Chapter 16: The Respiratory System: Pulmonary Ventilation
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
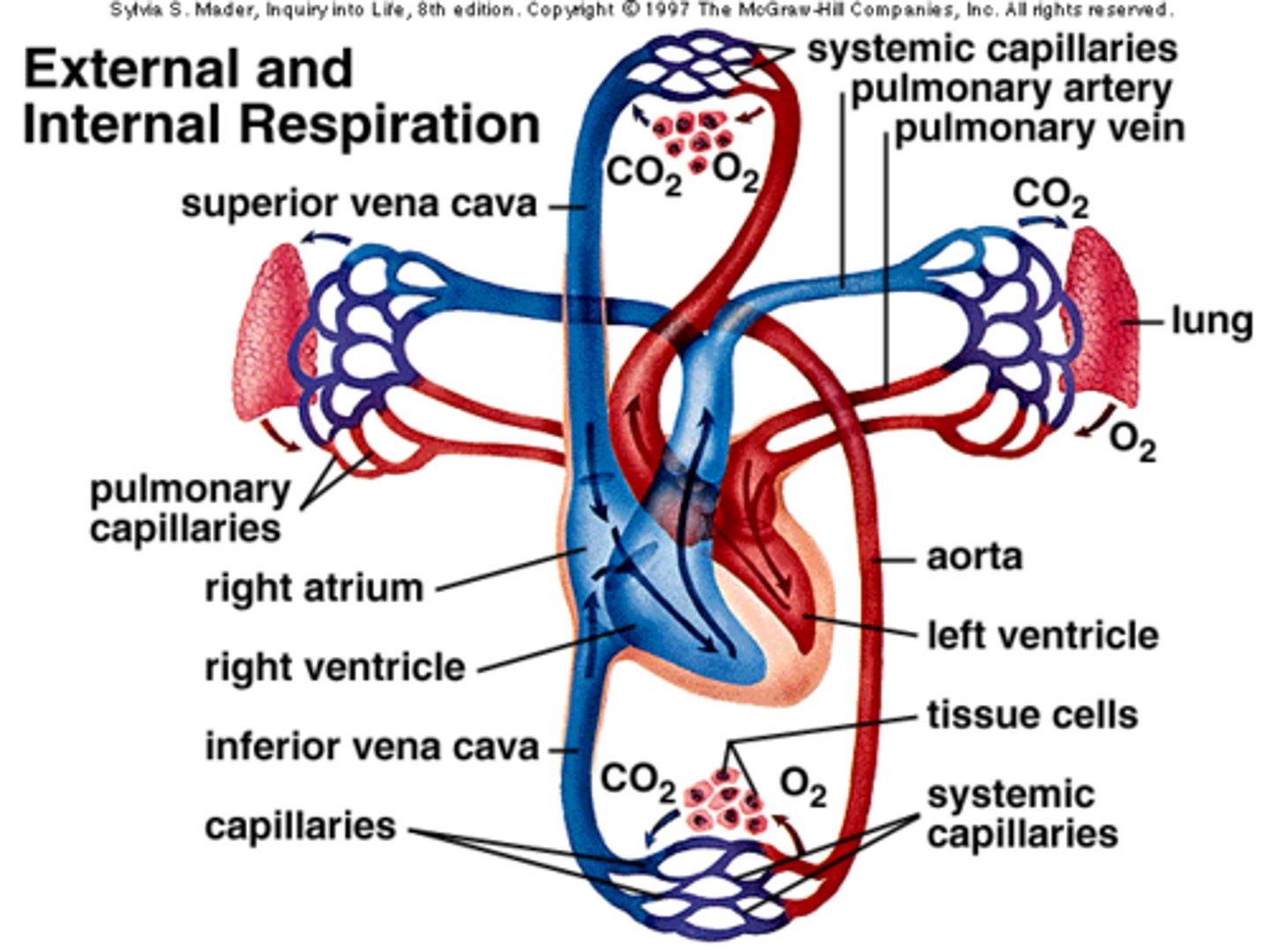
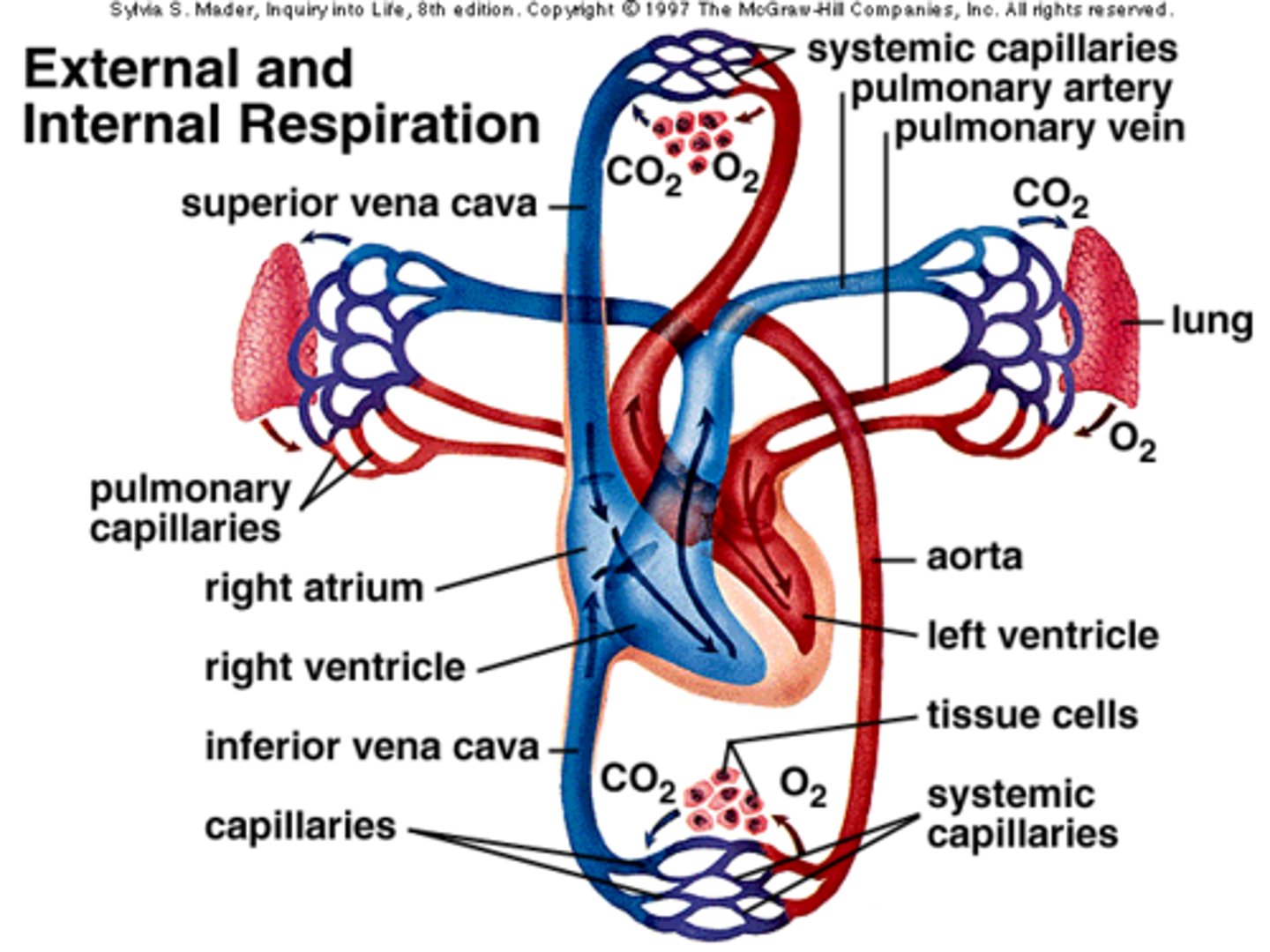
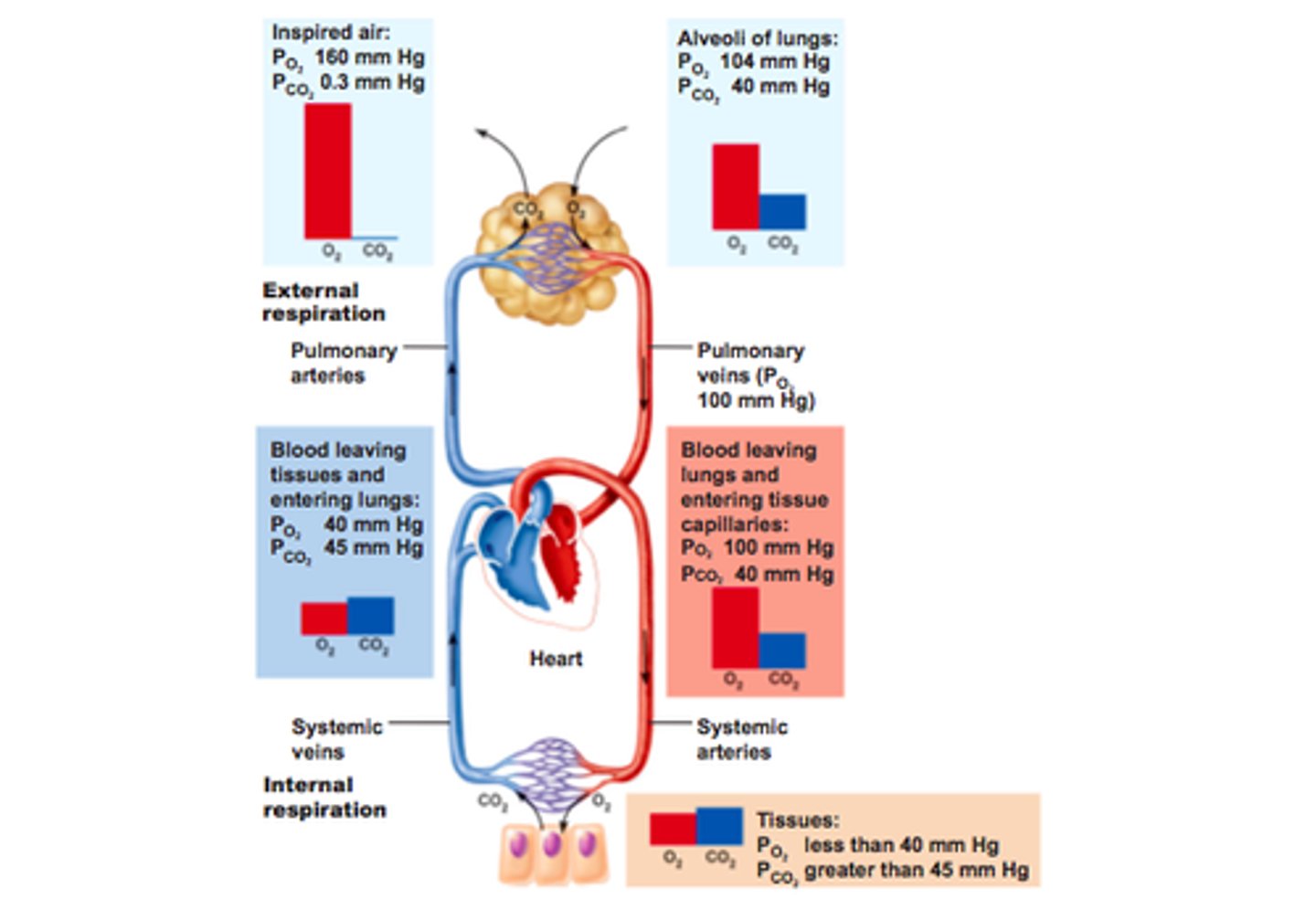
external respiration
exchange of gases between lungs and blood
internal respiration (cellular respiration)
the exchange of gases within the cells of the blood and tissues
pulmonary ventilation
movement of air into and out of the lungs
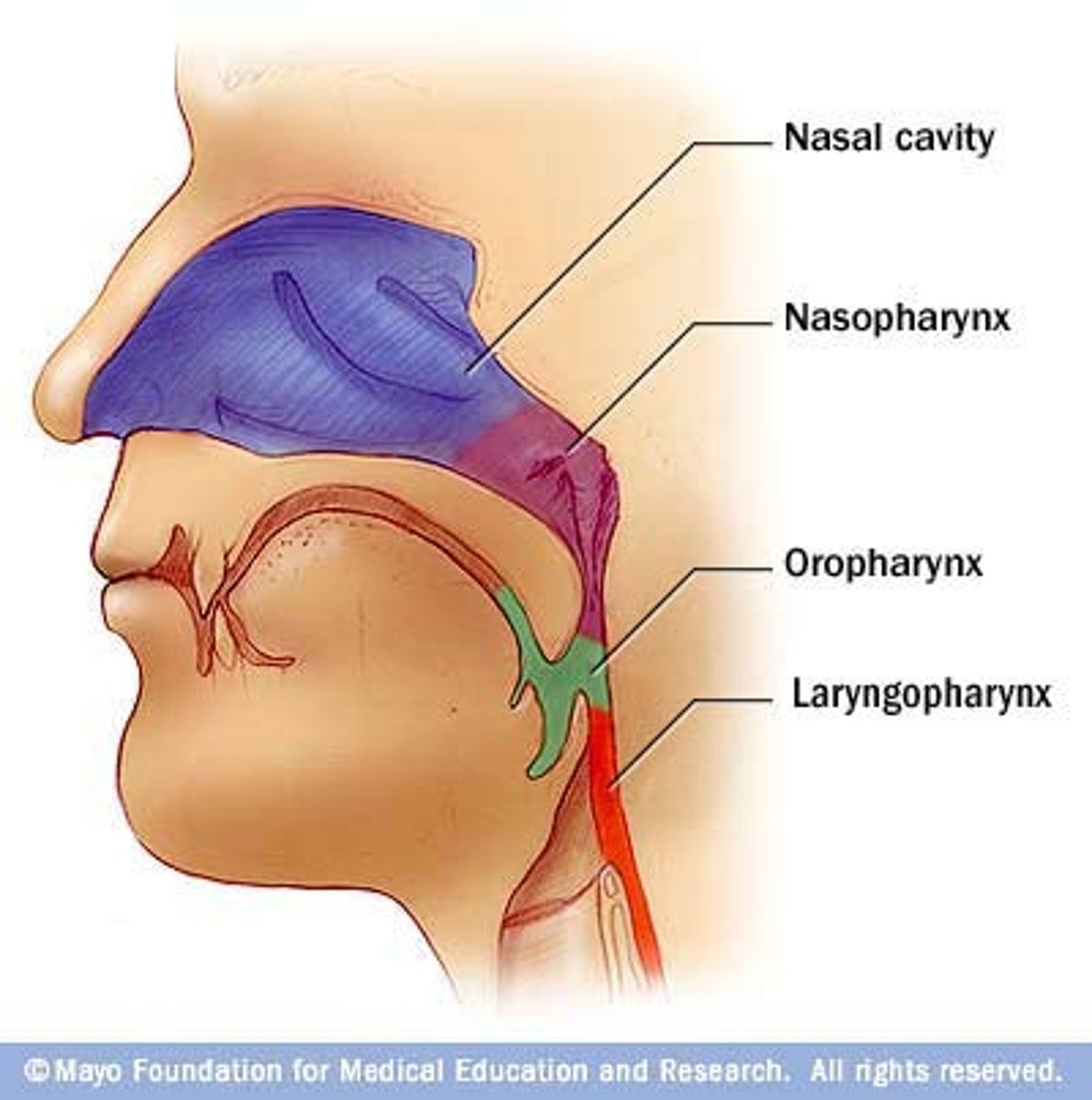
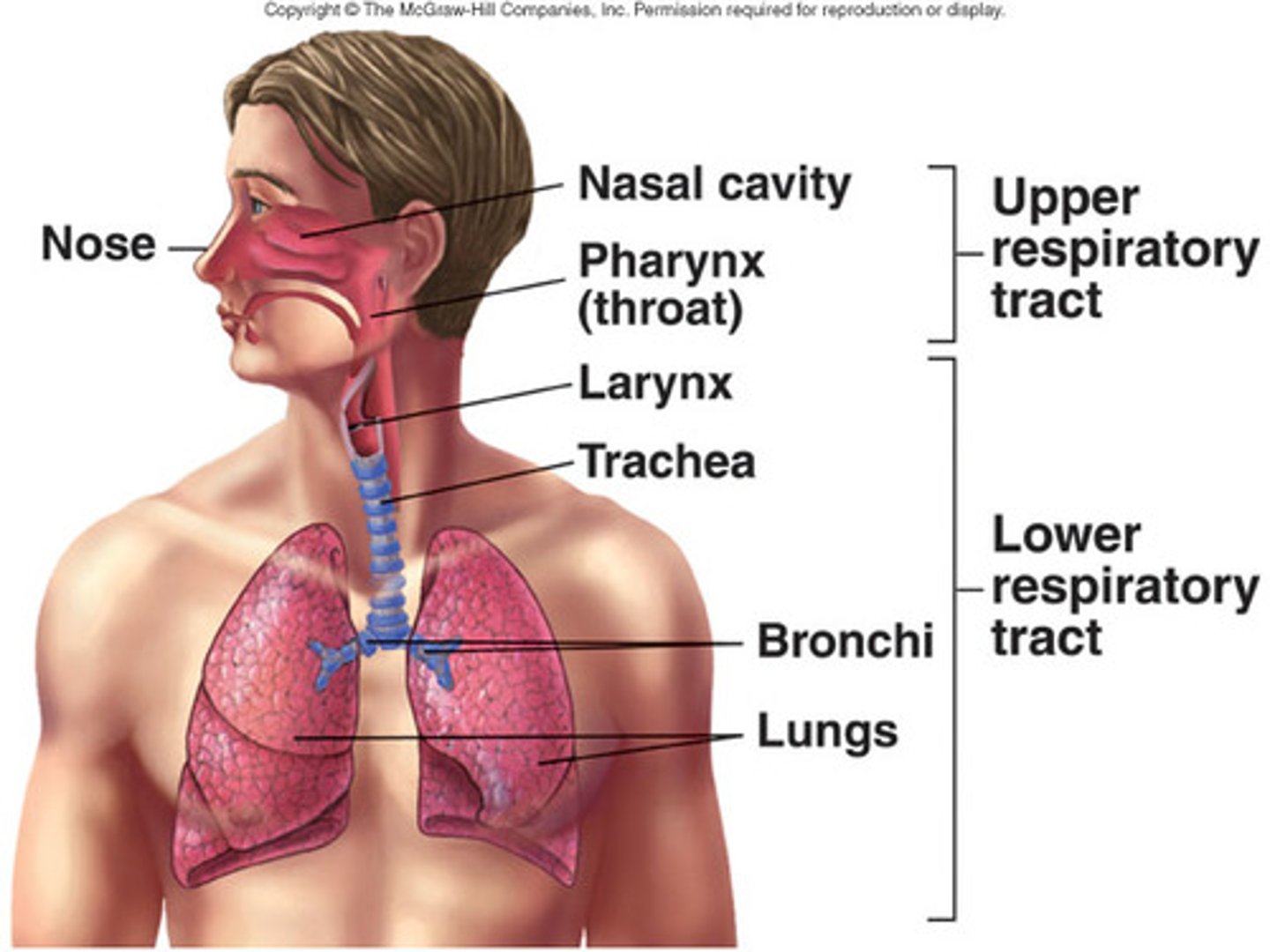
upper airways
nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx

respiratory tract
The passageway that makes breathing possible.
series of branching tubes that conduct air to and from the respiratory zone for gas exchange

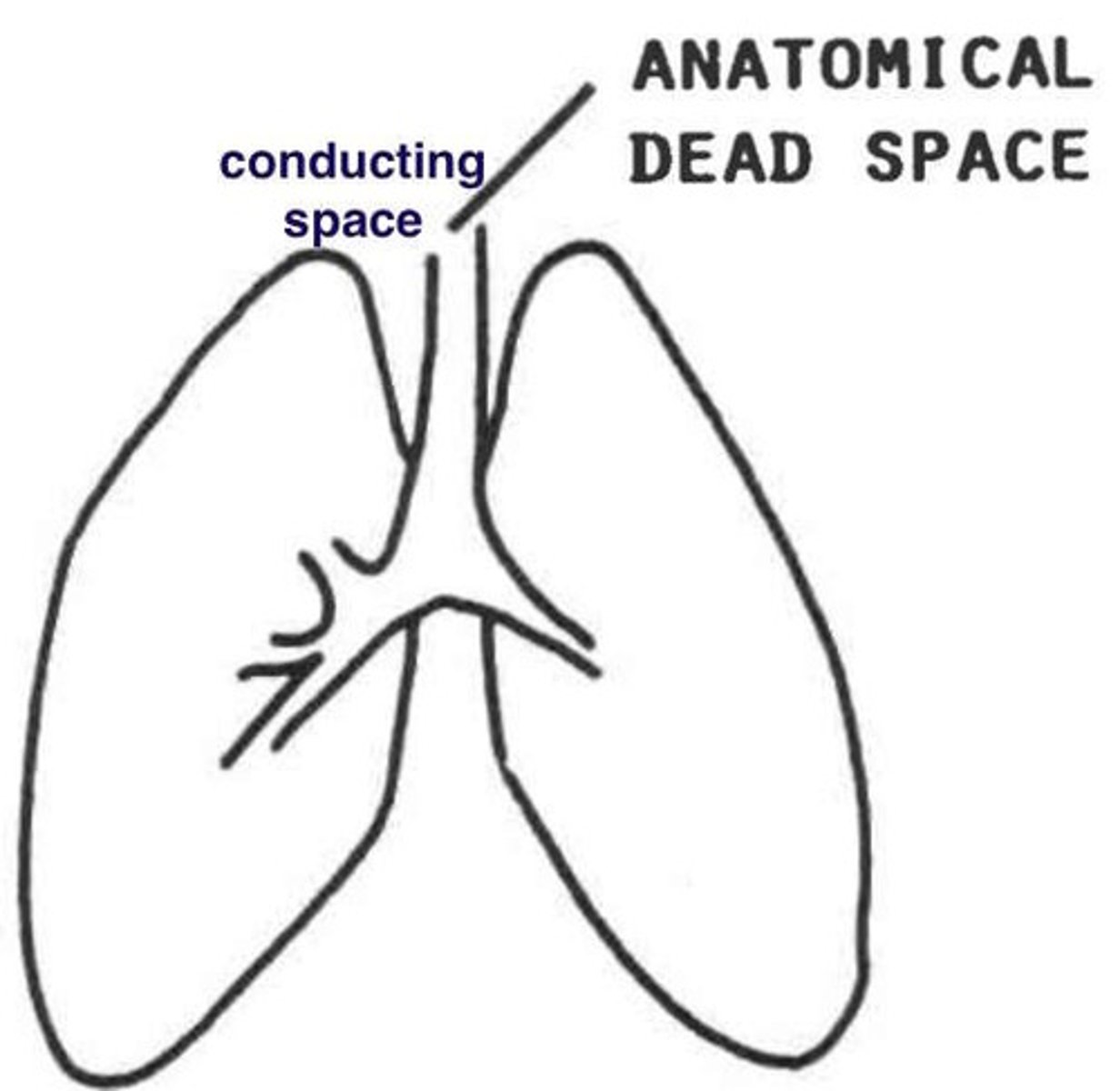
conducting zone
Includes respiratory passageways, cleanses, humidifies and warms incoming air
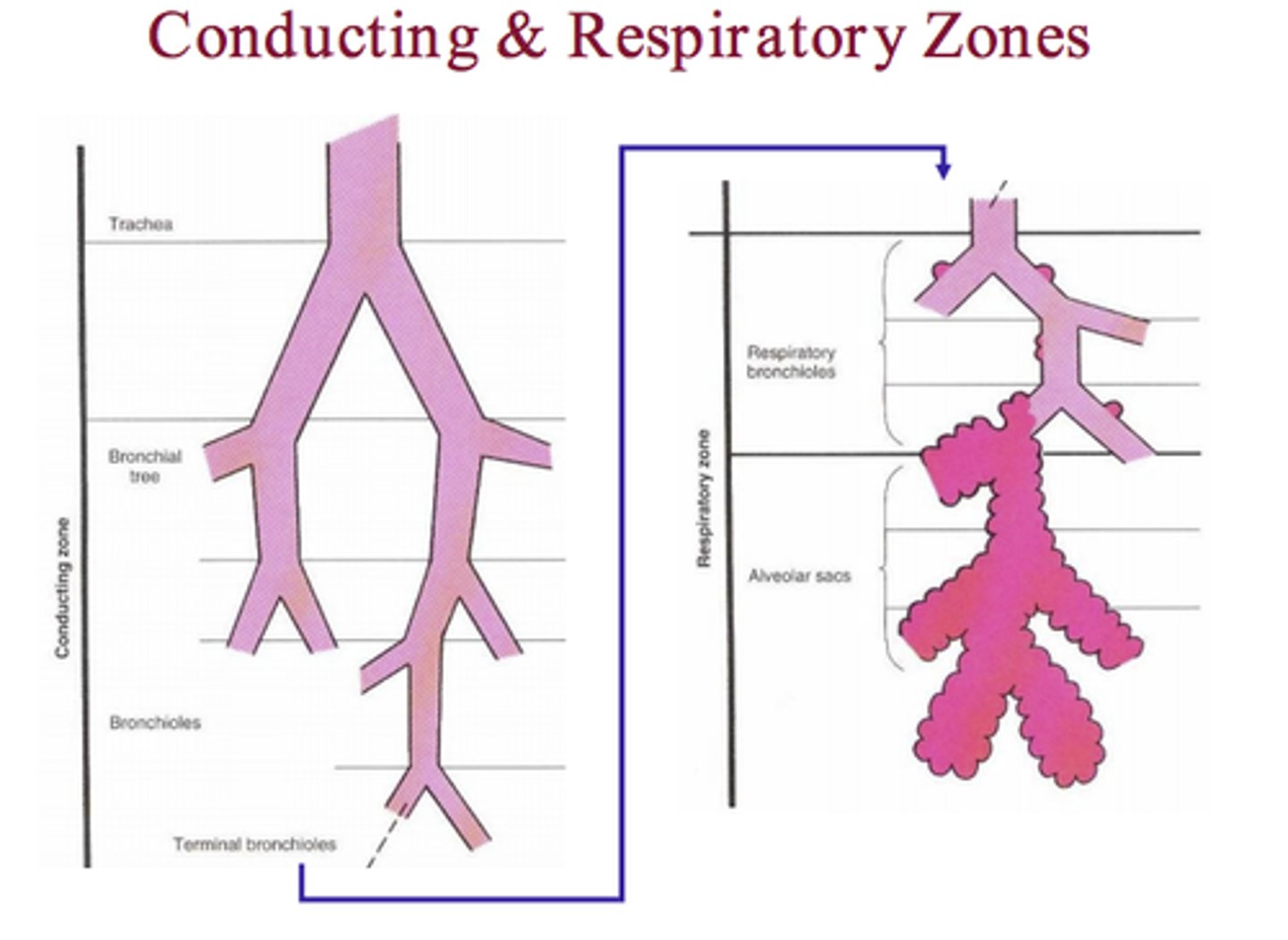
respiratory zones
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli
pharynx
the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus.
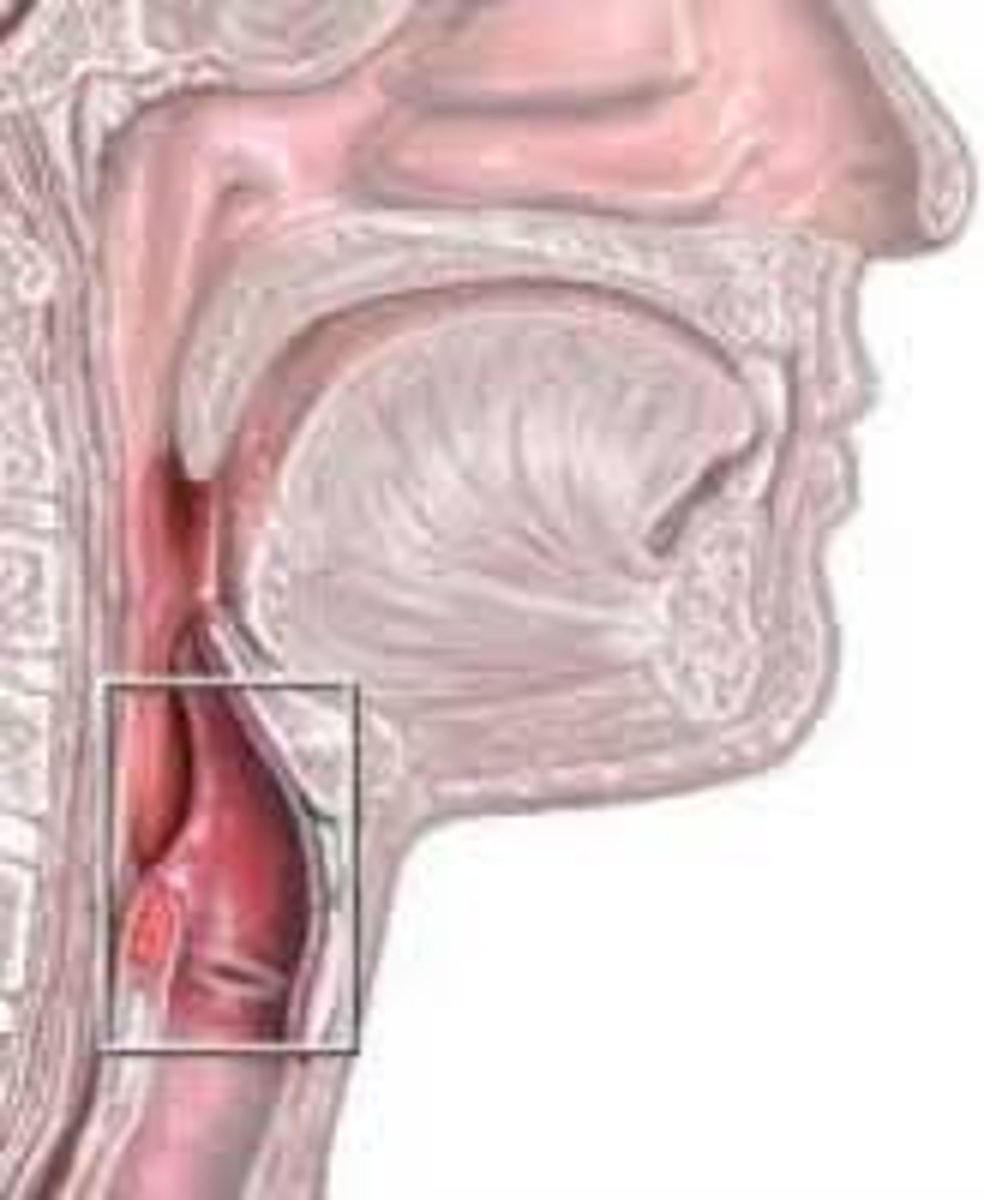
larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
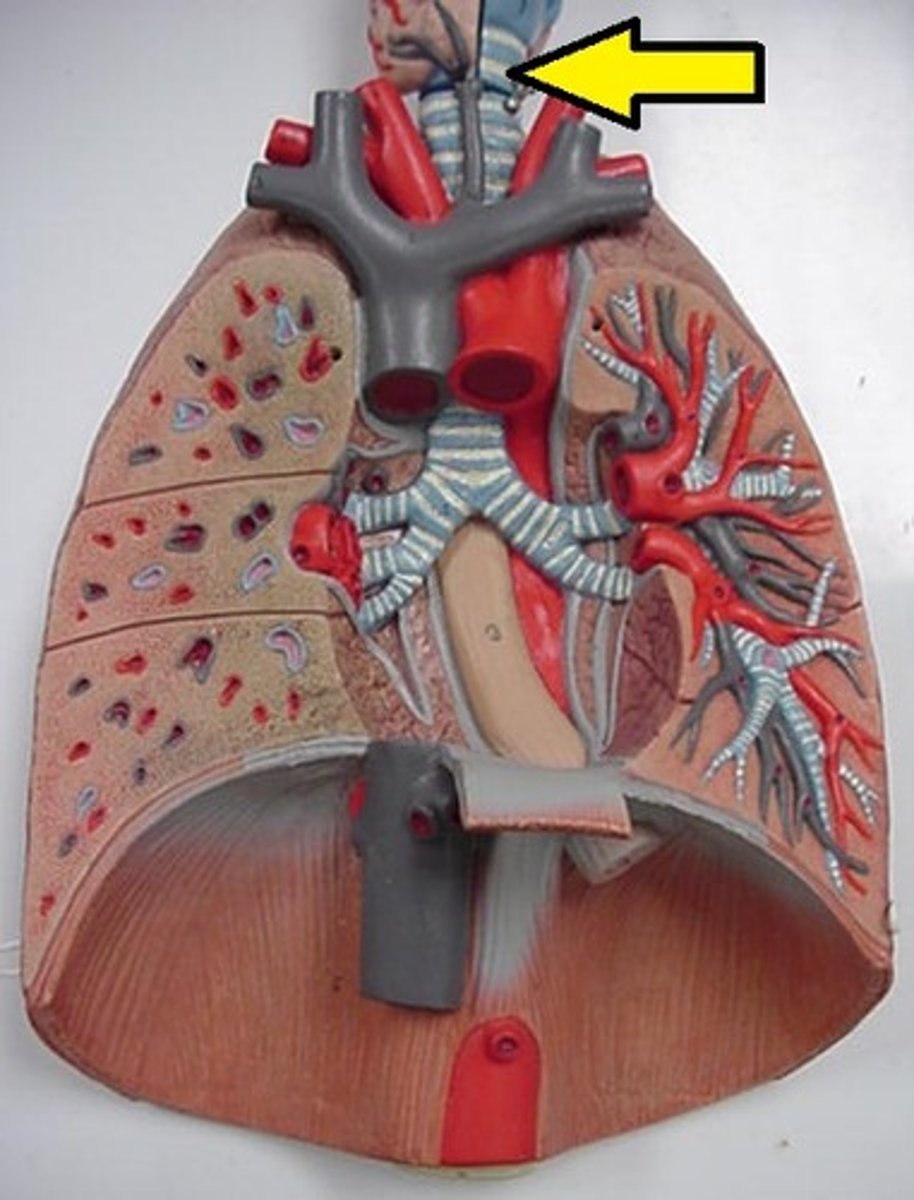
primary bronchi
The first branches of the trachea. There are two primary bronchi, one for each lung.
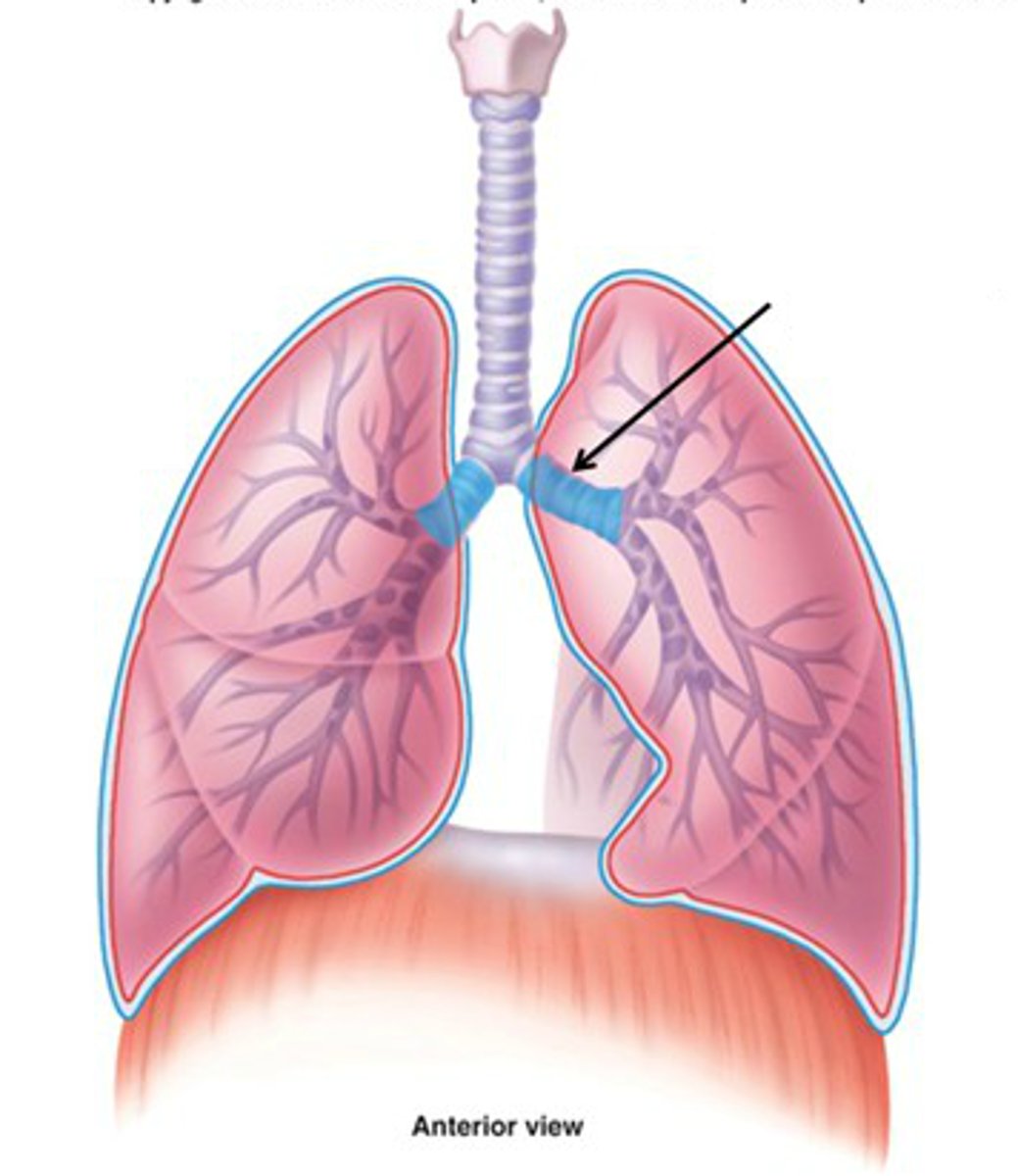
secondary bronchi
branches of the primary bronchi that lead to each lobe of the lung; also called lobar bronchi
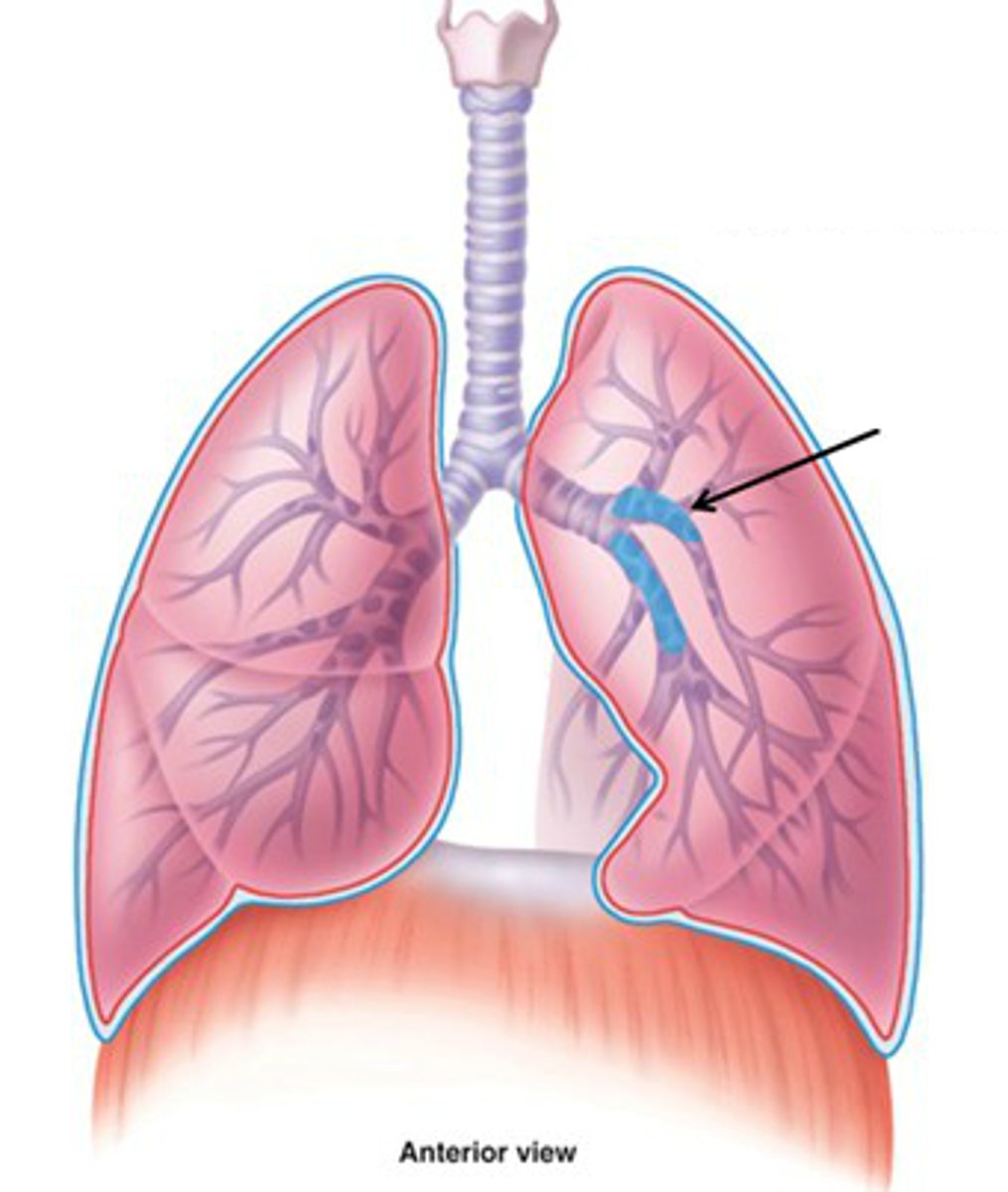
tertiary bronchi
branches of the secondary bronchi that divide into bronchioles; also called segmental bronchi
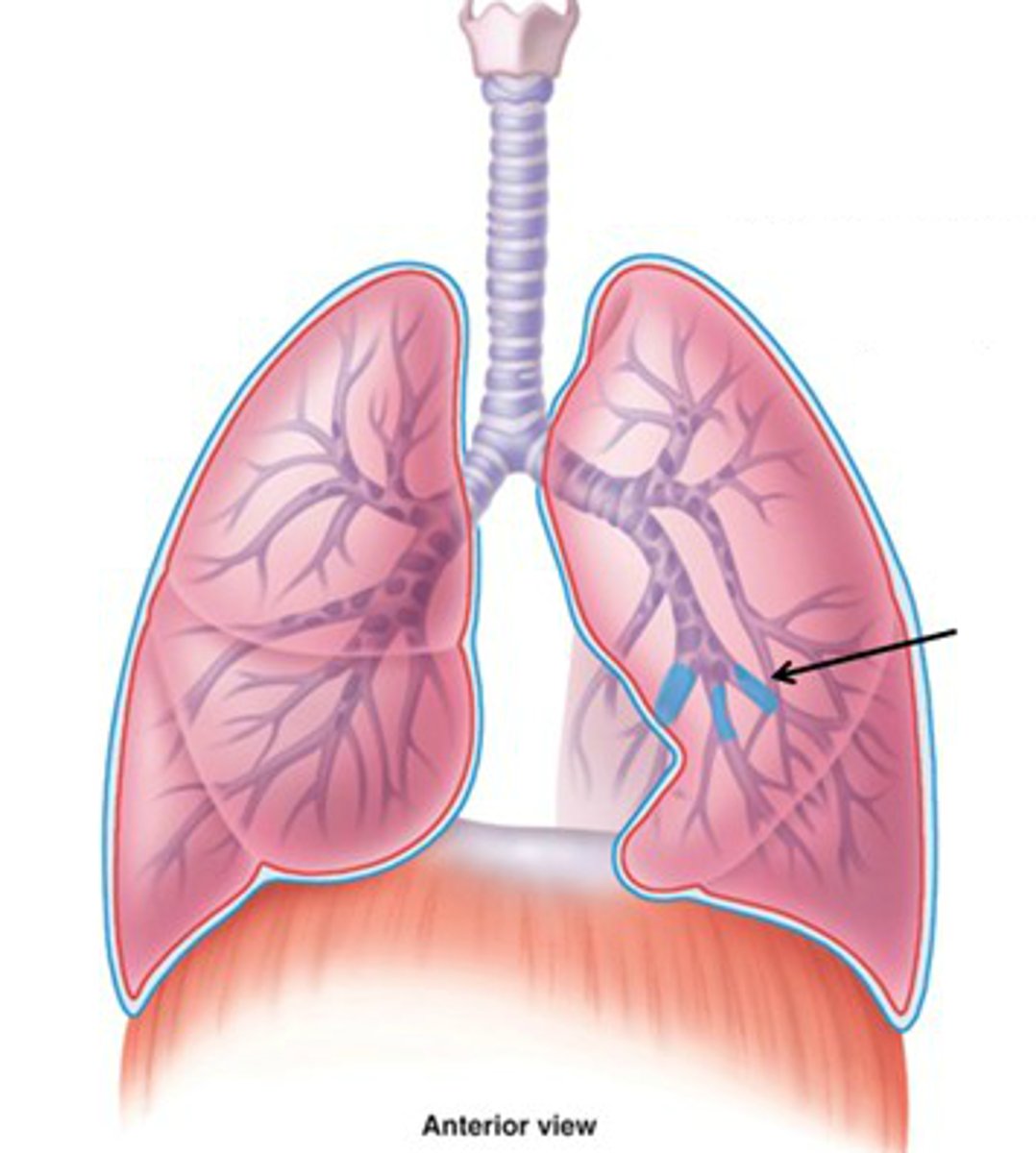
bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
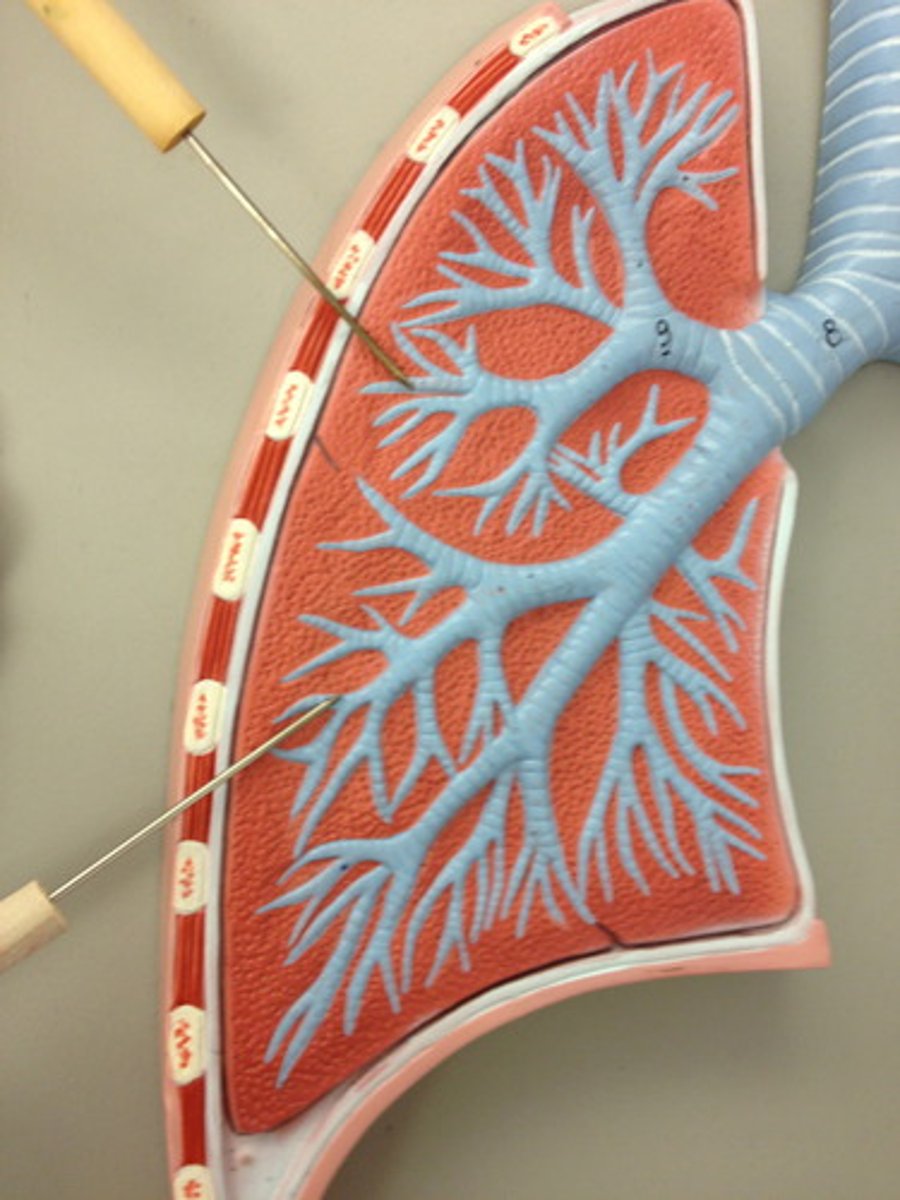
terminal bronchioles
smaller than 0.5 millimeter and these mark the end of the conducting zone
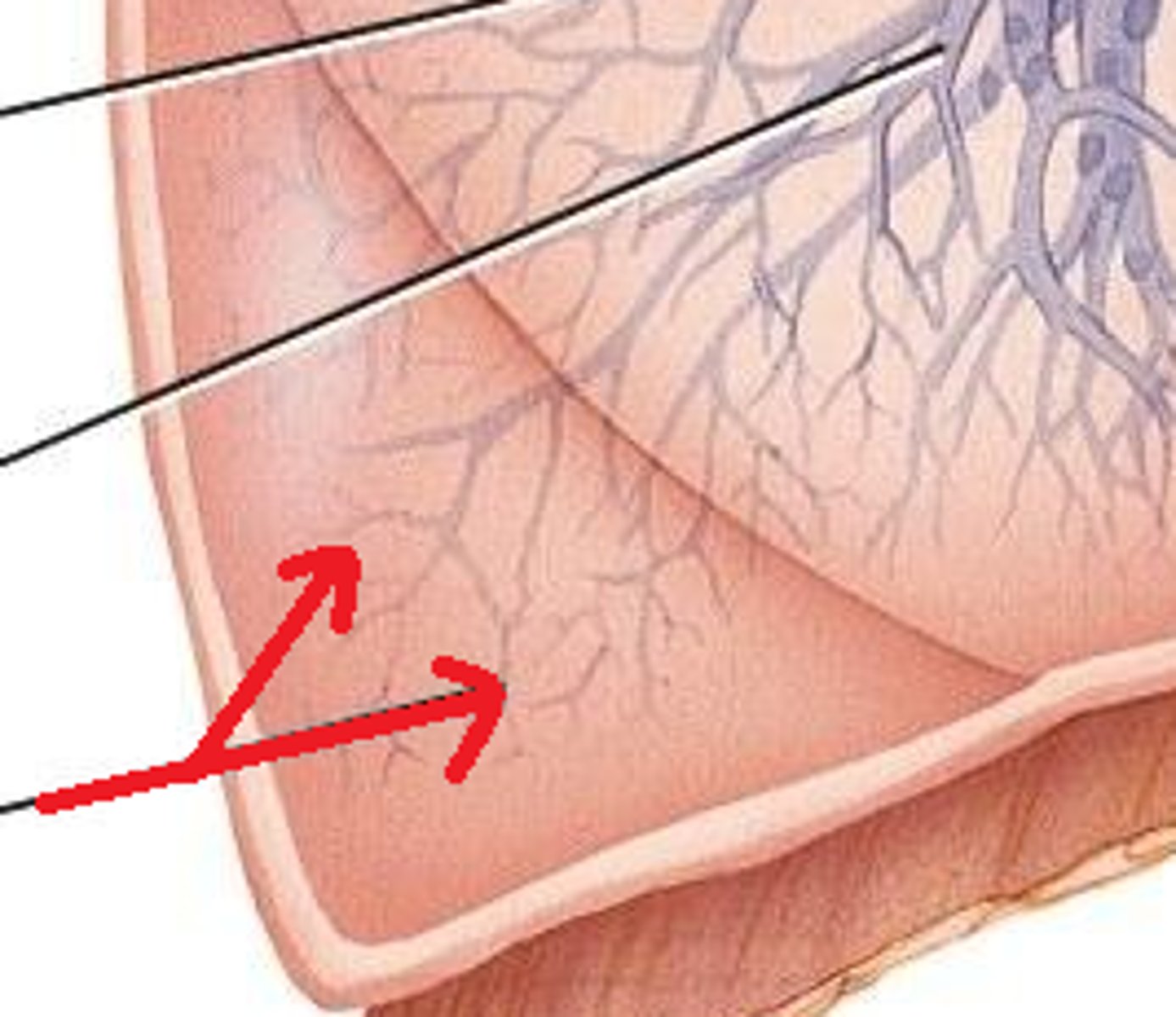
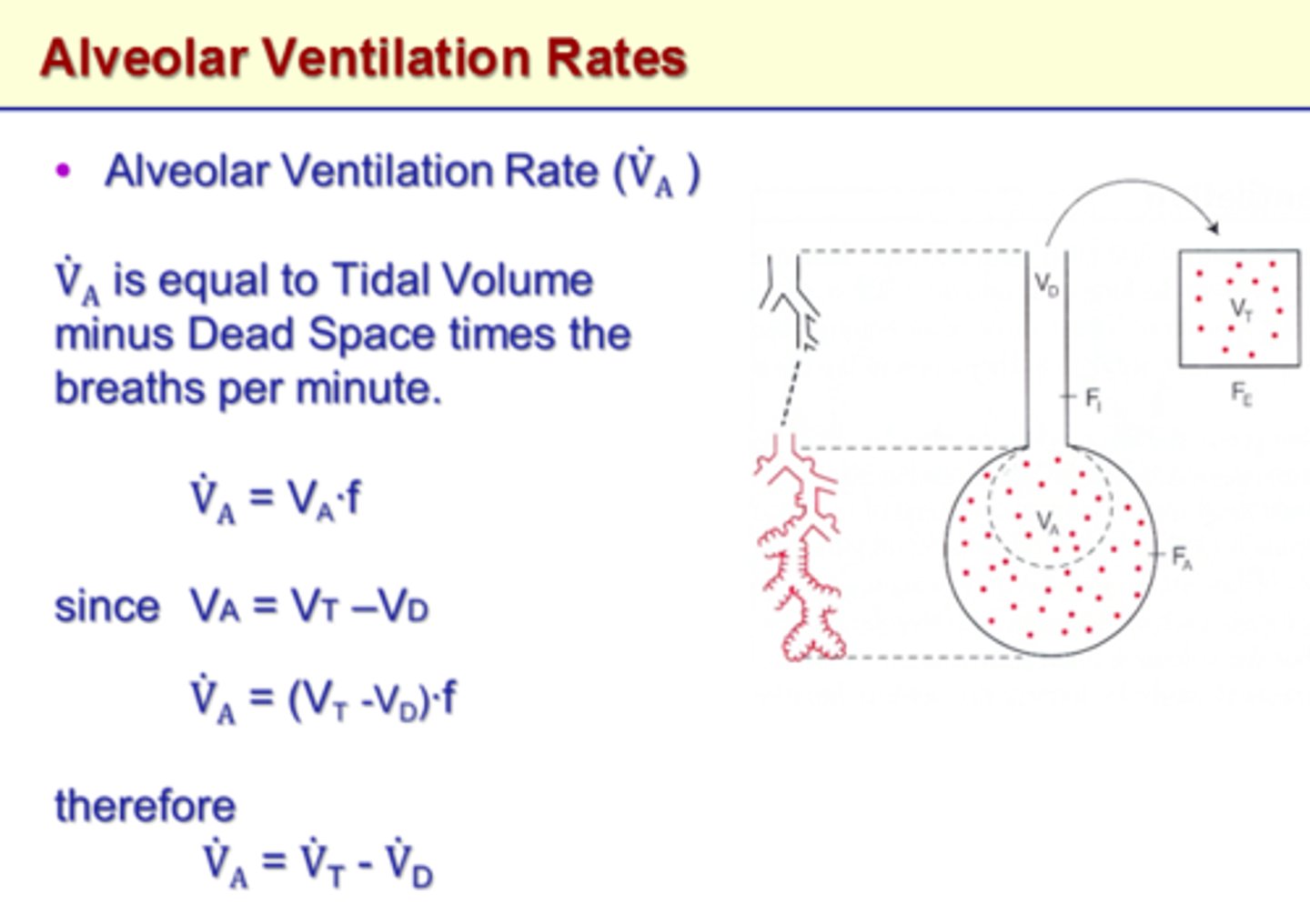
dead space
The portion of the tidal volume that does not reach the alveoli and thus does not participate in gas exchange.
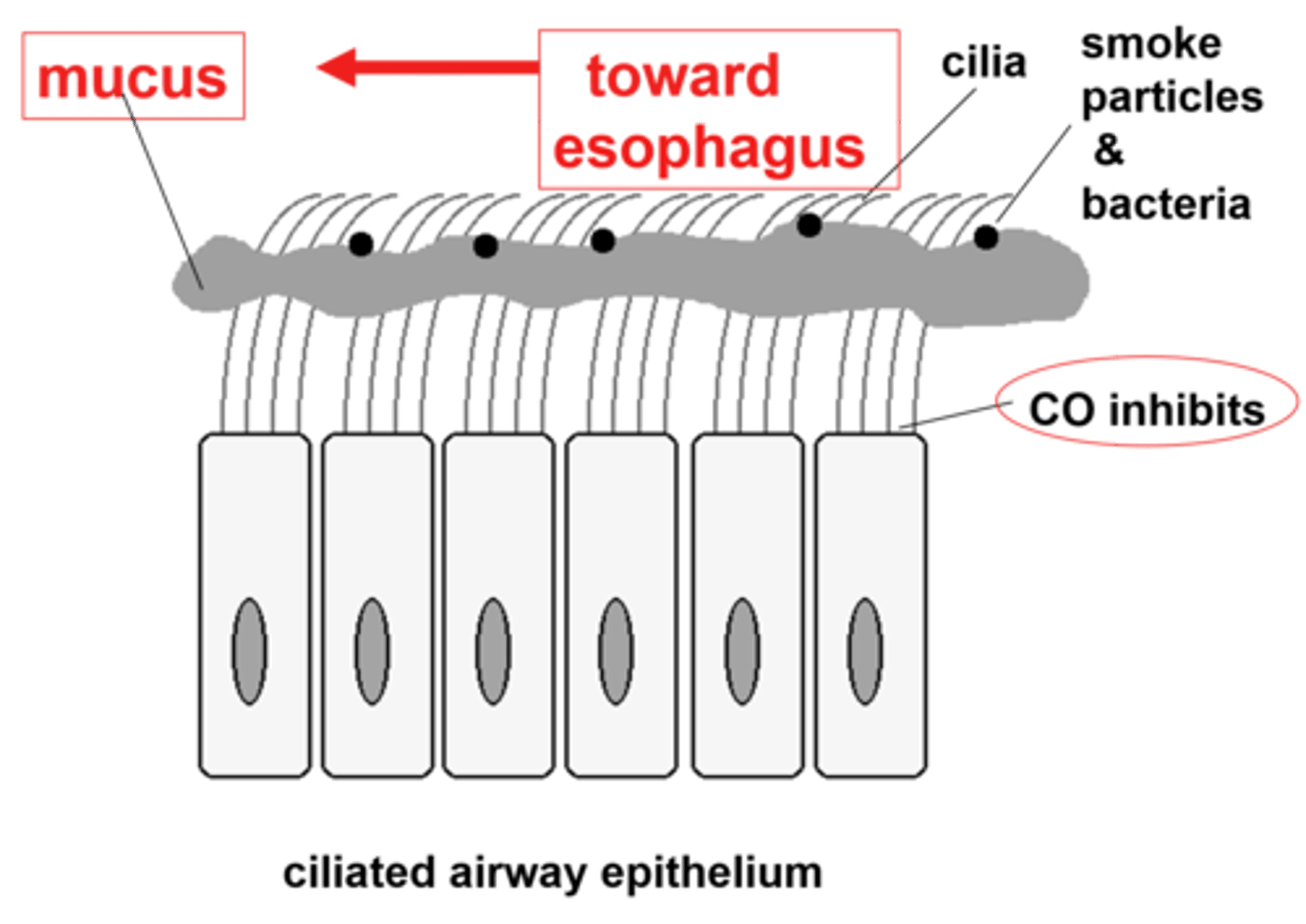
goblet cells
a column-shaped cell found in the respiratory and intestinal tracts, which secretes the main component of mucus.
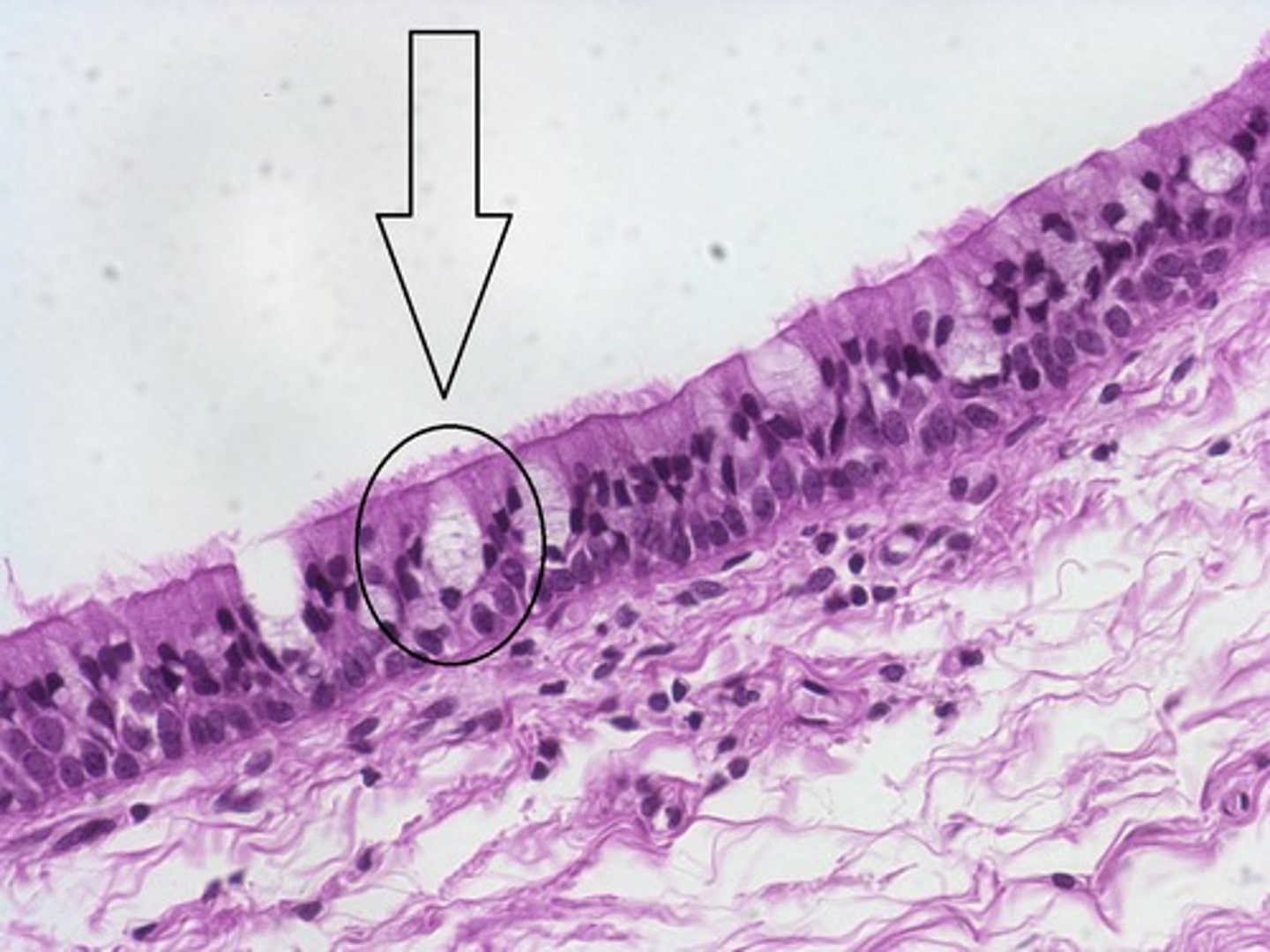
ciliated cells
can catch dust and microbes and move them out of the breathing system
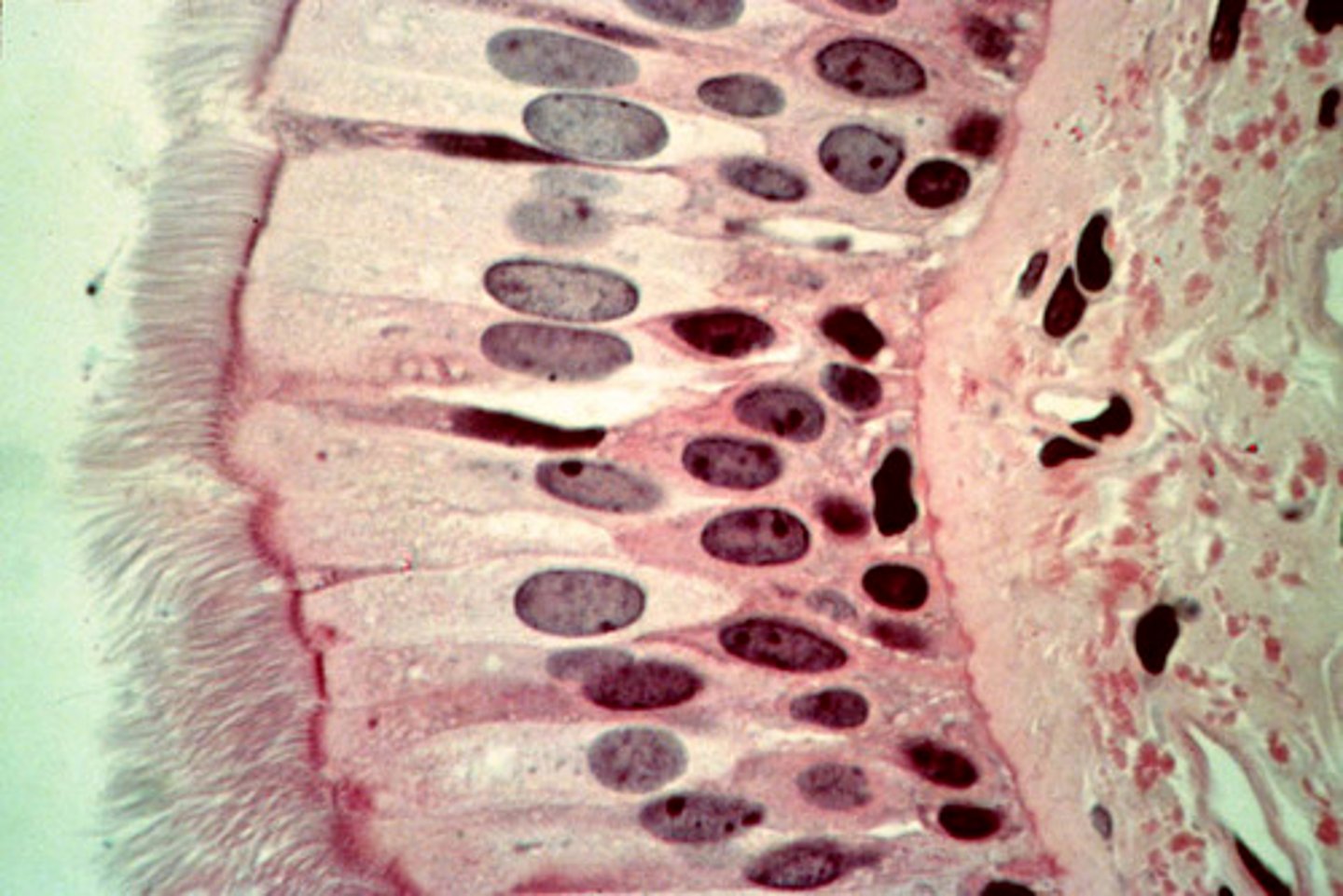
mucus escalator
The upward movement of mucus in the lungs caused by the coordinated movement of cilia.
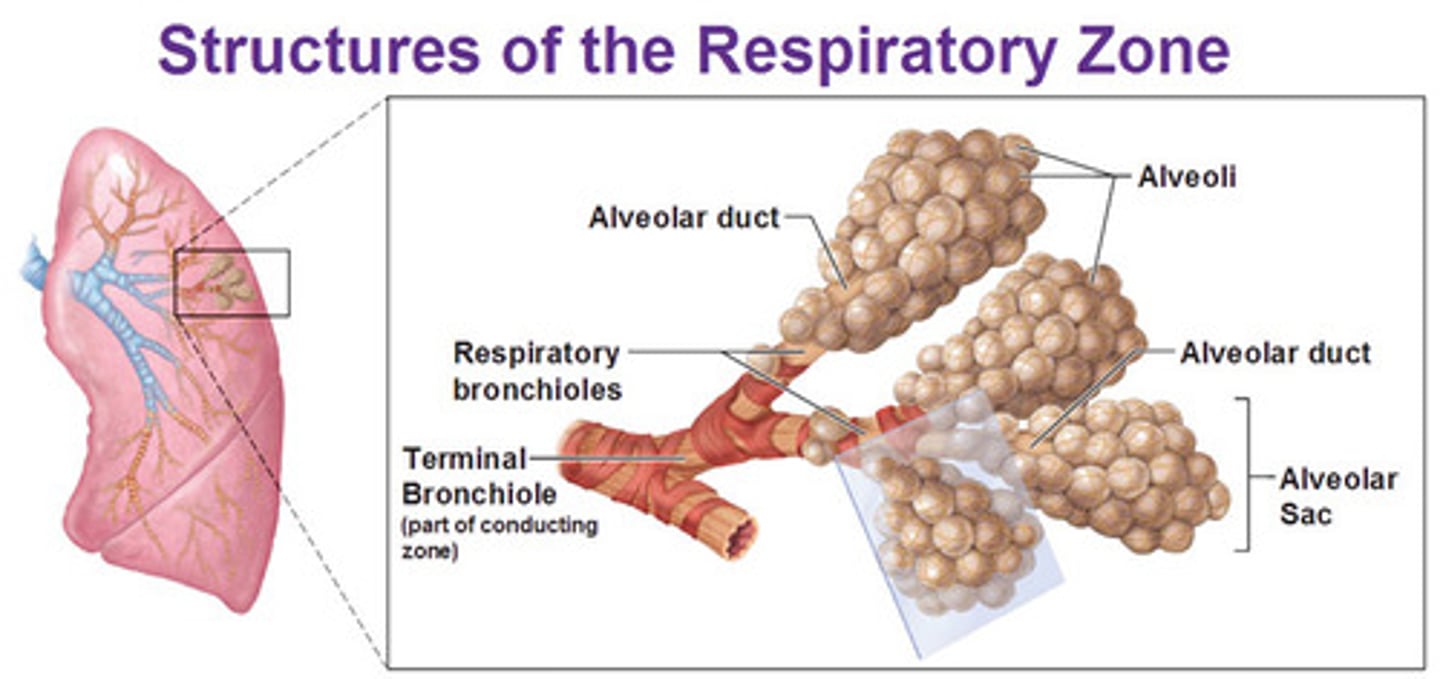
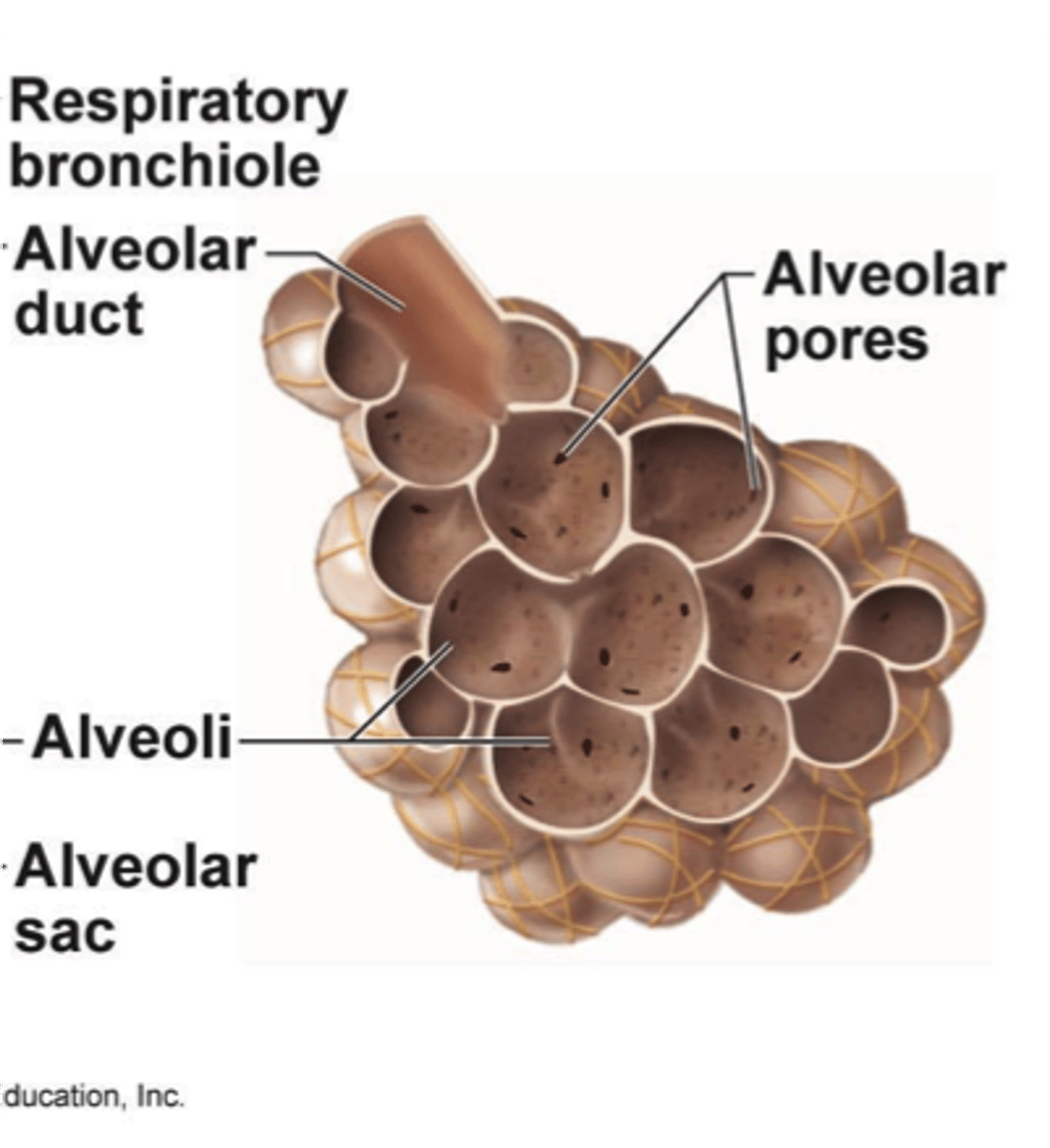
respiratory bronchioles
branches of the terminal bronchioles that subdivide into several alveolar ducts
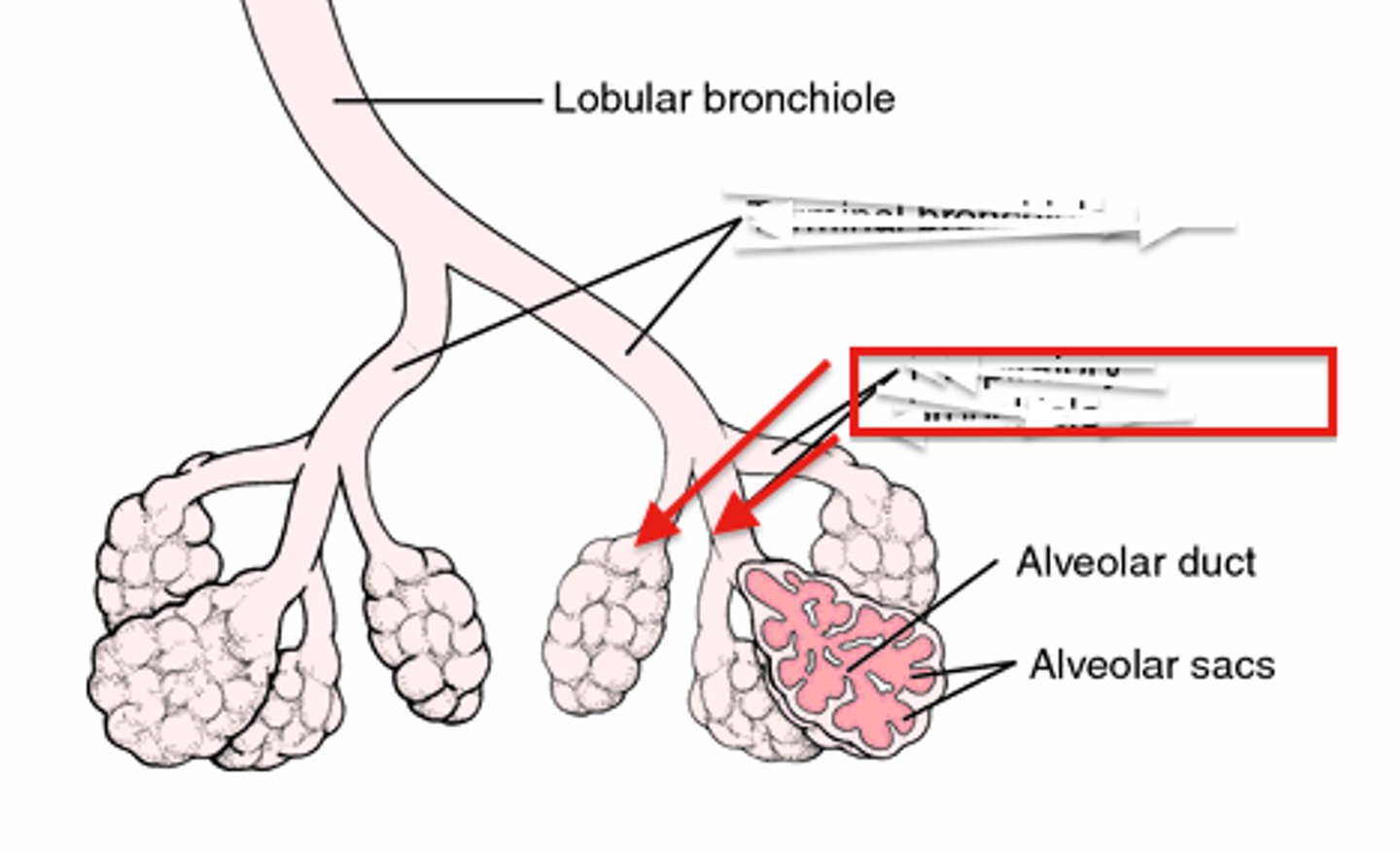
alveolar ducts
the subdivisions of the respiratory bronchioles, which terminate in the alveolar sacs that resemble clusters of grapes.
alveolar sacs
two or more alveoli that share a common duct or opening
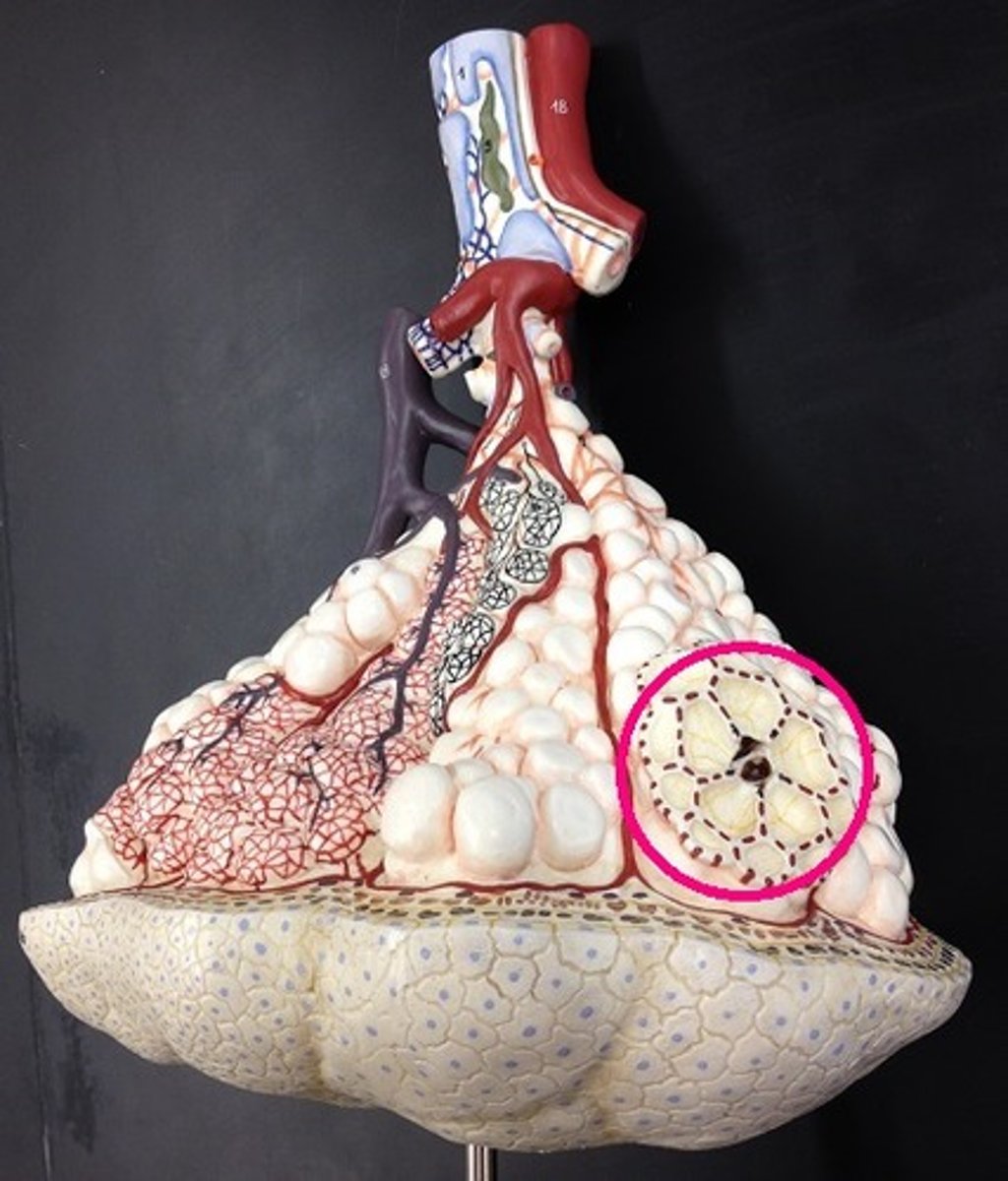
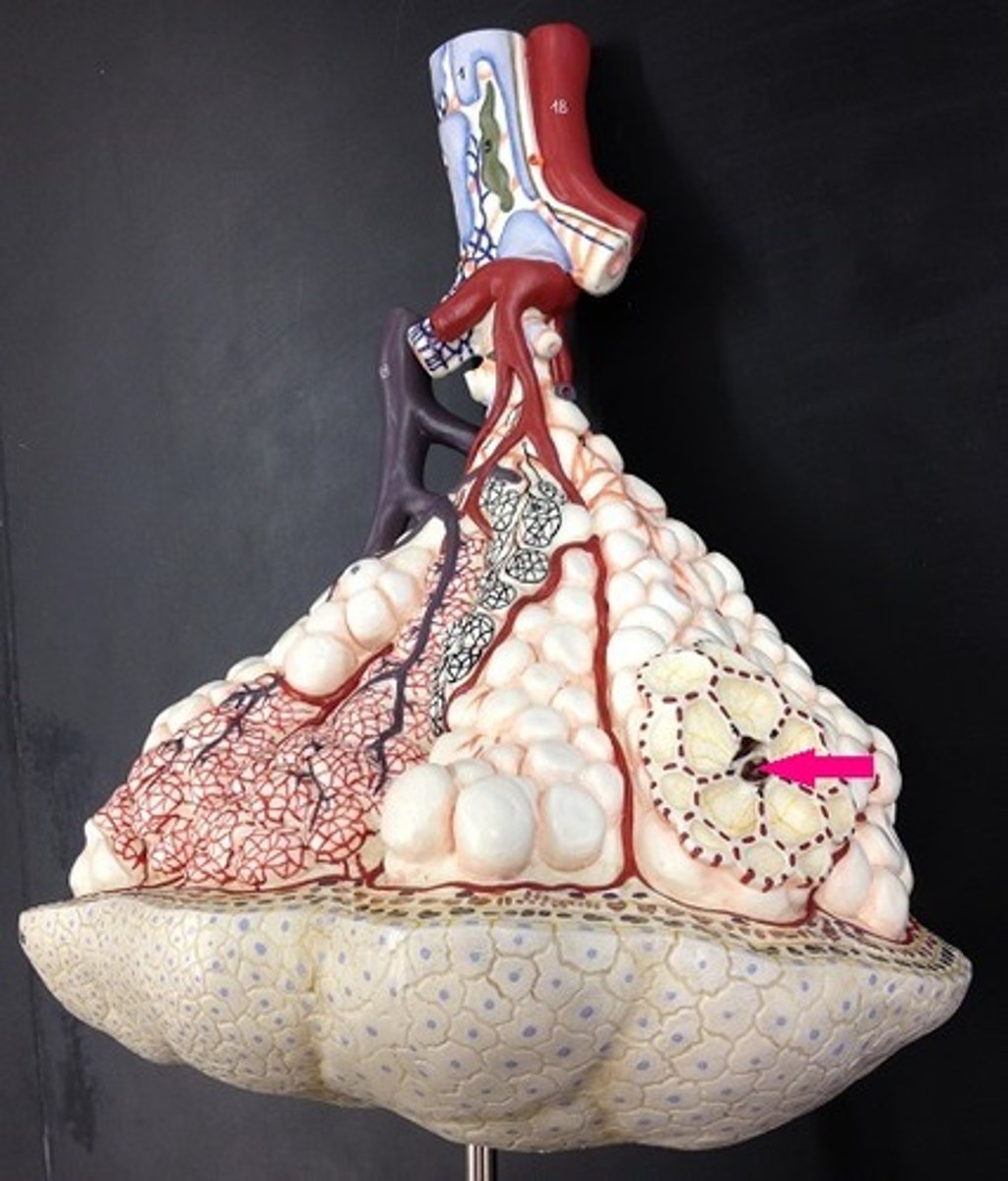
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
alveolar pores
Small opening in the wall of an air sac that permits air to pass from one alveolus to another
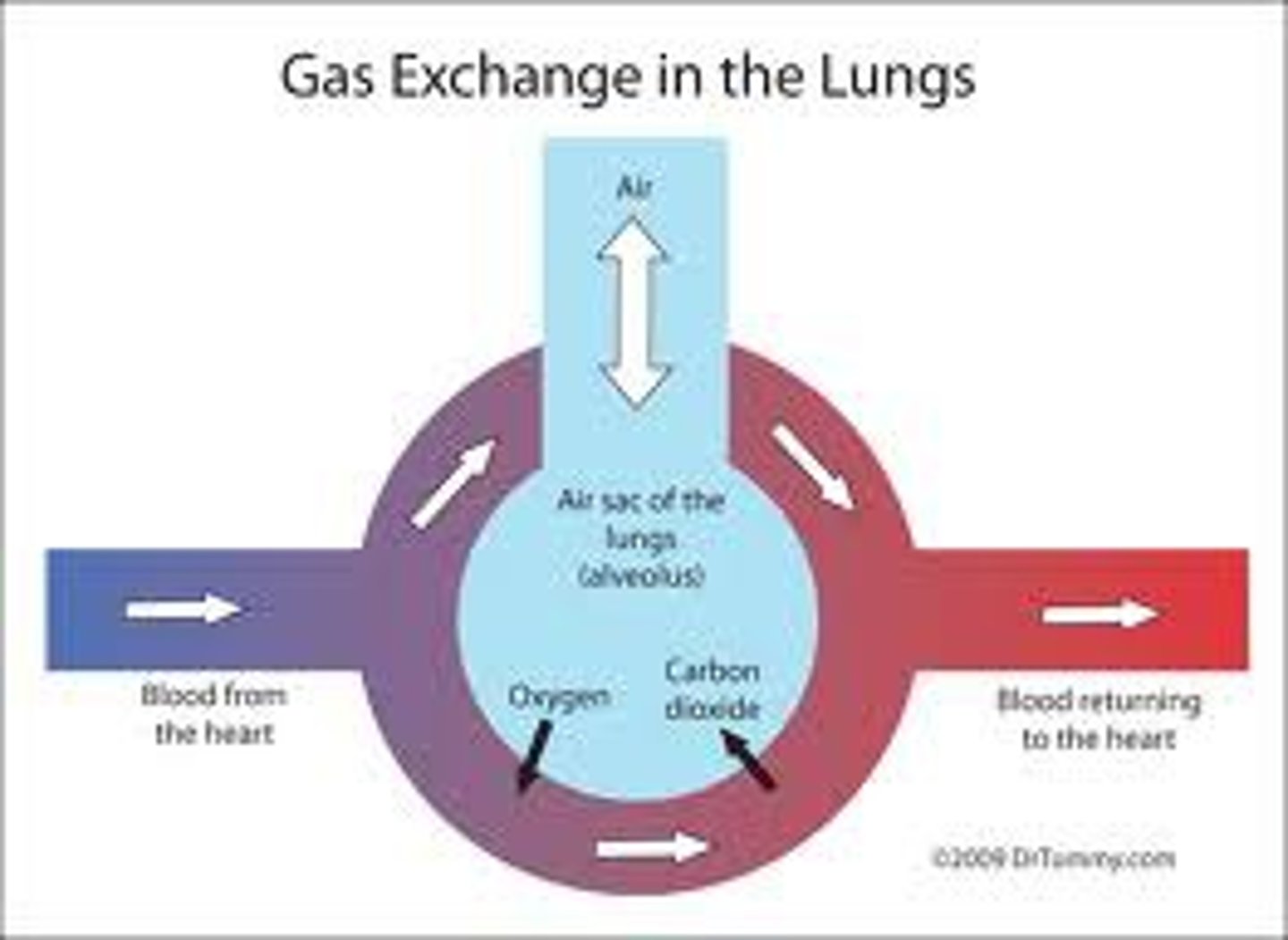
gas exchange
the process of obtaining oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide
pulmonary circuit
system of blood vessels that carries blood between the heart and the lungs
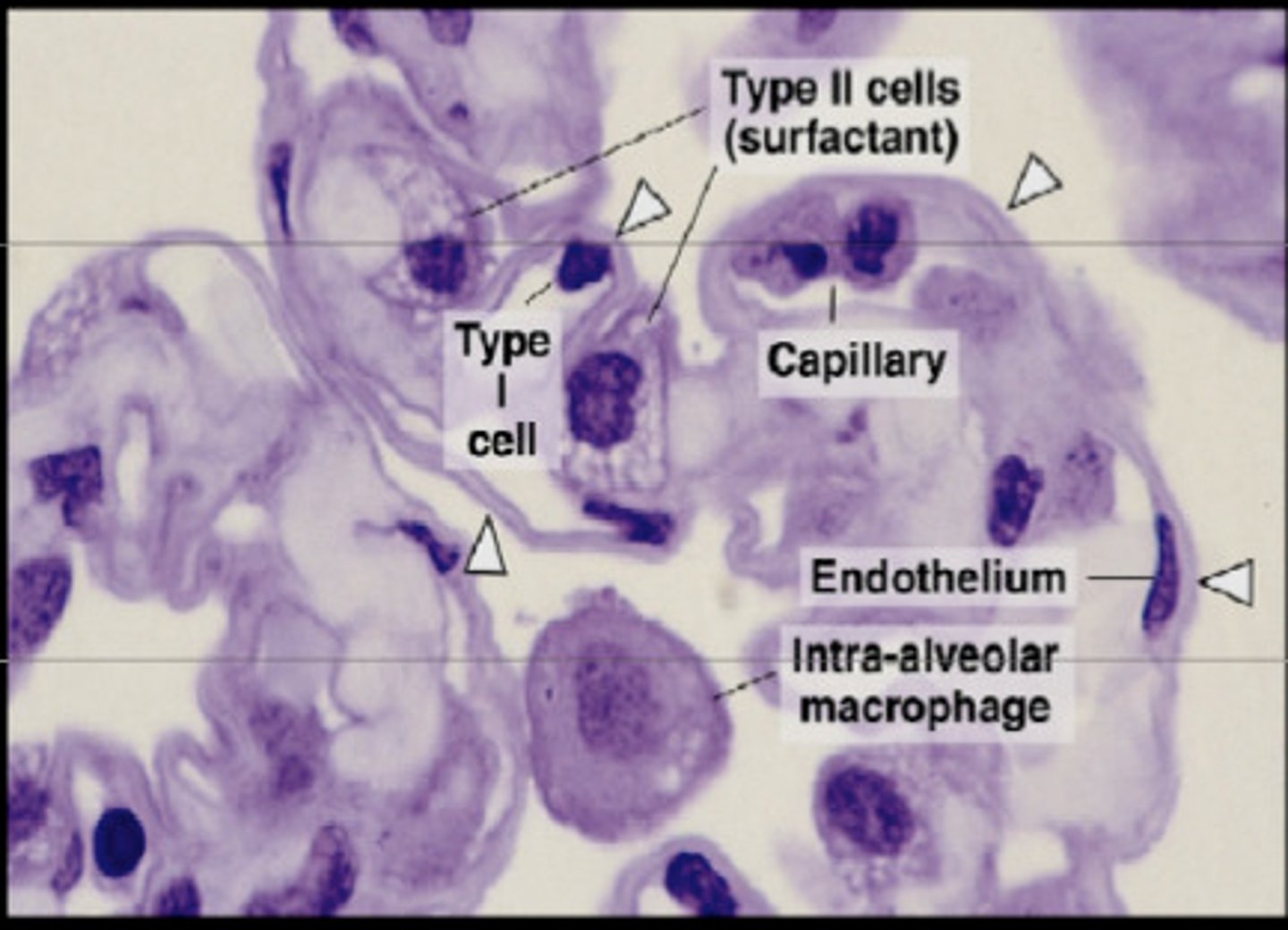
Type I alveolar cells
allow rapid diffusion of gases through their thin membranes
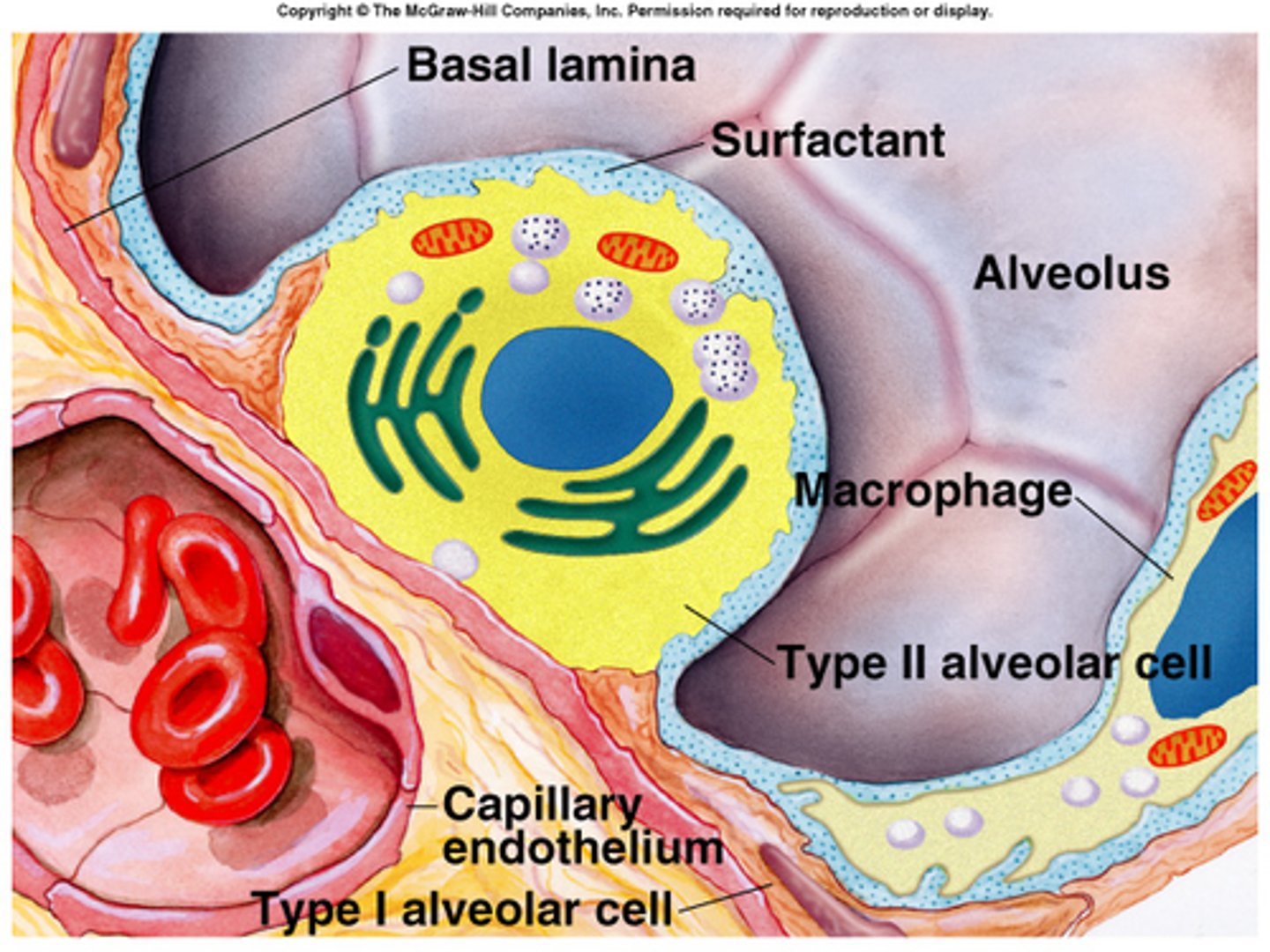
Type II alveolar cells
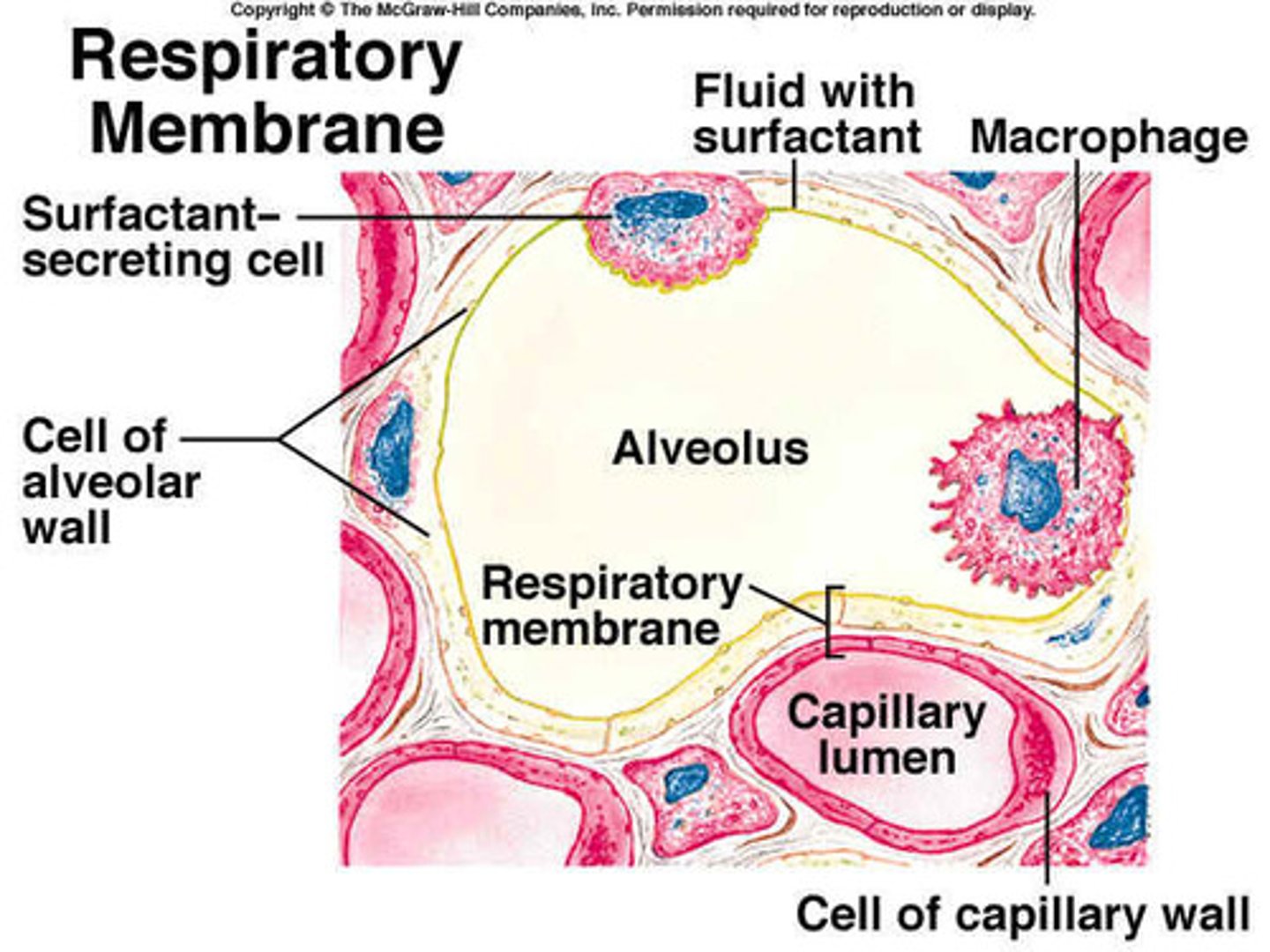
secrete a chemical known as surfactant.
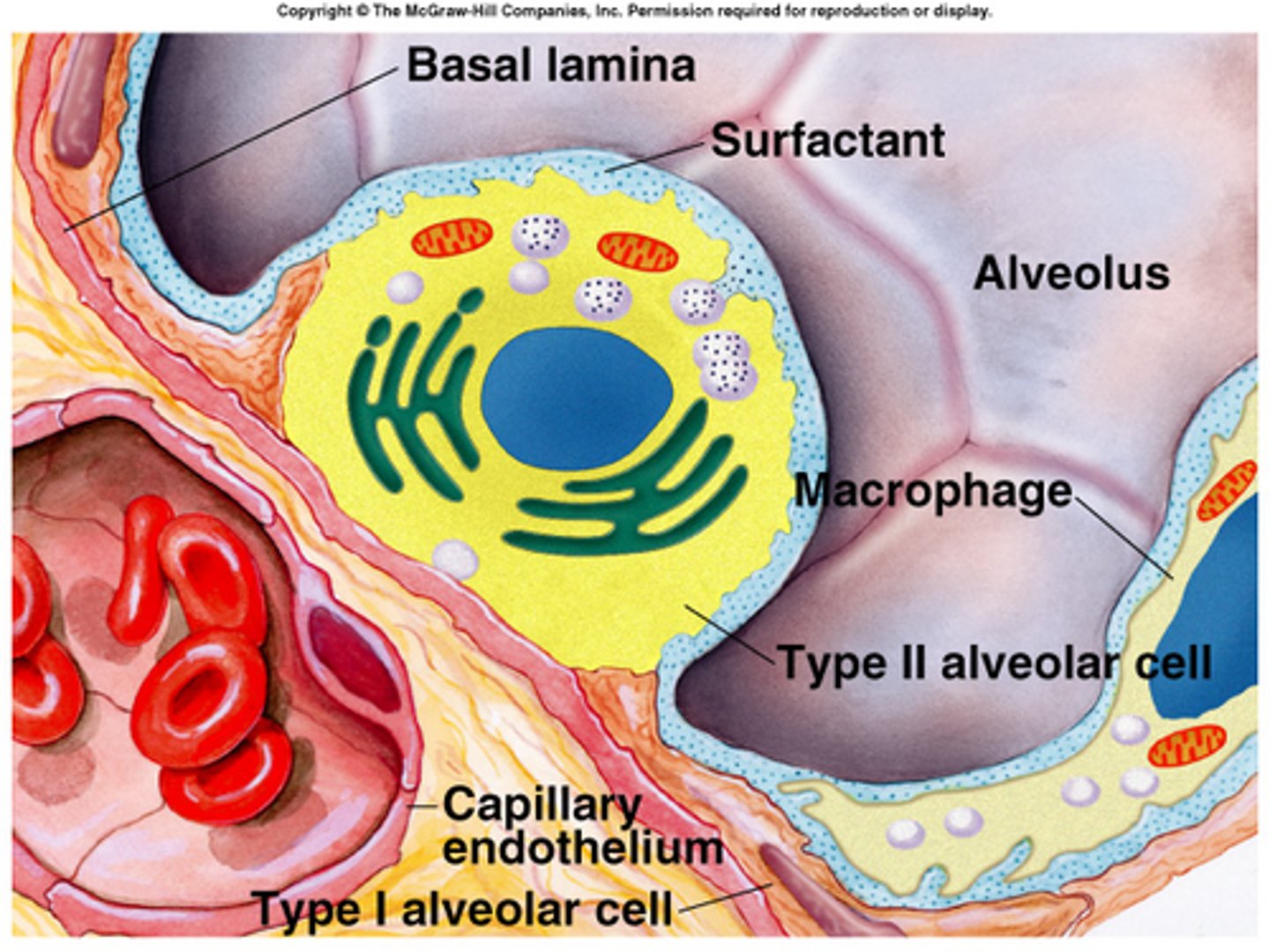
surfactant
any substance that interferes with the hydrogen bonding between water molecules and thereby reduces surface tension
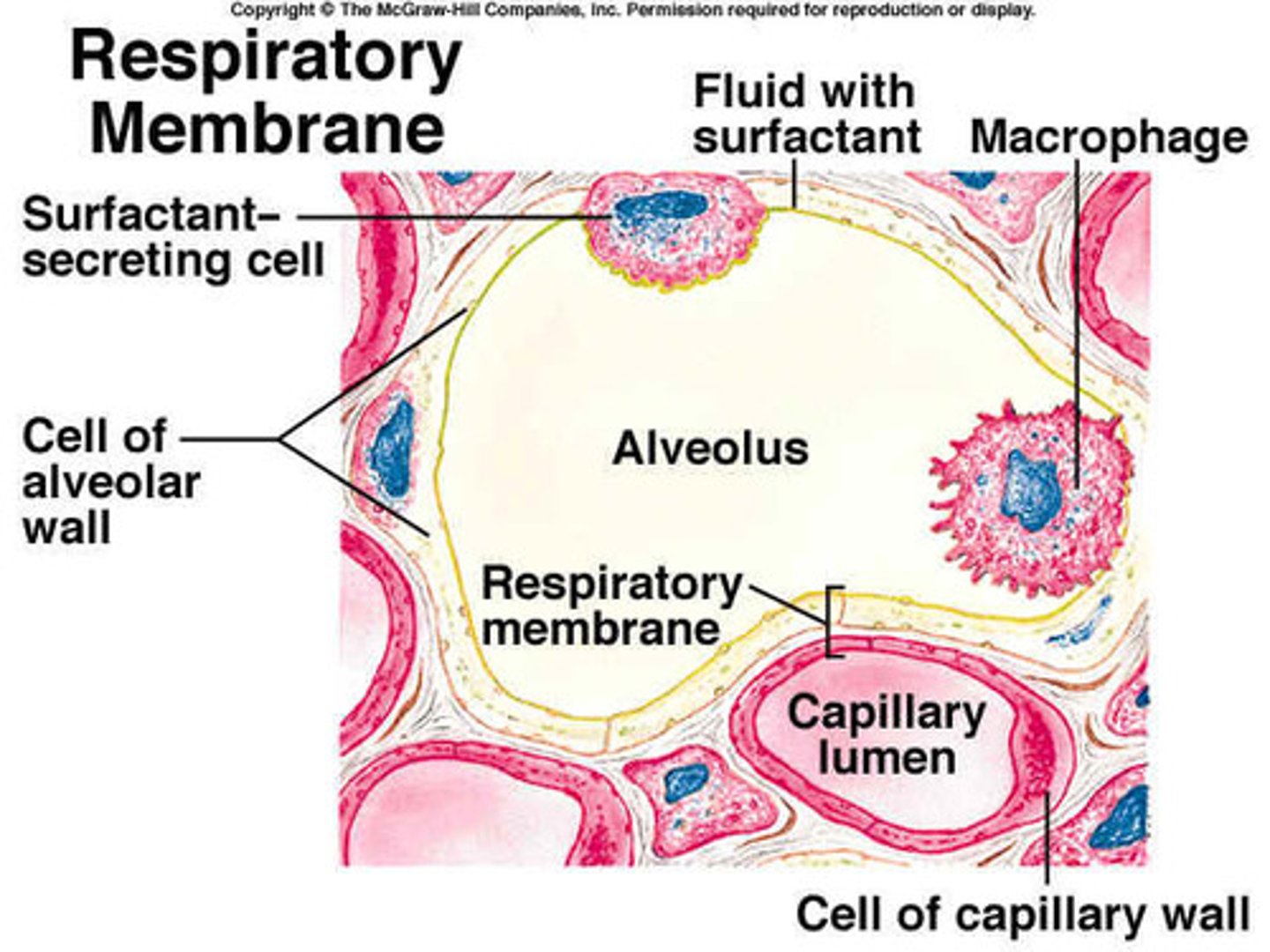
alveolar macrophages
dust cells
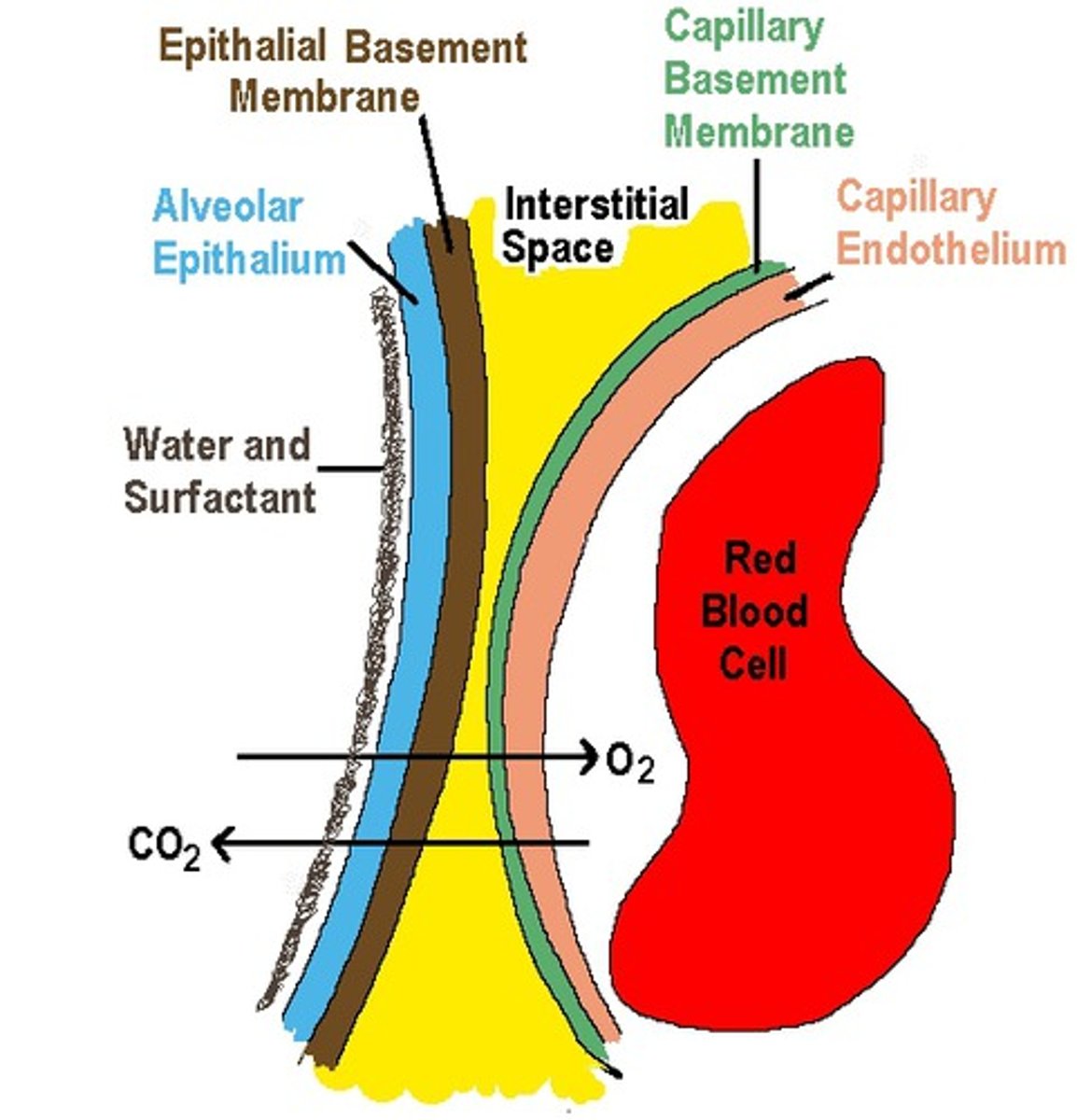
respiratory membrane
the barrier between the alveolar air and blood
thoracic cavity
cavity housing lungs and heart
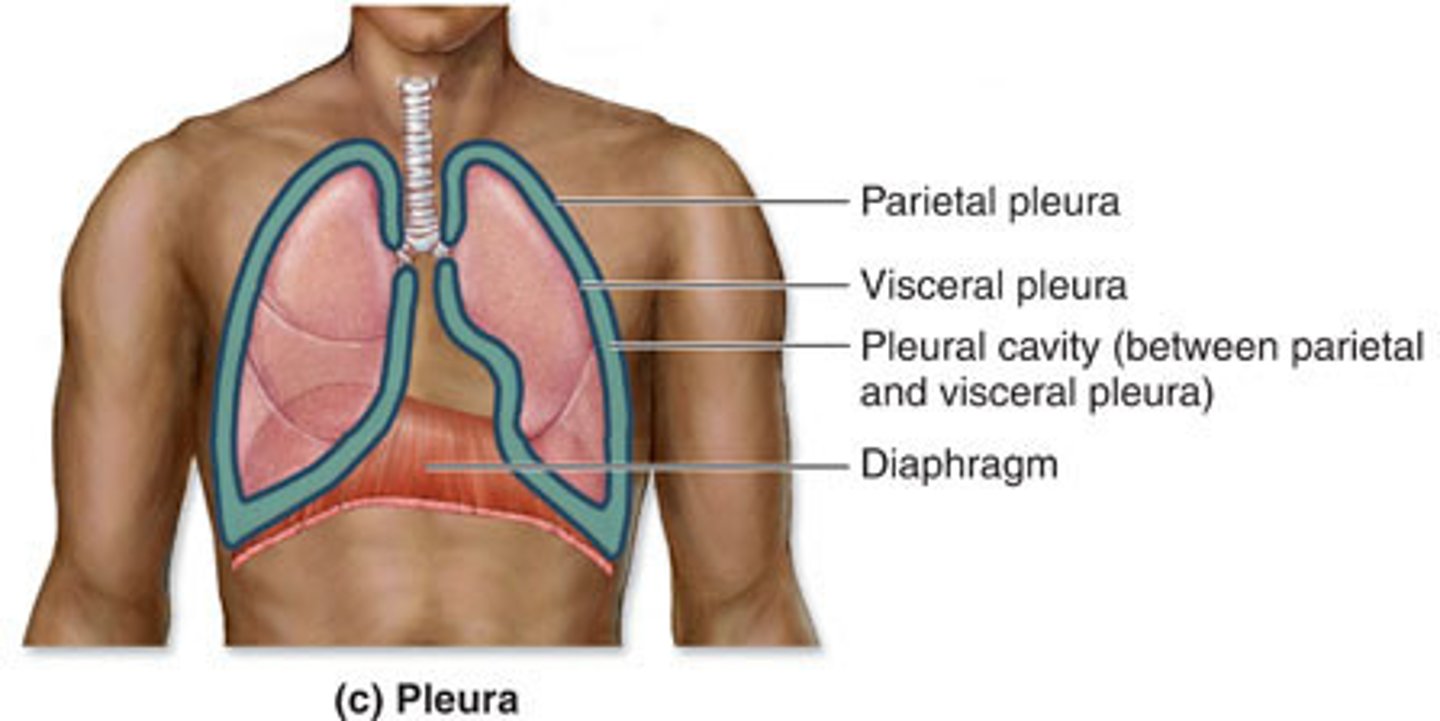
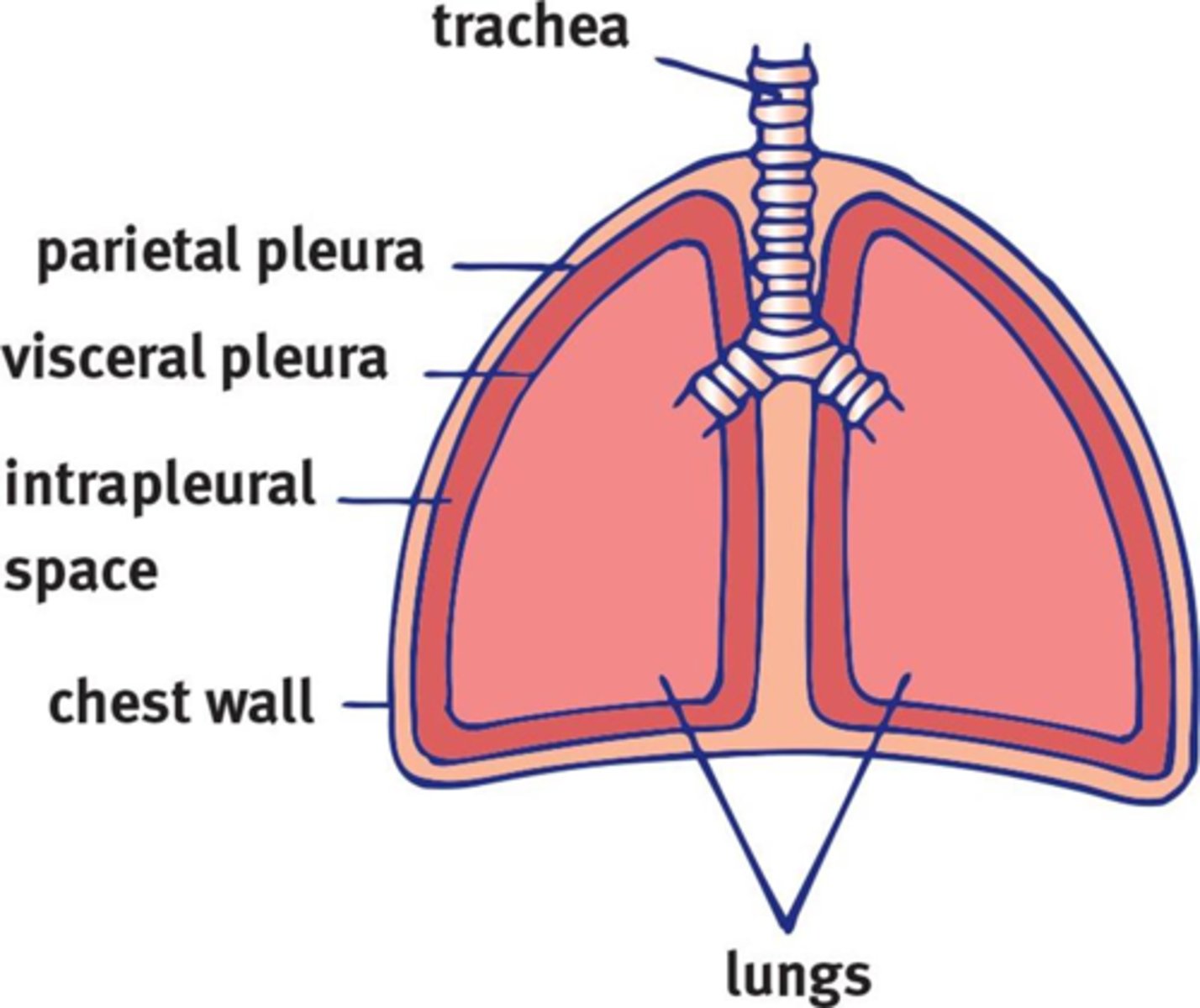
pleura
double-layered membrane surrounding each lung
pleural sac
the thin, double-walled serous membrane that surrounds the lungs
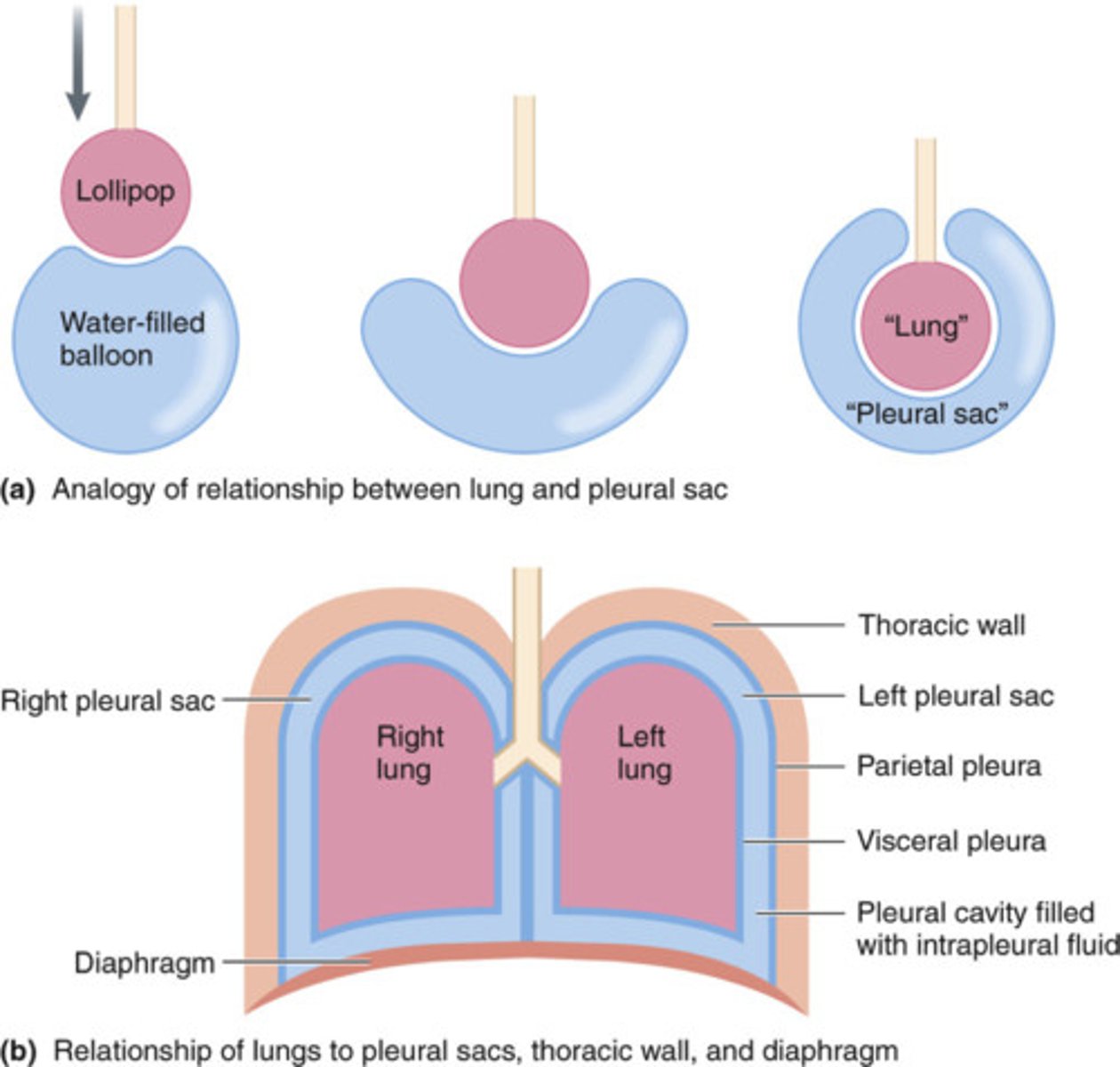
visceral pleura
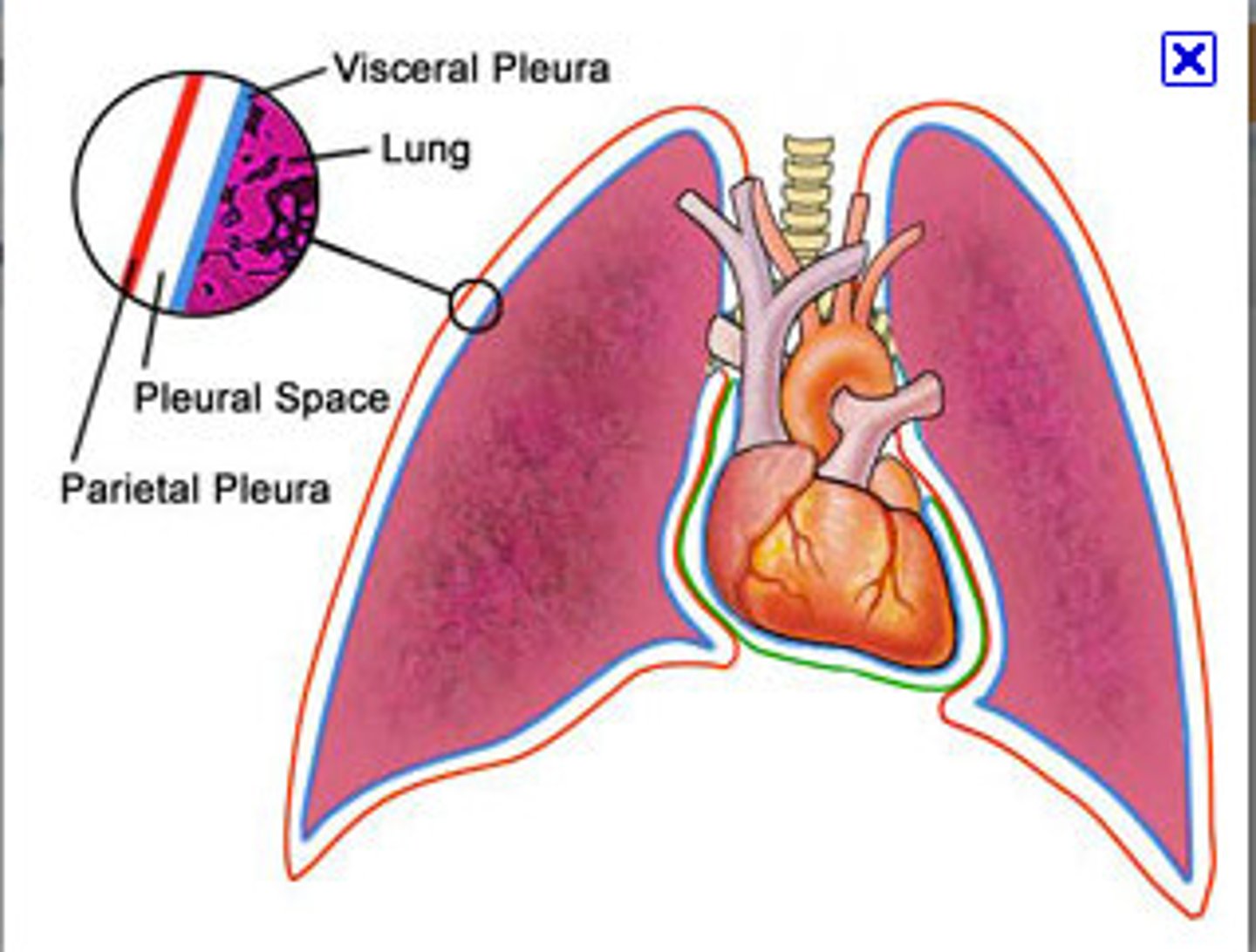
parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall
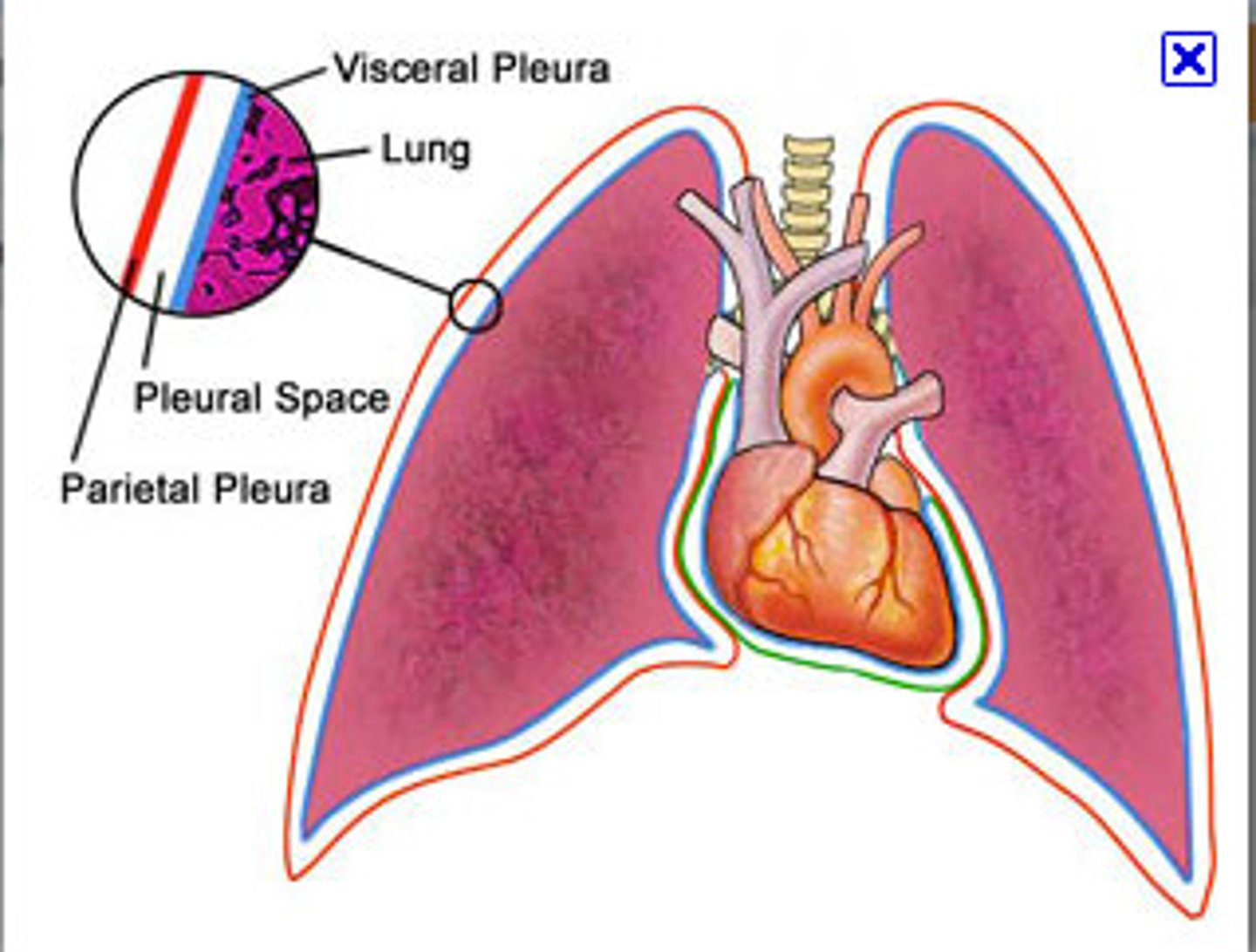
intrapleural space
Space between the two membranes, visceral pleura and parietal pleura, that cover the lungs.
pressure gradients
-difference between atmospheric and intrapulmonary pressure
-created by changes in volume of thoracic cavity
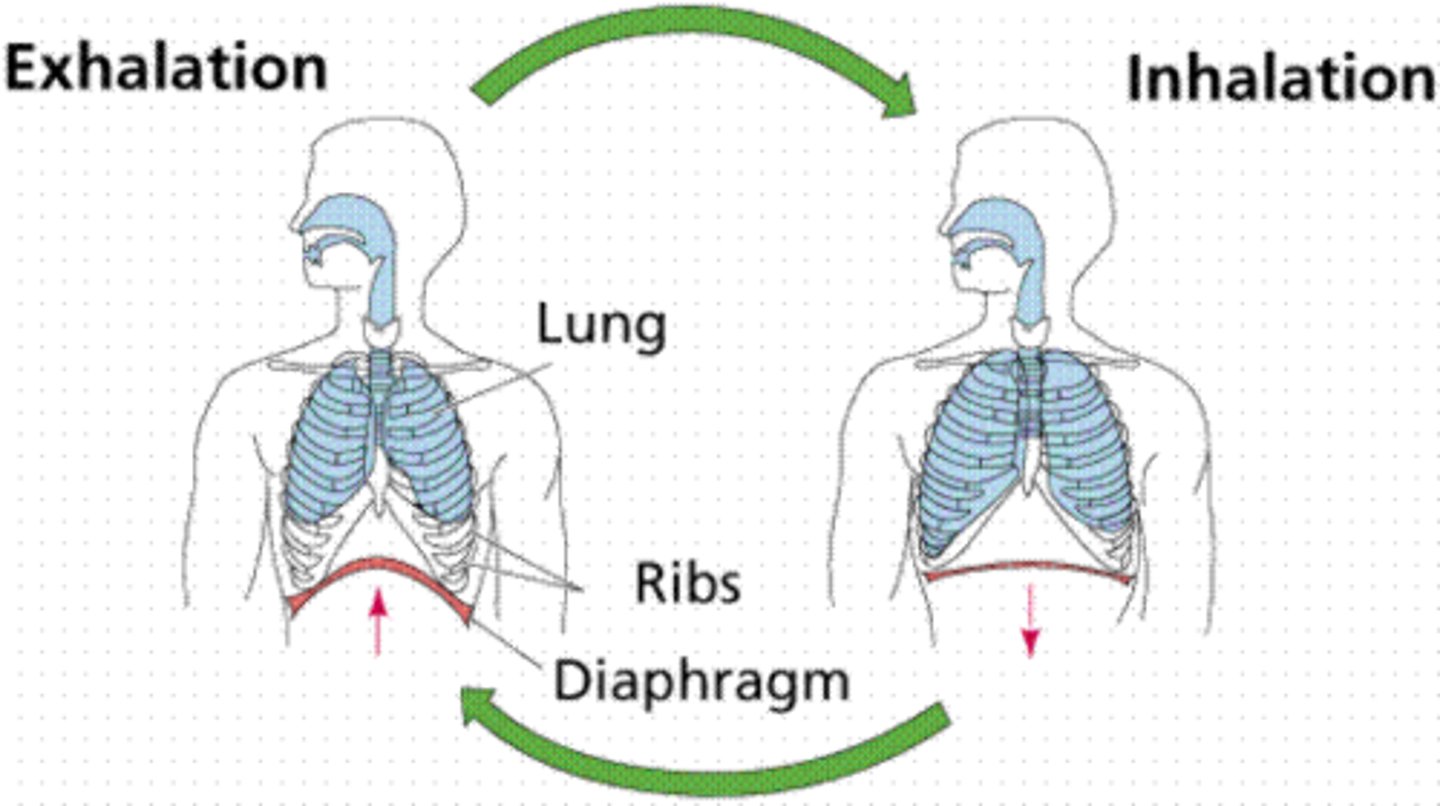
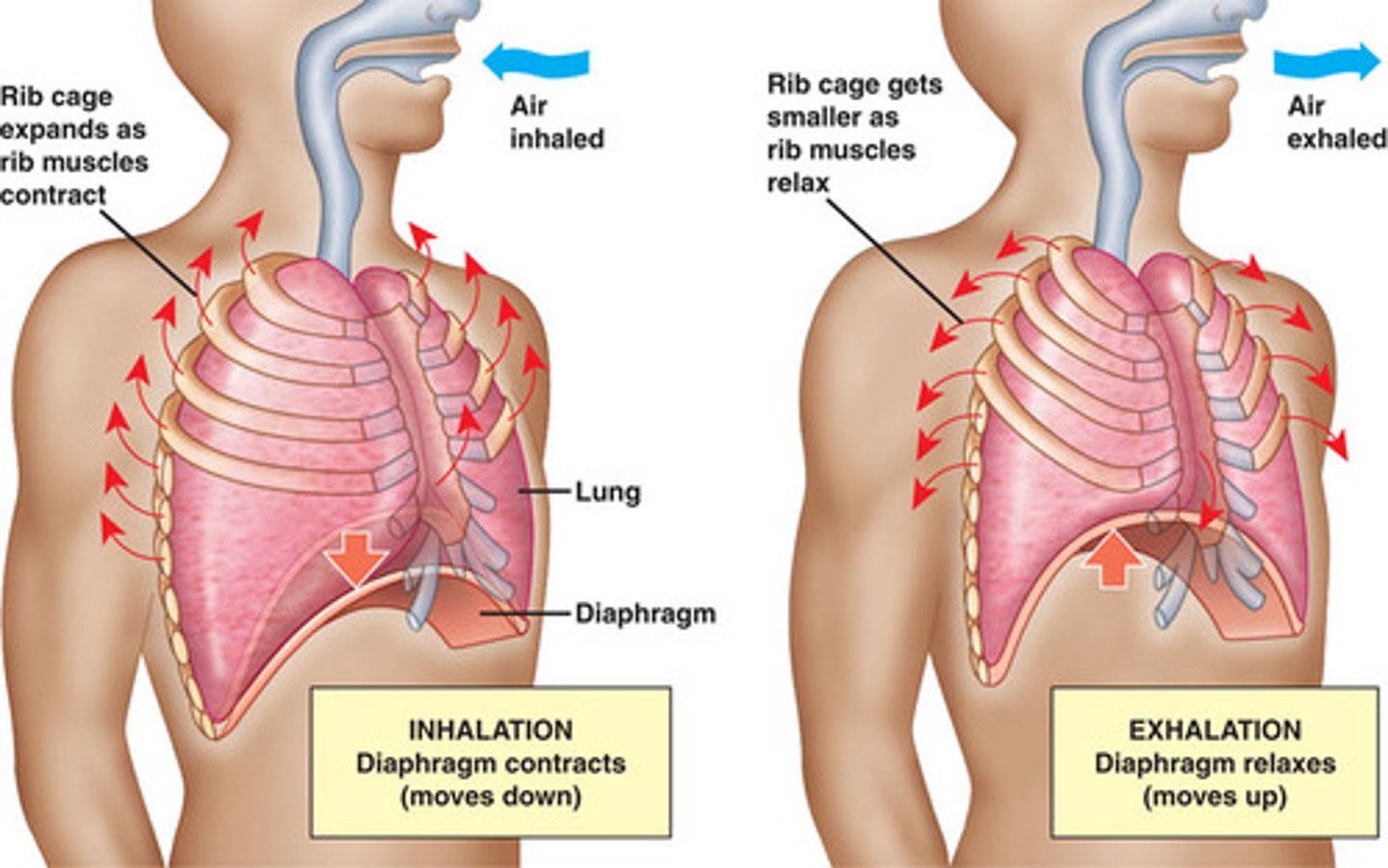
inspiration (inhalation)
breathing air into the lungs
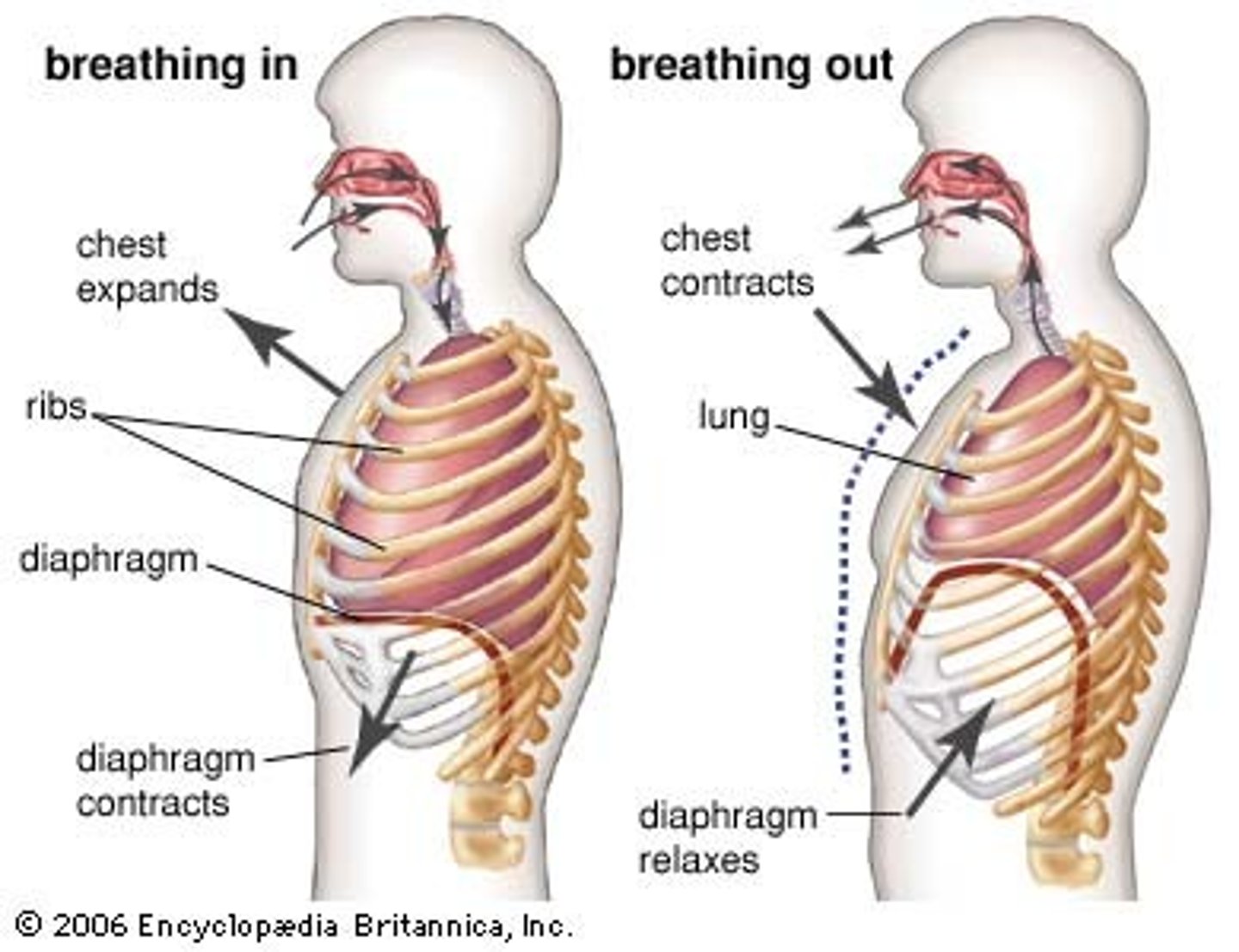
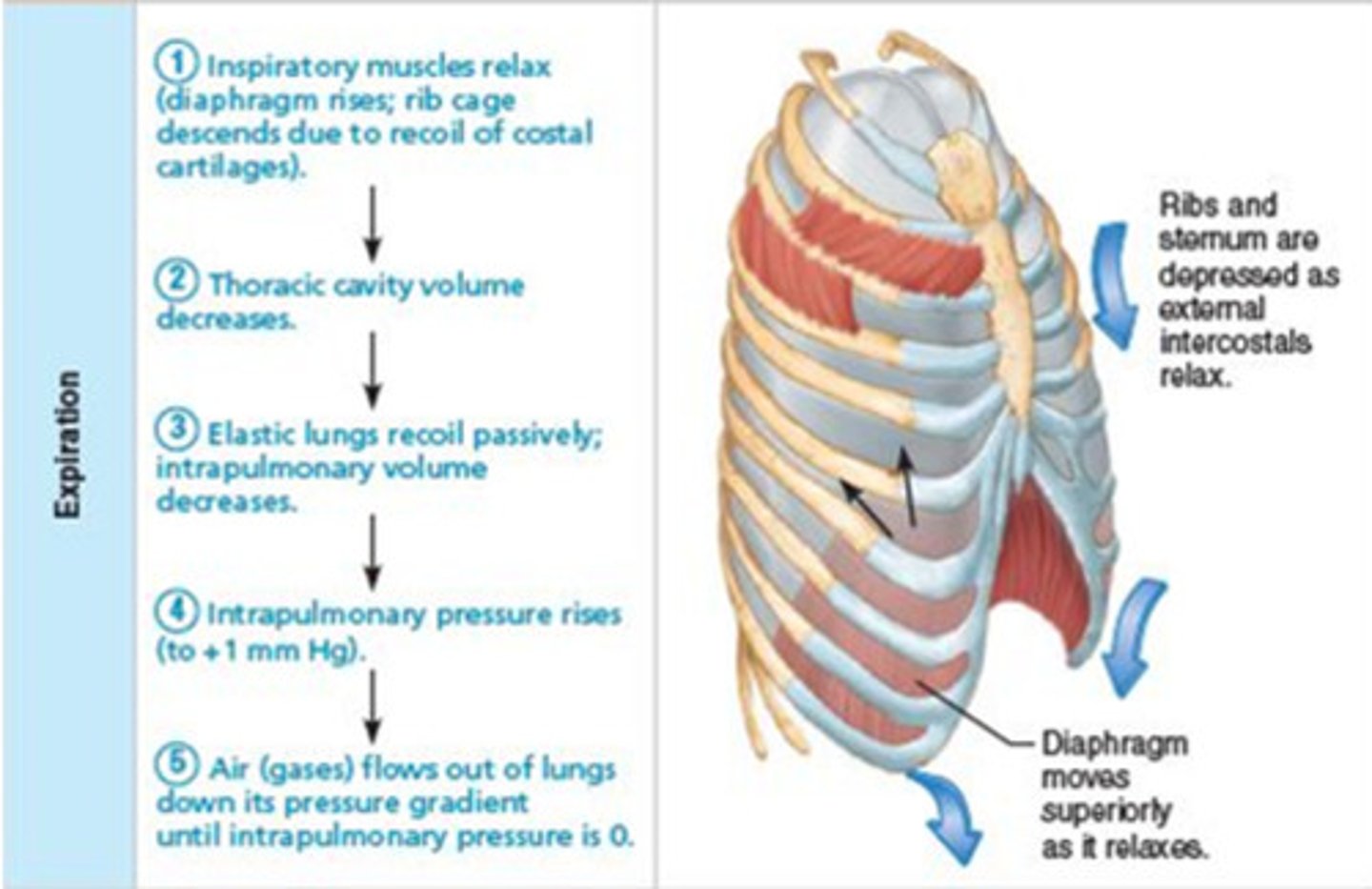
expiration (exhalation)
breathing out, expelling air from lungs
atmospheric pressure (Patm)
pressure exerted by the air surrounding the body
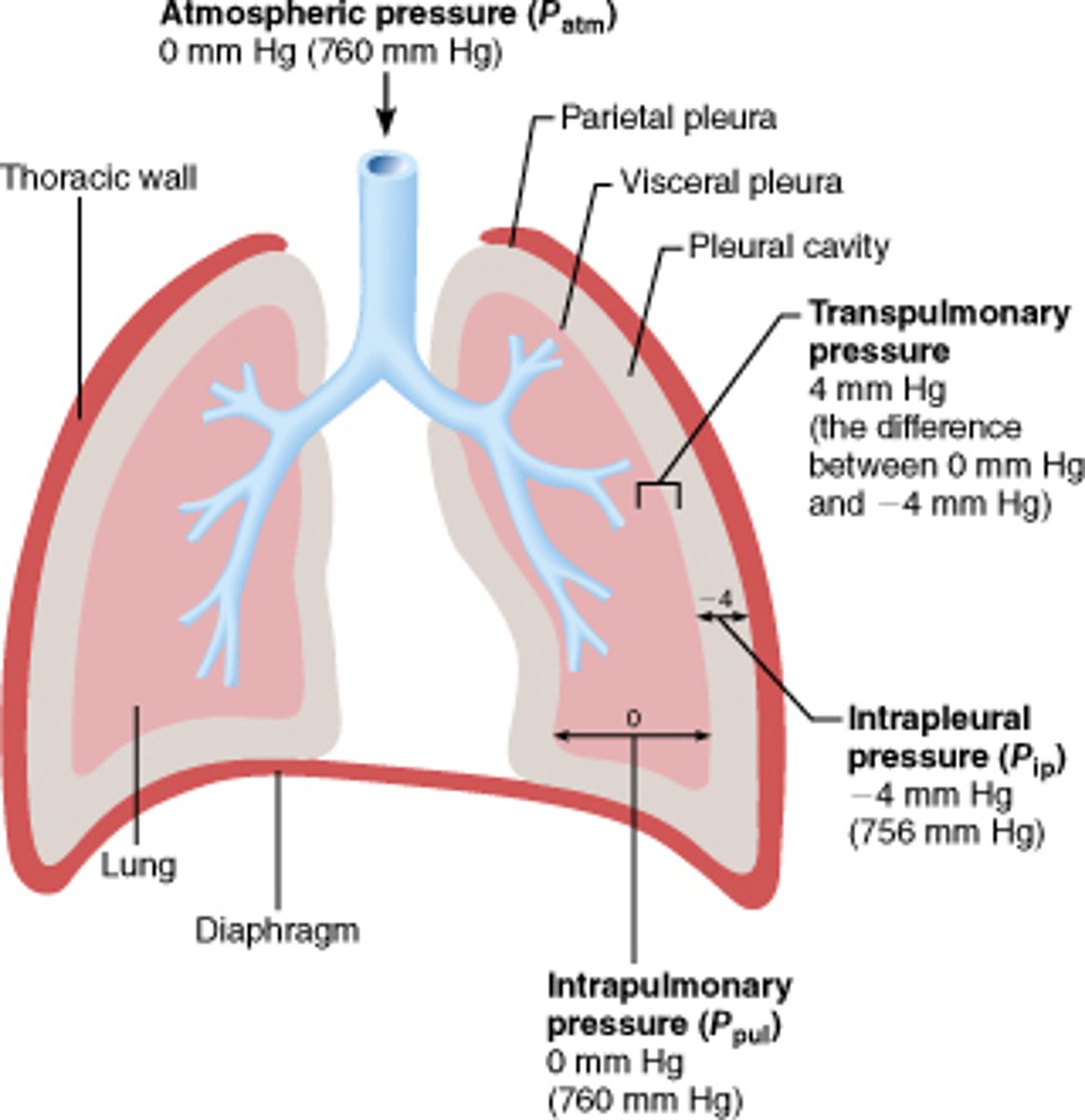
Intra-alveolar pressure (Palv)
pressure of the air in the alveoli; varies with each phase of respiration
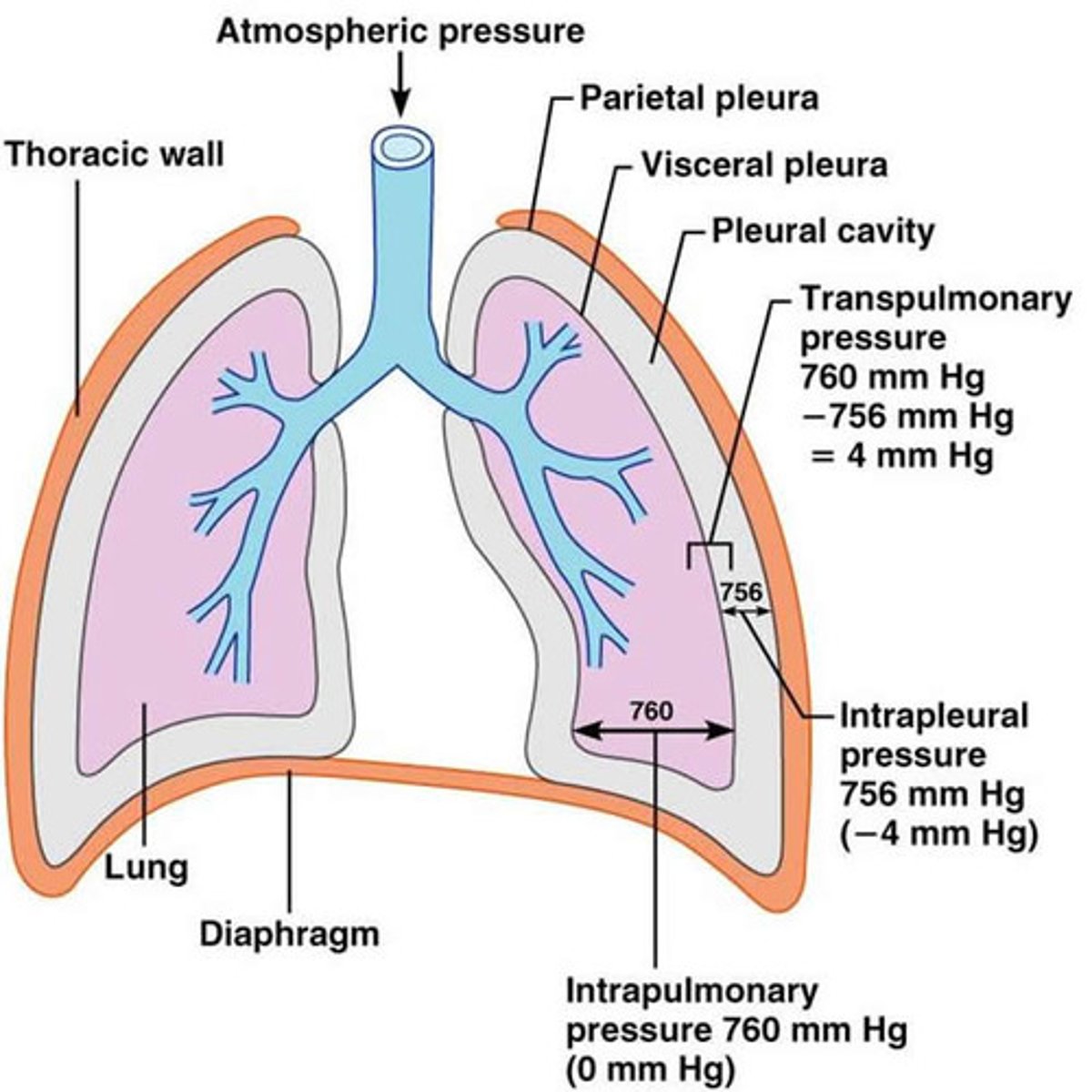
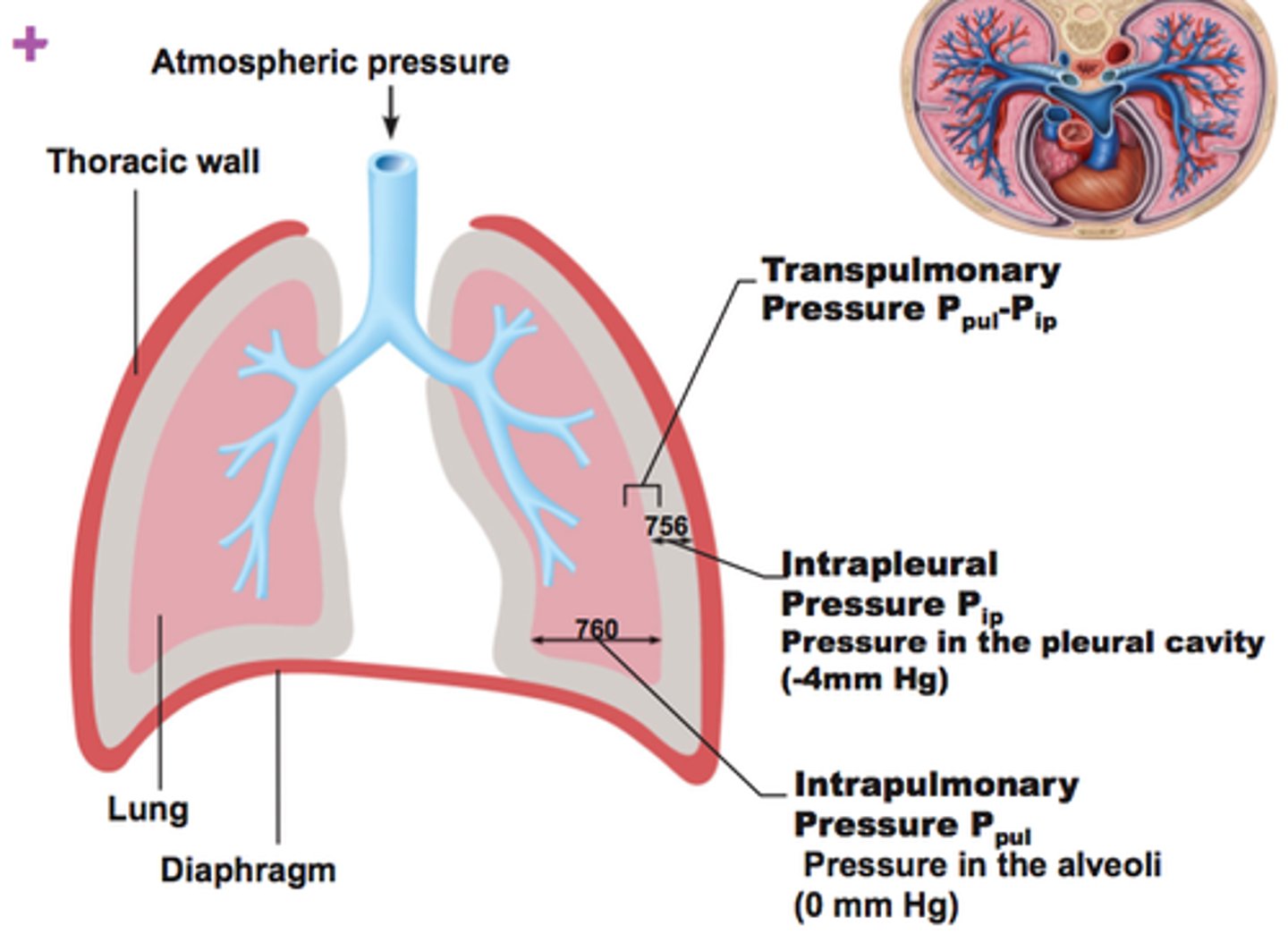
Intrapleural pressure (Pip)
pressure within the pleural cavity
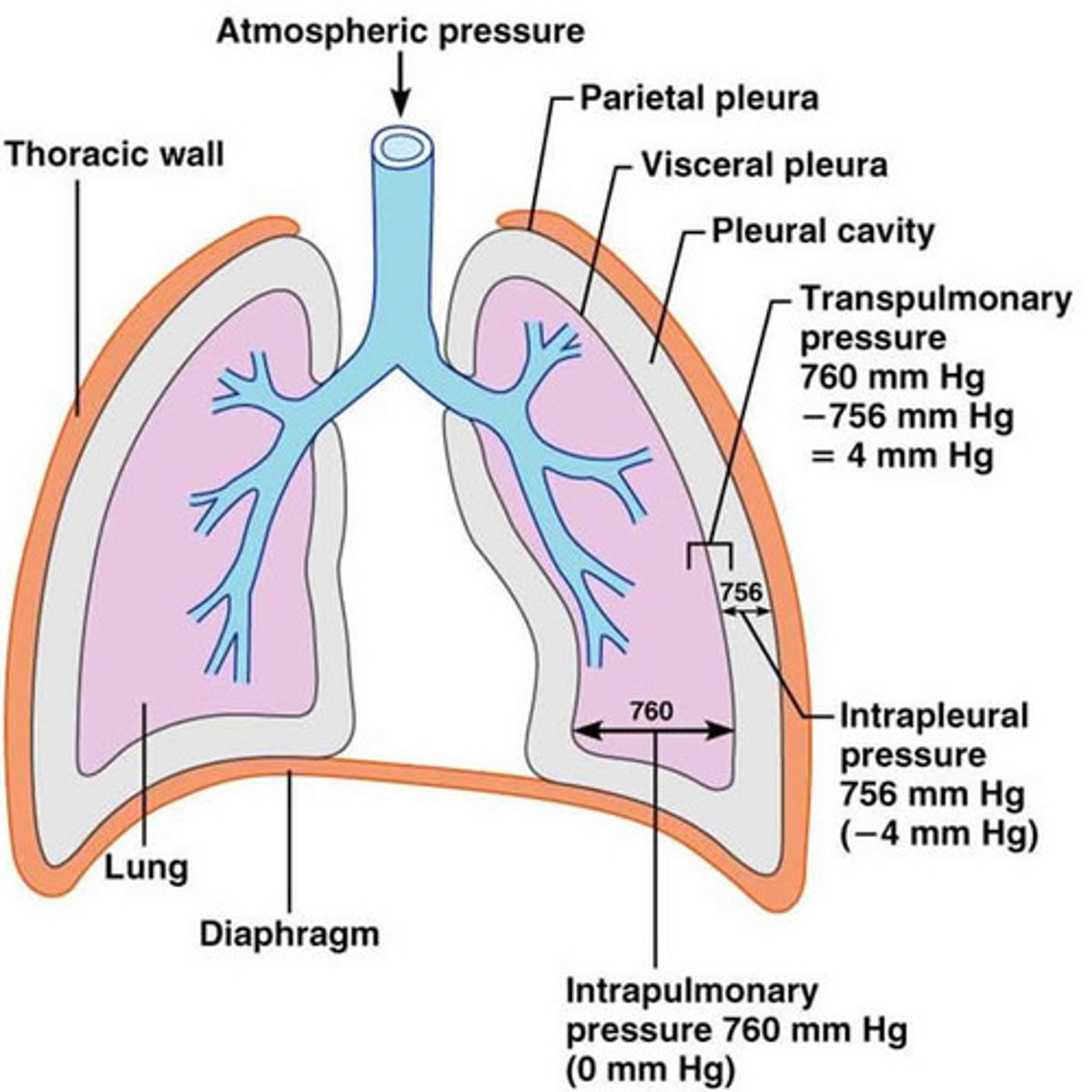
transpulmonary pressure
difference between intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressure
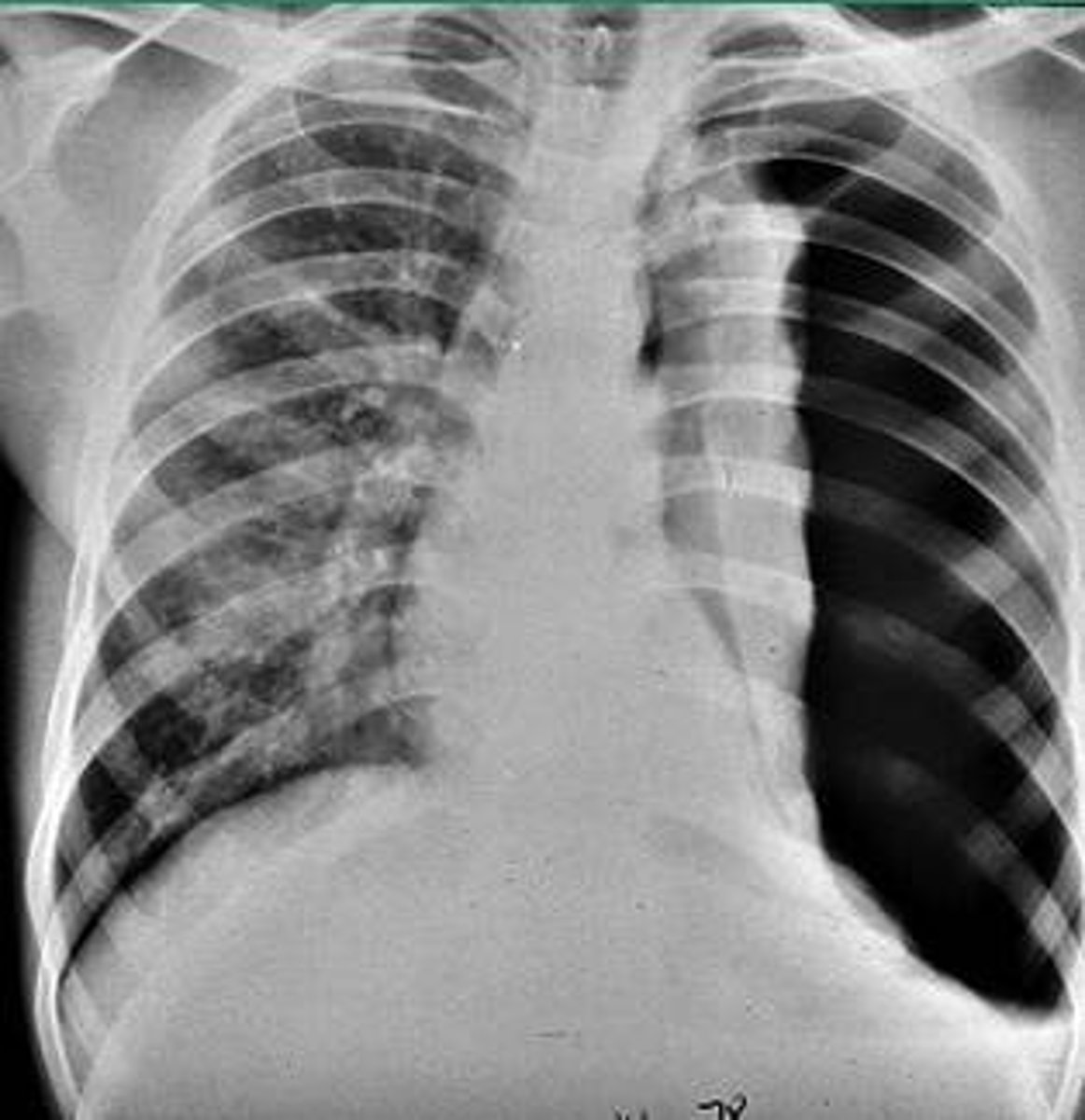
pneumothorax
air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall
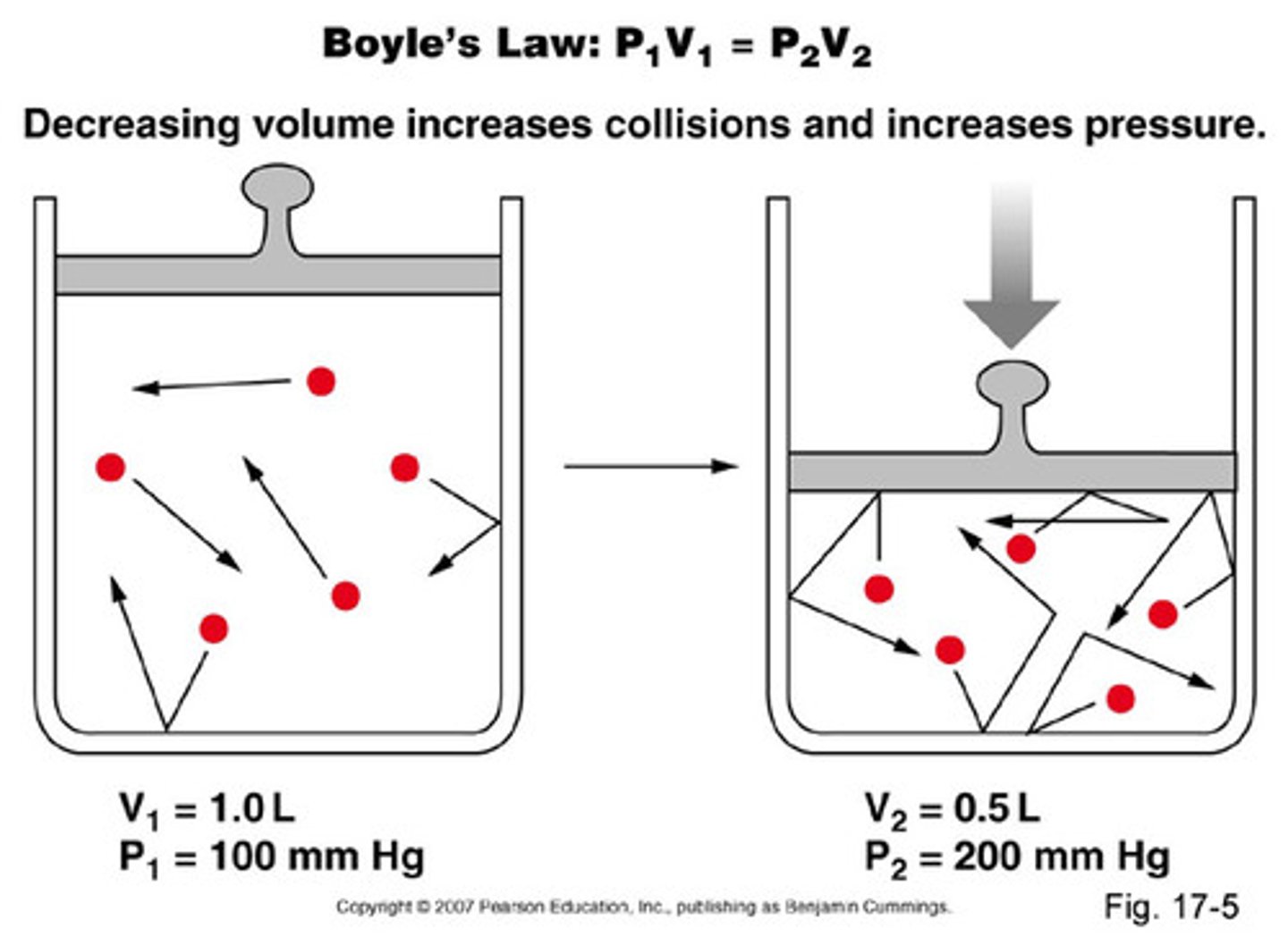
Boyle's Law
A principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature
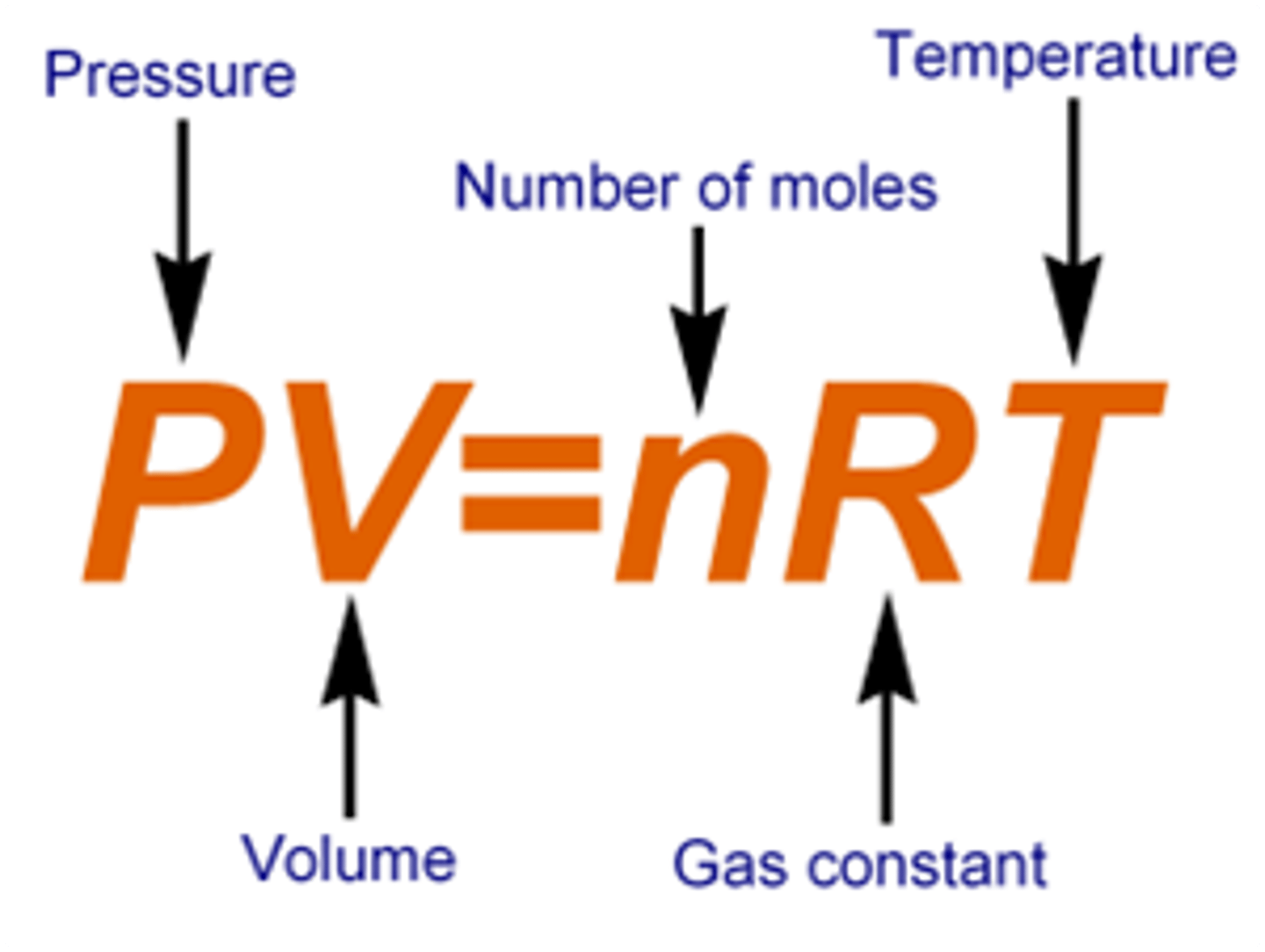
ideal gas law
the relationship PV=nRT, which describes the behavior of an ideal gas
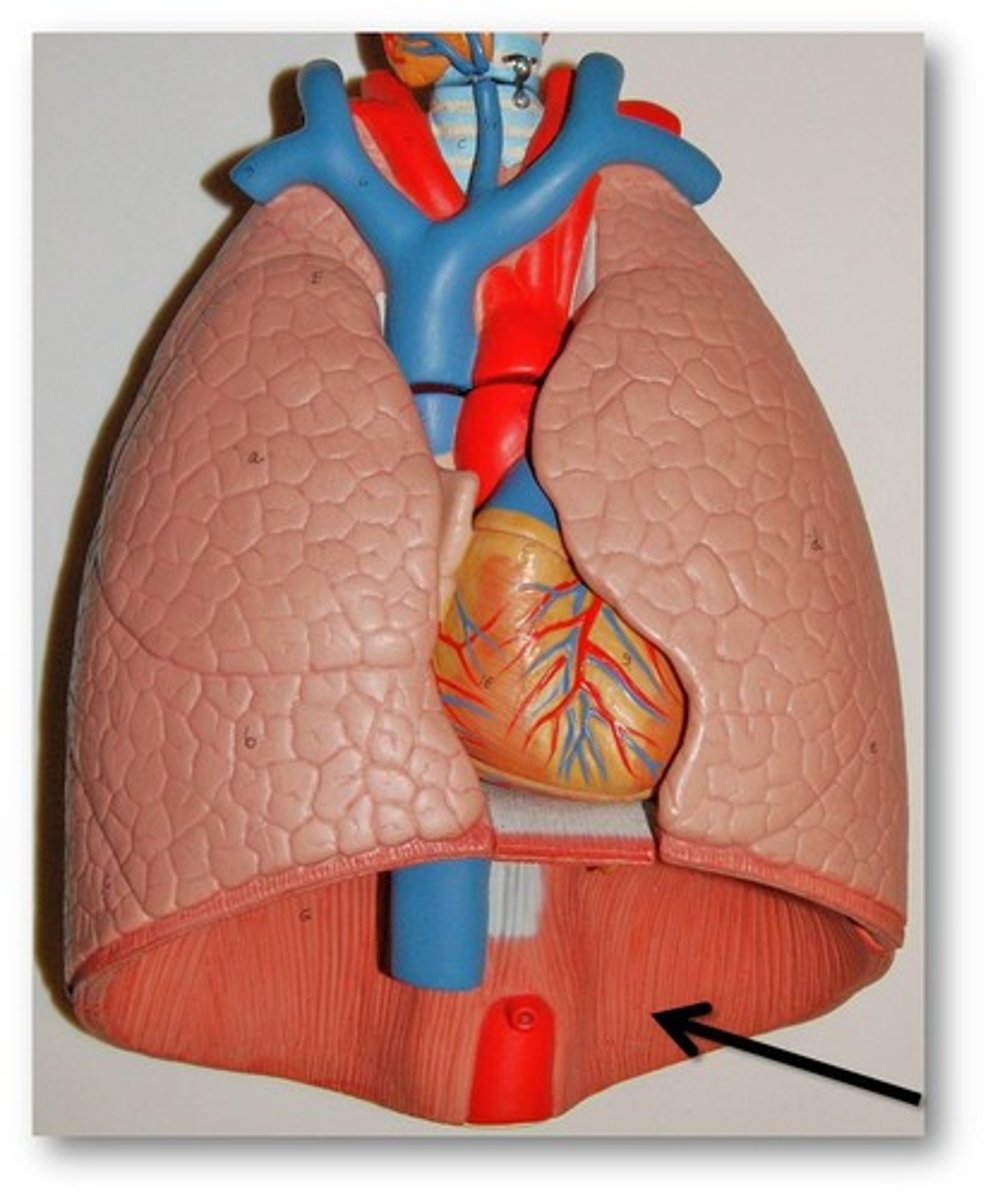
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
external intercostals
elevates ribs during inspiration
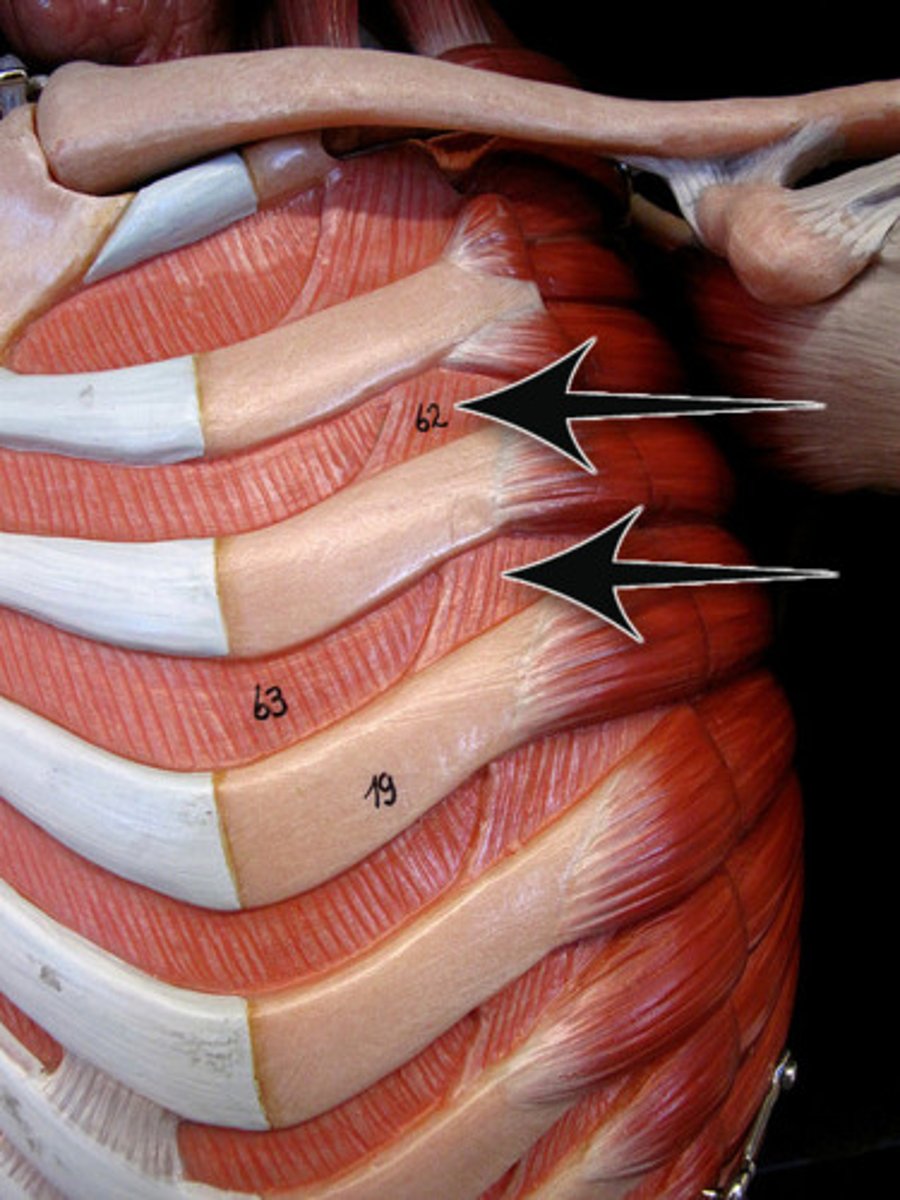
internal intercostals
depresses ribs
resistance
the resistance of the respiratory tract to airflow during inhalation and exhalation.
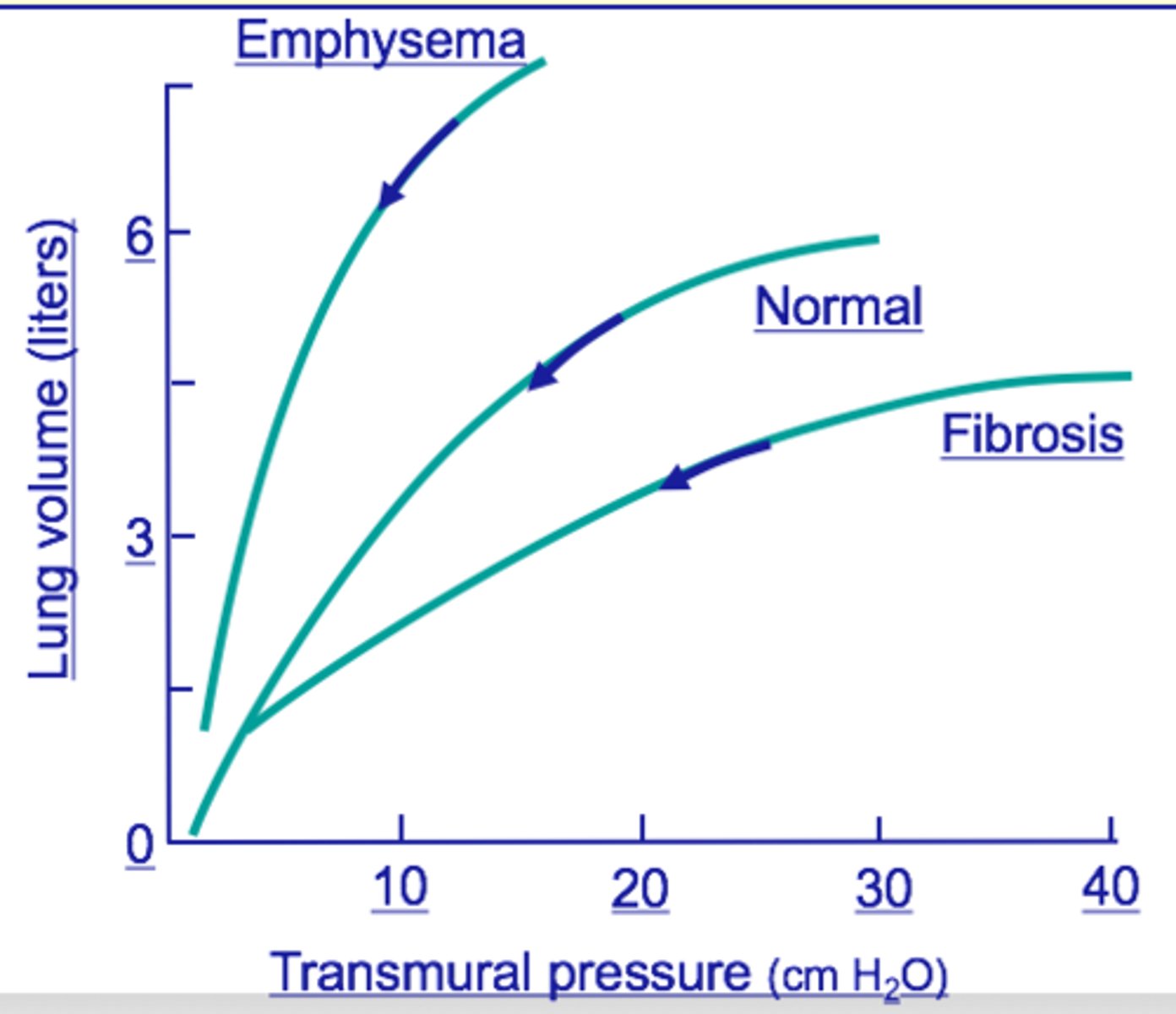
lung compliance
measure of change in lung volume that occurs with given change in trans pulmonary pressure
elasticity
the rebound of the lungs after having been stretched by inhalation, or rather, the ease with which the lung rebounds. With inhalation, the intrapleural pressure (the pressure within the pleural cavity) of the lungs decreases
surface tension of alveolar fluid
draws alveoli to their smallest possible size
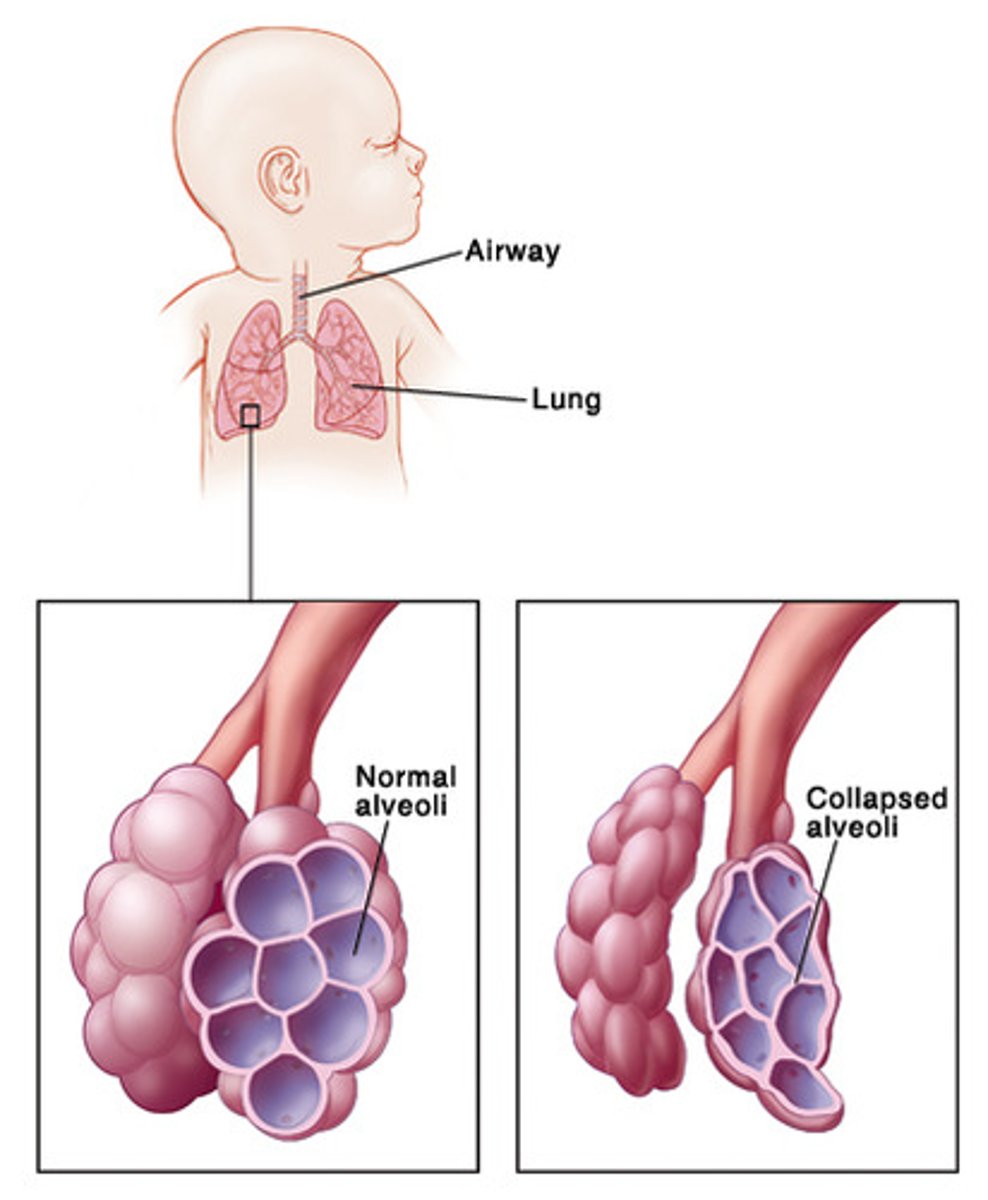
infant respiratory distress syndrome
lung condition most commonly found in premature infants that is characterized by tachypnea and respiratory grunting
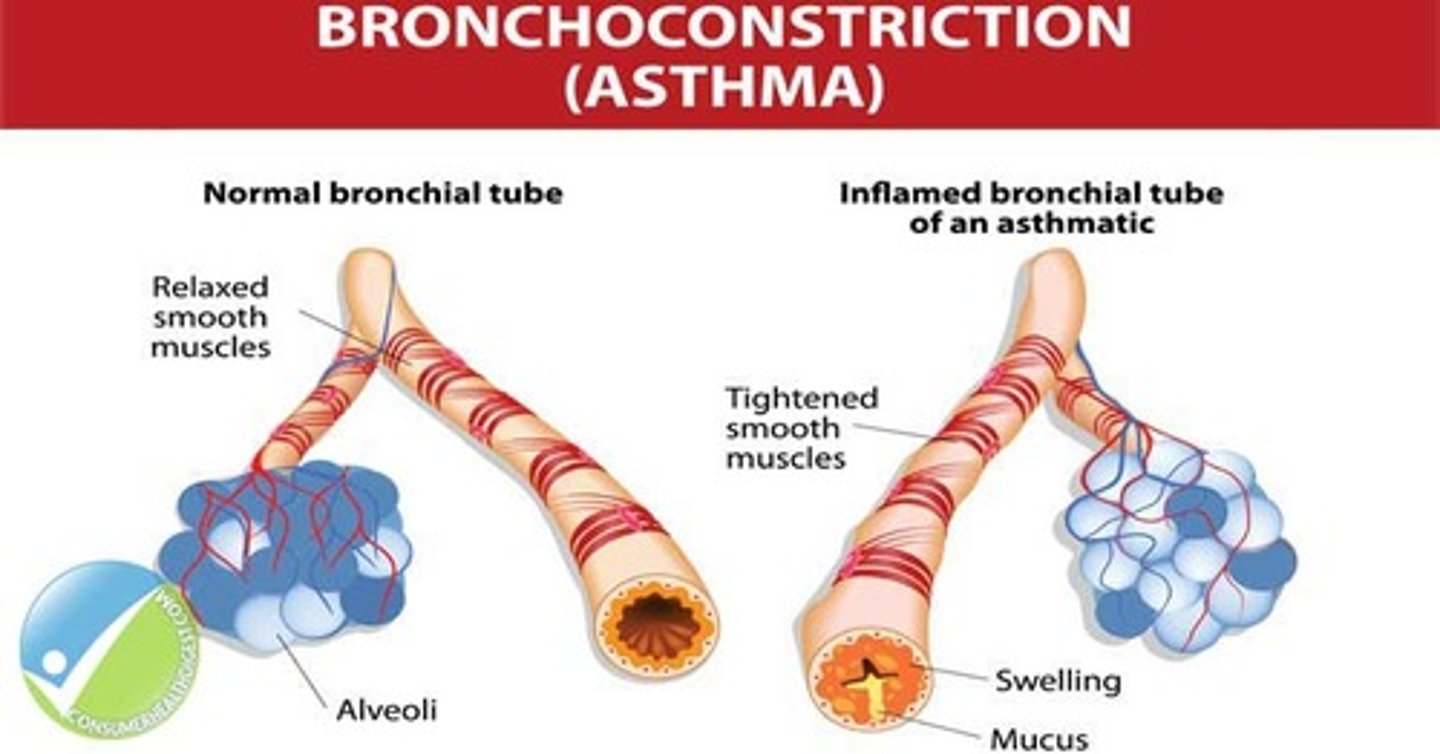
bronchoconstriction
reduction in diameter of a bronchus
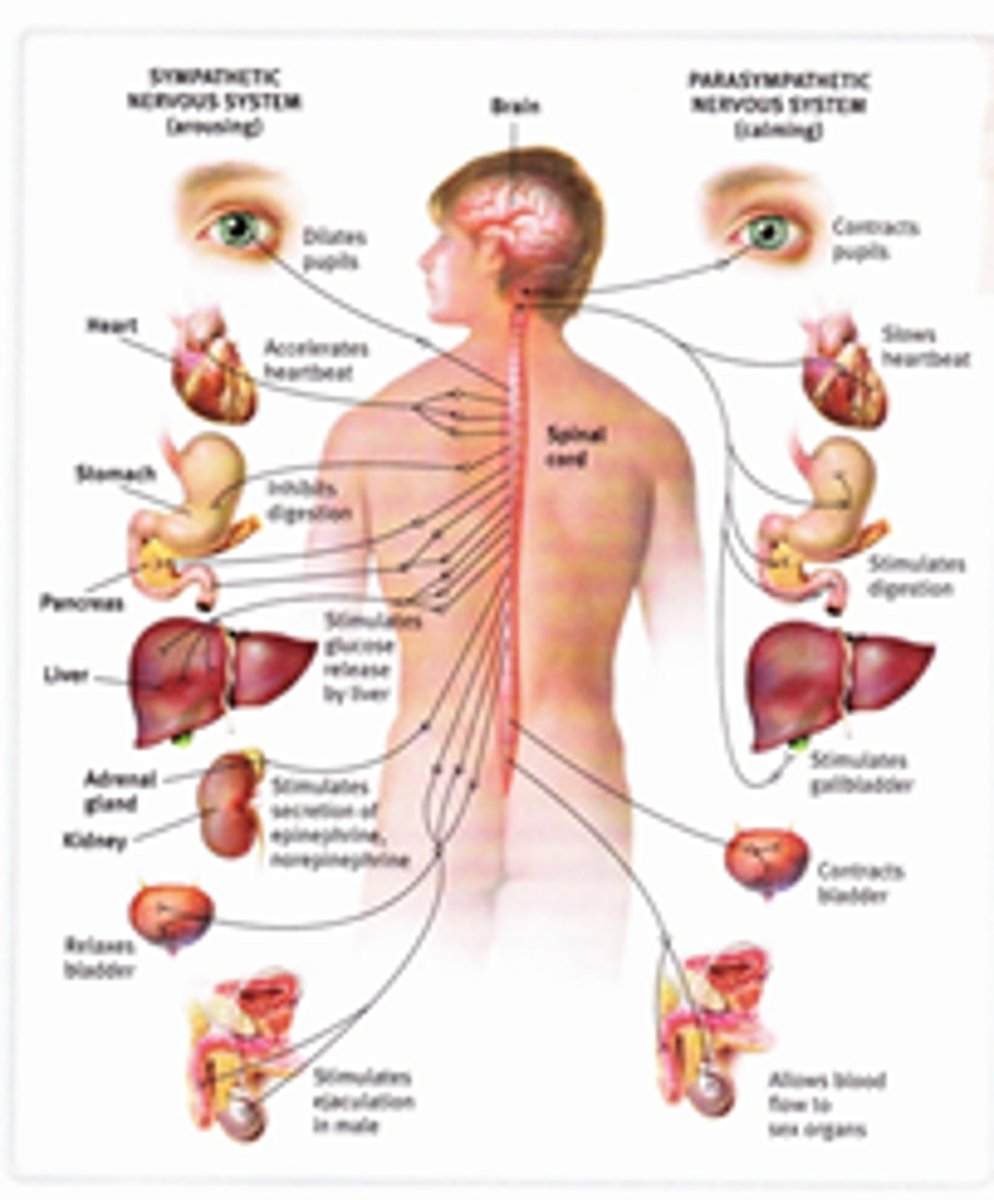
autonomic nervous system
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
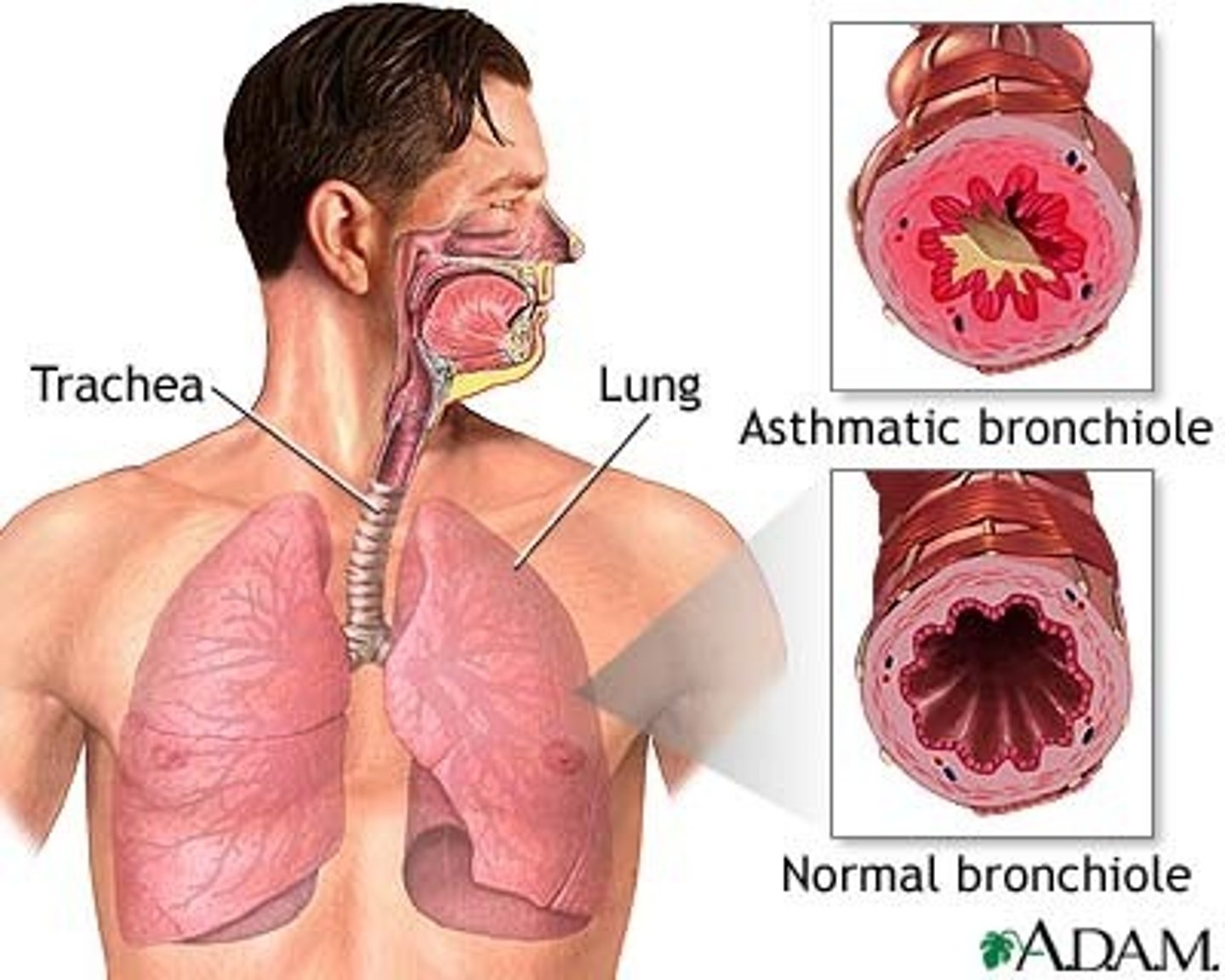
asthma
A chronic allergic disorder characterized by episodes of severe breathing difficulty, coughing, and wheezing.

COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe.
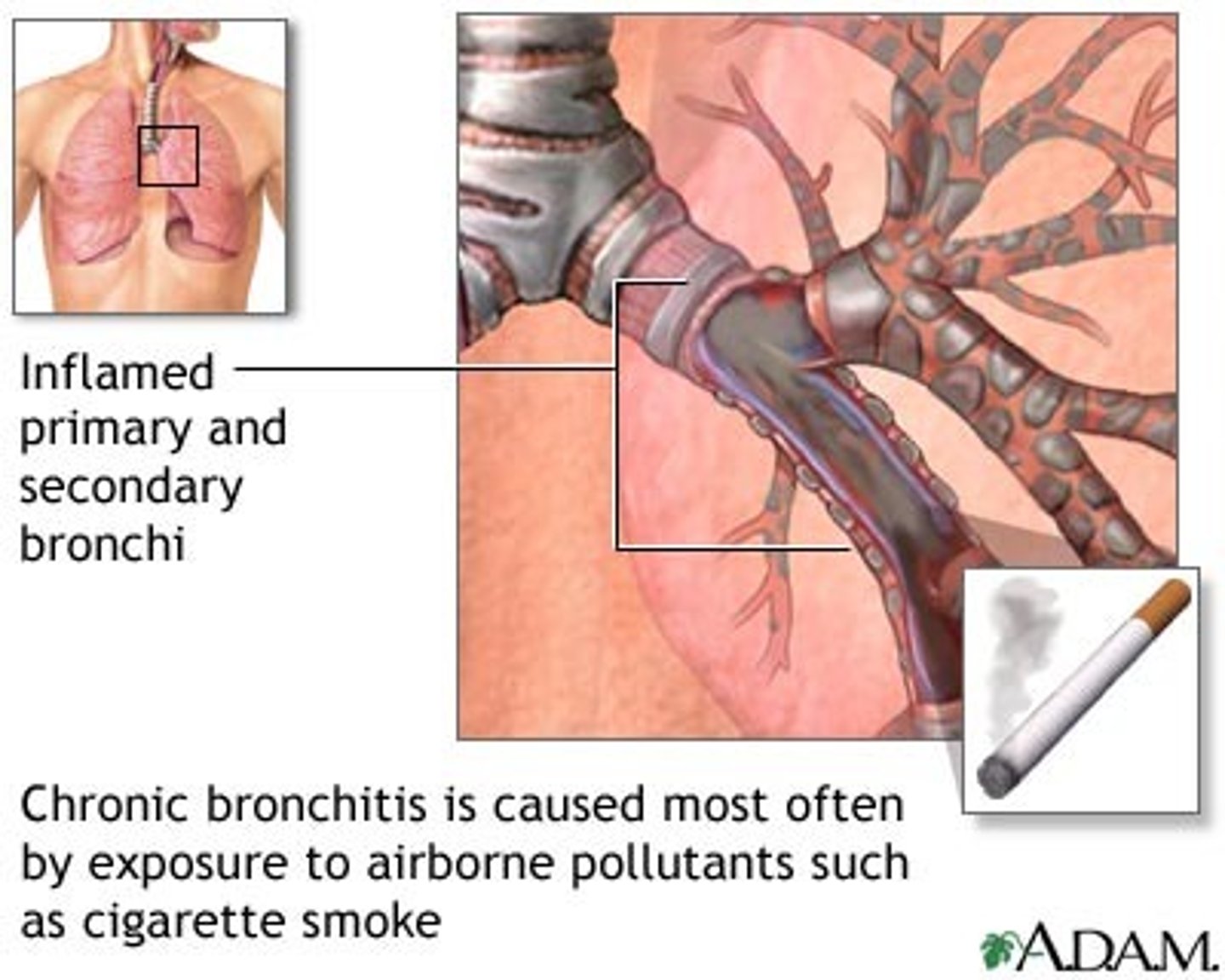
chronic bronchitis
a condition in which the bronchi in the lungs are constantly swollen and clogged with mucus
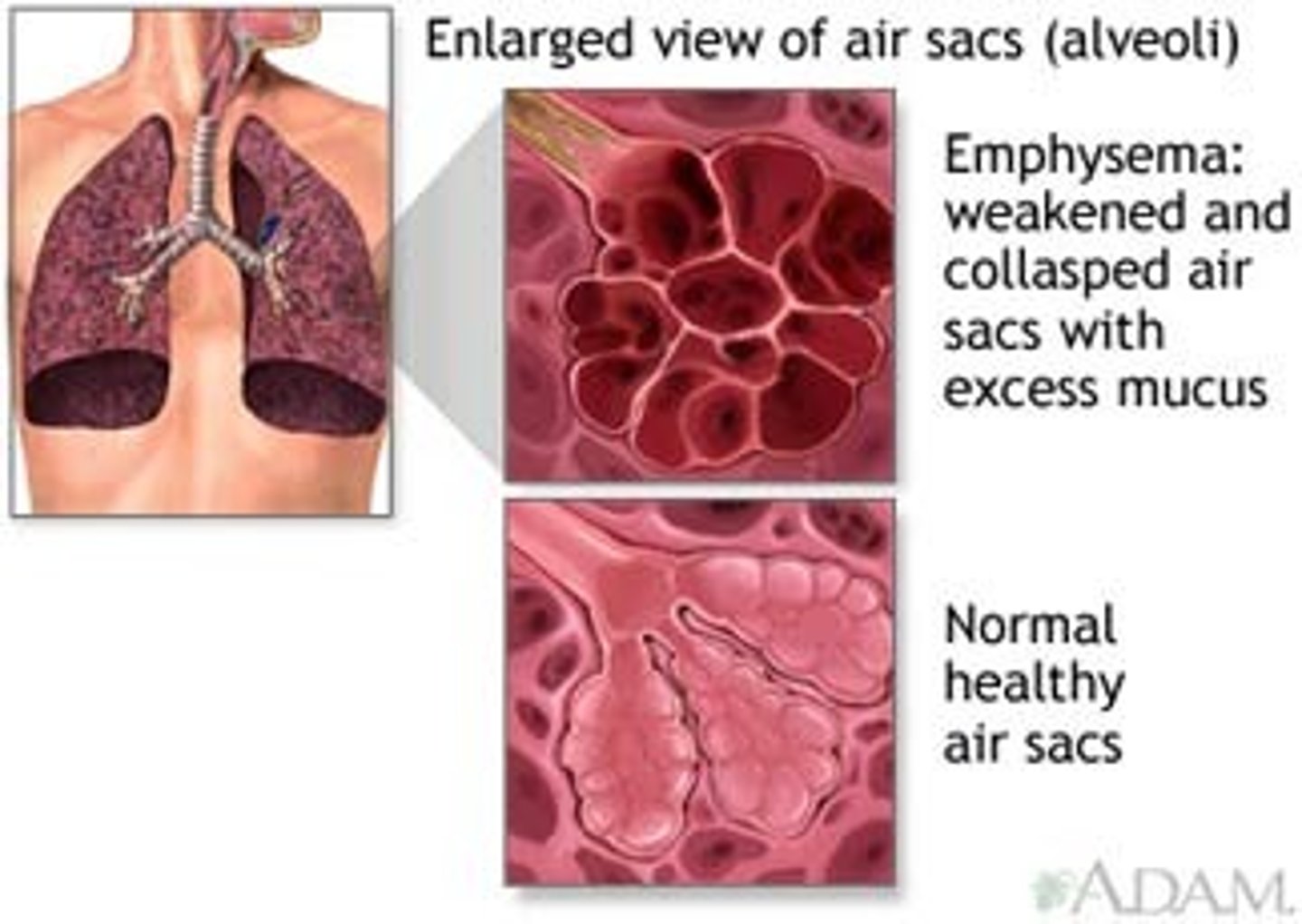
emphysema
A serious disease that destroys lung tissue and causes breathing difficulties.
spirometry
a measurement of breathing (or lung volumes)

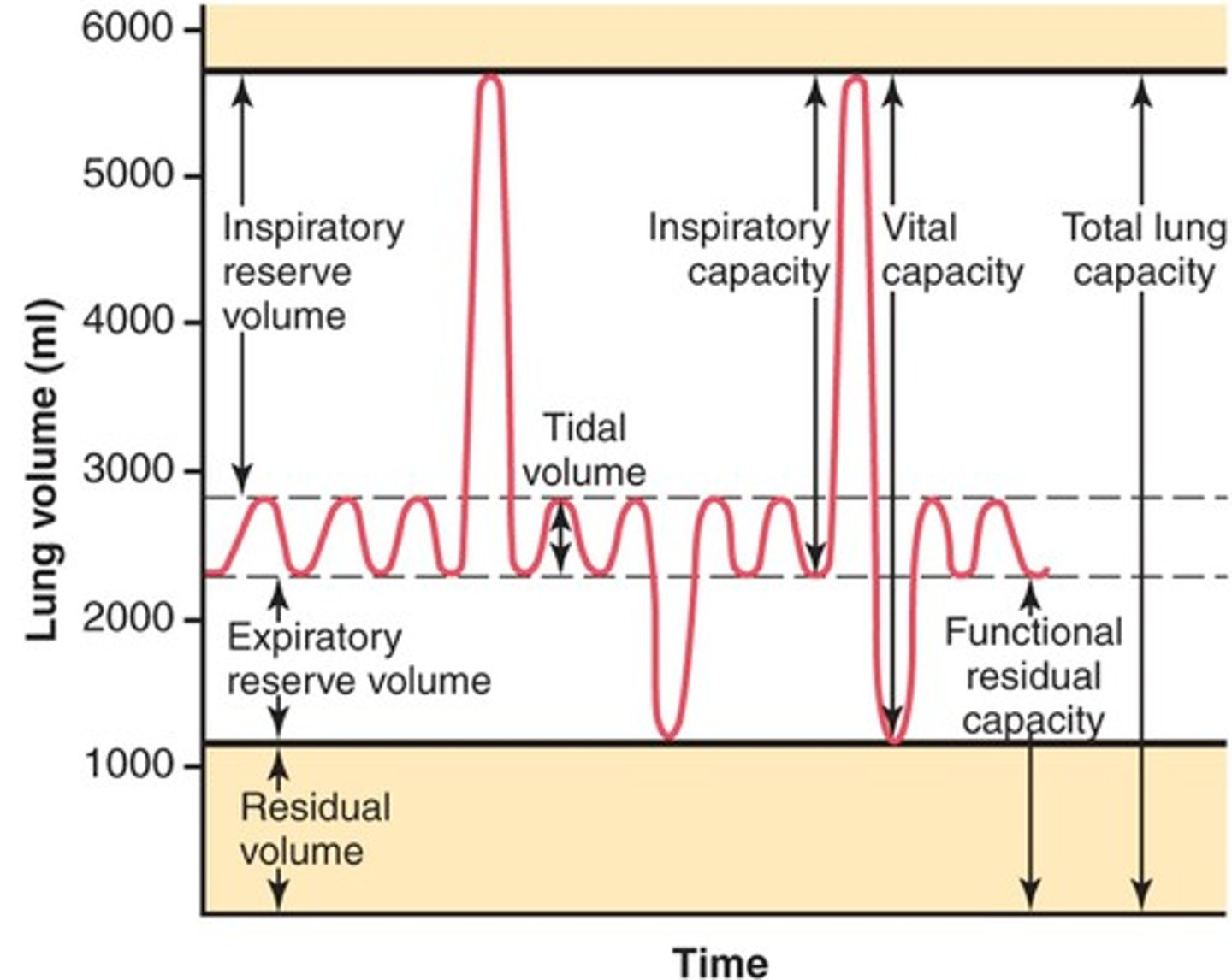
lung volumes
tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume
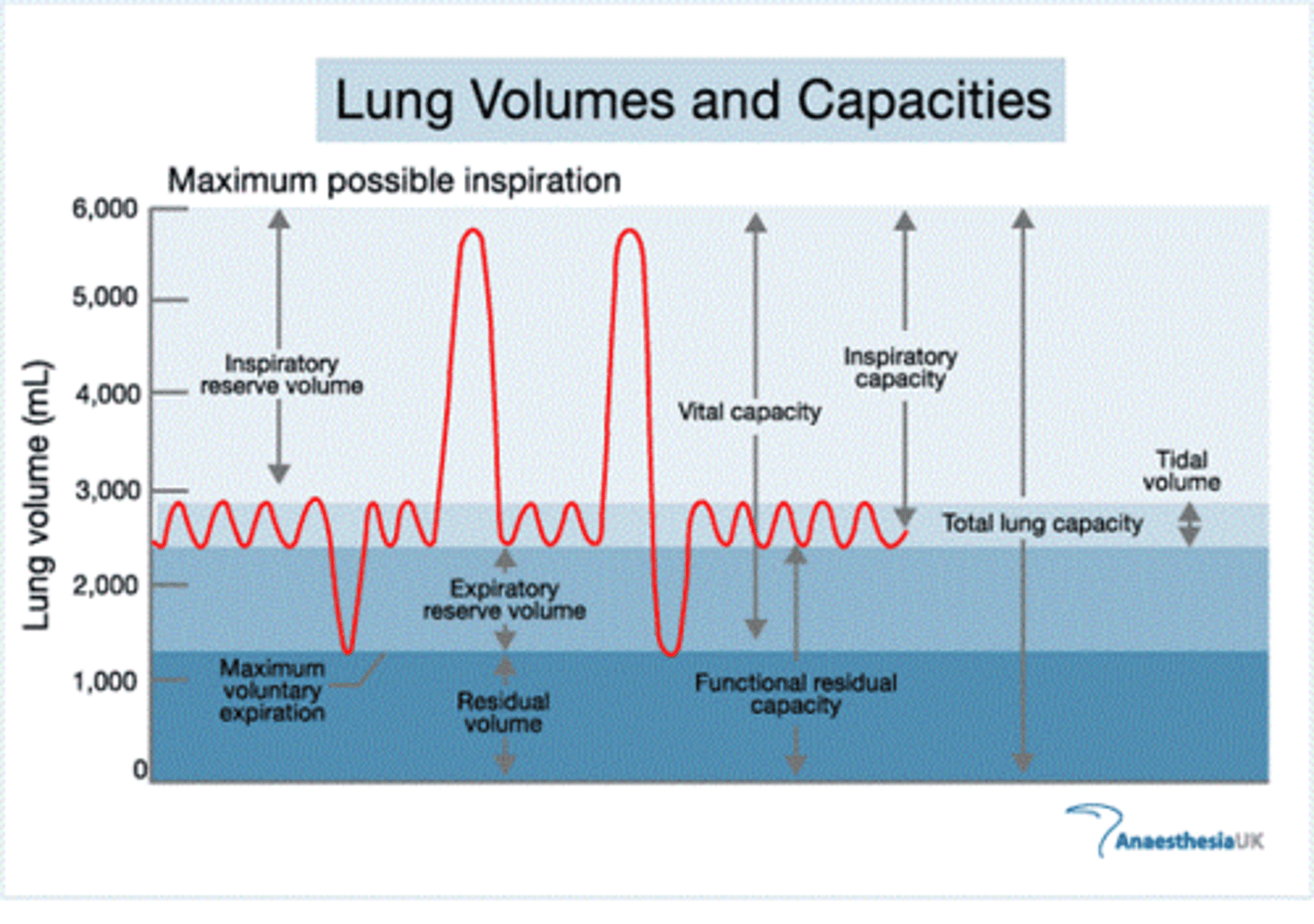
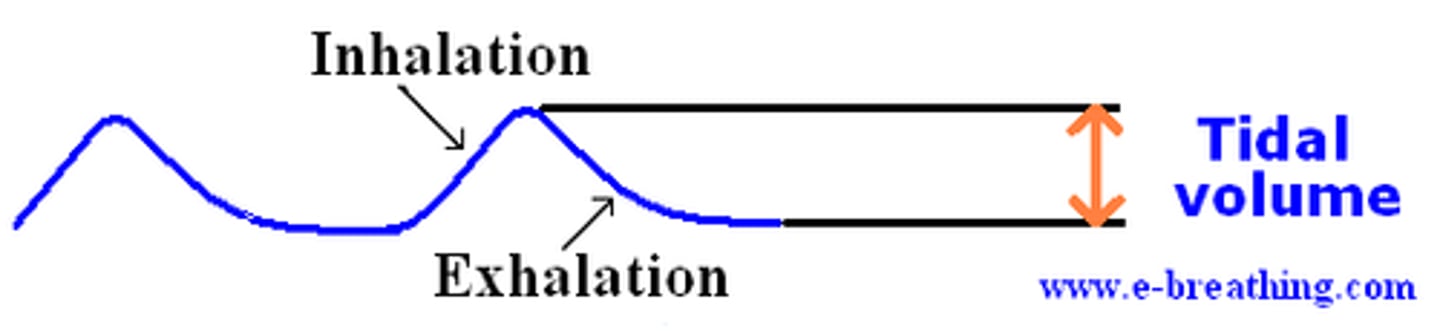
tidal volume (VT)
Amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs during a normal breath
inspiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inhalation
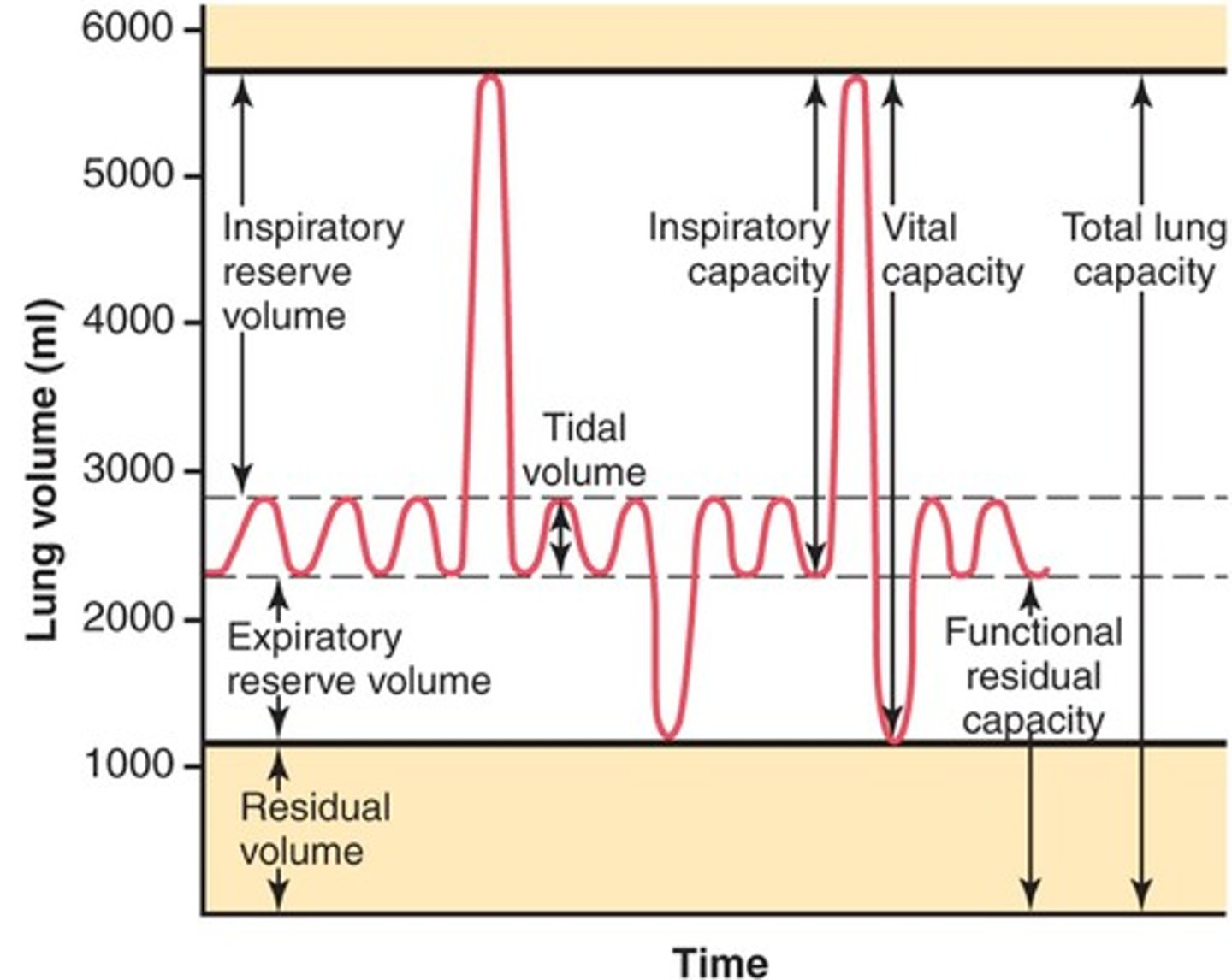
expiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation
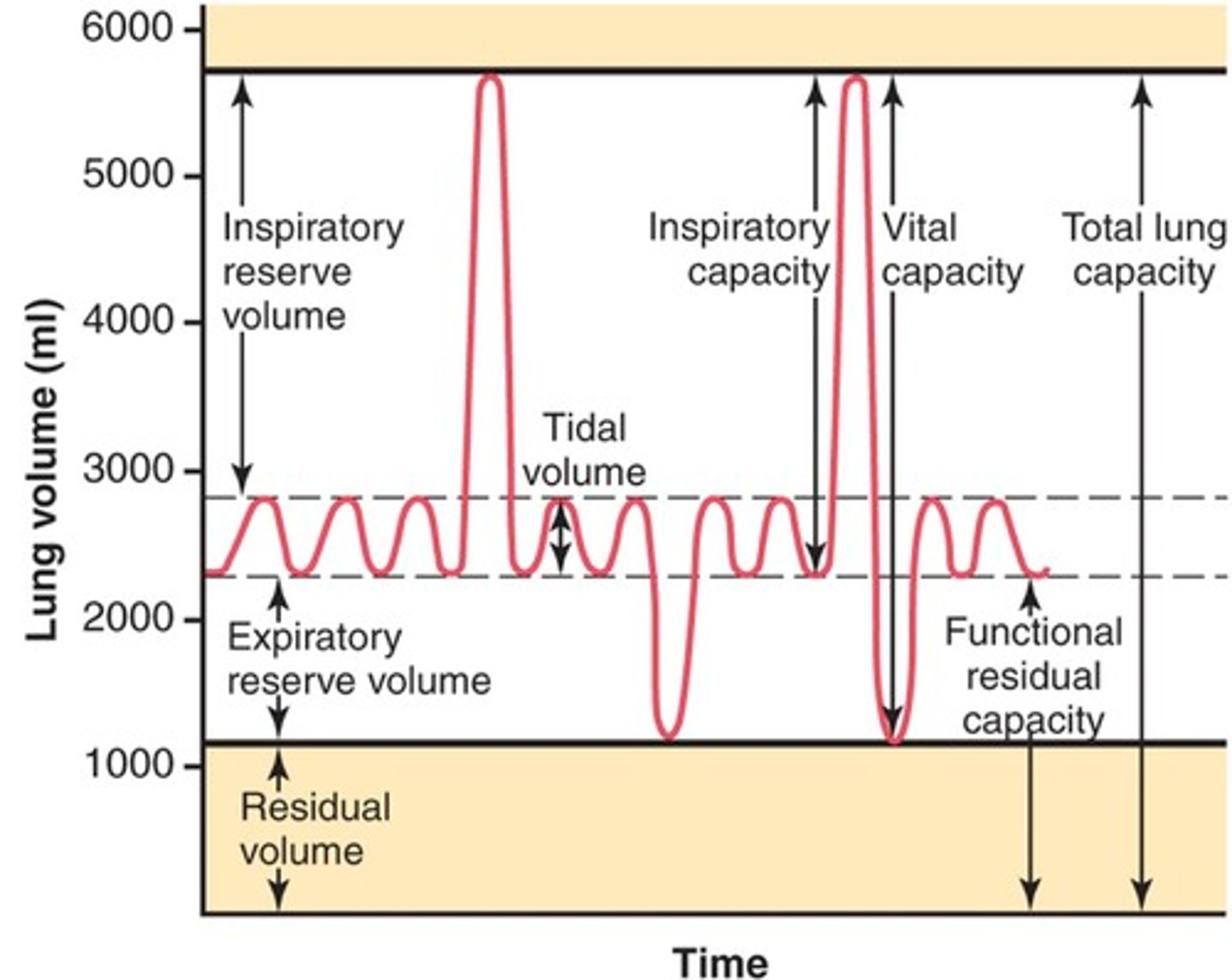
residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation
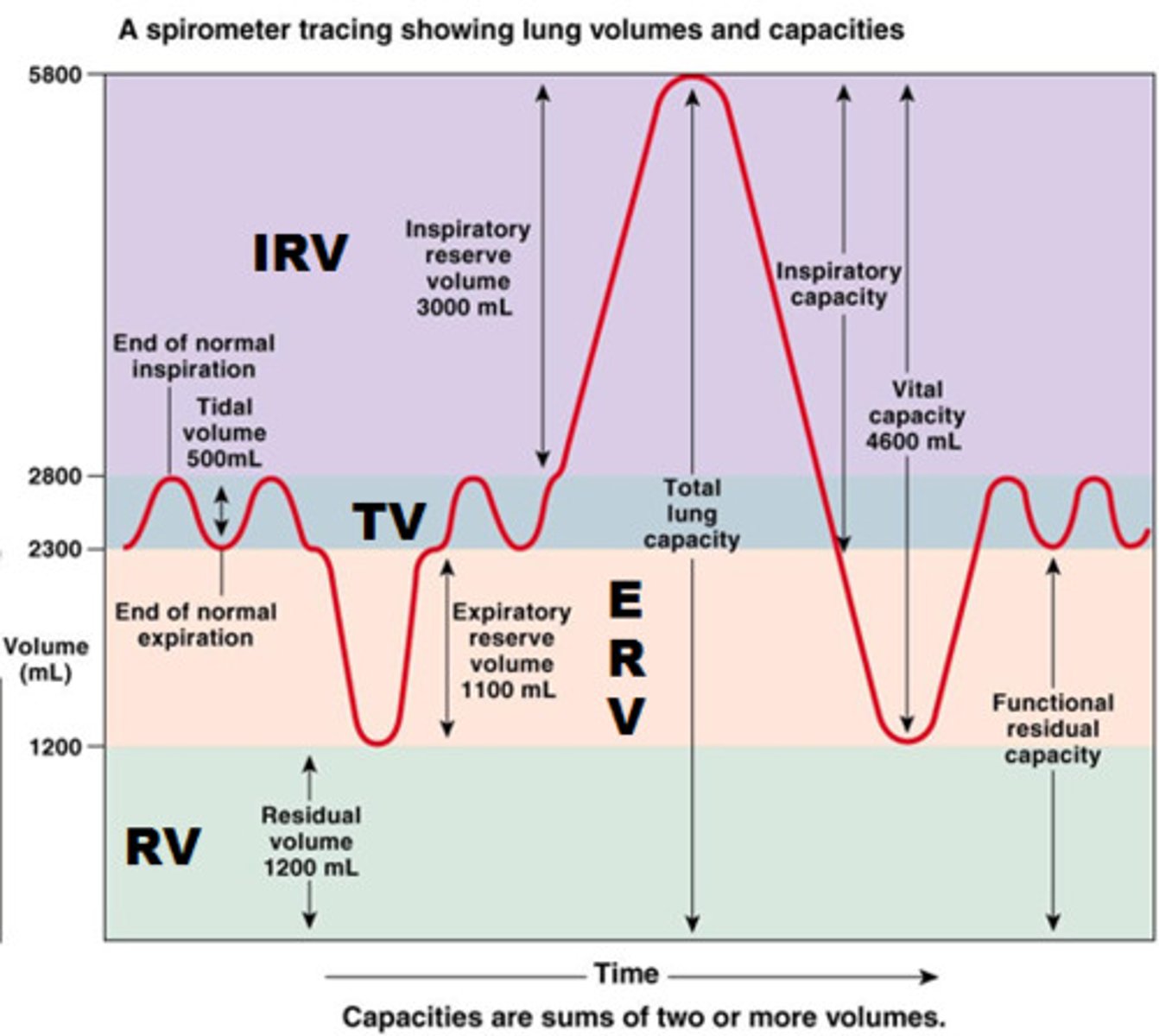
lung capacities
measurements that are the sum of two or more lung volumes
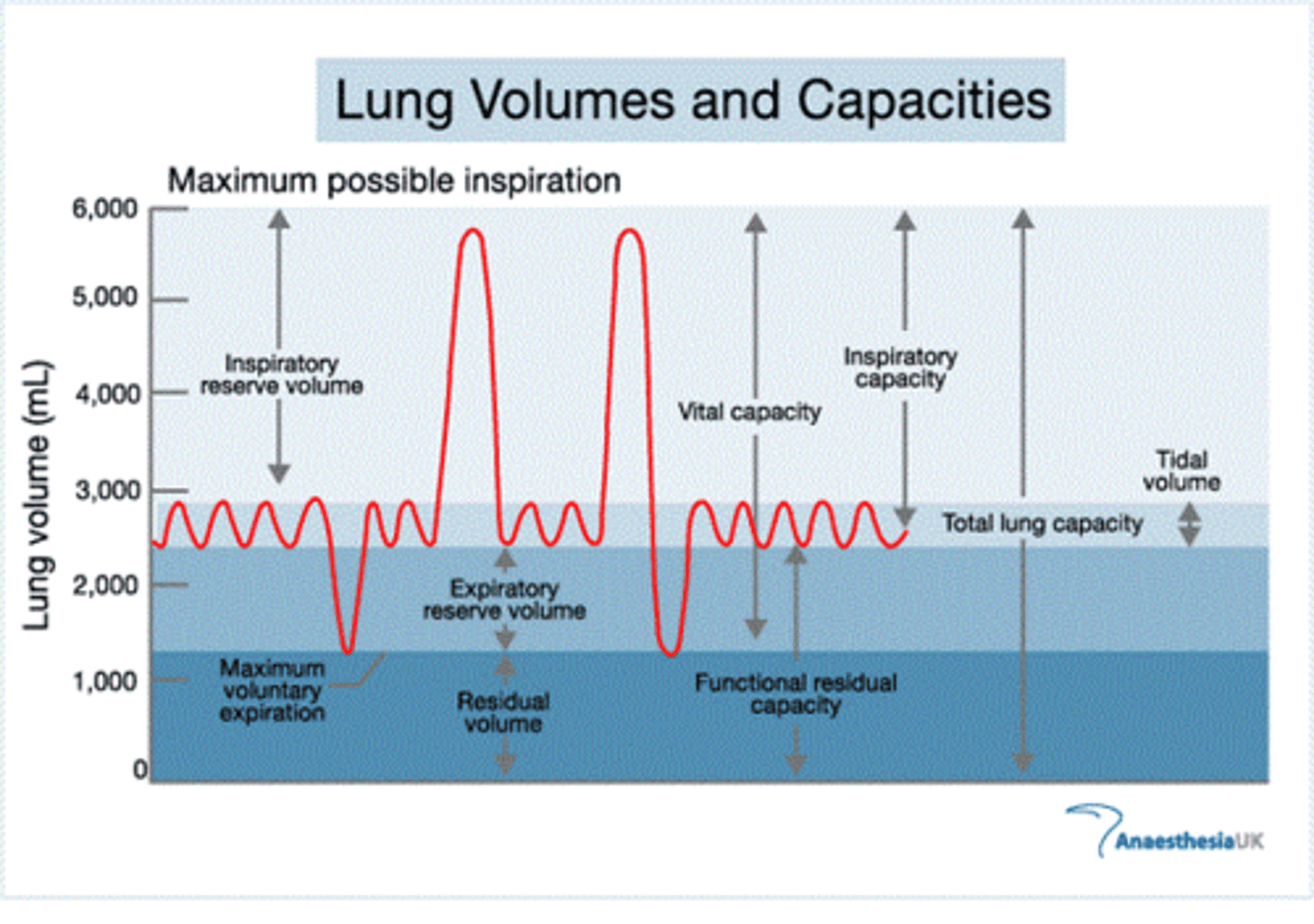
inspiratory capacity
tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume
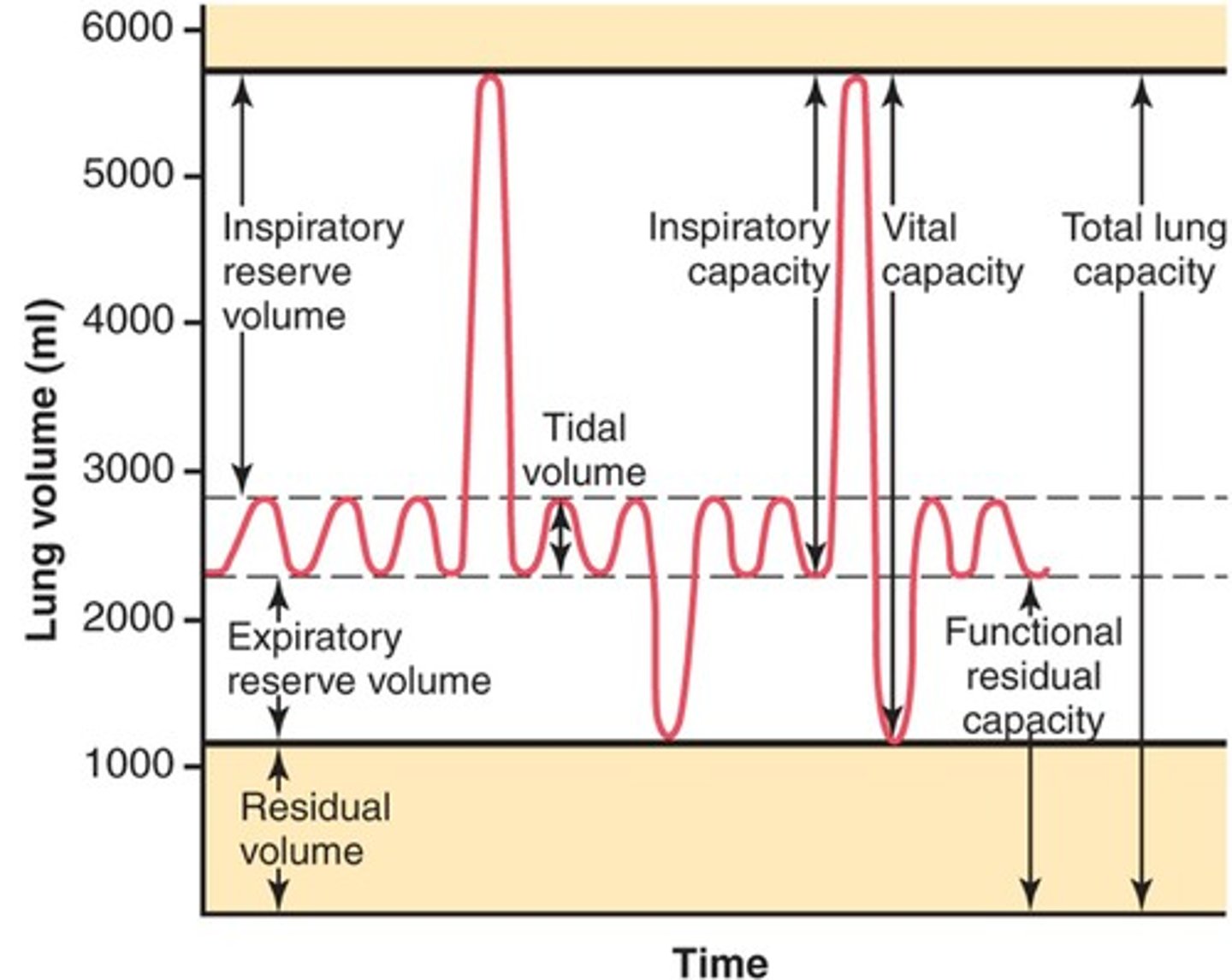
vital capacity
The total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation.
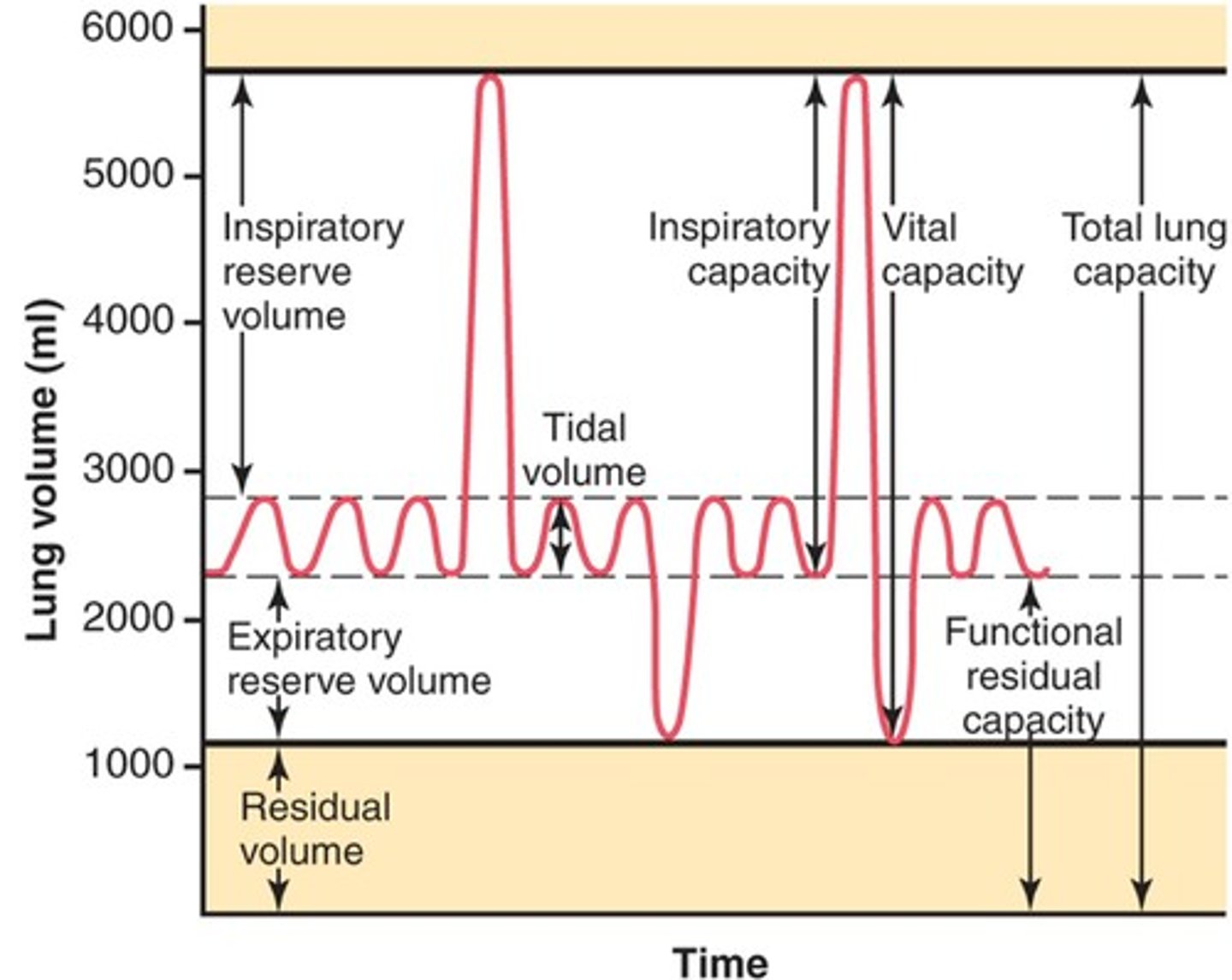
functional residual capacity
expiratory reserve volume + residual volume
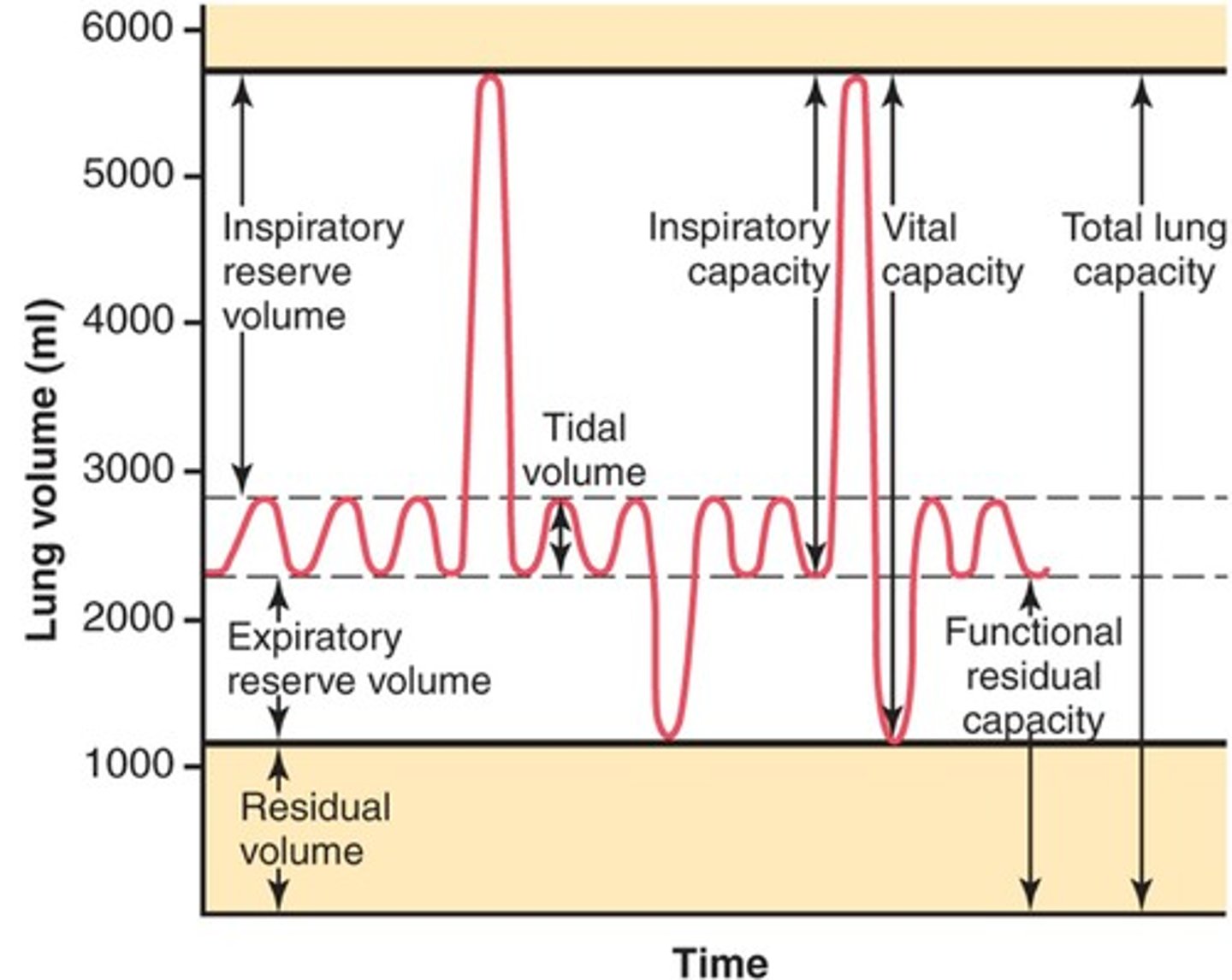
total lung capacity
vital capacity + residual volume
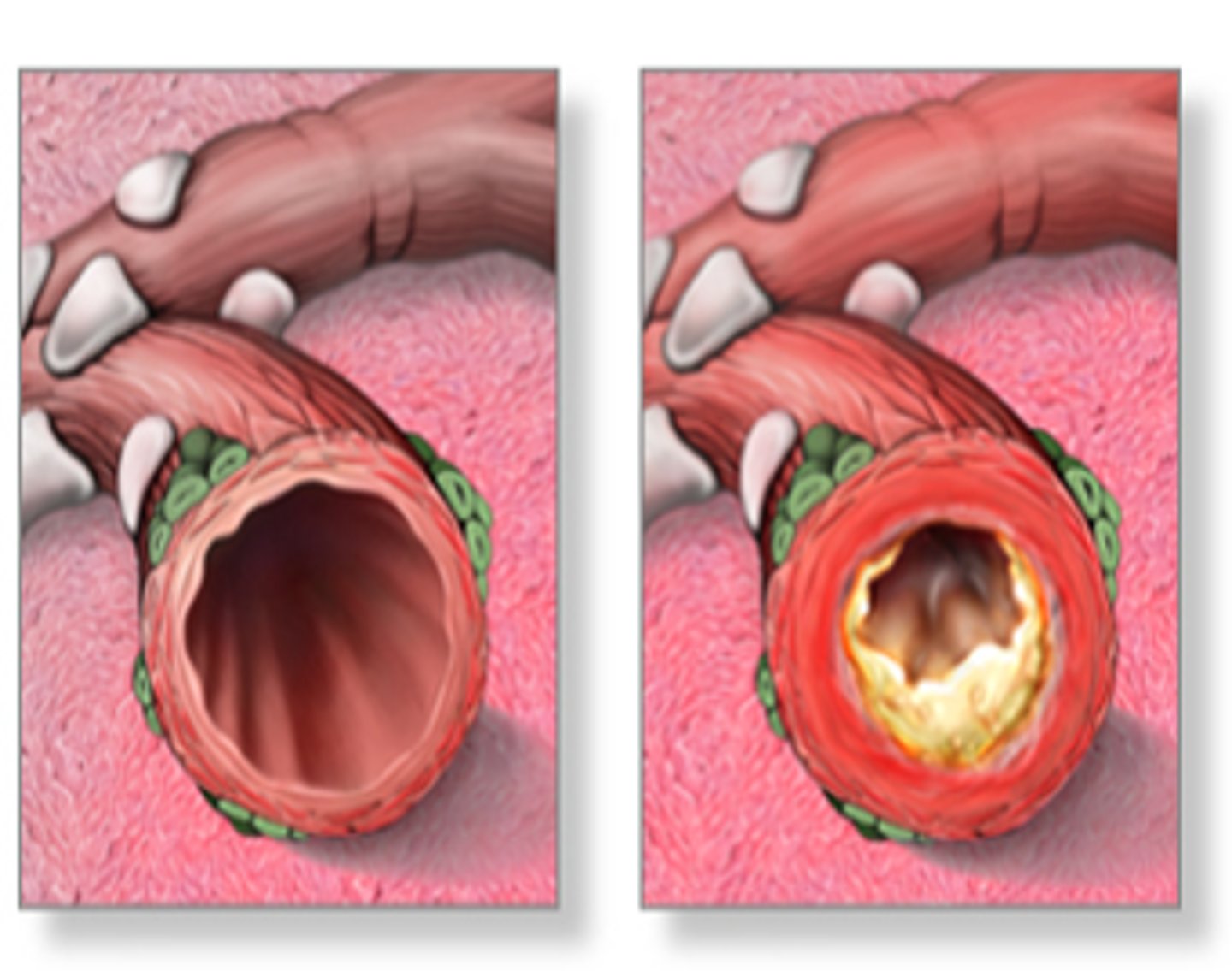
obstructive pulmonary diseases
emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma
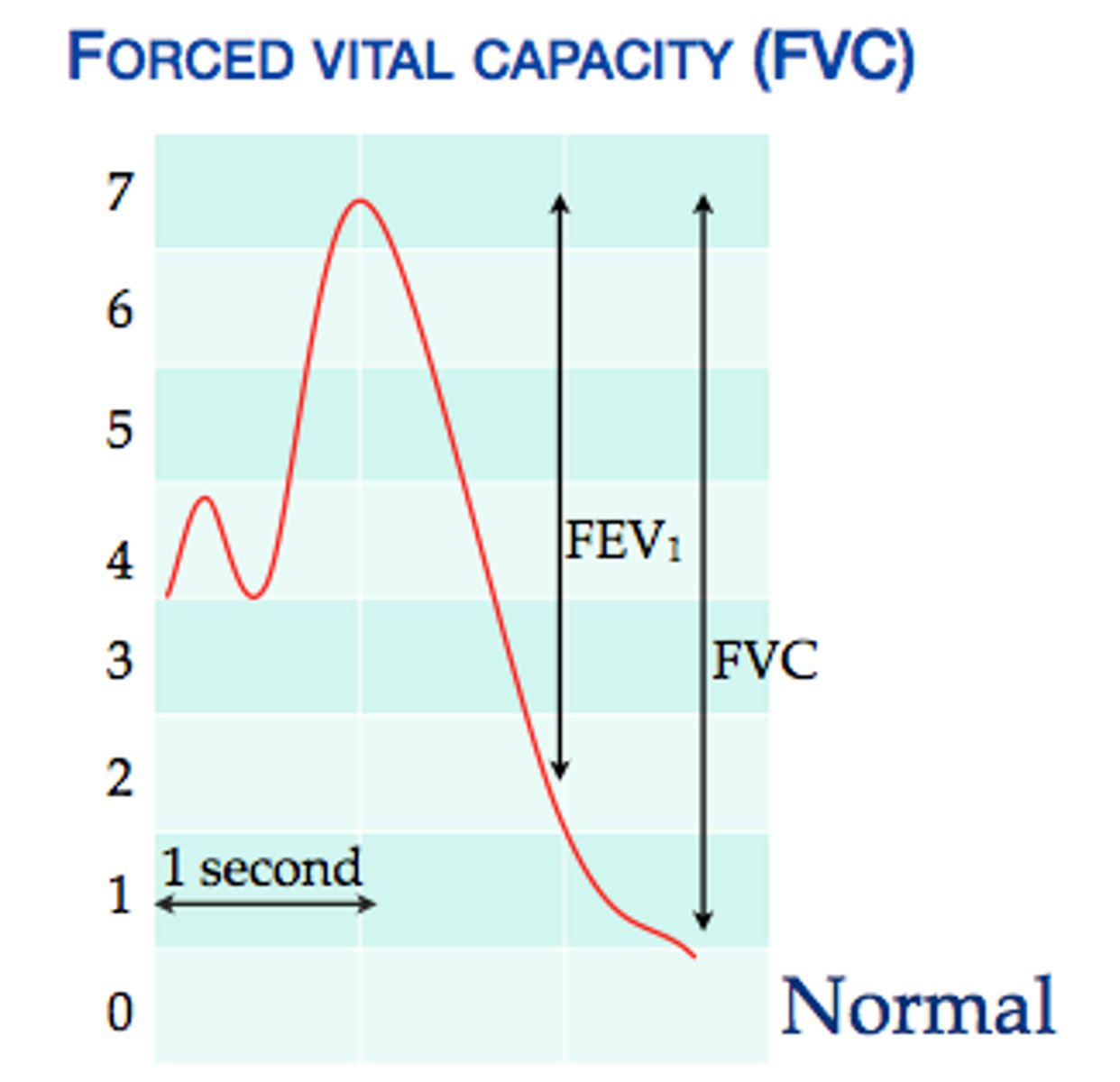
forced expiratory volume
amount of gas expelled during specific time intervals of FVC
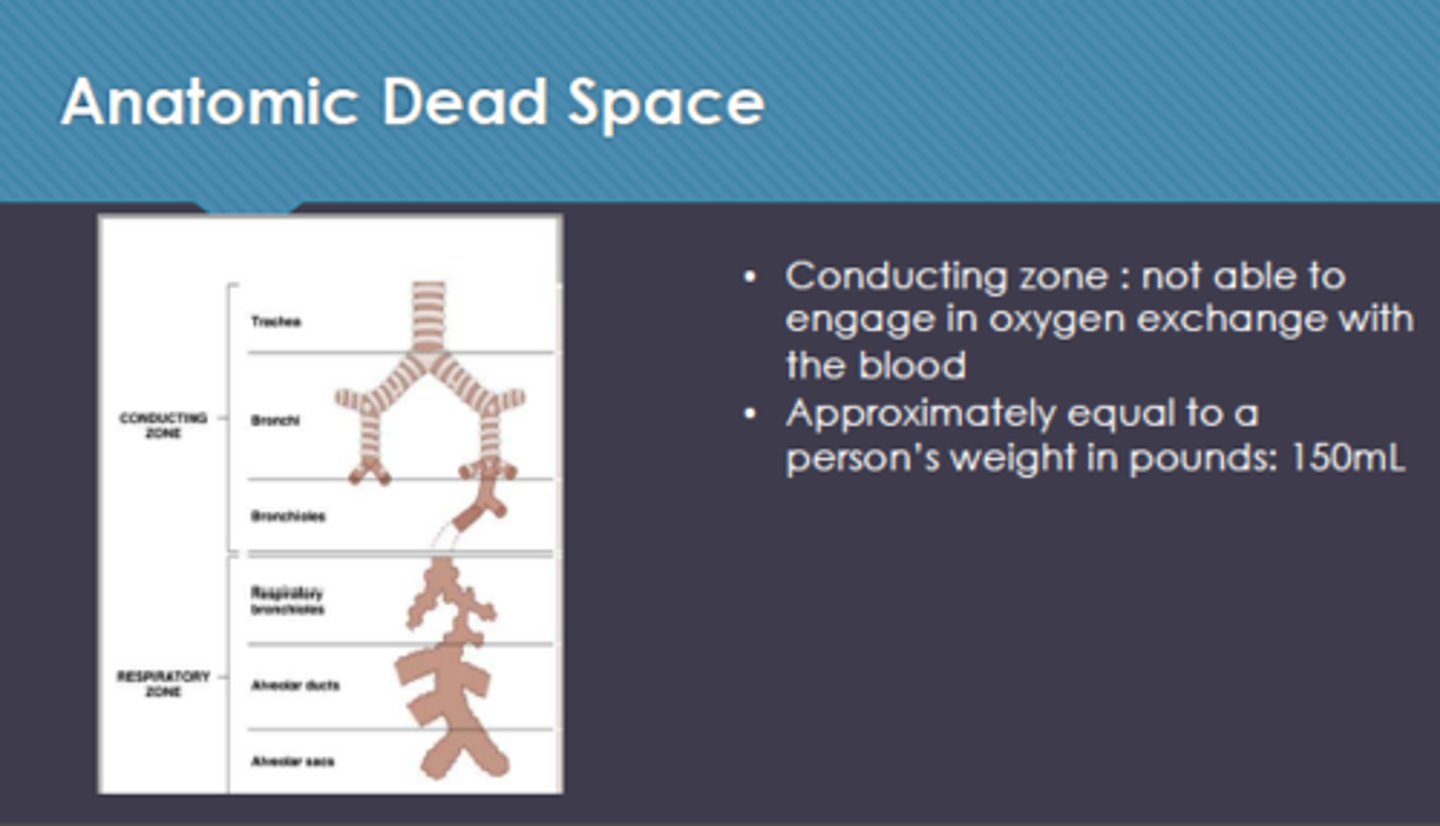
anatomical dead space
the conducting zone; airways that fill with air but cannot perform gas exchange
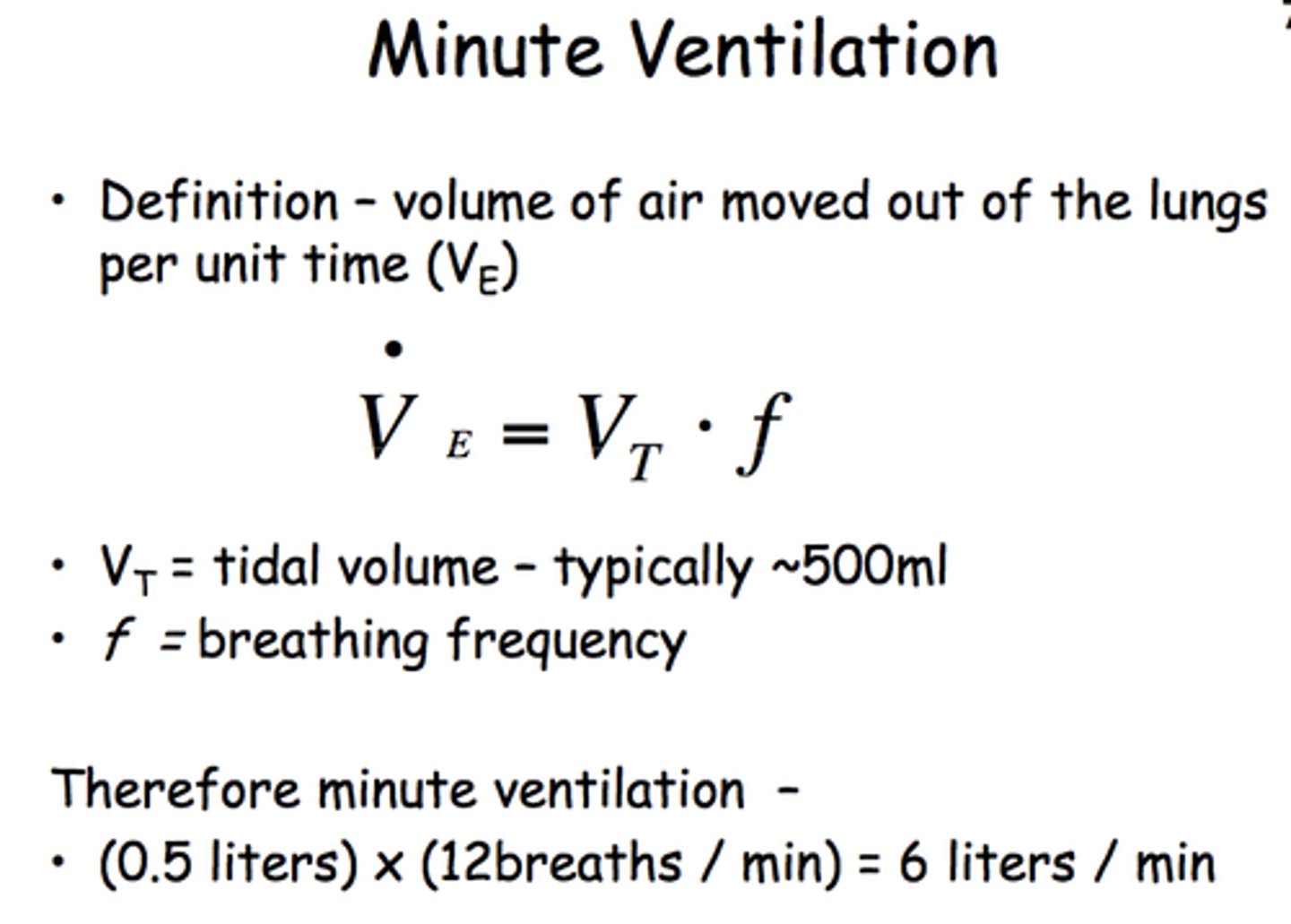
minute ventilation
The volume of air moved through the lungs in 1 minute minus the dead space; calculated by multiplying tidal volume (minus dead space) and respiratory rate; also referred to as minute volume.
alveolar ventilation
The volume of air that reaches the alveoli. It is determined by subtracting the amount of dead space air from the tidal volume.