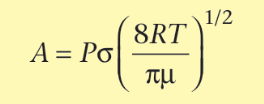kinetics
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what are the three assumptions about gas molecules?
size?
collisions?
energy?
size of molecules is negligible compared to size of container. molecules are point masses
collisions are perfectly elastic.
all interactions are negligible except during collisions. molecular energy is kinetic energy of translation.
what do ‘elastic’ collisions mean?
no energy lost or gained on collision
how does gas pressure arise?
collisions with the wall of the container
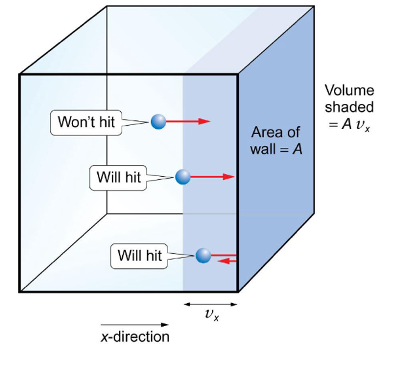
why do only some molecules hit the wall in a particular second?
in one second, a molecule moving at vx velocity (m/s) travels a distance of vx (m)
any molecule within this distance of the wall strikes it during the second, further away will not
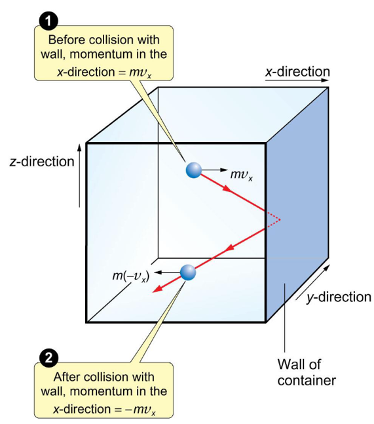
how does momentum in the x direction change after hitting the wall?
why?
becomes negative
velocity changes sign as changes direction
collision is perfectly elastic so momentum has same magnitude
what does pressure depend on?
how many molecules hit walls per second
the force exerted when they hit it (depending on how fast)
what does frequency of collisions depend on?
concentration of gas
what does speed of molecules depend on?
temperature
what does root mean square speed link?
molecular motion and gas temperature
what is effusion?
gas escapes through a hole
what is diffusion?
different gases mix
what does rate of effusion mean?
number of molecules that pass through a hole per unit time
what is Graham’s law? (rate of effusion)
rate of effusion inversely proportional to square root of molar mass

how to calculate relative rates of effusion?
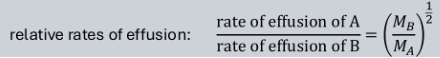
what is the equipartition theorem of kinetic energy?
Kx = Ky = Kz = ½ RT
what is the equation for total kinetic energy using equipartition theorem?
K = Kx + Ky + Kz = 3/2 RT
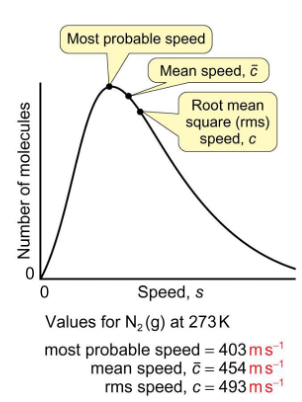
where is the most probable speed, mean speed, and root square mean speed on Maxwell Boltzmann graph?
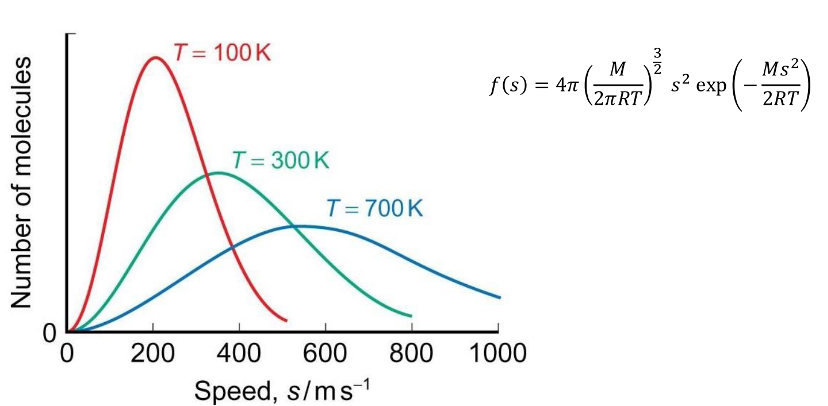
how does Maxwell Boltzmann distribution change at higher temperatures?
shifts to the right and becomes broader
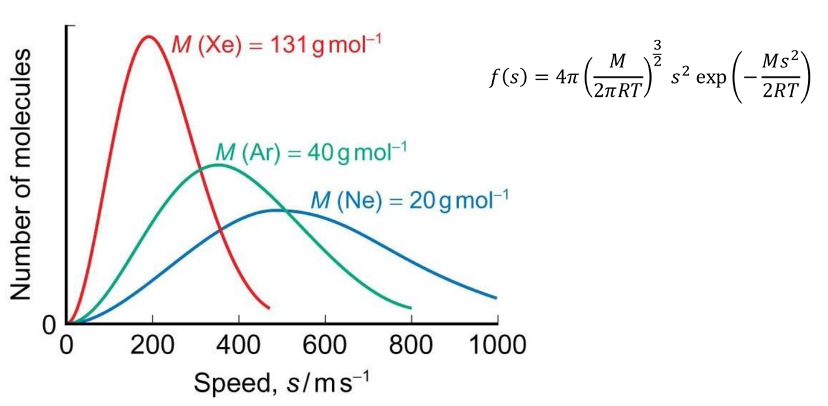
how does Maxwell Boltzmann change at higher mass?
shifts to the left and becomes narrower
how does molecular volume affect ideal gas equation?
molecules have size which reduces the volume available to move in
how does intermolecular forces affect ideal gas equation?
intermolecular forces reduce force with which they hit walls
attractive forces hold molecules back
what are the conditions of the deviations of ideal gas equation?
high pressures and low temperatures
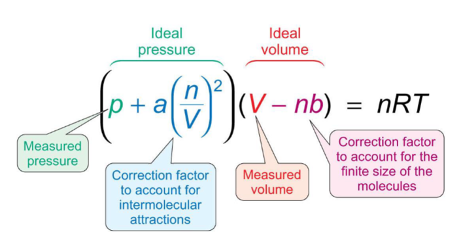
how do the terms in van der Waals equation account for non-ideal behaviour?
a term - corrects for intermolecular interactions
b term - corrects for finite size of molecules
how does the ideal gas equation not account for gas liquefaction?
it assumes you can indefinitely increase pressure but at some point it will turn into a liquid and is more difficult to compress
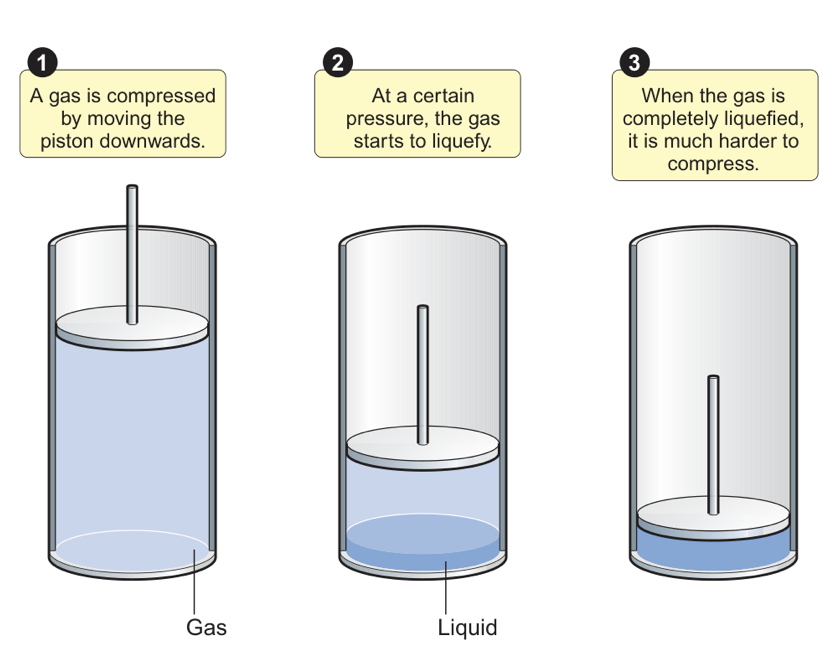
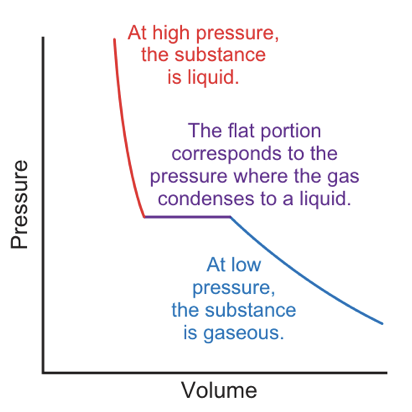
pressure vs volume graph of liquefaction
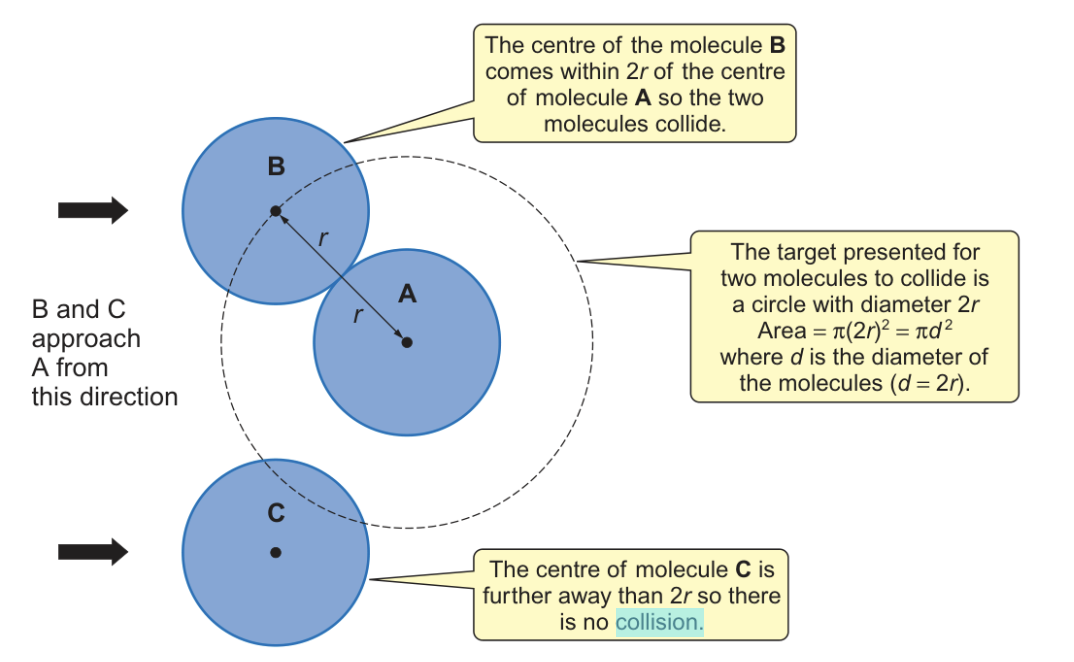
where must a molecule be for a collision to occur (collision cross section)?
centre of a molecule must be within one diameter of the centre of another
one radius from edge of molecules
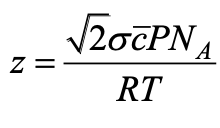
what do the different terms mean in collision frequency equation?
NAP/RT is the density of molecules
the rest is the volume of collision tube - moving molecule sweeps
what is mean free path in words?
what does it determine?
mean distance travelled per unit time / mean number of collisions per unit time
determine how far molecules travel between collisions
what is the rate of a reaction?
change in concentration of reactants/products over time
what graph is a straight line for first order?
what is the gradient?
ln[A] vs time
gradient = -k
what graph is a straight line for zero order?
what is the gradient?
[A] vs time
gradient = -k
what graph is a straight line for second order?
what is the gradient?
1/[A] vs time
gradient = +2k
what is the first order rate equation?
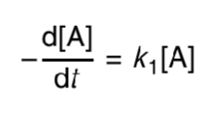
what is the integrated first order rate equation?
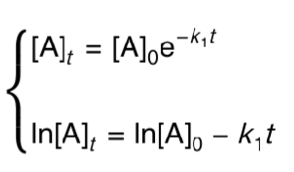
what is the second order rate equation?
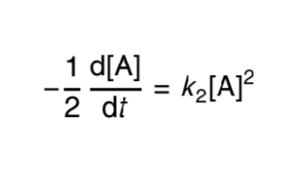
what is the integrated second order rate equation?
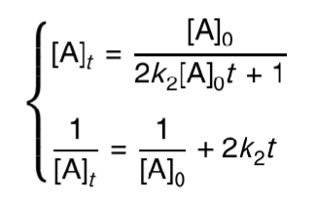
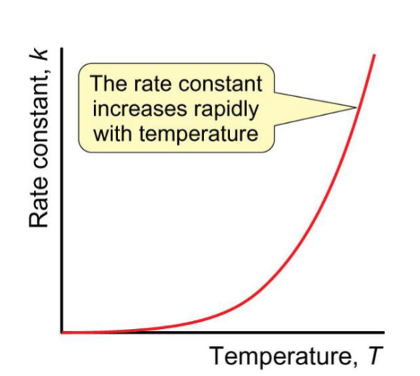
how does rate change with temperature?
why?
increase exponentially
molecular collisions become more energetic
rate constant vs temp graph
what is the gradient?
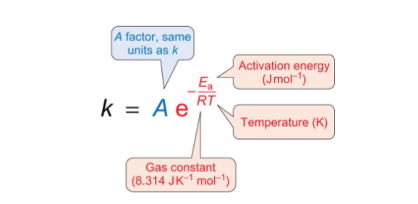
what does blue term mean?
what does red term mean?
A = rate constant if all collisions had enough energy to overcome the energy barrier
e-Ea/RT = fraction of collisions with minimum energy for reaction
what is activation energy?
minimum energy barrier that reactants must overcome to form products
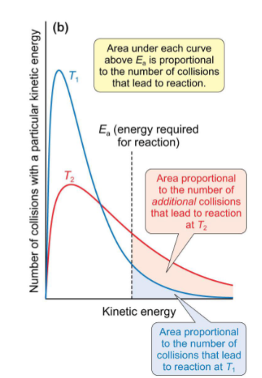
what is area under graph above Ea proportional to in Maxwell Boltzmann?
proportional to number of collisions leading to reaction
what is transition state theory?
assumes there is a pre-equilibrium between reactants and transition state
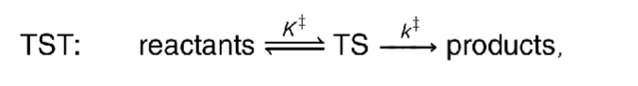
what is the rate equation for the TST equation?
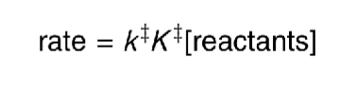
in the Arrhenius equation, what is the A factor related to?
what is the activation energy related to?
A factor related to ΔS
activation energy to ΔH
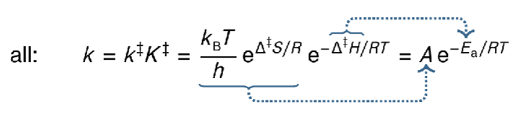
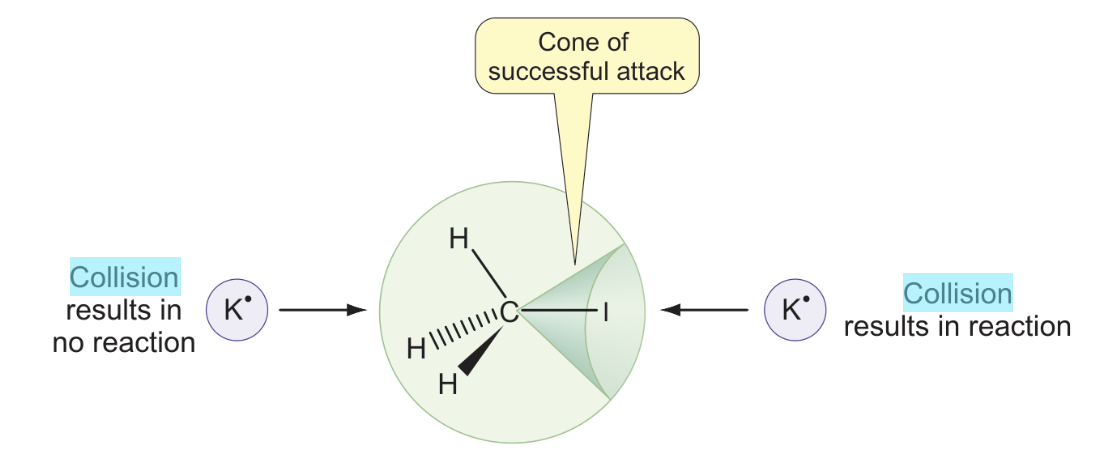
what is collision theory?
two molecules must collide with a minimum kinetic energy to overcome activation energy
what is the cone of successful attack?
what is the Arrhenius equation using collision theory?
what is P?
P is a probability factor as not all collisions with sufficient energy go on to form products
steric factor = reactants need to collide in specific orientation to react