Demand/Supply Integration: Forecasting and S&OP
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Matching supply with demand
forecast are inputs, outputs of plans
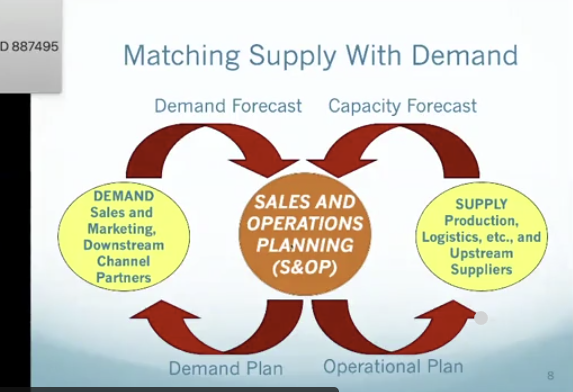
S&OP stands for
sales and operations planning
Demand
is what customers would buy from us if they could. This is unconstrained demand (by firms ability to supply)
The demand forecast
is a projection into the future of expected demand, given a stated set of assumptions. Unconstrained forecast- not infulenced by ability to supply.
Plans
are the managerial actions that result from the demand/supply integration process.
Supply (ordering & manufacturing) , Inventory (buildering inv buffer), Demand (adjust marketing effort to bring into valance) , Financial (working capital, telling wall street)
Forecast are ______________. Plans are ___________
Forecast are best guessed about what we think will happen. Plans are decisions we make about what we will actually do.
How do companies manage this forecasting process?
techniques (statistical and qualitative), systems (keep track of data), management
Measure performance at center
The nature of the business determines the nature of the process
nature of customer base
Nature of the date
nature of products
nature of the people
Nature of the customer base
narrow: boeing, small- forecasting demand is easy just go ask the 100 customers
broad: think coca-cola, billions of customers in thousands of retailers. Need to use alot of statical
regional differences
Nature of data
age
detail
quality
previous purchase data
Nature of the products
new products- harder to forecast, don’ have any past history
seasonal demand: christmas vs toliet paper
shelf life:
Nature of the people
resources
education/training- many SC people start in demand planning
Two Categories of Demand Forecasting Techniques
quantitative or statistical: time series, regression & casual models
Qualitative: includes salesforce composite
Statistical forecasting
looks in rear view mirror, looking for patterns in historical data and project them into the future to get foercast
some patterns are function of time (demand for christmas trees going up and down), try to idenfiy using time series techniques
some patterns are a function of the way that other factors affect demand, and we try to identify patterns with regression analysis
Components of Time Series (3)
Trend: continuing pattern of demand increase or decrease, can be straight line or curve
Seasonality: repeating pattern of demand increases or decreases. Normally think of seasonality as occurring within a single year, and cycles as occurring over longer than one-year periods
Noise: random fluctuation, that part of demand history which the other time series components cannot explain
Regression Analysis
is useful when you think there are measurable factors that affect demand. Demand is always your dependent variable (y axis). The measurable factors are you independent variables (are measurable and can be internal or external)-
spendiny money in adversting hope will increase demand, regession can give insight into how much
Demand Forecasting Tecniques
statiscal forecasting -lookinng in review mirror, may get hit by truck. Need insight about how the future is likely to look different from the past. Need qualtiative forcasting
Qualitative forecasting
subjective or judgmental forecasting
process of turning the experience, judgements, and intuition of experienced people into formal forecasts
When would you use it?: when you have reason to believe that the future will not necessarily look exactly like the past. New products with no historical data, new conditions will change previous patterns- effectiveness of TV adversting has gone down
Salesforce Composite
The most common example of qualitative forecasting
salesforce composite
Salesforce Composite forecasting
when does it make sense for salespeople to forecast? When they have insight into changing demand patterns at their large customers- P&G changing shelf space at Walmart. When they have insights into probabilities of securing large orders (IBM asked him are we likely to win the business, have to prepare the supply chain)
What gets measured gets _____. and what gets ______ gets done
measured, example course evaluation incentive.
Dimensions of demand forecasting performance (4)
Bias: is the forecast systematically to high or low
Accuracy: How close was the forecast to the actual demand? (always going to be wrong)
Bias & Accuracy how measure forcasting performance
Cost Reduction: inventory, expedited freight, purchasing cost
Customer Satisfaction: improved fill rates, have enough product available when need it
Cost reduction and customer satisfaction- result of forecasting excellence
How we measure forecasting performance
bias & accuracy
Result of forecasting excellence
cost reduction & customer satisfaction
What is S&OP
the process by which a company matches its demand in the marketplace with its supply capabilities
Why do companies do S&OP
so that marketing will create demand for products that can be produced. So that operations will supply products for which there is demand. Bottom line-so both sides of a company will be singing out of the same hymnal. One the same page
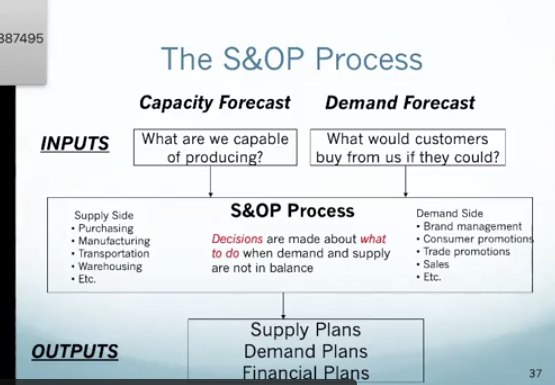
S&OP process
inputs: capacity forecast (what are we capable of producing) & demand forecast (what would customers buy from us if they could?)
process: decision about what to do when demand and supply are not in balance, both demand and supply side of business
outputs: supply plans, demand plans, financial plans
S&OP regularly scheduled meetings
normally monthly process,
demand meeting: forecaster, marketers and sales- consensus demand forecast
supply meeting: operations, purchasing, and logistics, consensus capacity forecast
Partnership meeting: executives from both sides & finance, balancing demand with supply, outcome: agreed-upon demand & supply plans
S&OP should be both tactical and strategic in nature
Tactical: What should we make, and what should we sell over the next 1-6 months (short-term)
Strategic: What are the longer term trends that will affect both demand and supply over the next 6-24 months, and beyond? make big investments in building or shutting down capacity