AP Human Geography, Unit 2.2
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
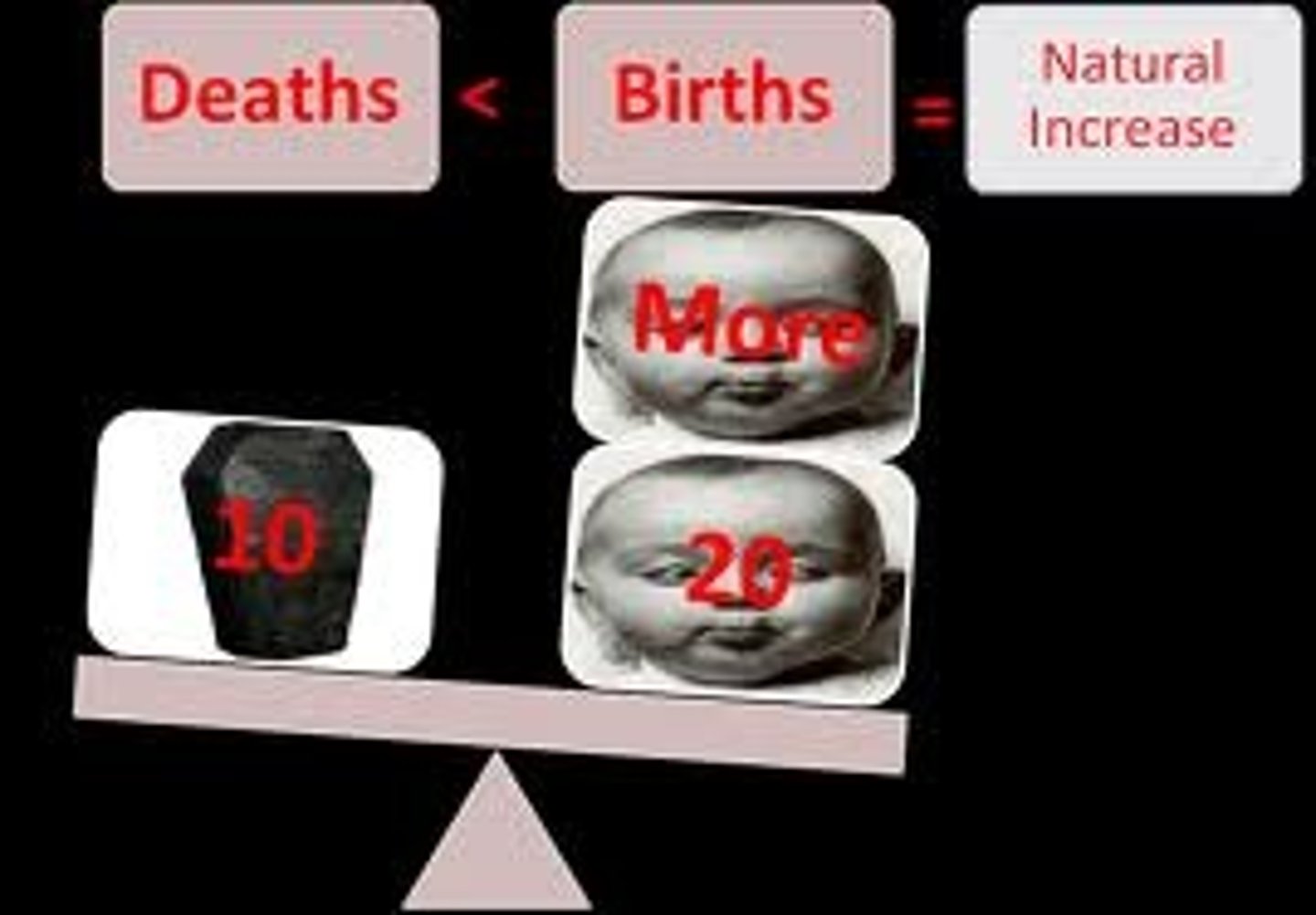
Natural Increase Rate
The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.

Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.

Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.

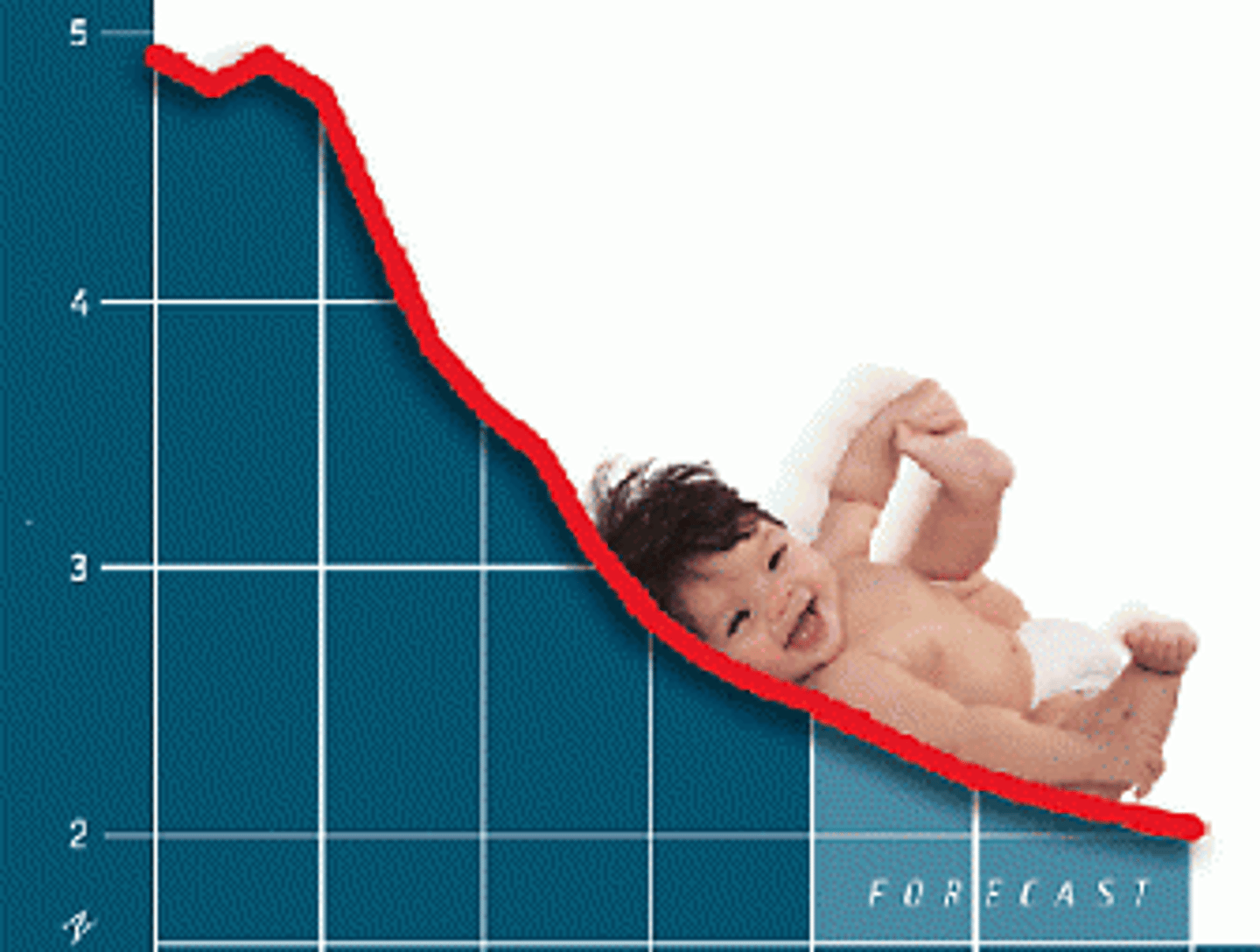
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.

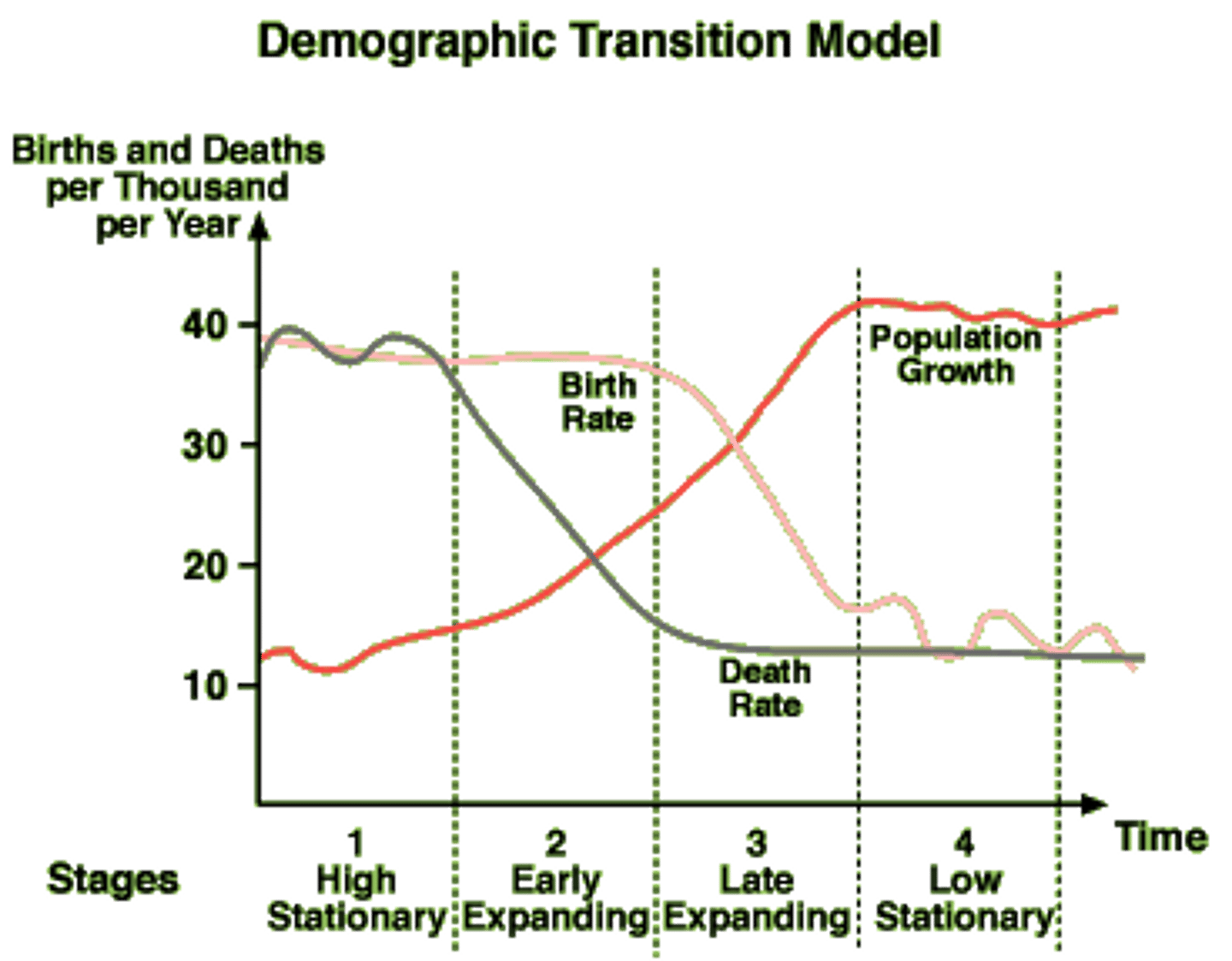
Demographic Transition Model
The process of change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth and death rates, low rate of natural increase, and a higher total population.
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods.
Medical Revolution
Medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to the poorer countries of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. Improved medical practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death in poorer countries and enabled more people to live longer and healthier lives.
Agricultural Revolution
The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering.

population explosion
a sudden increase or burst in the population in either a certain geographical area or worldwide
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
A decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.
