Practical #3
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
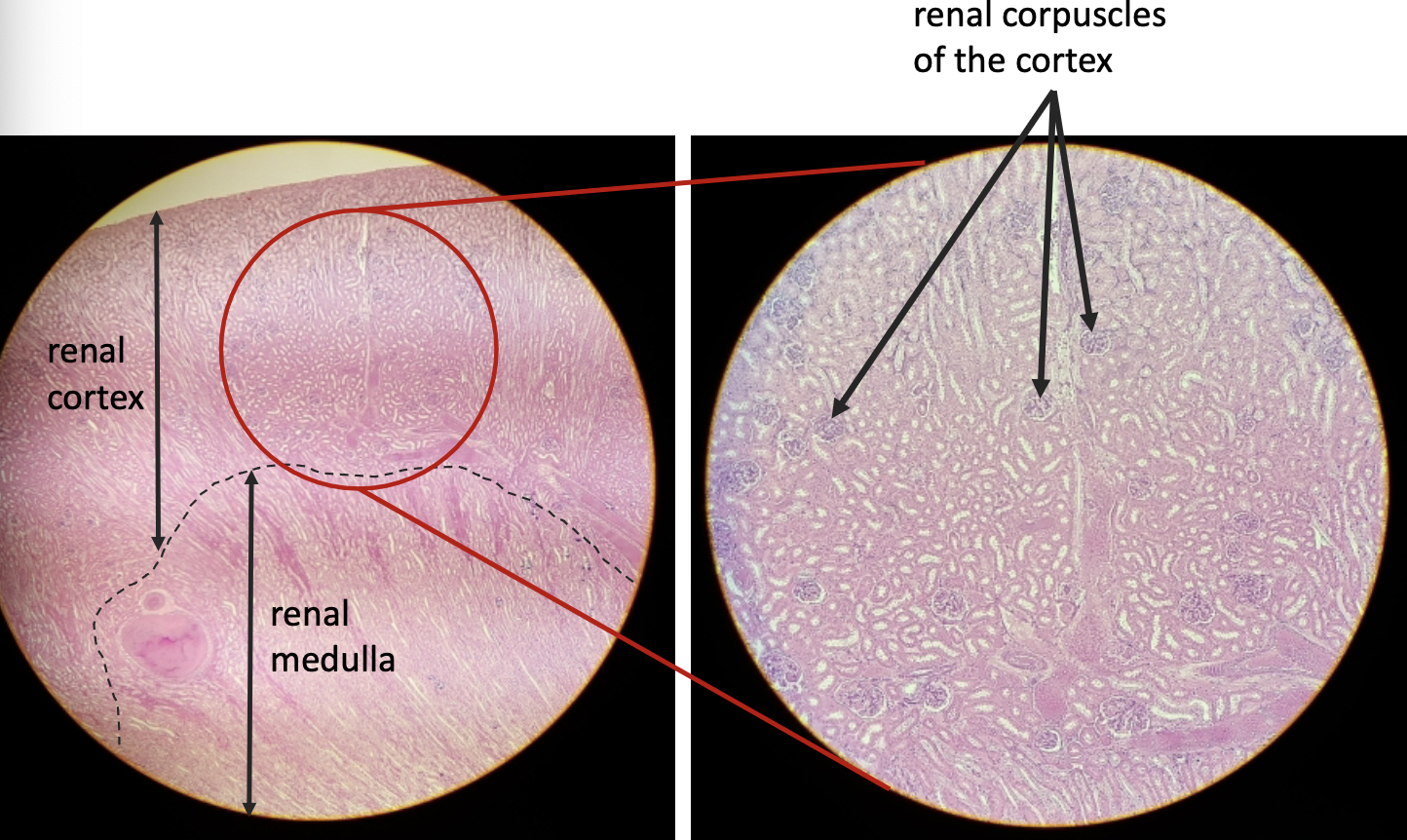
what is this?
entire kidney
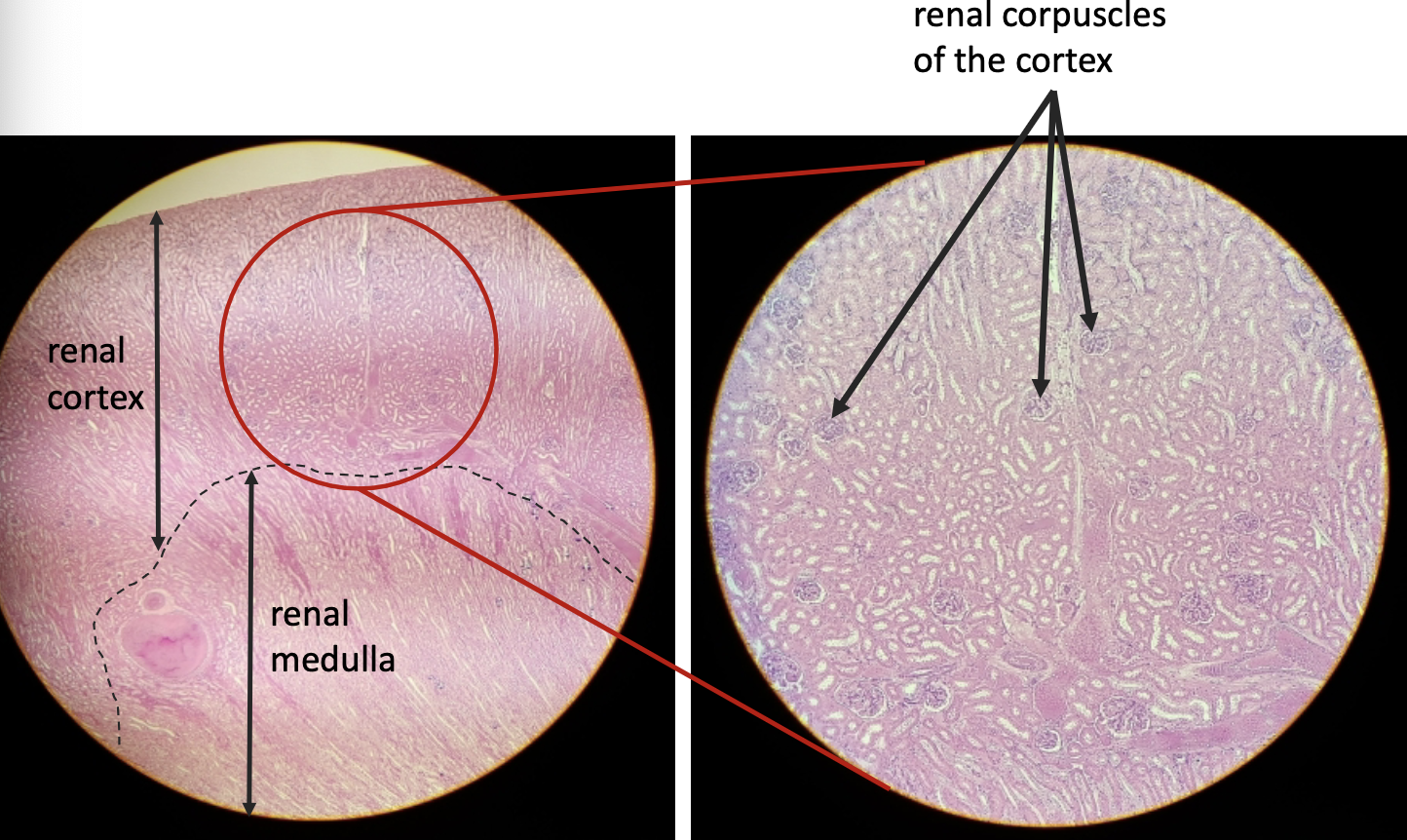
what is this?
kidney section
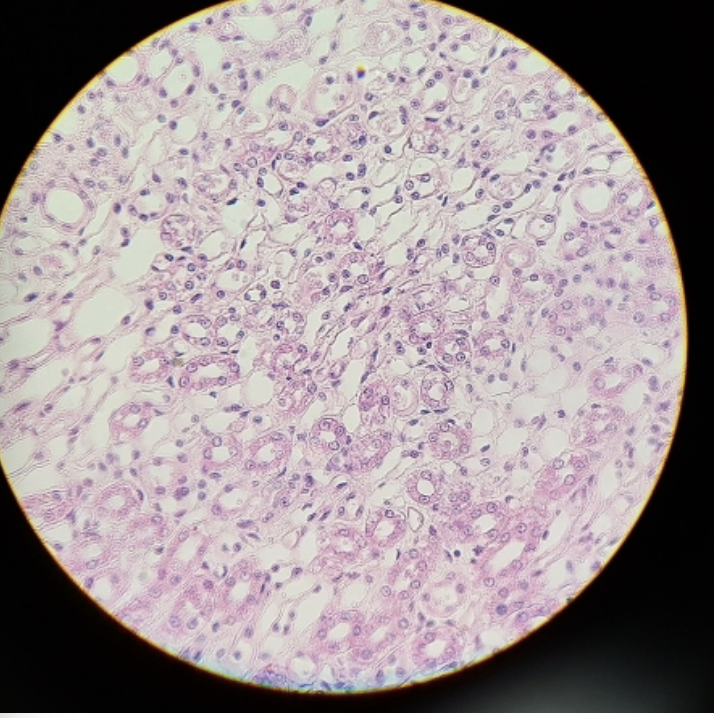
what is this?
healthy kidney
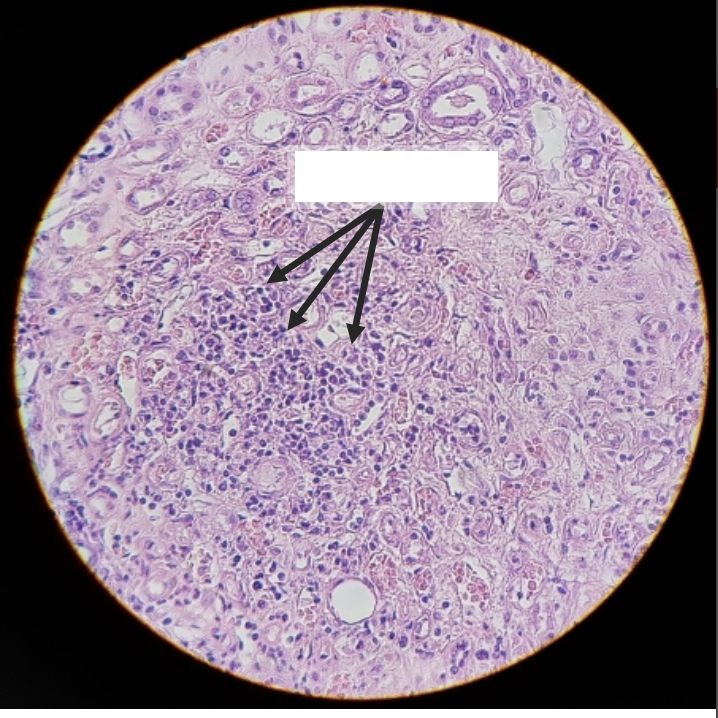
what is this?
kidney carcinoma
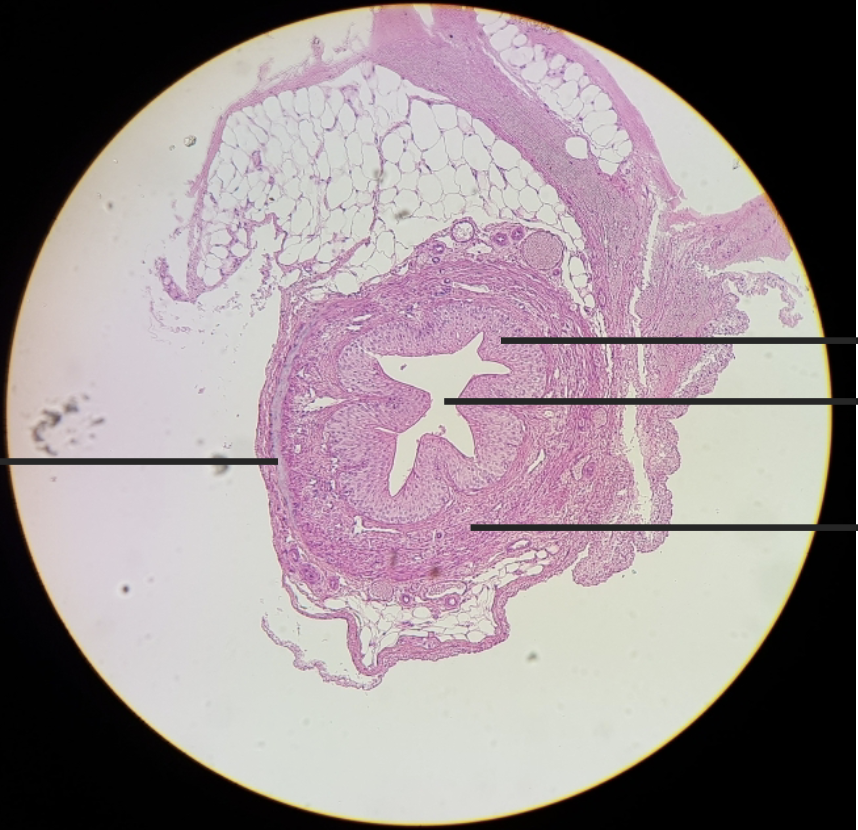
what is this?
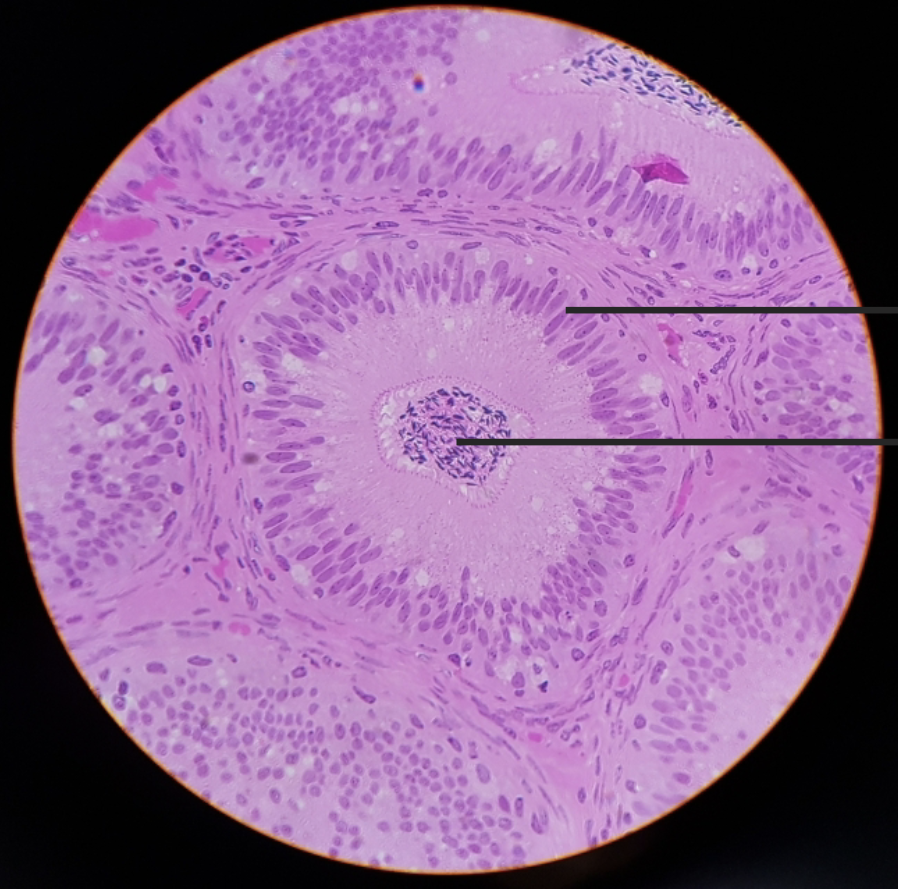
mammal ureter
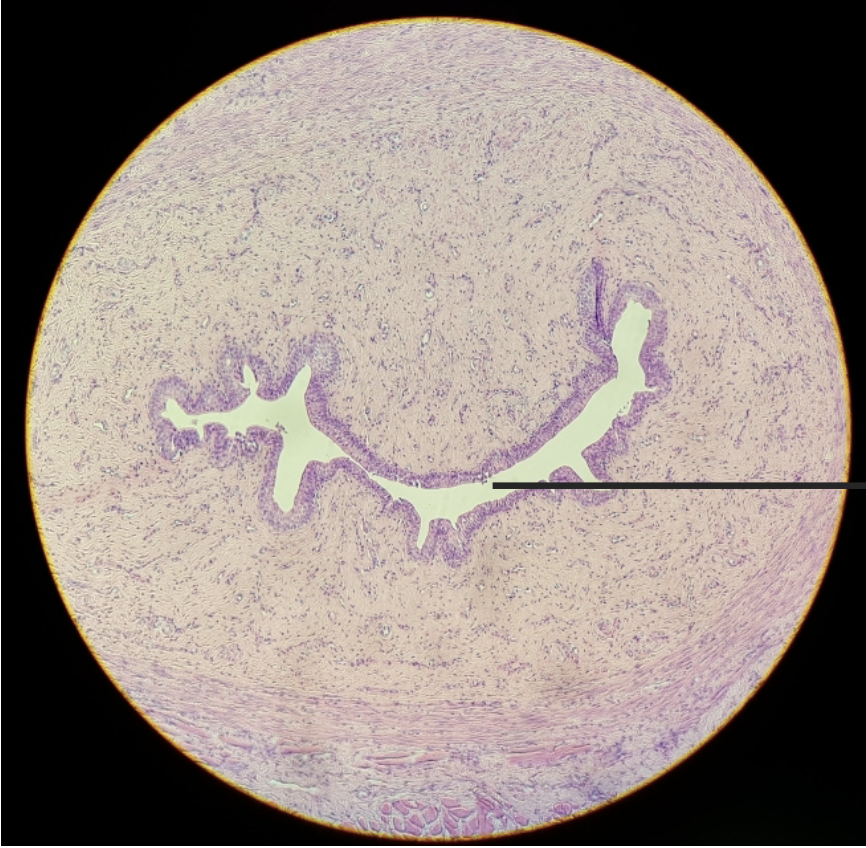
what is this?
female mammal urethra
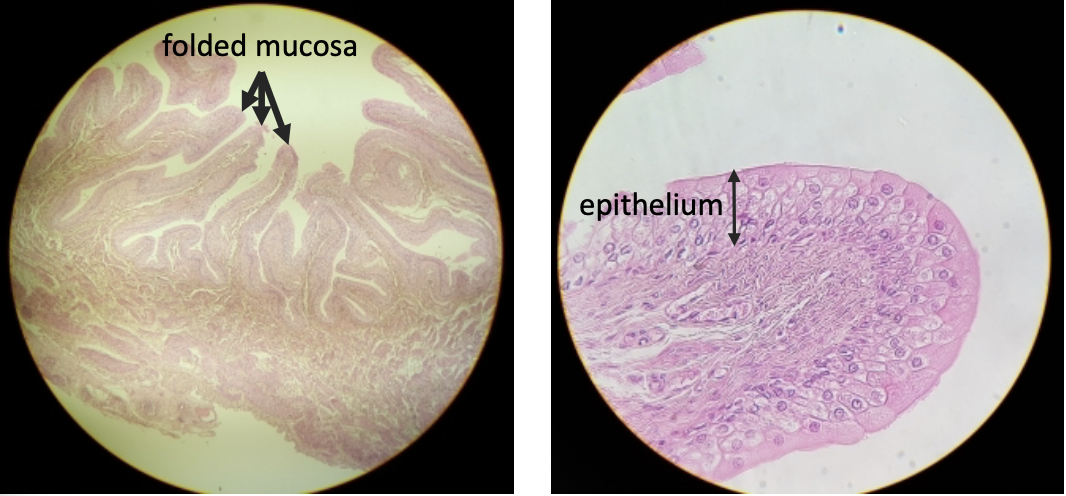
what is this?
collapsed bladder
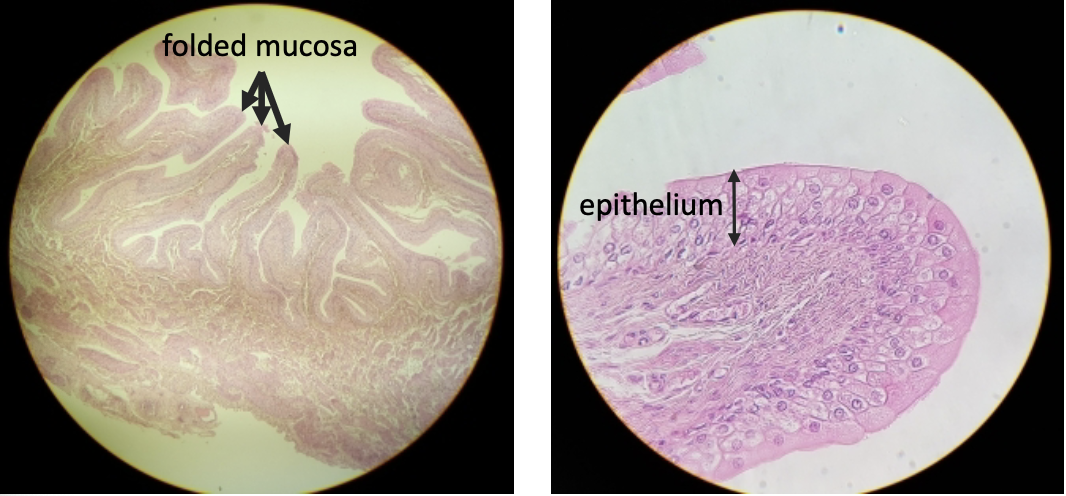
what is this?
distended bladder
what are some notable characteristics of the distended bladder?
decrease in mucosa folding —> expansion when filled with urine
thinning of the epithelium
what is this?
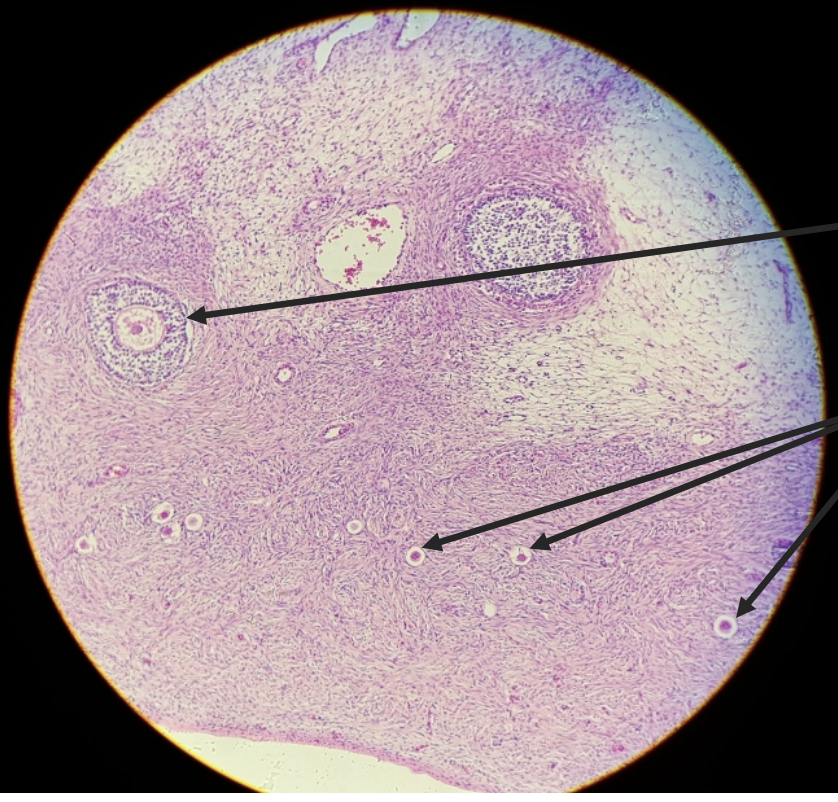
ovary
what is this?
secretory uterus
what is this?
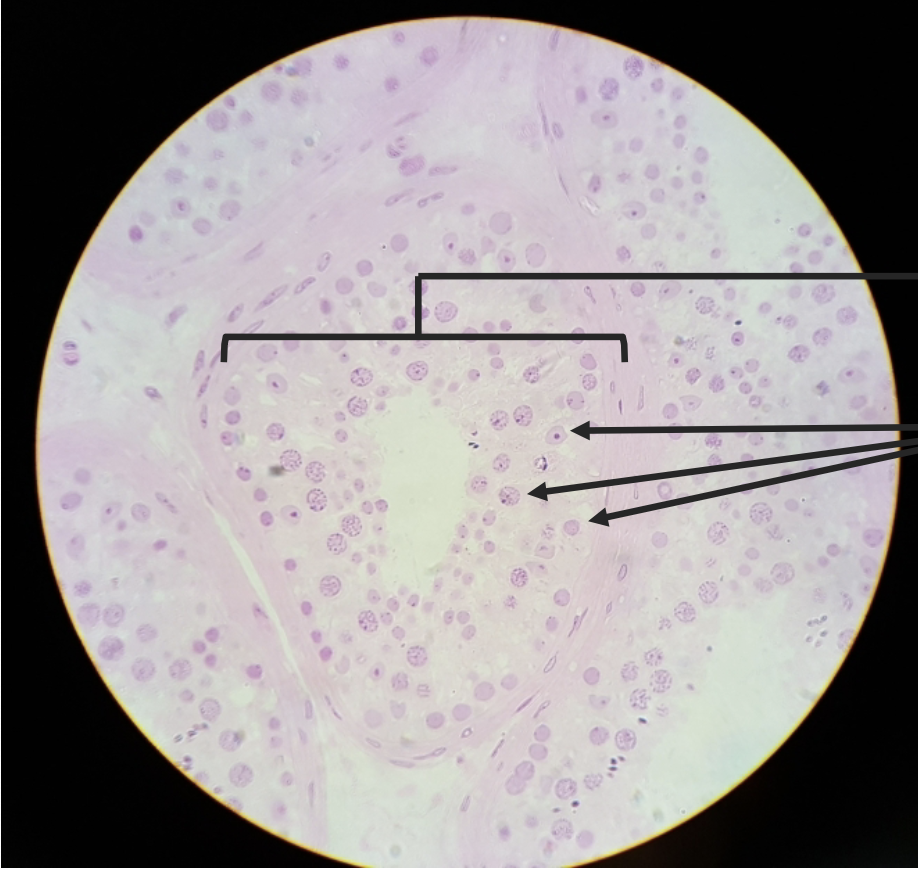
testis
what is this?
epididymis
what is this?
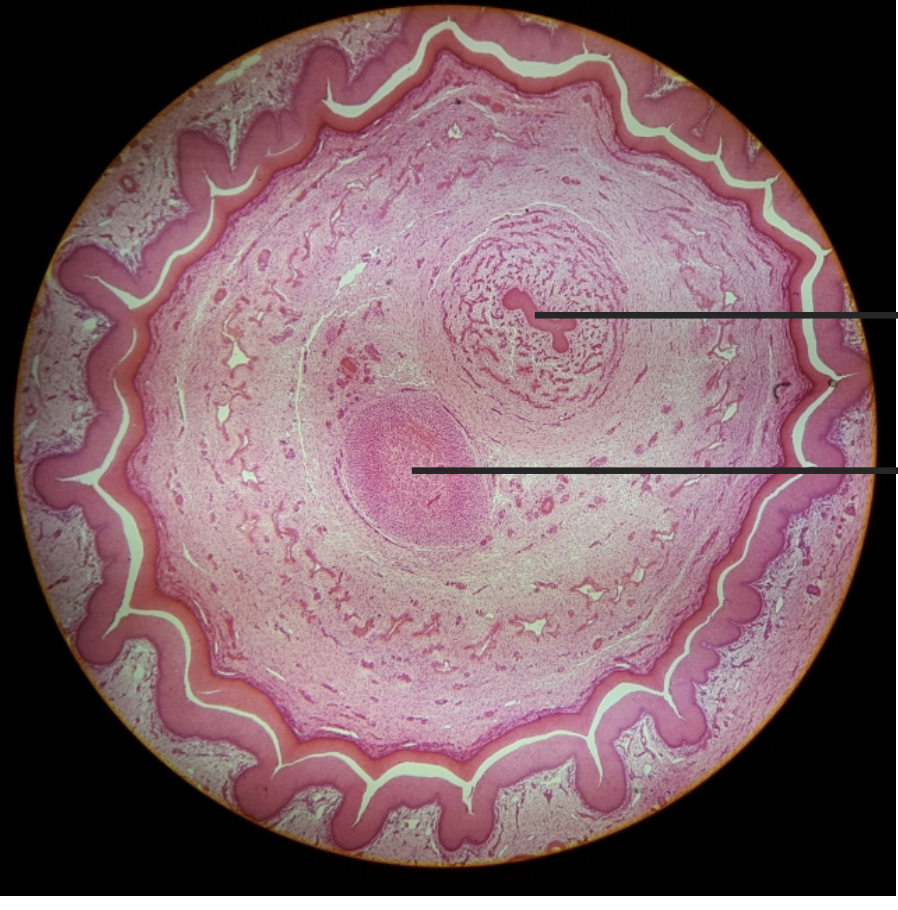
penis
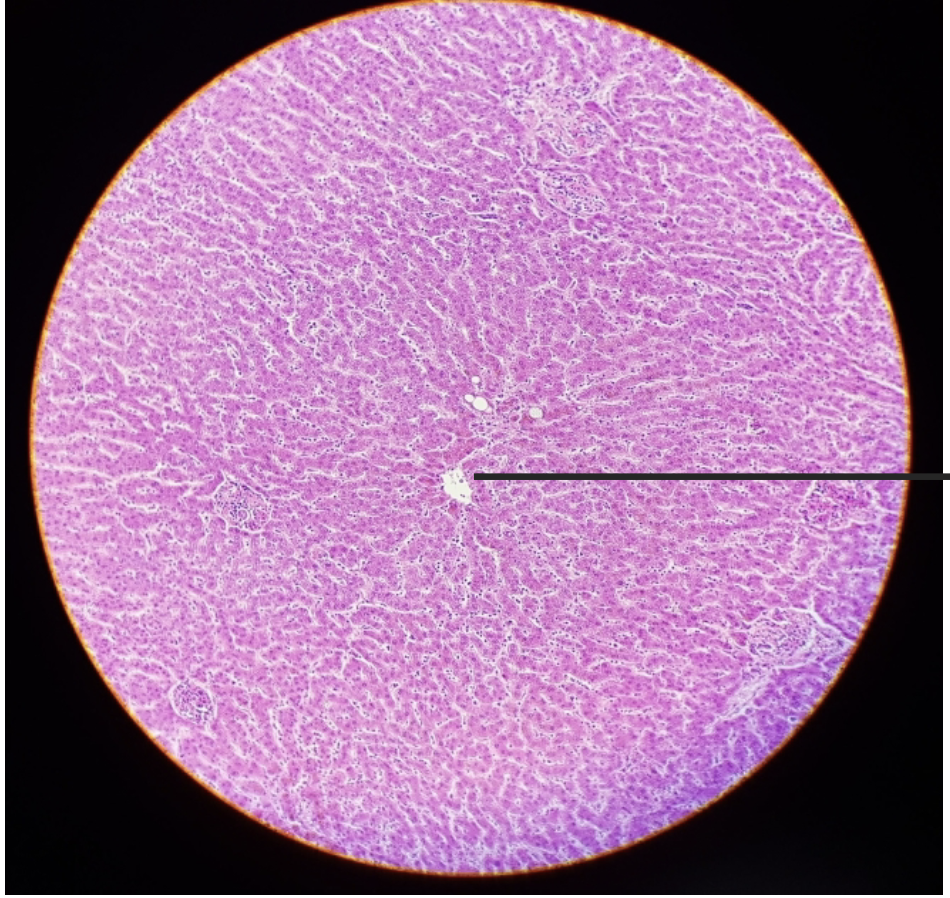
what is this?
liver
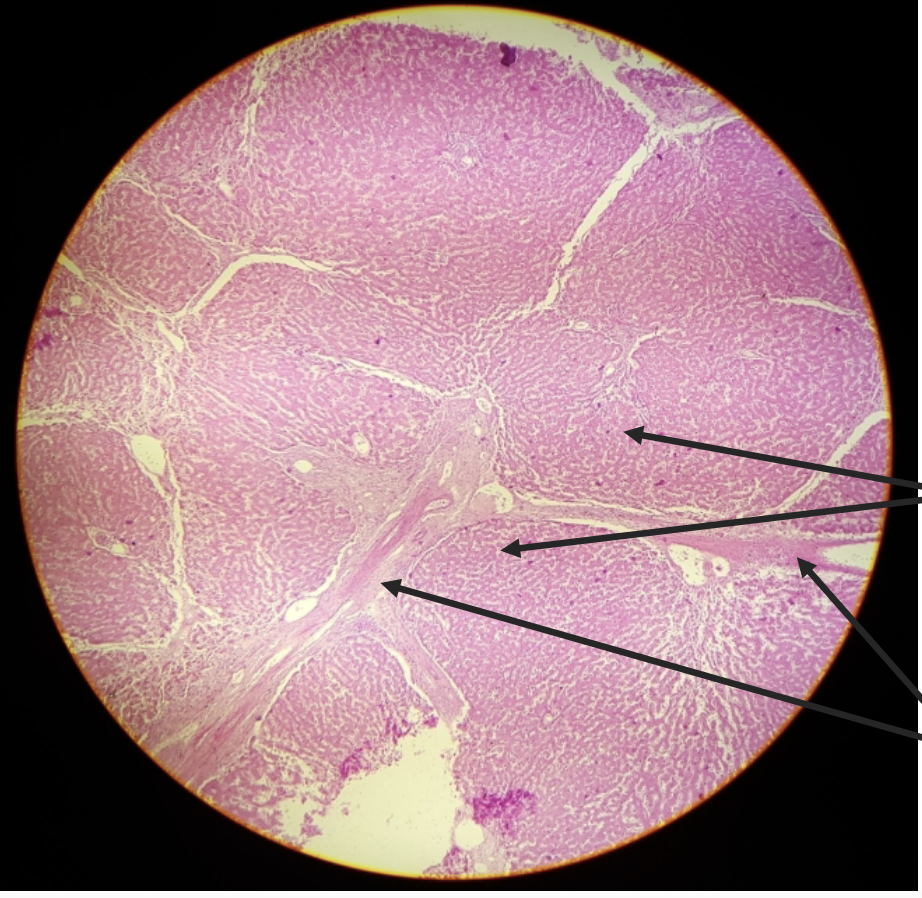
what is this?
cirrhosis of liver
what happens in the cirrhosis of the liver?
scar tissue develops and replaces normal hepatic tissue
separation of hepatocyte nodules
impedes blood flow and liver function
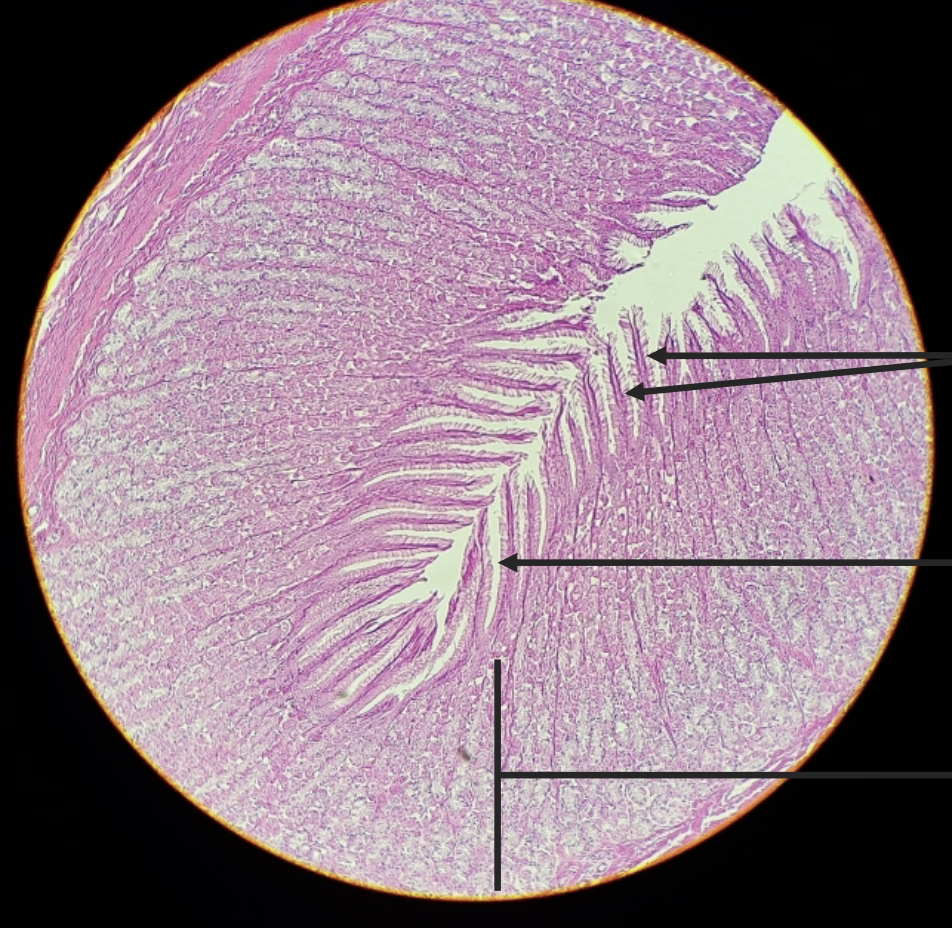
what is this?
fundic
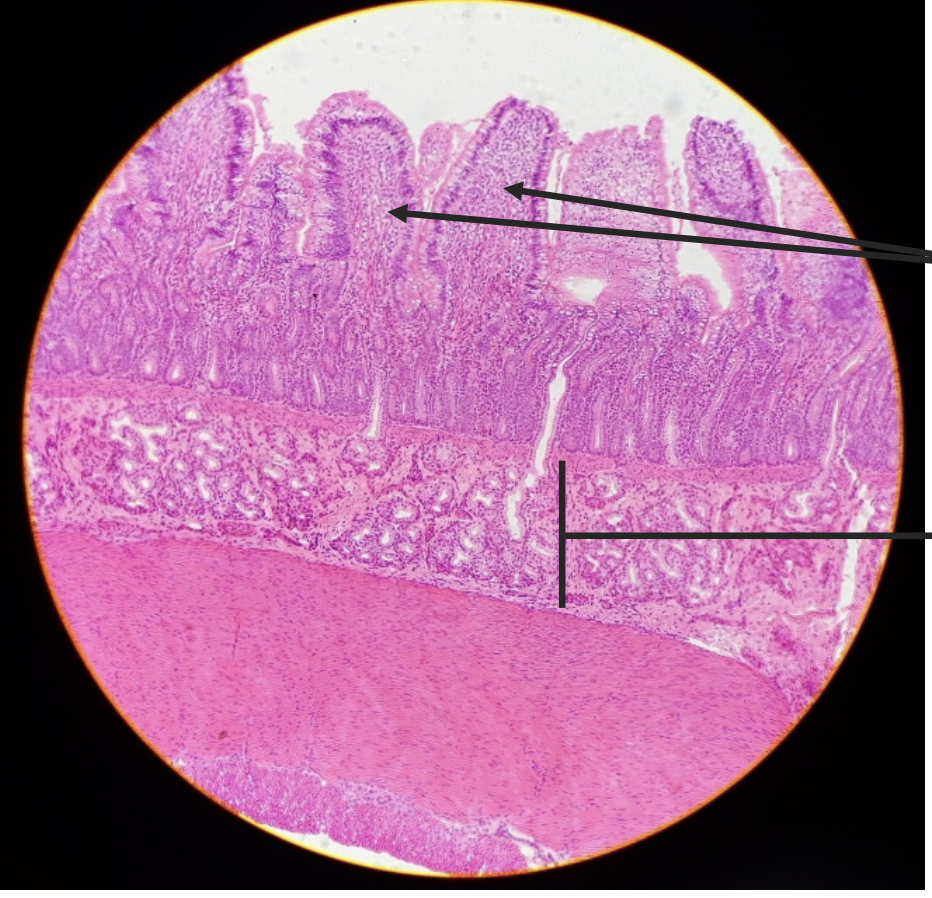
what is this?
duodenum
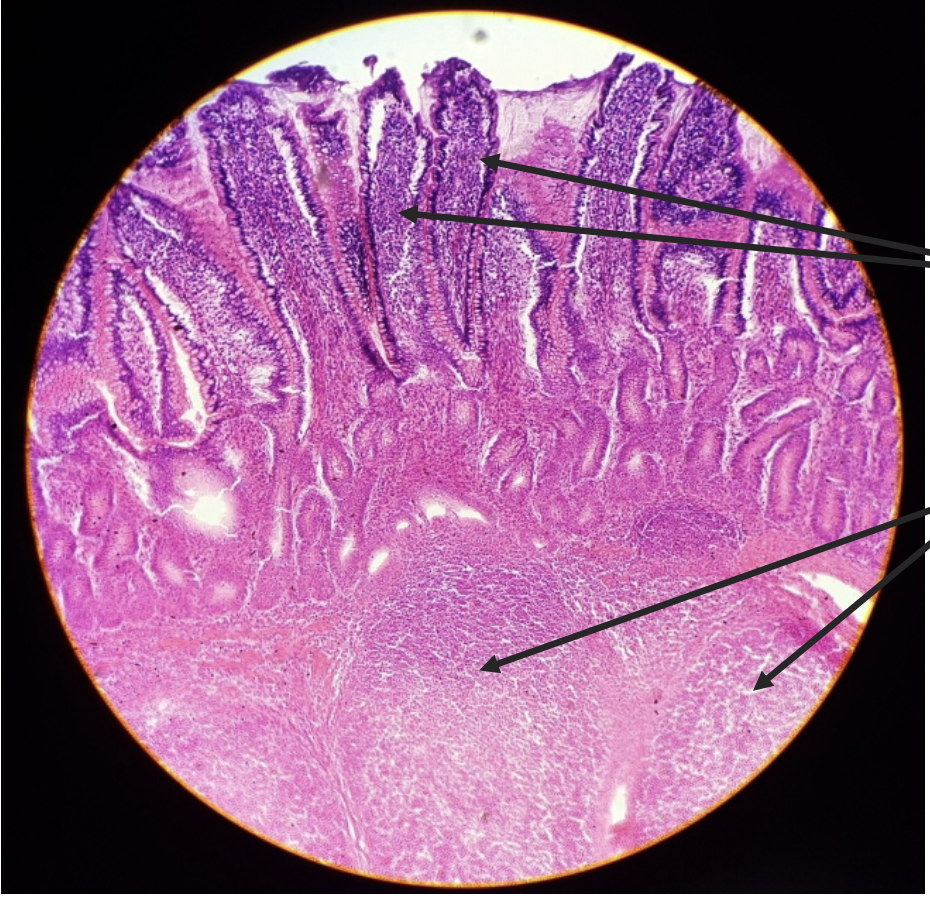
what is this?
jejunum
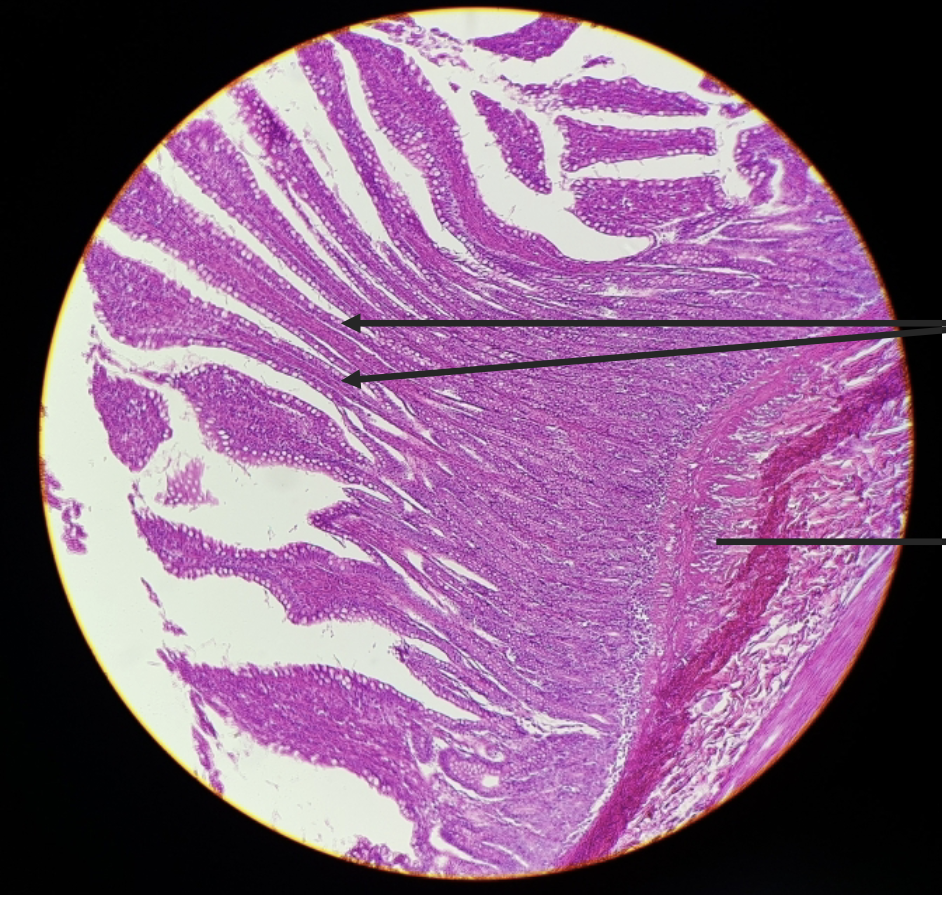
what is this?
ileum
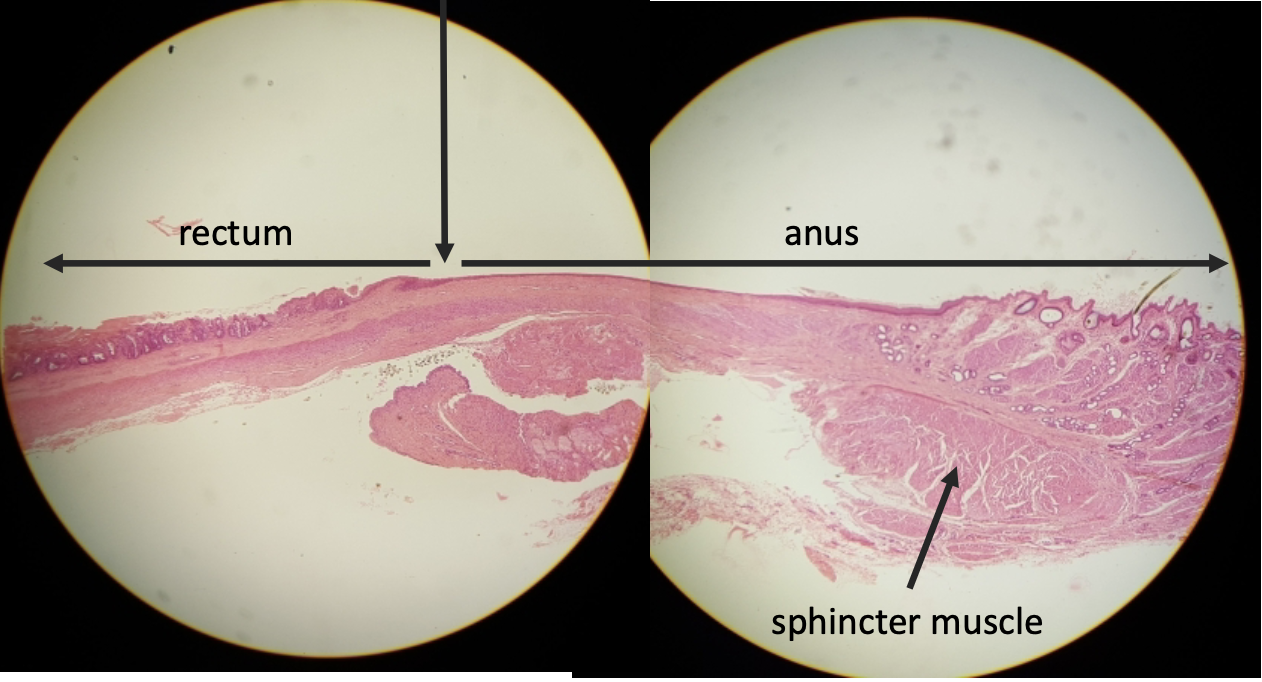
what is this?
recto-anal junction
why is the recto-anal junction called a junction?
it transitions from simple columnar to stratified squamous
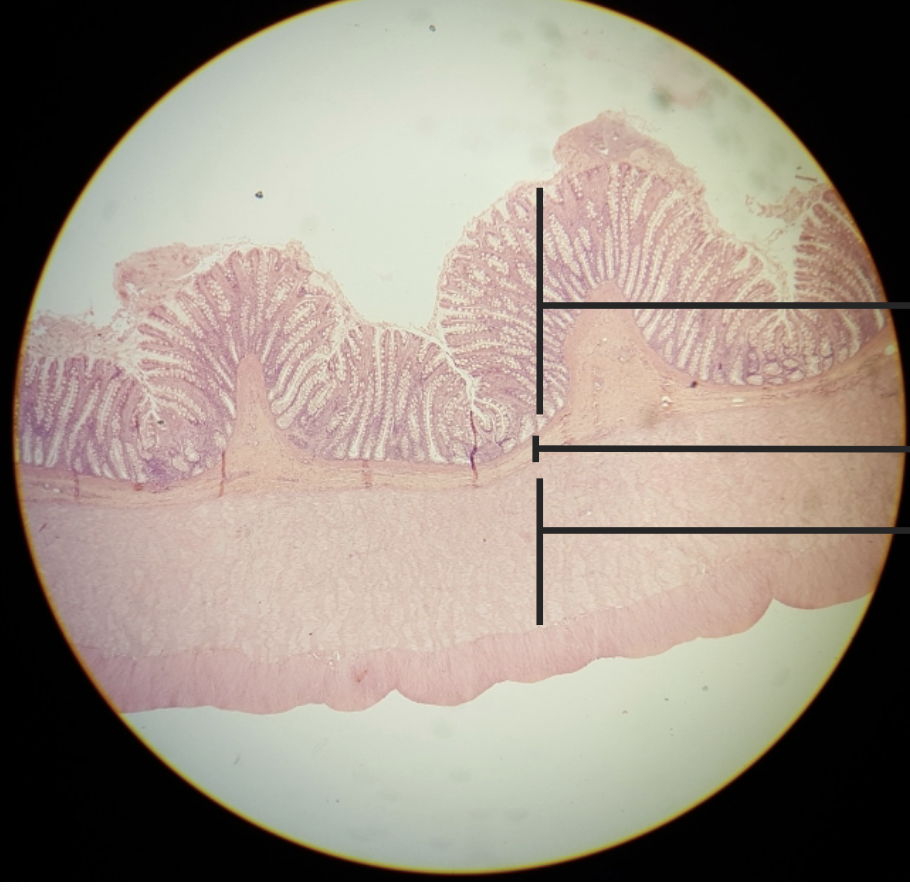
what is this?
colon
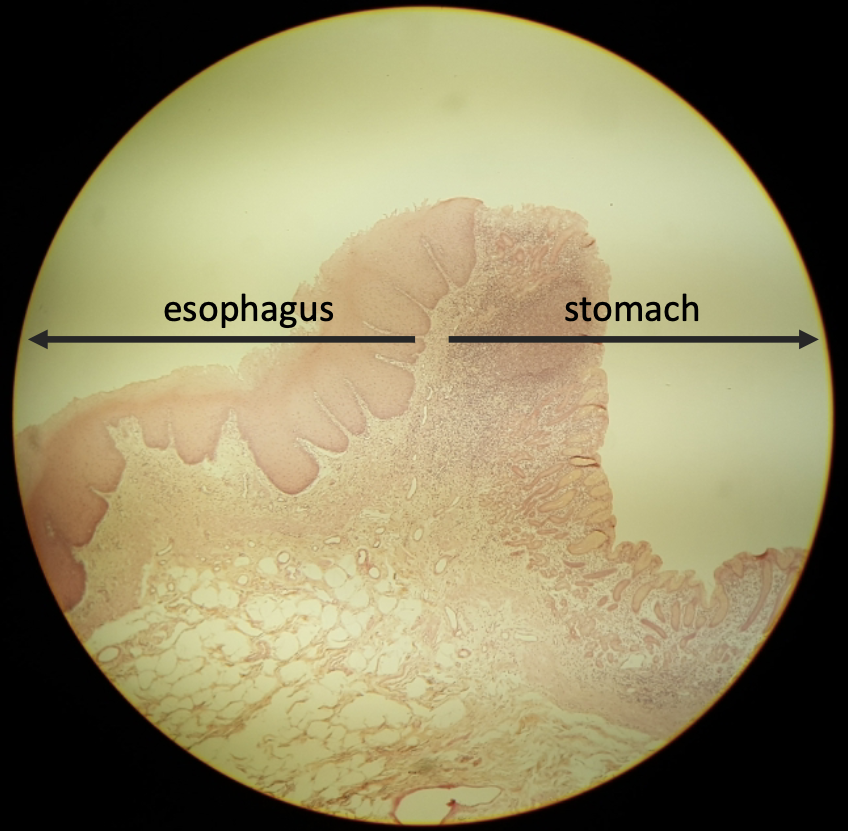
what is this?
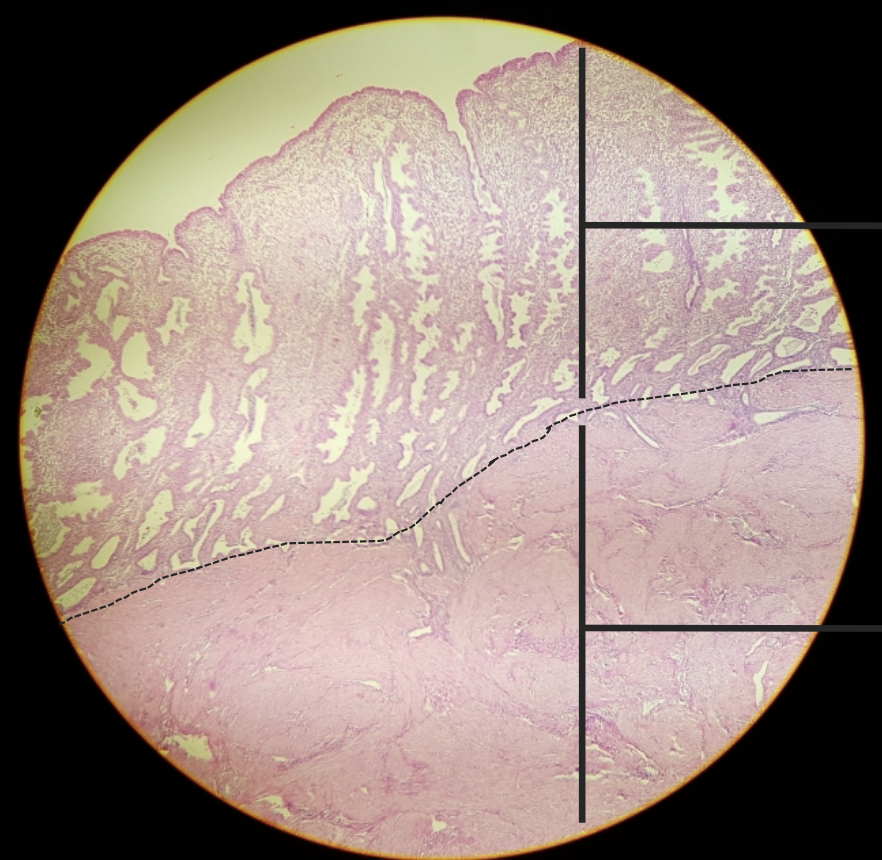
primate esophagus-stomach junction
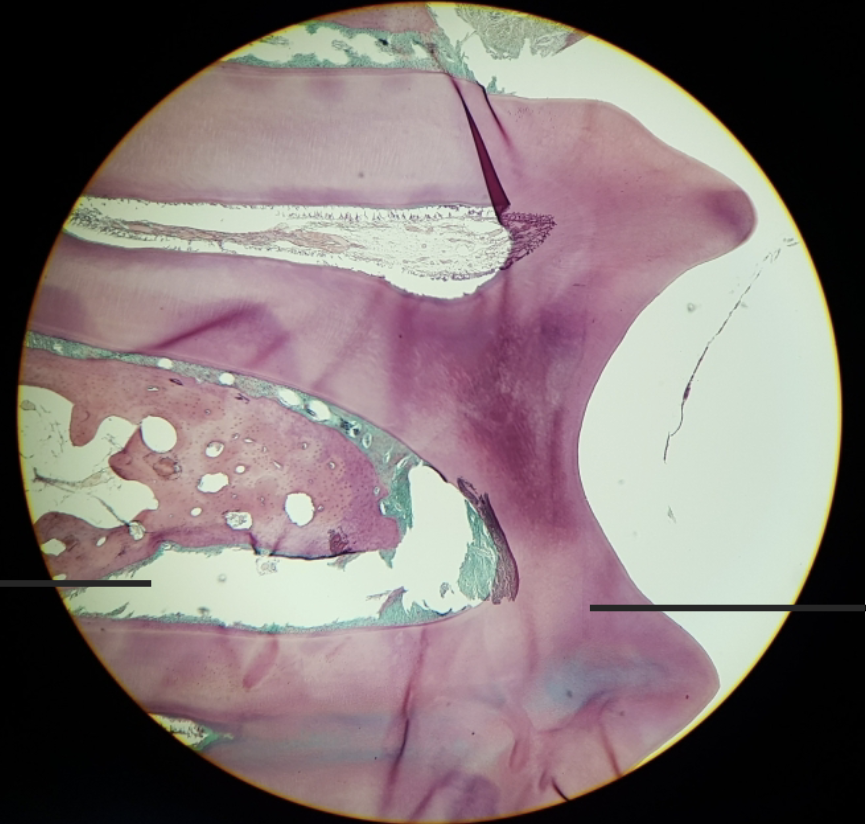
what is this?
tooth
what are the 2 main functions of the urinary system?
regulate homeostasis
eliminate of waste products
major structures of the urinary system
kidneys
ureters
bladder
urethra
blood vessels enter/exit the ____ at the _____
kidney; hilum
what delivers blood to the kidneys for processing?
renal arteries
what carries blood away from the kidneys?
renal veins
kidneys produce ____ as a result of carrying out the major functions of the _____
urine; urinary system
ureters ____ urine from ____ to ____
transport; kidneys; bladder
bladder are _____ storage _____ for _____
temporary; reservoir; urine
urethra ____ urine from ____ out of the ____
excrete; bladder; body
ureters are ___ of ___ as there’s one per kidney
pair; tubes
ureters run from the ____ to the ____
kidney; bladder
ureters are continuous with the ____
renal pelvis
ureters enter the ____ and ____ aspect of the ____
posterior; aspect; bladder
ureters runs behind the ____
peritoneum
peristalsis in ureters is aided by ____ in urine transport
gravity
how would you describe the bladder?
smooth, collapsible muscular sac
a moderately full bladder is about _____ long and holds about ____ of urine
5 inches; 500 mL
____ is a triangular region of the bladder base
trigone
what are the 3 openings of the bladder?
2 from the ureters
1 to the urethra
in males the _____ surrounds the neck of the bladder
prostate gland
the bladder wall has ___ layers of ____ that is collectively called the ____
3; smooth muscle; detrusor muscle
the bladder wall has mucosa made of ______
transitional epithelium
bladder wall is ___ and folds when it’s ___
thick; empty
bladder can expand significantly without _________
increasing internal pressure
the urethra is a ___ walled tube that ____ urine from the ____ to the ____ of the body by ____
thin; carries; bladder; outside; peristalsis
what are the 2 sphincters that control the release of urine?
internal urethral sphincter
external urethral sphincter
what’s the difference between internal and external urethral sphincters?
internal: involuntary and made of smooth muscle
external: voluntary and made of skeletal muscle
female vs male: urethra length
female: 3-4 cm
male: 20 cm
female vs male: urethra location
female: next to the wall of the vagina
male: through the prostate and penis
female vs male: urethra function
female: only carries urine
male: carries urine and passageway for sperm cells
the kidneys are located against the _____ body wall and at the level of the ____ to ____ vertebrae
dorsal; T12; L3
why is the right kidney slightly lower than the left kidney?
position of the liver
renal cortex is the ___ region
outer
renal medulla is ____ the cortex
inside
renal pelvis is the _____ tube
inner collecting
renal hilum is a ________ where several structures ____ or ____ the kidney
medial indentation; enter; exit
an adrenal gland sits ____ each kidney
on top
the ____ surrounds each kidney
renal capsule
the ______ is the outermost capsule
renal fascia
what are the 2 functions of the renal fascia?
hold the kidneys in place against the trunk wall muscles
divides the fat that surrounds the kidney into 2 layers
what are the 2 layers of fat that surrounds the kidney?
inner fat: perirenal fat
outer fat: pararenal fat
perirenal fat is between the _____
capsule of the kidney fascia
what is the purpose of the perirenal fat?
cushions against blows
attachment to body wall
what’s the purpose of having fat surround the kidney?
keeps it properly situated
what is nephroptosis?
aka renal ptosis
position changes and drops in the body cavity
maybe due to loss of perirenal fat
_____ is triangular regions of tissue in the medulla
renal medullary pyramids
______ are extensions of cortex-like material inward that ____ the renal pyramids
renal columns; separate
______ are cup-shaped structures that funnel urine towards the _____
calyces; renal pelvis
___% of total body blood volume passes through the kidneys each minute
25
renal artery branches from the ______ and provides _____ to the kidney
abdominal aorta; arterial blood
renal vein drains blood from the _____ into the ______
kidneys; inferior vena cava
aorta —> ____ —> ____ —> ____ —> ____ —>____ —>____ —> glomerulus —>____ —> peritubular capillaries —>____ —>____ —>____ —>____ —> inferior vena cava
renal artery —> segmental artery —> interlobar artery —> arcuate artery —> cortical radiate artery —> afferent arteriole
efferent arteriole
cortical radiate vein —> arcuate vein —> interlobar vein —> renal vein
nephrons are the ____ and ____ units of the kidneys
structural; functional
what is responsible for forming urine?
the nephron
what are the 2 capillary beds associated with the nephron?
glomerulus
peritubular capillaries
what are the 2 major structures of the nephron?
renal corpuscle
renal tubule
what is the renal tubule start and end?
glomerular capsule
proximal convoluted tubule
nephron loop
distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct
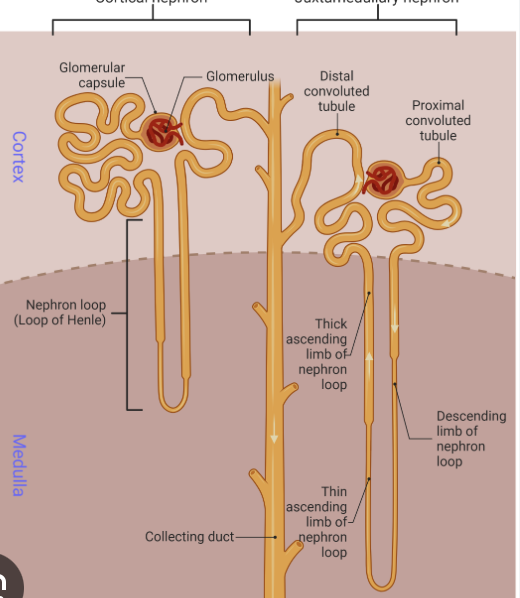
what is the site of nephron filtration?
renal corpuscle (blood flows glomerular capillaries —> glomerular capsule)
what is the glomerulus?
knot of capillaries
_____ supplies the glomerulus and it is drained by _____
afferent arteriole; efferent arteriole
what happens to the glomerulus under high pressure?
fluid and small solutes are forced out of blood and into the glomerular capsule
glomerulus is covered by ____ on the ____ layer of the glomerular capsule
podocytes; visceral
where is the glomerular capsule located and function?
beginning of the renal tubule
encloses the glomerulus
what are the 2 layers of the glomerular capsule?
visceral layer
parietal layer
describe the visceral later of the glomerular capsule
composed of podocytes with foot processes that form part of the filtration membrane
describe the parietal layer of the glomerular capsule
outer impermeable wall
where does peritubular capillary beds arise from?
efferent arteriole of the glomerulus
unlike the glomerulus, the peritubular capillary beds are _________
normal, low pressure
instead of filtration the peritubular capillary beds are adapted for _____
absorption
why does the peritubular capillary beds cling close to the renal tubule?
to reabsorb some substances from collecting tubes
what’s the function of the renal tubule?
site of tubular reabsorption and secretion
what is the flow of urine from collecting duct?
DCT empty into —> receive urine from nephrons —> run through pyramids —> deliver urine unto calyces and renal pelvis
what are the 2 types of nephrons
cortical nephrons
juxtamedullary nephrons
where is the cortical nephron located
entirely in renal cortex