3.3 Revenue and profit
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Total revenue
The revenue received by a firm from its sales of a good or service (quantity sold multiplied by the price)
Average revenue
The average revenue received by the firm per unit of output (total revenue divided by the quantity sold)
Marginal revenue
The additional revenue received by the firm if it sells an additional unit of output
Profit
The difference between the total revenue received by a firm and the total costs that it incurs in production
Profit = total revenue − total cost
Loss
When total revenue is smaller than total costs
Accounting profit
Profit made by a business based on explicit costs incurred but excluding opportunity cost
Normal profit
The return needed for a firm to stay in a market in the long run (making back on all accounting costs + opportunity costs)
Supernormal profit
The profit above normal profits
Marginal revenue formula
Change in total revenue divided by change in quantity sold
Total revenue curve
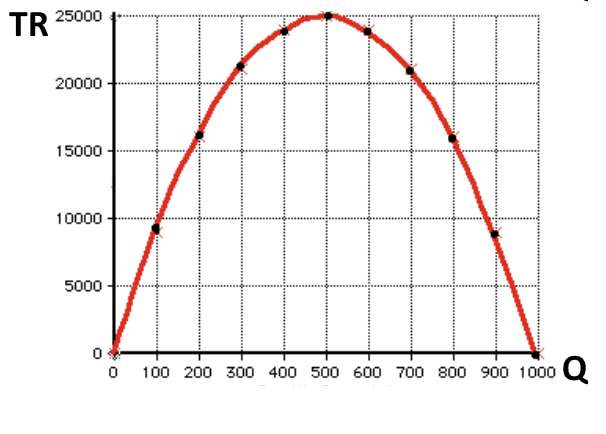
The demand curve and revenue
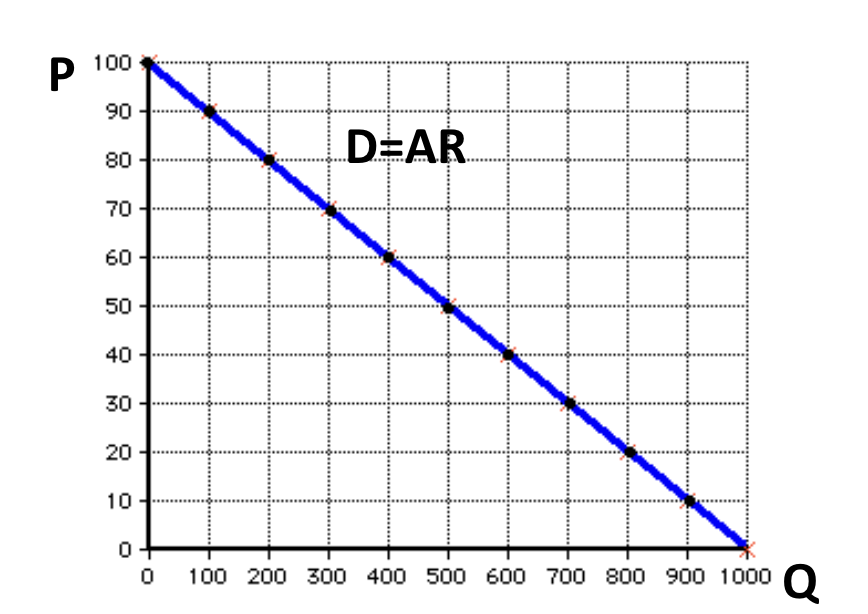
AR = TR/Q = P
The Demand curve tells at what price Q can be sold for
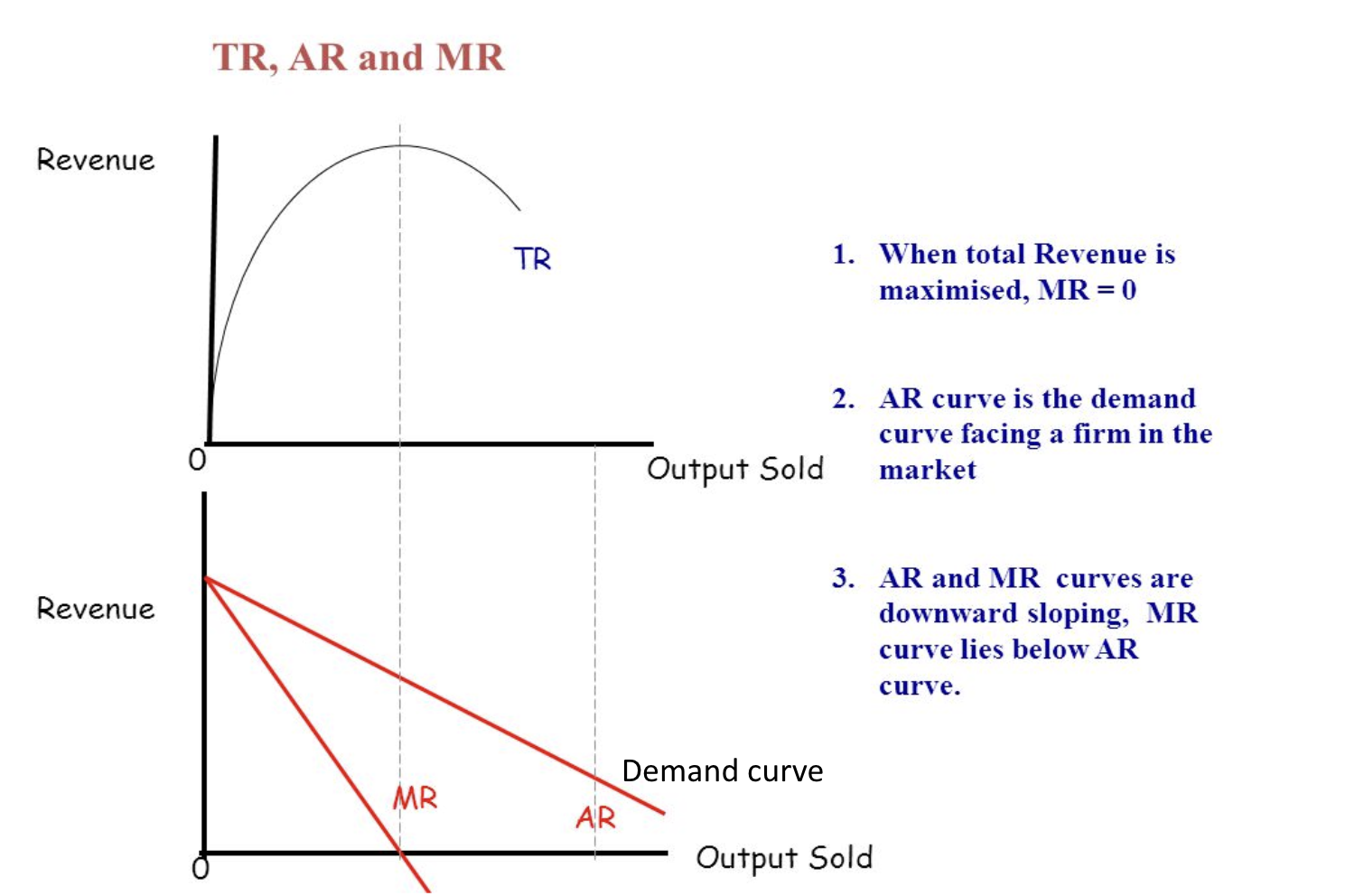
Revenue curves
MR is less than AR because the price changes as the quantity sold changes
Marginal revenue diminishes with each additional unit and will always be equal to or less than average revenue
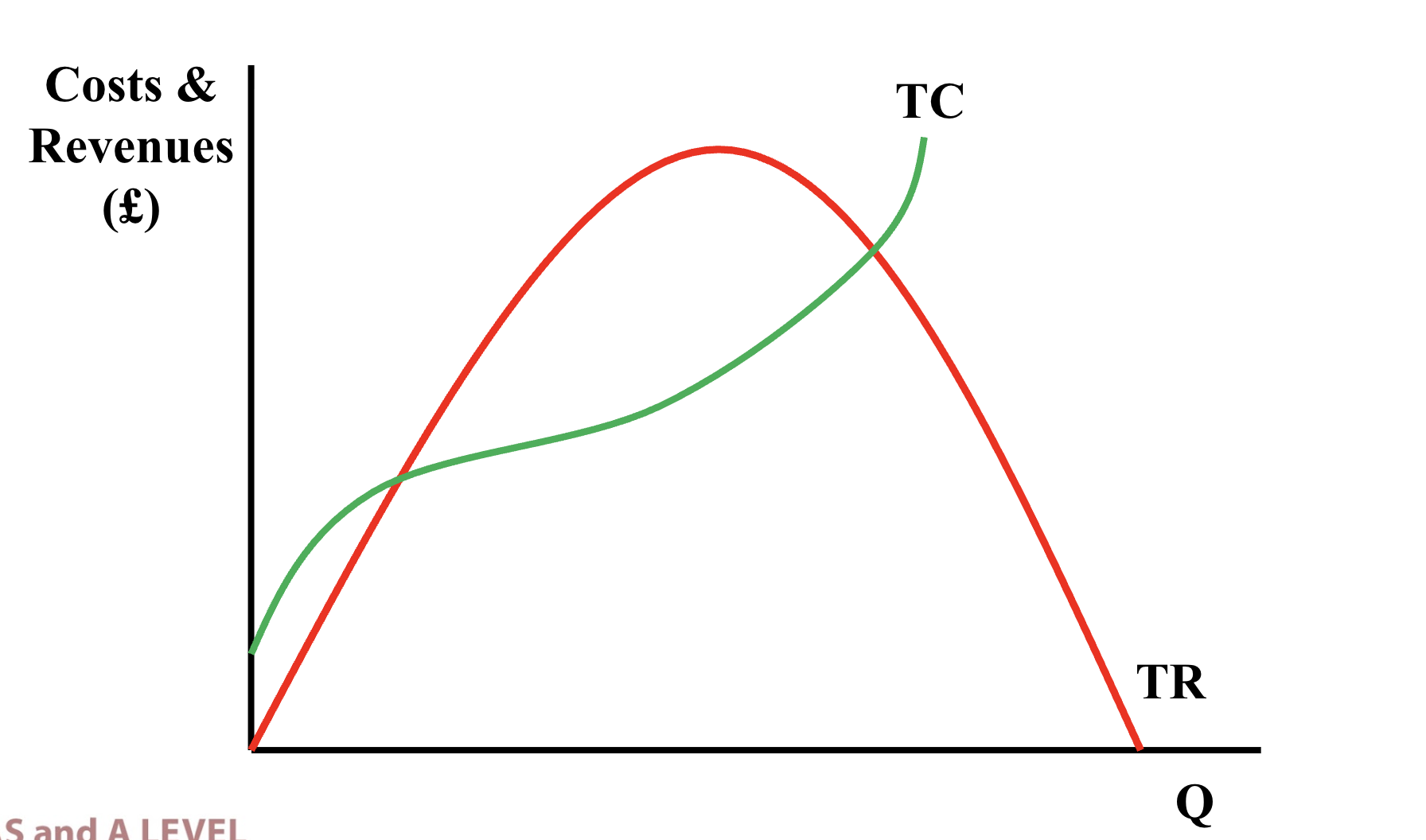
Total costs and total revenue curve
To find the quantity if sold that will maximise profits, find where the difference between TR and TC is greatest on the curve
You can also find the quantity at which marginal revenue = marginal costs (method more commonly used)
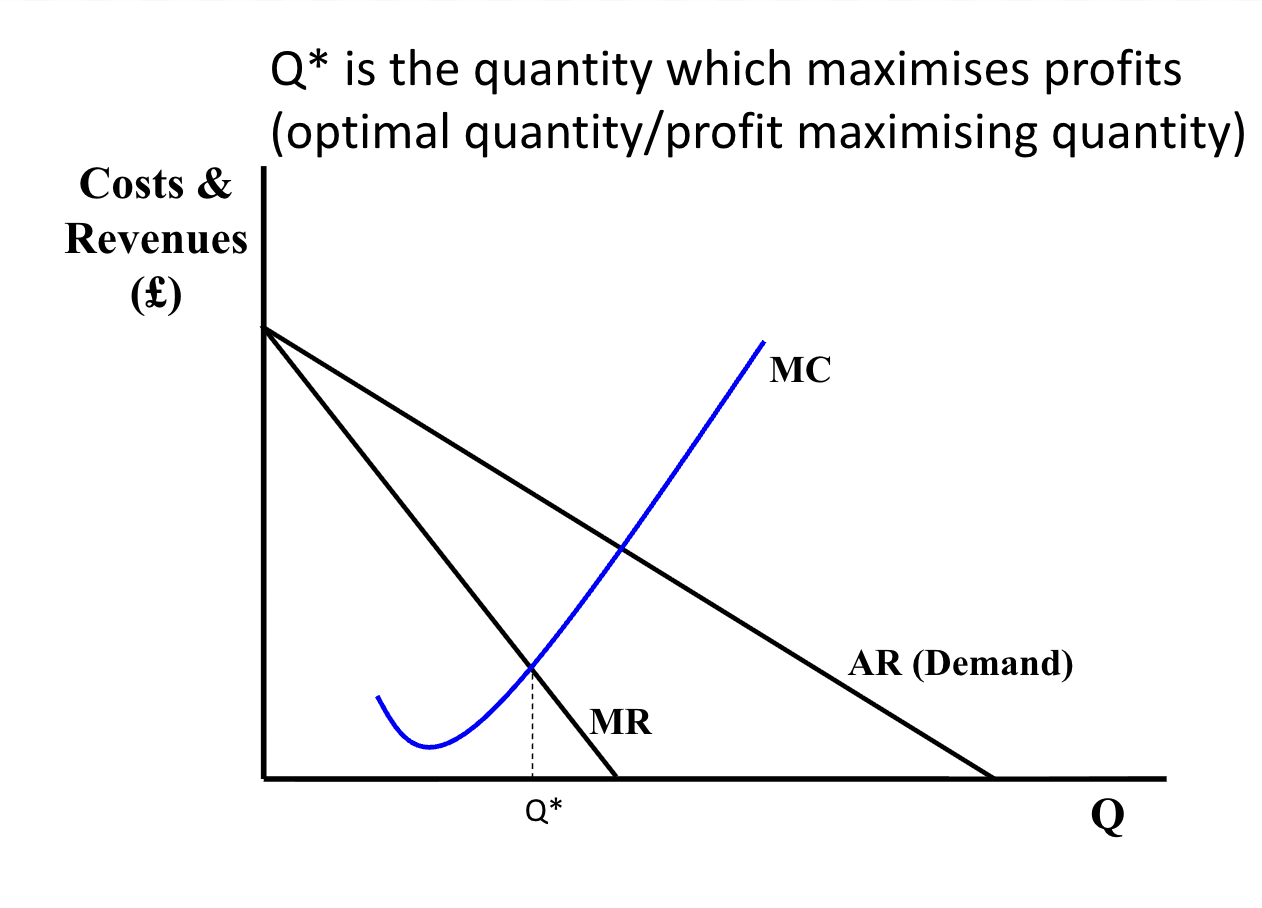
Profit maximising quantity curve
Q* is the quantity which maximises profits (where MR = MC)
P* is the price which corresponds to the optimal quantity Q*
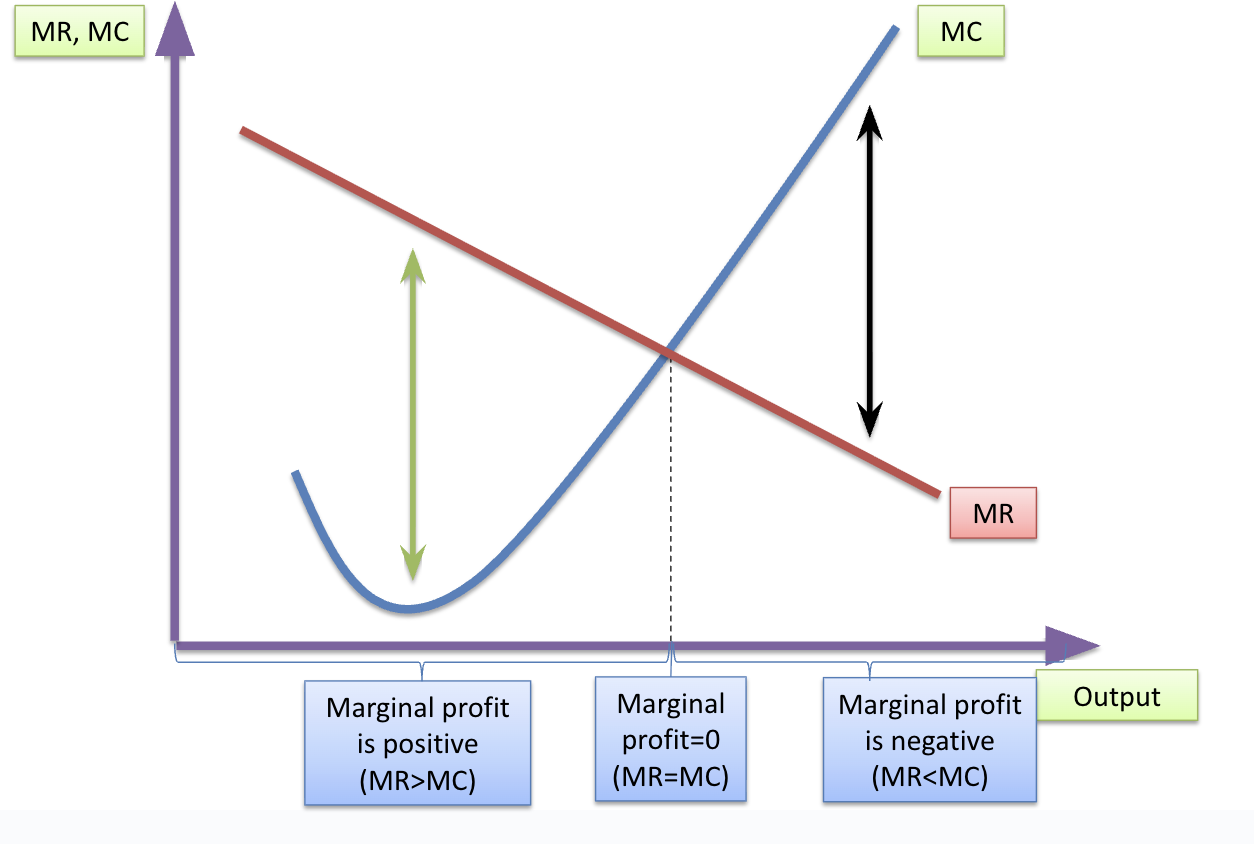
Marginal Profit
Marginal profit is the increase in profit when one more unit is sold
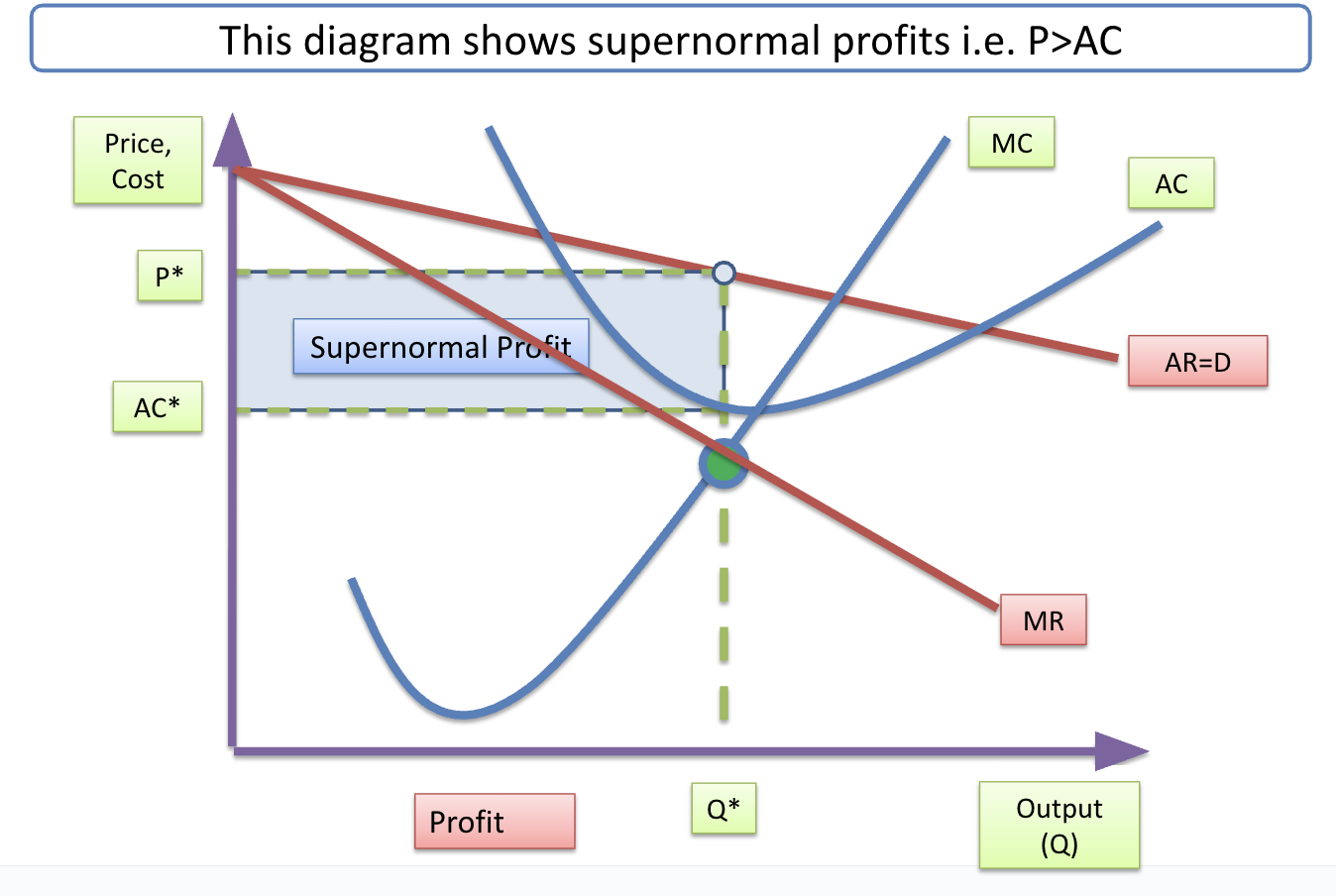
Supernormal profit curve
Profit achieved in excess of normal profit
Supernormal profits are made when P > AC
When firms are making supernormal profits, there is incentive for other producers to enter a market to acquire some of this profit
Sub-normal profit
This is profit less than normal (P < AC)
Disincentive for firms to enter the market
The Importance of Profit
Profit is an important objective of most but not all firm
Finance for capital investment and research: Retained profits are a key source of finance for businesses undertaking capital investment + funds for acquisitions
Market entry: Large/rising supernormal profits send signals to other producers within a market
Demand for and flow of factor resources: Resources flow where the risk-adjusted rate of profit is highest
Signals about health of the economy: Rising profits might reflect improvements in supply-side performance. They are also the result of higher levels of aggregate demand for example during an economic recovery.