Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry (Double award) flashcards
1/558
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
559 Terms
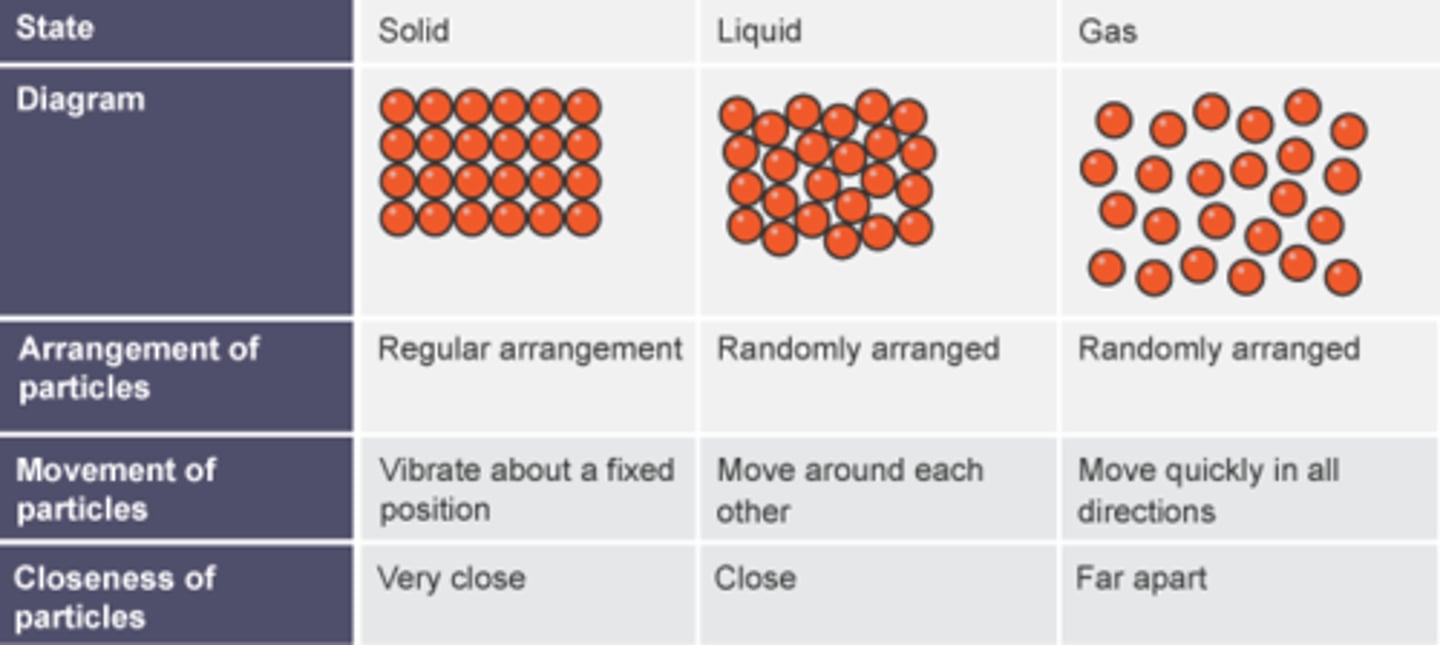
Describe the movement and arrangement of particles in a solid.
Vibrating around a fixed position.
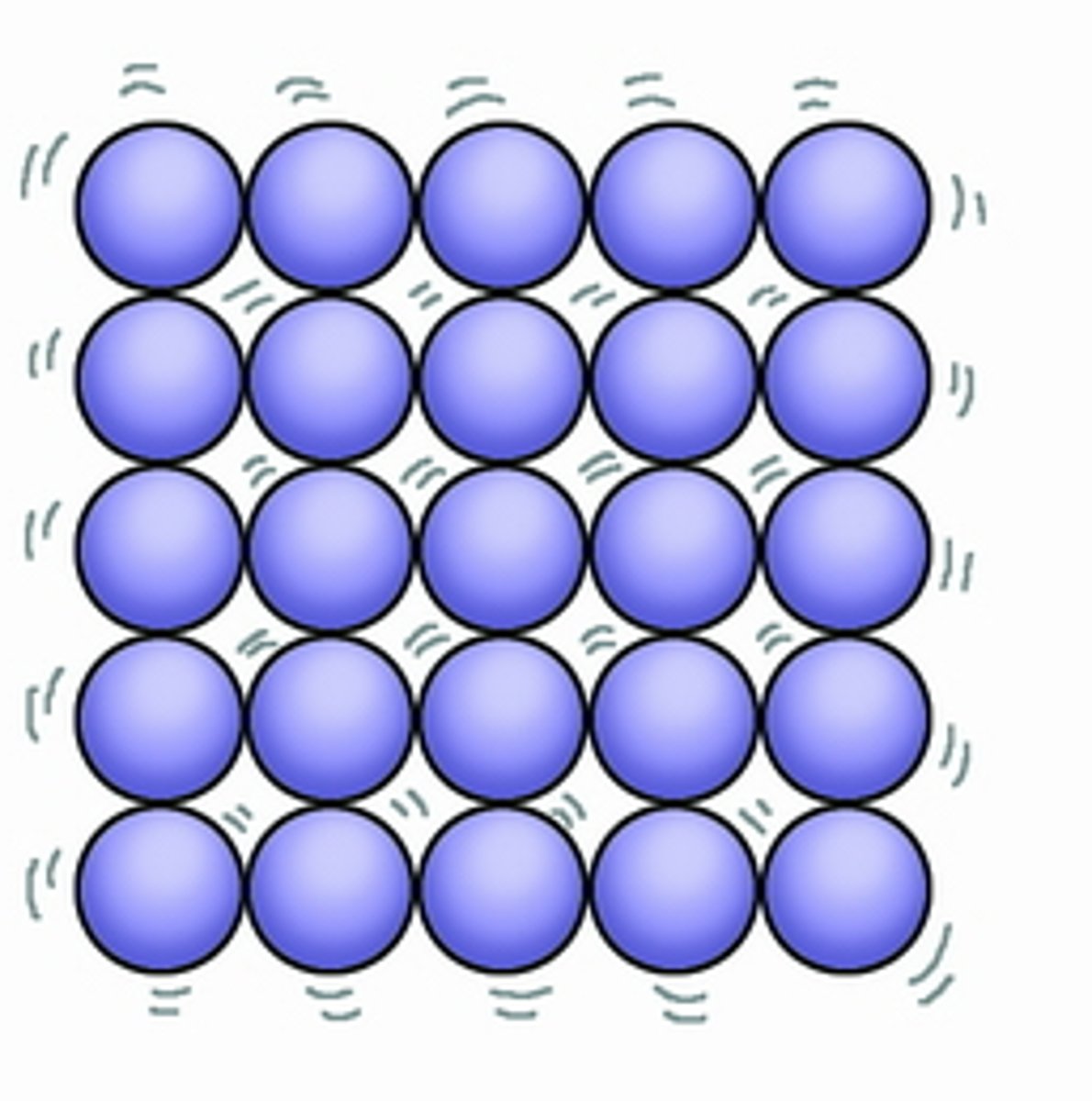
Describe the movement and arrangement of particles in a liquid.
Close and moving past each other.
Describe the movement and arrangement of particles in a gas.
Very far apart and whizzing around very fast.
In which state of matter do particles have a very large amout of kinetic energy?
Gas
In which state of matter do particles have a very small amout of kinetic energy?
Solid
Explain why evaporating water does not produce H and O atoms.
Because the covalent bonds between H and O atoms do not break during boiling. Only the intermolecular forces between water molecules break.
Explain what happens to the particles in a gas when the gas expands.
They move further apart from one another.
Name the three changes of state during which particles absorb energy.
Melting, evaporation, sublimation
Name the three changes of state during which particles lose energy.
Freezing, condensation, deposition.
Describe the temperature change of a solid while it's melting
The temperature is constant
Describe the temperature change of a liquid while it is boiling
The temperature is constant
What does soluble mean?
Dissolves in water

What does insoluble mean?
Does not dissolve in water

Define solute
The dissolved substance in a solution
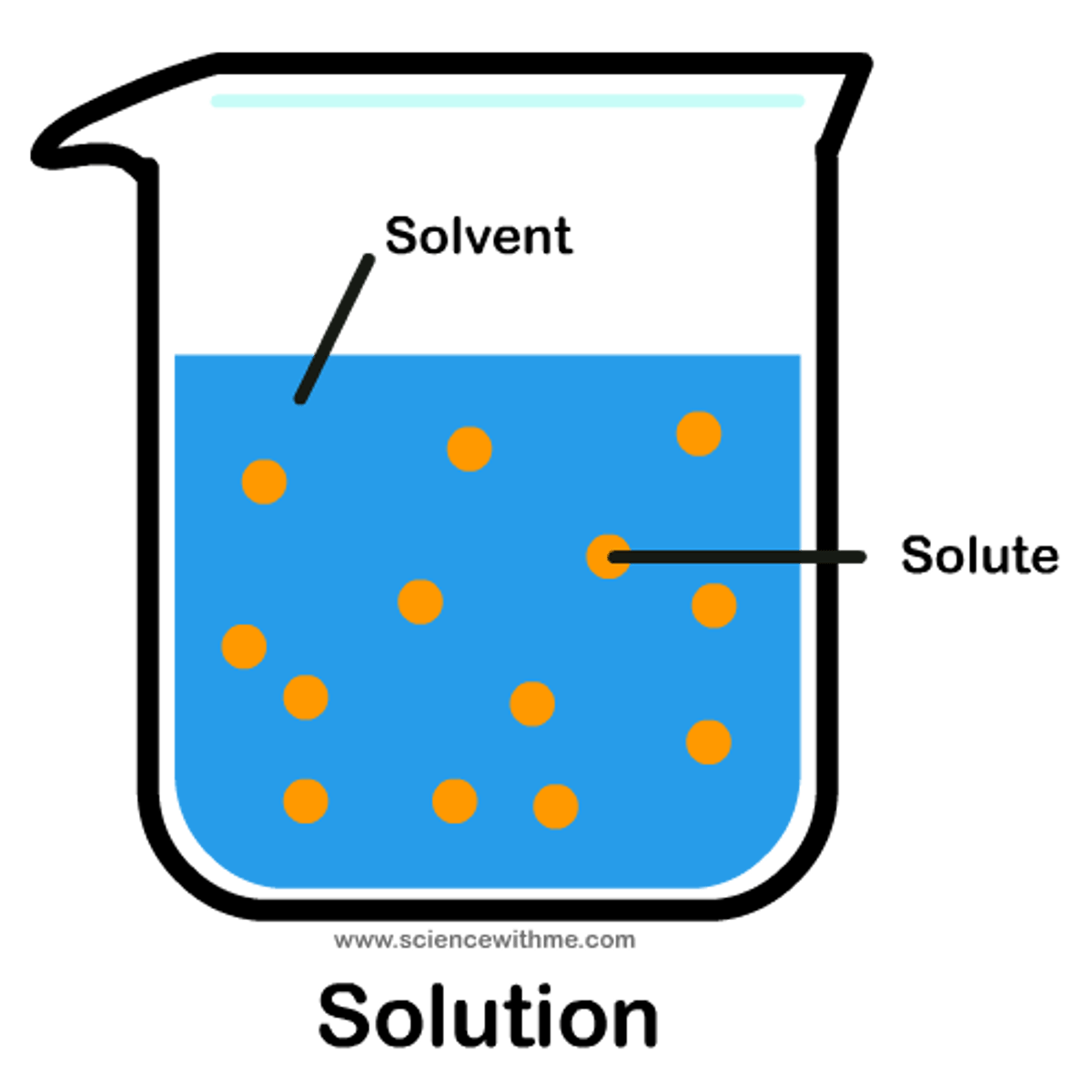
Define solvent
The liquid in which the solute dissolves to form a solution
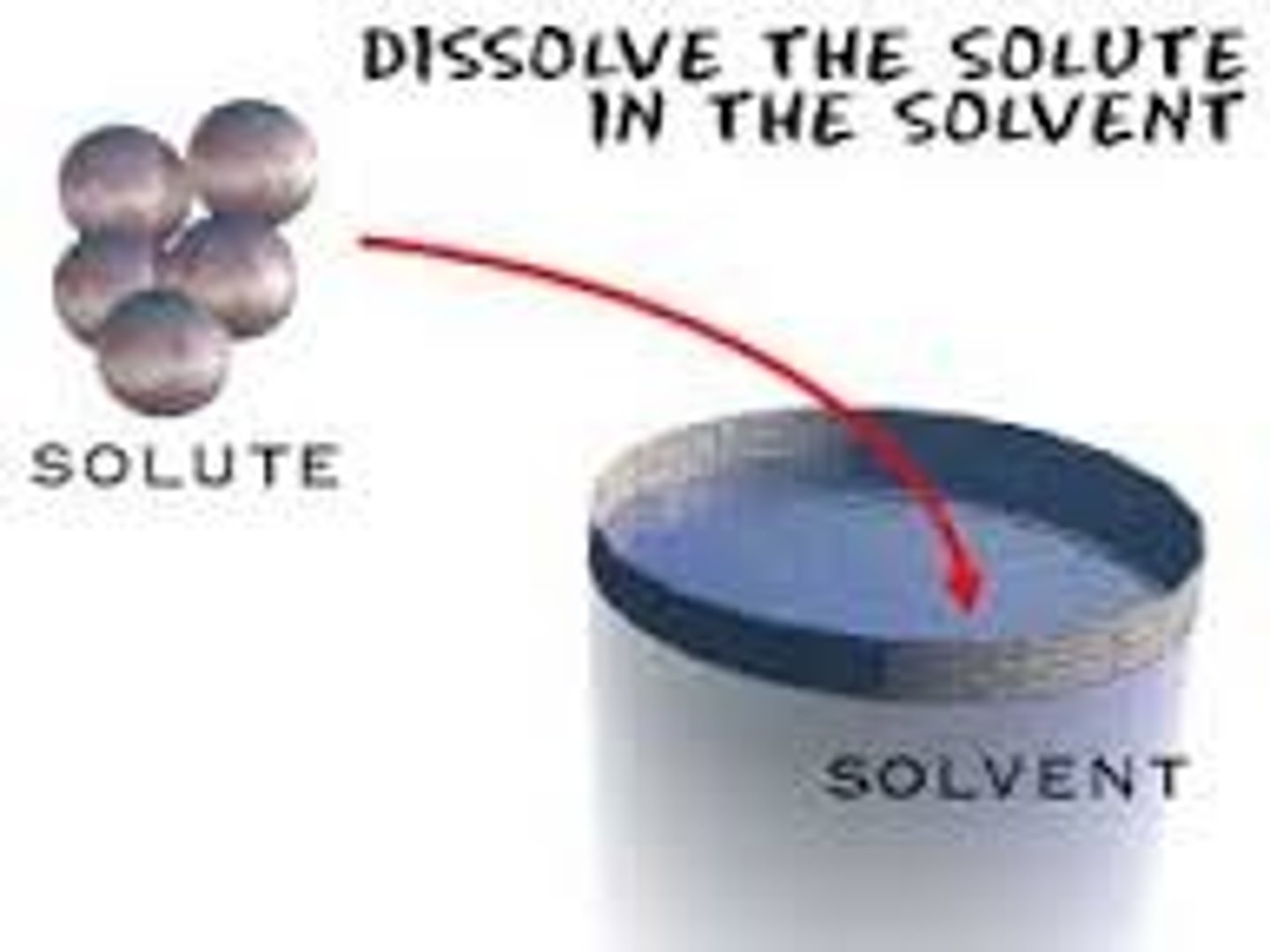
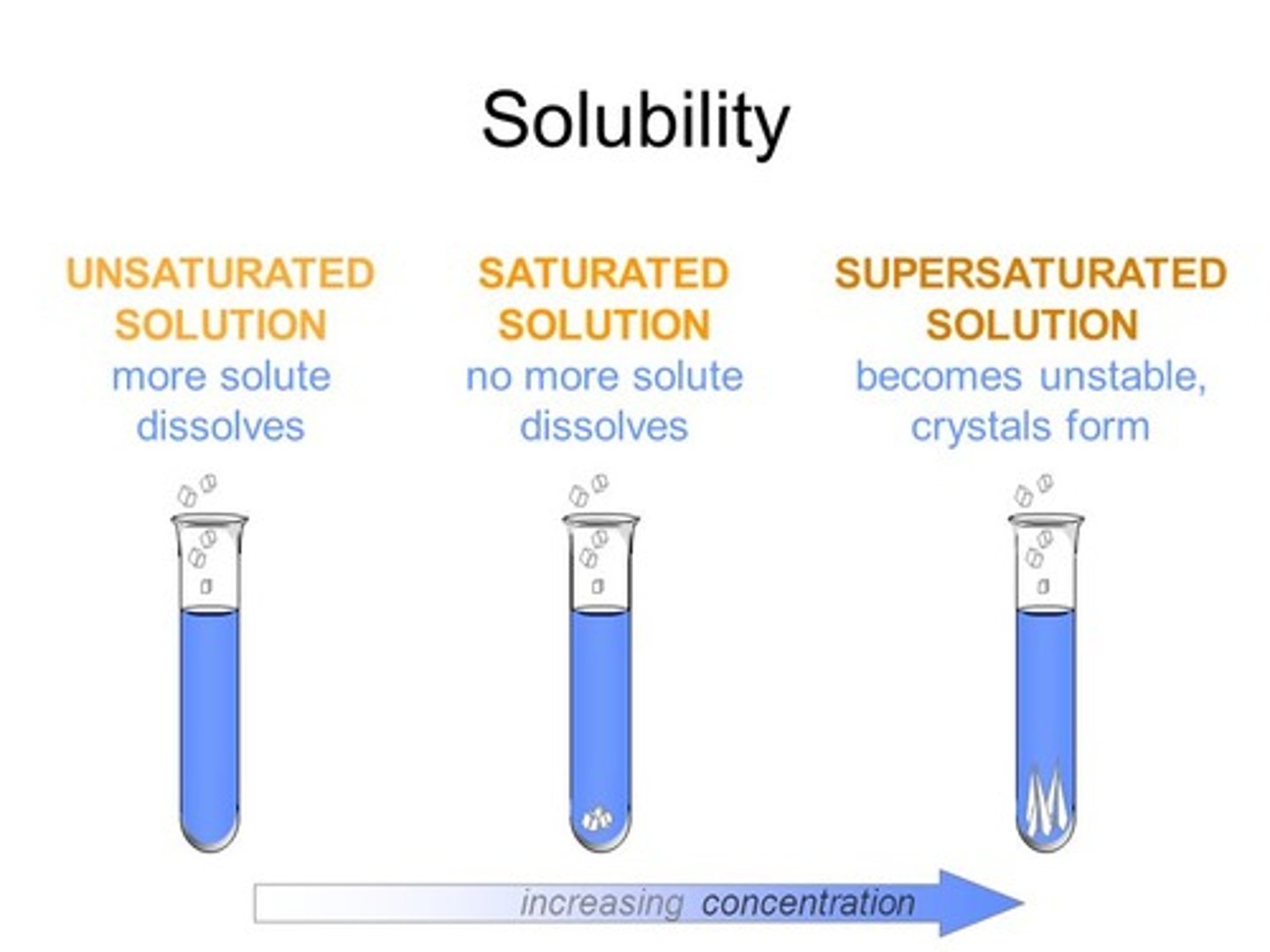
Define saturated solution
A solution in which no more solute can dissolve at a given temperature
In seawater, what is the solvent and what is the solute?
Solvent = water. Solute = salt
Is dissolving a physical change or a chemical reaction?
Physical change
What happens to particles when they dissolve?
The solute particles spread out and fit into the spaces between solvent particles.
Define diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
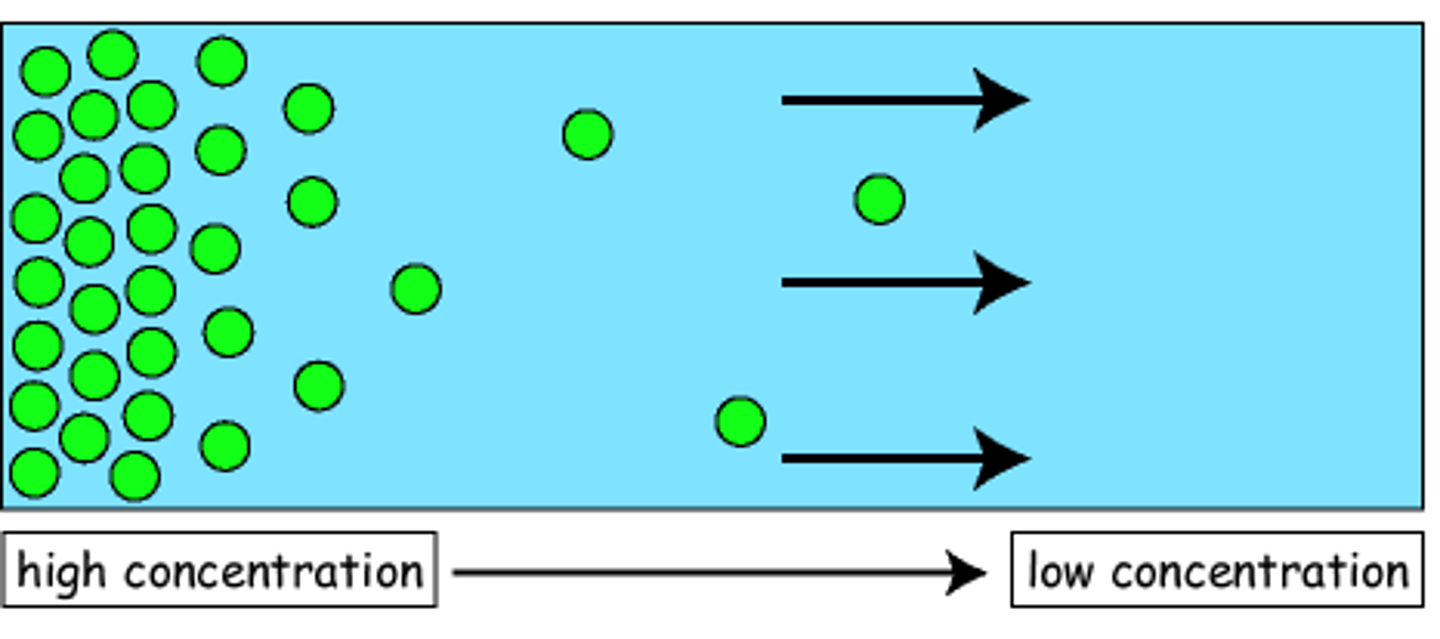
Describe what happens after a drop of ink is placed in a glass of water
The colour will spread slowly through the water until the ink particles are evenly spread out.
Explain why adding water to a coloured solution makes the colour paler
The coloured particles are now further apart
What colour solution is made when a white solid dissolves in water?
Colourless
Explain why diffusion is slower in liquids than in gases
Because the particles in a liquid move more slowly
Explain why diffusion does not happen in solids
Because the particle in a solid do not move from place to place
What happens to the solubility of a solid as you increase the temperature?
It increases
What happens to the solubility of a gas as you increase the temperature?
It decreases
Define atom
The smallest part of an element that can still be recognised as that element
Define element
A substance made of only one type of atom
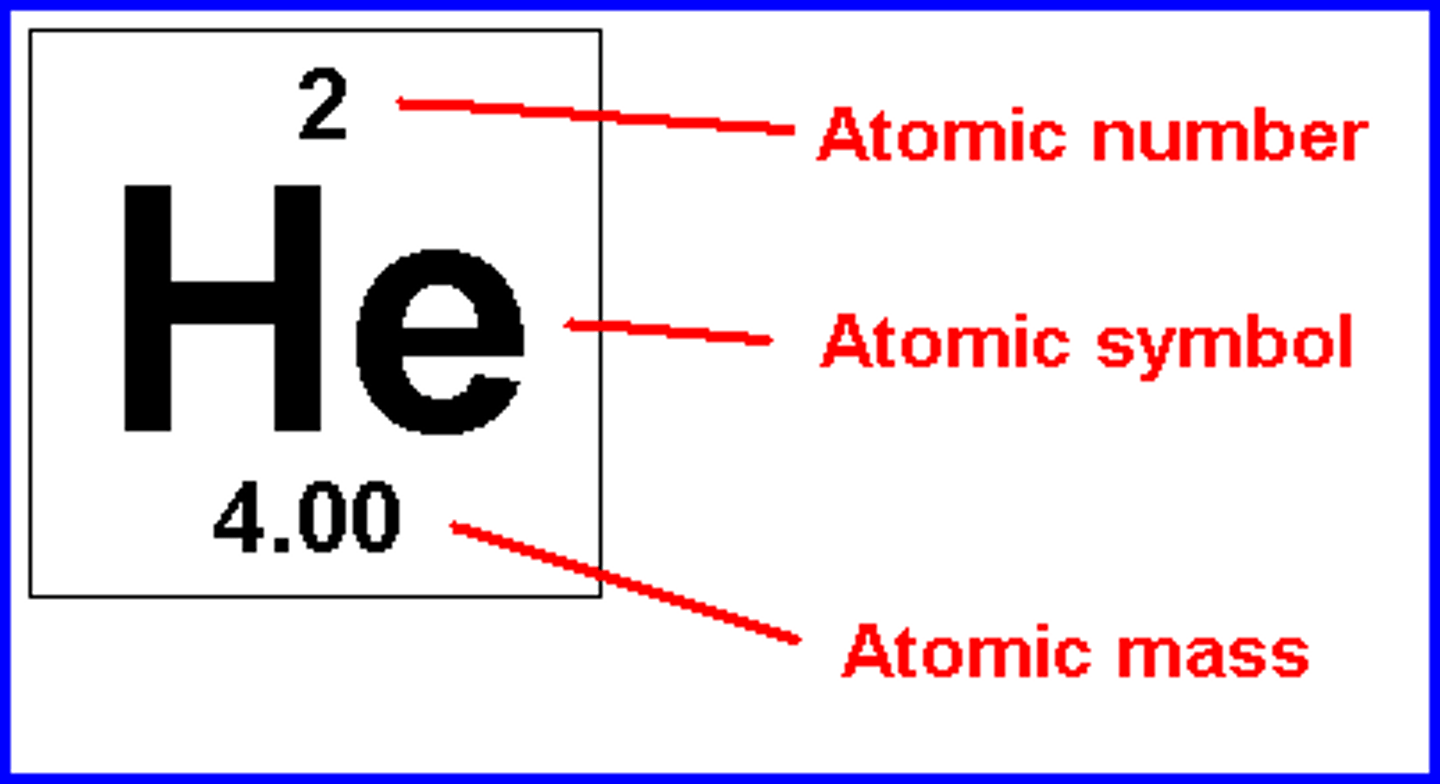
Define compound
A substance made of two or more different atoms chemically bonded together and in a fixed ratio
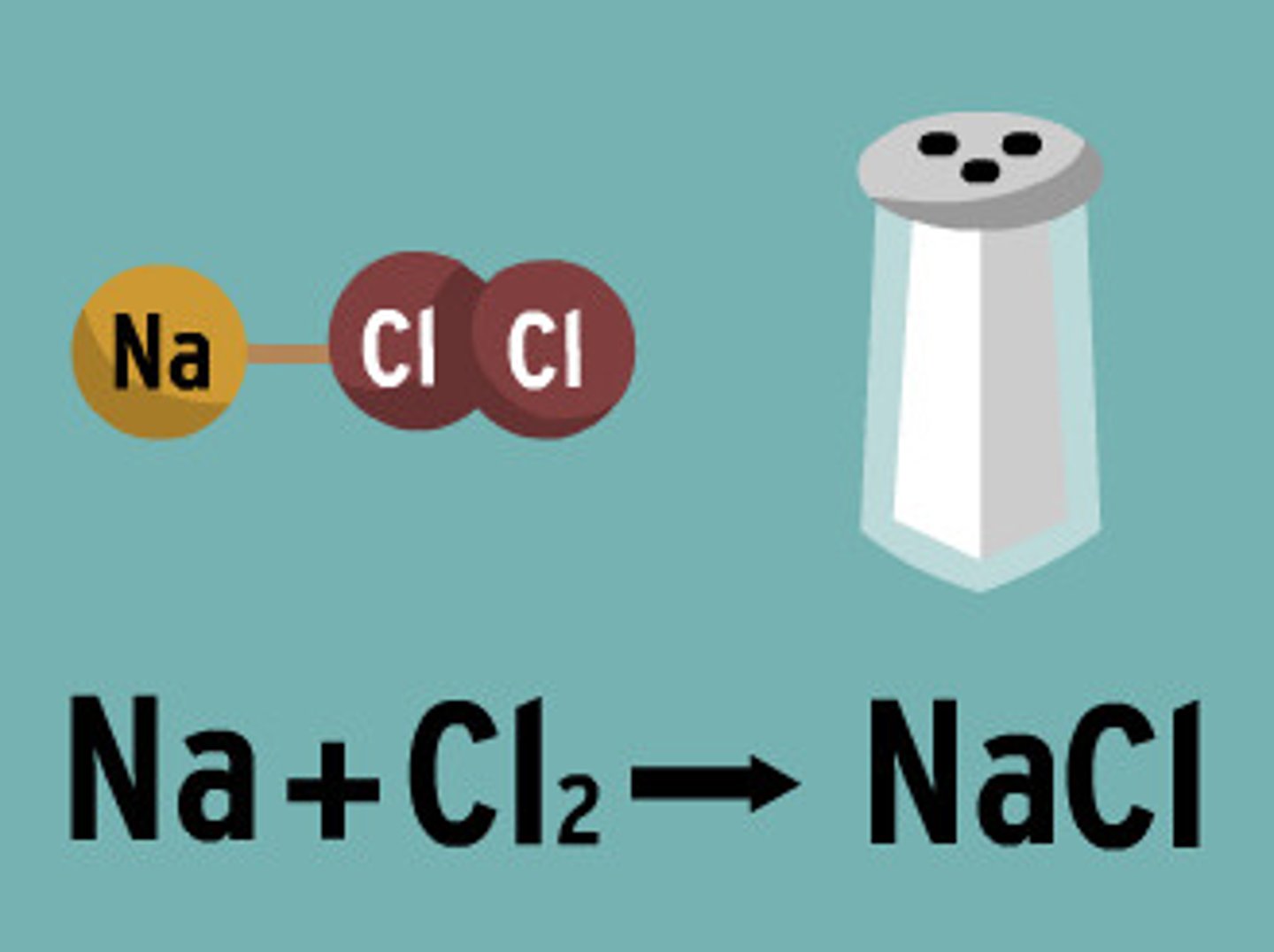
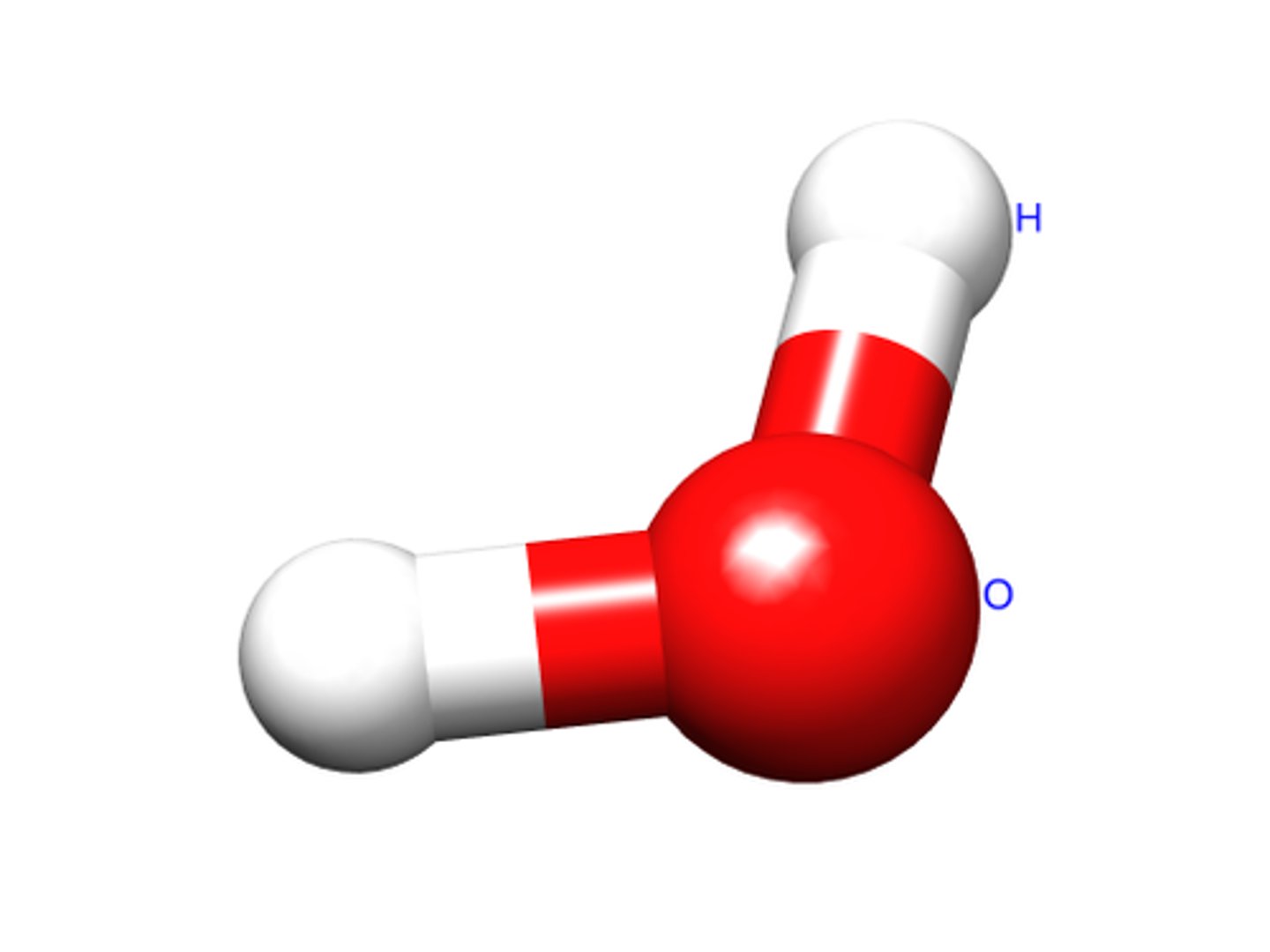
Define molecule
A substance made of more than one atom chemically bonded together (can be atoms of the same type!)
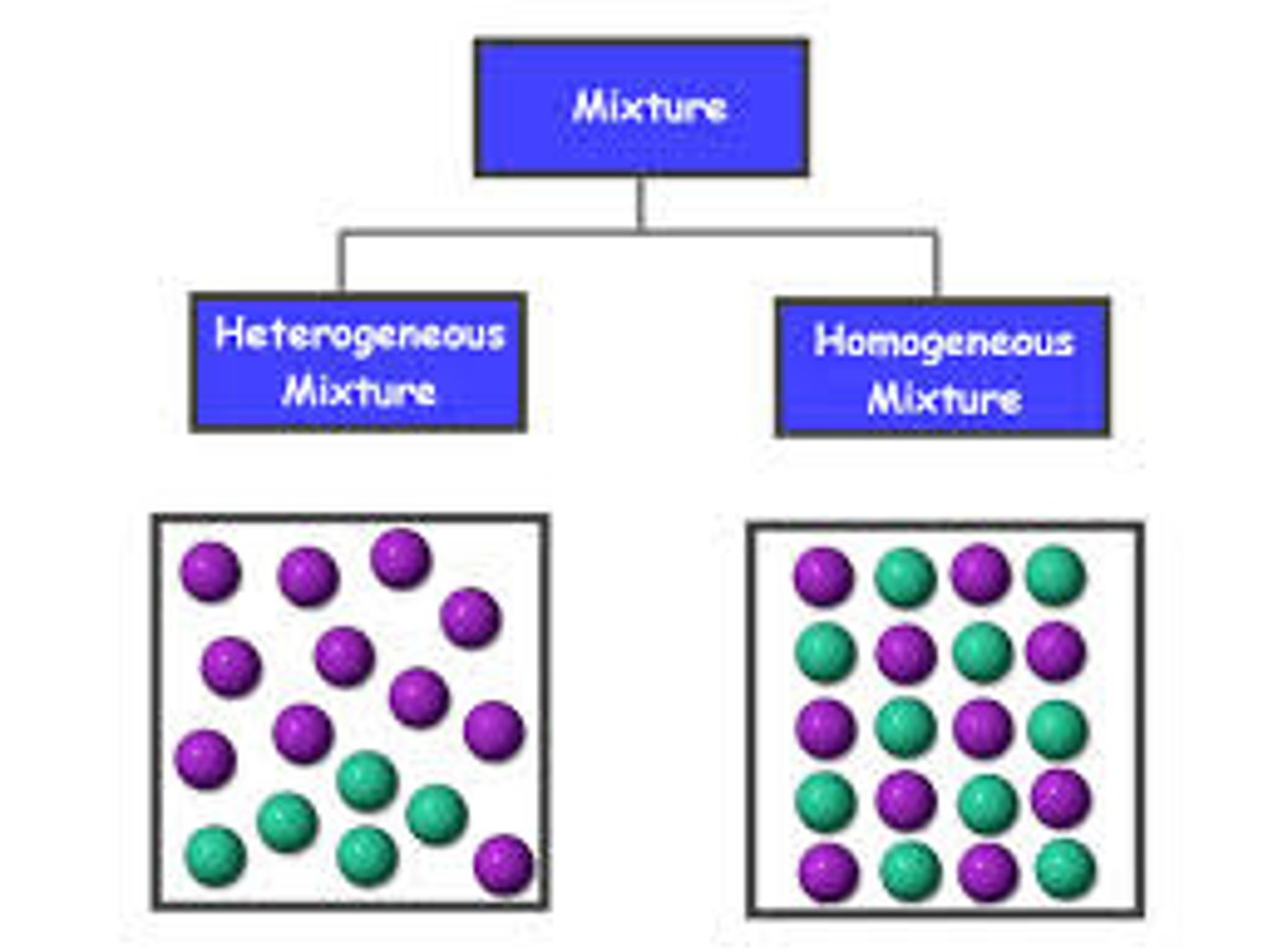
Define mixture
A substance made of more than one thing not chemically bonded together and not in a fixed ratio
Describe the melting point of pure substances
Fixed melting point
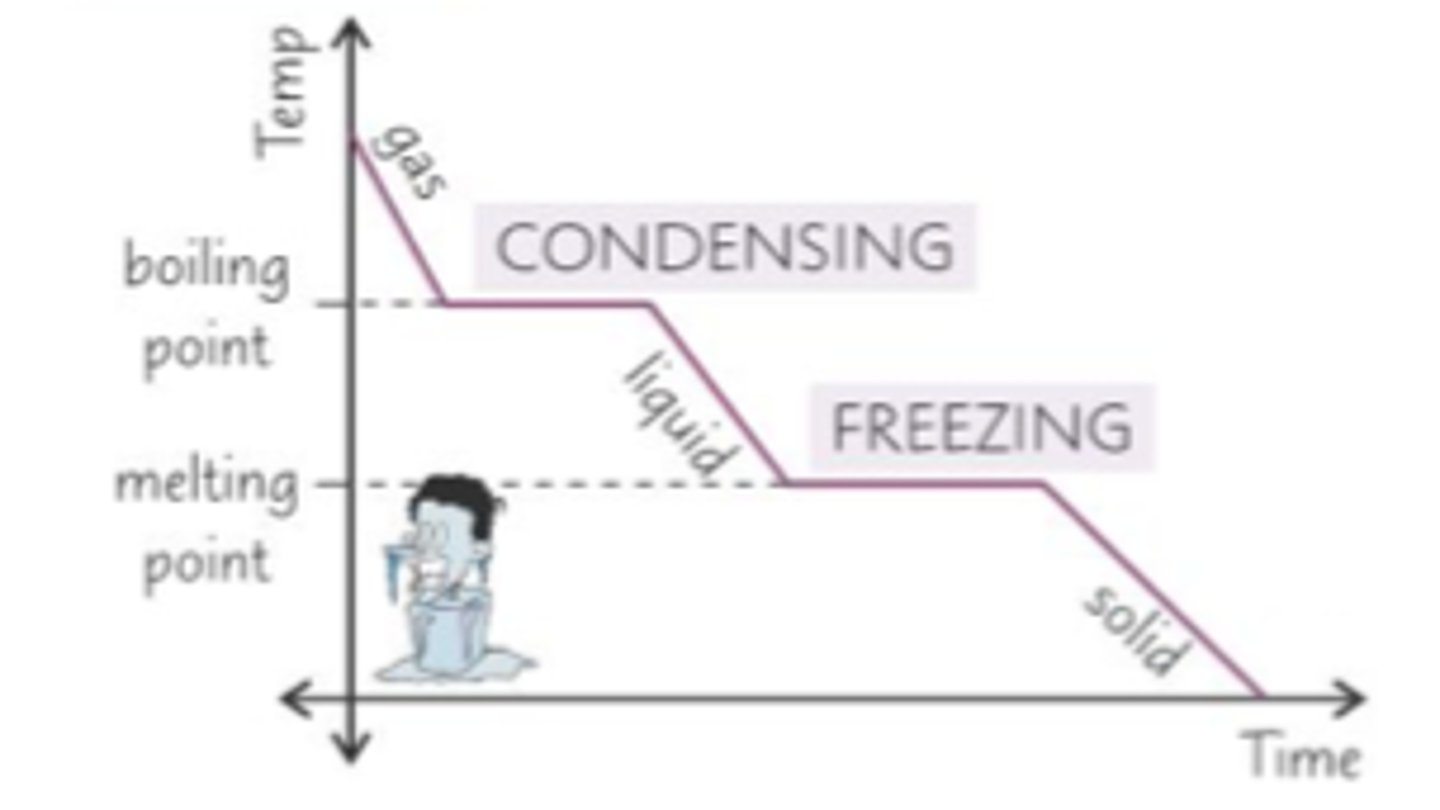
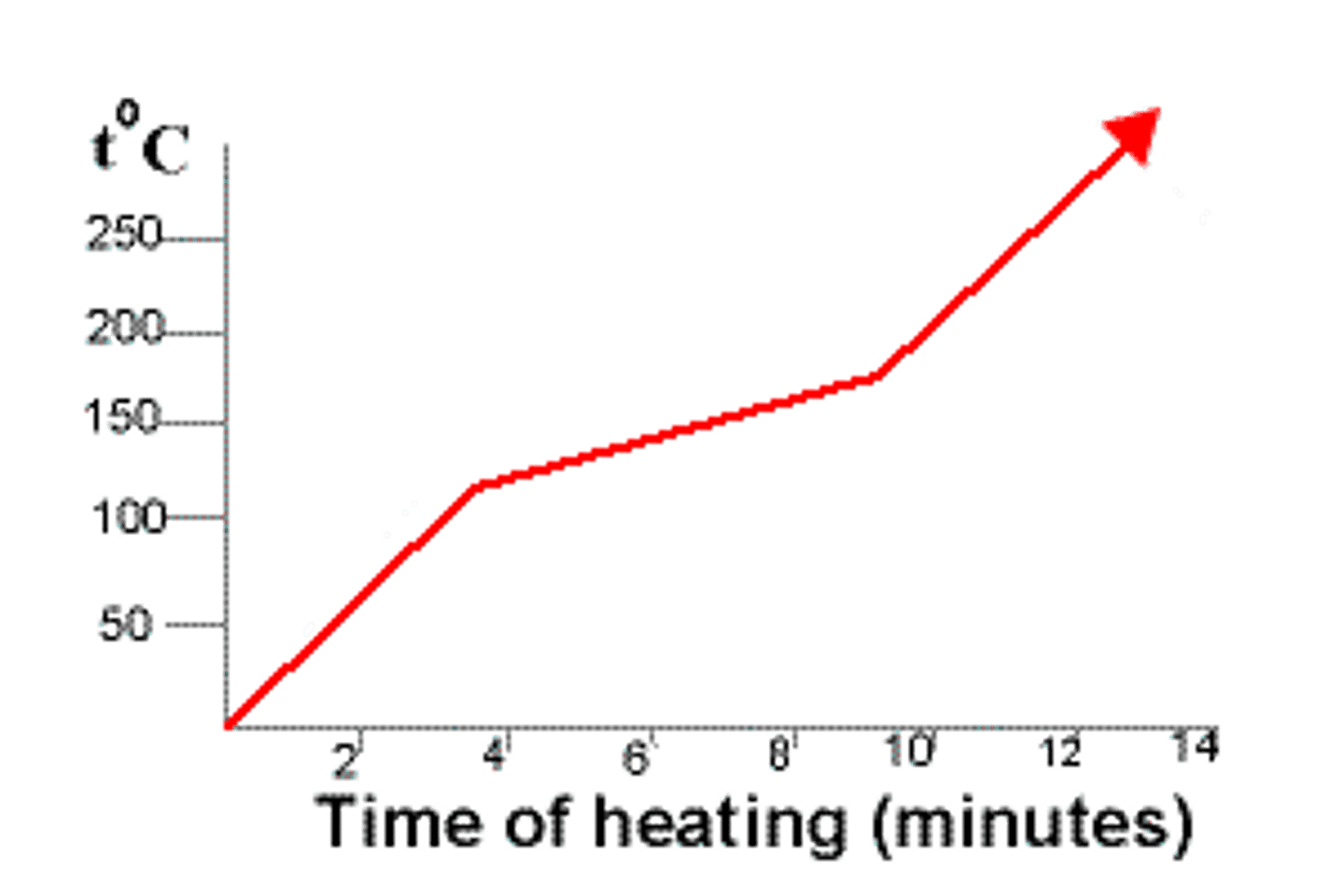
Describe the melting point of mixtures
Mixtures may melt or boil over a range of temperatures
How could you separate a mixture of sand and water?
Filtration
How could you obtain the salt from a salty water solution?
Crystallisation
How could you obtain the water from a salty water solution?
Simple distillation
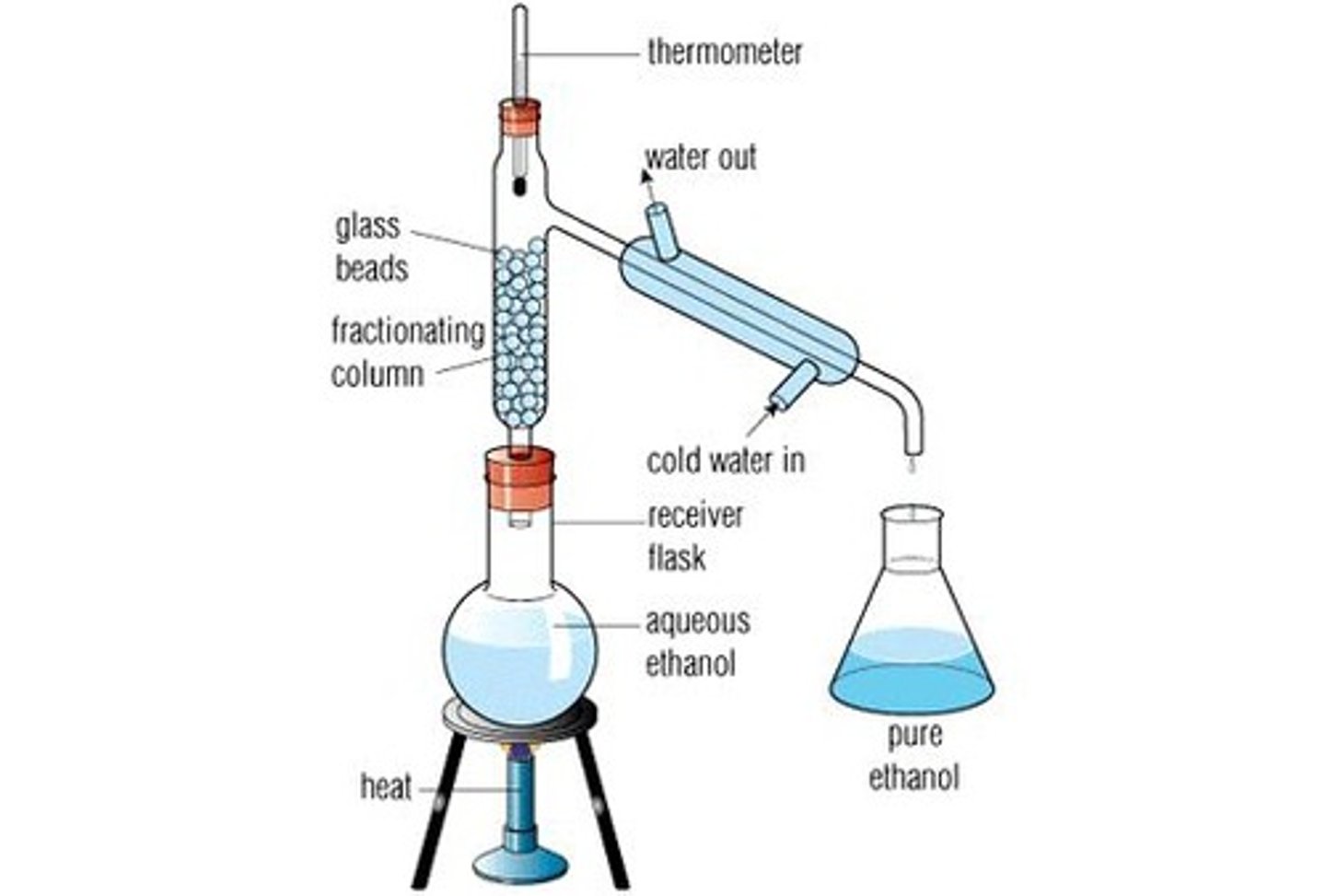
How could you separate a mixture of water and alcohol?
Fractional distillation
How could you separate a mixture of inks?
Paper chromatography
What is chromatography?
A process to separate a mixture
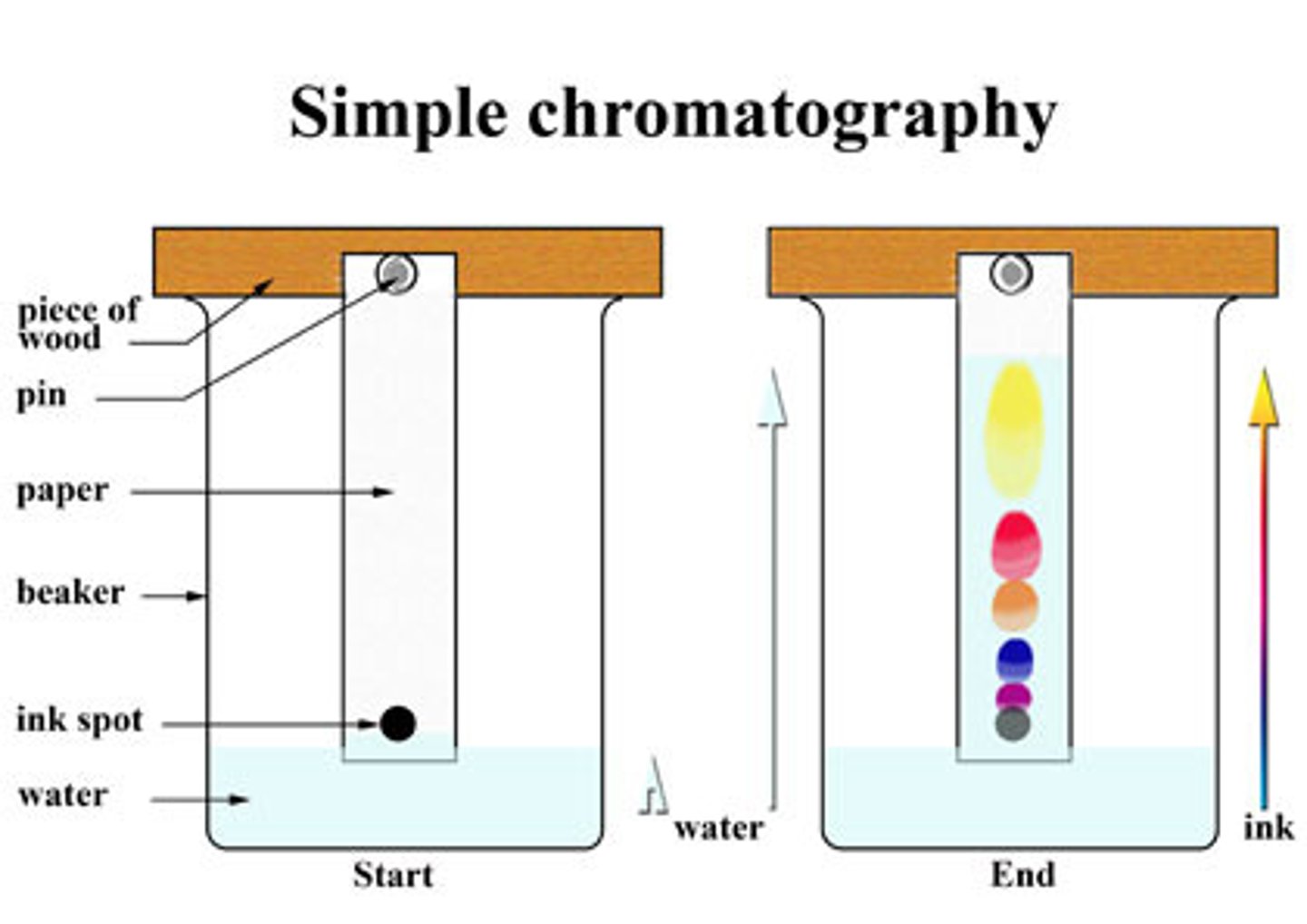
In paper chromatography, what is the stationary phase and what is the mobile phase
Paper is stationary, solvent (usually water or ethanol) is mobile
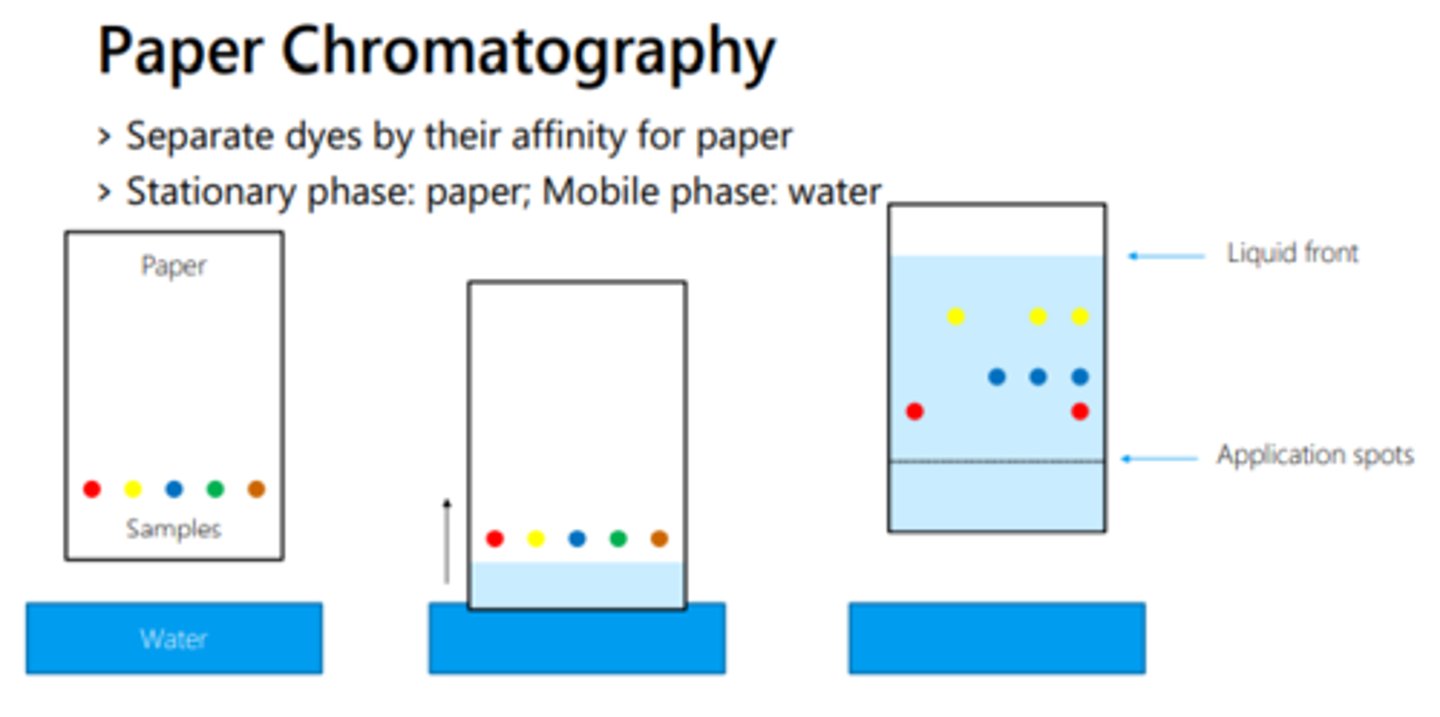
How can chromatography show the difference between pure and impure substances?
Pure ones will not separate into a number of spots
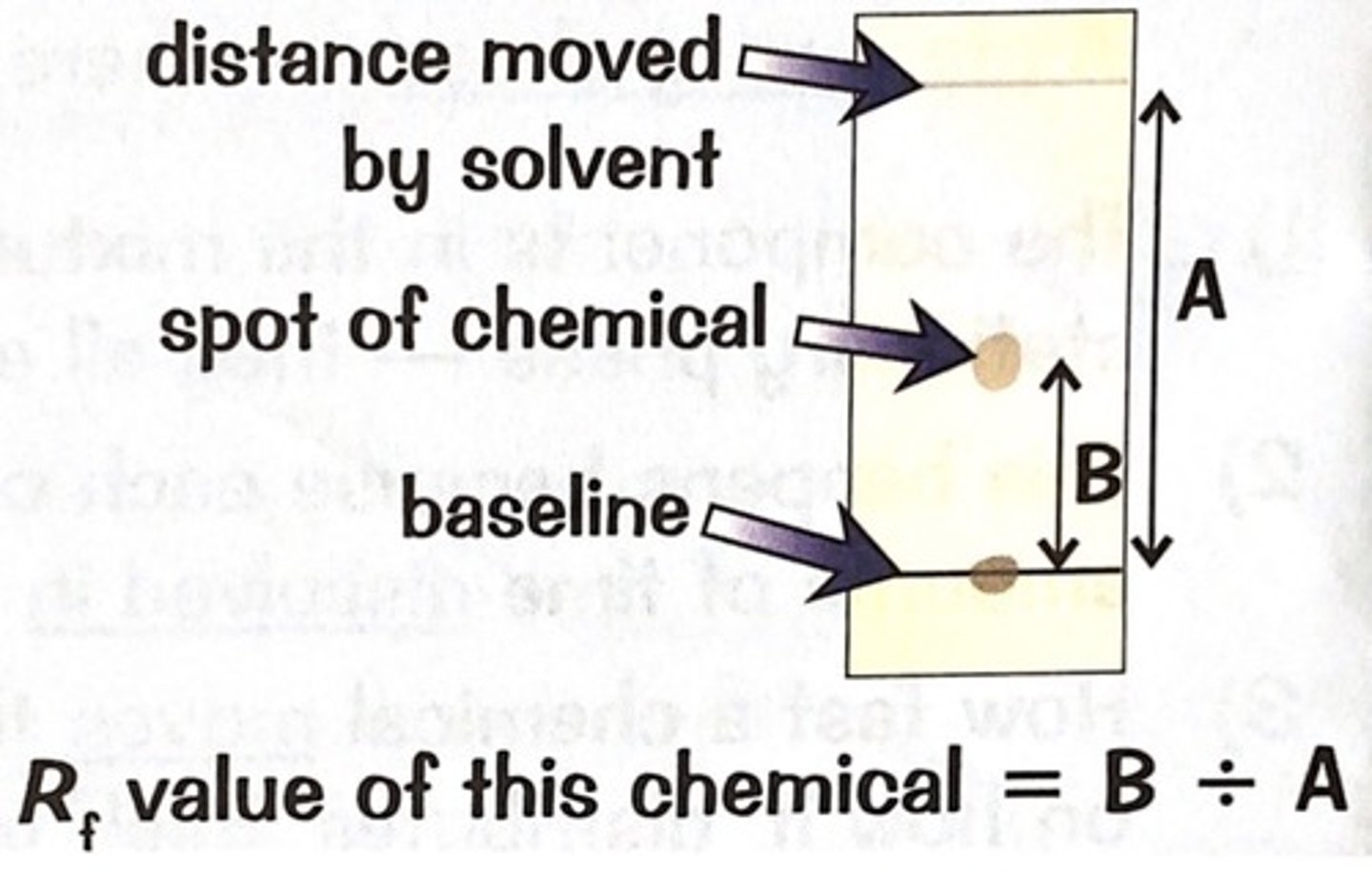
How is the Rf value calculated?
distance moved by spot/distance moved by solvent

What does a substance's Rf value depend on?
How soluble it is in the solvent
In chromatography, why must the substances be placed on a pencil line?
Pencil will not dissolve in the solvent
In chromatography why must the solvent height be lower than the pencil line?
So that the substances do not dissolve into the solvent off the paper
Define chromatogram
The results of separating mixtures by chromatography
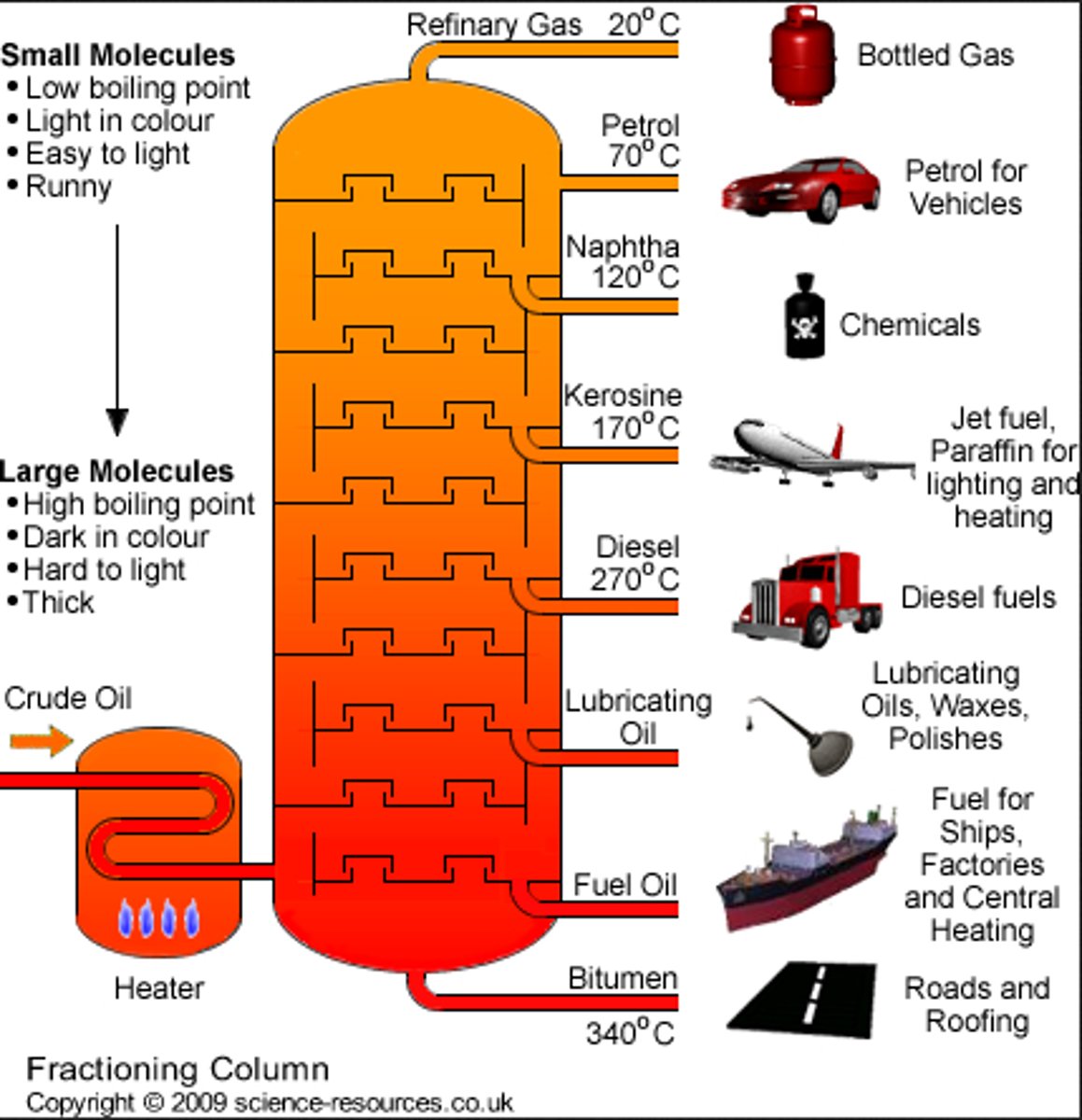
What is fractional distillation?
A process used to separate mixtures of substances that have different boiling points
Define molecule
Two or more atoms joined by a chemical bond
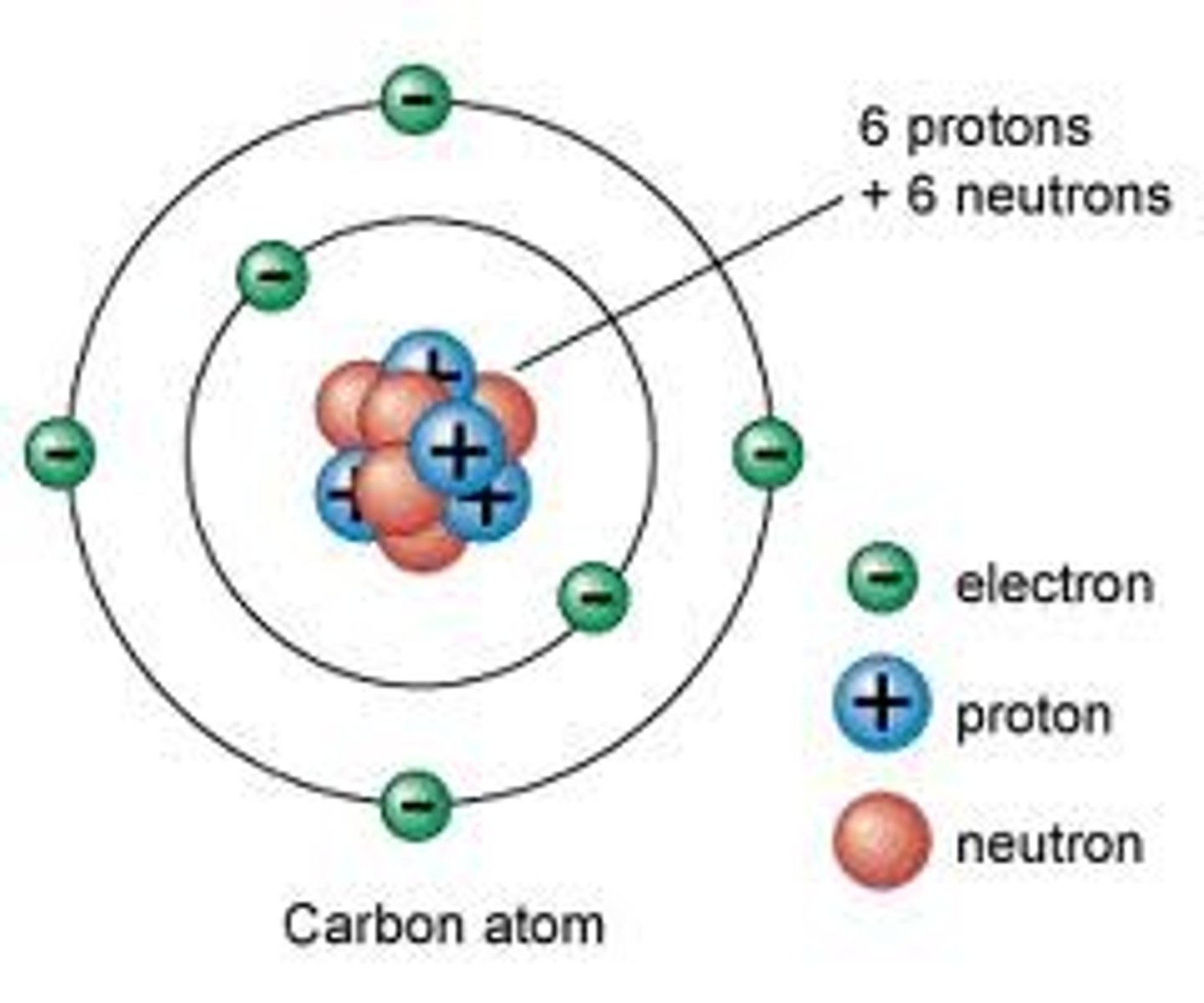
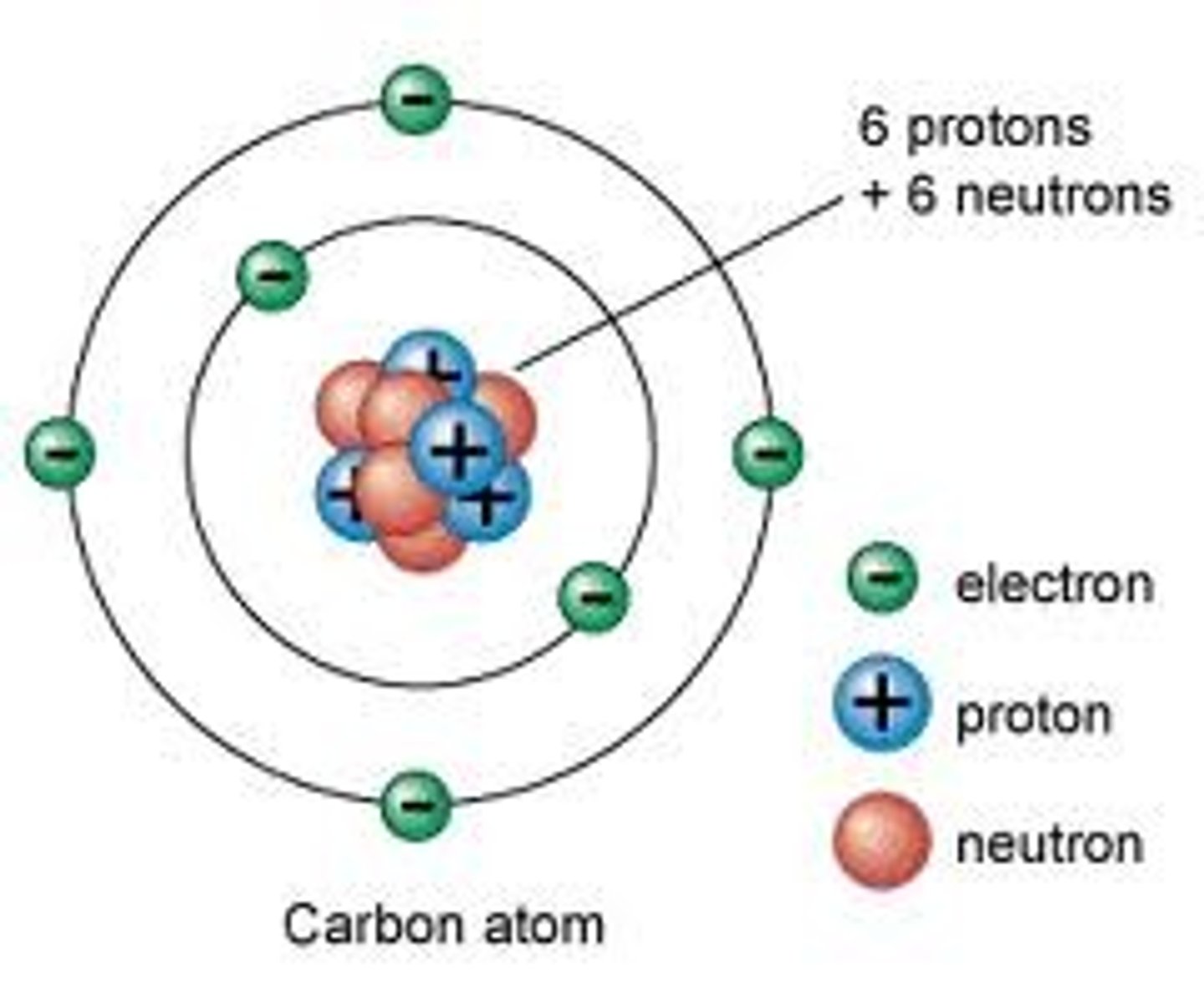
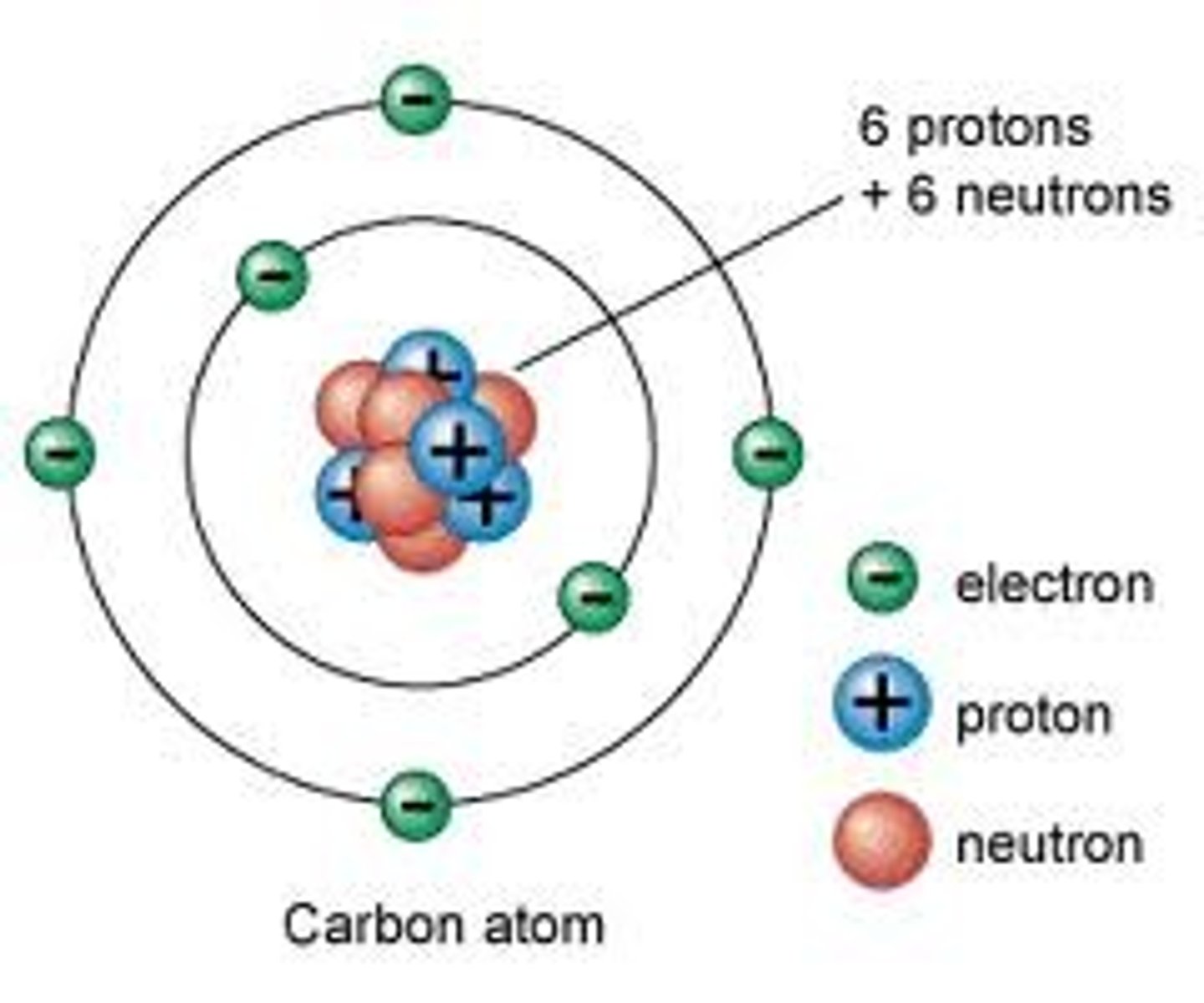
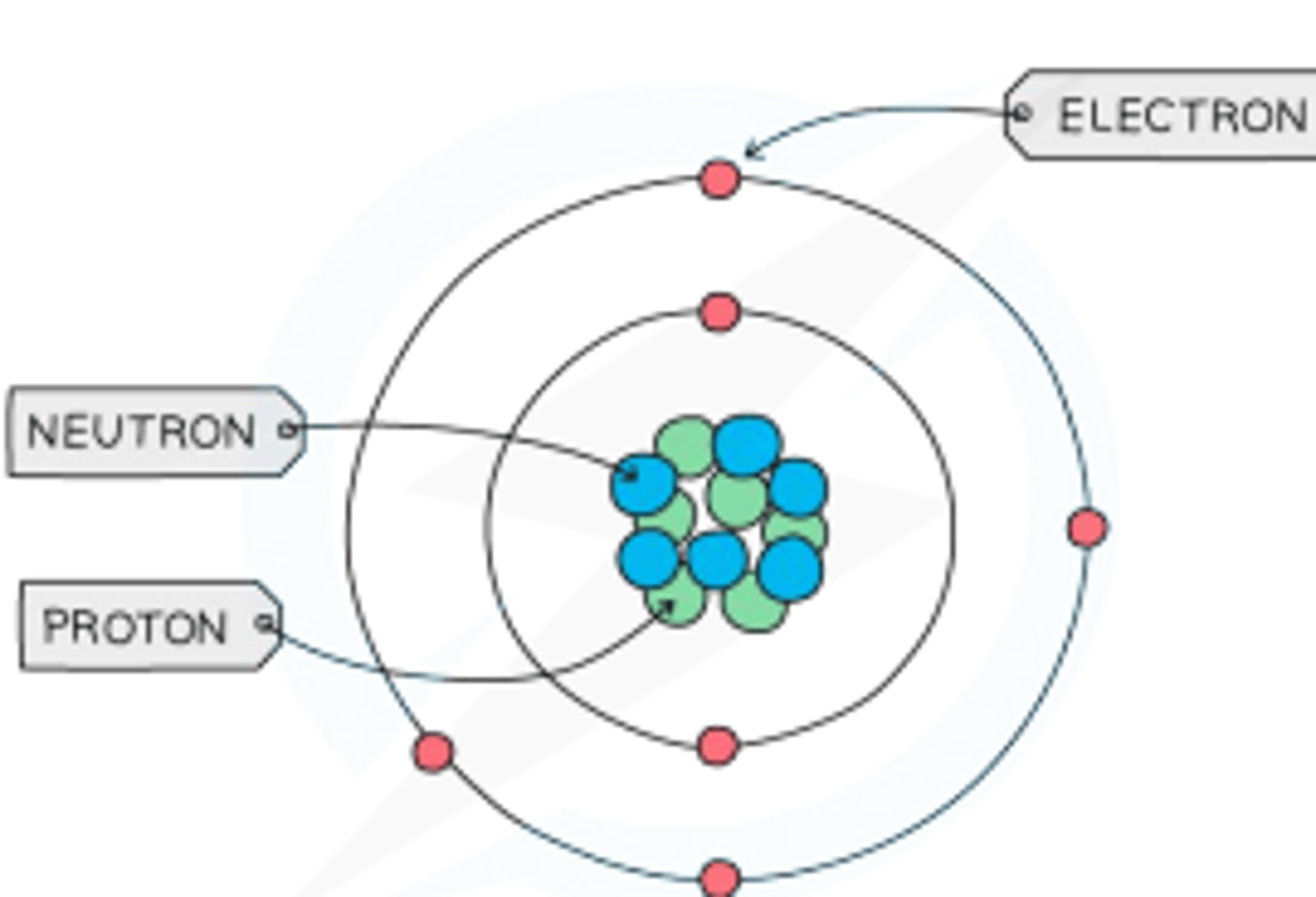
State the three subatomic particles
Protons, neutrons, electrons
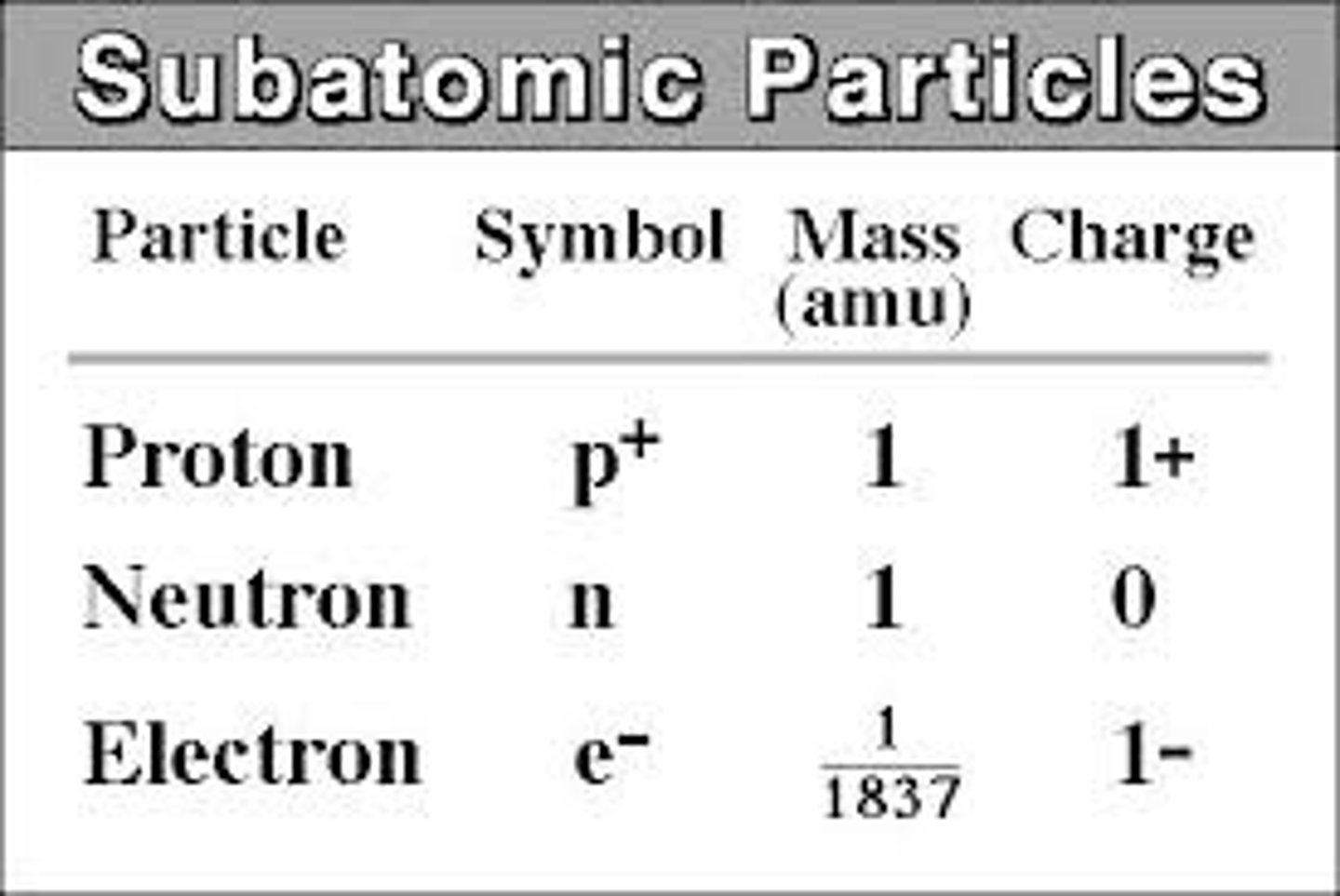
State the masses of the subatomic particles
Protons: 1, neutrons: 1, electrons: 0
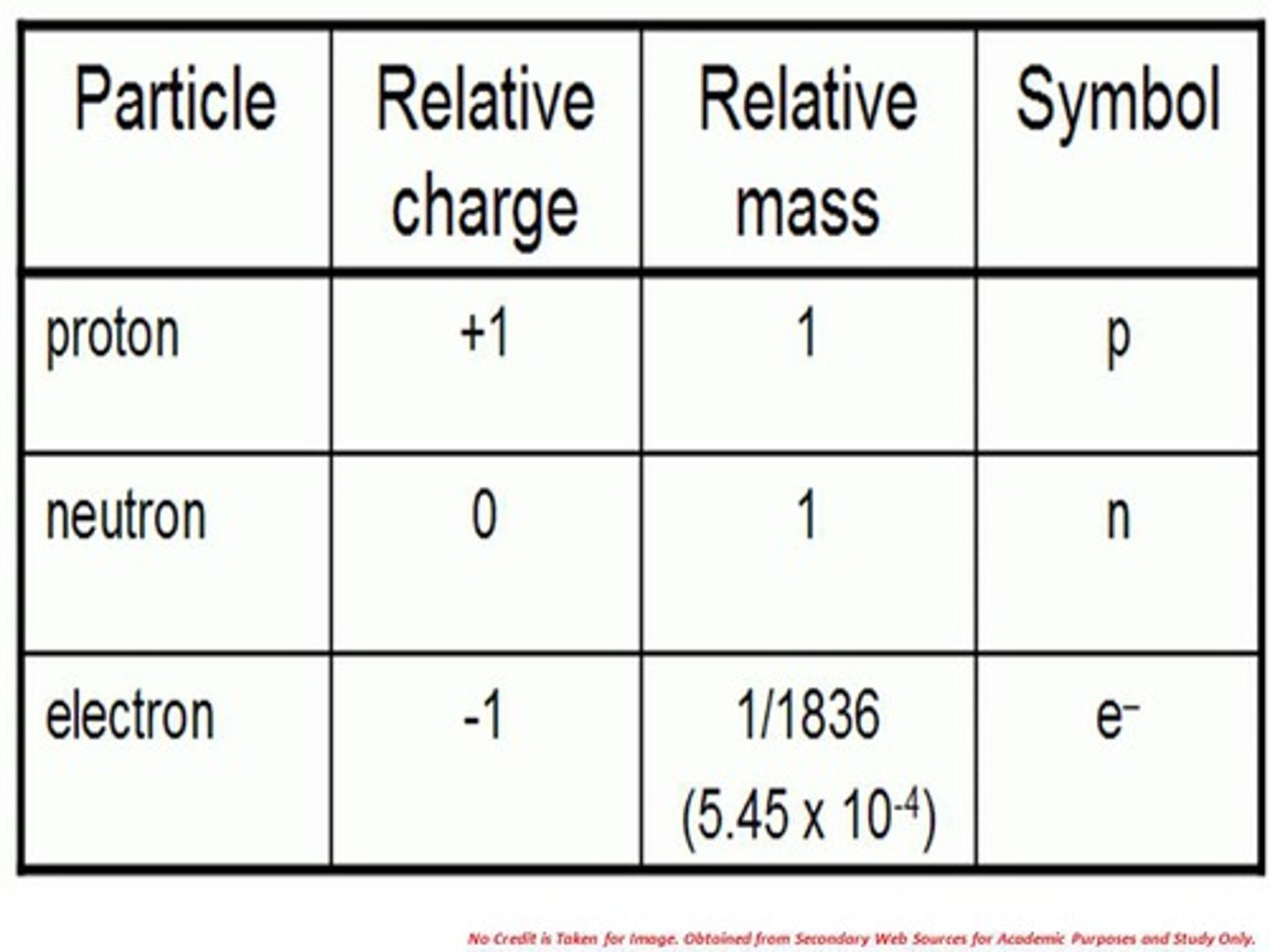
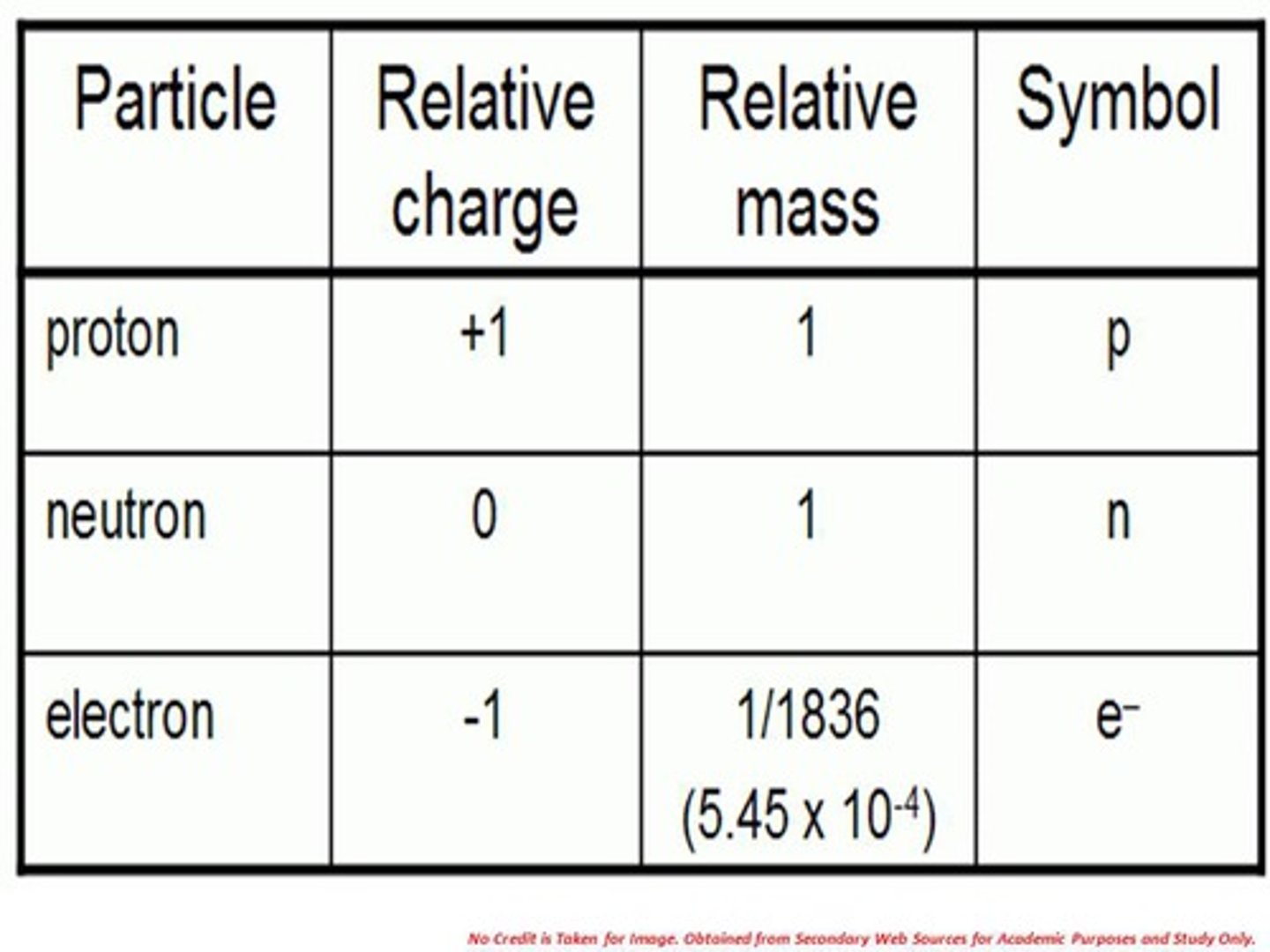
State the relative charges of the subatomic particles
Protons: +1, neutrons: 0, electrons: -1
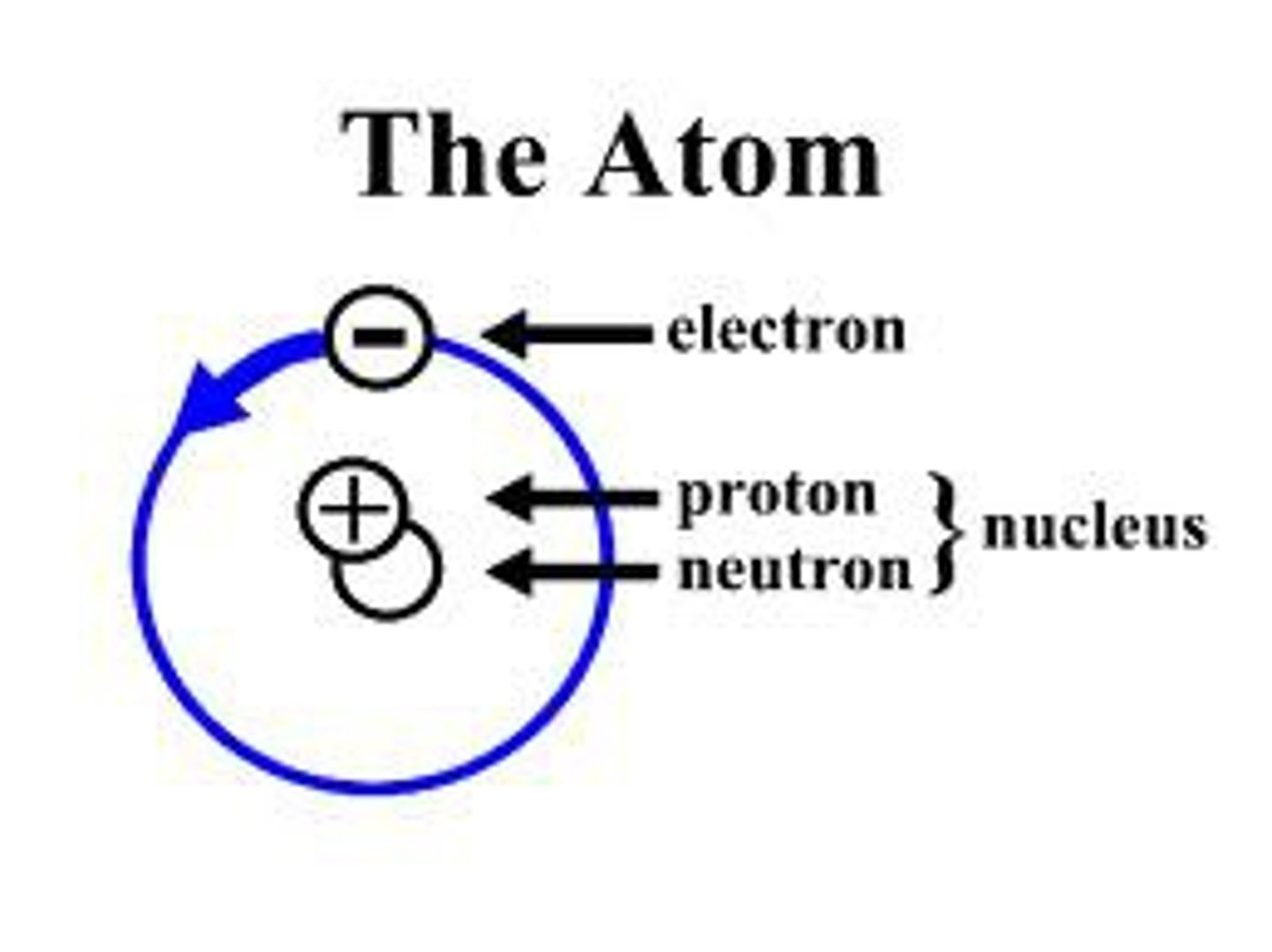
How are the subatomic particles arranged in an atom? (3 marks)
Protons and neutrons in the nucleus, electrons orbiting in shells
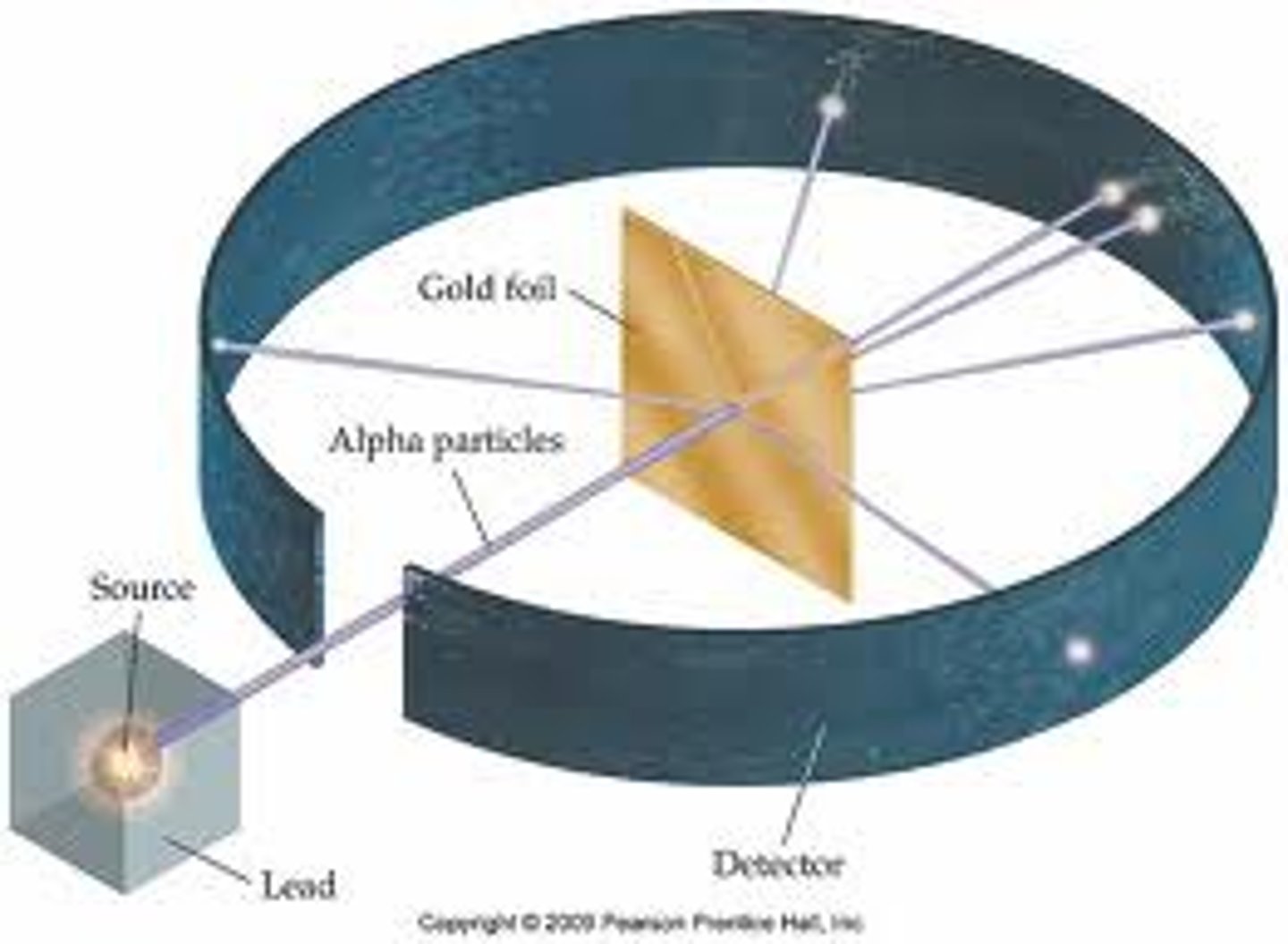
What did the gold foil experiment suggest?
That atoms have dense nucleuses with a positive charge
What is the atomic number of an atom?
The number of protons in an atom
What is the mass number of an atom?
The number of protons + the number of neutrons in an atom
How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom?
Mass number - atomic number
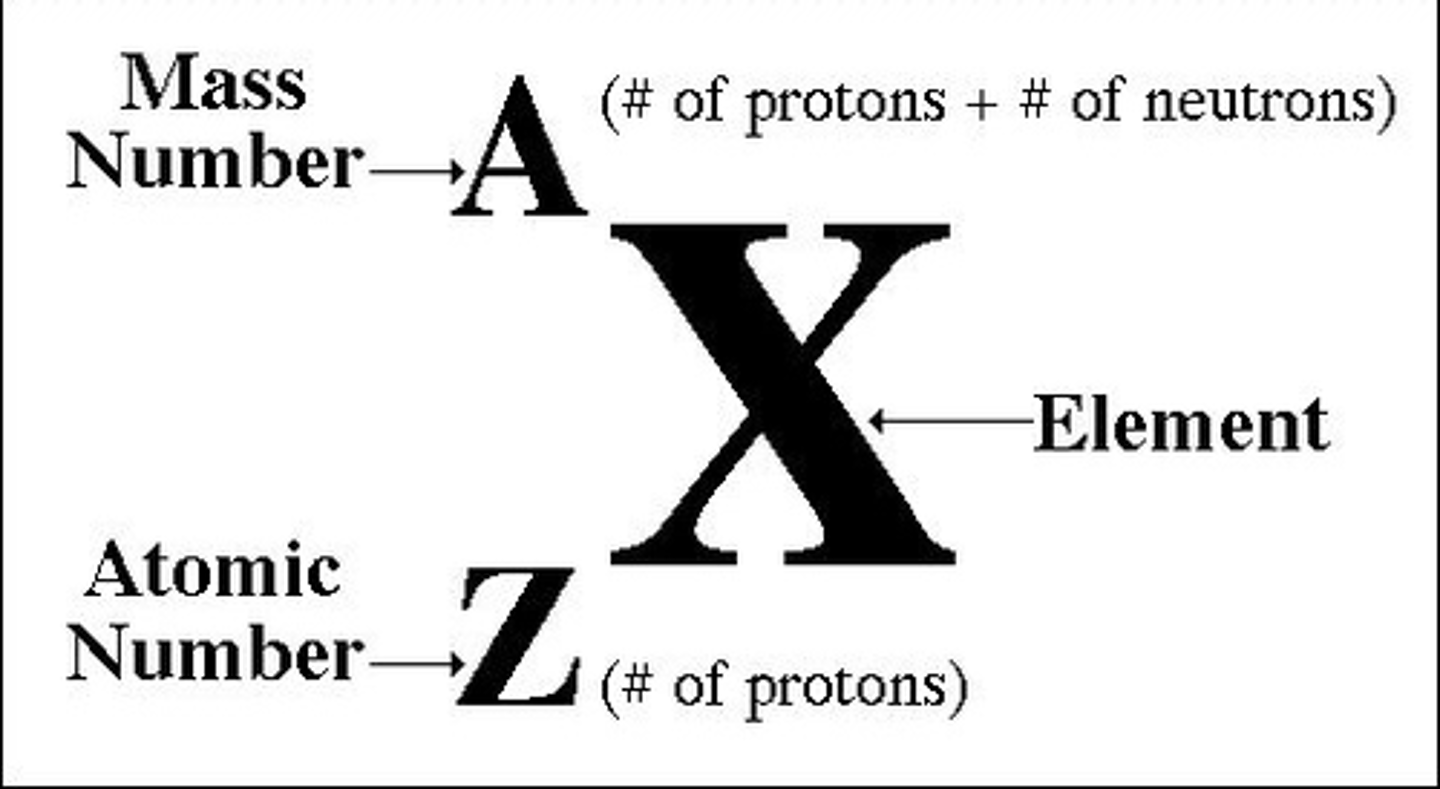
How are the electrons arranged in atoms?
Orbiting the nucleus in shells
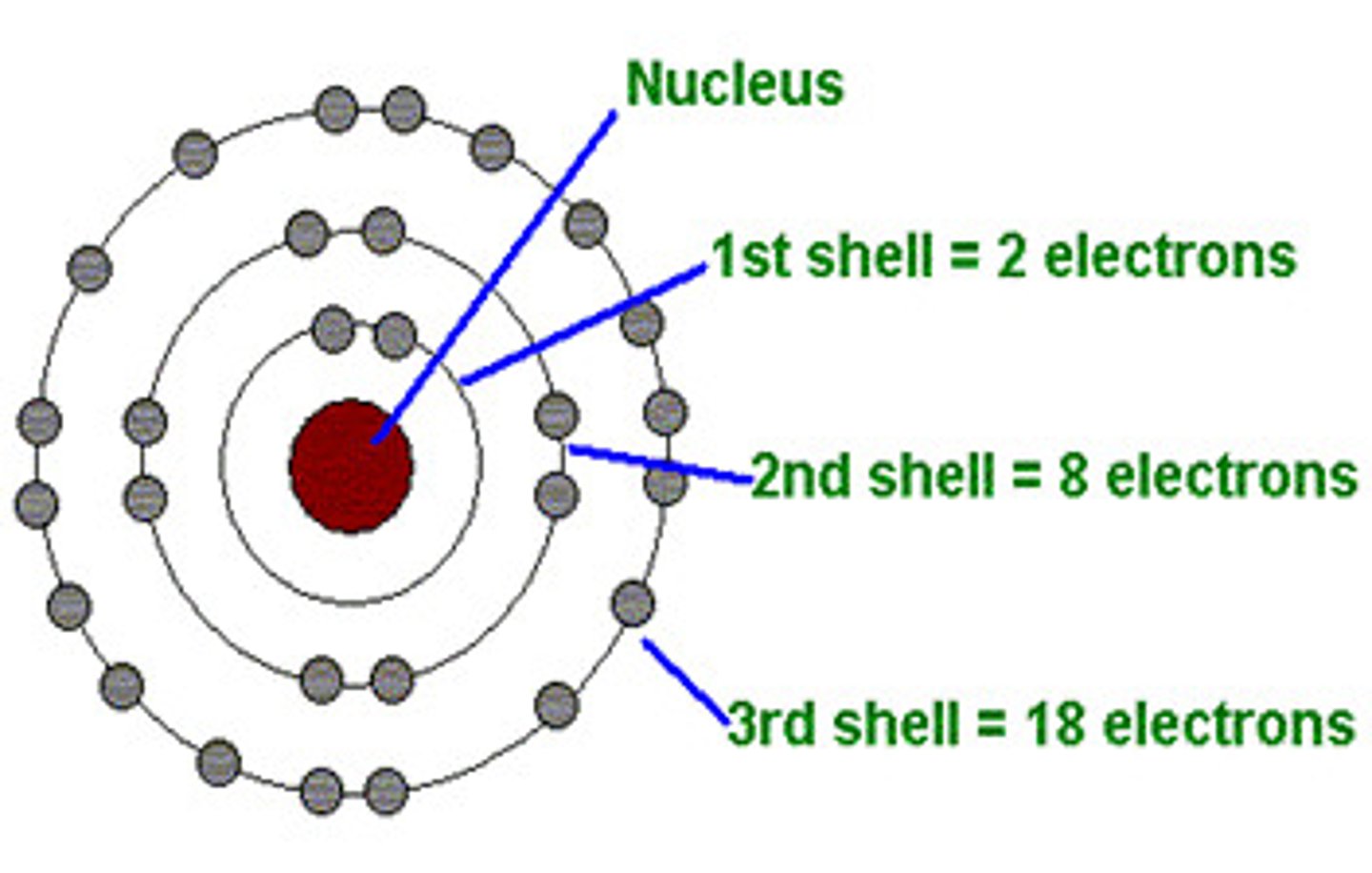
How many electrons can go in the first shell?
2
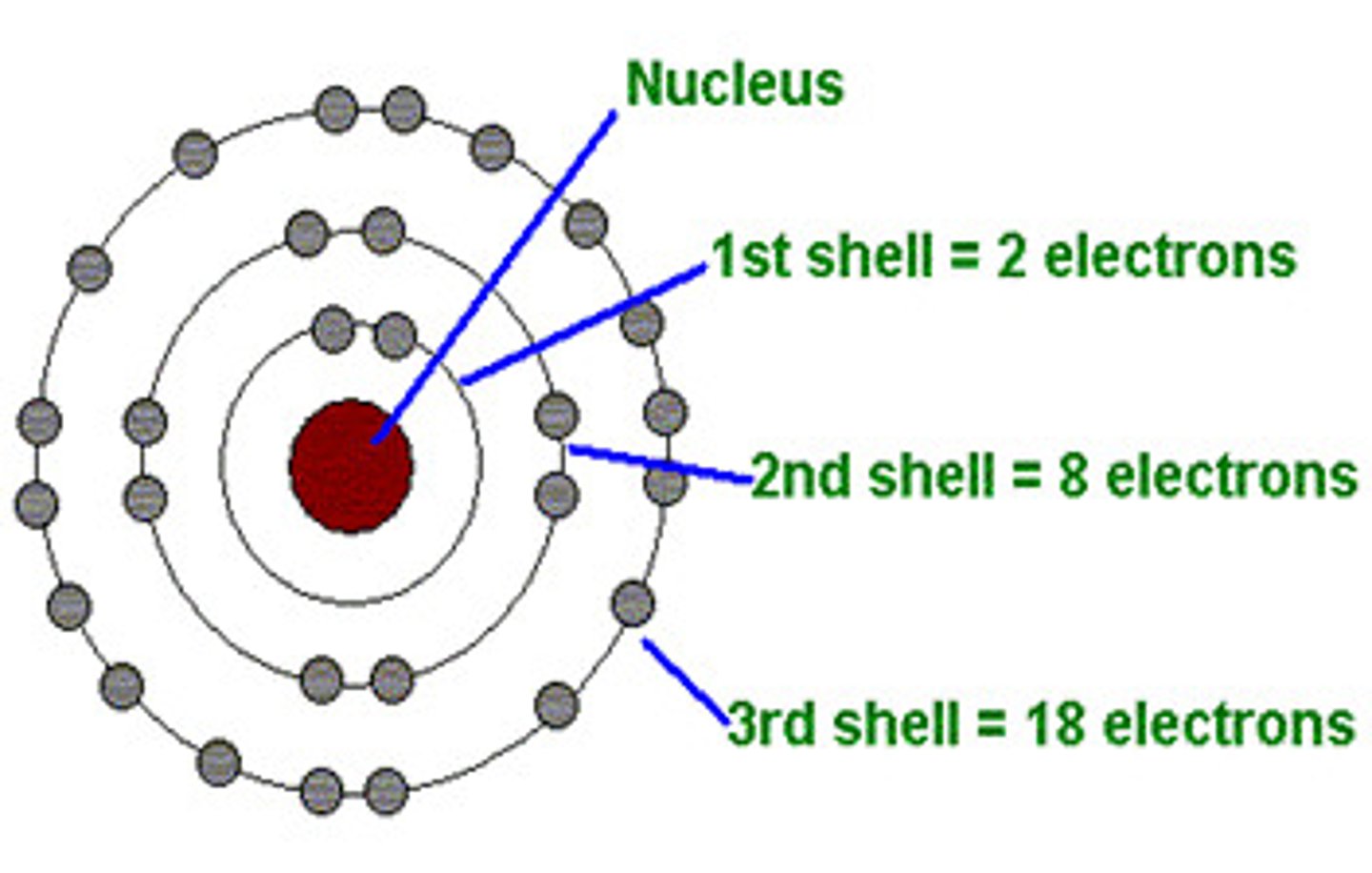
How many electrons can go in the second and third shells?
8

How many electrons does a calcium atom have?
20

How many electrons does a silicon atom have?
14

How are the electrons in sulphur arranged?
2,8,6
How are the electrons in magnesium arranged?
2,8,2
How many electrons are in the outer shell of boron?
3
How many electrons are in the outer shell of phosphorous?
5
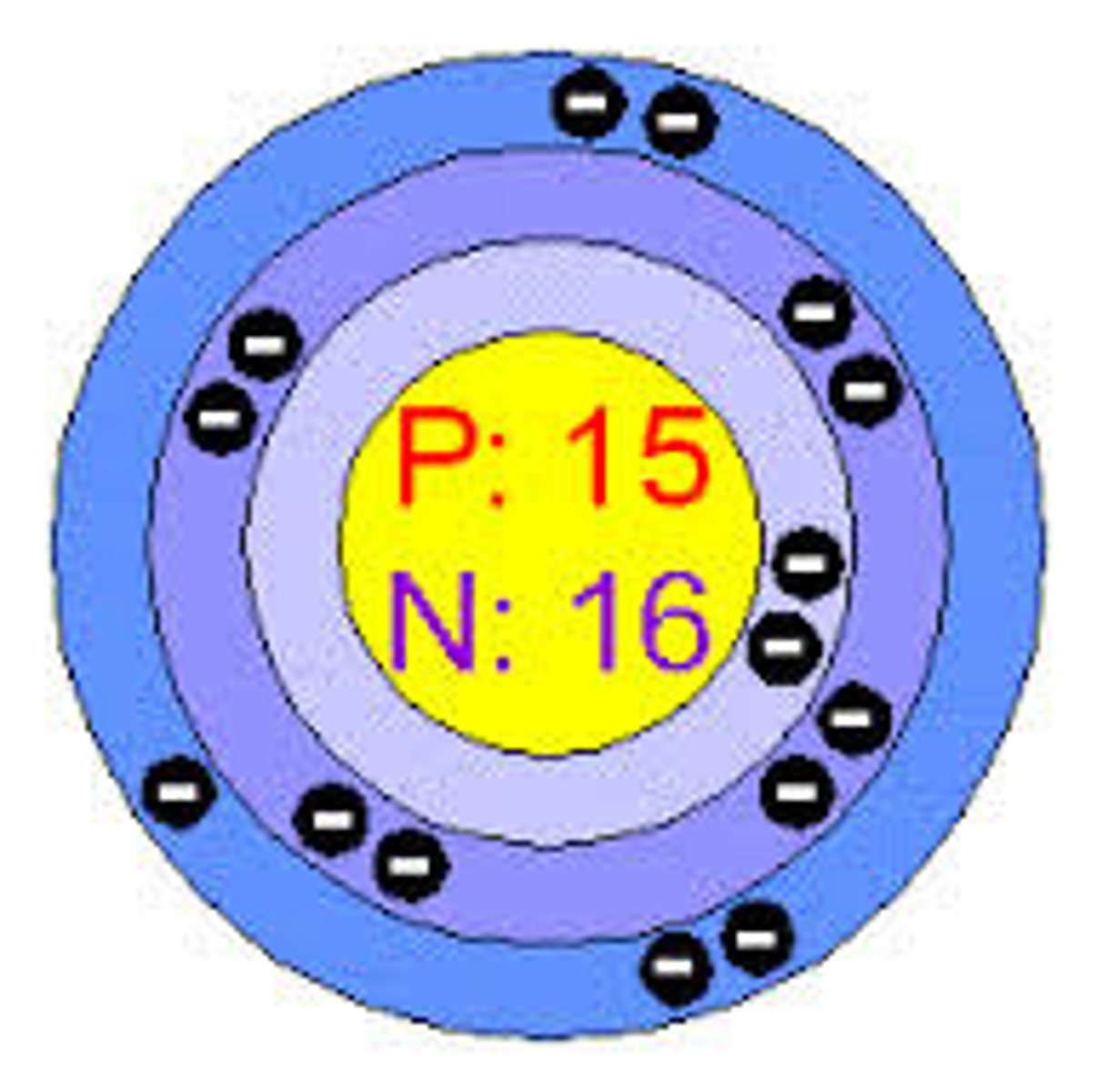
How many electrons are in the outer shell of sodium?
1
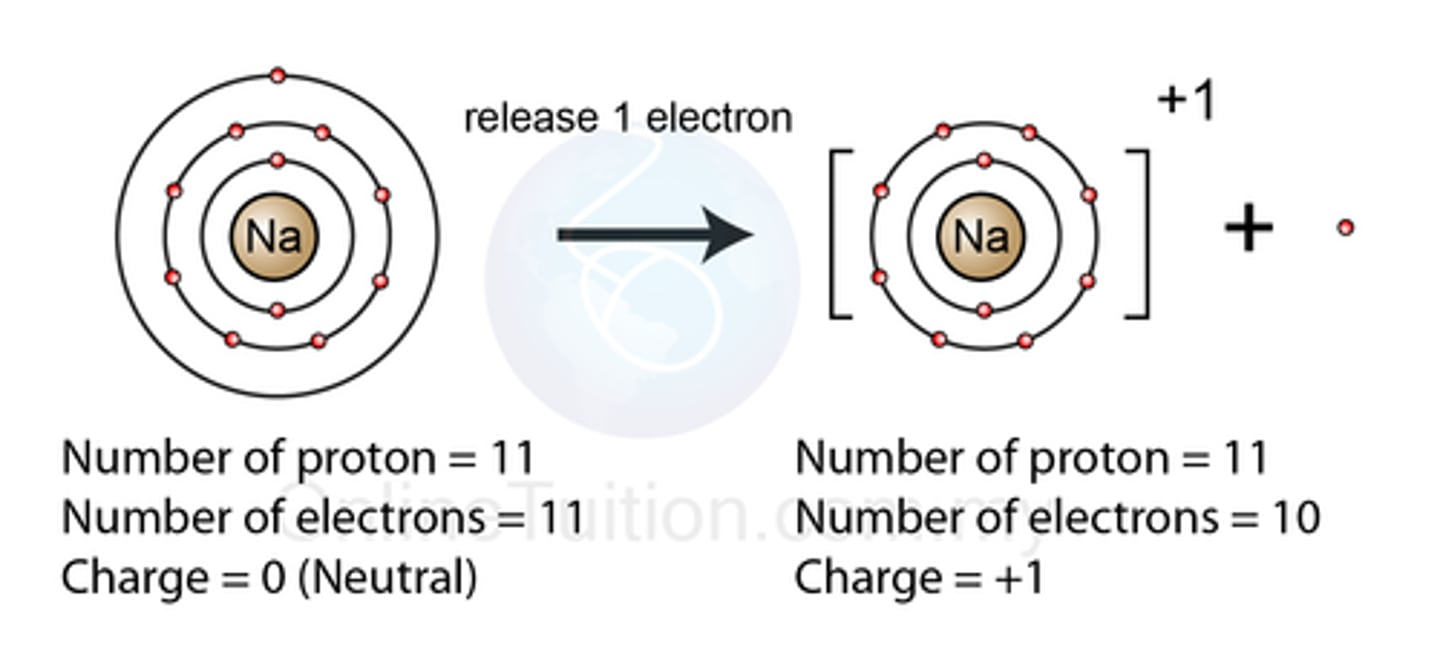
An element has three shells and three electrons in the outer shell. What element is it?
Aluminium (group 3, period 3)
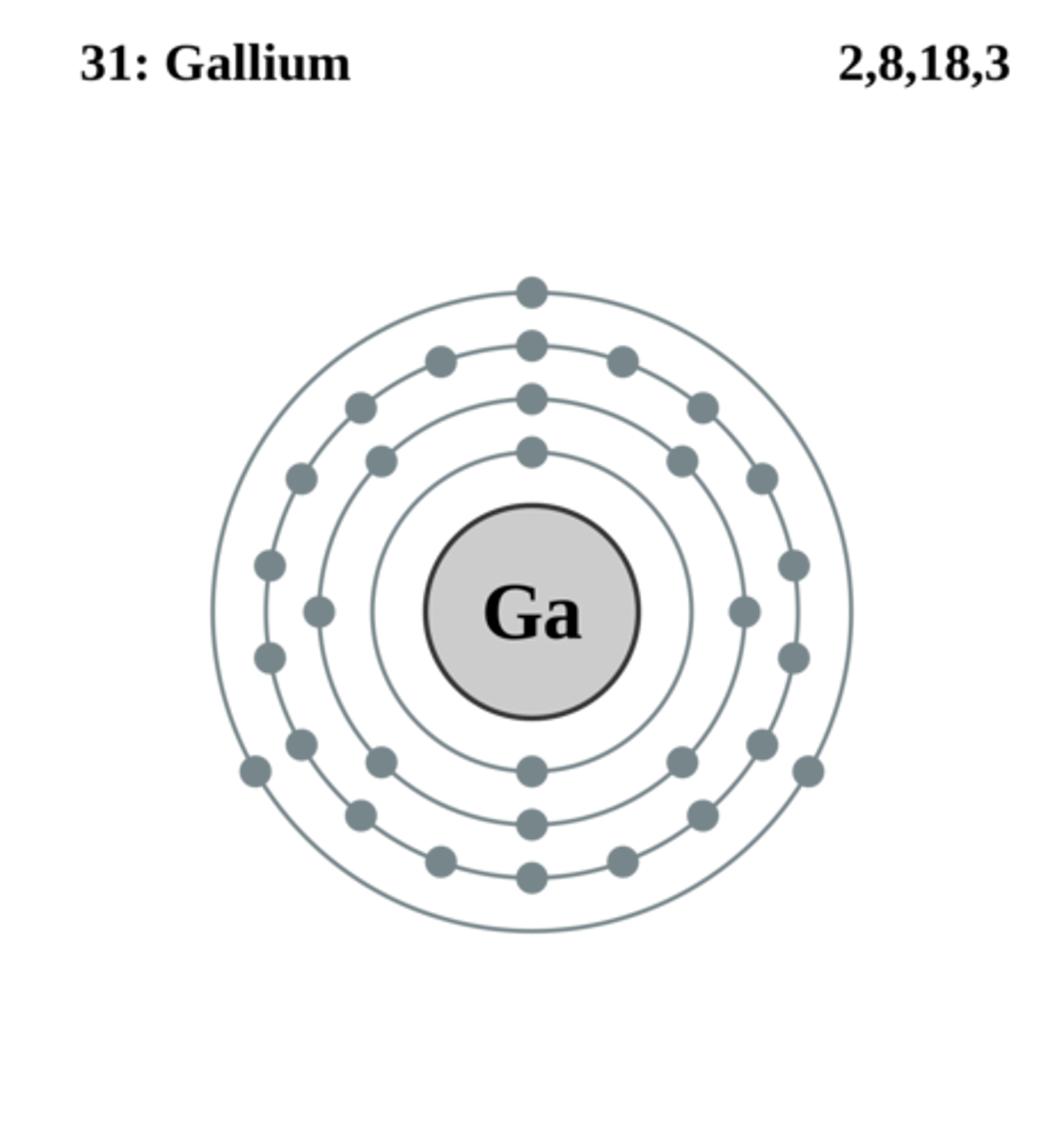
How many electrons are in the outer shell of Gallium?
3
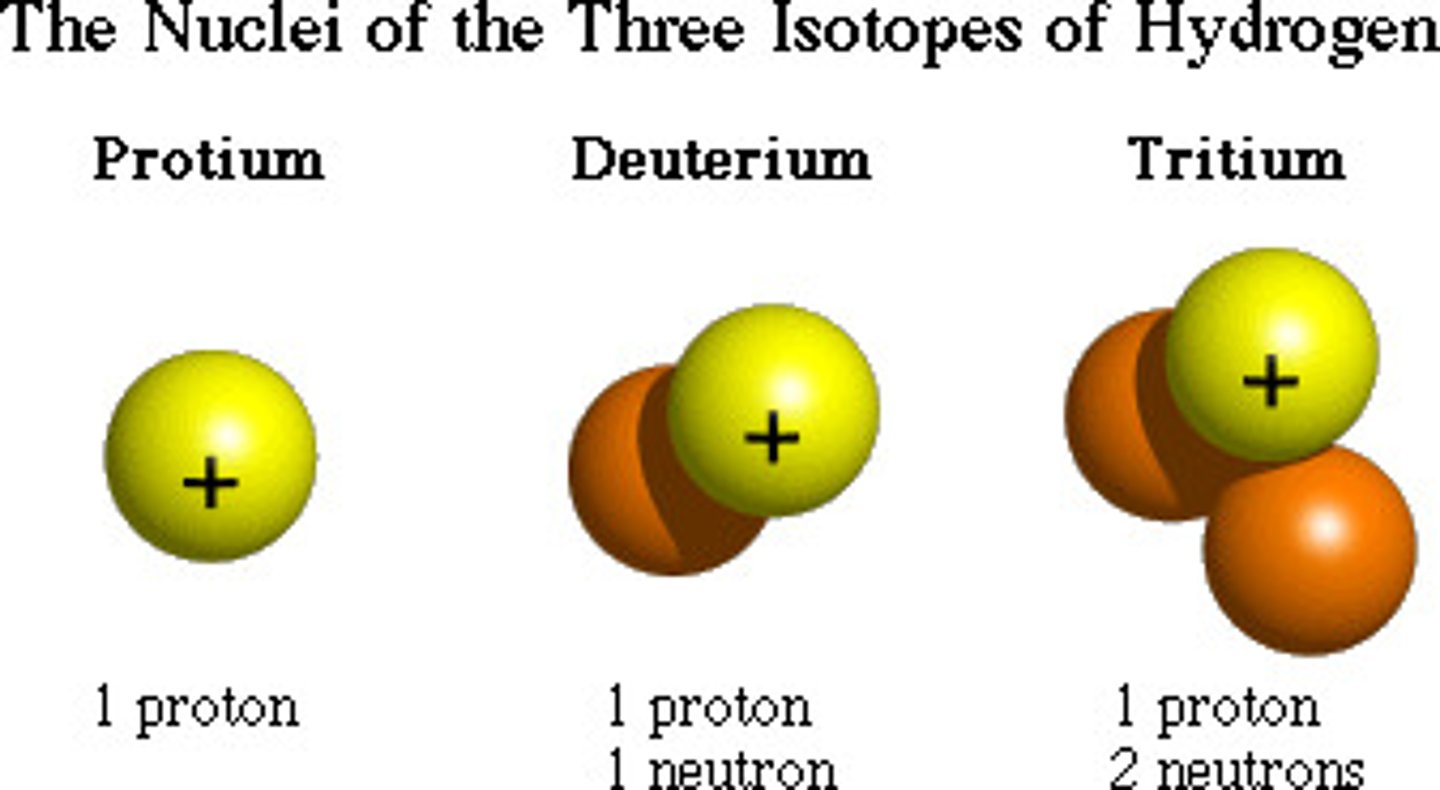
What are isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Explain why atoms have no overall charge.
They have equal numbers of protons and electrons
Define relative atomic mass
The average mass of one atom of an element, relative to carbon-12
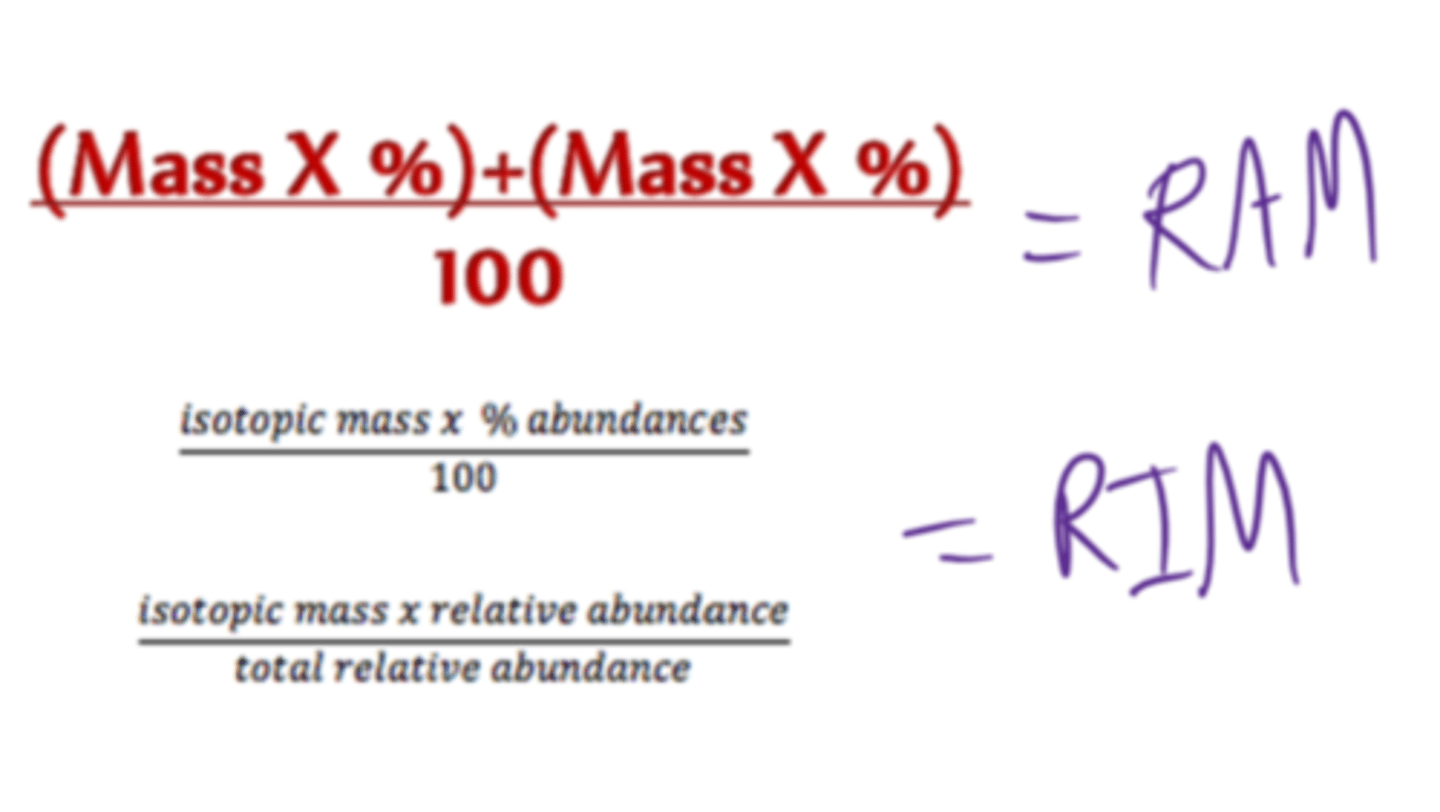
Why are relative atomic masses not whole numbers?
Because they are weighted averages of the masses of all the known isotopes of an element

Describe how to calculate relative atomic mass
(atomic mass1 x abundance1)+(atomic mass2 x abundance2) etc
What are groups in the periodic table?
The columns, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0
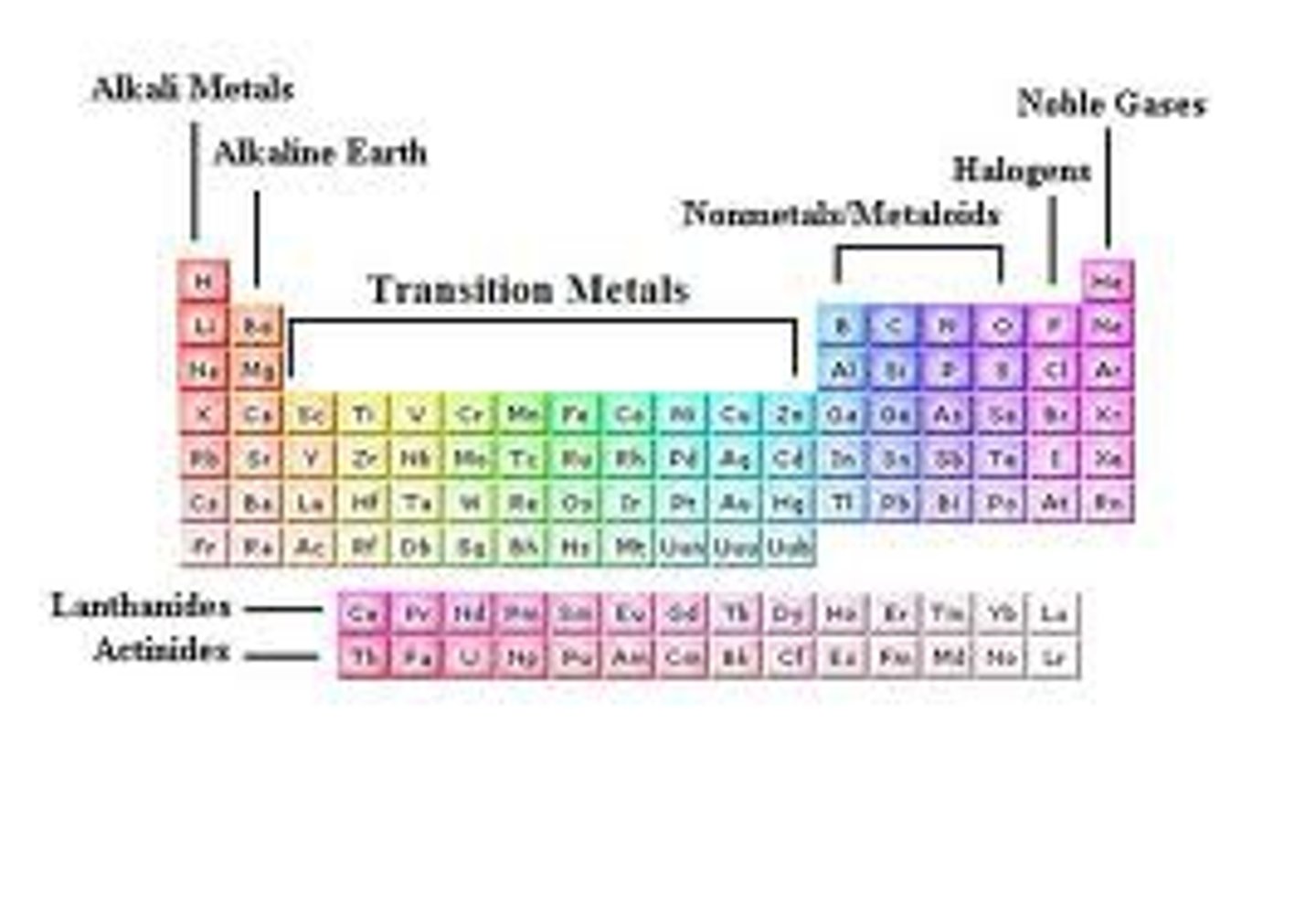
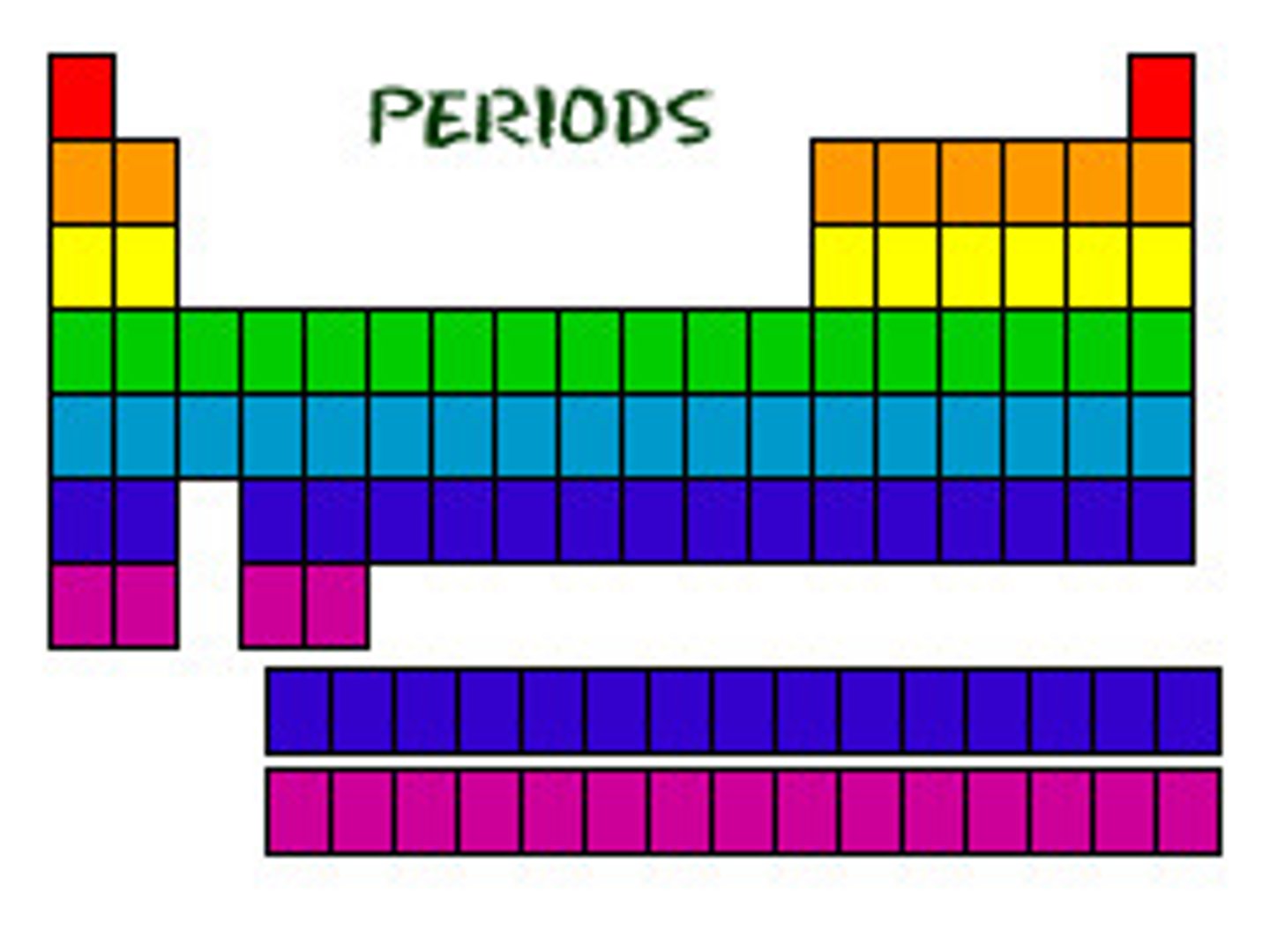
What are periods in the periodic table?
The rows in the periodic table
The elements in the periodic table are in order of...
... increasing atomic number
What can the group tell you about the electrons in an atom?
How many electrons in the outer shell. E.g. carbon is in group 4 so has 4 electrons in the outer shell
What can the period tell you about the electrons in an atom?
How many shells an atom has. E.g. carbon is in the second period so has two shells
An atom has four shells and two valence electrons. What element is it?
Calcium
How many valence electrons do the group3 elements have?
3
What is special about the valence shell of the group 0 elements?
They are full
How many electron shells do the period 2 elements have?
2
How many valence electrons do the group 7 elements have?
7
Metals are generally _________ (good/poor) electrical conductors and non-metals are generally _________ (good/poor) electrical conductors.
good, poor
Metal oxides are generally ________ (acidic/basic)
basic
Non-metal oxides are generally ________ (acidic/basic)
acidic
Describe how the acid-base character of the oxides period 3 elements changes as you move across the period.
basic to acidic
Explain why the group 1 elements are called alkali metals
They are metals that form alkalis when they react with water
Describe how the metallic and non-metallic character of the elements in period 3 changes as you go across the period.
metallic to non-metallic
What is the name given to the elements that have a mixture of metallic and non-metallic properties?
Metalloids (or semi-metals)
Why do the elements in the same group often have similar chemical properties?
They have the same number of valence electrons.
In terms of electrons, what do group 1 elements have in common?
1 electron in the outer shell
In terms of electrons, what do group 7 elements have in common?
7 electrons in the outer shell
In terms of electrons, what do group 0 elements have in common?
Full outer shell
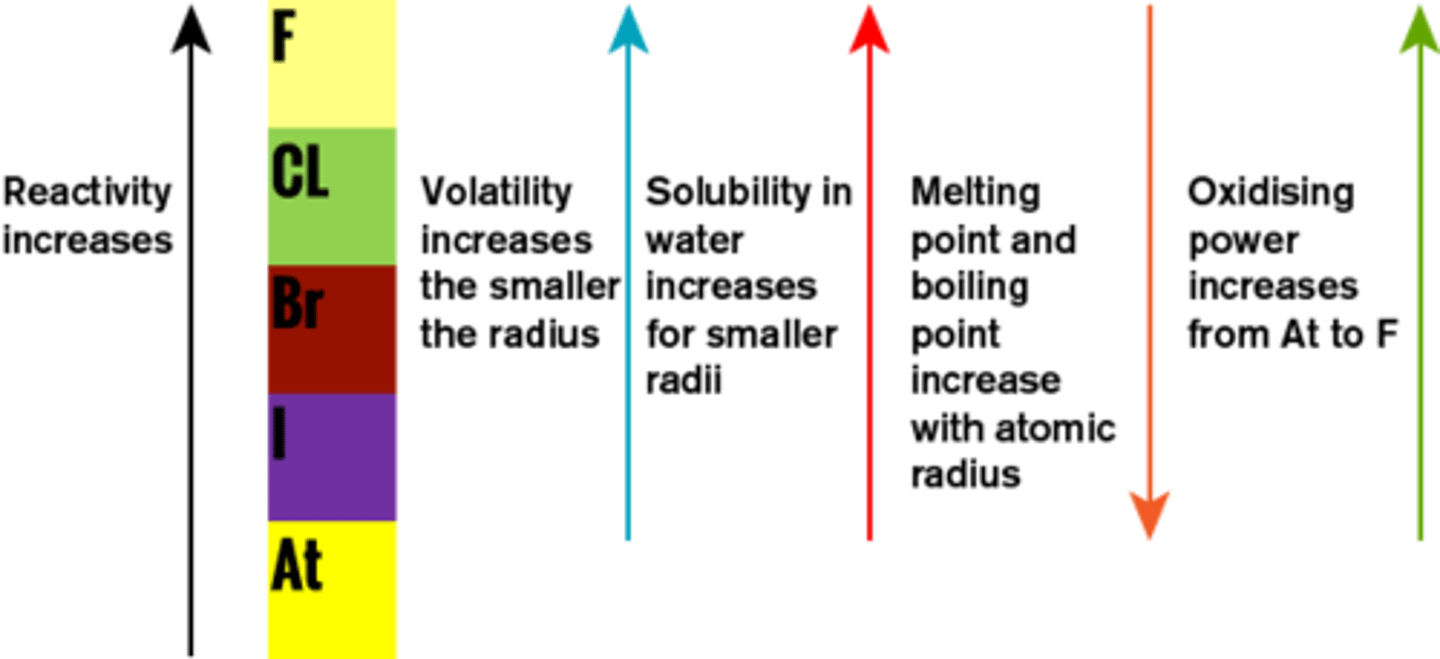
What is more reactive, lithium or sodium?
Sodium

What is more reactive, chlorine or bromine?
Chlorine
Define inert
Unreactive
Explain why the noble gases are inert
They have full outer shells, so do not need to gain or lose electrons

What is a trend?
A pattern in properties
