Ochem 2 Exam 3 multiple choice
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is the hybridization state of the carbon attached to the alcoholic OH group?
sp3
What is the hybridization state of the oxygen in the alcoholic OH group?
sp3
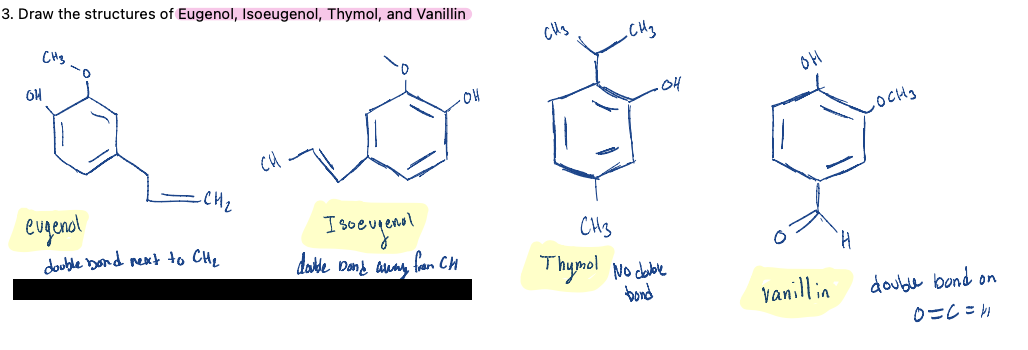
Draw the structures of Eugenol, Isoeugenol, Thymol, and Vanillin
Know how to write/identify primary/secondary/tertiary alcohols.
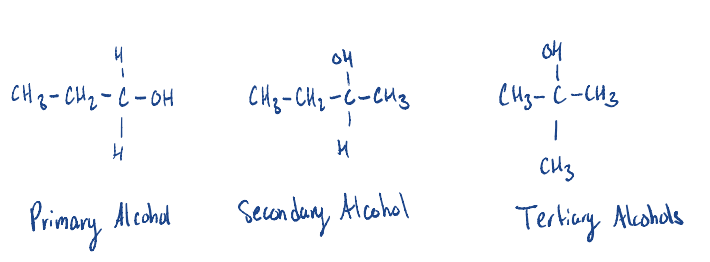
2-Pentanol is a …………………. alcohol.
Secondary
The IUPAC name of allyl alcohol is……………
2-propen-1-ol
The IUPAC name of n-amyl alcohol is…………….
1-pentanol
Alcohols form ………………. ion in the presence of a strong acid
oxonium
The order of reactivity of alcohols with alkali metals is…………………
Primary Alcohol > Secondary Alcohol > Tertiary Alcohol
The oxidation state of carbon in methanol………………………………
-2
K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 is used for ………………………. reaction
Oxidation
Primary alcohols oxidize to form …………., which then oxidize to form …………………….
Aldehydes; Carboxylic Acid
Secondary alcohols oxidize to form …………………….
ketones
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is used for …………………of alcohols to the corresponding………
oxidation; aldehydes and ketones
A protonated alcohol is called ……………………...
Oxonium ion
Na2Cr2O7/acetic acid is used for ………………………. reaction
oxidation
Ethyl alcohol on chromic acid oxidation produces…………………
acetic acid
In the “alcohol breath analyzer test,” the chemical used is……………
potassium dichromate
Ethanol is oxidized in the liver to produce………………
Acetaldehyde
Predict the product: Ethanol is heated at a high temperature with conc. sulfuric acid.
CH2=CH2 and H2O (dehydration of ethene)
Ethyl chloride is boiled with aqueous NaOH. Write the structure of the product
(ethanol/ ethyl alcohol) and sodium chloride
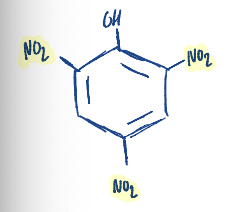
The common name of picric acid is…………………….
2,4,6 - trinitrophenol
Write the structure of picric acid.
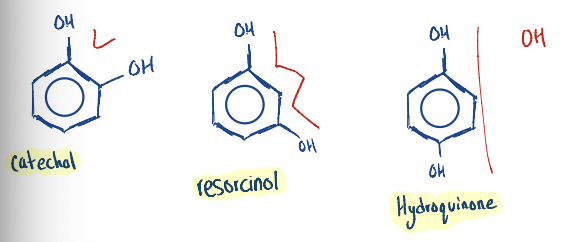
Know to write the structure of (i) Catechol, (ii) Resorcinol, and (iii) Hydroquinone
Write the structure of BHT.
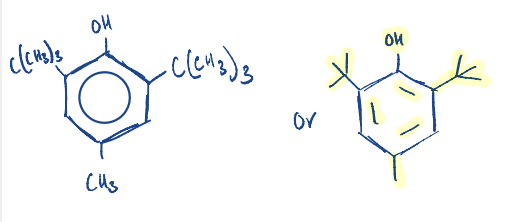
The active irritants in poison ivy and poison oak are………………….
Urshiols (phenols)
Write the general structure of Urushiols.
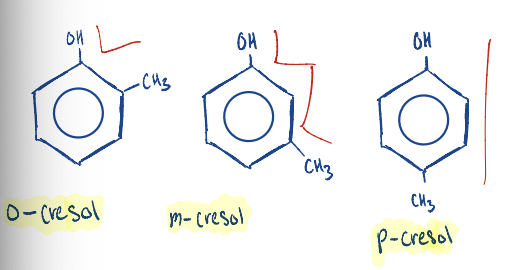
Know to write the structure of cresols.
The phenolic compound which is used as an acid-base indicator is…………………………….
phenolphthalein
The toxicity of phenols to micro-organisms makes them excellent ………….
antiseptics
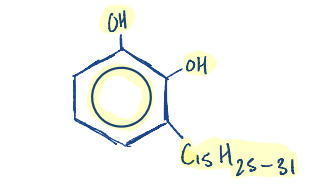
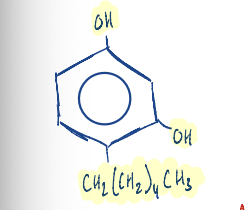
The compound 4-hexylresorcinol is used as an……………………….
antiseptics in pharaceutical preparation
Write the structure of 4-hexylresorcinol.
Alcohols and phenols are weak……………………acids.
Bronsted
Methanol is more acidic than ethanol—why?
more alkyl group = weaker acid
Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) make an alcohol a stronger …………… by stabilizing the ……………………. base
Acid; Conjugate
Alcohols are weak acids and require a strong base to form the corresponding …………….
alkoxide
An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more …… by ………………. the negative charge.
acidic; delocazlizing
Reduction of ……………………. gives primary alcohols, whereas reduction of ketones gives ………………… alcohols.
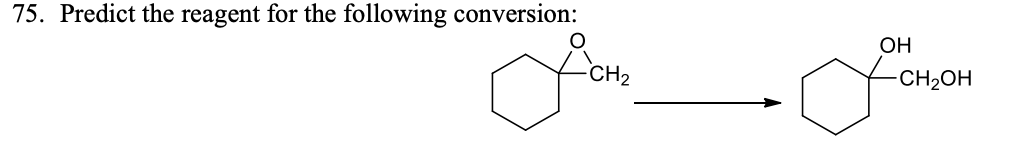
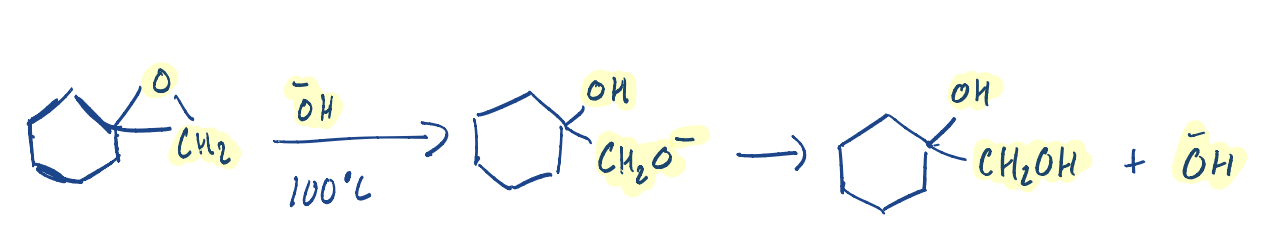
aldehydes;secondary
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) is a more powerful reducing agent than ……………………. but less specific, and very reactive with ……………
NaBH4; water
Which reducing agent would you prefer to reduce carboxylic acids to primary alcohol?
LiAlH4
Treatment of secondary and tertiary alcohols with phosphorus oxychloride in pyridine at low temperature follows………………. route.
E2
If 1° and 2° alcohols are treated with SOCl2 or PBr3 the reaction follows ……………….mechanism
SN2
Write two separate notes on (i) Woodward cis-hydroxylation and (ii) Prevost trans hydroxylation
woodward cis-hydroxylation: reaction of alkene with iodine in wet acetic acid to form Cis-diol
Prevost trans hydroxylation: reation of alkene with iodine and silver benzoate form vicinal trans-diol
Write a note on DMP. Why is this reagent unique?
Dess martain periodinane;regant is selective oxidation with no chromium
Primary alcohols: aldehydes
secondary alcohols: ketones; hypervalent iodine (have greater valence energy than usaul)
What is ‘Jones oxidation’?
strong oxidation reaction used to convert
Primary alcholos to carboxylic acid
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Alkyl tosylates react like alkyl ………….
halides
The SN2 reaction of an alcohol via an alkyl ……………… proceeds with ………. inversion
Halides; two
Grignard reagents react with …………… compounds to yield……………...
carbonyl; alcohols
An ether solvent is essential for the formation of a …………….
Grignard Reagents
The non-bonded electrons from an ether help to …………..a Grignard reagent
stabilize
The first part of the Grignard reaction is the formation of the Grignard reagent. This mechanism involves a…………………reaction.
Radical transfer
Grignard reagents act as……………….. in adding to a carbonyl group.
nuceophilic carbon anions
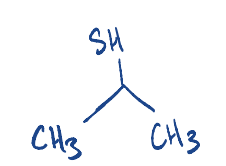
Write the structure of 2-Propanethiol.
Thiols are organic compounds that contain the ……….. group, also called……………….
-SH; mercaptans
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a ……………… ether.
cyclic
The IUPAC nomenclature of diethyl ether is…………………………
ethoxyethane
The other name of epoxy-alkane is ………………………….
oxirane
An anticancer drug with oxirane moiety is …………………
epothilone B

methyl phenly ether
Ethers oxidize in air to form explosive ……………………. and ……………………….
hydroperoxides; peroxides
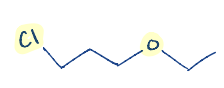
Write the chemical structure of the compound 1-Chloro-3-ethoxy propane.

2-methyl-2,3-epoxybutane
“Crown” ethers are useful as …………………. in nucleophilic substitution and other reactions
enchancers
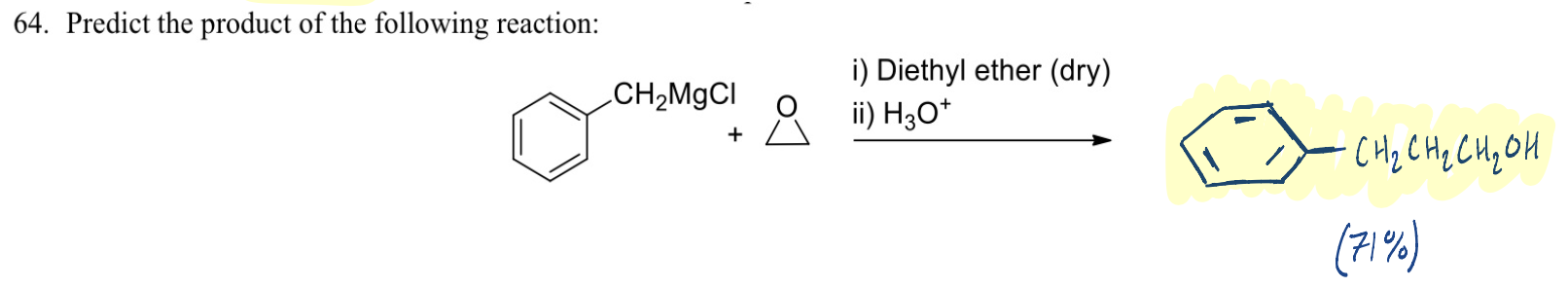
The Williamson Ether Synthesis follows ……………………….route
SN2
Give examples of five symmetrical and five unsymmetrical ethers.
Write down the full name and structure of m-CPBA.
meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid
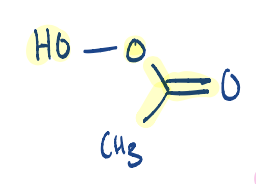
What is the structure of peroxyacetic acid?
The anti-hypertensive beta-Blocker drug (Propranolol) can be synthesized by exploring……………ring-opening methodology.
epoxide
A naturally occurring polyether that interferes with Na+ ion transport across cell membranes is ………………………….
Brevetoxins (neurotoxins)
The ………………. ring opening methodology is used to synthesize the bronchodilators salmeterol and albuterol.
epoxide
What do you mean by host-guest complex? Indicate the ‘host’ and the ‘guest’.
Crown ether - host
cation- guest
makes stable complexes with metal ions
What is molecular recognition?
ability of host molecule to bind to specific guests
The ability of crown ethers to complex cations can be exploited in …………….
Nucleophililc subsitituion reaction
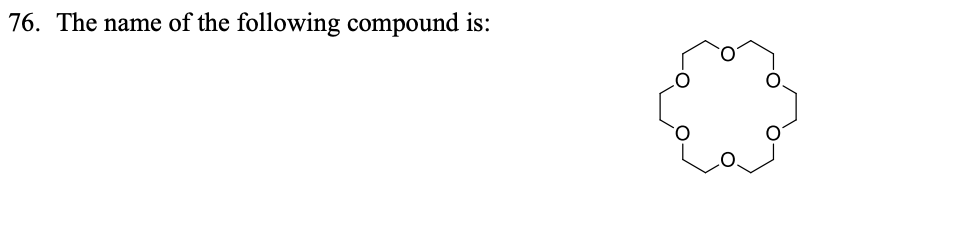


Nicotinic acid (niacin) or vitaminB3
Oxirane is a synonym of (i) oxygen (ii) metal oxide (iii) anhydrous alcohol (iv) epoxide (v) octane.
expoxide
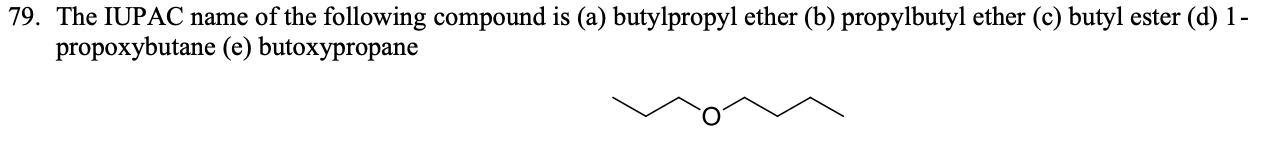
1-propoxybutane
Intramolecular Williamson’s ether synthesis is an example of………………….reaction. ( e.g. SN1, SN2, E1, E2 etc.).
SN2
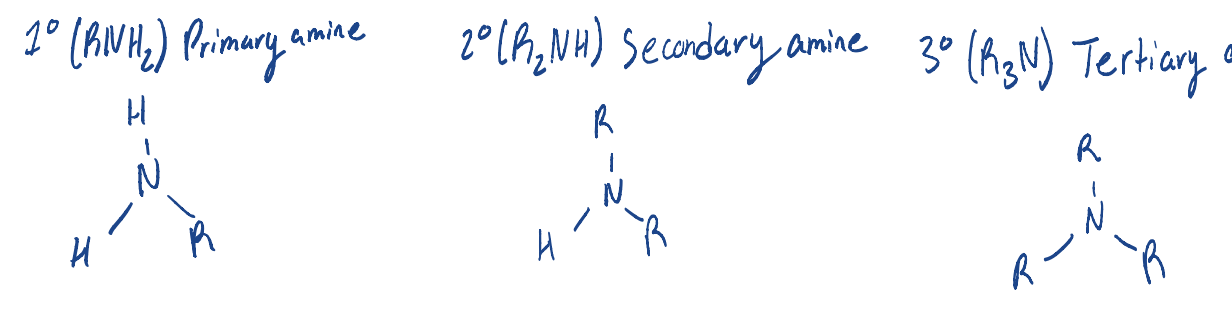
Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines both ……………. and…………………….
Basic; Nucleophilic
Know how to identify primary, secondary, and tertiary amines
Write the structure of ortho-toluidine
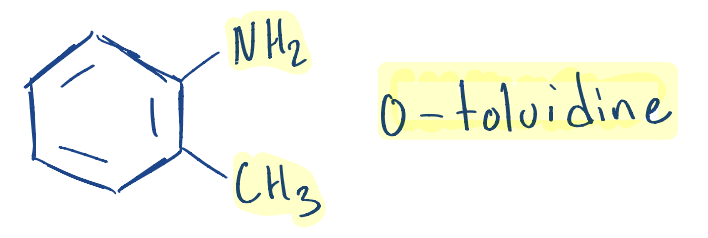
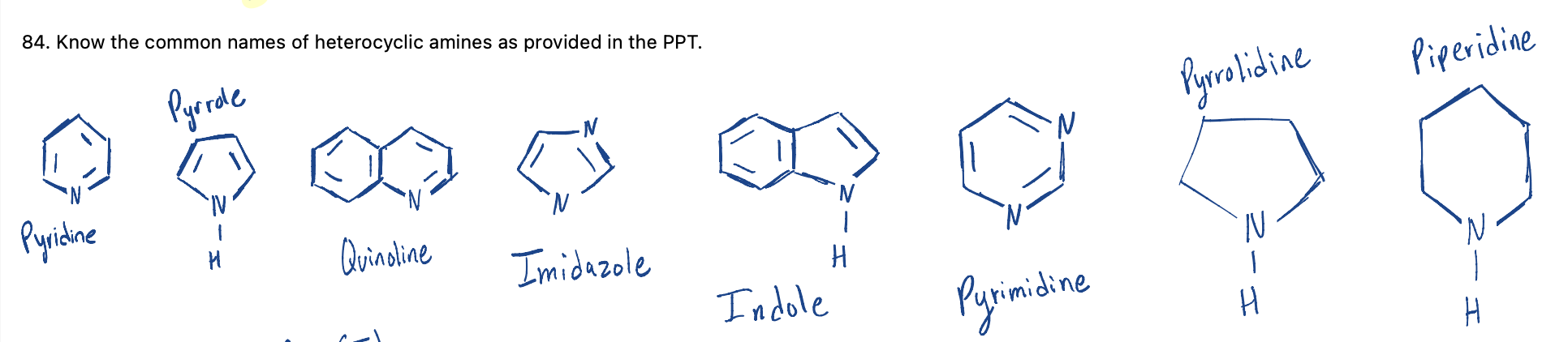
Know the common names of heterocyclic amines as provided in the PPT.
Amines with fewer than ……………………………. carbons are water-soluble
5
Primary and secondary amines form …………………… bonds, increasing their boiling points
hydrogen
The nitrogen of an amine can behave as an……………………
lewis base
Amines are stronger ……………………… than alcohols, ethers, or water.
base
A phthalimide alkylation for preparing a primary amine from an alkyl halide is known as ………………………. synthesis
Gabriel
Carboxylic acid derivatives can be converted into primary amines with loss of one carbon atom by both the ……………………. rearrangement and the ………………………… rearrangement.
Hofmann;Curtius
Alkyl azides are not nucleophilic, but they are ………………………
explosive
Why are arylamides instead of arylamines used for Friedel-Crafts Reactions of arylamines?
amino group of arylamine forms lewis acid-base complex with AlCl3 catalyst prevents further reaction; use corresponding amide instead
Azo-coupled products have extended conjugation that leads to low energy ……………. transitions that occur in visible light (dyes).
electronic

1,3,7- Trimethylpurine 2,6- dione
In amines, the nitrogen is ………………. hybridized.
sp3
In amides, the C=O group is strongly electron-withdrawing, making the nitrogen very (a) weak base (b) strong base (c) weak acid (d) strong acid (e) electron-rich
weak base
Example of electron donating and electron withdarwing groups are: (a) ⎯CH3, ⎯NH2 (b) ⎯OCH3 and ⎯CH3 (c) ⎯Cl, ⎯NO2 (d) ⎯CN, ⎯CH3 (e) ⎯CH3, ⎯CN
(e) -CH3 and -CN
The product of Hofmann elimination is (a) alkane (b)alkyl halide (c) acyl azide (d) alkene (e) isocyanate
alkene
Primary arylamines react with nitrous acid (HNO2), yielding stable …………….. salts. This reaction is known as …………………………reaction.
arenediazonium; sandmeyer
Base-promoted hydrolysis of an ester is called……………………………
saponification