Chemistry: Types of Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
ionization isomers
result from the interchange of an anionic ligand within the first coordination sphere with an anion outside the coordination sphere
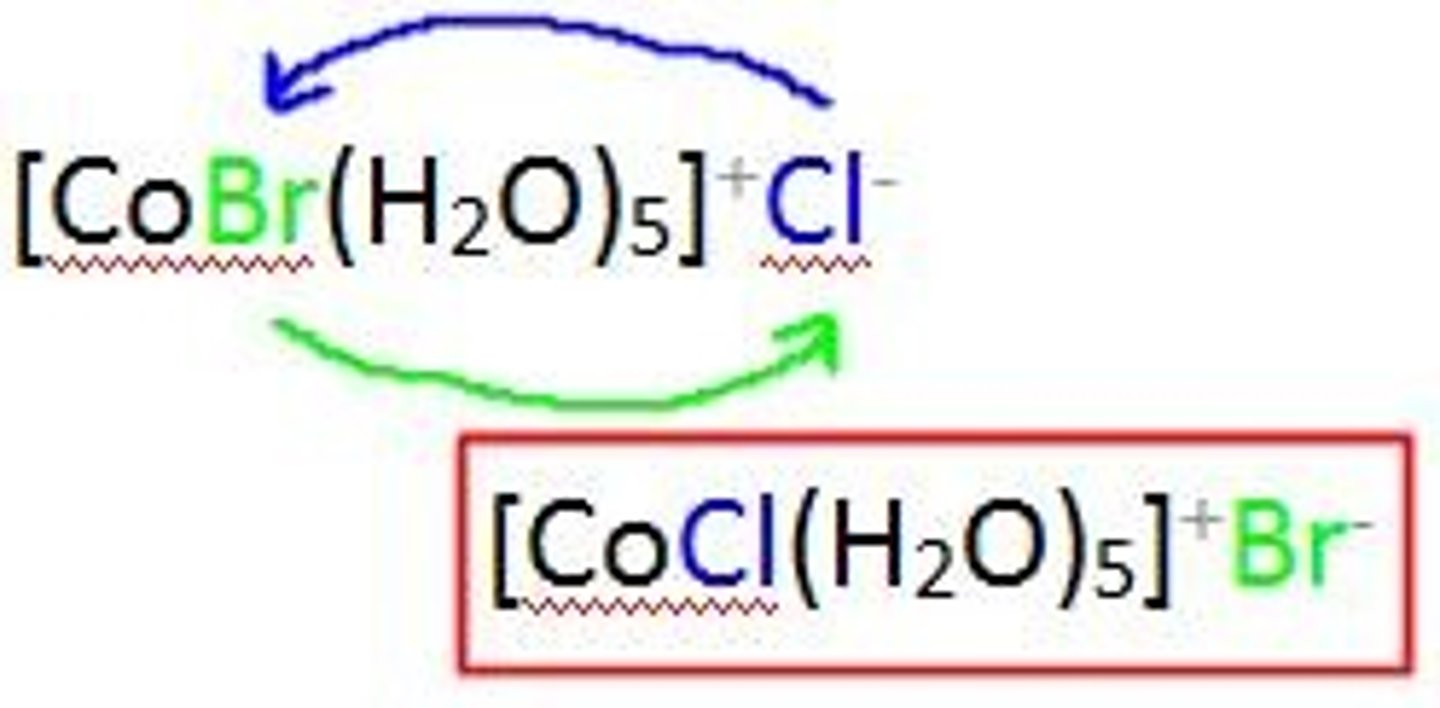
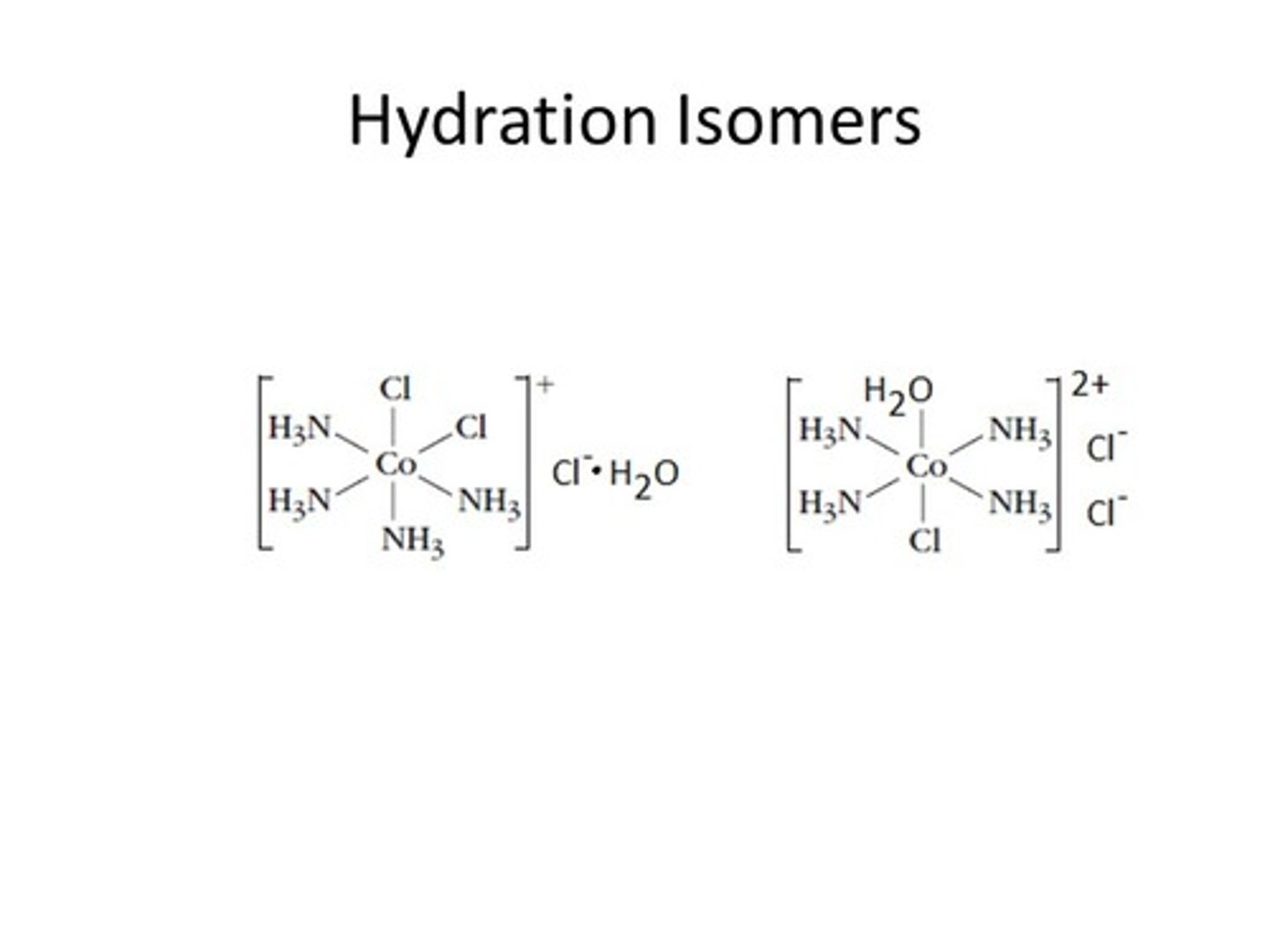
hydration isomers
Result from the interchange of H2O and another Ligand between the first coordination sphere and the ligands outside it.
coordination isomers
isomers consisting of complex cations and complex anions that differ in the way the ligands are distributed between the metal atoms

Linkage Isomerism
isomerism involving a complex ion where the ligands are all the same but the point of attachment of at least one of the ligands differs.

Polymerization isomer
occurs when two or more compounds have the same elemental composition but different molecular weights, often seen in metal clusters or certain polymers
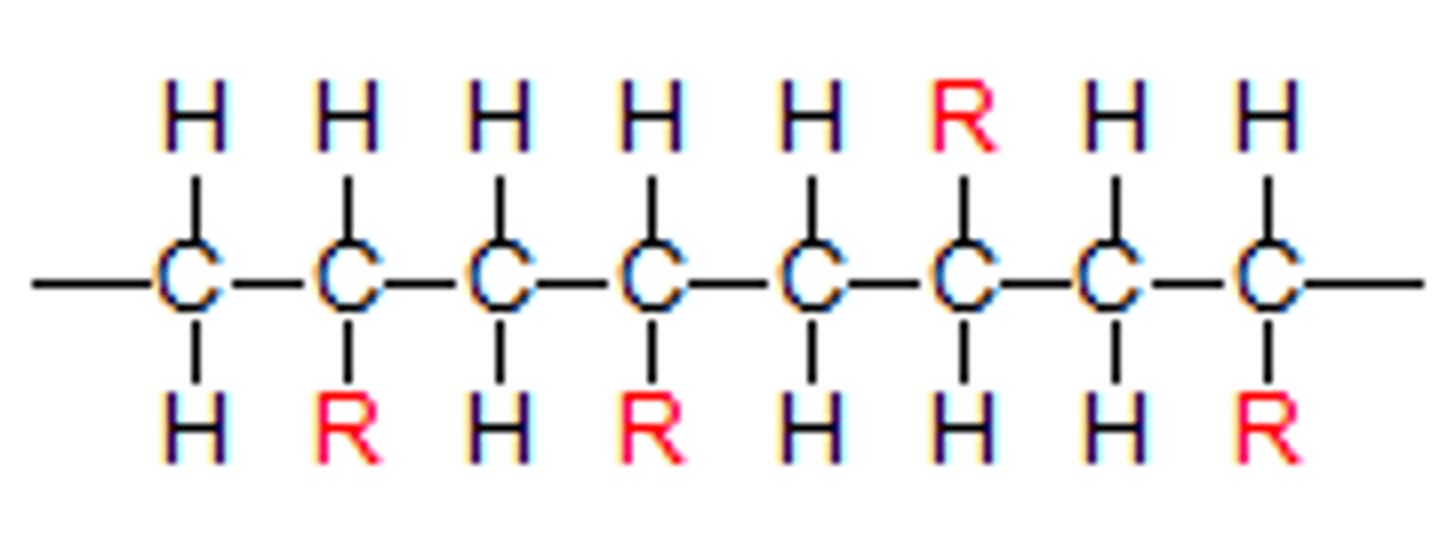
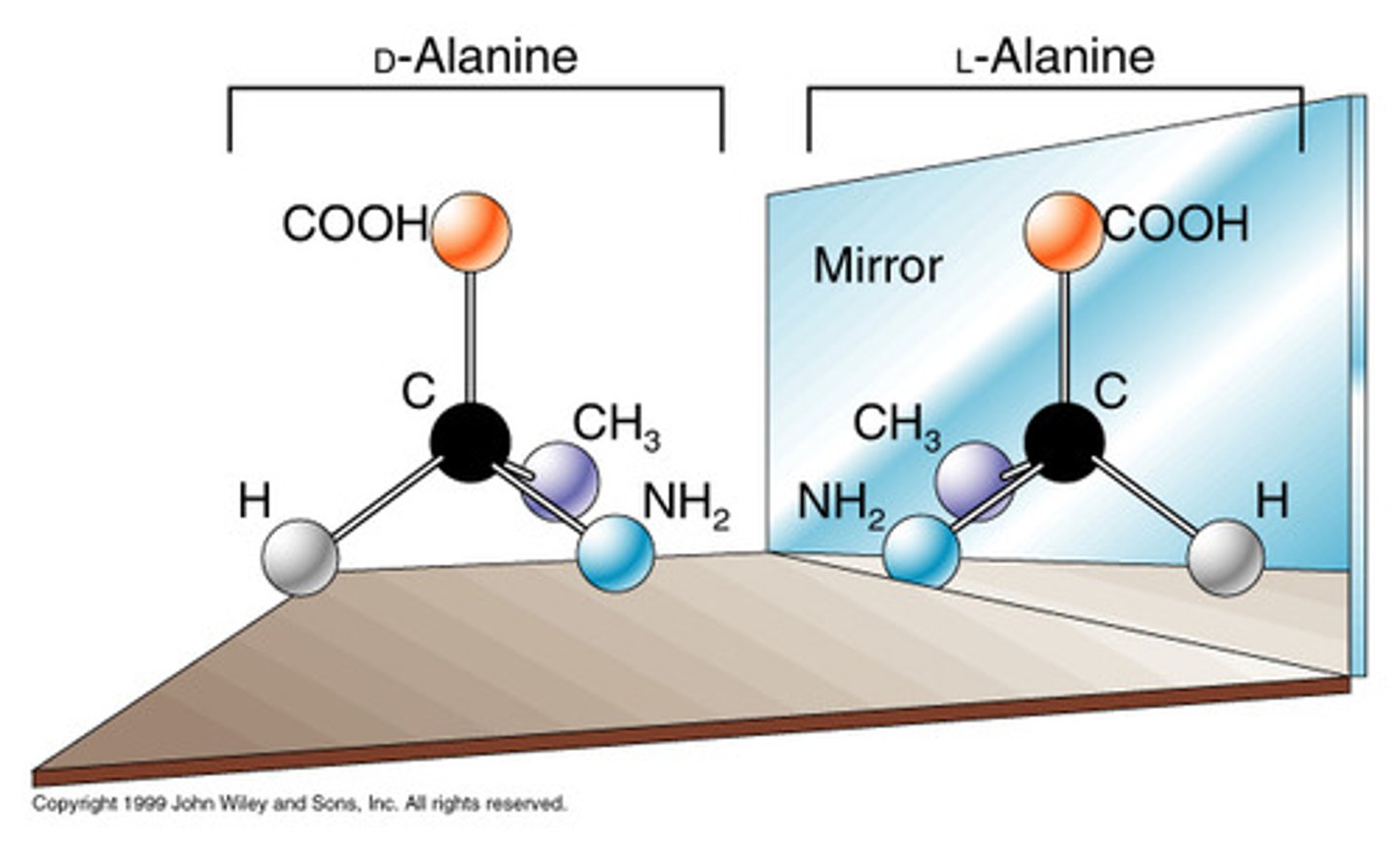
optical isomers
Stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
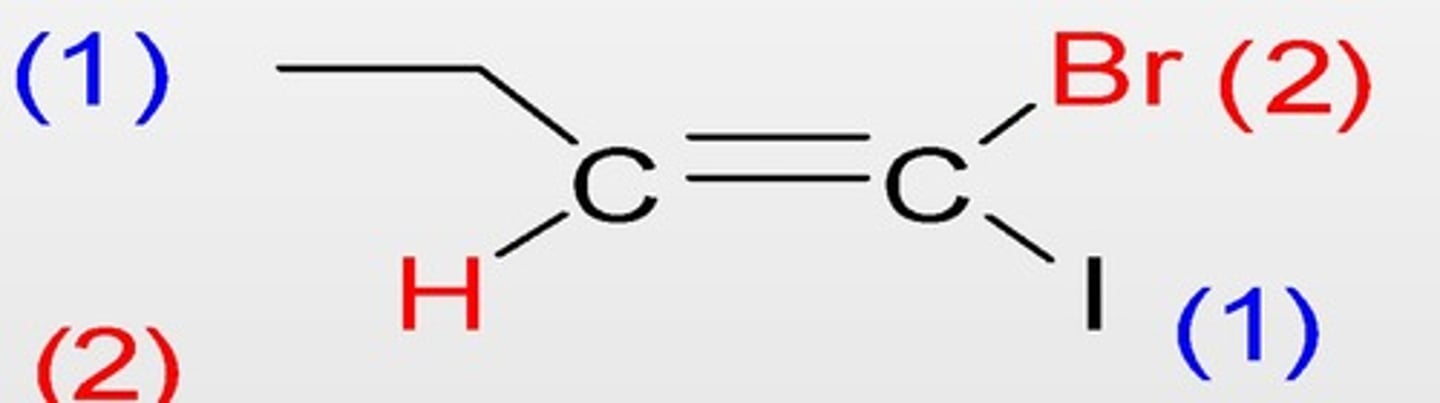
Geometrical isomer
isomerism where atoms or groups of atoms can take up different positions around a double bond or a ring. This is also called cis- trans- isomerism.