✅️✅️2 - General Concepts of Bones & Joints
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
true
True or false?
A bone is an organ
2 multiple choice options
organ
-Store minerals and fat, blood cell formation.
-Is an actively metabolizing tissue that change in in shape, size, and position by mechanical or biochemical demands
skeleton
Group of bones that serves for support, protection, providing levers for muscular action and movement
osteology
The science of bones
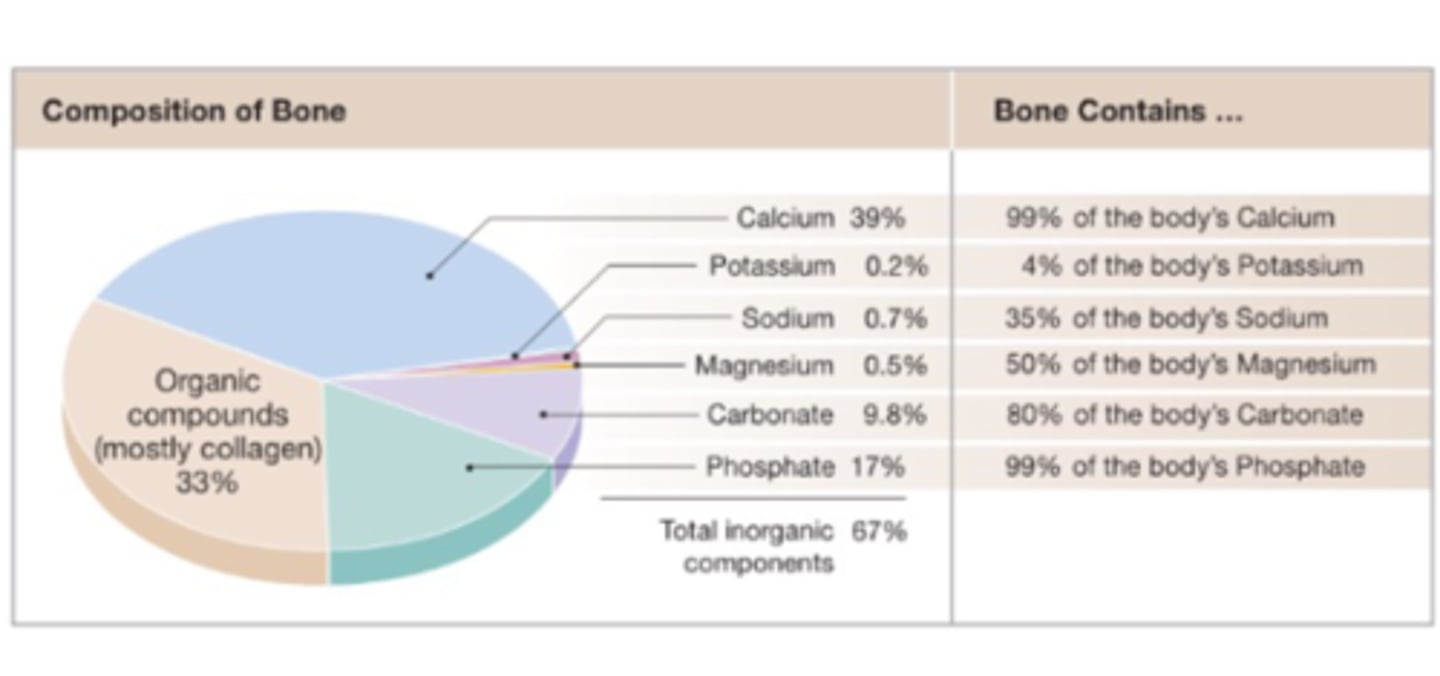
67%
_____% of the bones structure consists of minerals
3 multiple choice options
33%
_____% of the bones structures consist of organic material
3 multiple choice options
minerals
Nitric acid removes the [minerals/organic compounds] from the bone, making them soft while maintaining their shape
2 multiple choice options
![<p>Nitric acid removes the [minerals/organic compounds] from the bone, making them soft while maintaining their shape</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/50f06ccc-9940-4042-bc86-e1b75f3043ab.jpg)
organic compounds
The shape of a bone is from the [minerals/organic compounds]
2 multiple choice options
Reviewed
Review
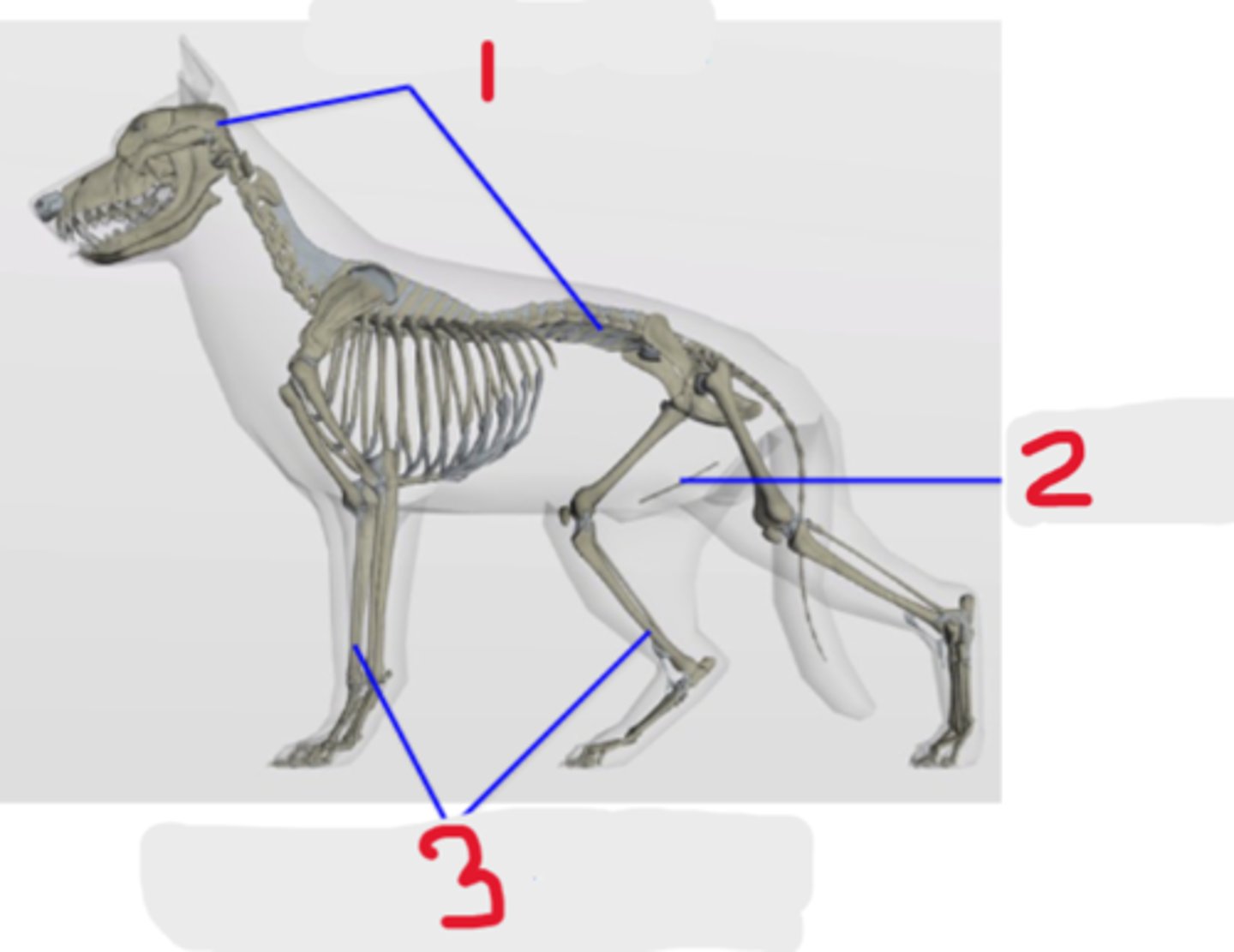
axial skeleton
Classification of bones
What is #1?
3 multiple choice options
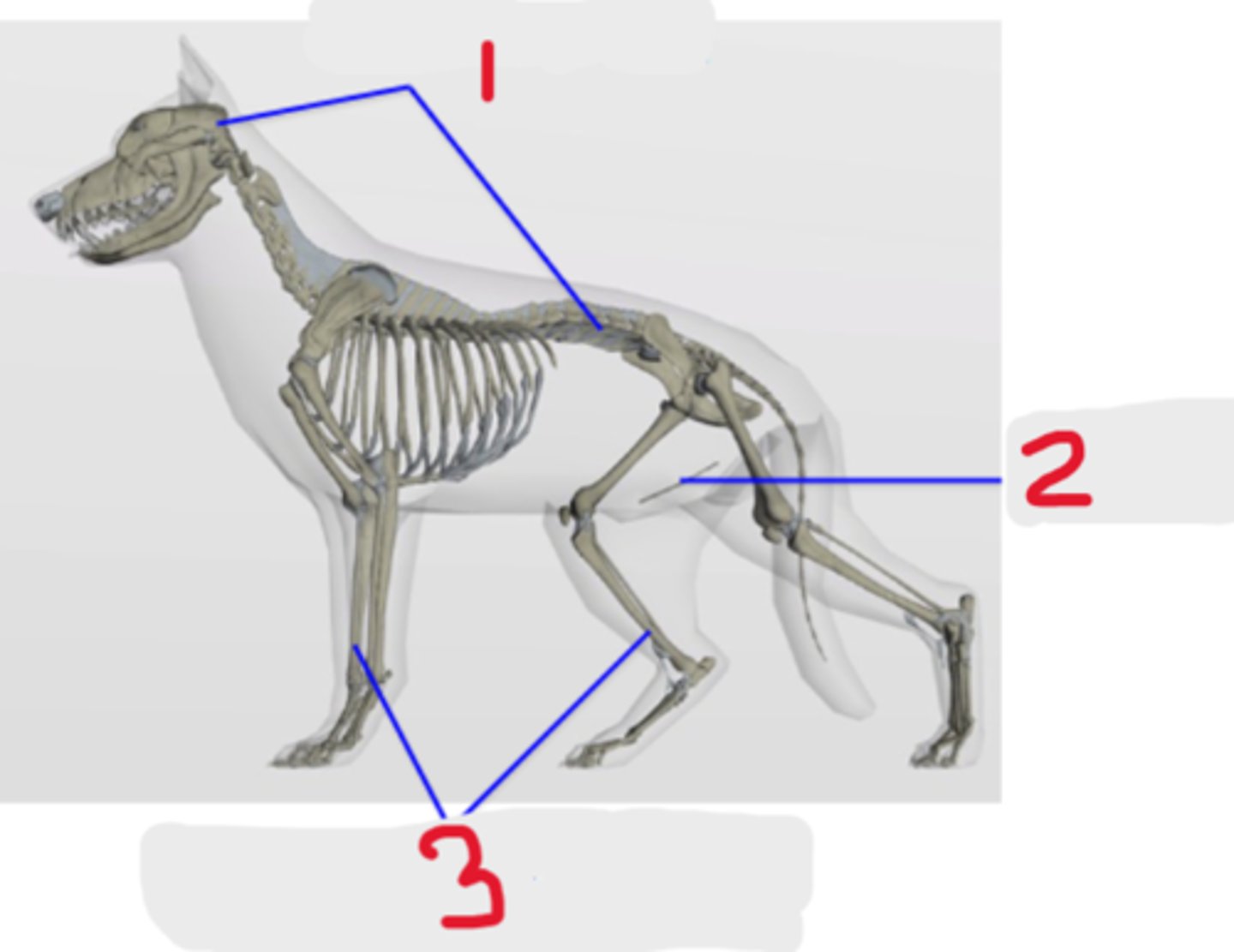
heterotopic skeleton
Classification of bones
What is #2?
3 multiple choice options
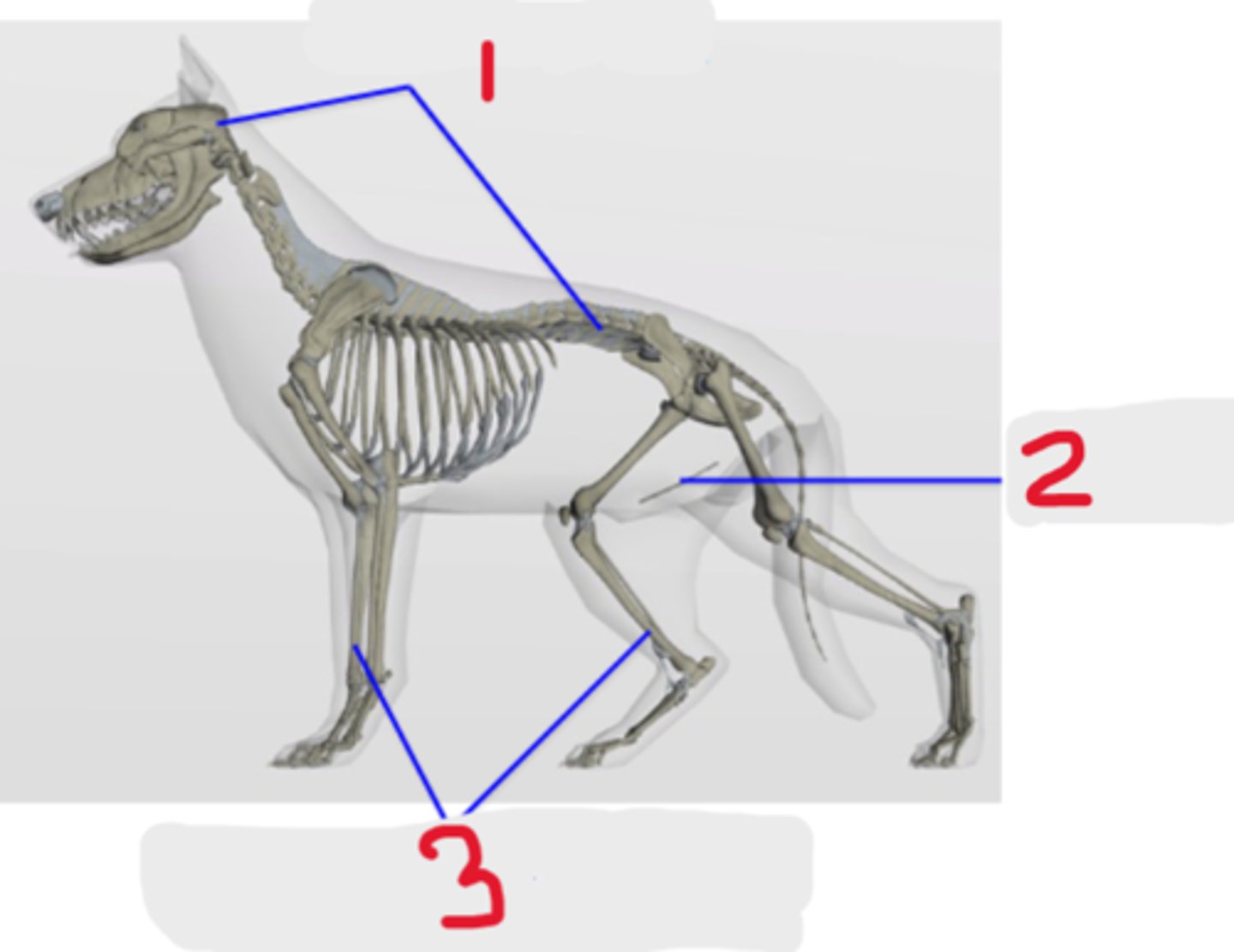
appendicular skeleton
Classification of bones
What is #3?
3 multiple choice options
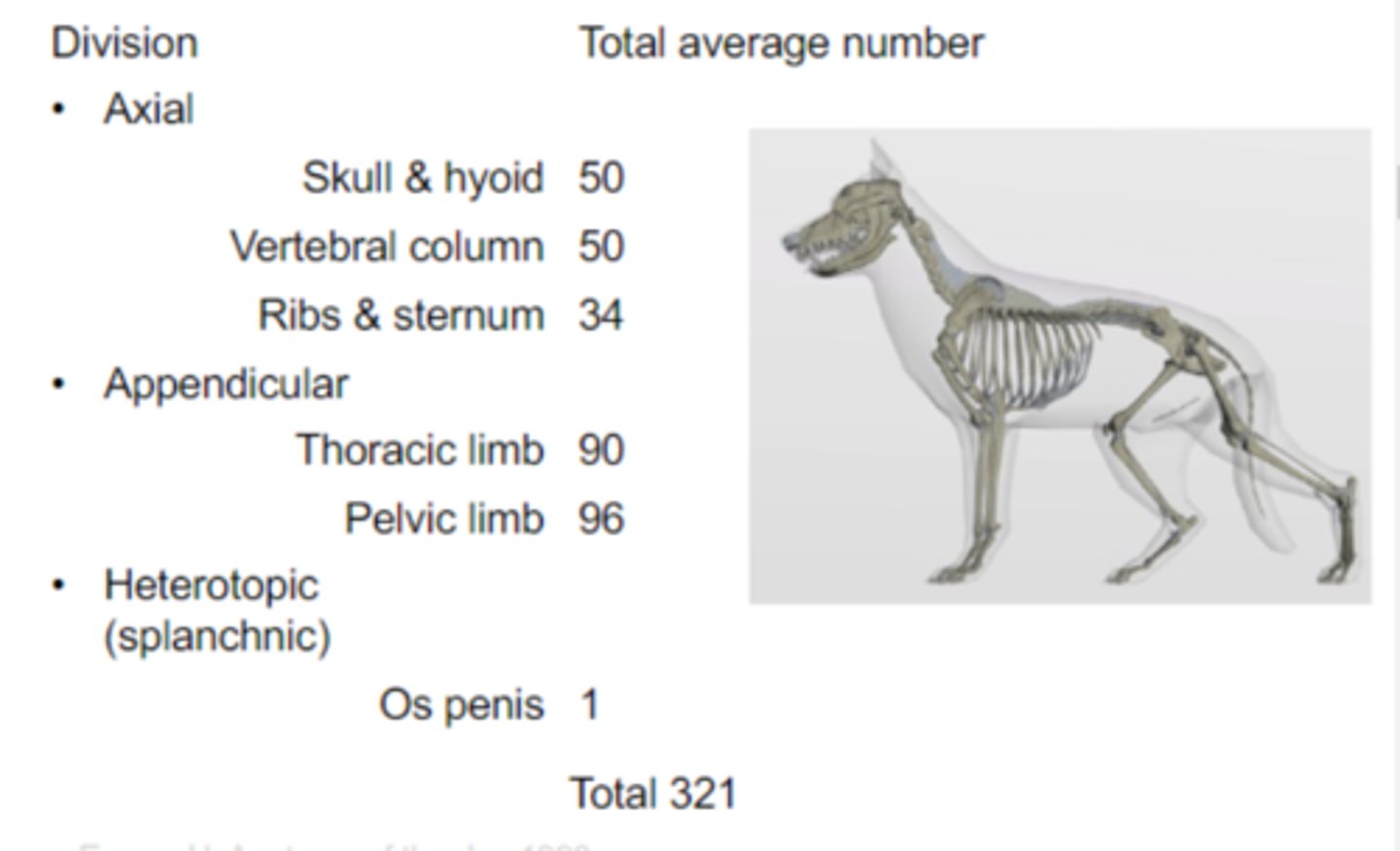
321
How many bones does a canine have?
3 multiple choice options
Reviewed
Review
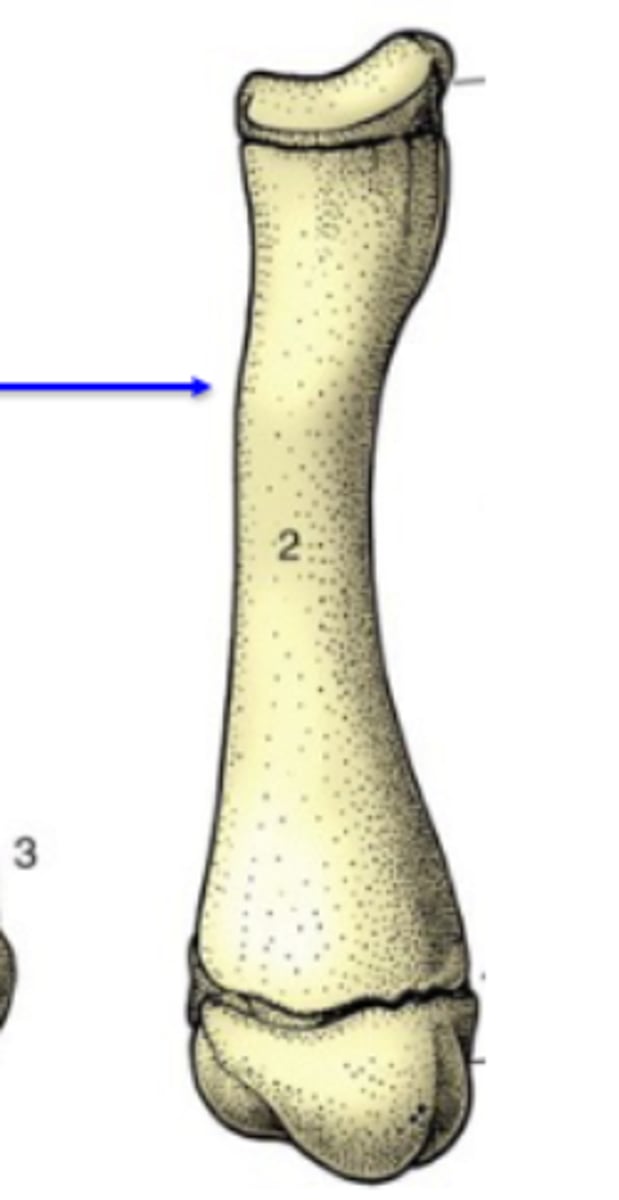
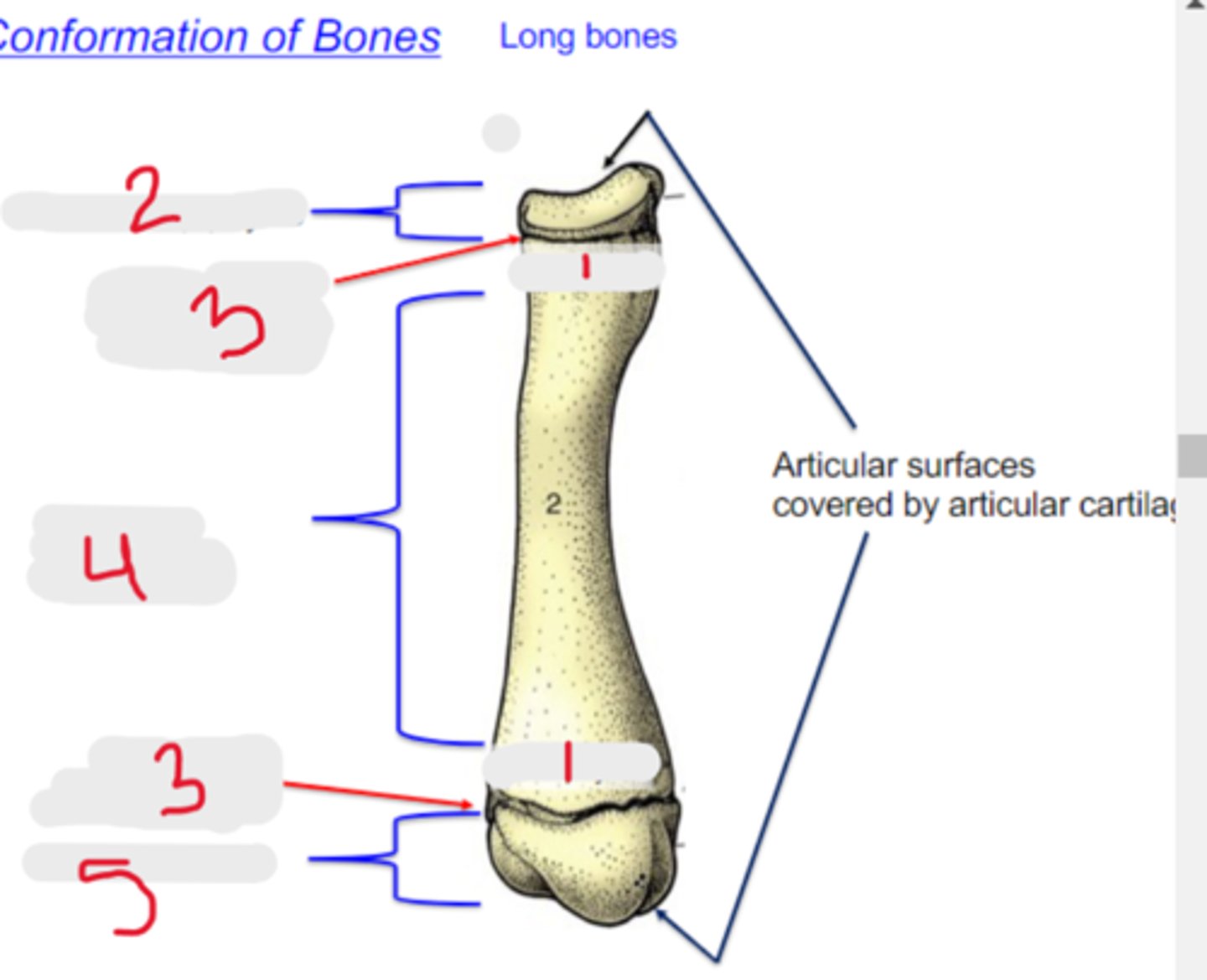
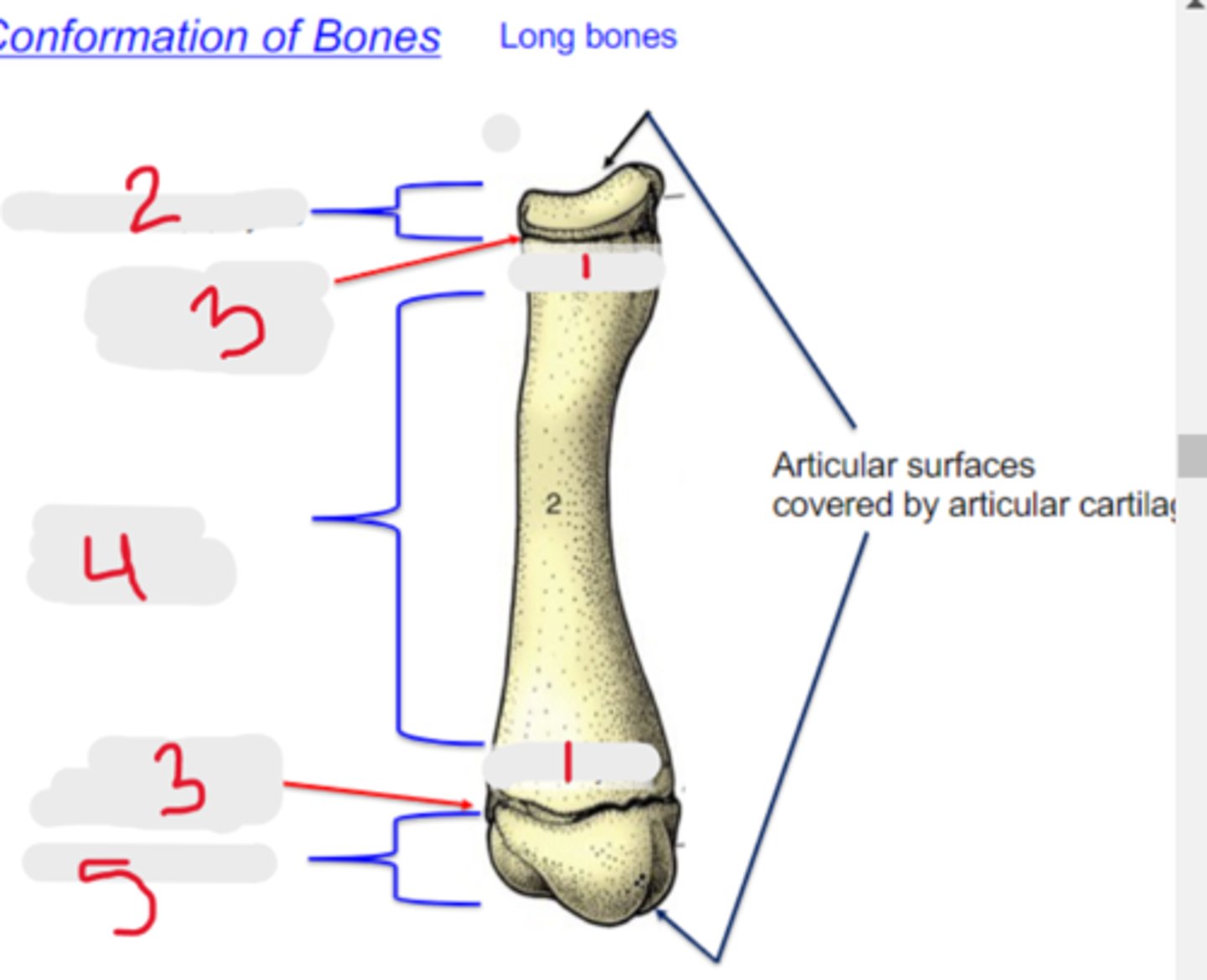
long
Bone shape?
-typical of the limbs
-three centers of ossification: one for the shaft (diaphysis), and one for each extremity (epiphysis)
-have a medullary cavity
3 multiple choice options
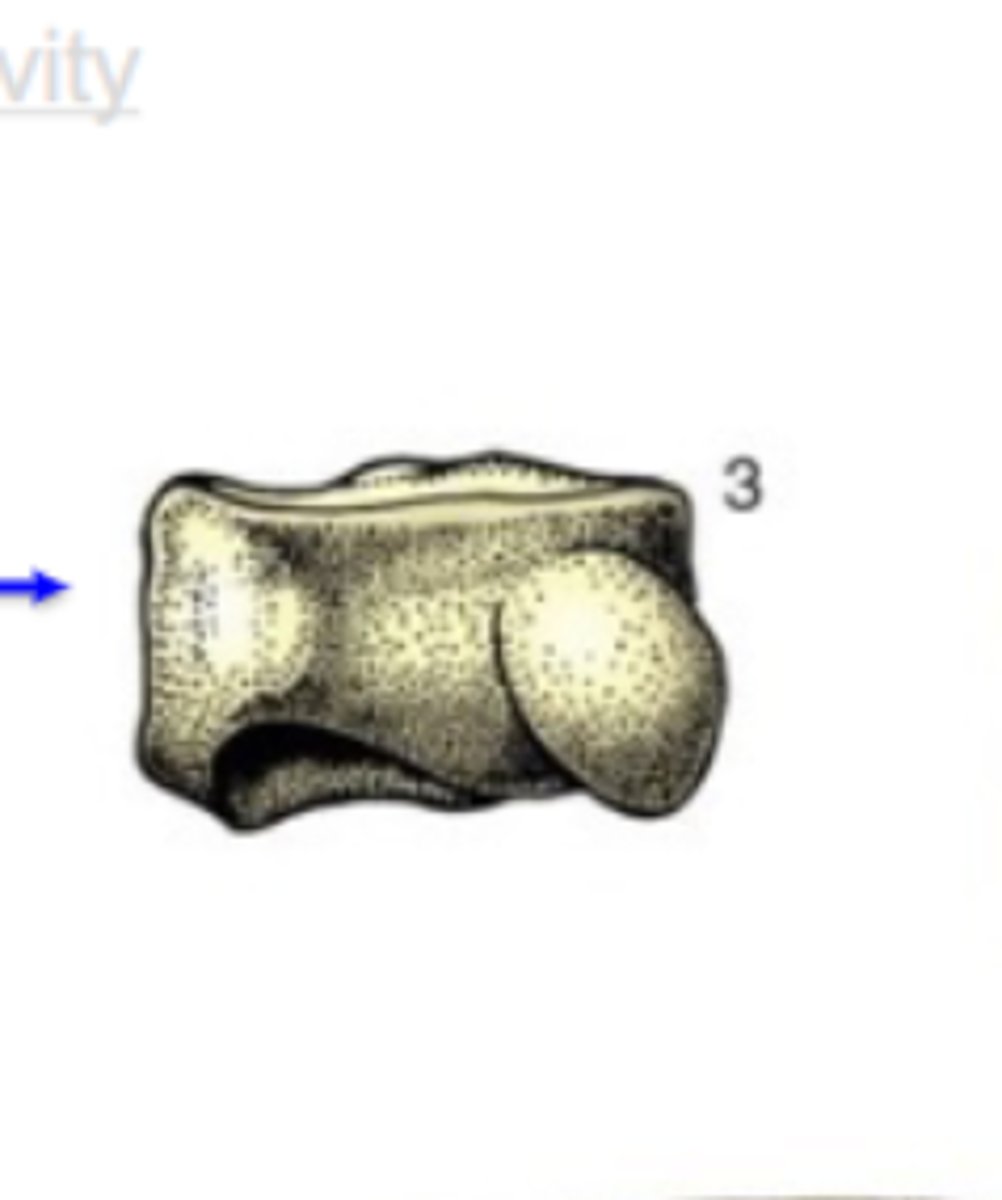
short
Bone shape?
-have no dimension that greatly exceeds the others
-no medullary cavity
3 multiple choice options
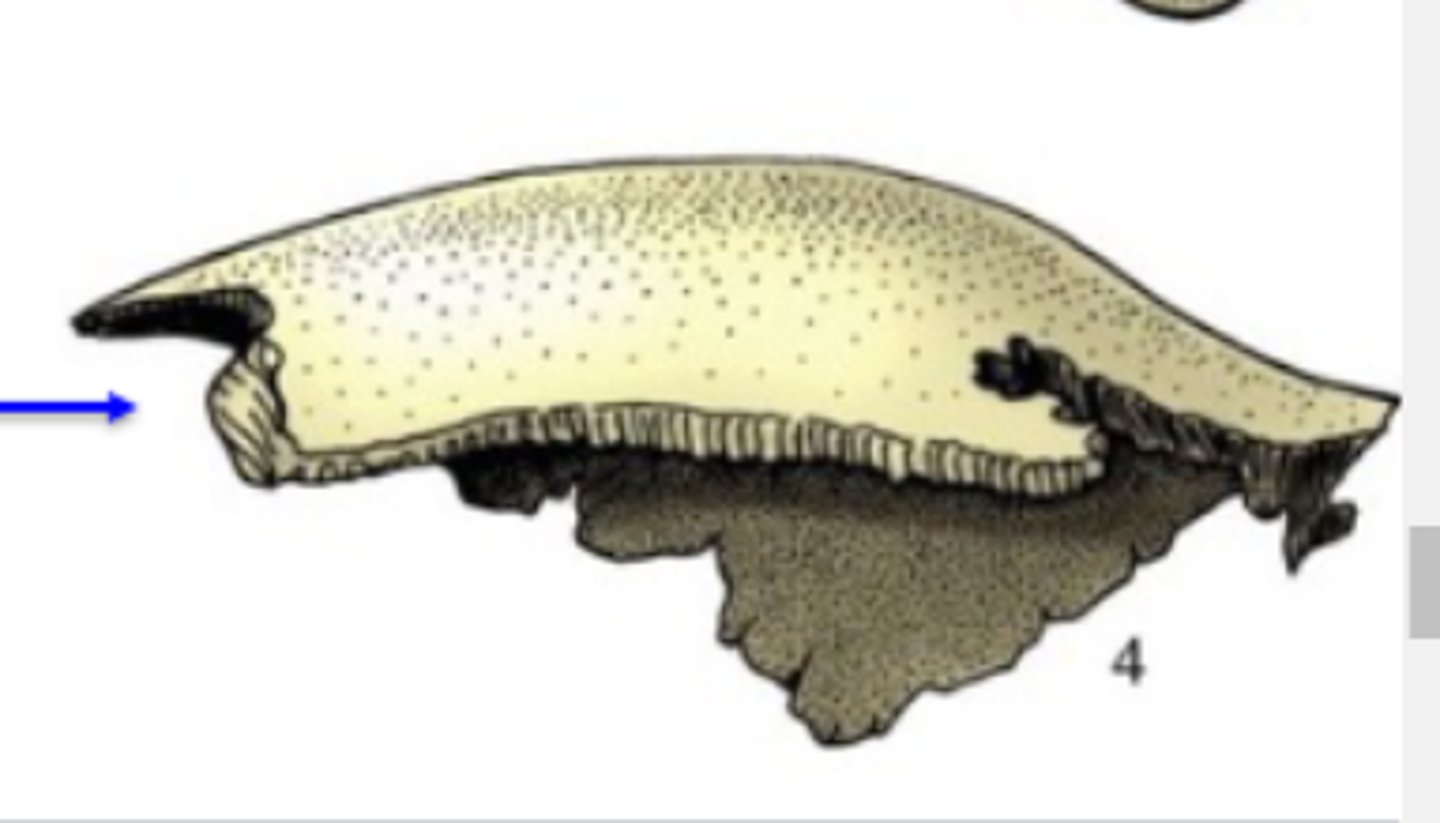
flat
Bone shape?
-expanded in two directions
-no medullary cavity
3 multiple choice options
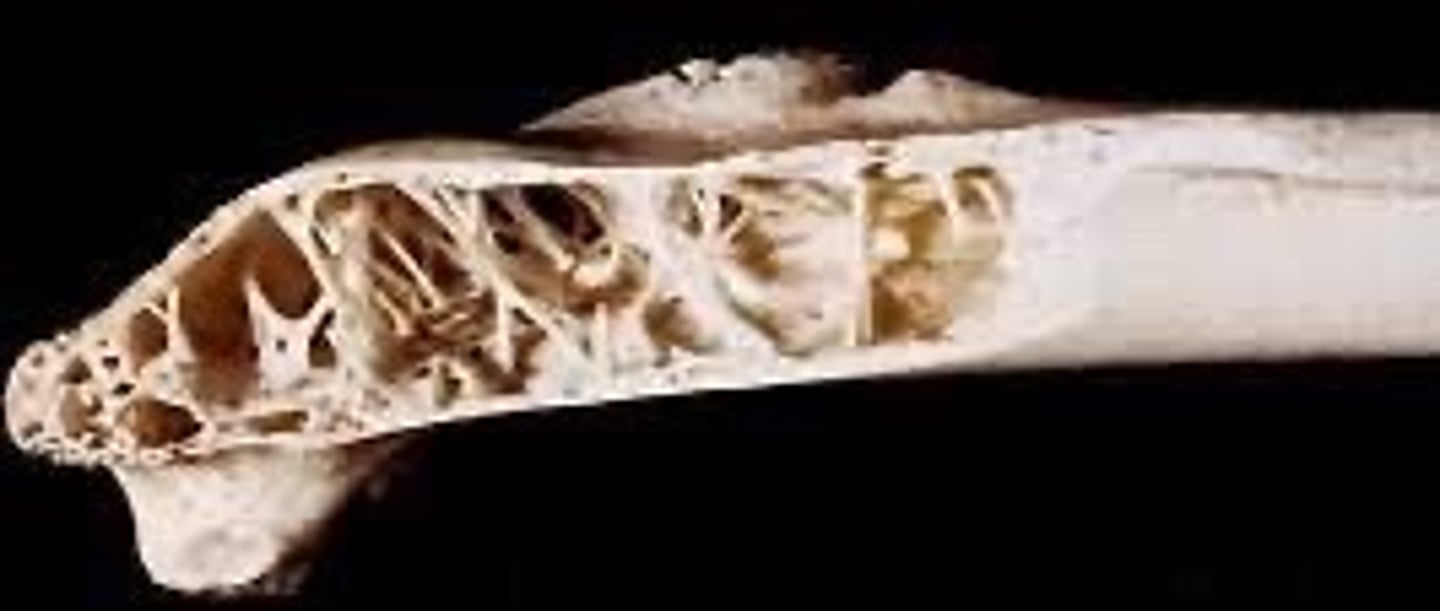
pneumatic bones
-Not a shape classification, but a characteristic of some flat bones of the skull in domestic mammals
-Excavated to contain air-filled spaces
-In mammals, these are confined to the skull and contain the paranasal sinuses
birds
In _____, some of the long bones have air pockets that communicate extensively with the respiratory system
3 multiple choice options

irregular
This is an example of a _____ bones
3 multiple choice options
physis
The growth plate of a long bone is known as the _____
3 multiple choice options
diaphysis
The body/shaft of a long bone is known as the _____
3 multiple choice options
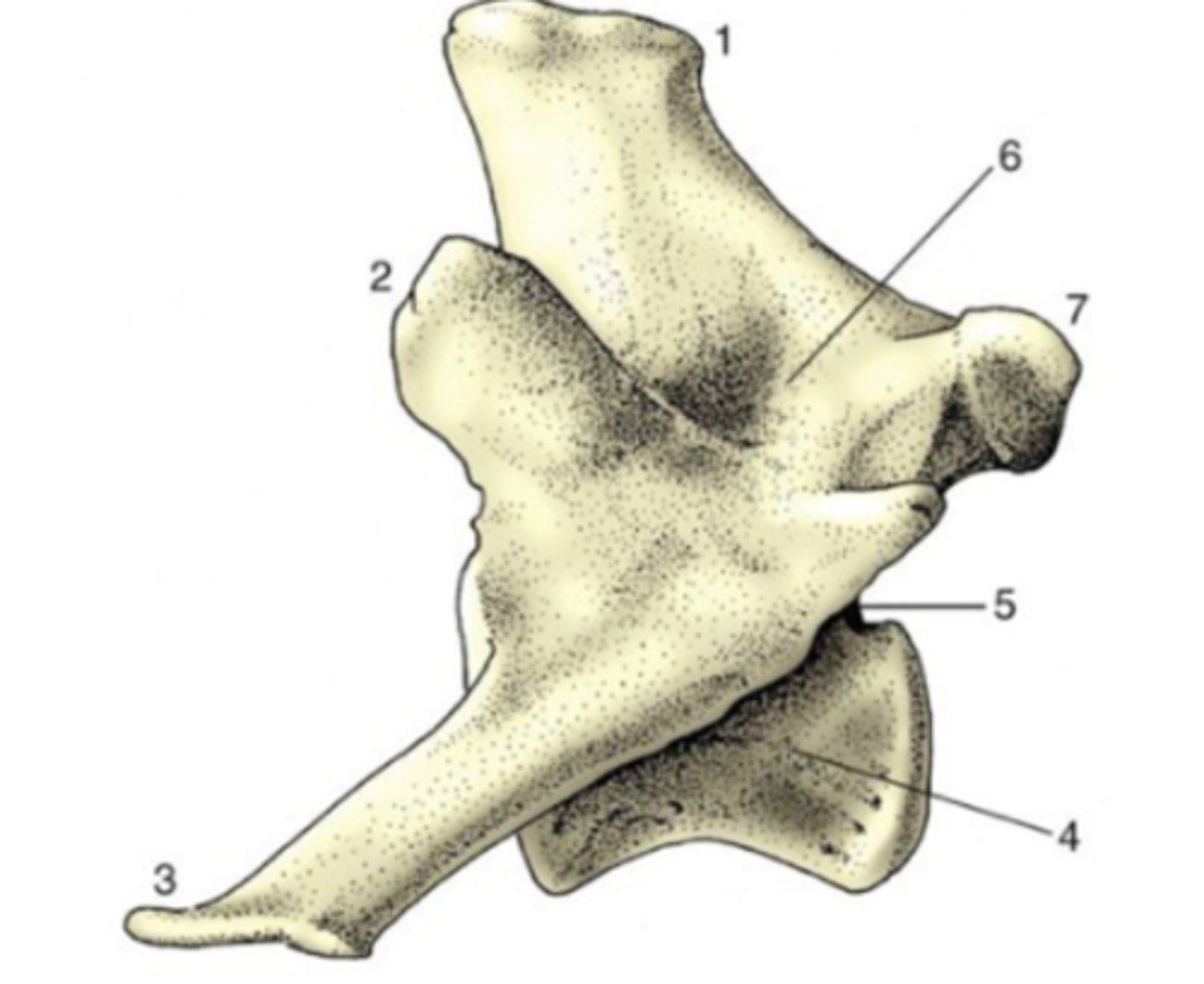
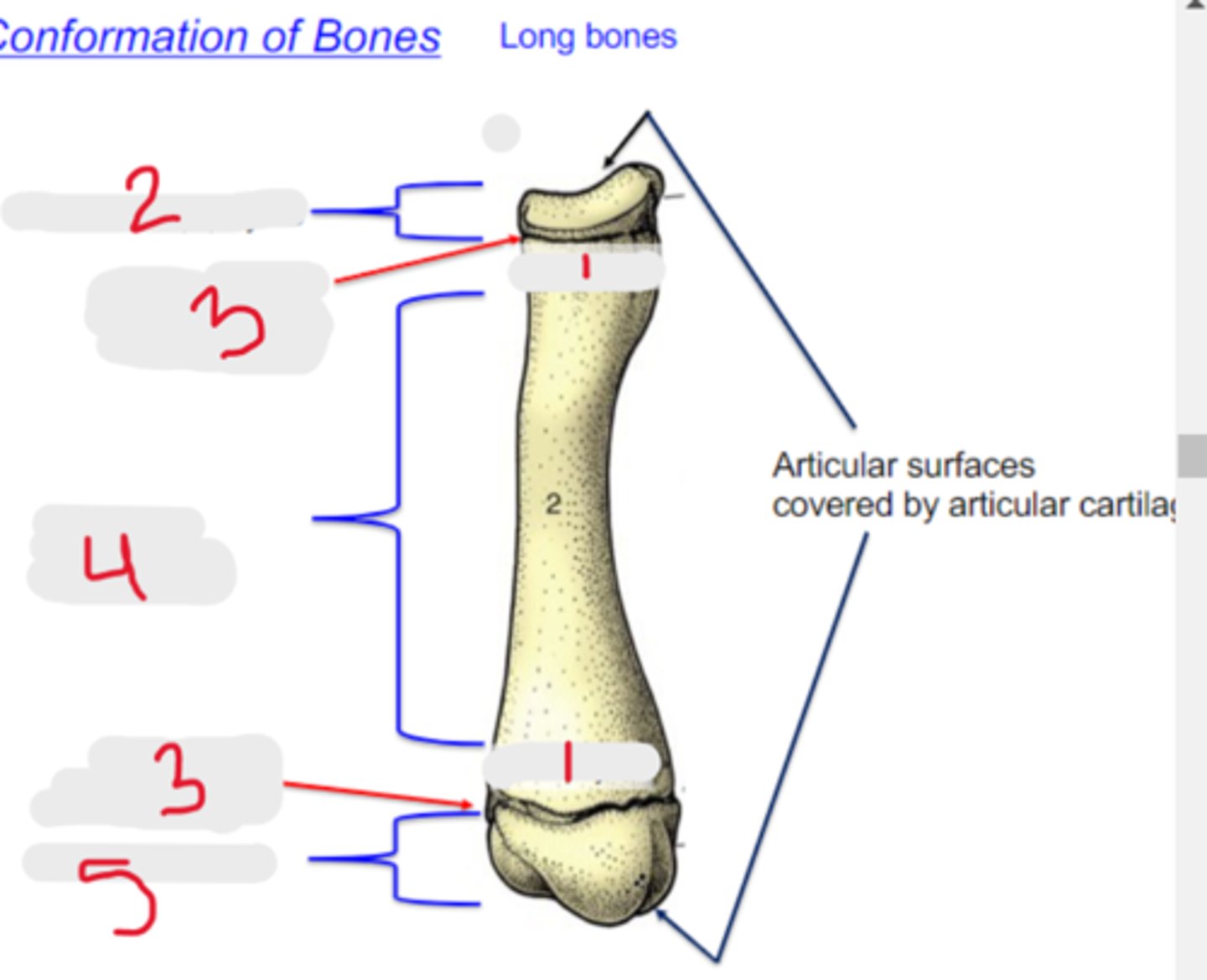
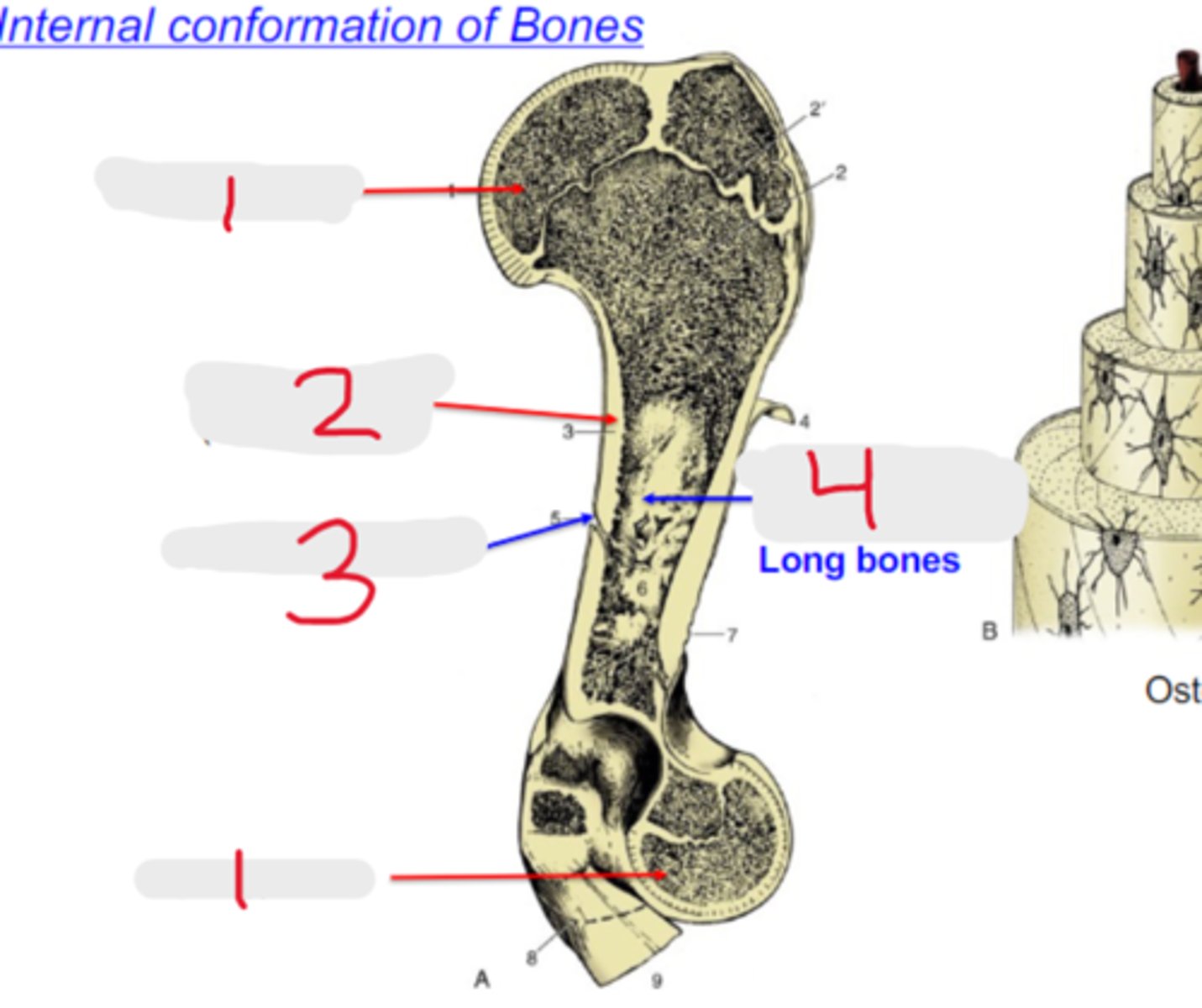
metaphysis
What is #1?
3 multiple choice options
proximal epiphysis
What is #2?
3 multiple choice options
physis
What is #3?
3 multiple choice options
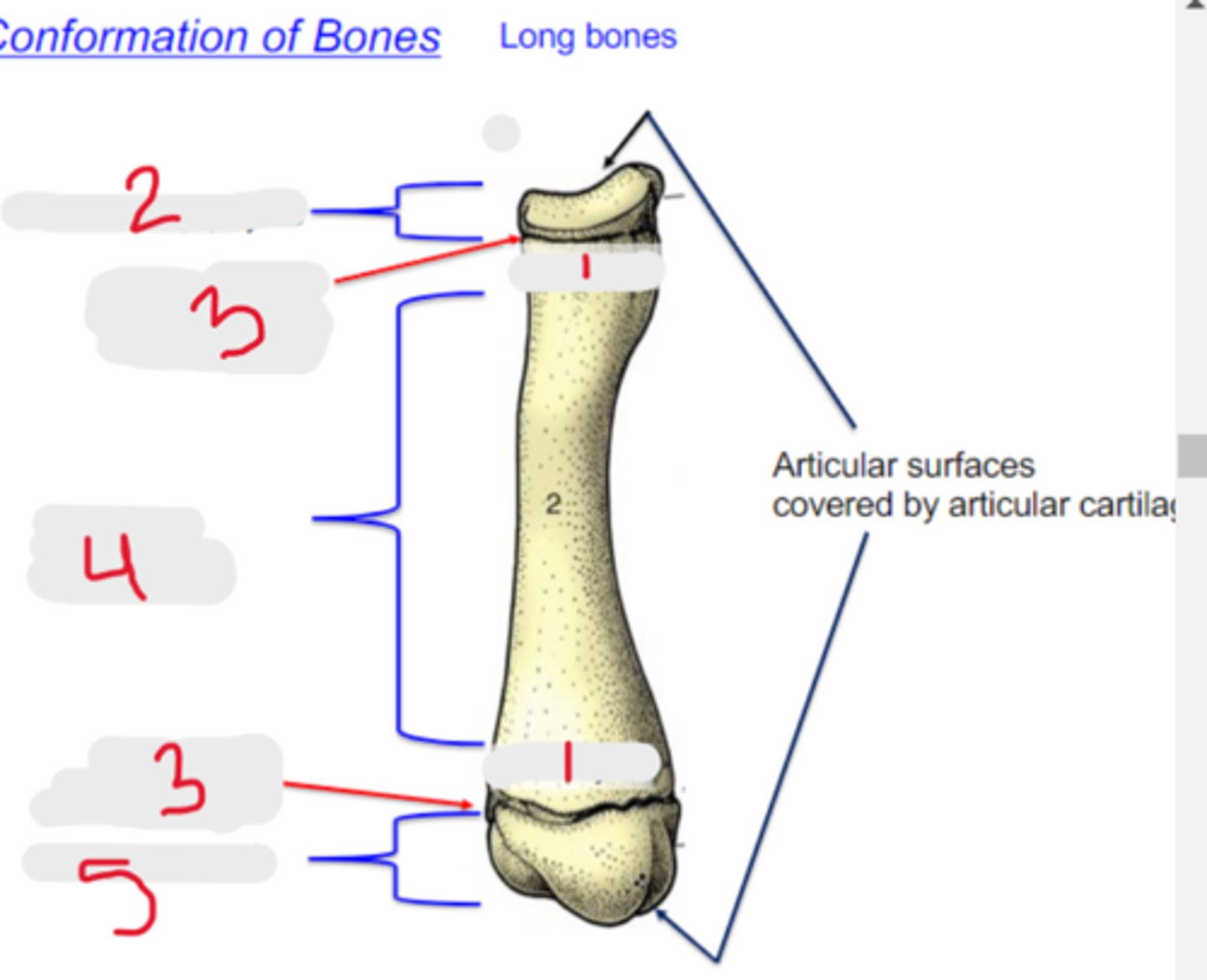
diaphysis
What is #4?
3 multiple choice options
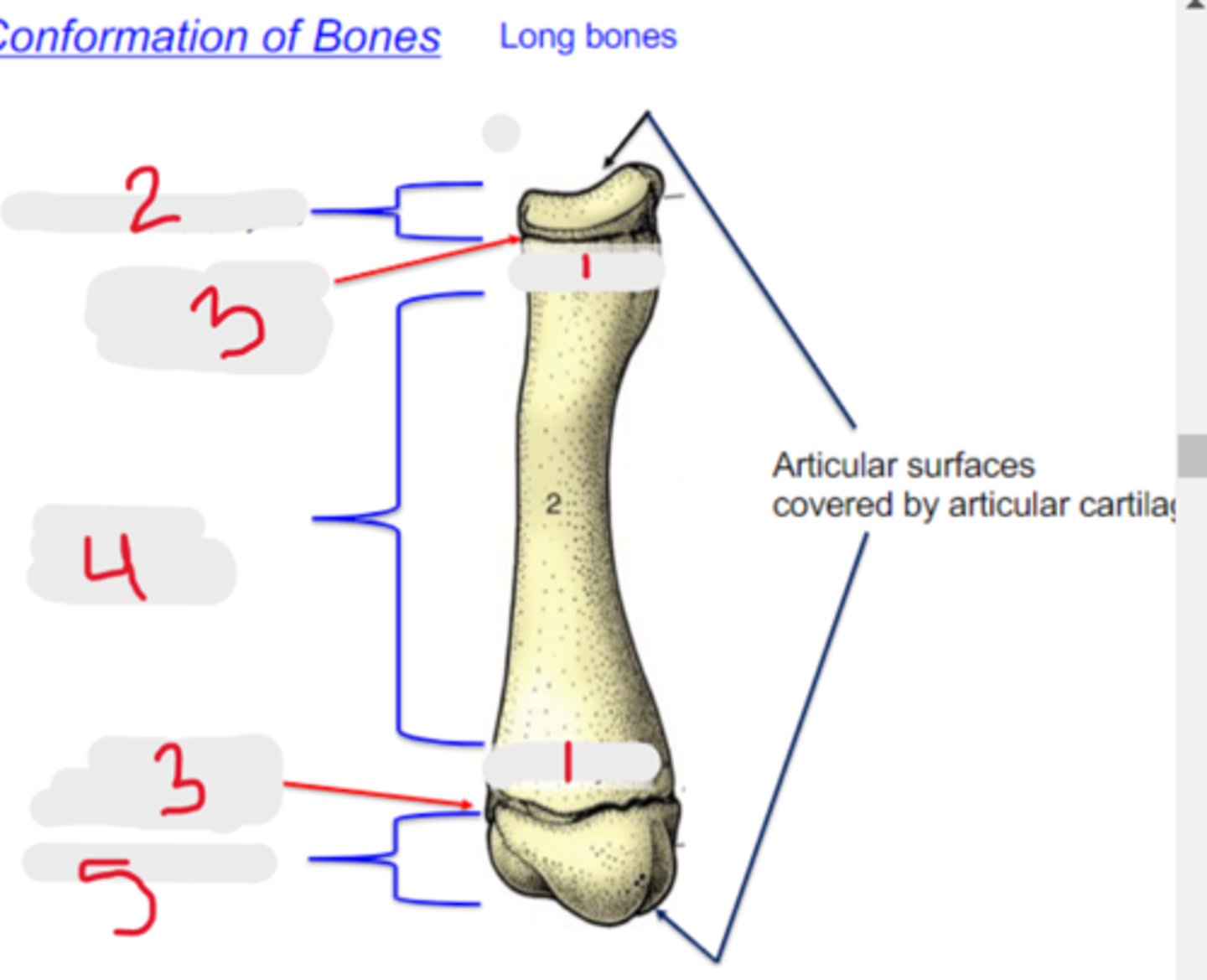
distal epiphysis
What is #5?
3 multiple choice options
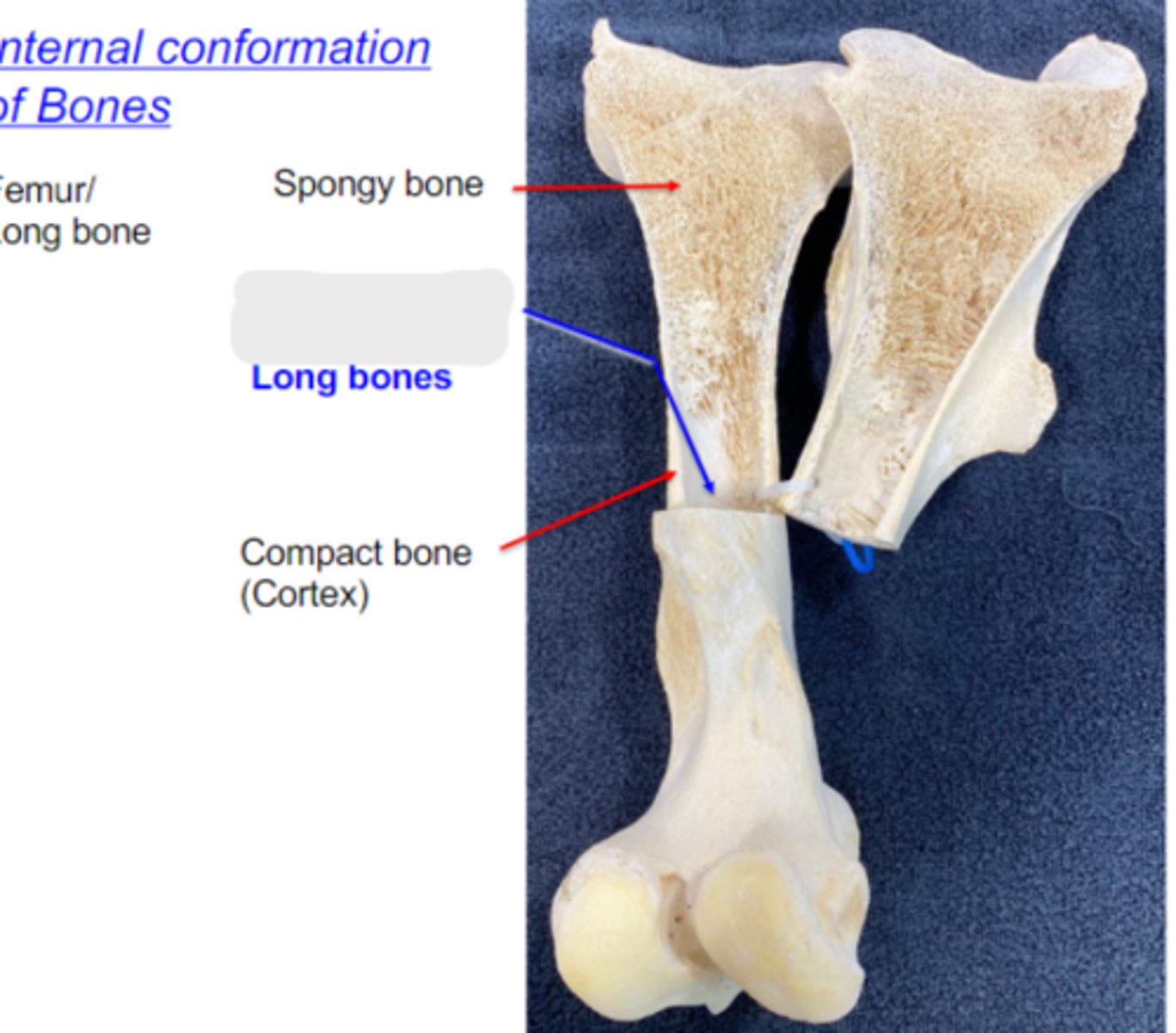
spongy bone
What is #1?
3 multiple choice options
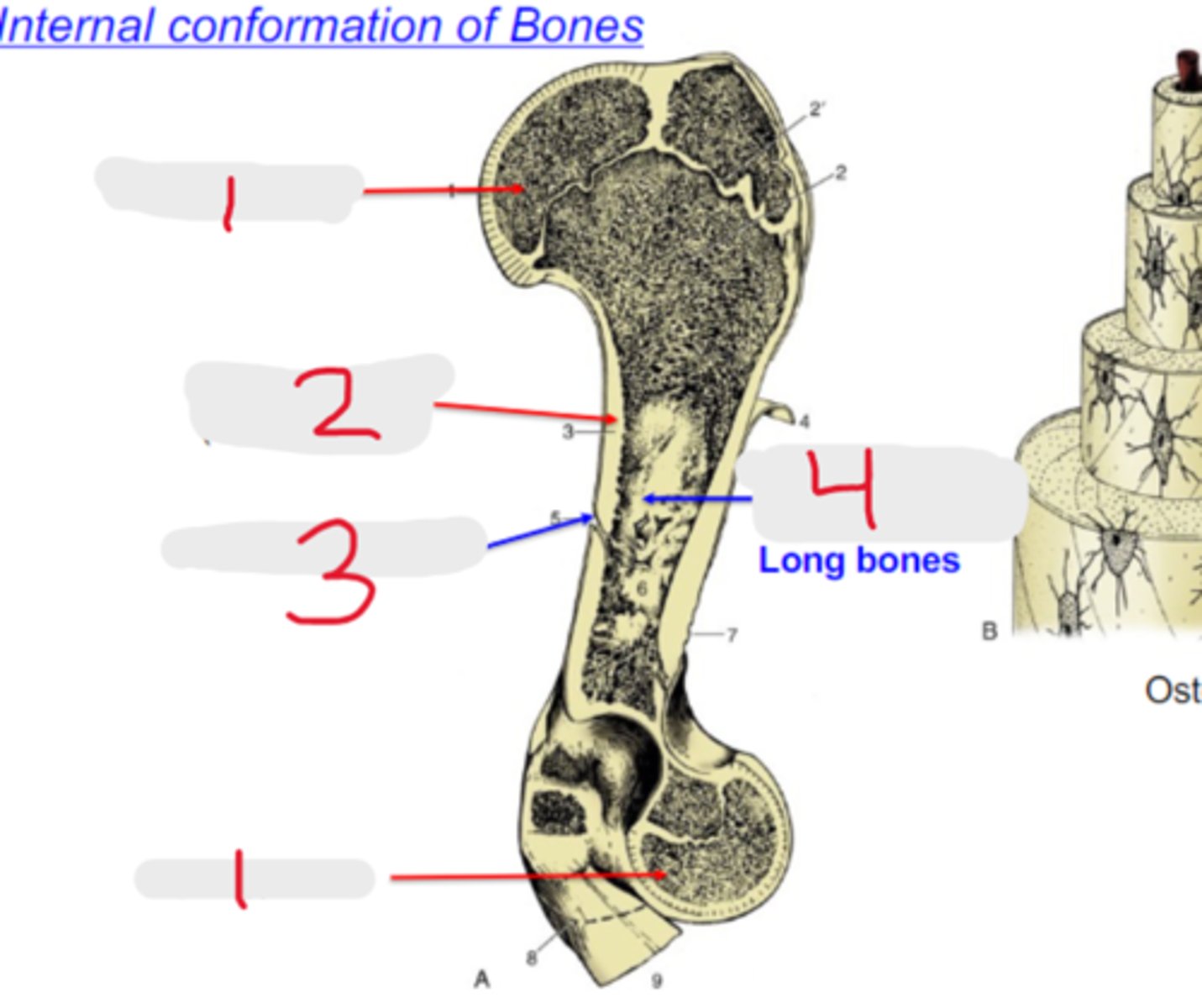
compact bone
What is #2?
3 multiple choice options
nutrient foramen
What is #3?
3 multiple choice options
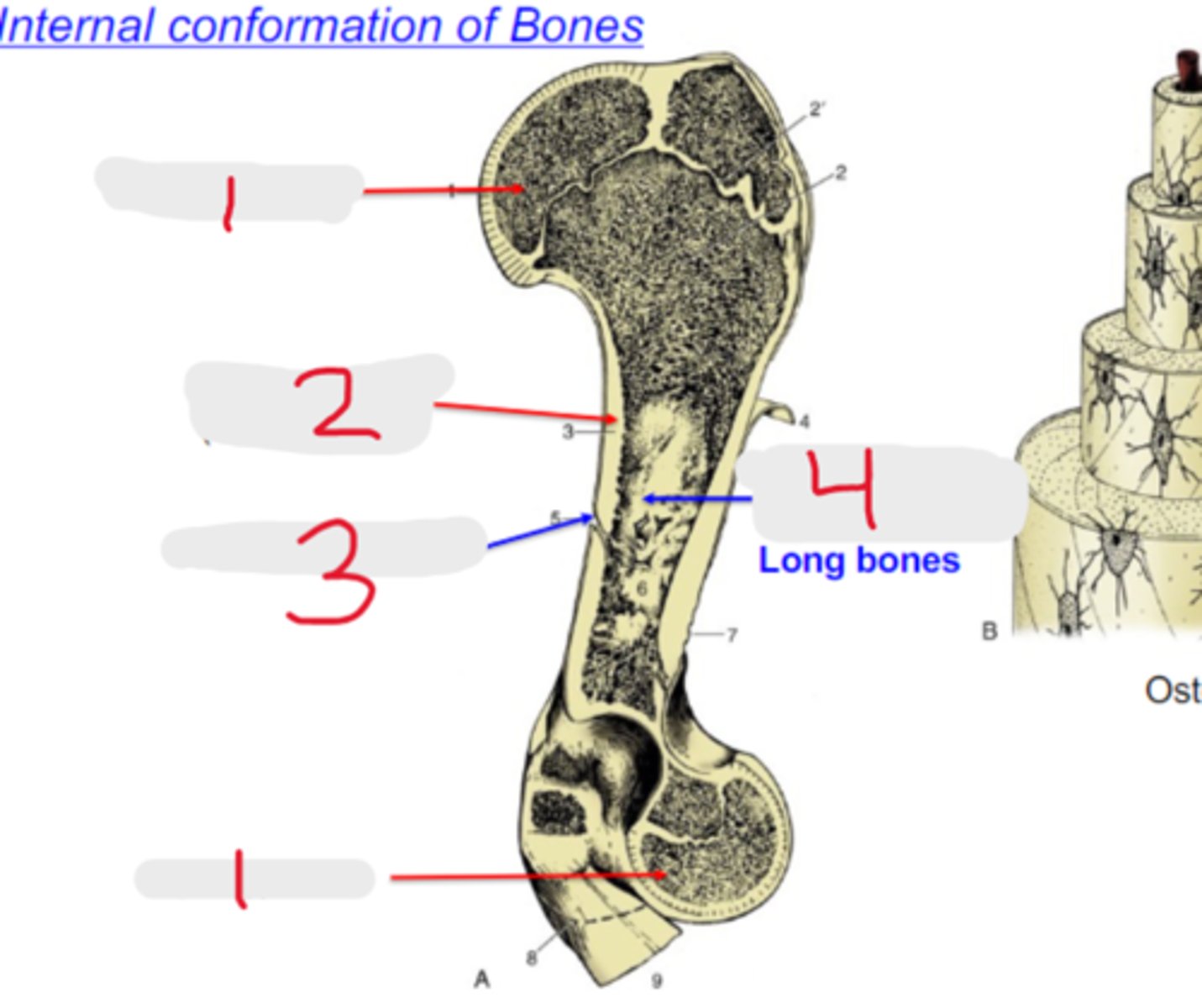
medullary cavity
What is #4?
3 multiple choice options
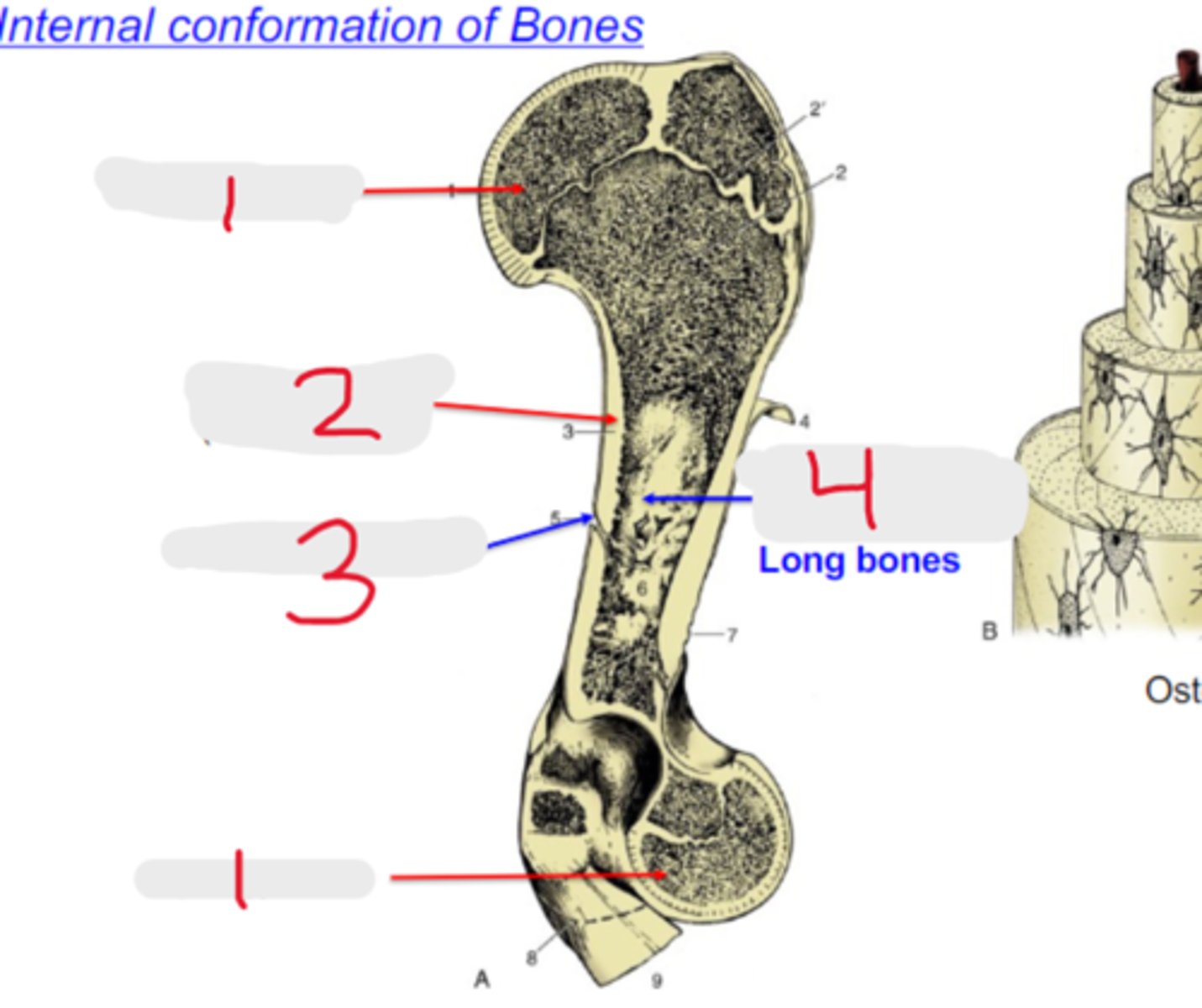
cortex
Compact bone is also referred to as the _____
3 multiple choice options
marrow cavity
The medullary cavity is also referred to as the _____
3 multiple choice options
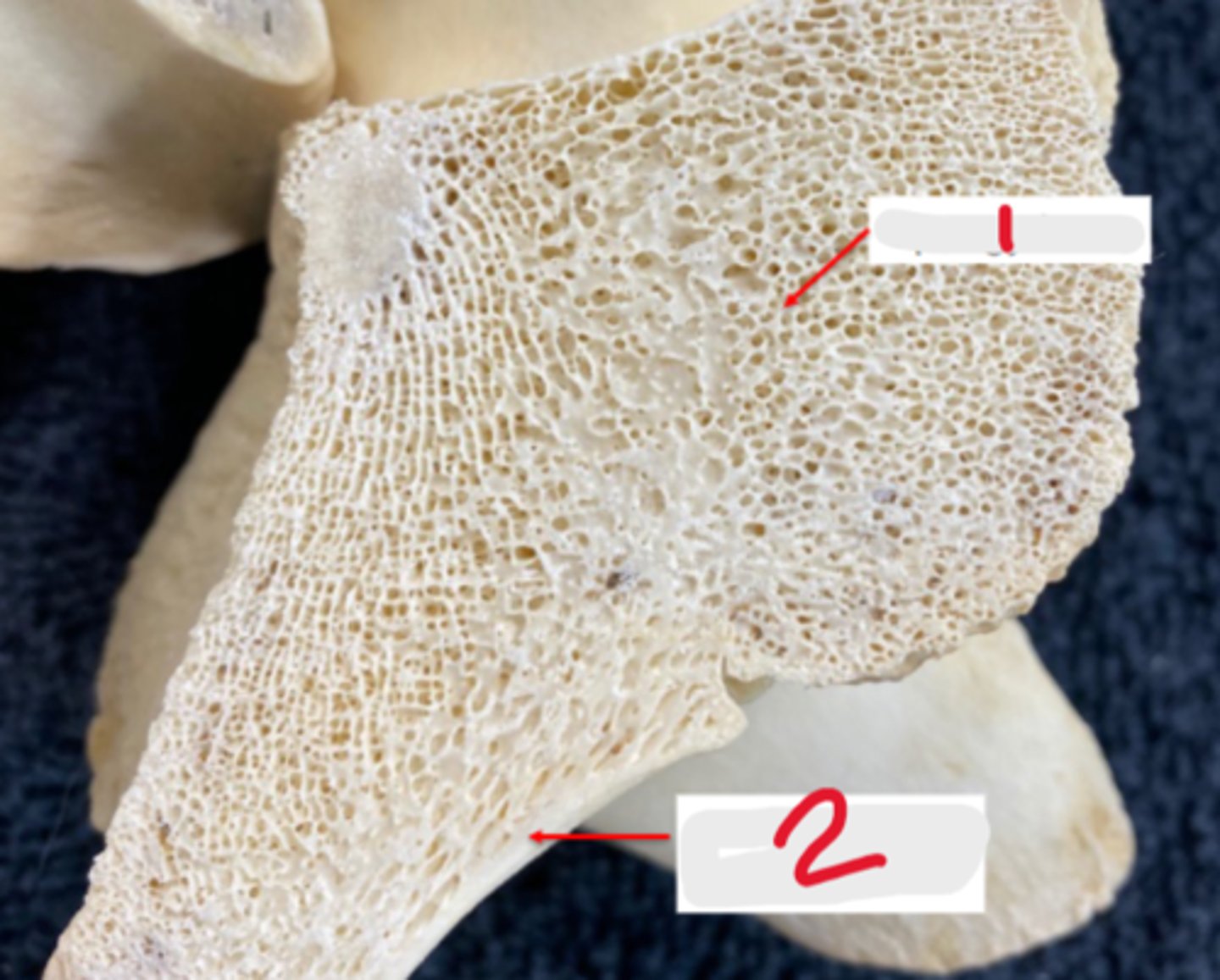
spongy bone
What is #1?
2 multiple choice options
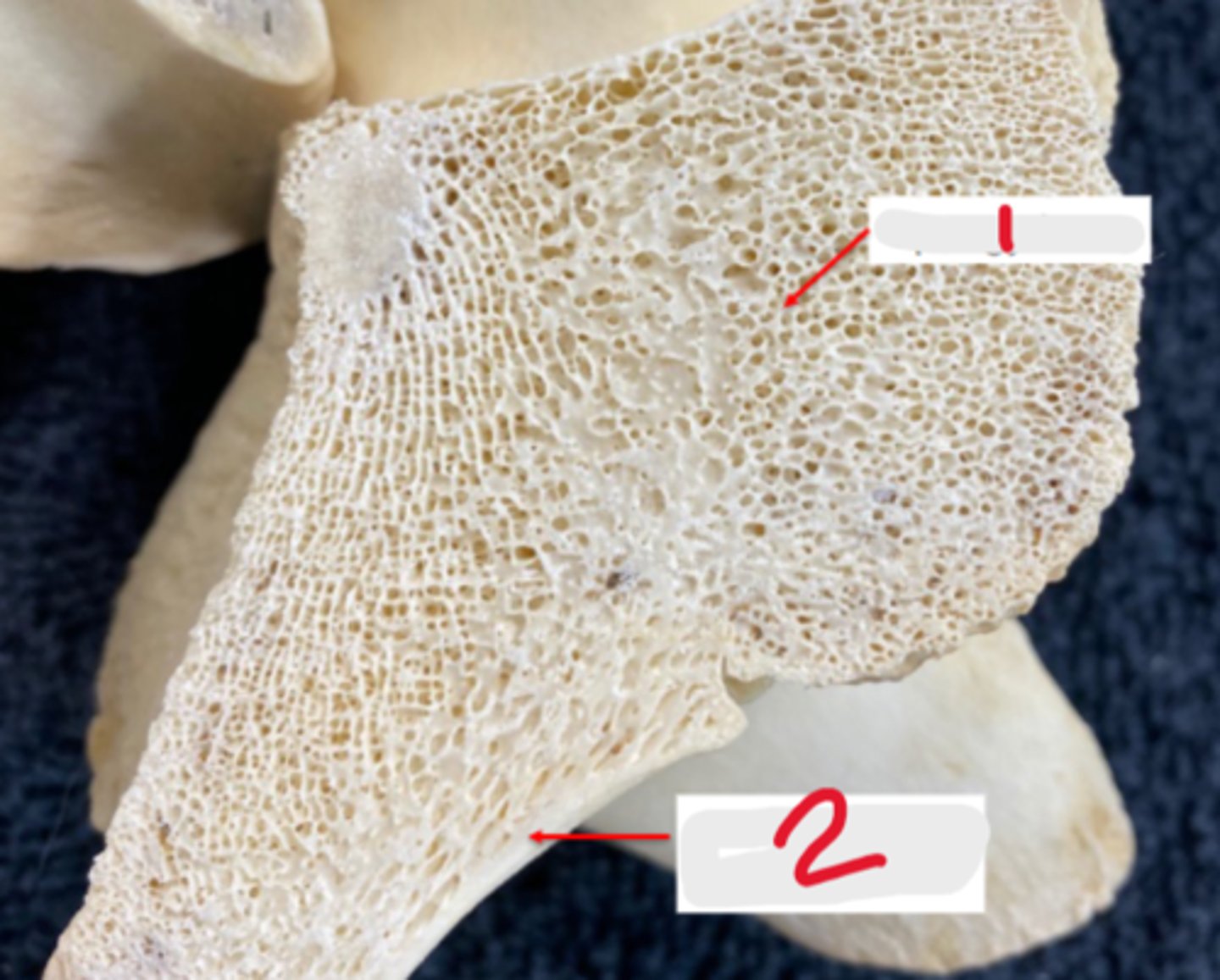
compact bone
What is #2?
2 multiple choice options
compact bone
What is #1?
2 multiple choice options
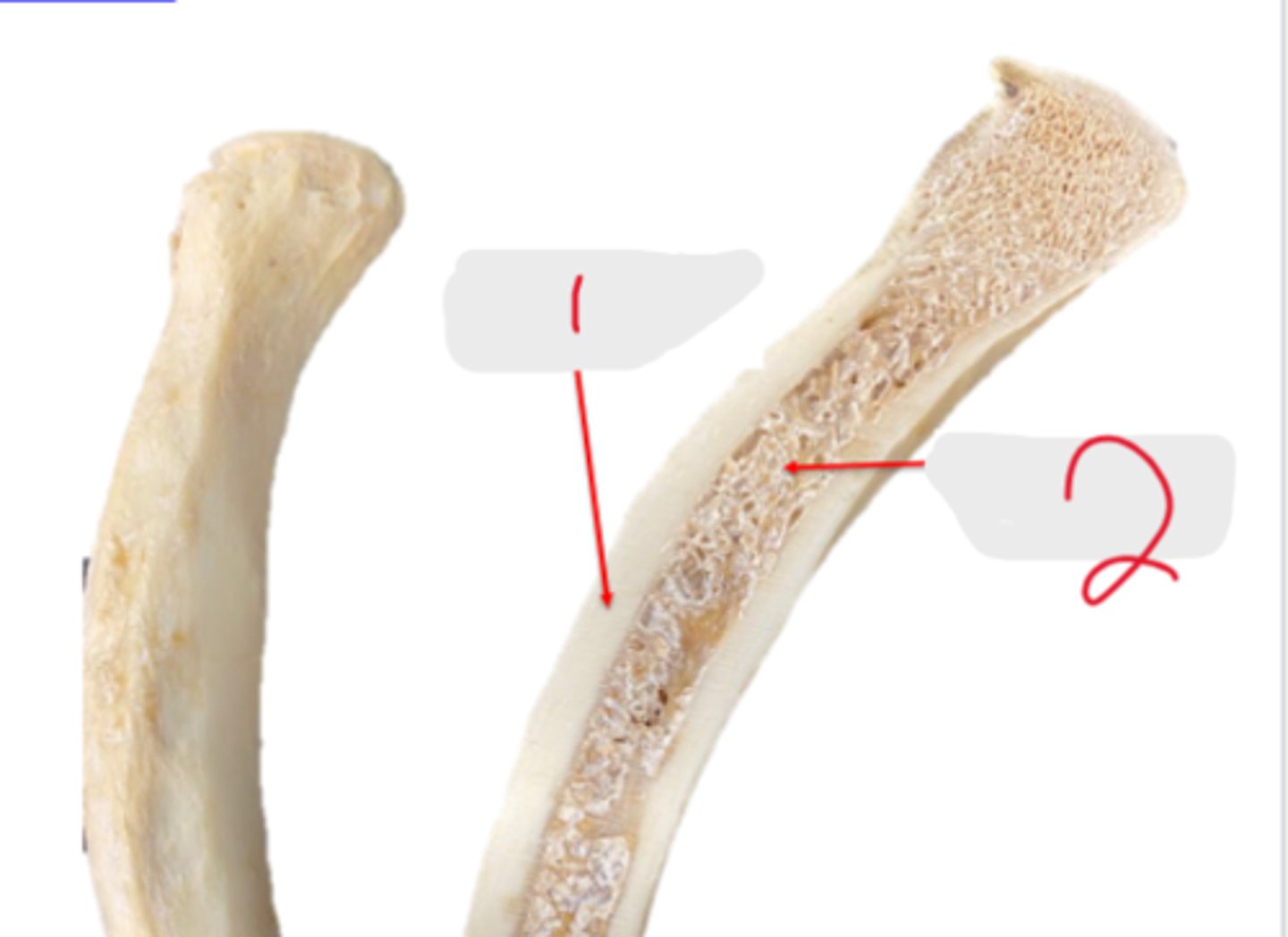
spongy bone
What is #2?
2 multiple choice options
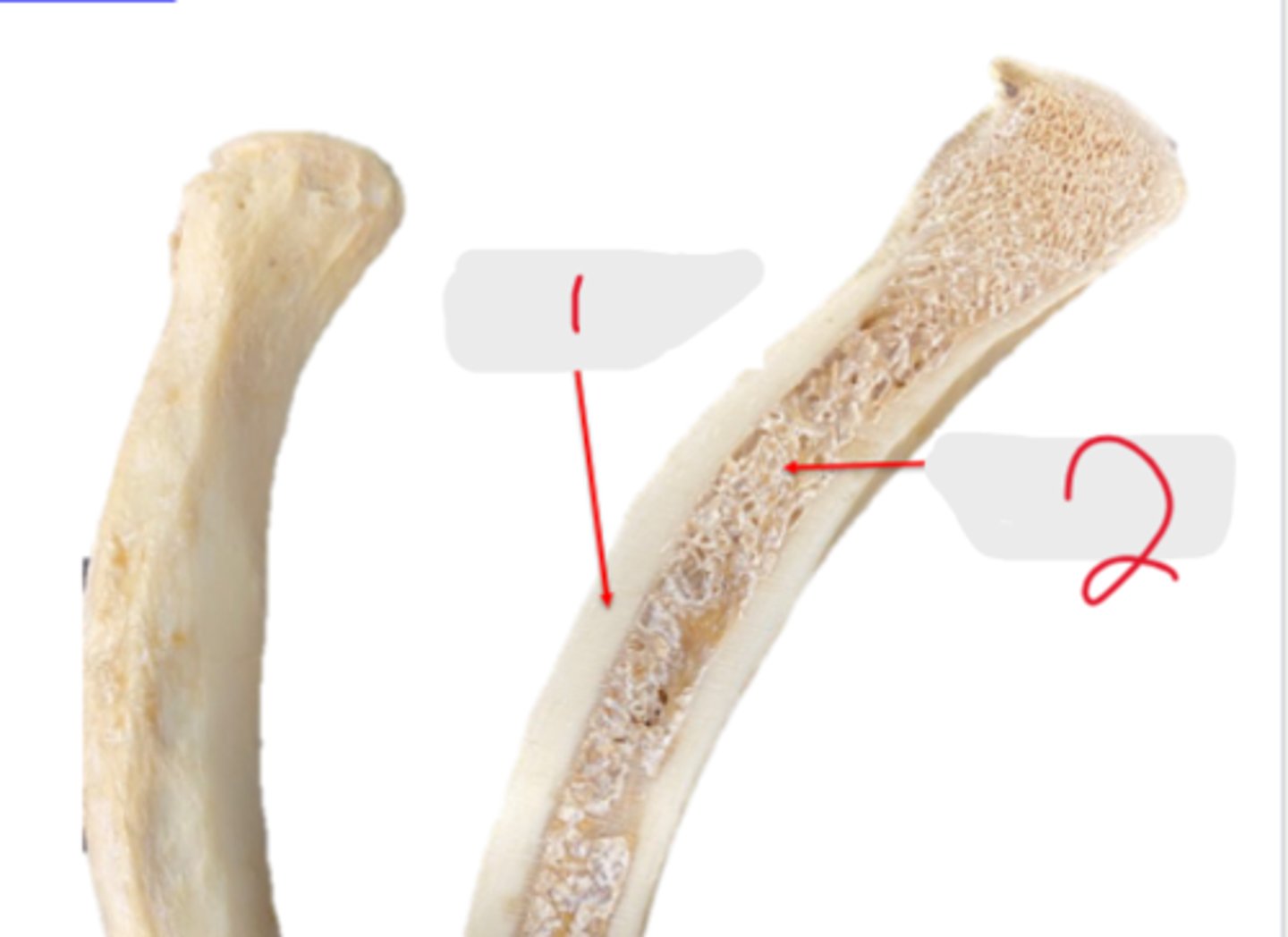
medullary cavity
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
bone marrow
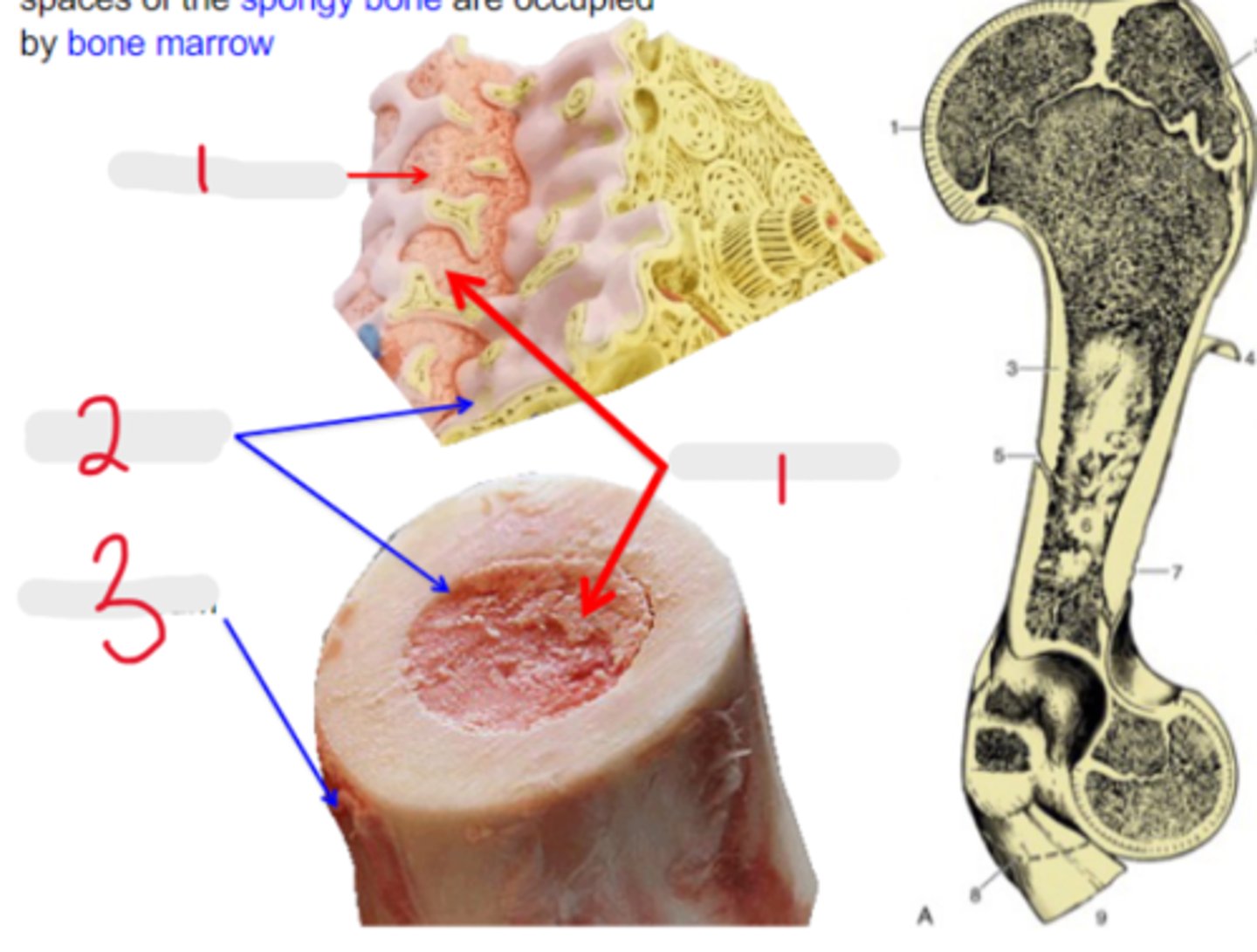
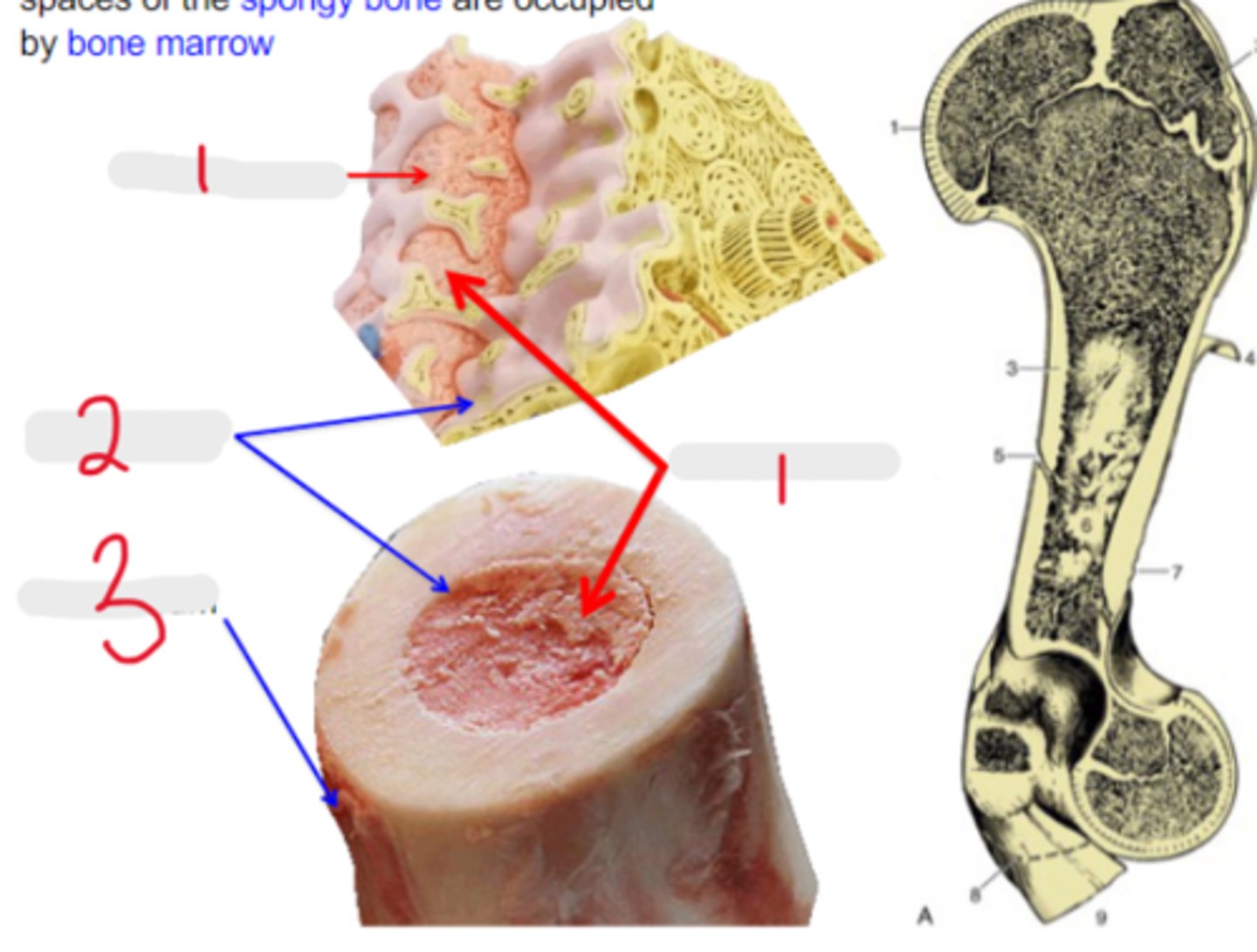
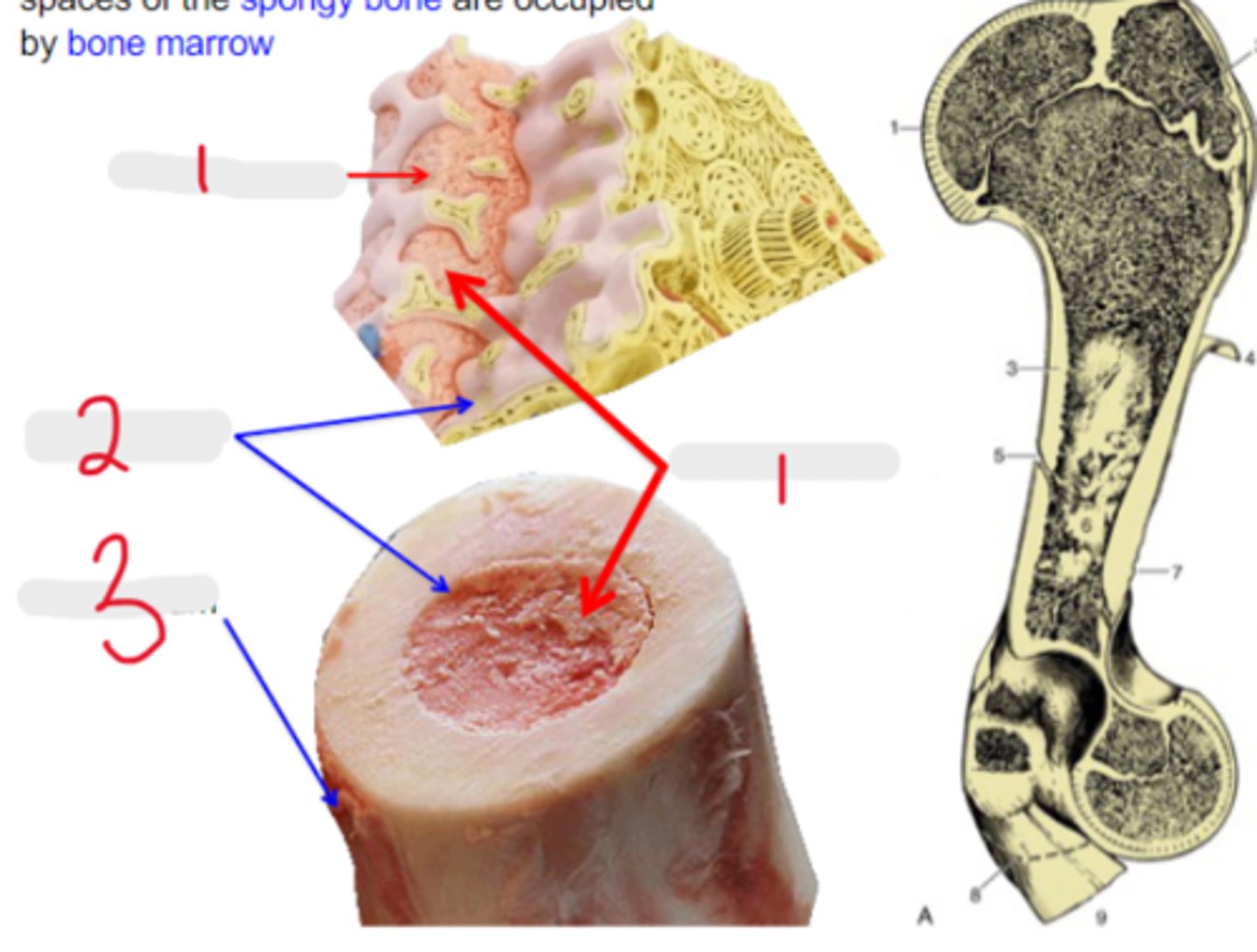
Medullary cavity and the interstitial spaces of the spongy bone are occupied by _____
bone marrow
What is #1?
3 multiple choice options
endosteum
What is #2?
3 multiple choice options
periosteum
What is #3?
3 multiple choice options
hyaline articular cartilage
Articular surfaces are clothed in _____, which is calcified in its deepest layer, which is firmly attached to the underlying cortex
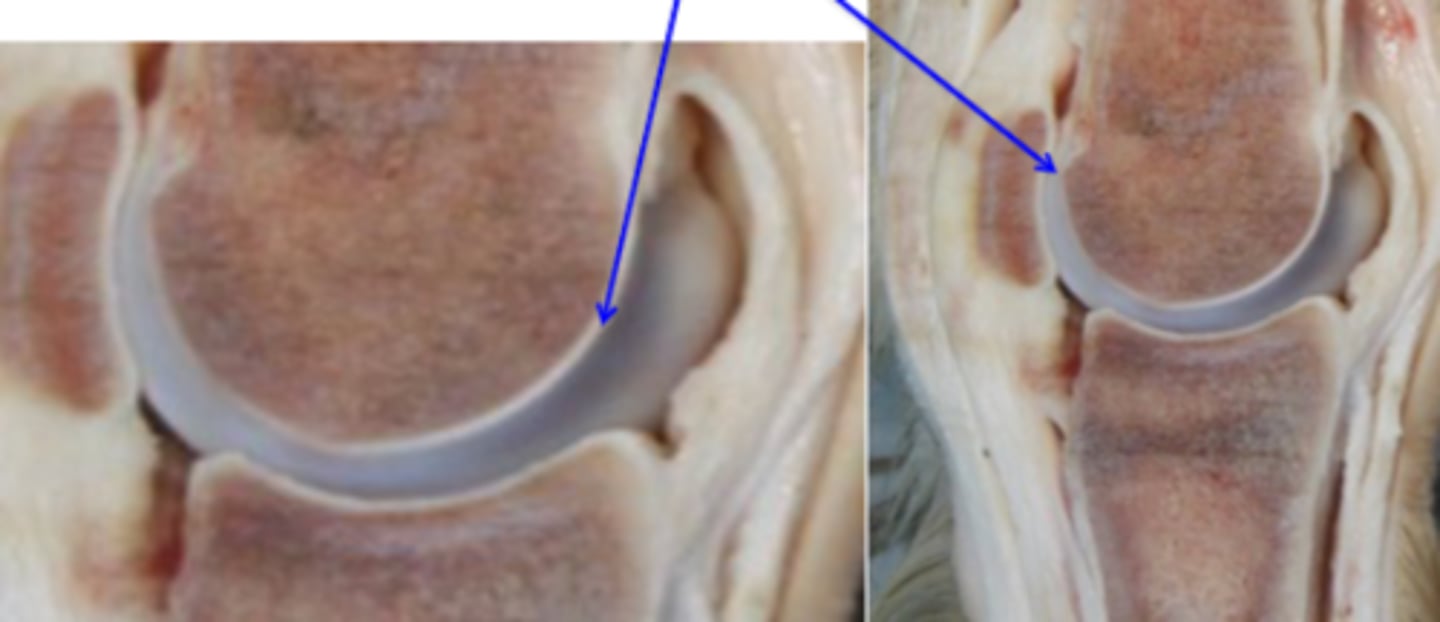
fibrous
Hyaline articular cartilage becomes _____ toward the periphery, where it blends with the periosteum and joint capsule
hyaline articular cartilage
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
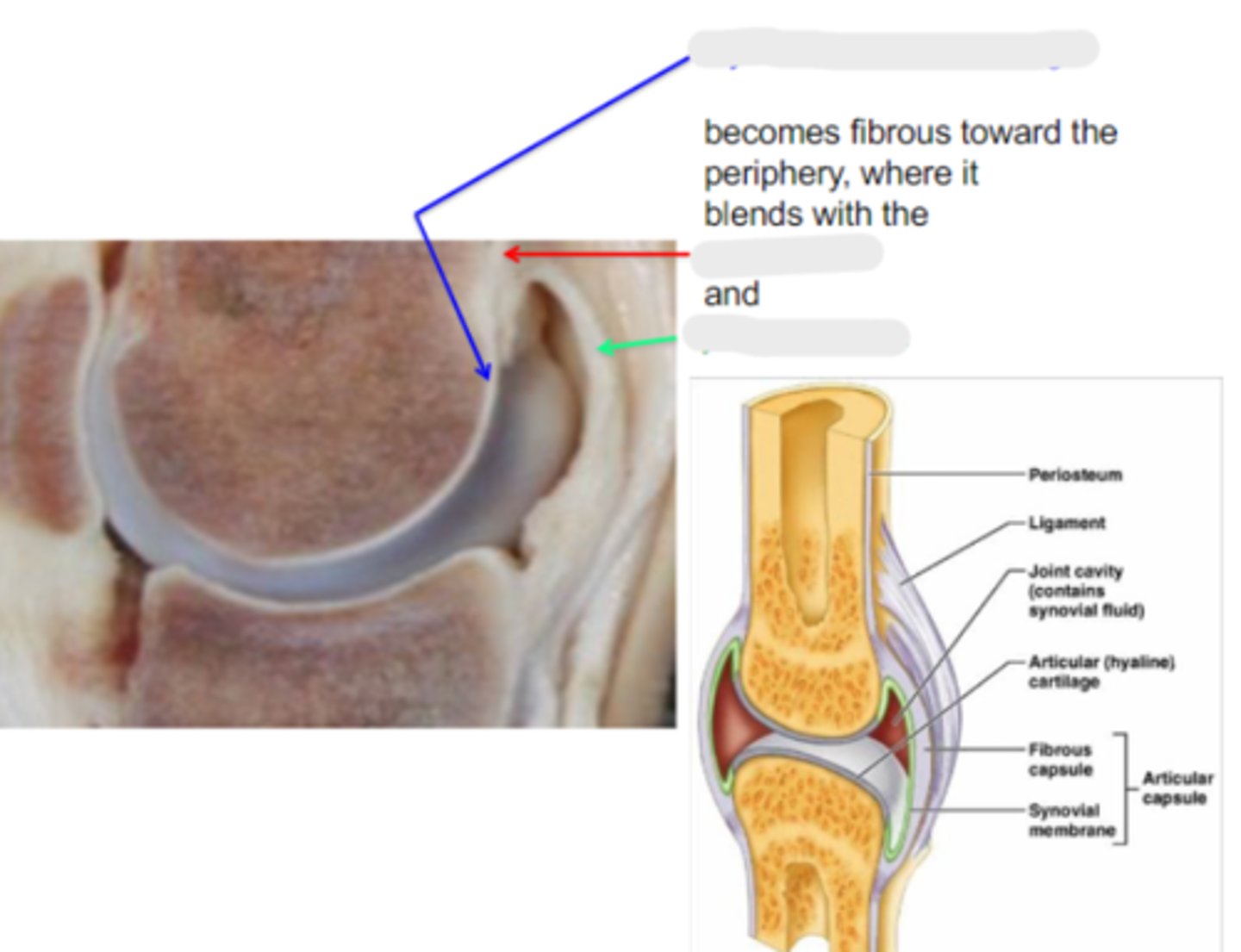
periosteum
What is the red arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
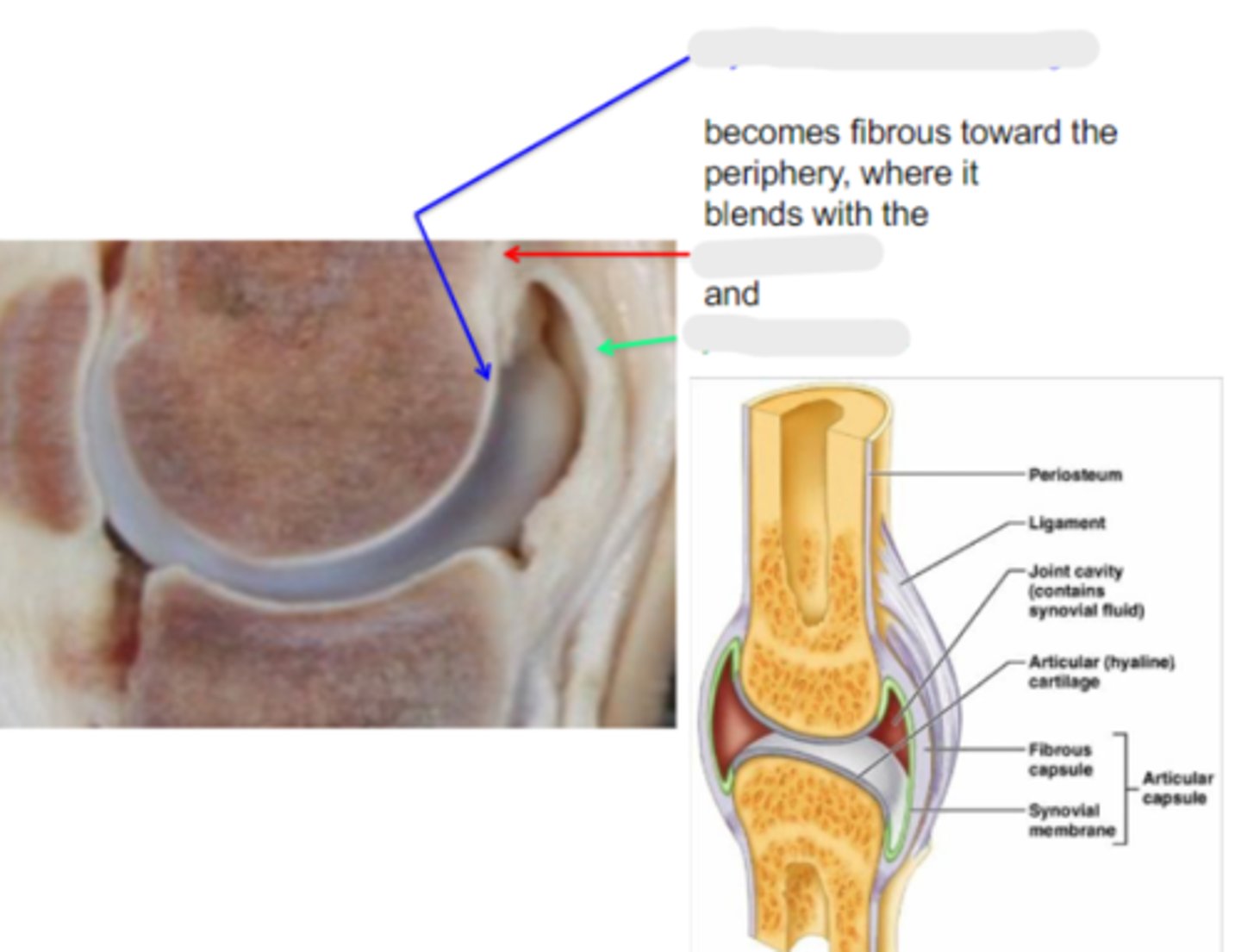
joint capsule
What is the green arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
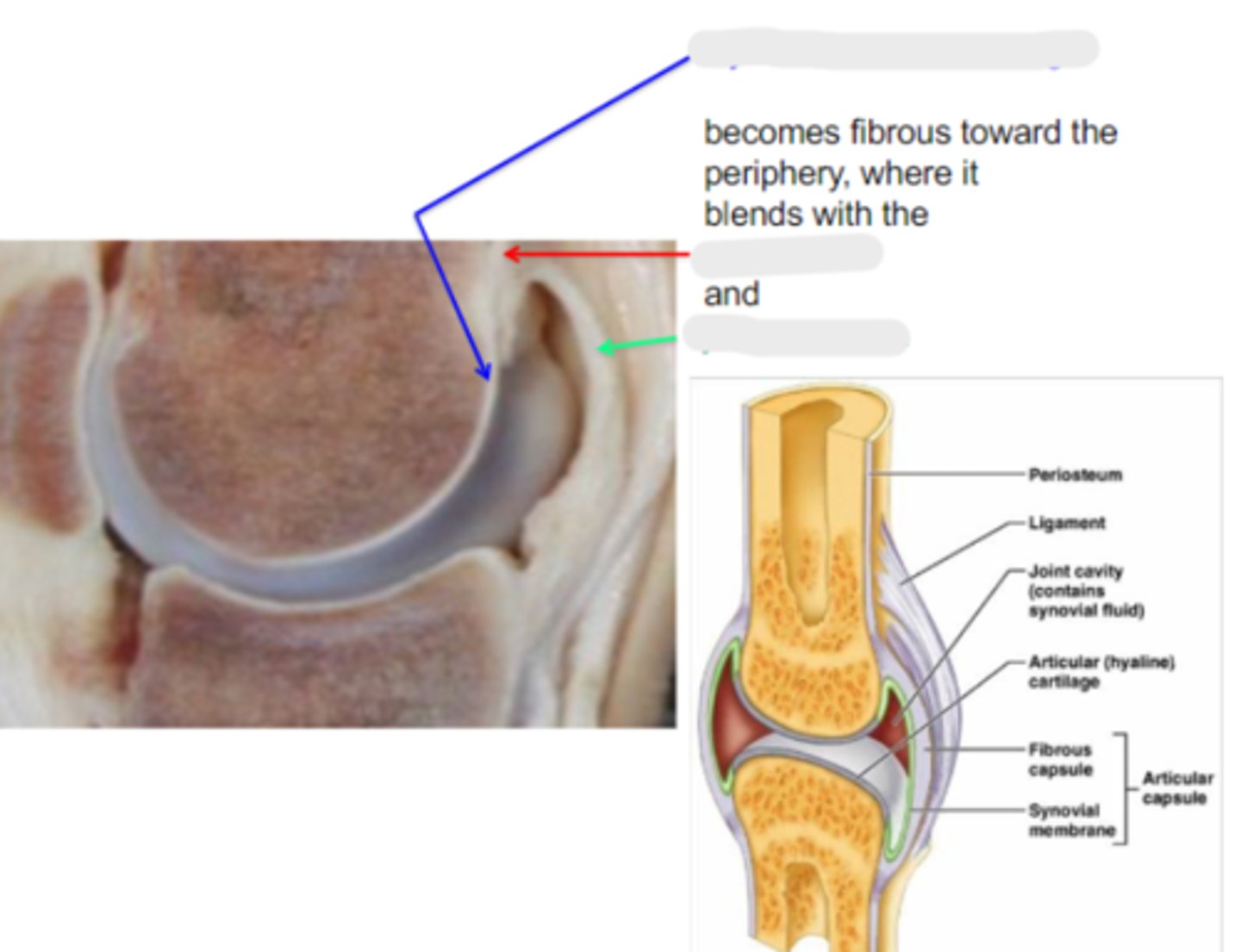
yellow
With [yellow/red] bone marrow, the hemopoietic potential is "inactive"
2 multiple choice options
![<p>With [yellow/red] bone marrow, the hemopoietic potential is "inactive"</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e46dbbd2-4b42-4097-a383-70303d5fc36c.jpg)
red
The [yellow/red] bone marrow is richly vascularized, gelatinous tissue, with hemopoietic properties
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The [yellow/red] bone marrow is richly vascularized, gelatinous tissue, with hemopoietic properties</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/da1f5364-6ab3-4cae-9494-75cc94a90eab.jpg)
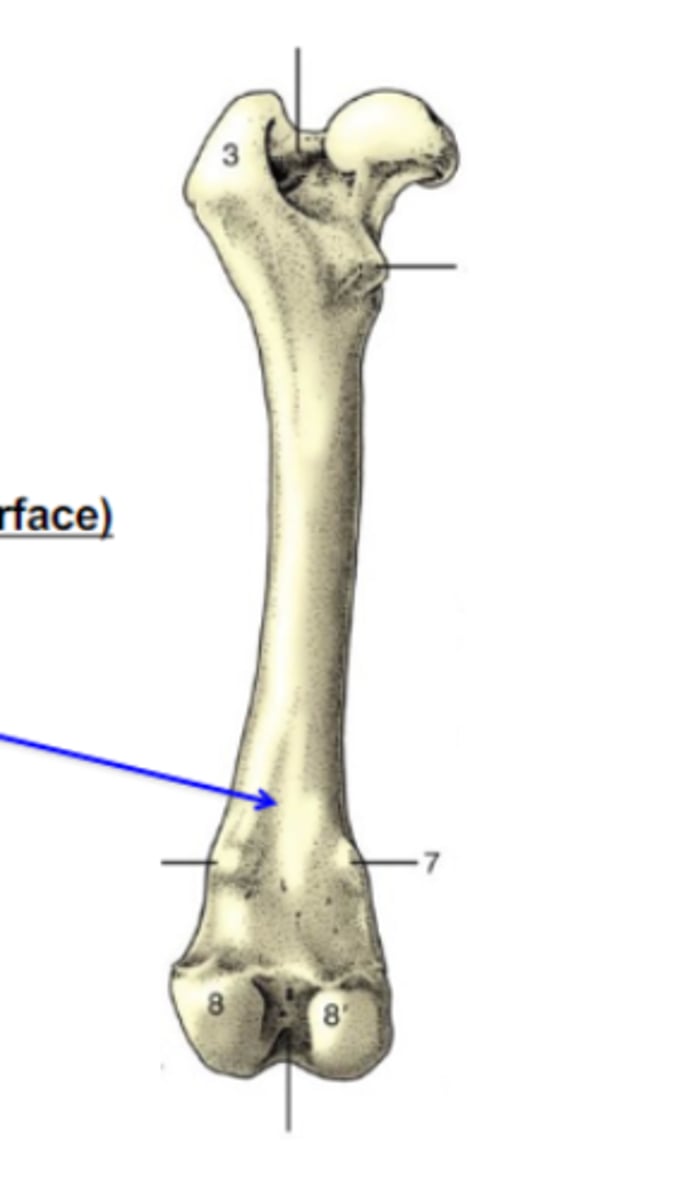
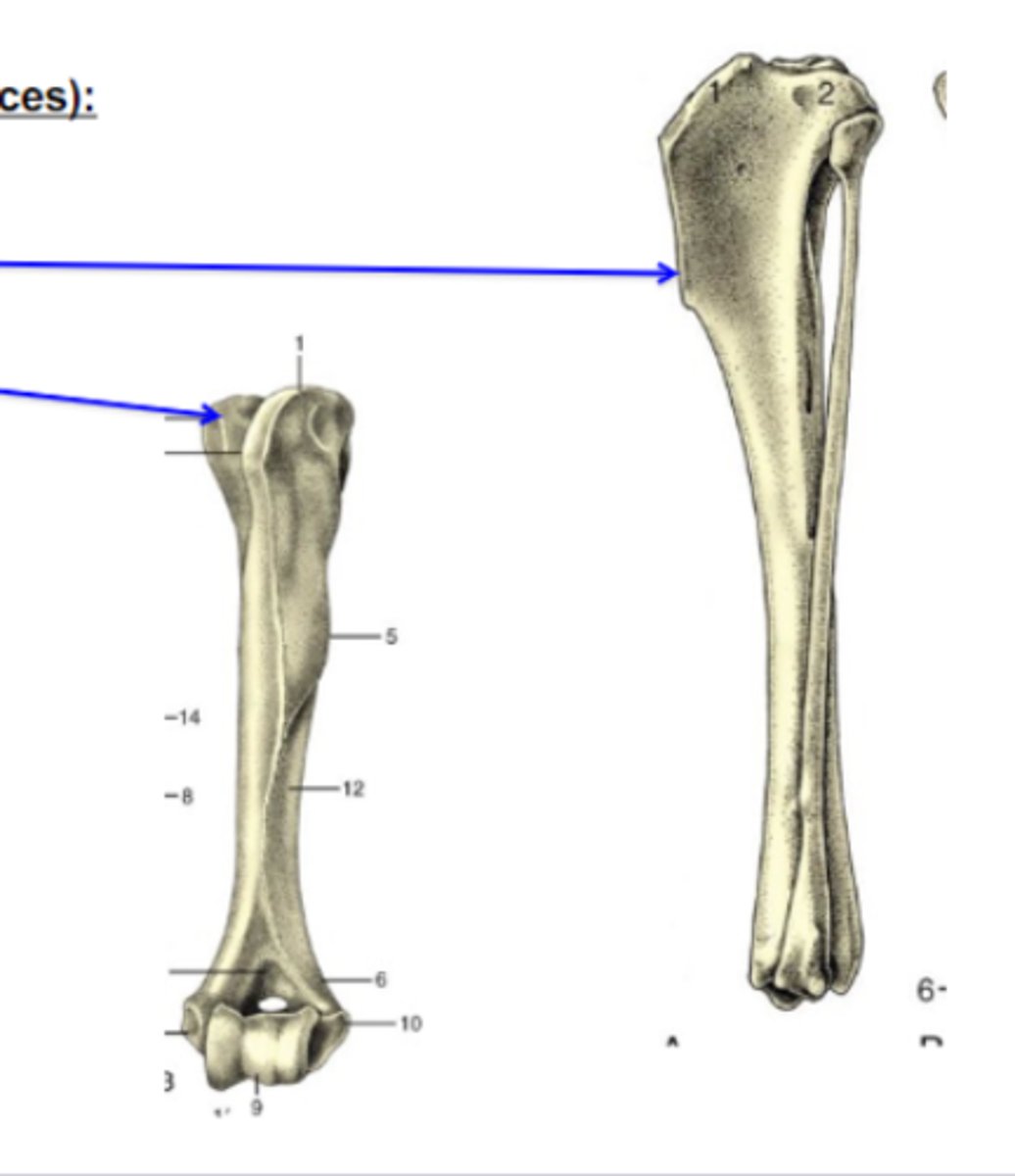
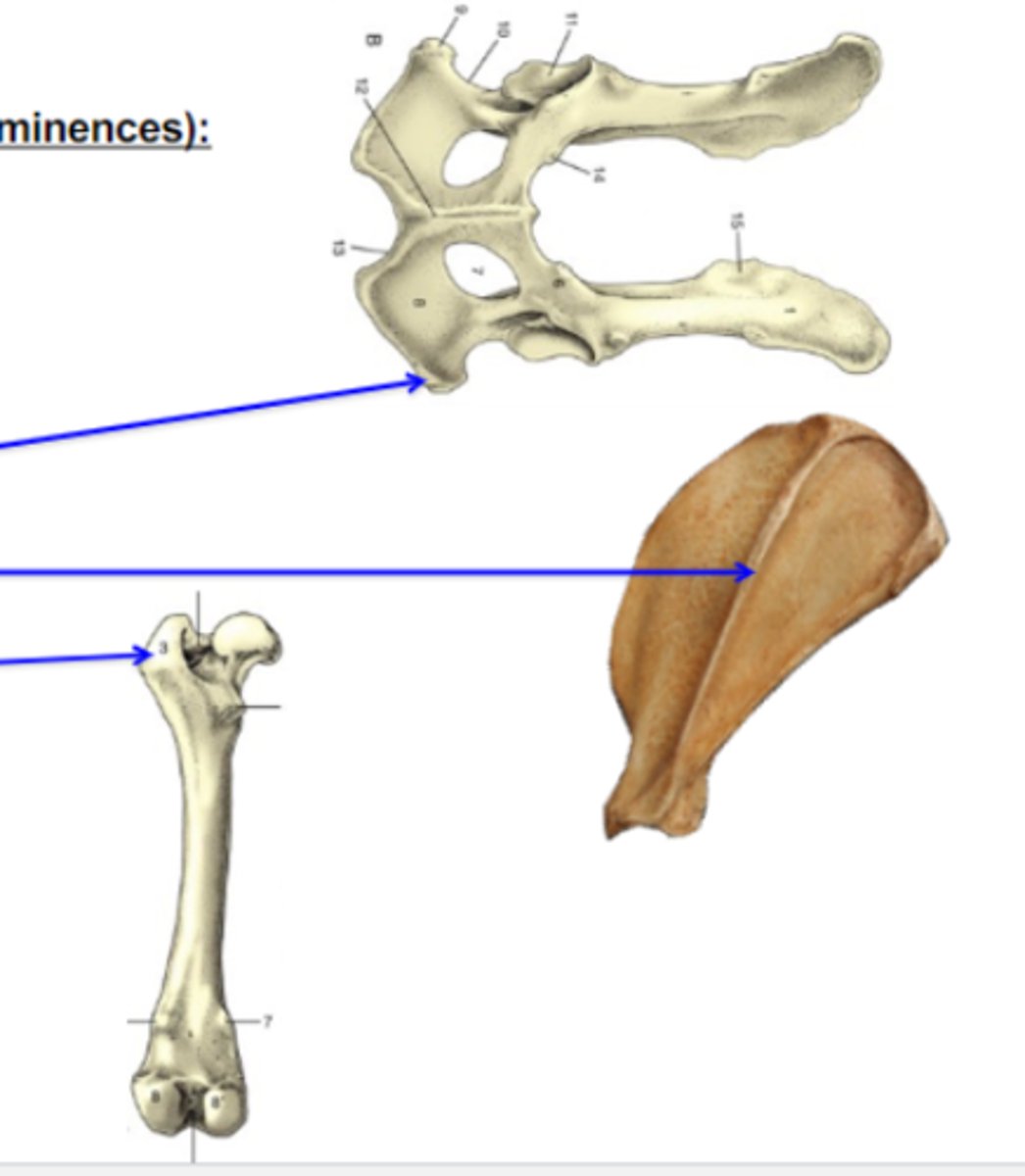
lines
Bone elevations
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
crests
Bone elevations
What is the TOP blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
tubercles
Bone elevations
What is the BOTTOM blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
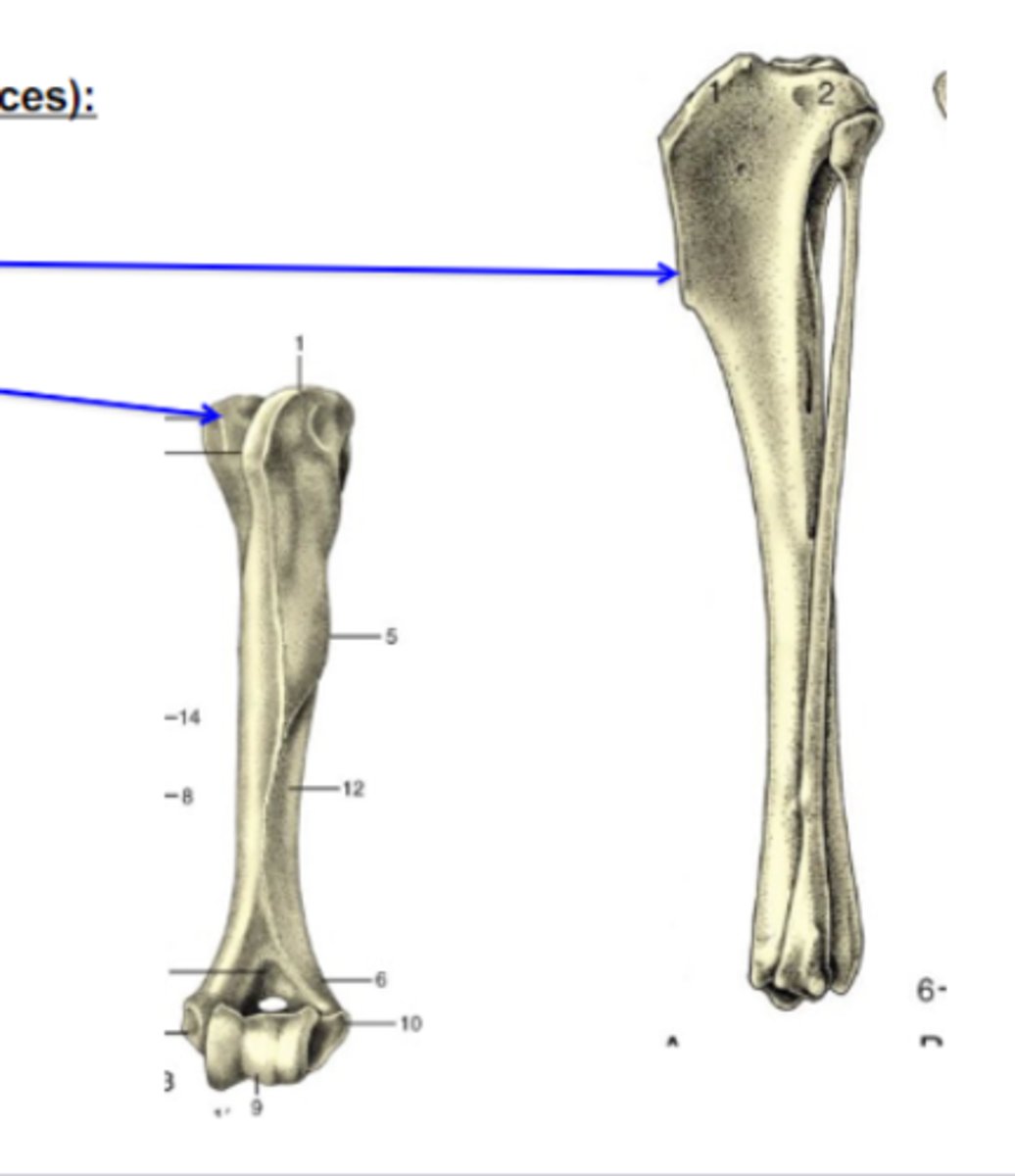
tuberosities
Bone elevations
What is the 1st (top) blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
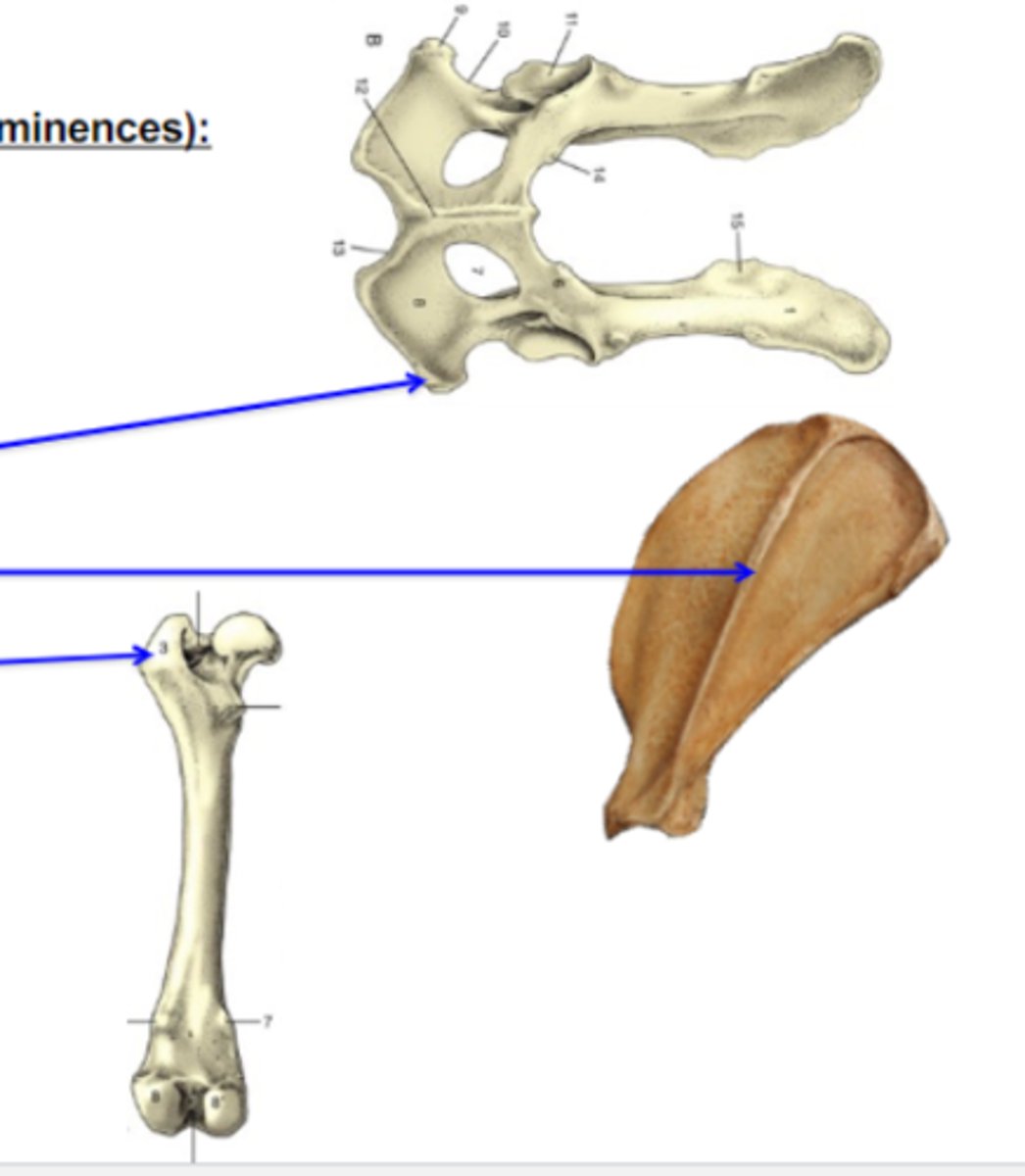
spines
Bone elevations
What is the 2nd (middle) blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
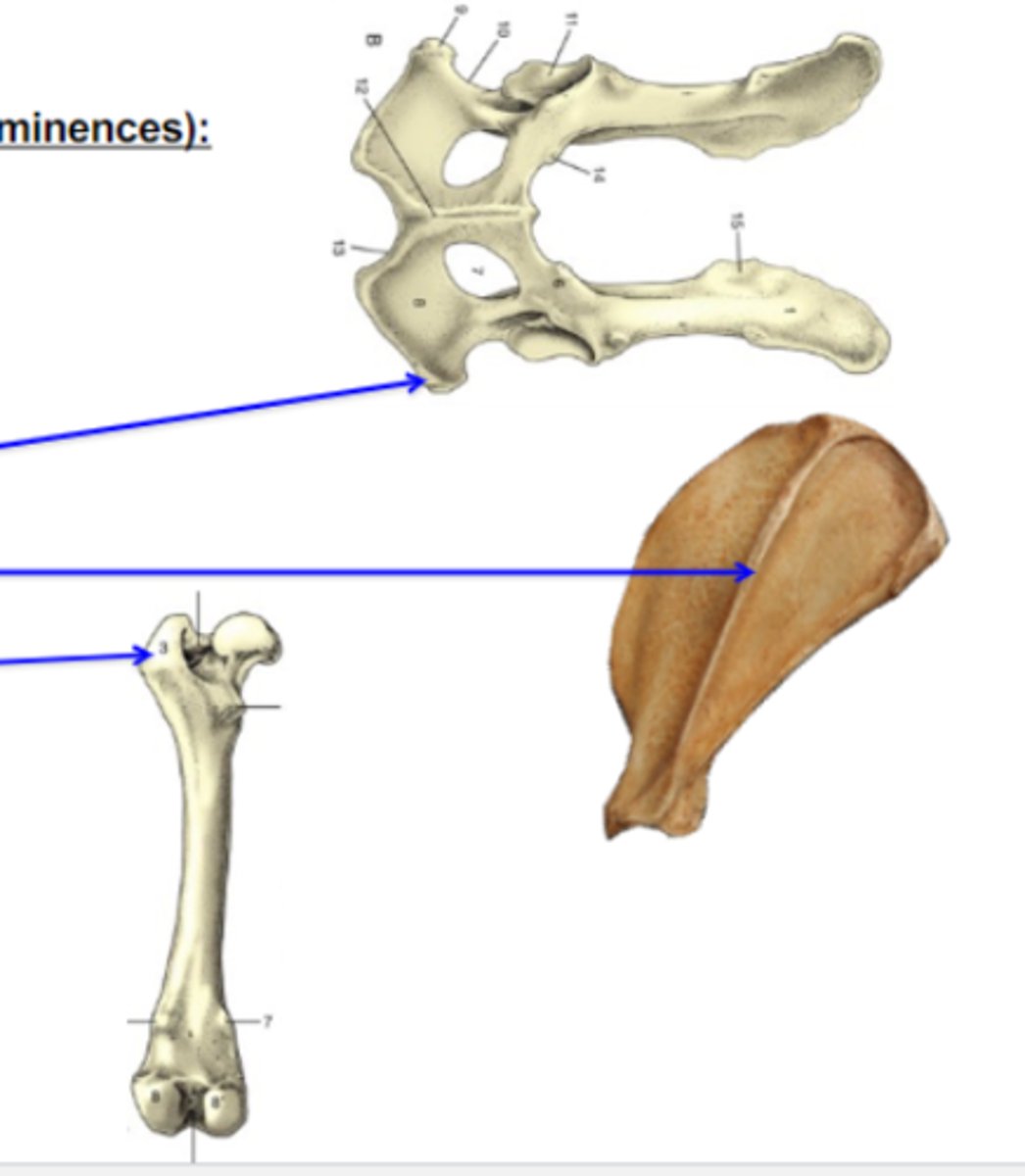
trocanters
Bone elevations
What is the 3rd (bottom) blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
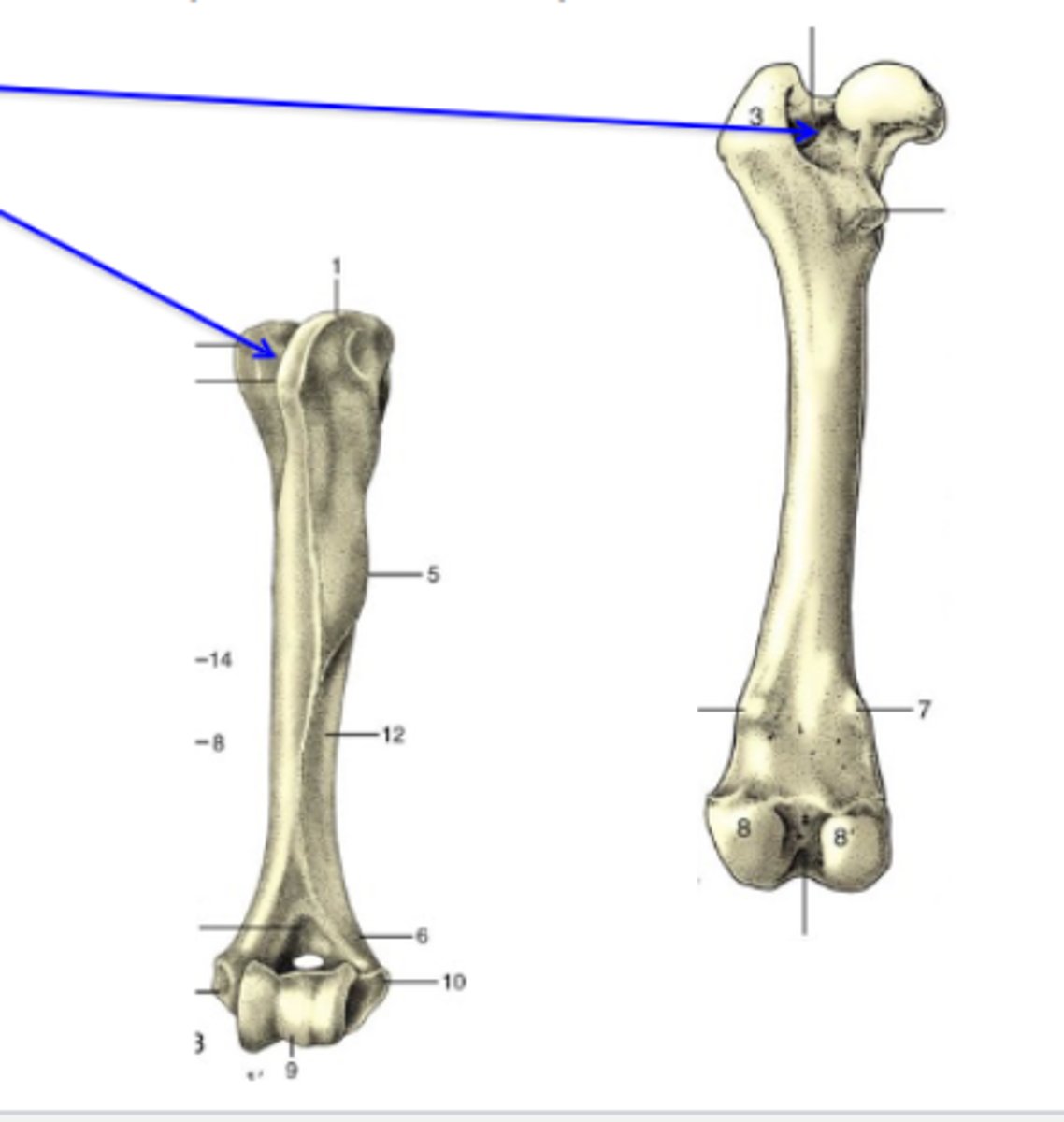
fossa
Bone depressions
What is the TOP blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
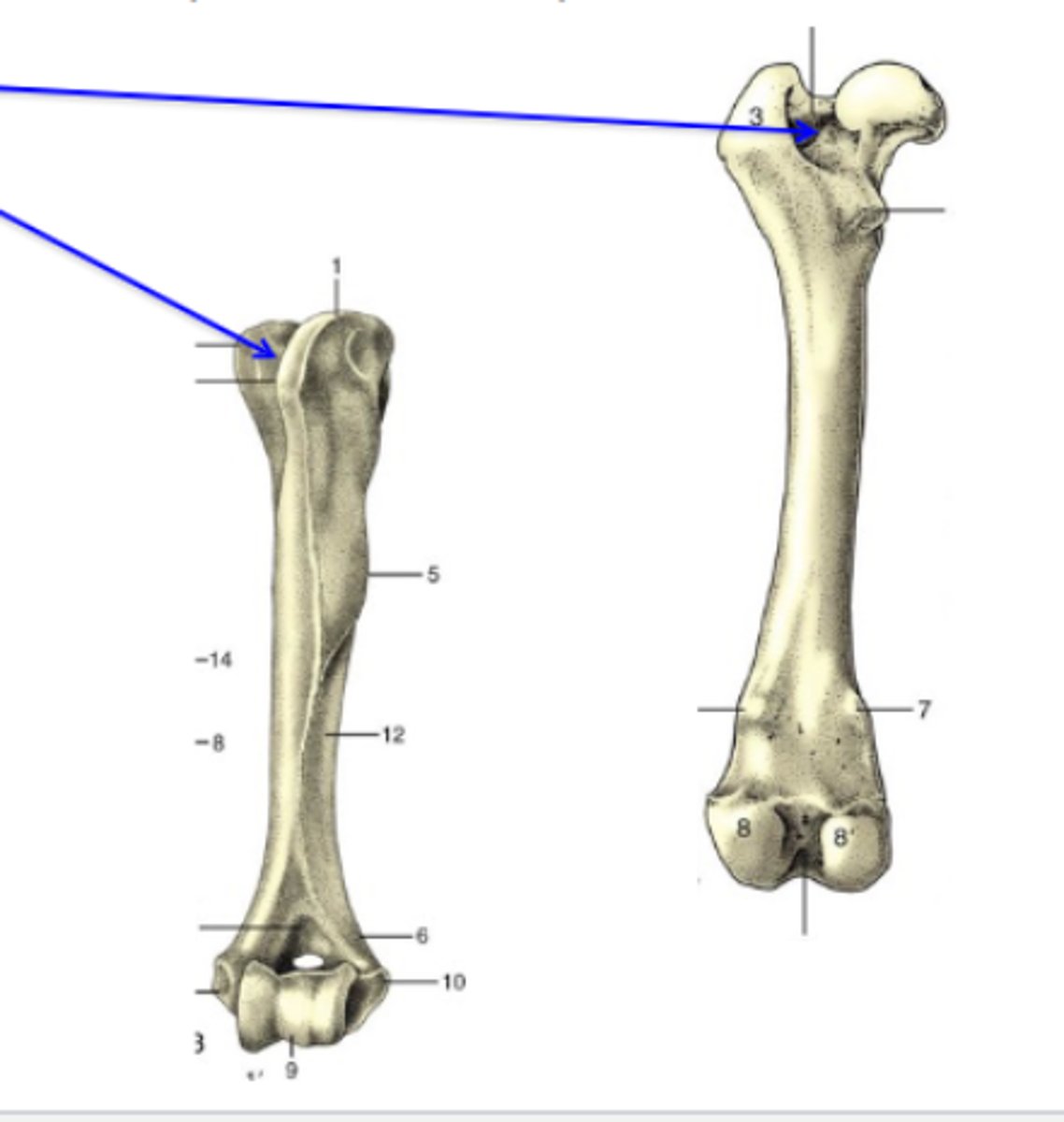
grooves
Bone depressions
What is the BOTTOM blue arrow pointing to?
3 multiple choice options
endochondral ossification
-Initial formation of a cartilage model that is subsequently resorbed while serving as a matrix for bone development
-Areas within this model that initially start to mineralize are called "centers for ossification" - primary and secondary
-Cartilaginous plate (physis) remains btwn and separates adjacent centers until bone is mature
-Contiguous cartilage production, with subsequent resorption and ossification, at these plates is what allows a developing bone to elongate
2 multiple choice options
primary
The [primary/secondary] centers of ossification form before birth and are located in the diaphysis
(TOP image)
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The [primary/secondary] centers of ossification form before birth and are located in the diaphysis</p><p>(TOP image)</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5e0efe84-eac7-4594-8a52-f5a044371f5c.jpg)
secondary
The [primary/secondary] centers of ossification form after birth and are located in epiphysis and large eminences
(BOTTOM image)
2 multiple choice options
![<p>The [primary/secondary] centers of ossification form after birth and are located in epiphysis and large eminences</p><p>(BOTTOM image)</p><p>2 multiple choice options</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1ca6dc0f-6990-442a-b4b0-582a6af85ab4.jpg)
intramembranous ossification
-Bone forms directly within a sheet of connective tissue
-No cartilage model is involved
-Characteristic of many flat bones
-Also occurs under the periosteum as bones grow in diameter, so most bones actually develop from a mixture of endochondral and intramembranous ossification
2 multiple choice options
nutrient foramina
-May resemble an oblique fracture on radiographs
-Often where signs of panosteitis are first detectable
-Position is fairly consistent for each bone
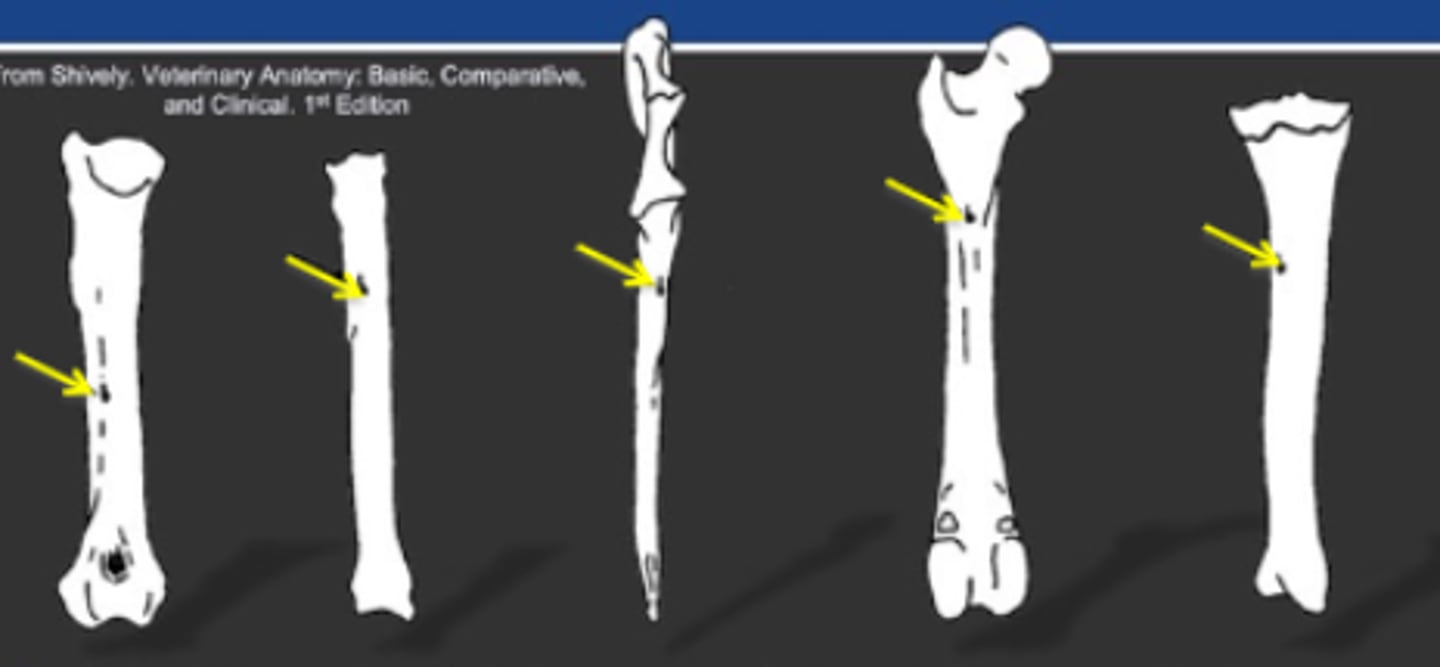
nutrient artery
Bone blood supply
Penetrates toward the middle of the diaphysis
3 multiple choice options
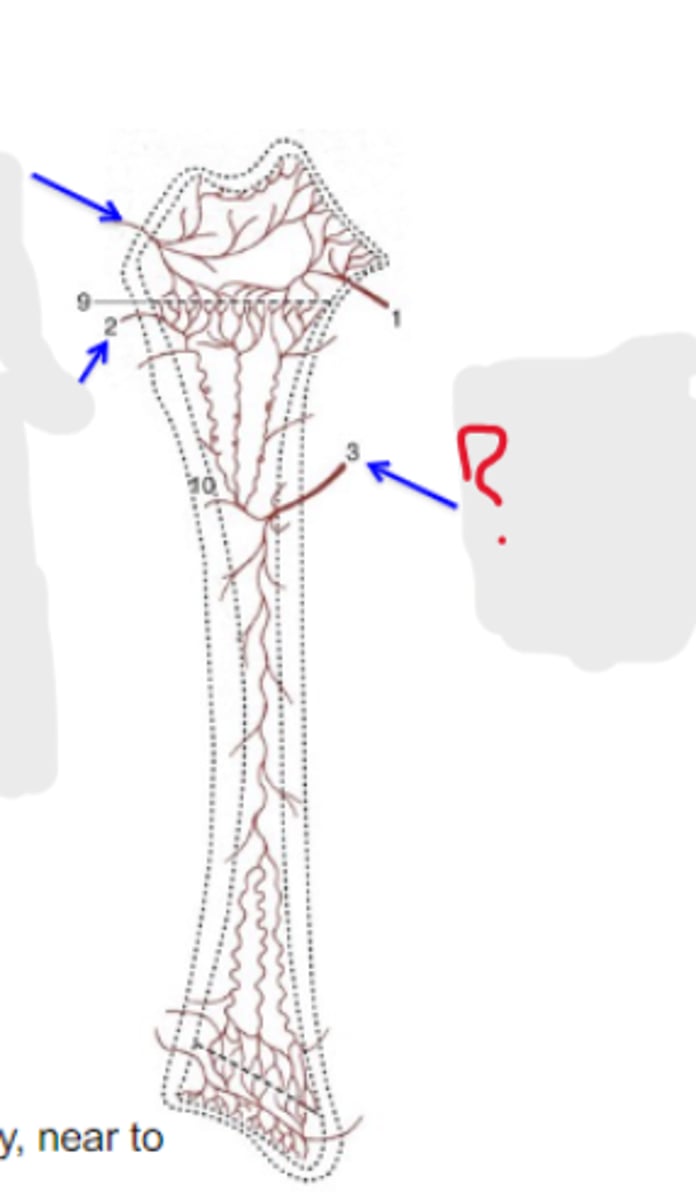
epiphysial arteries
Bone blood supply
What is #1?
2 multiple choice options
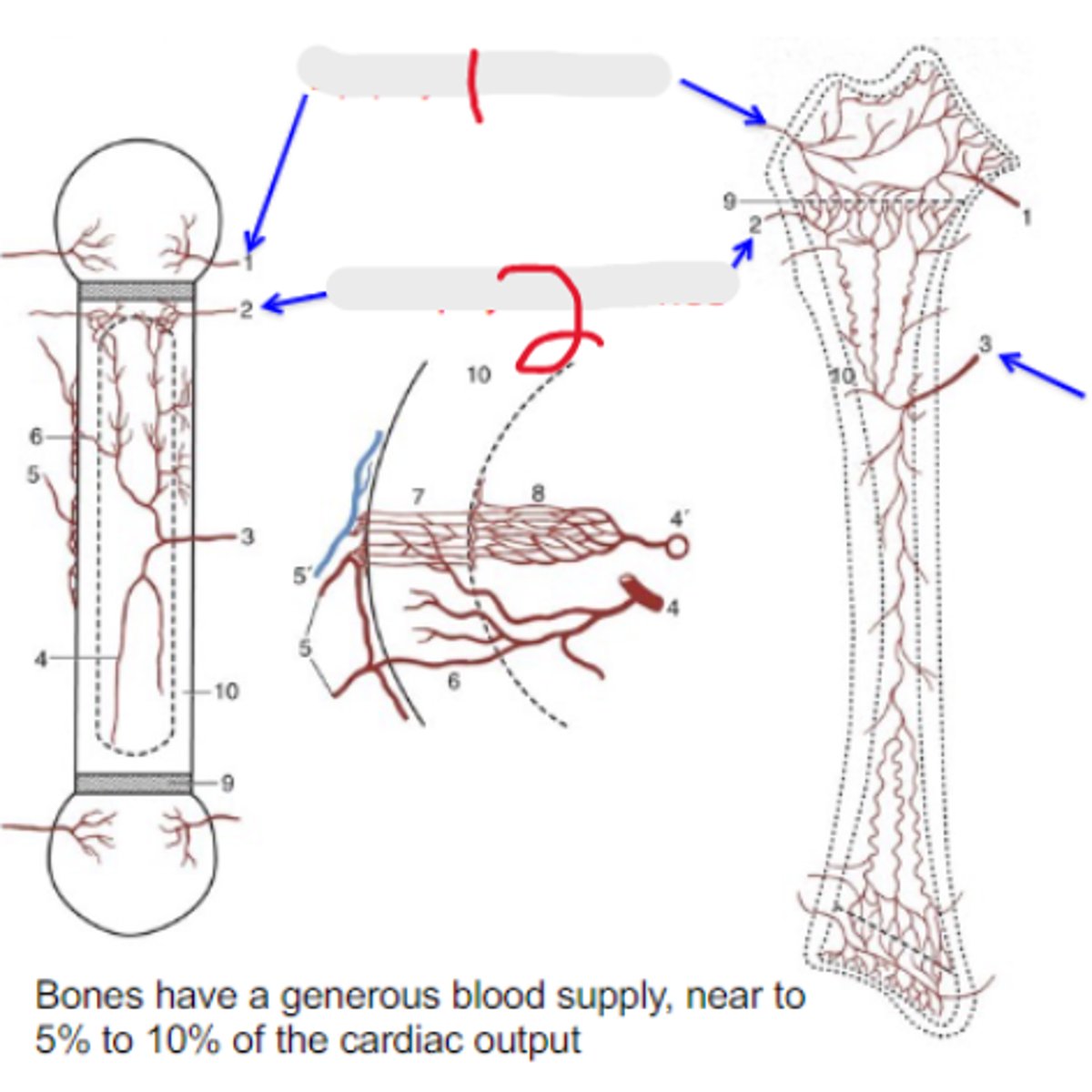
metaphysial arteries
Bone blood supply
What is #2?
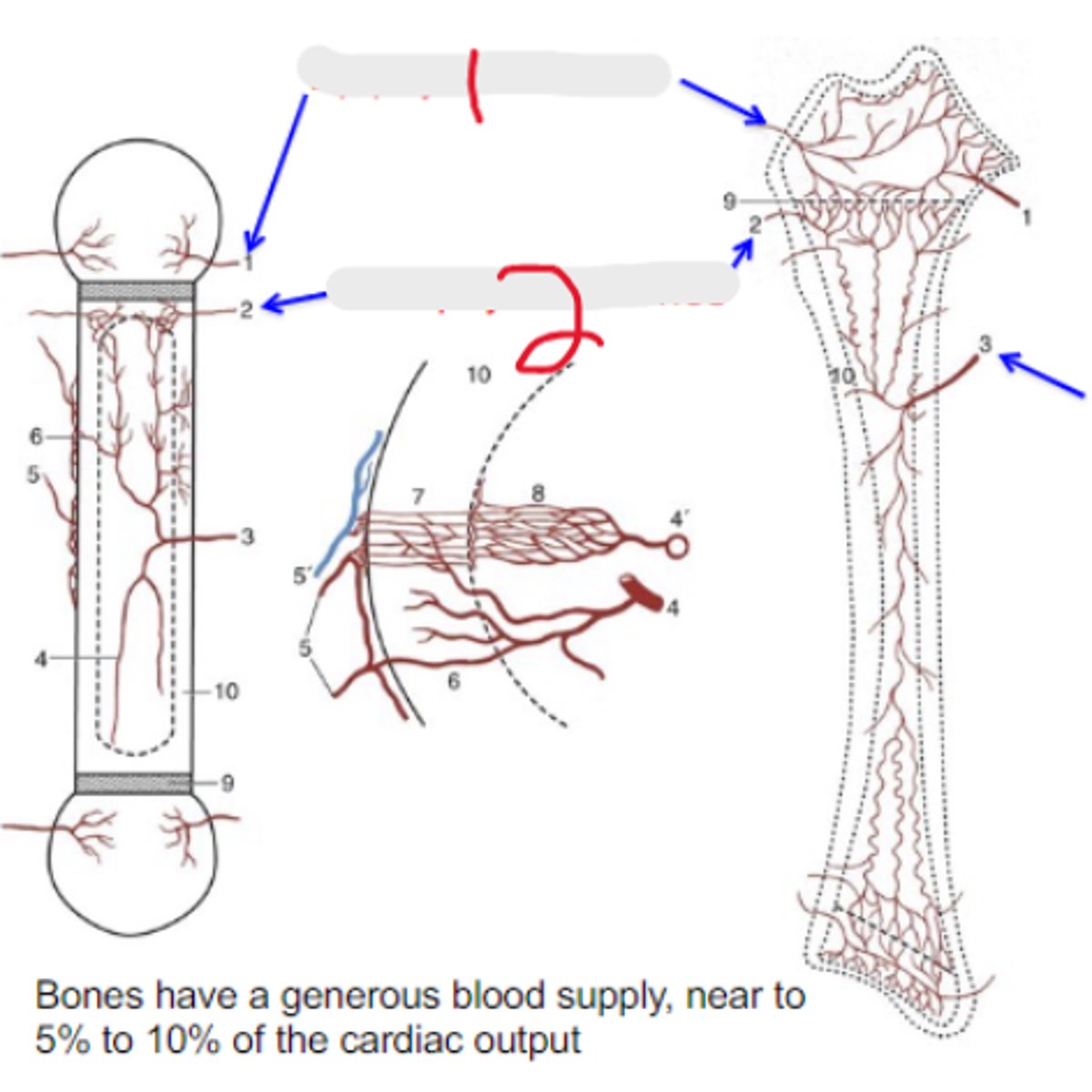
5-10%
Bones have a generous blood supply - near to _____-_____% of the cardiac output
3 multiple choice options
sesamoid bones
-"Seed-like" bones
-Example: Patella
anthrology
The science concerned with the study of anatomy, function, dysfunction and treatment of joints or articulations
simple joints
bone + bone = ?
2 multiple choice options
composite joints
bone + more than 1 bone = ?
2 multiple choice options
fibrous joints
Categories of joints
United by dense connective tissues and are immobile
3 multiple choice options
cartilaginous joints
Categories of joints
United by cartilage and are semi-mobile
3 multiple choice options
synovial joints
Categories of joints
A fluid filled cavity intervenes between bones and allows mobility
3 multiple choice options
fibrous joints
Sutures, gomphosis, and syndesmoses are associated with what category of joints?
3 multiple choice options
cartilaginous joints
Synchondroses and symphysis are associated with what category of joints?
3 multiple choice options
synovial
Plane, hinge, pivot, condylar, ellipsoidal, saddle, and ball-and-socket/spheroidal joints are all types of _____ joints
3 multiple choice options
fibrous joint
-United by dense connective tissues
-Immobile
cartilaginous joint
-United by cartilage
-Semi-mobile
synovial joints
-A fluid-filled cavity intervenes between the bones
-Mobile
fibrous
Sutures are _____ joints
sutures
Fibrous joints in the skull that connect the skull's bones together
fibrous
Gomphosis are _____ joints
gomphosis
Specialized fibrous joint that anchors a tooth to its alveoli in the maxilla, incisor or mandible bones
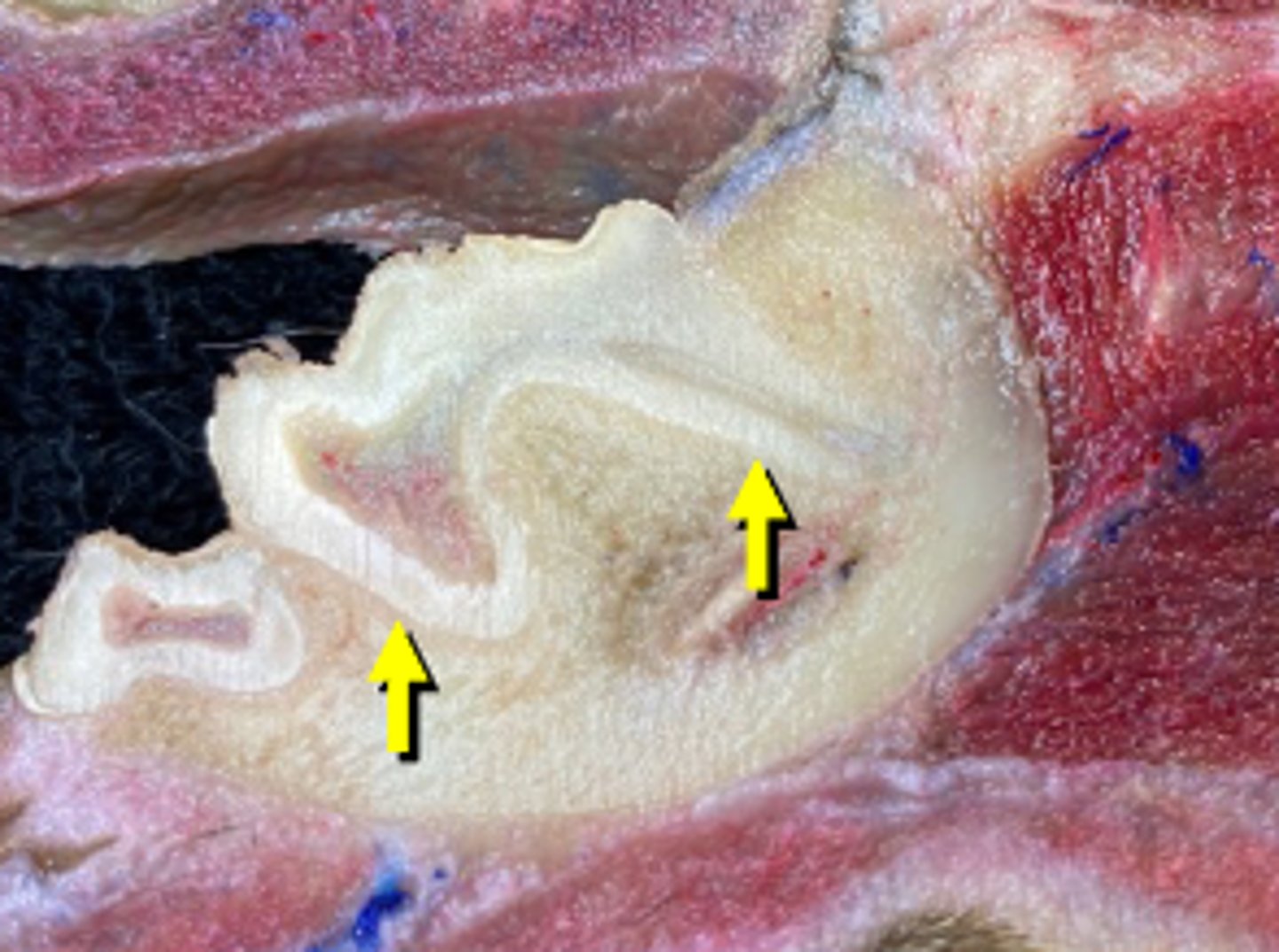
fibrous
Syndesmosis are _____ joints
syndesmosis
A fibrous that holds two or more bones/ cartilages with ligaments or a strong membrane
syndesmosis
The interosseous membrane is a _____ joint
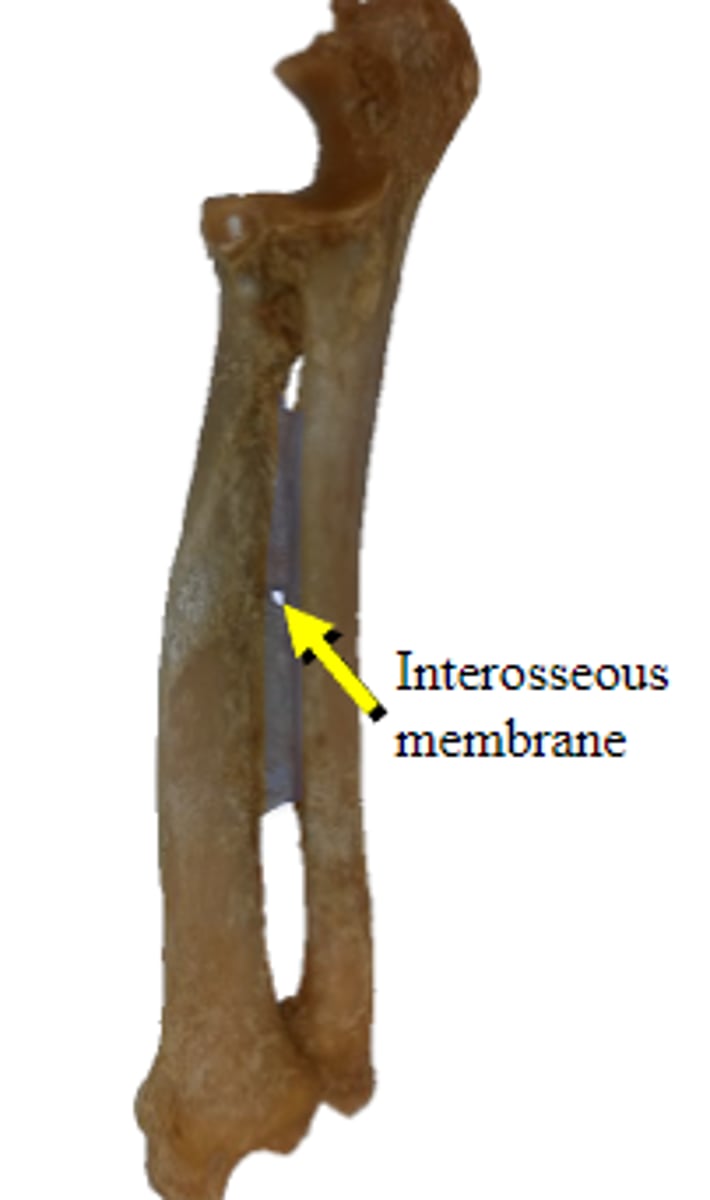
cartilaginous
Synchondrosis is a _____ joint
synchondrosis
Cartilaginous joint where the bones/cartilages are joined by hyaline cartilage
synchondrosis
Epiphysial cartilage (growth cartilage) is a _____ joint
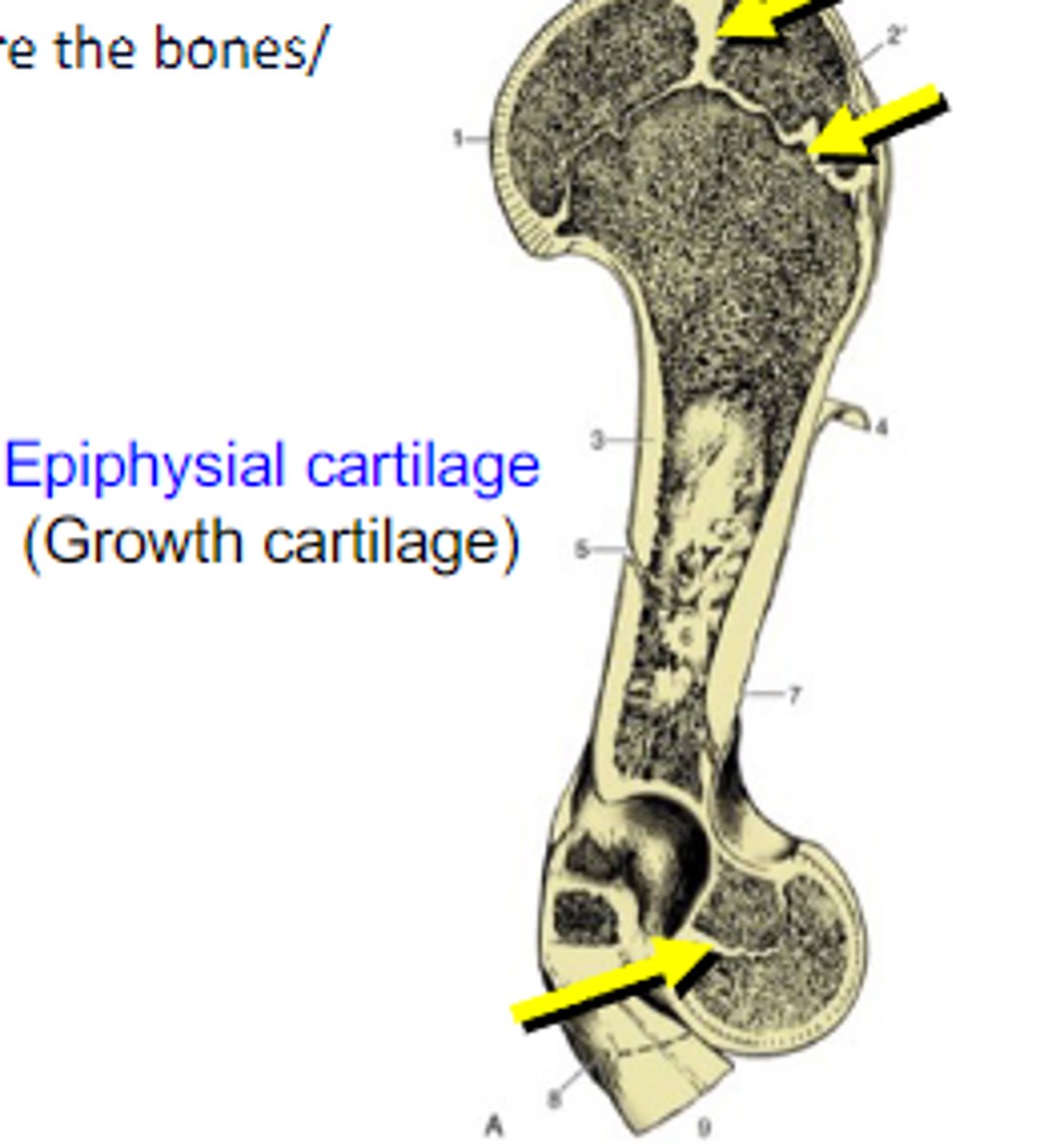
cartilaginous
Symphysis is a _____ joint
symphysis
Fibrocartilaginous joint between two bones
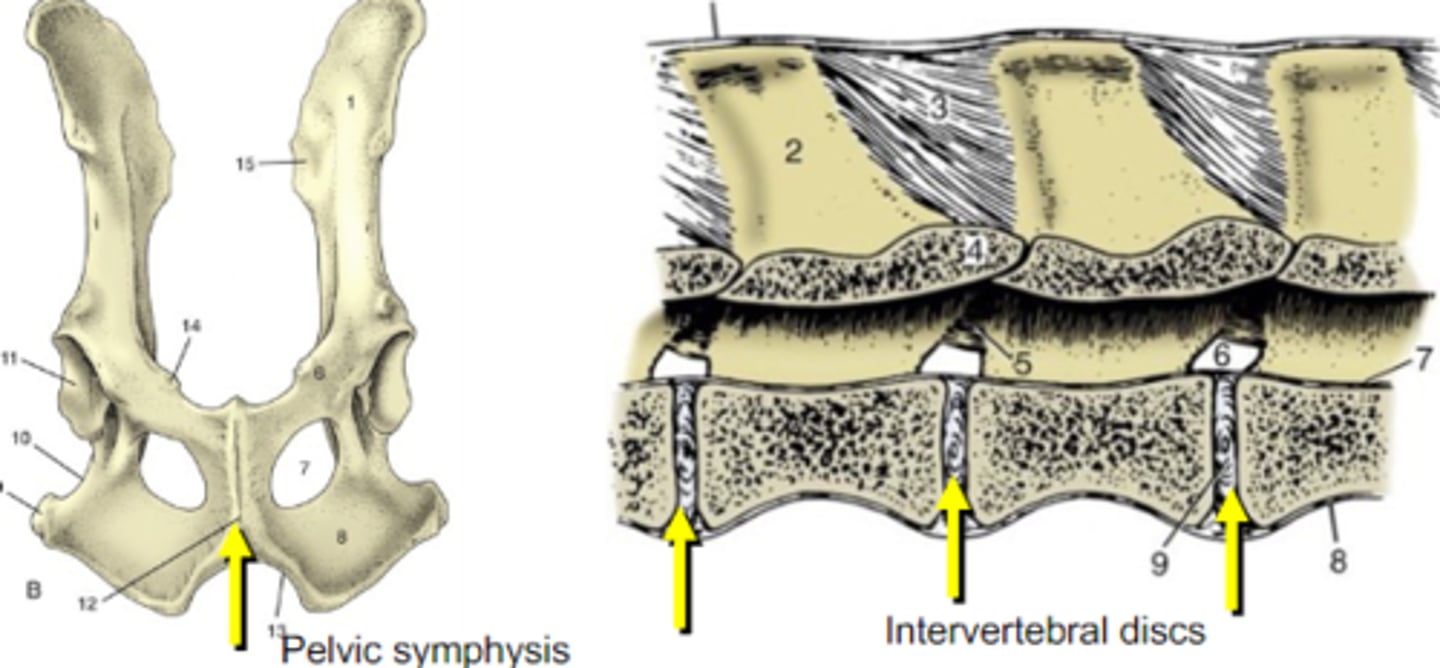
synovial joint
-Keep bones or cartilage together with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones.
-This joint unites long bones and permits free mobility.
osteosarcoma
Bone tumor
osteomyelitis
Infection of bone (from cat bite, for example)
osteotomy
Cutting of a bone
cells
The _____ of a bone modify its shape
can
Bones [can/can not] be modified
33%
What is the total organic compounds found in bone?
67%
What is the total inorganic compounds found in bone?
collagen
What is the main component of organic compounds found in bones?