Atmosphere
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Albedo, EMR, Greenhouse effect, Layers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
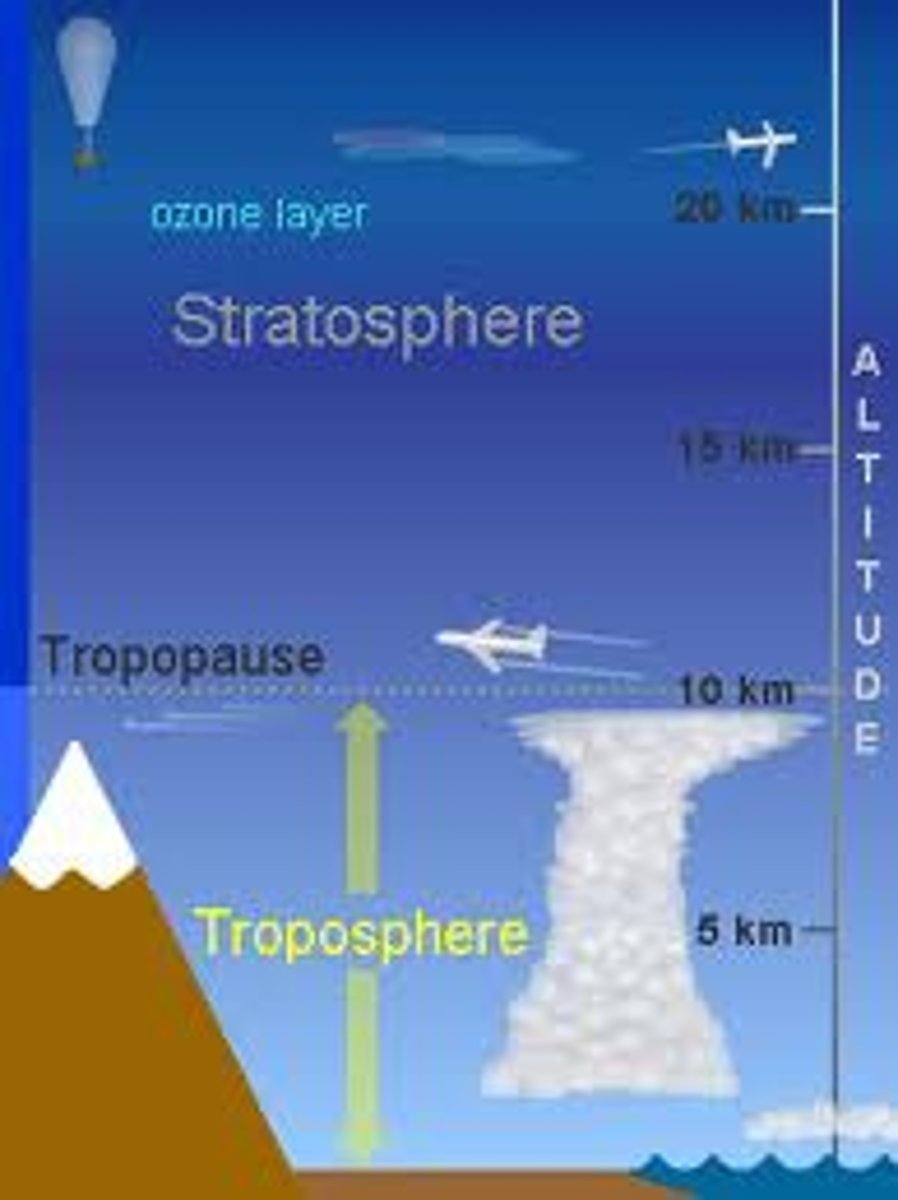
Troposphere
0-17 km above Earth's surface, site of weather, organisms, contains most atmospheric water vapor.
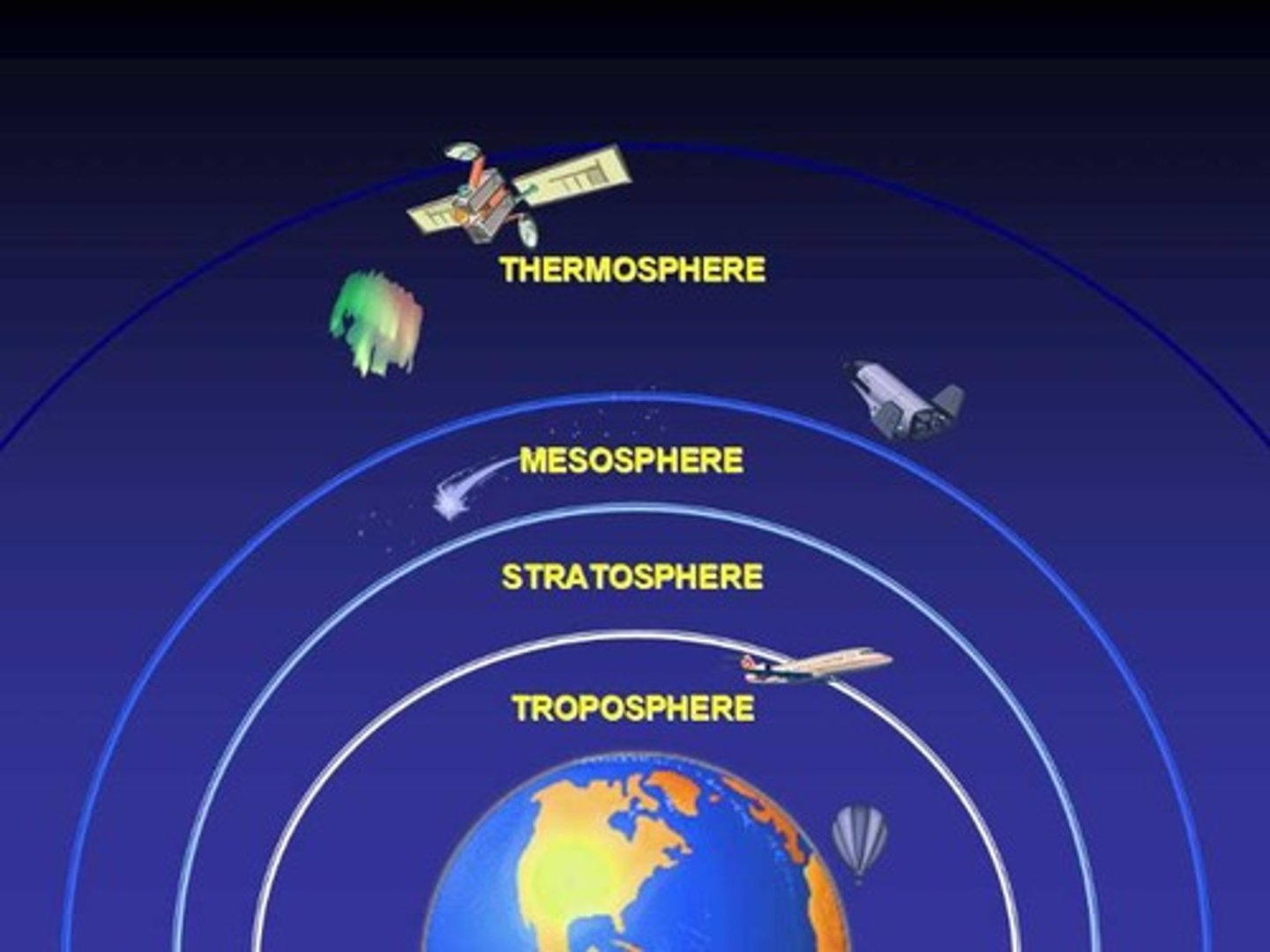
Thermosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
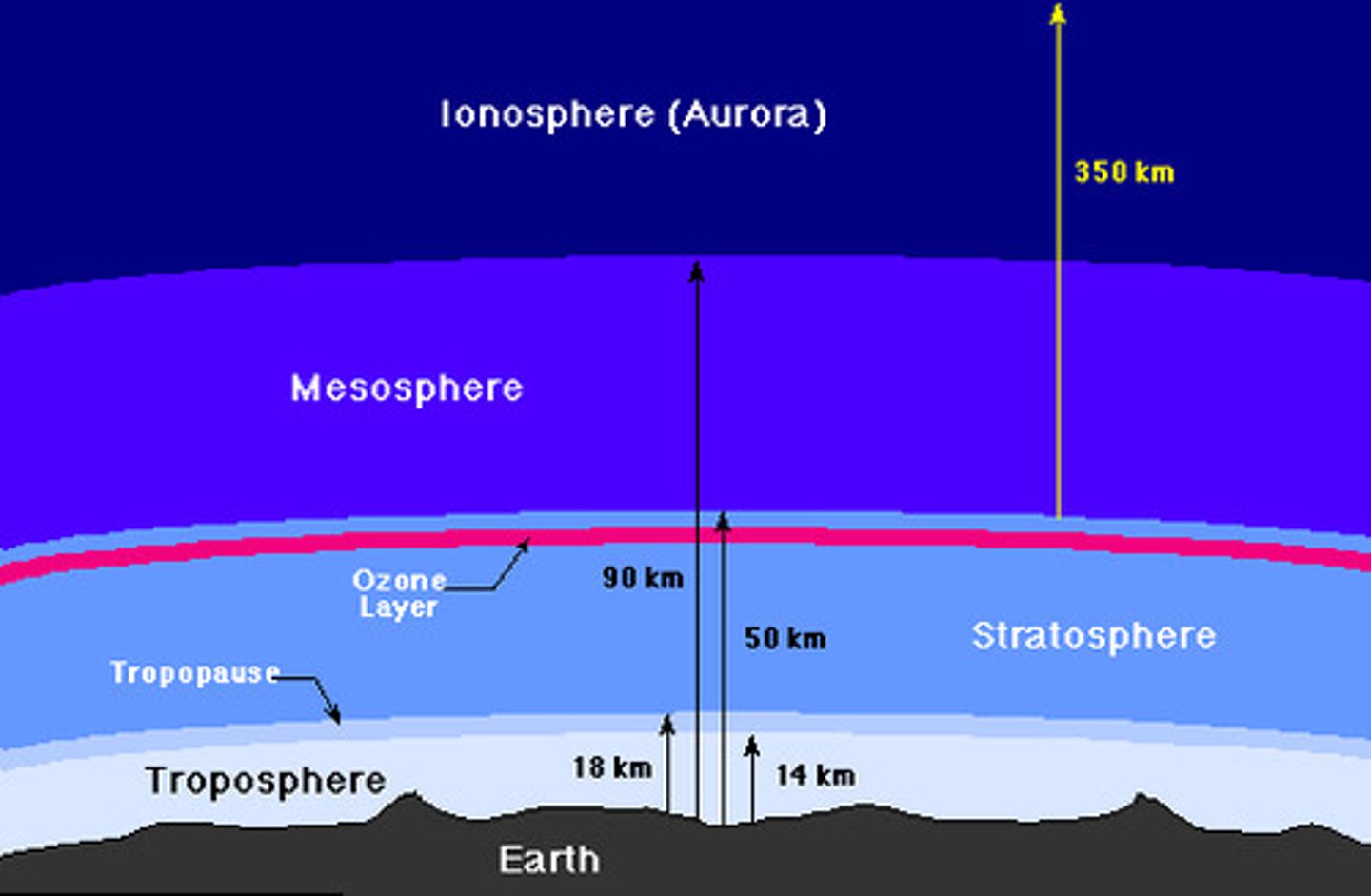
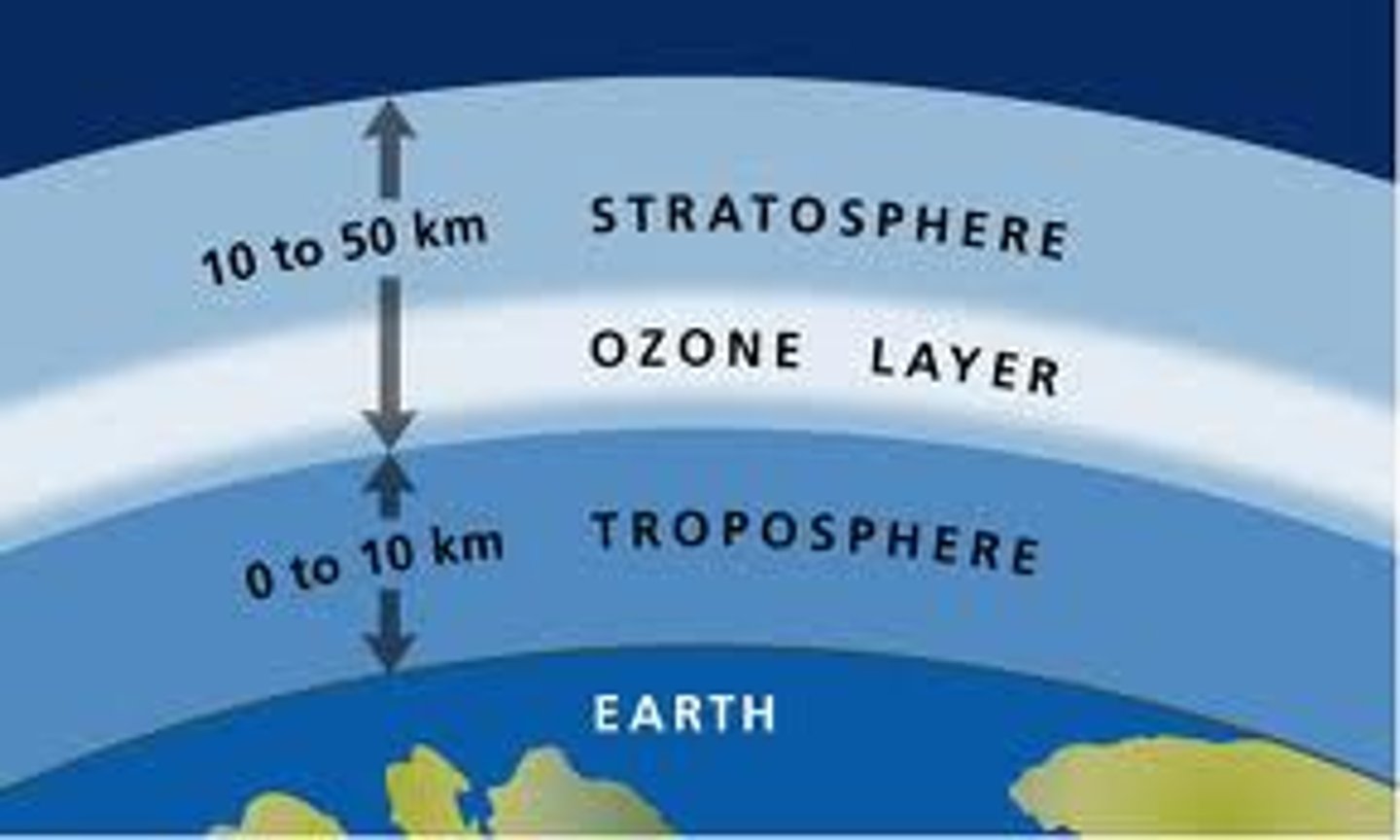
stratosphere
2nd layer of atmosphere-12 to 50 km, Ozone held here, absorbs UV radiation
mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere
ozone
Thin layer of atmosphere that absorbs harmful radiation. “Good up high, bad nearby”
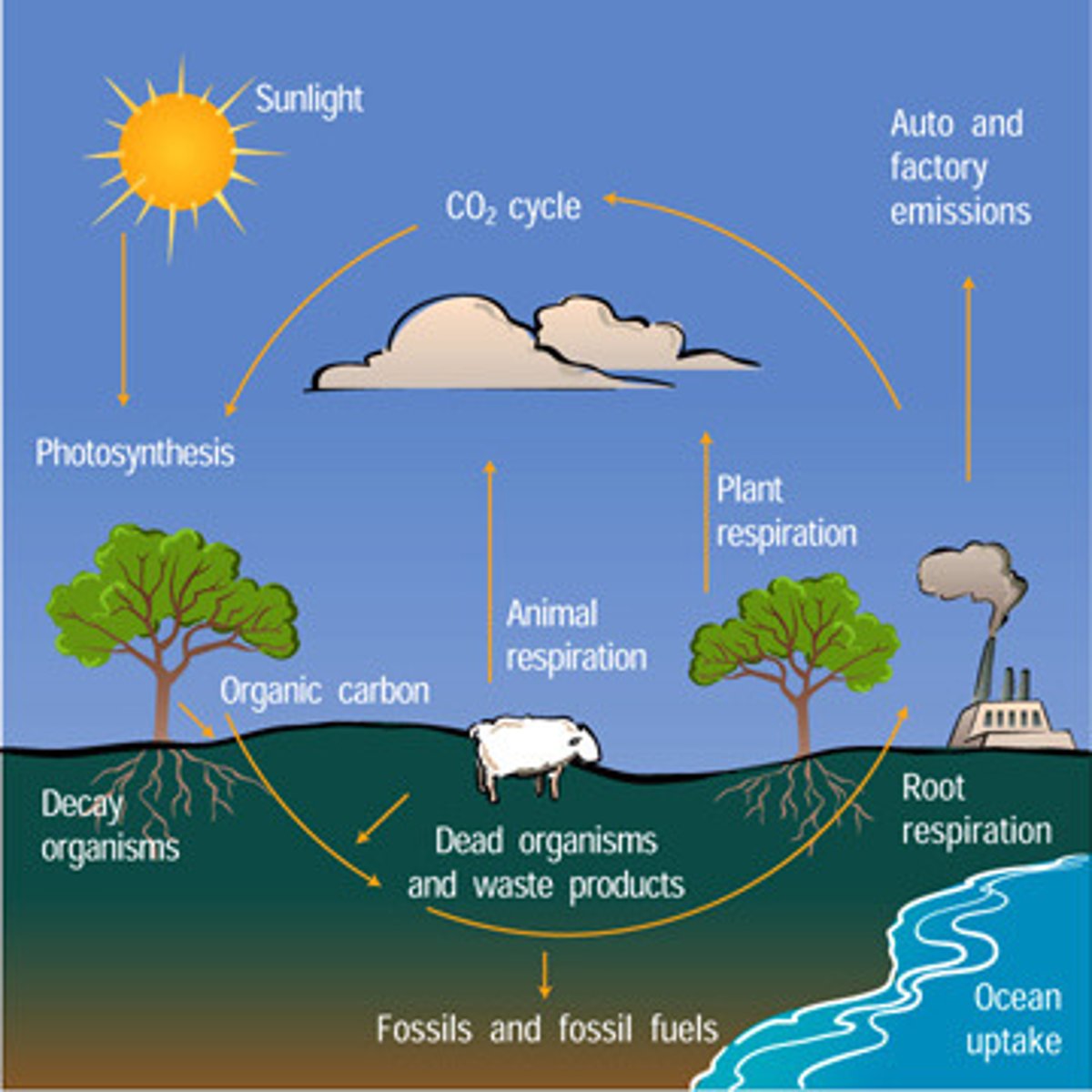
carbon cycle
the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back
radiation
Energy transmitted as particles or waves; especially from the sun
3 major components (gasses) of the atmosphere
Nitrogen, oxygen, argon
conduction
The process through which heat is transferred through direct contact between materials.
convection
a process by which air or a liquid rises or sinks because of differences in temperature
EMR
Electromagnetic Radiation - energy that travels from the sun to the earth in waves
Earth’s energy budget
The balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing energy from the Earth. It includes the absorption, reflection, and reradiation of energy in different forms.
Albedo
The amount of solar radiation reflected by a surface
Greenhouse Effect
the process by which an atmosphere warms a planet. Some gases in the atmosphere absorb some of the sun’s light energy. This energy is then reradiated as heat
why ozone is good
Up high, It protects life on Earth from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays (UV-b).
why ozone is bad
Ground-level or "bad" ozone is an air pollutant that damages human health, vegetation, and many common materials. It is a key ingredient of urban smog
Main greenhouse gasses
water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide