class 11 - ATP + energy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
metabolism
the chemical reaction occurring within cells that convert one molecule into another and transfer energy in living systems
catabolism
break down molecules into smaller units
produces ATP
anabolism
build molecules from smaller units utilizing an input of energy
uses ATP
results in net energy storage within cells and the organism
energy
makes work possible, can be transferred, cannot be created or destroyed
kinetic energy
energy of motion
anything that’s moving
examples: thermal (heat), electricity (movement of electrons), light (movement of photons)
potential energy
energy due to position (location, structure, orientation)
also known as enthalpy
stored energy- can be released if position changes
what types of energy do molecules have?
molecules have both kinetic and potential energy if not at absolute zero temperature
KE from constant motion
PE from arrangement of bonds and atoms
what type of energy is in gradients?
potential energy
molecules have a higher PE where they are more abundant, and are able to spontaneously (no external energy needed) move down the gradient
applies to concentration and charges
chemical energy
a form of potential energy held in the chemical bonds between pairs of atoms in a molecule
what is the chemical energy of strong bonds or a stable molecule?
weak chemical energy
what is the chemical energy of weak bonds or a less stable molecule?
high chemical energy
high because the bond is fighting against the randomness of the universe to stay together
when a weak bond is broken, more energy is released
when a bond becomes more stable, what happens to the chemical energy?
becoming more stable releases chemical energy
why is carbohydrate a fuel storage molecule?
it contains weak bonds (C-C and C-H), which require high energy to stay intact
when broken, energy is transformed from chemical potential energy a form of energy that can do work
what is the role of ATP in the cell?
ATP controls the transformation of energy in the cell
how much potential energy does ATP have?
ATP contains a high amount of potential energy due to its phosphate bonds, which when broken, release energy that can be utilized for cellular work.
the phosphate bonds are unstable (their negative charges repel), so a lot of energy is used to hold them together. therefore, breaking it releases a lot of usable energy
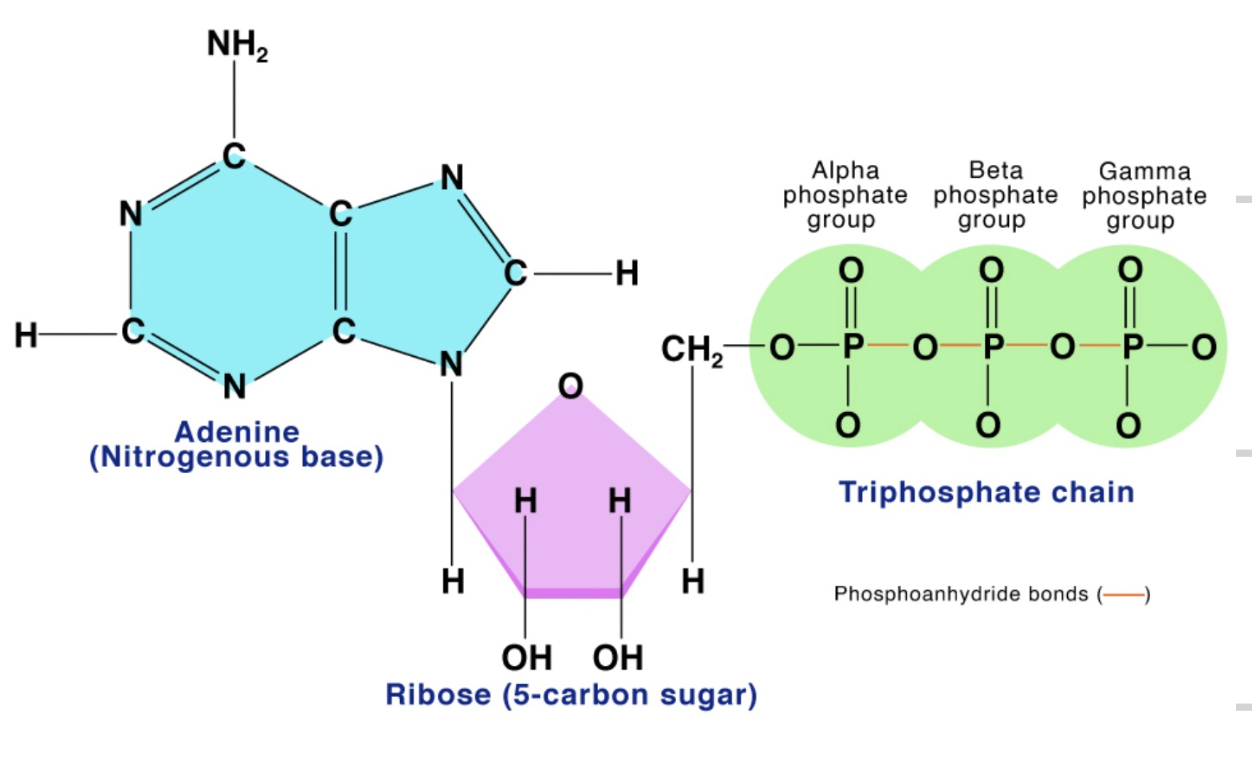
ATP structure
ribose, adenine (base), 3 phosphate groups