Final AP CSP '24
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
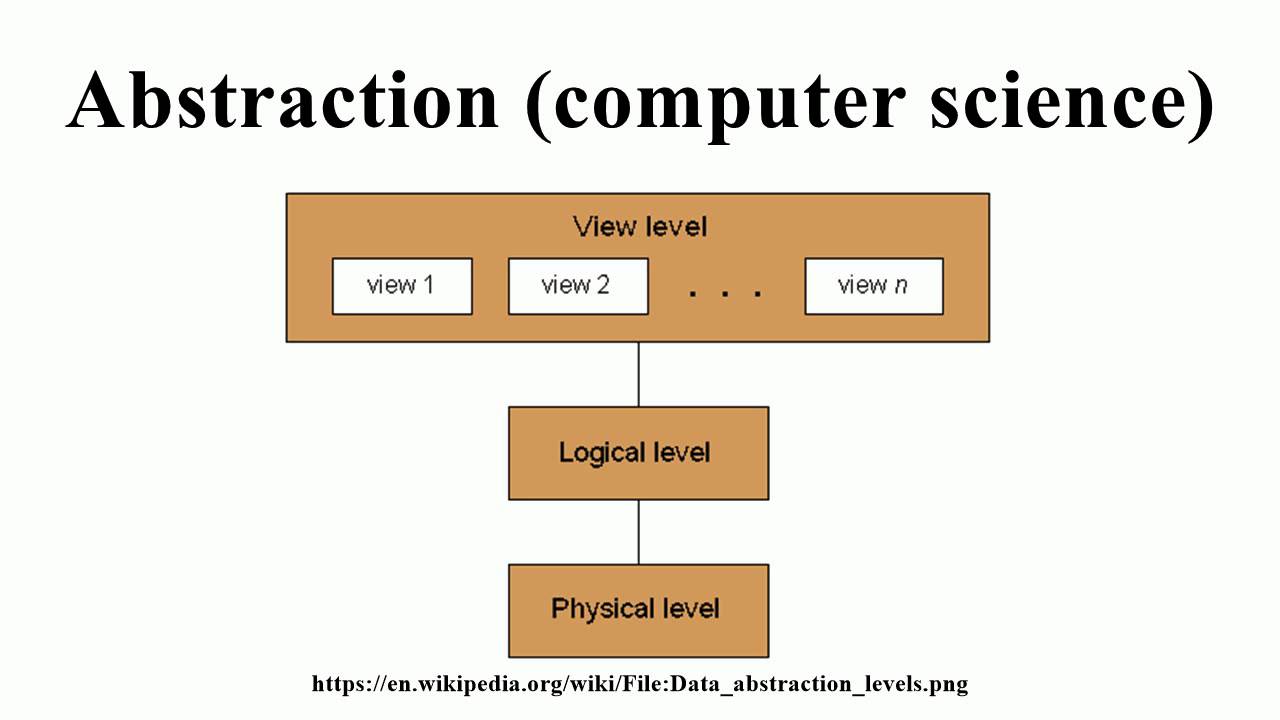
Abstraction
The process of reducing complexity by removing unnecessary details to focus on essential features.
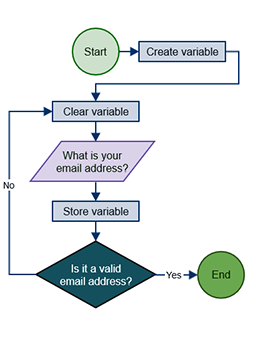
Algorithm
A step-by-step procedure or formula for solving a problem.
Ambiguity
The quality of being open to more than one interpretation; in computing, it refers to issues that can arise in code or logic.
Boolean
A data type that has two possible values: true or false.
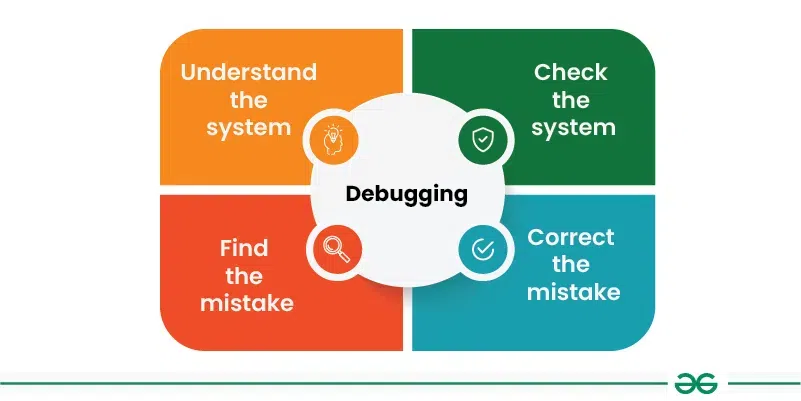
Debug
The process of identifying and removing errors or bugs from a computer program.
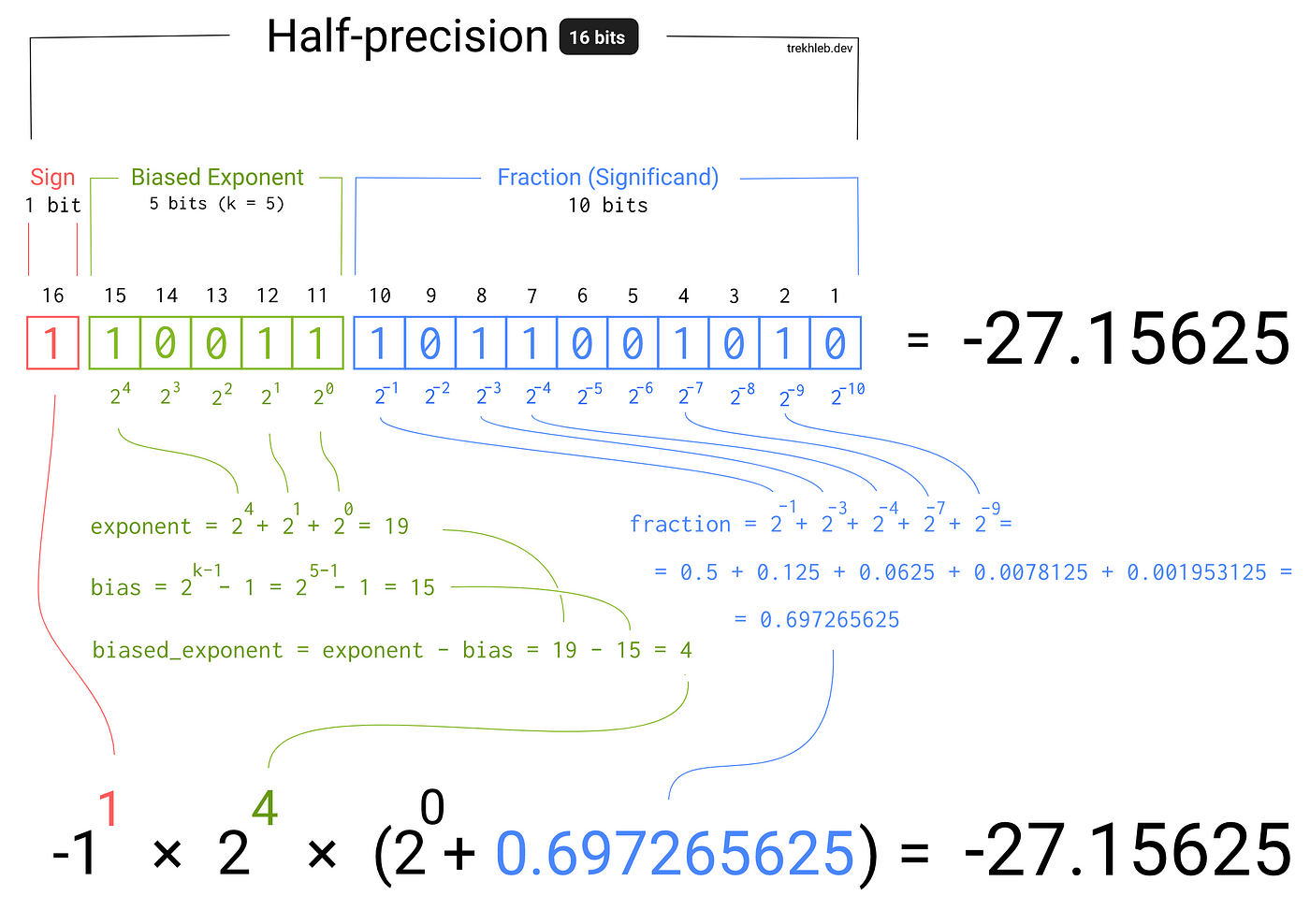
Float
A data type that represents real numbers and can contain fractions.
High-level Language
A programming language that is user-friendly (readable/easiest for humans to understand), often abstracting away the hardware details.
Example: Text-based code
Input
The data fed into a program for processing.
Integer
A data type used to represent whole numbers.

Iteration
The process of repeating a set of instructions until a specific condition is met.
Loop
A programming structure that repeats a sequence of instructions.

Low-level Language
A programming language that is closer to machine code and hardware operations.
Output
The data produced by a program after processing the input.
Program
A set of instructions that a computer follows to perform a task.
Program documentation
Written text that explains the purpose, functionality, and usage of a program.
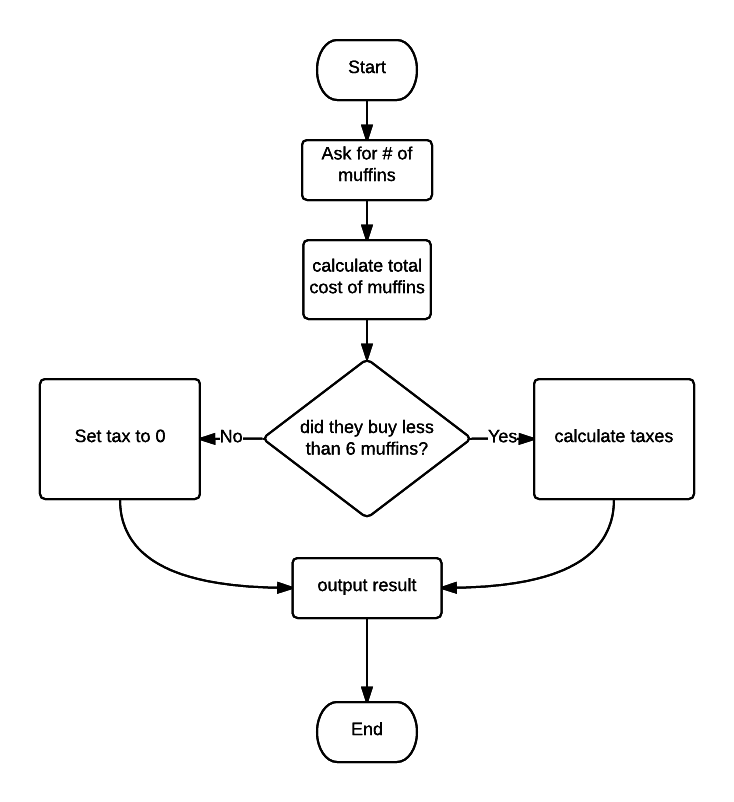
Selection
A programming structure that chooses between different paths of execution based on conditions.
Sequencing
The order in which instructions are executed in a program.
String
A sequence of characters used to represent text.
Variable
A named storage location in a program that can hold different values during execution.
Conditionals
Statements that perform different actions based on whether a specified condition is true or false.
Flowchart
A visual representation of a process or algorithm, using symbols to denote operations and flow direction.
Heuristics
Problem-solving methods that use practical approaches and shortcuts to find adequate solutions.
If block or statement
A conditional statement that executes a certain block of code if a specified condition is true.
If else block or statement
A conditional statement that executes one block of code if a condition is true and another block if it is false.
Indefinite Loop
A loop that continues until it is explicitly terminated, often based on an external condition.
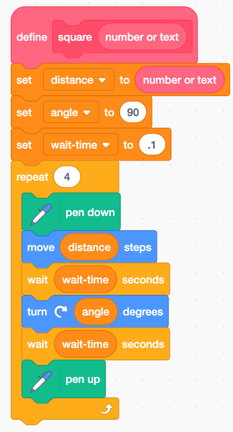
Parameter
A variable used in a function that allows the user to pass data into that function.
Procedure
A set of coded instructions that performs a specific task, also known as a function or method.
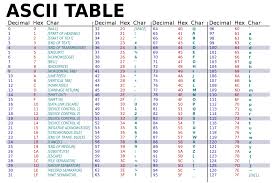
ASCII
A character encoding standard that uses numerical values to represent text in computers.
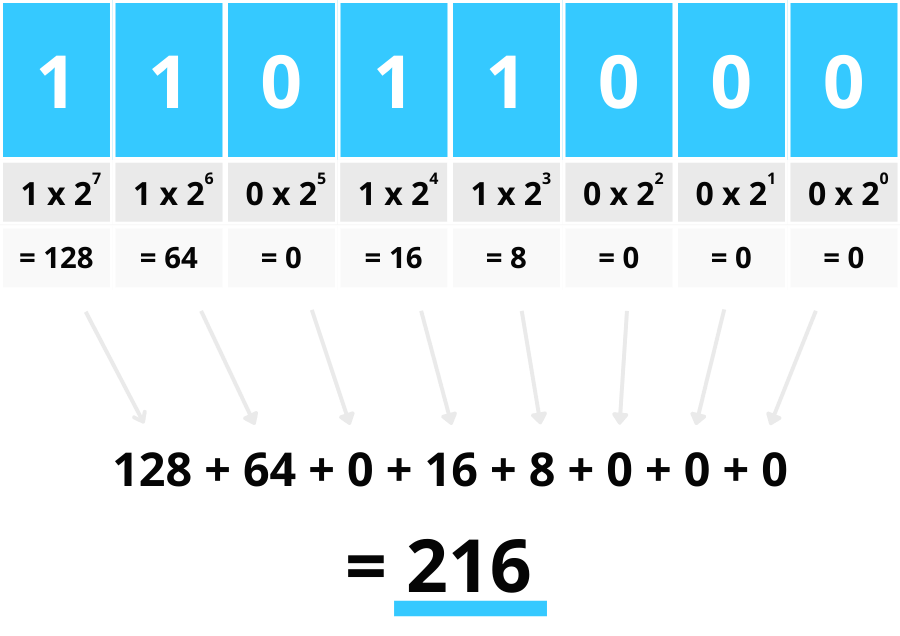
Binary code
A system of representing data using two symbols, typically 0 and 1.
Bit
The smallest unit of data in a computer, representing a binary value of either 0 or 1.
Bit sequence
A sequence of bits that can represent various forms of data.
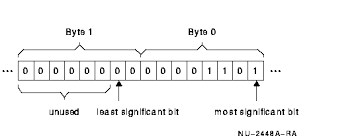
Bitstring
A contiguous sequence of bits.
Decimal
A base-10 numeral system that uses digits from 0 to 9.
Element
An individual item within a data structure, such as in a list or array.
Index value
A numerical representation of the position of an element in a data structure.
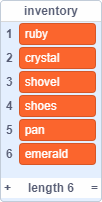
List
A data structure that holds an ordered collection of items.
Simulate
To imitate the operation of a real-world process or system using a computer program.