ceutics parenterals 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
what is a pyrogen
bacterial endotoxins; large molecules of lipoglycans; cause fever in excessive amounts
t/f: parenterals are sterile and considered pyrogen free if under the endotoxin limit (EU)
true
what is an endotoxin limit
endotoxin concentration that must not be exceeded in parenterals
parenterals must be packaged in __________ containers
hermetically sealed (airtight; protected from environment)
what does "pyrogen free" imply in parenterals
there may be pyrogens present but they do not exceed the endotoxin limit
can coloring agents be used in parenteral preparations
no
why are parenteral preparations used over other dosage forms?
1. rapid action
2. patient is unconscious/uncooperative/ cant take it orally
3. drug is ineffective orally (unstable in GI, poor absorption)
R= rapid action
U= unconcious
G= GI unstable
what are the 5 official USP injectable products
1. injection (liquid drug solution)
2. for injection (solid drug for vehicle)
3. injectable emulsion (drug dispersed in emulsion)
4, injectable suspension (drug dispersed in medium)
5. for injectable suspension (solid drug for suspension)
referring to the 5 types of USP injectable products, what does "for" mean
this is a solid that must be dissolved or suspended before injecting. it is not immediately mixed with the solvent because of stability and shelf life
IV route advantages and disadvantages
adv:
1. rapid action= no need for absorption
2. optimum blood levels in short time
dis:
1. non-removable
2. possible thrombus/embolus
thrombus vs embolus
Thrombus- blood clot
Embolus- a thrombus that is not stationary and travels
causes of thrombus/embolus
1. IV needles or catheters damaging walls of vein
2. irritation of the vein by the drug/ foreign particles
3 things required prior to injection
1. sterile product
2. sterile syringe
3. disinfected injection site
3 injection methods
1. manual
2. infusion pump (hospitals)
3. patient controlled devices
t/f: injectable solutions are preferred to be aqueous to mix readily with blood
true
IM advantages and disadvantages
adv:
1. less rapid than IV
2. longer duration of action than IV
3. can be aqueous, oil, solution[fastest absorption], or suspension
dis:
1. cannot be removed
if a drug requires a longer duration of action and later onset, would you give it IV or IM?
IM; less rapid and longer duration
t/f: both IV and IM can be given as aqueous, oil, solution, or suspension
false. IV is preferred to be aqueous so that it mixes with blood. IM can be any of them
what cannot be given SQ
-volume >2mL
-irritating drugs/ thick suspensions
potential side effects of giving irritating drug SQ
1. induration: skin hardening
2. sloughing: skin depression
3. abscess: pus
4. pain
does the physical form of the product (ex: suspension vs solution) have effect on drug onset and duration?
yes.
aqueous= fast acting
non-aqueous= long action
which physical form of a preparation has the fastest action
solution
WFI
-purified by:
-requirements:
-Purified by distillation or by reverse osmosis
-MUST be pyrogen free (not required to be sterile)
-Should be stored in tight, STERILE, pyrogen free containers
T/F: WFI does not have to be sterile nor stored in sterile containers
false. it does not have to be sterile, but it must be stored in sterile containers
Sterile WFI
-pyrogen free (like WFI)
-for SMALL volume parenterals
t/f: WFI can be used for small volume parenterals
false. must be sterile or bacteriostatic WFI
bacteriostatic WFI
-WFI+ antimicrobial
-NOT STERILE
- small volume parenterals
-NOT FOR NEONATES
USP labeling "not for neonates" is placed on which injection vehicles? why?
-toxicity due to benzoyl alcohol
bacteriostatic WFI, bacteriostatic NaCl
NaCl injection
STERILE NaCl in WFI
-for sterile solutions/susps an IV line flush
bacteriostatic NaCl injection packages at ___mL or less
30
what is bacteriostatic NaCl used for
IV line flush
t/f: bacteriostatic NaCl injection can be used as IV line flush in neonates
false. contains benzoyl alcohol which is toxic to neonates due to limited liver detoxification
as little as ___mL/kg of benzoyl alcohol could kill a neonate
11mL/kg/d
Ringer's Solution
-sterility?
-composition?
-use?
sterile WFI
NaCl, KCl, CaCl2
drug vehicle, electrolyte replenisher, fluid extender
lactated ringer's solution
-composition
-use?
same as ringer's + sodium lactate
-fluid, electrolyte replenisher, alkalizer (acts as buffer in acidosis)
examples of non-aqueous vehicles
vegetable oils, glycerin, PEGs, alcohol
properties of non-aqueous vehicles
1. non-irritating, nontoxic
2. pharmacologically inert
3. HIGH bp
4. LOW vapor pressure
5. constant purity
describe boiling point and vapor pressure of non-aqueous vehicles
high boiling point to withstand sterilization and low vapor pressure
added substances in parenterals must have
NO THERAPEUTIC EFFECT and harmless
why does USP require a preservative in multidose containers
to prevent microbial contamination during repeat drug removals
why is air in vials sometimes replaced with inert gas
to reduce oxidation rate of drug by removing the air (with O2) and adding inert gas like N or He
sterilization is defined as
destruction or removal of all living organisms and their spores
what are the 5 methods of sterilization
Steam/moist heat
Dry heat/hot air
sterile filtration
gas
radiation
sterilization method of choice for thermostable products
steam sterilization or dry heat
steam sterilization
-temps?cycles?
15 psi steam, 121C, 20 min
*lag times(small=5-10mins, large 20+mins)
lag times for steam sterilization
small: 5-10mins
large: 20+mins
t/f: steam sterilization has a higher temp than dry heat
false. steam=121C, dry heat=170C
dry heat requirements
160-170C for >2 hours
-thermostable materials
-for materials not fit for moisture (oils, glycerin, glassware)
examples of products for dry heat sterilization
oil, glycerin, heat stable powders, glassware, surgical instruments
describe sterile filtration
bacterial removal by adsorption on filter or retention due to small pore size
sterile filtration is affected by
1. electrical charge (of filter and/or bacteria)
2. pH
3. temp
4. pressure/vaccuum
filter pore size for sterile filtration
0.2 micrometers
RBC size? bacteria size? cornoa virus size? which one of these does not pass sterile filtration
RBC: 6.5 micrometer
bacteria: 0.2 micrometer
corona virus: 0.1 micrometers
-> virus will pass bc filter is 0.2 micrometers
advantages and disadvantages of sterile filtration
adv:
-quick, inexpensive
- good for thermolabile materials (cant use heat)
-removes BOTH living and dead
- can be used on line during filling
dis:
-fragile membranes
-possible drug adsorption onto filter
what is gas sterilization used for
medical/surgical supplies; thermolabile drugs
which forms of sterilization cannot be used for thermolabile drugs
steam and dry heat
gas sterilization uses
ethylene oxide diluted with CO2 or freons
gas sterilization disadvantages
1. highly flammable
2. more variable than steam (temp, gas concentration, humidity)
3. assure absence of chemical rxn btwn drug and gas
4. must have low amounts of gas in final product
radiation sterilization
-via gamma rays
-need highly specialized personnel; expensive
biological indicator for sterility parameter
adding microorganisms resistant to a particular sterilization process used to monitor a sterilization cycle
main forms of biological indicators for sterilization
1. spores on a carrier (permeable membrane)
2. spores in bulk
bacillus stearothermophilus
biological indicator of sterilization for moist heat or EtO (bc highly resistant)
bacillus subtilis
biological indicator for dry heat (bc resistant to dry heat)
effectiveness of thermal sterilization is determined by
F value= time of thermal death=time required to kill a particular organism
in ALL sterilization processes, microorganisms will die according to a __________ relationship between concentration of LIVING microbes and _____
logarithmic; time of exposure to treatment
D-value
amount of time required to kill 90% (or 1 log) of microorganisms present
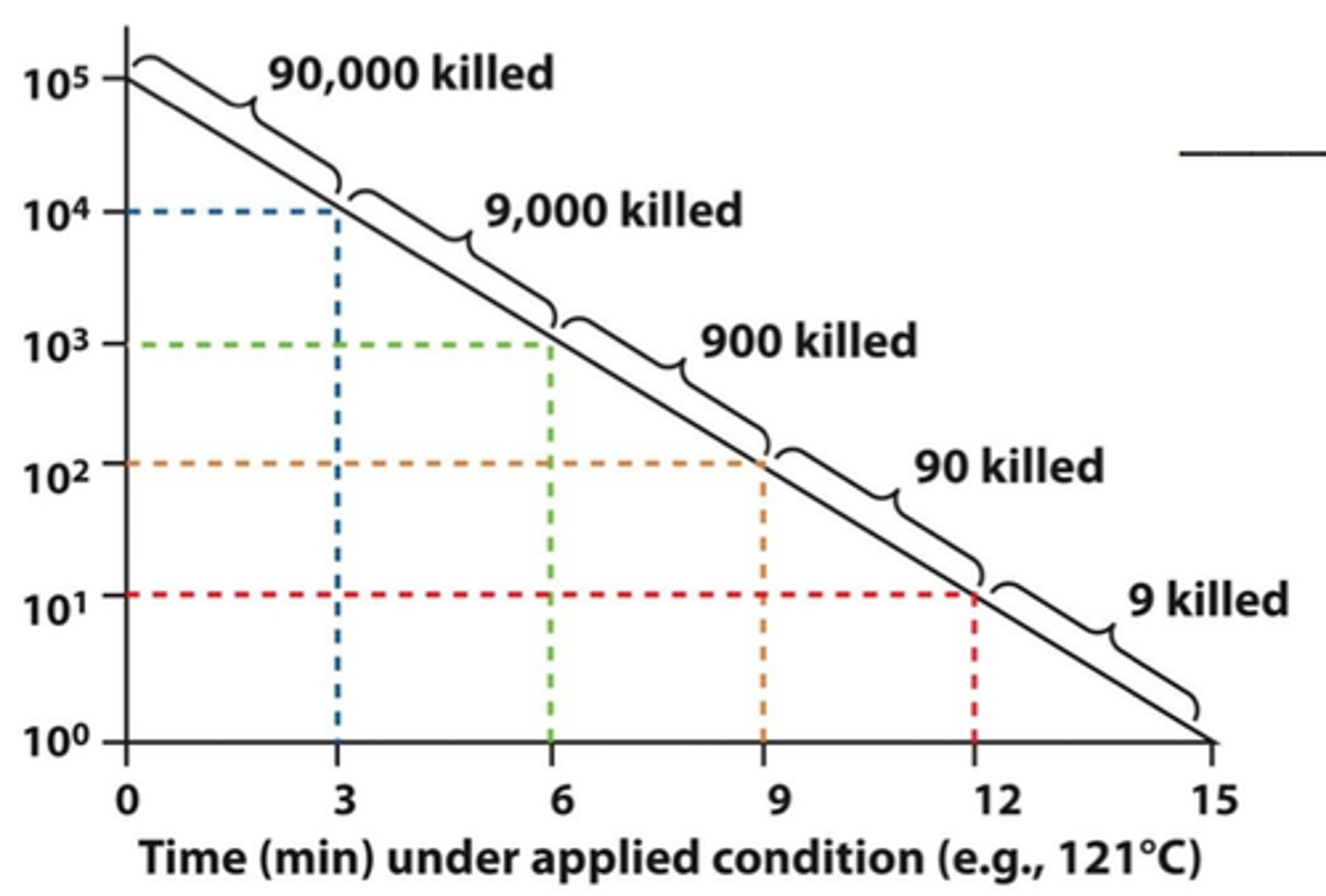
interpret a d value of 6
takes 6 minutes to kill 90% (or 1 log = 10) of microbes
equation used to relate F0 (time to kill organism) to D (time to kill 90%)
F= D (logA-logB)
A= initial population
B= final population
what temp does the d value refer to
121C
if D=1 min, A=10^6 and B=10^-6, what is F0?
F0= D (logA-logB)
F0= 1 (6--6)= 12 minutes
what is the time for a 12-D process to occur if the D-value is 0.21 minutes
12-D means reduced by 12 logs
F0= 0.21 (12)= 2.52 minutes
lipopolysaccharides can be classified as
pyrogens/endotoxins
t/f: pyrogens are organic and could therefore be oxidized
true
how can pyrogens be removed
fractional distillation
describe USP pyrogen test
1. healthy rabbits-> control and test
2. pyrogen free needles, glassware
3. warm product to 37C
4. inject 10mL/kg/10min into ear vein of 3 rabbits
5. record temp at 30 minute intervals, 1-3 hours
PASS: no rabbits temp raises more than 0.5C
-if temp rises, continue test with 5 more rabbits
PASS-> if LESS THAN 3 of 8 rabbits show temp rise
PASS-> sum of temps are NOT >3.3C
LAL test
limulus amebocyte lysate; blood cells derived from the horseshoe crab used to detect and quantify bacterial endotoxins
-has enzymes that coagulate with lipopolysaccharides
which endotoxin test is most sensitive
LAL test (compared to rabbit test)
t/f: because the LAL test is the most sensitive, it is used for all parenteral testing
false. some parenterals cannot be used with LAL because the active ingredient interferes with the outcome
(ex: oxacillin sodium and vancomycin HCl)
examples of drugs tested with LAL
diphenhydramine HCl, ephedrine HCl, thiamine HCl
how is the following prepared for parenteral sterilization:
1. aseptic suites
2. sanitized equipment
3. sterilized items
1. aseptic suites= UV lights, filtered air
2. sanitized equipment= equipment lyophilizers
3. sterilized items
describe validation methods for sterility
=evaluation of 3 consecutive production batches
= extensive sampling-> beginning`, middle, end
which department reviews routine production monitoring for sterile products
quality control department
air quality of 1) compounding room and 2) aseptic filling rooms
1) compounding room= class 10,000
2) aseptic filling room= class 100 (stricter, sterile, no more than 100 particles)
ideal vs normal manufacturing sequence
ideal: (drug and additive)-sterile filtration-aseptic fill- terminally sterilize
normal= same as above but no terminal sterilization
examples of drugs requiring isolated manufacturing facilities
penicillins, cephalosporins, cancer agents
t/f: osmotic pressure is a colligative property of drugs
true
osmotic pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane

lyophilized products
products that have been freeze dried. Lyophilization removes water from a product, which stabilizes it and extends its shelf life
filling area for injections is supplied with.... to control for particulates
1. HEPA filter
2. direct laminar airflow
3. glass washed 3x with WFI and dry heat sterilized
4. garbing
why is control for particulates in injections important?
may cause thrombi or vessel blockage
volume of single dose injectables
0.5 to 2.0 mL
multiple dose containers usually contain _______________. volume?
antibacterial preservatives; 30-50mL
why would tubing length be reduced for an adsorbent small dose drug
sometimes drugs adsorb onto tubing. lowering the SA/reducing length makes it less likely for drug to adsorb
(ex: nitroglycerin and PVC)
USP labeling: "sterile" was eliminated from all labels except _____
sterile WFI
USP labeling guidelines for sterile products
1.name
2. liquid product drug %
3. dry product amount of API
4. route of administration
5. storage conditions
6. expiration date
7. manufacturer/distributor
8. lot#
large volume parenterals are >___
100mL
large volume parenterals examples
water, electrolytes, caloric requirements
who are large volume parenterals for
1. unconscious
2. unable to take fluids orally
3, severe loss of fluid/electrolytes
replacement therapy
administration of a naturally occurring substance that the body is not able to produce in adequate amounts to maintain normal function (ex: water, electrolytes)
=uses large volume parenterals
maintenance therapy
few days: water, dextrose, Na, K
weeks: total parenteral nutrition