🧠Psych Lecture 1- Mood Disorders Flashcards (part 2)
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
An 62-year-old female with a recent history of hypertensive emergency is being started on an antidepressant. Which of the following medications should be avoided?
• A) Sertraline • B) Mirtazapine • C) Fluoxetine • D) Desvenlafaxine • E) Fluvoxamine
D;Because SNRIs (venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, etc.) can raise blood pressure, they should be avoided in patients with a history of hypertensive crisis/emergency.
An 18-year-old male with MDD reports forgetting to take his antidepressant 2-3 times per week. Which of the following medication would be best to minimize withdrawal and maintain more stable blood levels? • A) Paroxetine • B) Mirtazapine • C) Fluoxetine • D) Sertraline • E) Aripiprazole
✅ Correct Answer: C) Fluoxetine
Because of its long half-life, fluoxetine is least likely to cause withdrawal symptoms if doses are missed and helps maintain more stable drug levels.
When should you consider stopping antidepressant treatment?
When the patient has been in remission for \sim1 year and has a low risk of recurrence or severe depression.
When should you consider switching antidepressants?
If the patient has intolerance OR no clinically significant response (at least partial) after >6 weeks at a therapeutic dose.
When should you consider augmenting antidepressant therapy?
If the patient has only a partial response, or if they have treatment-resistant or refractory depression.
How does ECT treat depression?
Electrical current —> induce a seizure in the sedated patient’s brain.
What is ECT the most effective treatment for?
Severe depression.
When is ECT especially indicated?
severe depression with suicidality
mania
pregnancy
What are the main side effects of ECT?
Headache and memory disturbances.
How does TMS treat depression?
Magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in mood-control brain regions.
What conditions is TMS FDA-approved for?
Depression (poor response to meds)
Migraines
OCD
What are the main side effects of TMS?
Headache and lightheadedness
Name 4 supplements that may support mood in depression.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids 🐟 – Supports heart & brain health; mood stabilizing
Magnesium ⚡ – Calms nerves, aids muscle & nerve function
Vitamin B12 💉 – Needed for RBCs & nerve health; low levels → depression, neuropathy
Folate (Vitamin B9) 🌿 – Supports DNA synthesis & mood; low levels linked to depression
Which herbal supplement is widely used for mild to moderate depression but has drug–drug interaction risks?
St. John’s Wort.
Which compound, also known as SAMe, has been studied as a mood support supplement?
S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe).
According to DSM-5, how many symptoms must be present to diagnose PMDD?
Five or more symptoms during the week prior to menses, resolving within a few days after menses begins.
Can PMDD symptoms be attributed to another psychiatric illness?
No — they must not be explained by another disorder.
What are recommended treatments for mild PMDD symptoms?
Exercise 🏃♀ – Improves mood & reduces PMS symptoms
Relaxation Techniques 🧘♀ – Lowers stress and anxiety
Chasteberry 🌿 – Balances hormones; helps with PMS & breast tenderness
Evening Primrose Oil 🌸 – May reduce breast pain & mood swings
Vitamin B6 💛 – Supports neurotransmitter balance; may ease irritability
Vitamin E 🌻 – Antioxidant; helps with breast tenderness
Magnesium ⚡ – Reduces bloating, cramps, and mood symptoms
What is the treatment of choice for moderate PMDD symptoms?
SSRIs (e.g., sertraline, citalopram).
How can SSRIs be administered for PMDD treatment?
Either continuous therapy or intermittent therapy
(day 14 or luteal phase only)
How is bipolar characterized?
severe mood swings btw depression and elation → remission—> reoccurrence
What are the types of bipolar disorders?
Bioloar 1 (mania)
Bipolar 2 (hypomania)
Cyclothymia
Which neurotransmitter systems are dysregulated in bipolar disorder?
Dopamine and serotonin systems.
What is the average age of onset for bipolar disorder?
25 years.
How does childhood-onset bipolar affect prognosis?
It has a poorer prognosis.
What symptom does bipolar most often start with?
Depression.
What percentage of patients with a single manic episode are likely to have another?
90%.
What defines rapid cycling in bipolar disorder?
>4 episodes per year
Which substance can mimic bipolar symptoms?
Cocaine.
What is the first priority in treating Bipolar I disorder?
Patient safety
(because the most common complication is suicide)
When should a patient with Bipolar I be hospitalized?
At risk for suicide or homicide
In need of diagnostic procedures
If symptoms are rapidly progressing
What is the overall treatment goal in Bipolar I?
The goal is to achieve and maintain a stable (euthymic) phase, preventing mood swings and relapses to support long-term health and quality of life.
How long must manic symptoms last to diagnose bipolar I?
At least one week.
What exception allows mania to be diagnosed without a full week of symptoms?
If hospitalization is necessary.
How many symptoms are required during a manic episode if mood is elevated/expansive?
Three symptoms.
How many symptoms are required if mood is irritable?
Four symptoms.
What are some DSM-5 symptoms of mania? (*7)
🌪 Mania Symptoms — “DIG FAST”
🎯 D – Distractibility (easily sidetracked)
💸 I – Indiscretion / Risky behavior (spending, sex, drugs, driving)
😎 G – Grandiosity / Inflated self-esteem
💡 F – Flight of ideas / Racing thoughts
⚡ A – Activity increased (goal-directed, social, sexual, work)
🌙 S – Sleep decreased (feels rested after little sleep)
🗣 T – Talkative / Pressured speech
What must the mood disturbance cause to meet criteria?
Marked impairment in social or occupational functioning, or hospitalization.
How many lifetime manic episodes are required to diagnose bipolar I disorder?
At least one.
Which psychiatric disorder has the highest rate of suicide (15%)?
bipolar
What is DIGFAST?
An acronym for the symptoms of a manic episode, including Distractibility, Indiscretion/impulsivity, Grandiosity, Flight of ideas, Activity increase, Sleep deficit, and Talkativeness.

How long must hypomanic symptoms last to diagnose bipolar II?
At least 4 consecutive days, most of the day, nearly every day.
How many symptoms are required if the mood is elevated/expansive?
How many symptoms are required if the mood is only irritable?
Three symptoms; Four symptoms
What type of change must the episode be associated with?
A clear change in functioning that is uncharacteristic of the individual.
**Is hypomania severe enough to cause marked impairment or hospitalization?
No. If psychotic features are present, the episode is considered manic instead.
What is the first-line mood stabilizer for Bipolar I? Why? Name an alternative.
Lithium carbonate (300–900 mg/day)
b/c it protects against suicide.
Can use Carbamazepine as an alternative
What protective effect does lithium have?
It reduces suicide risk.
What labs must be monitored on lithium? (*4)
Thyroid (TSH/T4)
Kidney (CMP, UA)
CBC
EKG
What are common side effects of lithium? (*7)
Hypothyroidism
Tremor/shakiness
Mild GI upset
Polydipsia
Parkinsonian effect
Weight gain/diabetes,
drug-drug interactions
What is valproic acid?
A mood stabilizer used to treat bipolar disorder.
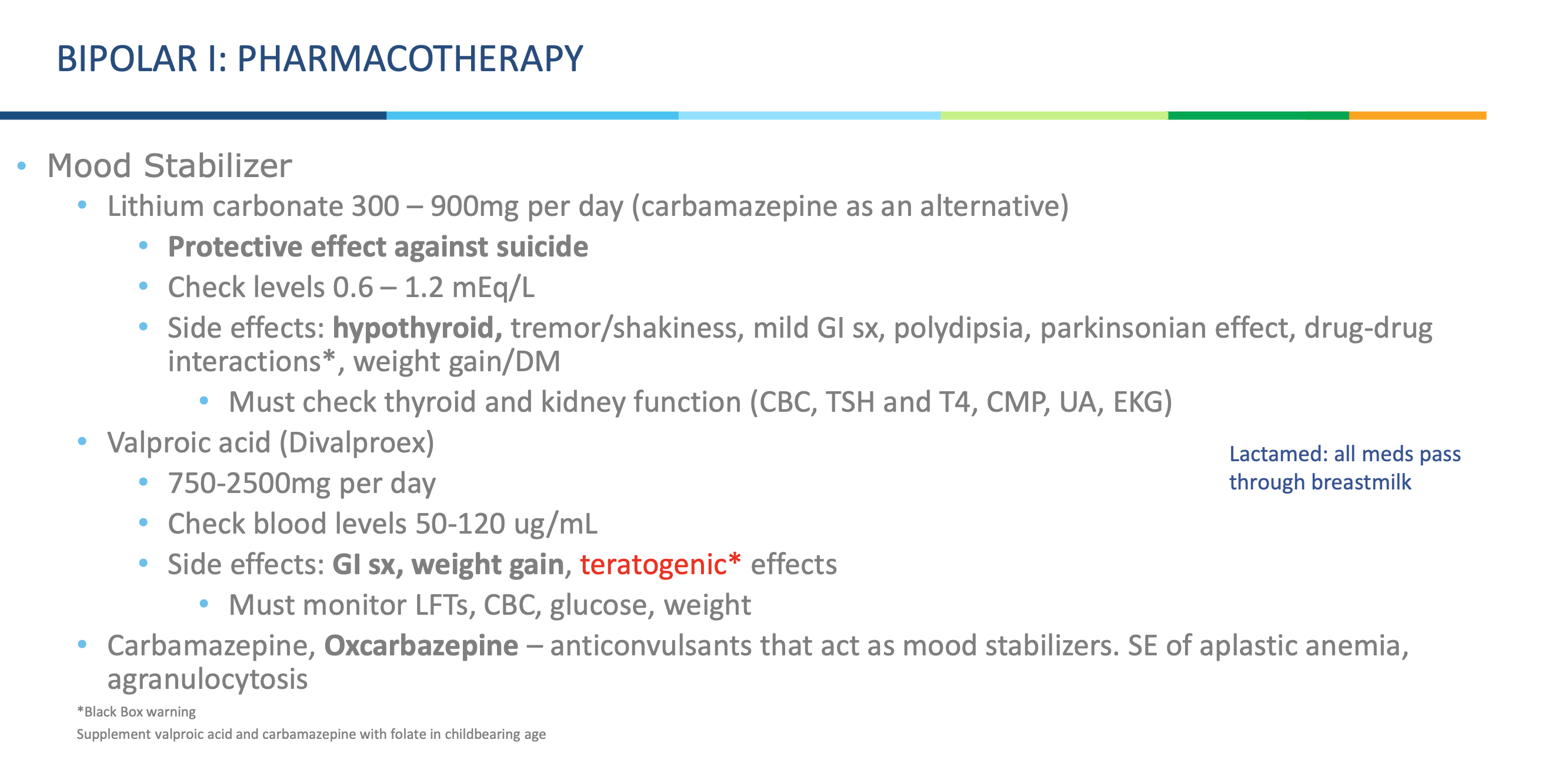
What are side effects of valproic acid?What should you monitor?
GI upset
weight gain
teratogenic effects (harmful to baby)
**Must monitor LFTs, CBC, glucose, weight.
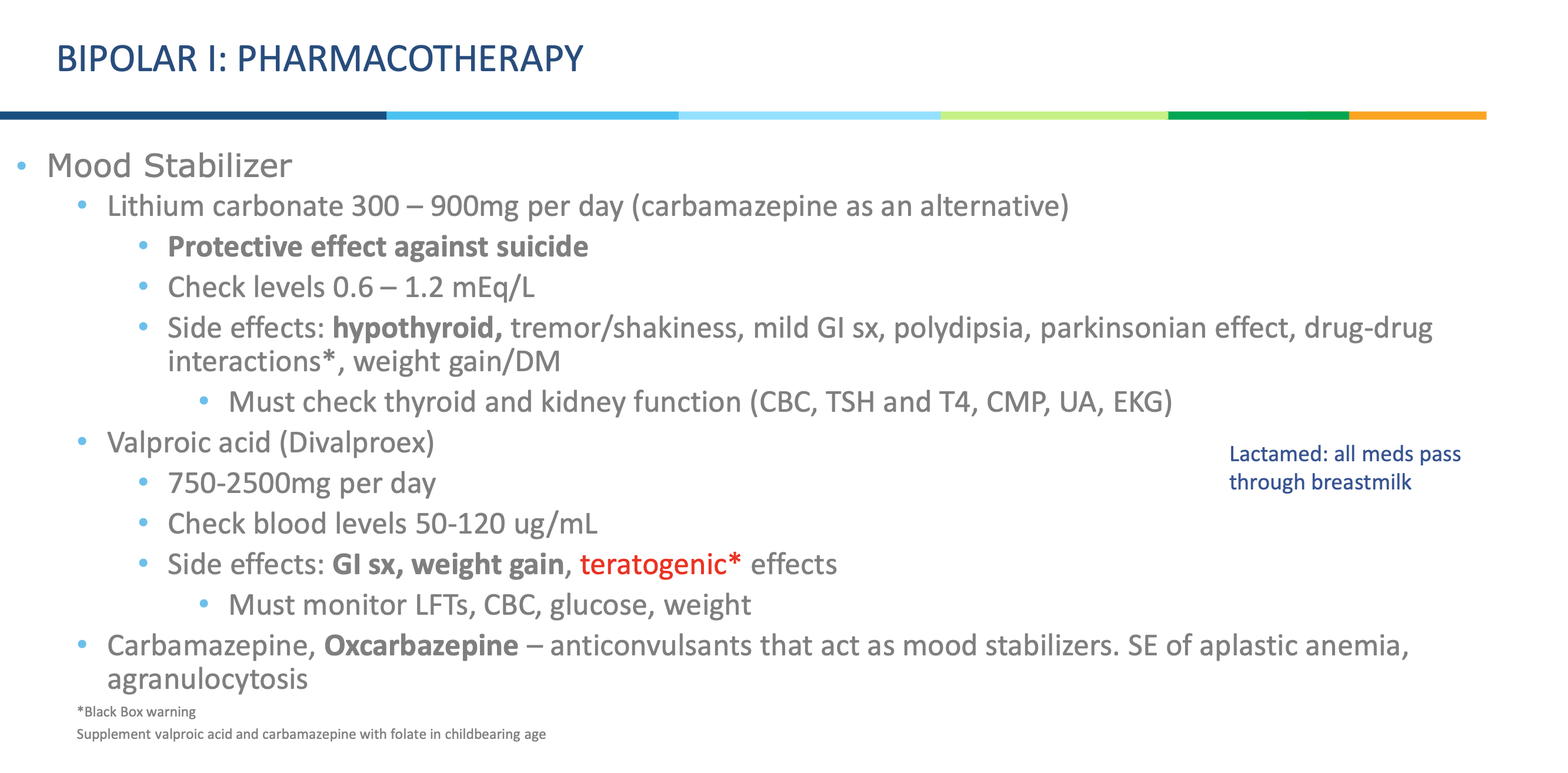
What type of drugs are carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine?
Anticonvulsants that also act as mood stabilizers.
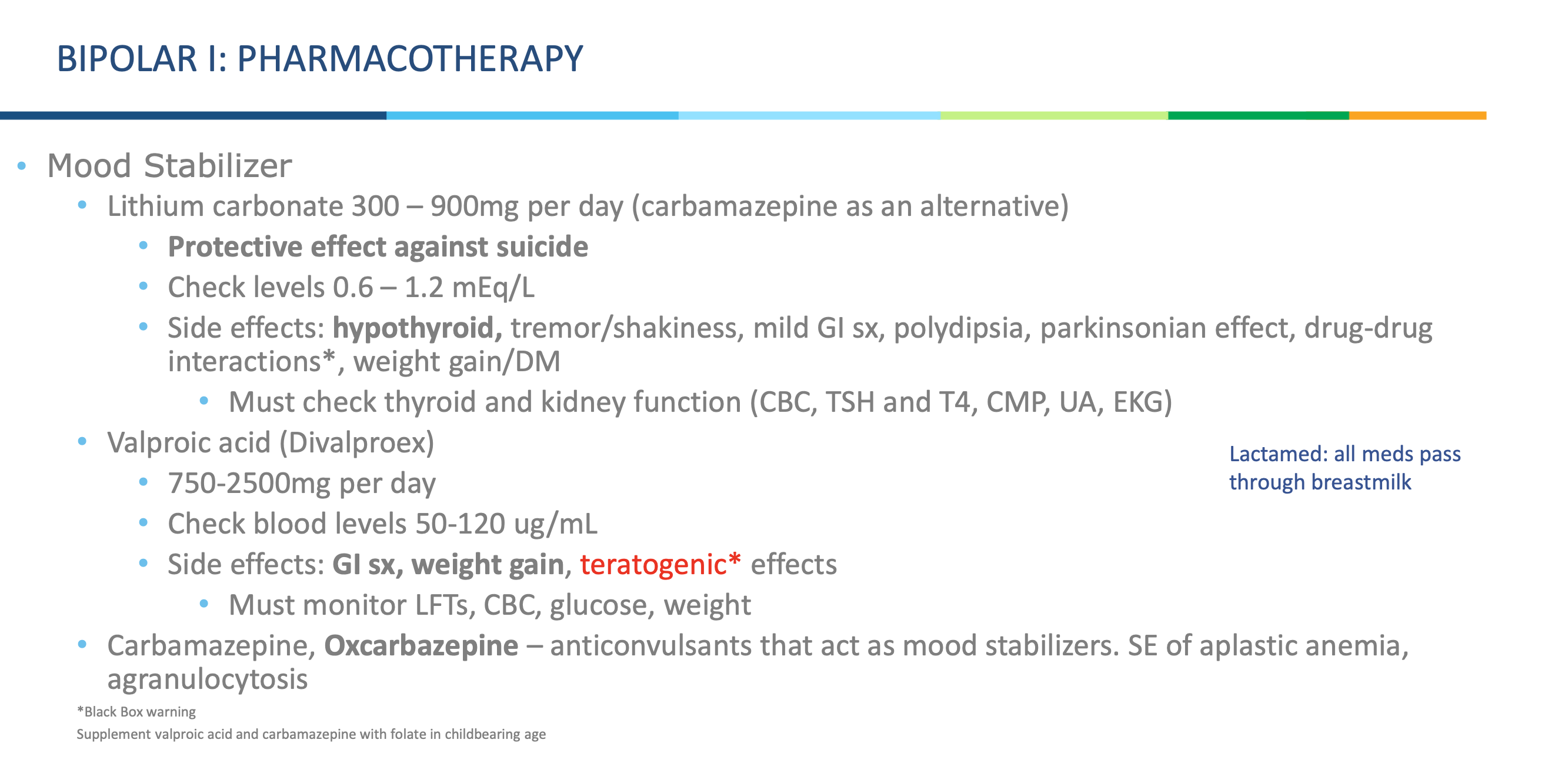
What dangerous side effects are linked with carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine?
Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis
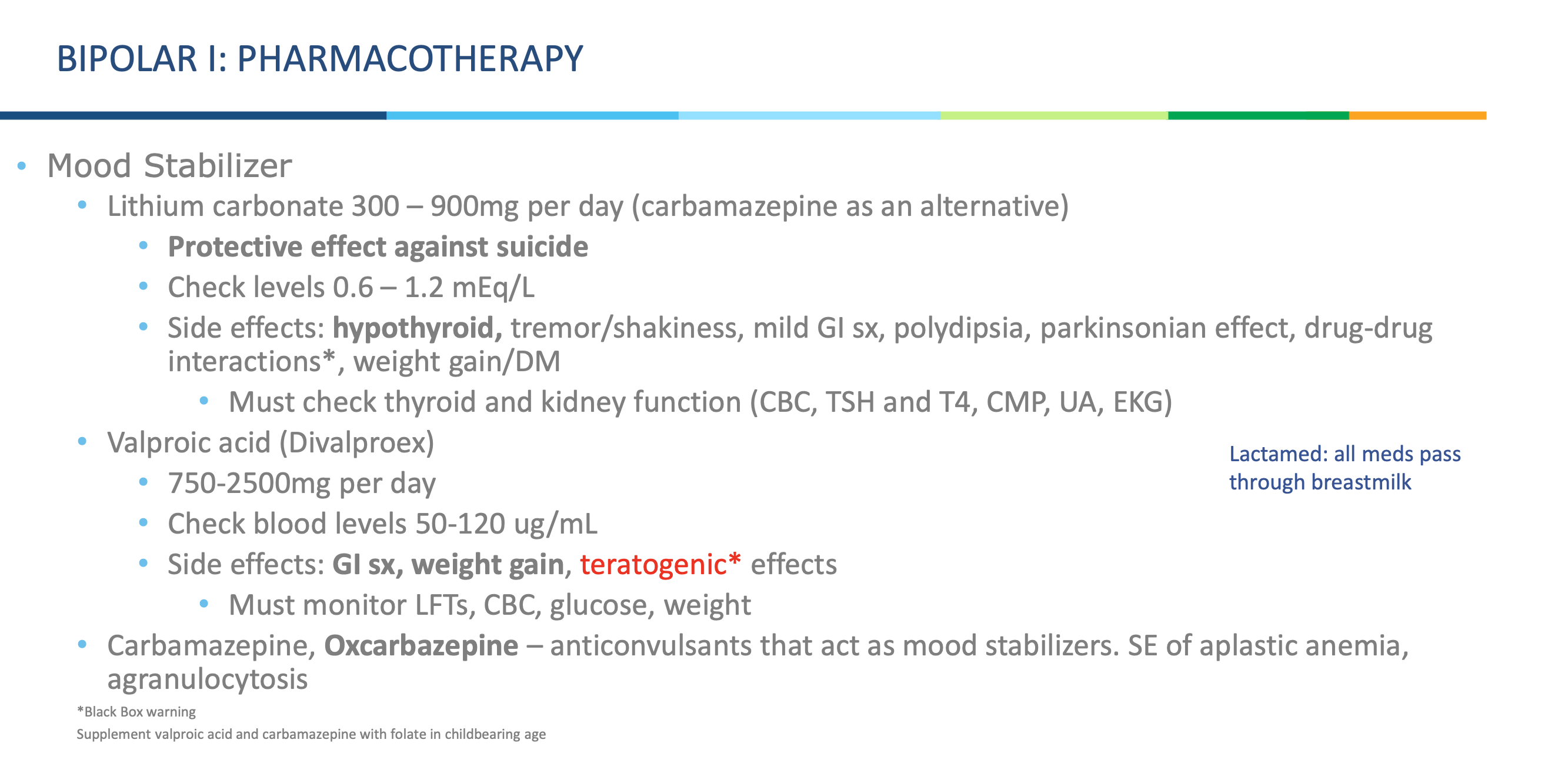
Do mood stabilizers pass through breast milk?
Yes — all of them do.
What supplements should be given to women of childbearing age who are taking valproic acid or carbamazepine?
*hint black box warning
Folic acid (folate) supplementation.
Why is folate supplementation important in these patients?
Both valproic acid and carbamazepine are teratogenic and increase the risk of neural tube defects— folate helps reduce this risk.
What is the general rule for treating an acute bipolar episode?
Use the same regimen that successfully treated a prior acute bipolar episode.
What is the first-line pharmacologic treatment for an acute bipolar manic episode?
Does the medication take effect right away?
Lithium or valproate + a 2nd generation antipsychotic.
No; several days

What are the 2nd- gen antipsychotics? (*3)
Olanzapine, risperidone, aripiprazole
Which antipsychotics do you use for acute bipolar mania episode to control behavior?? *hint there is a first gen one
Olanzapine IM or haloperidol IM (1st gen)
for behavior control
Name the antipsychotics that are serotonin and dopamine antagonists. 1st Gen Antipsychotic (AKA typicals) *4
Note: Typical antipsychotics or 1st generation (block D2 receptors)
Phenothiazine
Chlorpromazine
Haloperidol (Haldol) - comes in quick injectable form
Perphenazine
What are the SEs of 1st Gen Antipsychotics
(AKA typicals)? (*6)
dry mouth
muscle stiffness
tremors
weight gain
EPS
tardive dyskinesia
What is the mechanism of action of atypical (2nd gen) antipsychotics?
dopamine partial agonists
Name atypical antipsychotics (2nd Gen) (Bipolar I – Atypical) (*5)
Clozapine (Clozaril)
Risperidone (Risperdal) – comes in a depot (long acting) form
Olanzapine (Zyprexa) –
Quetiapine (Seroquel)
Ziprasidone (Geodon)
What are common side effects of atypical antipsychotics?
Dry mouth
blurred vision
dizziness
insomnia
extreme tiredness
weakness
bloating
Which newer atypical antipsychotic is commonly used in Bipolar I?
Aripiprazole (Abilify).
What are common side effects of aripiprazole? (*5)
Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, insomnia, restlessness.
What class of medications are clonazepam (Klonopin) and lorazepam (Ativan)?
High potency benzodiazepines.
Give two examples of high potency benzodiazepines.
Clonazepam (Klonopin)
Lorazepam (Ativan)
What are common side effects of high potency benzodiazepines?
Benzos:
Drowsiness
confusion
dizziness
vision problems
impaired coordination
What are the first-line and second-line treatments for acute bipolar depression?
First-line: Quetiapine, Lurasidone
Second-line: Antidepressant + atypical antipsychotic (e.g., Olanzapine + Fluoxetine) — but use antidepressants cautiously
Second-line monotherapy: Valproic acid
What are third-line options for treatment-resistant bipolar depression? Those who don’t respond to standard antidepressant
Lamotrigine
low-dose Ziprasidone
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Why lamotrigine?
has mood stabilizing and antidepressant properties, so
FDA approved for maintenance treatment of bipolar depression
What serious skin reaction can lamotrigine cause?
Stevens–Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis (>30% body involvement).
What are the early warning signs of Stevens–Johnson syndrome?
Flu-like symptoms (fever, malaise).
What happens a few days after Stevens–Johnson syndrome begins?
Skin starts to blister and peel. Can effect Mucous membranes, especially the mouth.
Why should lithium often be retained in the treatment regimen?
It has antisuicide and neuroprotective effects.
What dual focus must be maintained in the treatment of bipolar disorder?
Both acute short-term treatment and prophylaxis (long-term relapse prevention).
When treating bipolar which should you look out for as a medical emergency?
mania
BIPOLAR II: TREATMENT HYPOMANIA
Name the 2 classes: atypical antipsychotics and mood stabilizing agents.
How long do most medications for bipolar disorder take to determine efficacy?
• Atypical antipsychotics: Olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, aripiprazole, and ziprasidone
• Mood stabilizers: Lithium, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, valproate
About 2 weeks.
Why should all antidepressants be discontinued in bipolar II depression treatment?
To prevent triggering mania.
What are the first-line treatment options for bipolar II depression?
The same medications as bipolar I depression- Lithium or lamotrigine (Lamictal) also studied as 1st line
When can an antidepressant be added to treatment for bipolar II depression?
Which antidepressants are preferred if added in bipolar II depression?
It can be added later, once mood stabilization is achieved.
Bupropion or paroxetine.SSRIs, SNRIs, or MAOIs.
How does DSM-5 define cyclothymic disorder?
As a chronic, fluctuating mood disturbance with many periods of hypomania and depression, lasting at least 2 yearswithout more than 2 months in remission.
Cyclothymic disorder is considered a mild form of which disorder? How is cyclothymic disorder differentiated from bipolar II disorder?
A mild form of bipolar II disorder.
By the presence of “minor” depressive symptoms and hypomanic episodes, rather than full major depressive episodes.
Which personality disorder frequently co-exists with cyclothymic disorder?
Borderline personality disorder.
What traits may characterize individuals with cyclothymic disorder as children?
They may have been described as sensitive, hyperactive, or moody.
In what decade of life does cyclothymic disorder often occur?
Most often in the 20s.
How does cyclothymic disorder impact functioning in school or social interactions?
It can hinder academic performance and make interaction with others difficult.
Despite challenges, how do many people with cyclothymic disorder manage long-term functioning?
They often develop adaptive strategies that allow them to hold long-term jobs.
What medications are considered first-line treatment for cyclothymic disorder?
Mood stabilizers and antipsychotics.
What are the goals of psychosocial therapy in cyclothymic disorder?
To increase awareness of the condition, develop coping mechanisms during mood swings, and provide family/support group therapy.