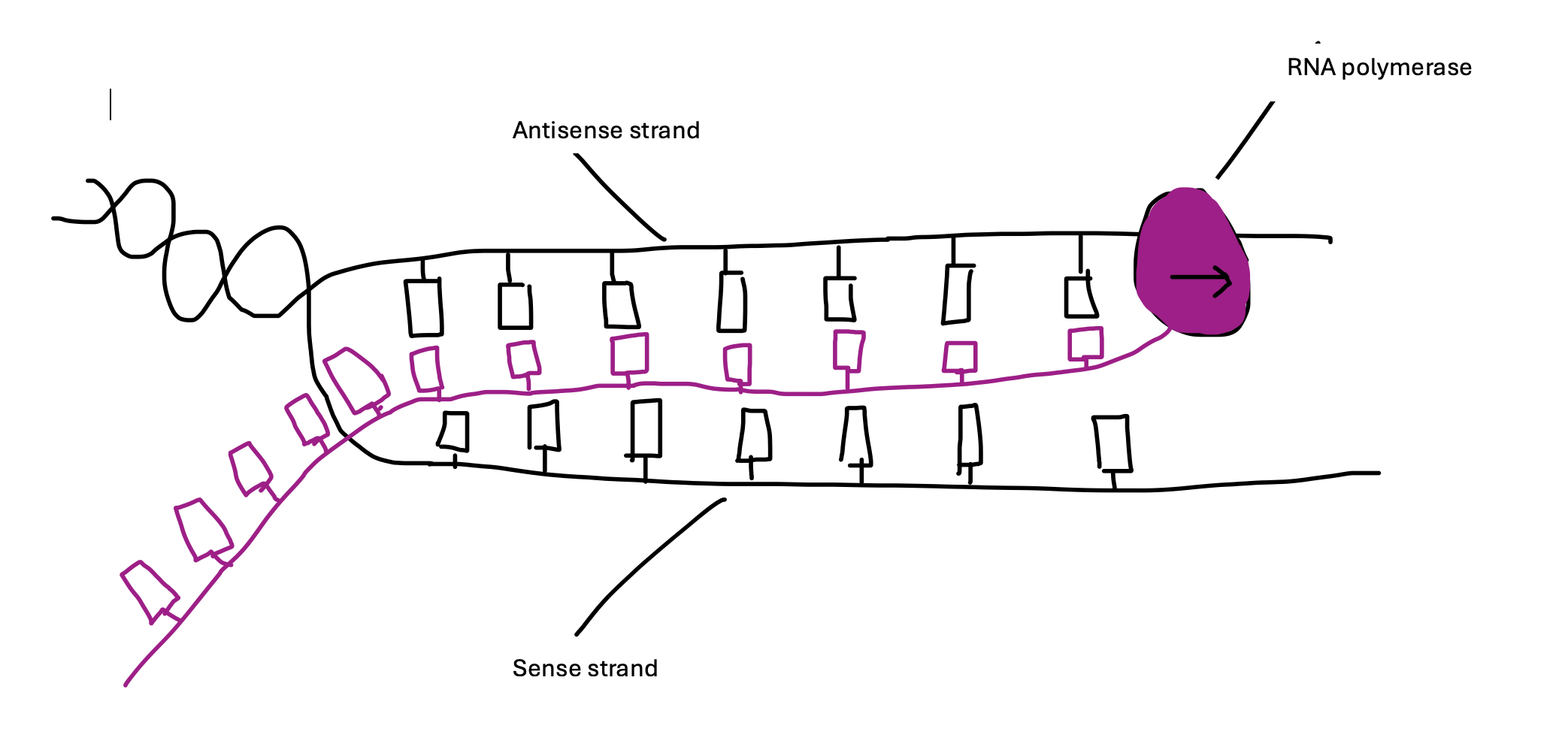
How are the strands separated in DNA for transcription to occur?
RNA polymerase separates the strands and creates the new RNA strand from the existing DNA.
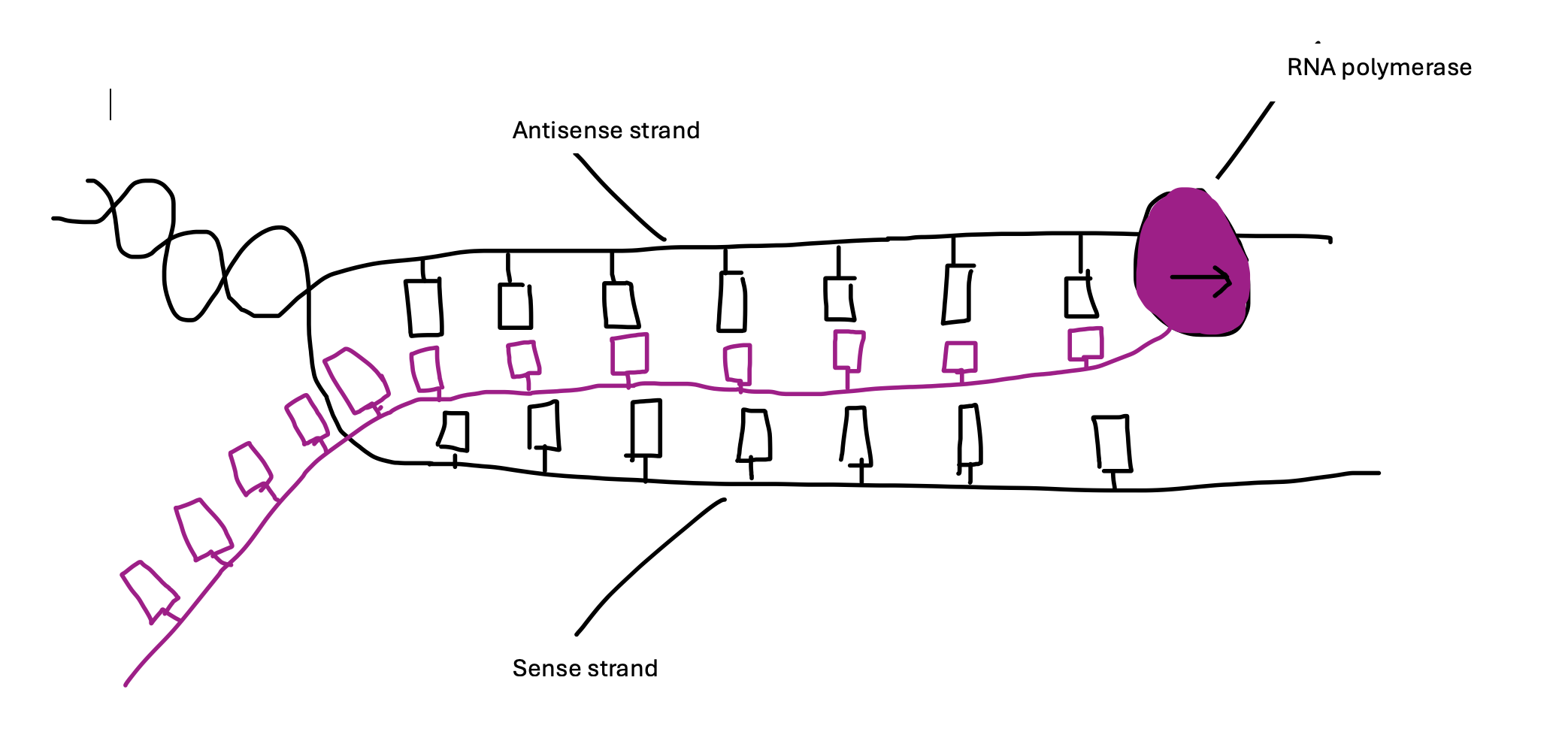
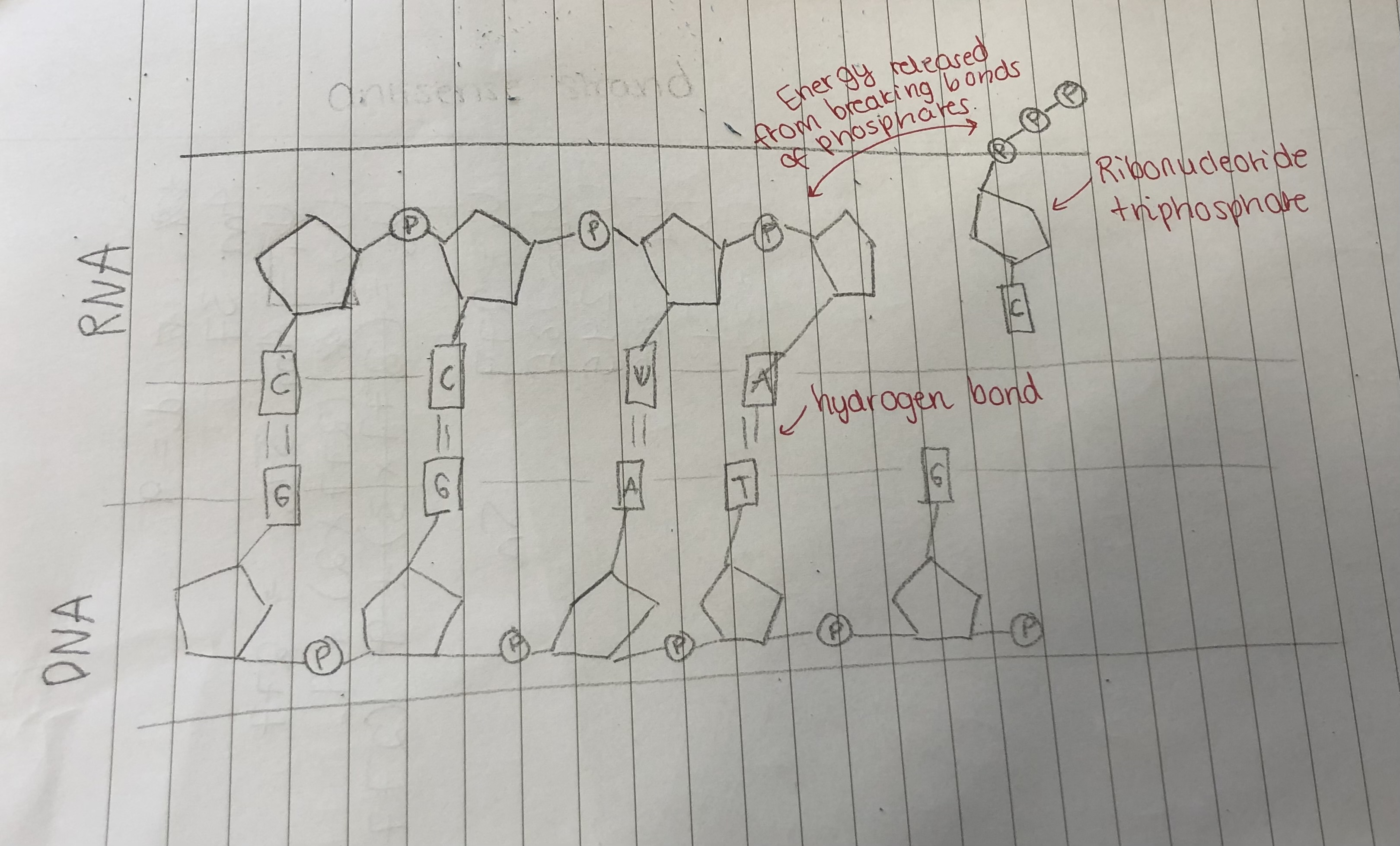
How does RNA polymerase create the RNA strand?
RNA polymerase gets the complementary base pairs to match the DNA strand, which are ribonucleotide triphosphates. These are covalently bonded together, with the energy that comes from releasing the two phosphates which aren’t needed.
What occurs once the RNA sequence has been synthesized?
RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA antisense strand. The RNA detaches from the DNA (the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs break), and the double helix between the two seperated DNA strands reforms
How can DNA be stabilized to prevent genetic changes from occurring during transcription?
The DNA strands are only separated for a short amount of time, and they pair up again after transcription has occurred, and the hydrogen bonds form between the complementary base pairs
What is translation?
This occurs after transcription, when the mRNA strand travels out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm, where a polypeptide chain is created
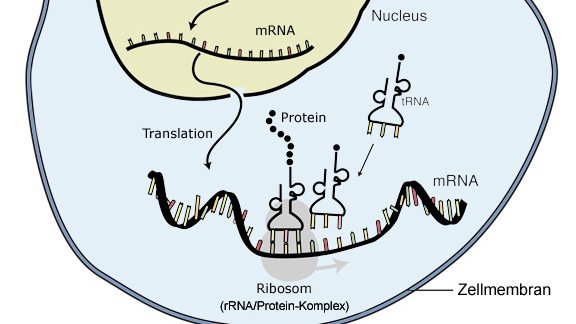
How does the ribosome bind to the RNA strand?
It is composed of a large and a small subunit. These assemble onto the RNA and act as the binding site between the tRNA codons and the mRNA. The ribosome creates the peptide bonds between each amino acid.
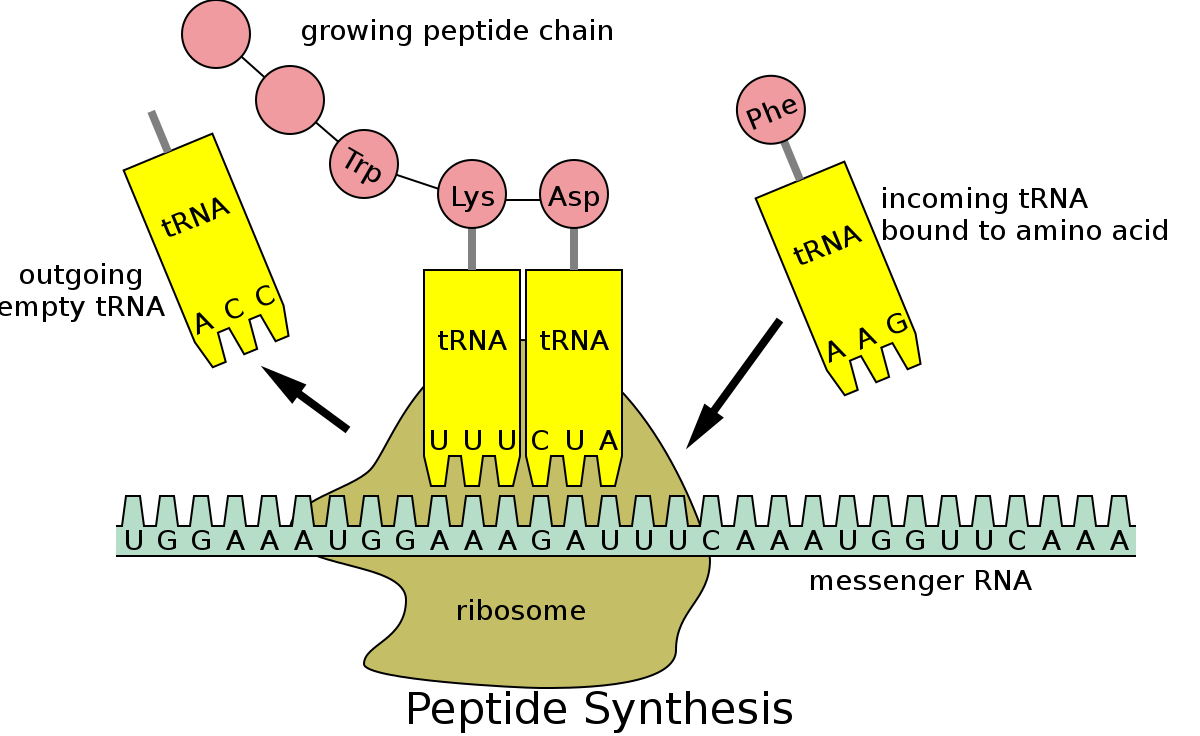
What is tRNA and the codons it has?
tRNA brings amino acids to the mRNA in order to create the polypeptide chain from the sequence. tRNA molecules have an anticodon, which are three bases that bind to the complementary codon on the mRNA strand.
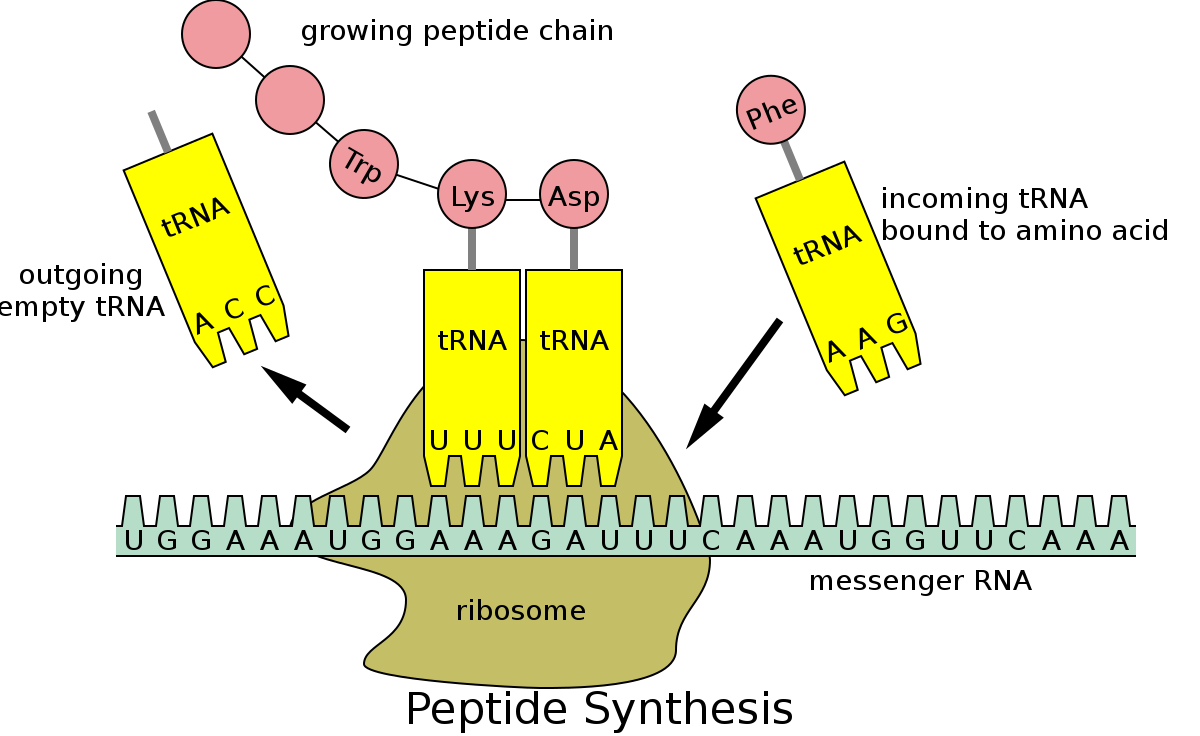
What are codons?
These are triple bases. The codons on the mRNA and the anti-codons on the tRNA are complementary. Three nitrogenous bases make up a codon, which codes for one amino acid
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code are the instructions within a gene. Codons, which are three nucleotides, can code for a specific amino acid (there are 20 amino acids). Different codons can translate for the same amino acid
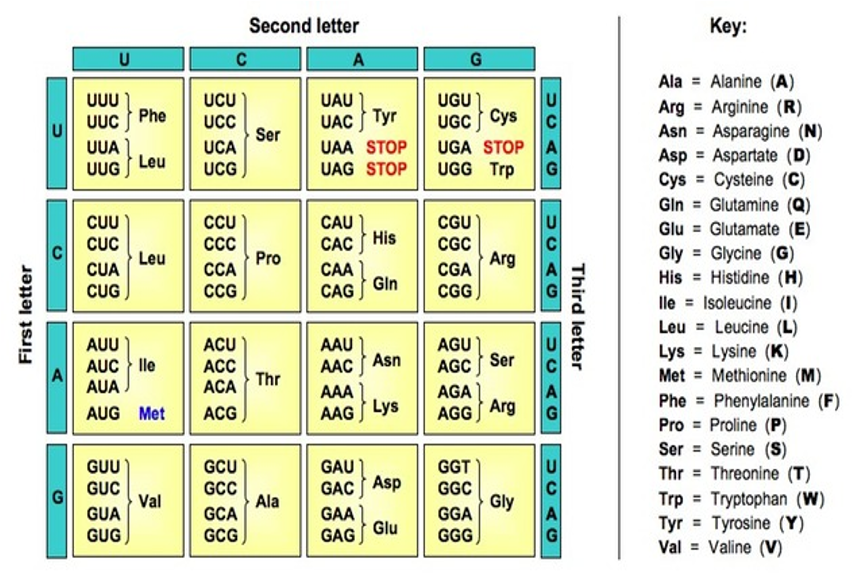
What are start and end codons?
The start codon is AUG and there are a couple of end codons. The ribosome moves along the RNA strand until it reaches the start codon, and only then does tRNA start to bring the linking amino acids. This stops when the ribosome reaches one of the end codons
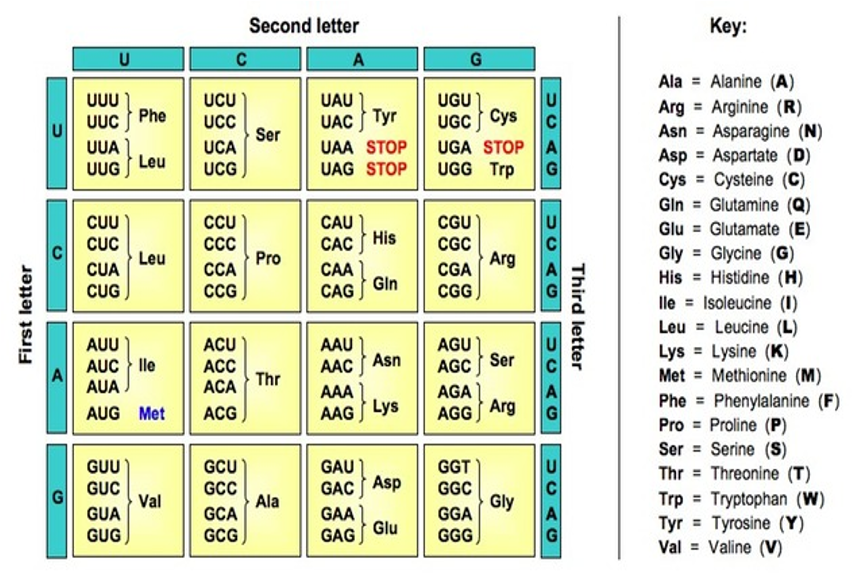
Summarize the whole translation process
The mRNA travels to the ribosome. It attaches to the small subunit. The ribosome travels along it until it reaches the start codon. This is AUG. Then the large subunit attaches to the ribosome and the tRNA starts attaching with the codon complementary base pairs. As soon as one tRNA has brought an amino acid, the next tRNA arrives and the large subunit of the ribosome creates peptide bonds between these amino acids. The tRNA is released and the next one arrives and binds to the amino acid. This ends up creating a long polypeptide chain, until the ribosome reaches the end colon on the mRNA strand, and then the ribosome dissembles again, and the polypeptide chain is released
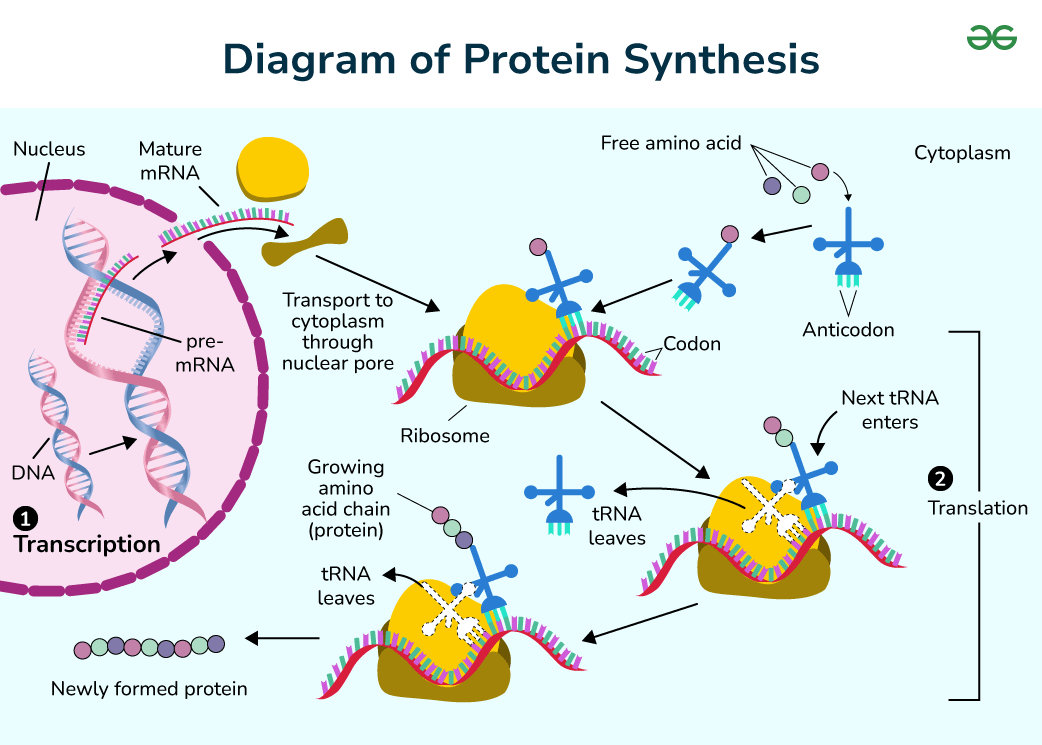
What is a mutation?
A permanent change in the base sequence of the DNA. This may cause a gene to be wrongly expressed
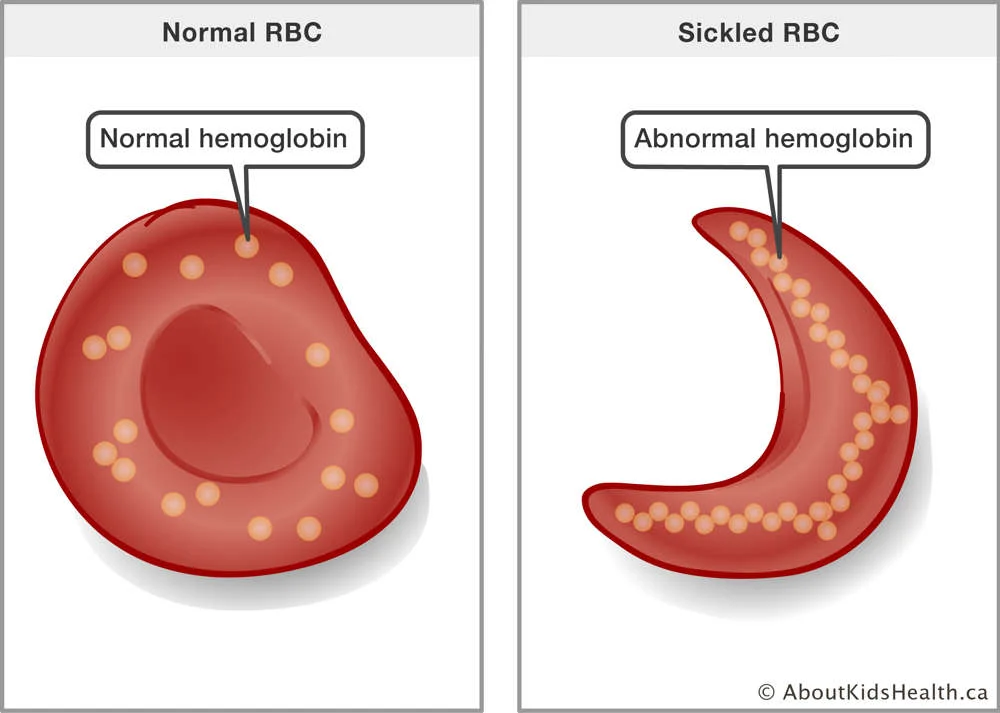
Give an example of a mutation
Sickle cell disease. This occurs because of a single base mutation, and leads to haemoglobin having the wrong shape, which means that red blood cells have a curved shape, can’t carry oxygen as well and aren’t flexible anymore. This causes blood to clot and blocks blood flow