MGF - CH. 11
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1. Which statement is true?
A). The expected rate of return on any portfolio must be positive.
B). The arithmetic average of the betas for each security held in a portfolio must equal 1.0.
C). The beta of any portfolio must be 1.0.
D). The weights of the securities held in any portfolio must equal 1.0.
E). The standard deviation of any portfolio must equal 1.0.
D). The weights of the securities held in any portfolio must equal 1.0.
2. Systematic risk is defined as:
A). the total risk of an individual security.
B). any risk that affects a large number of assets.
C). diversifiable risk.
D). asset-specific risk.
E). the risk unique to a firm's management. (*C,D,E same thing)
B). any risk that affects a large number of assets.
3. Unsystematic risk can be defined by all of the following except:
A). unrewarded risk.
B). diversifiable risk.
C). unique risk.
D). asset-specific risk.
E). market risk.
E). market risk.
4. The capital asset pricing model states that the expected return on a risky asset depends only on the asset’s _____________ risk.
A). unique
B). diversifiable
C). market
D). asset-specific
E). unsystematic
C). market
5. Which one of the following is the best example of unsystematic risk?
A). Inflation exceeding market expectations
B). Decrease in corporate tax rates
C). Decrease in the value of the dollar
D). A warehouse fire
E). Increase in consumer spending
D). A warehouse fire
6. Which one of these represents systematic risk?
A). Major layoff by a regional manufacturer of power boats
B). Increase in consumption created by a reduction in personal tax rates
C). Surprise firing of a firm's chief financial oƯicer
D). Closure of a major retail chain of stores
E). Product recall by one manufacturer
B). Increase in consumption created by a reduction in personal tax rates
7. Which one of these is the best example of systematic risk?
A). Discovery of a major gas field
B). Decrease in textile imports
C). Increase in agricultural exports
D). Decrease in gross domestic product
E). Decrease in management bonuses for banking executives
D). Decrease in gross domestic product
8. Which one of the following best exemplifies unsystematic risk?
A). Unexpected economic collapse
B). Unexpected increase in interest rates
C). Unexpected increase in the variable costs for a firm
D). Sudden decrease in inflation
E). Expected increase in tax rates
C). Unexpected increase in the variable costs for a firm
9. Which term best refers to the practice of investing in a variety of diverse assets as a means of reducing risk?
A). Diversification
B). Systematic
C). Unsystematic
D). Security market line
E). Capital asset pricing model
A). Diversification
10. Diversifying a portfolio across various sectors and industries might do more than one of the following. However, this diversification must do which one of the following?
A). Increase the expected risk premium
B). Reduce the beta of the portfolio to one
C). Increase the security's risk premium
D). Reduce the portfolio's unique risks
E). Reduce the portfolio's systematic risk level
D). Reduce the portfolio's unique risks
11. Portfolio diversification eliminates:
A). all investment risk.
B). the portfolio risk premium.
C). unsystematic risk.
D). market risk.
E). the reward for bearing risk
C). unsystematic risk.
12. The beta of a risky portfolio cannot be less than _____________ nor greater than _____________.
A). 0; 1
B). 1; the market beta
C). the lowest individual beta in the portfolio; market beta
D). the lowest individual beta in the portfolio; the highest individual beta in the portfolio
(*weighted average betas of individual security)
E). the market beta; the highest individual beta in the portfolio
D). the lowest individual beta in the portfolio; the highest individual beta in the portfolio
(*weighted average betas of individual security)
13. When calculating the expected rate of return on a stock portfolio using a weighted average, the weights are based on the:
A). market value of the investment in each stock.
B). number of shares owned of each stock.
C). market price per share of each stock.
D). cost per share of each stock held.
A). market value of the investment in each stock.
14. A portfolio is comprised of 35 securities with varying betas. The lowest beta for an individual security is .74 and the highest of the security betas of 1.51. Given this information, you know that the portfolio beta:
A). must be 1.0 because of the large number of securities in the portfolio.
B). will be greater than or equal to .74 but less than or equal to 1.51.
C). is the geometric average of the individual security betas.
D). must be less than the market beta.
E). will be between 0 and 1.0
B). will be greater than or equal to .74 but less than or equal to 1.51.
15. Which one of the following statements is accurate?
A). Portfolio betas range between −1.0 and +1.0.
B). A portfolio of U.S. Treasury bills will have a beta of +1.0. (*zero)
C). The beta of a market portfolio is equal to zero. (*=1)
D). A portfolio beta is a weighted average of the betas of the individual securities contained in the portfolio.
D). A portfolio beta is a weighted average of the betas of the individual securities contained in the portfolio.
16. The addition of a risky security to a fully diversified portfolio:
A). must decrease the portfolio's expected return.
B). may or may not aƯect the portfolio beta.
C). must increase the portfolio beta.
D). will increase the unsystematic risk of the portfolio.
E). will have no eƯect on the portfolio beta or its expected return.
B). may or may not aƯect the portfolio beta. (*depending on the beta of the new security)
17. The most important reason to diversify a portfolio is to:
A). eliminate asset-specific risk.
B). eliminate systematic risk.
C). increase both returns and risks.
D). increase returns only.
A). eliminate asset-specific risk.
18. For a risky security to have a positive expected return but less risk than the overall market, the security must have a beta:
A). of zero.
B). of one.
C). that is > 0 but < 1. (*beta of overall market =1; positive E(R) indicates positive beta)
D). that is > 1.
C). that is > 0 but < 1. (*beta of overall market =1; positive E(R) indicates positive beta)
19. Systematic risk is:
A). totally eliminated when a portfolio is fully diversified. (*cannot be eliminated)
B). risk that affects a limited number of securities. (*affect a large number of securities)
C). measured by beta.
D). measured by standard deviation. (*STD measures total risk)
C). measured by beta.
20. Which one of the following portfolios will have a beta of zero, theoretically?
A). A portfolio comprised solely of U. S. Treasury bills
B). A portfolio that is equally as risky as the overall market
C). A portfolio that consists of a single stock
D). A portfolio with a zero variance of returns (*zero total risk does not indicate zero market
risk)
A). A portfolio comprised solely of U. S. Treasury bills
21. Standard deviation measures _____________ risk while beta measures _____________ risk.
A). systematic; unsystematic
B). unsystematic; systematic
C). total; unsystematic
D). total; systematic
E). asset-specific; market
D). total; systematic
22. Which of the following statements best describes the principle of diversification?
A). Concentrating an investment in two or three stocks will eliminate all of the unsystematic risk.
B). Concentrating an investment in three companies all within the same industry will greatly reduce the systematic risk.
C). Spreading an investment across many diverse assets will eliminate some of the total risk.
D). Spreading an investment across multiple diverse companies will not lower the total risk.
E). Spreading an investment across many diverse assets will eliminate all of the systematic risk
C). Spreading an investment across many diverse assets will eliminate some of the total risk.
23. Which of the following statements are accurate?
I. Nondiversifiable risk is measured by beta.
II. The risk premium increases as diversifiable risk increases.
III. Systematic risk is another name for nondiversifiable risk.
IV. Diversifiable risks are market risks you cannot avoid.
A). I and III only
B). II and IV only (*IV: Diversifiable risk= firm-specific risk= can be eliminated)
C). I and II only (*II: as Nondiversifiable increases)
D). III and IV only
E). I, II, and III only
A). I and III only
24. The amount of systematic risk present in a particular risky asset relative to that in a market portfolio is measured by the:
A). squared deviation.
B). standard deviation.
C). beta coefficient.
D). variance.
C). beta coefficient.

25. Use the financial information below to choose the correct statement.
Pic
A). ABC has a larger market risk than XYZ. (*Smaller)
B). Both ABC and XYZ are fairly priced based on CAPM. (*insuƯicient information to assess)
C). ABC expects a higher expected return than XYZ based on the Capital Asset Pricing Model.
(*lower)
D). ABC has greater stock return volatility than XYZ. (*STDABC>STDXYZ)
D). ABC has greater stock return volatility than XYZ. (*STDABC>STDXYZ)
26. According to the capital asset pricing model, the expected return on a security will be affected by all of the following except the:
A). market risk premium.
B). risk-free rate.
C). security’s standard deviation.
D). market rate of return.
E). security’s beta
C). security’s standard deviation.
27. According to the capital asset pricing model, the expected return on a security is not affected by the:
A). risk-free rate.
B). security’s risk premium.
C). security’s beta.
D). security’s unique risks. (*diversified away)
E). market rate of return
D). security’s unique risks. (*diversified away)
28. The capital asset pricing model:
A). assumes the market has a beta of zero and the risk-free rate is positive.
B). rewards investors based on total risk assumed. (*based on market risk)
C). considers the relationship between the fluctuations in a security’s returns versus the market’s returns. (*this describes beta)
D). applies to portfolios but not to individual securities. (*apply to both
C). considers the relationship between the fluctuations in a security’s returns versus the market’s returns. (*this describes beta)
29. Which one of the following represents the amount of compensation an investor should expect to receive for accepting the unsystematic risk associated with an individual security?
A). Security beta multiplied by the market rate of return (*beta does not measure unsystematic risk)
B). Market risk premium
C). Security beta multiplied by the market risk premium (*beta does not measure unsystematic risk)
D). Zero
E). Risk-free rate of return
D). Zero
30. The slope of the security market line represents the:
A). market risk premium.
B). risk-free rate. (*the intercept of SML to the y-axis)
C). beta coeƯicient. (*x-axis)
D). risk premium on an individual asset.
E). market rate of return
A). market risk premium.
31. The security market line is defined as a positively sloped straight line that displays the relationship between the:
A). beta and standard deviation of a portfolio.
B). expected return and beta of either a security or a portfolio.
C). systematic and unsystematic risks of a security.
D). nominal and real rates of return.
E). risk premium and beta of a portfolio
B). expected return and beta of either a security or a portfolio.
32. Which statement is correct?
A). A portfolio that contains at least 30 diverse individual securities will have a beta of 1.0.
(*will have a weighted average beta)
B). A portfolio that has a beta of 1.12 will lie to the left of the market portfolio on a security market line graph. (*to the right: 1.12 > 1)
C). An underpriced security will plot above the security market line.
D). A risk-free security plots at the origin on a security market line graph. (*not necessarily, only if rf=0)
C). An underpriced security will plot above the security market line.
33. Which statement is correct?
A). An underpriced security will plot below the security market line. (*above)
B). A portfolio with a beta of 0.93 will plot to the right of the overall market. (*to the left)
C). A security with a beta of 0.99 will plot above the security market line if it is correctly
priced. (*on the SML)
D). A security with a beta of 1.54 will plot on the security market line if it is correctly priced.
(*“plot on the SML” = correctly priced)
E). A risk-free security will plot at the origin. (*not necessarily, only if rf=0)
D). A security with a beta of 1.54 will plot on the security market line if it is correctly priced.
(*“plot on the SML” = correctly priced)
34. If a security plots to the right and below the security market line, then the security has _____________ systematic risk than the market and is _____________.
A). more; overpriced
B). more; underpriced
C). less; overpriced
D). less; underpriced
E). less; correctly priced
A). more; overpriced
NOTE: right (left) to the market portfolio: beta > (<) 1 ;
above (below) [on] SML: under- (over-) [correctly] valued
Under- (over-) valued: buy (sell)
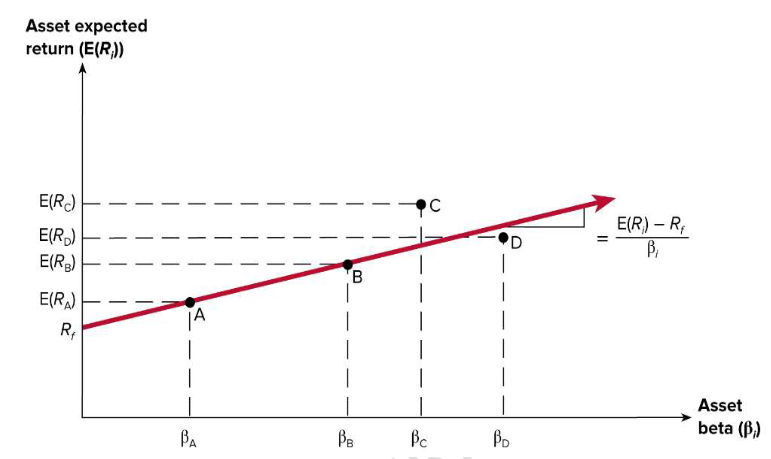
35. Based on the image on the right. The red line indicates the securities
market line. Which one of the stocks is undervalued?
A). Stock A
B). Stock B
C). Stock C
D). Stock D
C). Stock C
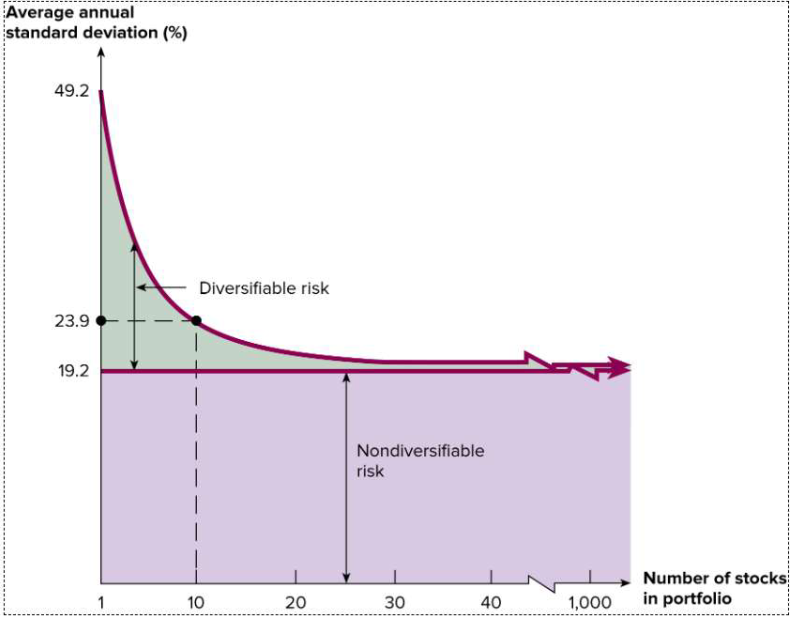
36. Based on the image on the right. Which one of the following is
correct?
A). Total risk of a portfolio decreases monotonically in the number of stocks in the portfolio.
B). Diversifiable risk decreases monotonically in the number of stocks in the portfolio.
C). Diversifiable risk virtually does not exist in a well-diversified portfolio.
D). Market risk virtually does not exist in a well-diversified portfolio.
C). Diversifiable risk virtually does not exist in a well-diversified portfolio.