World War 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Fascism
A political movement that promotes an extreme form of nationalism, a denial of individual rights, and a dictatorial one-party rule. Popular in Spain, Italy, and Germany in 1930s and 1940s

Nazi
Adolf Hitler became a member of this party in Germany;
Acronym for the National Socialist German Workers Party

Appeasement
Accepting demands in order to avoid conflict; Britain's use of this helped Hitler's power grow.

Axis Powers
Germany, Italy, and Japan, which were allied before and during World War II.
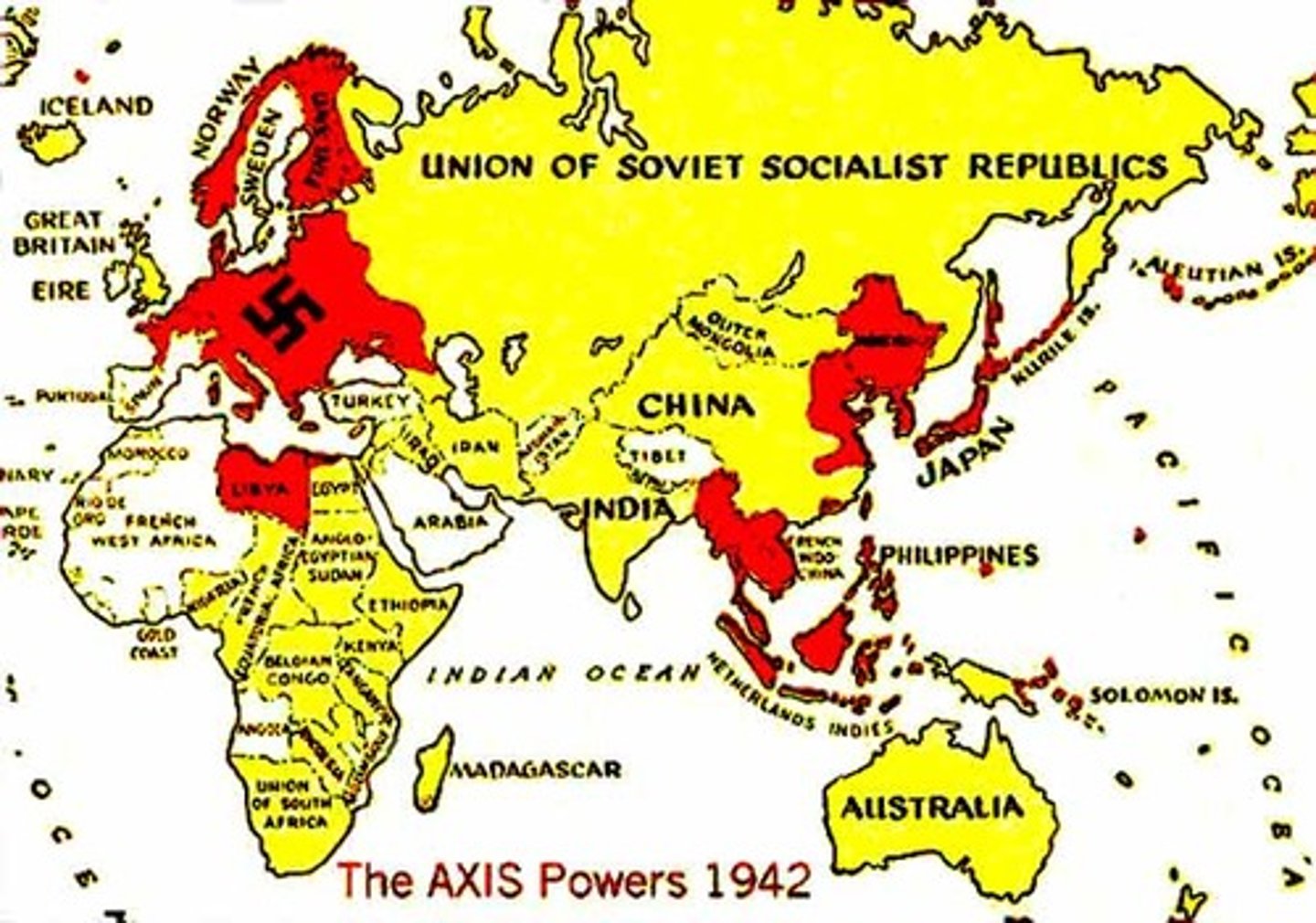
Allied Powers
Alliance of Great Britain, Soviet Union, United States, and France during World War II.
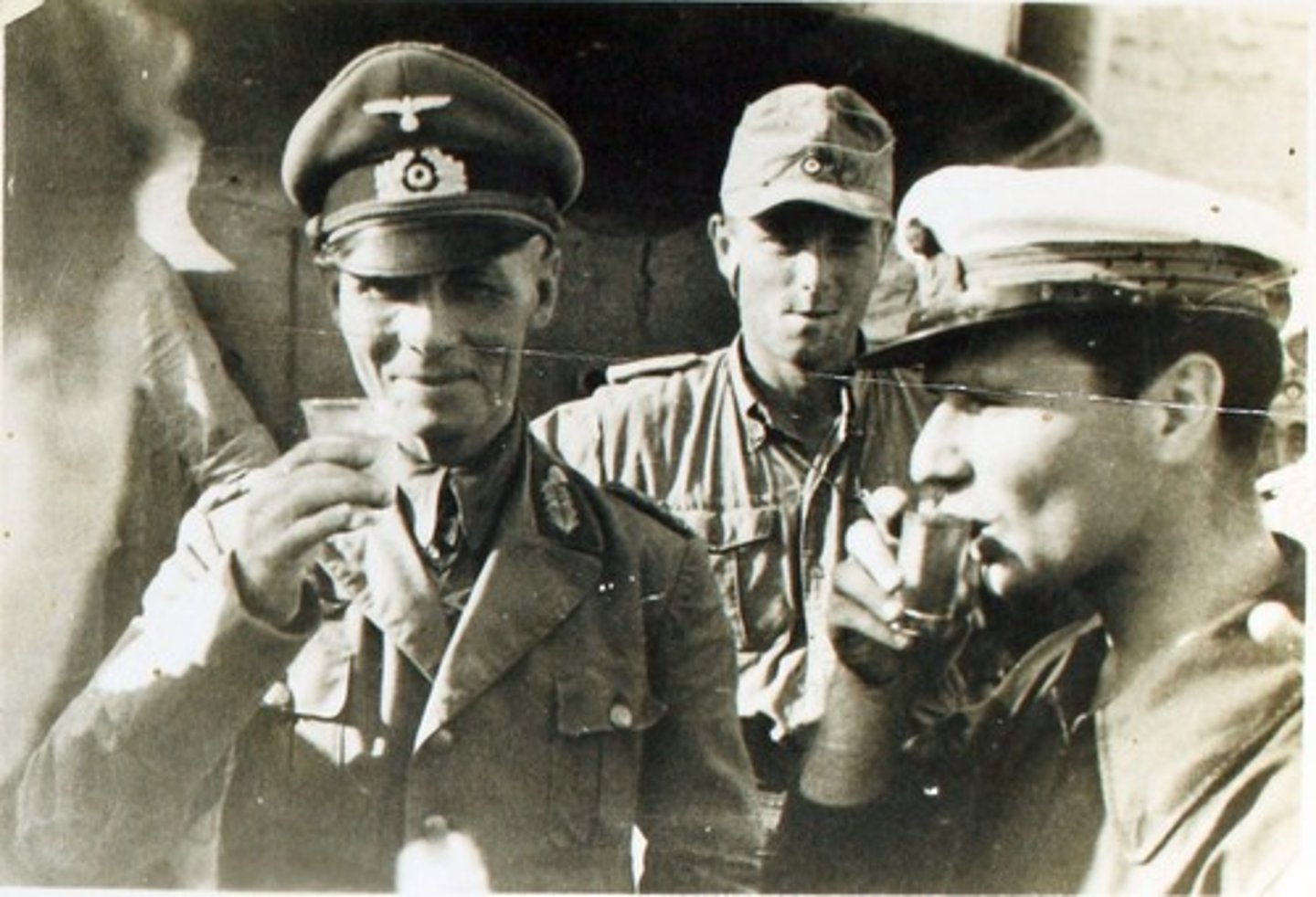
Erwin Rommel
The 'Dessert Fox', Field Marshal; Headed up German tank divisions in North Africa

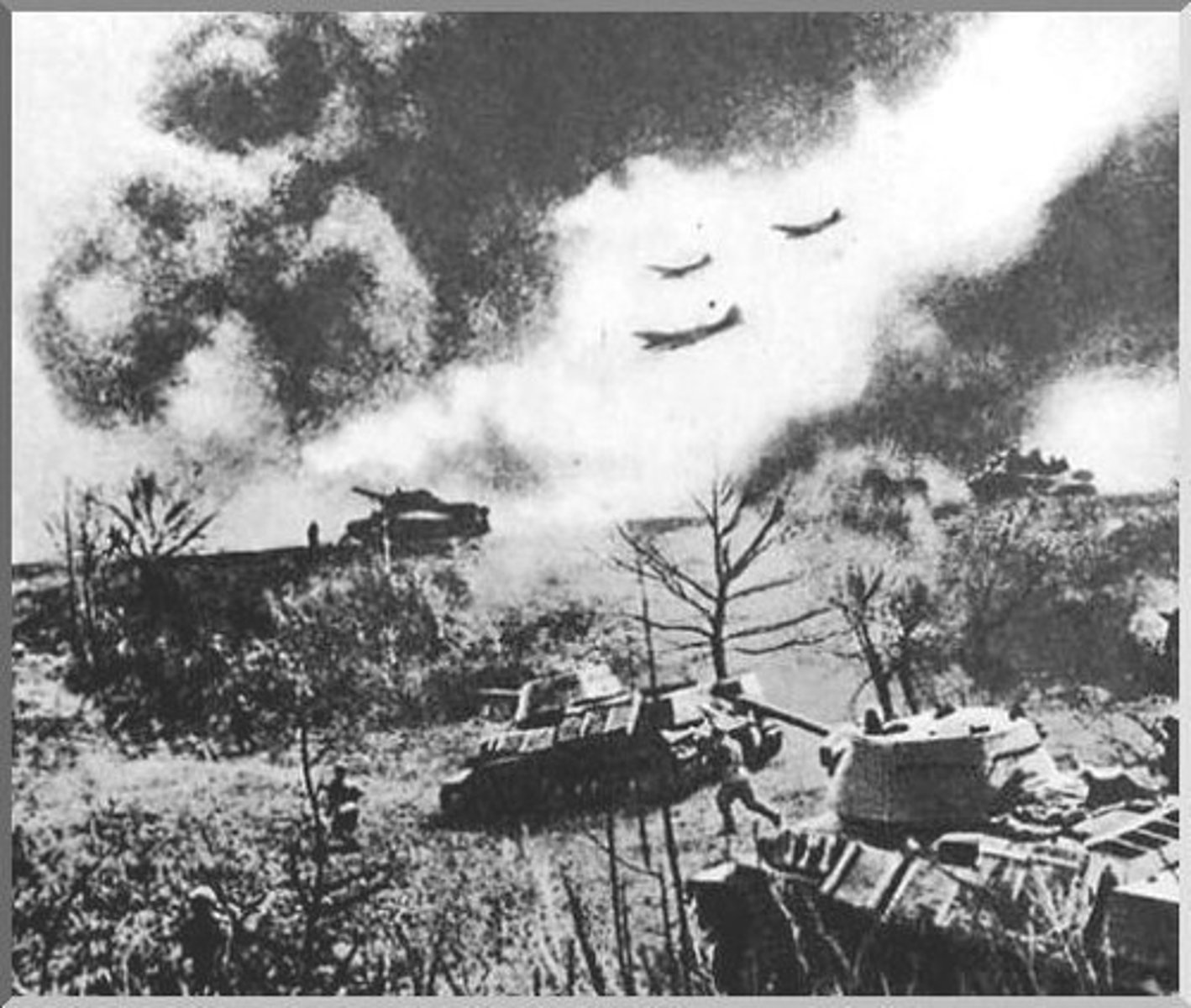
Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces 1st used against Poland in 1939. Innovative use of airplanes and tanks to overwhelm targets.

Poland
1st nation attacked by Germany (1939) Britain and France declared war, starting World War II

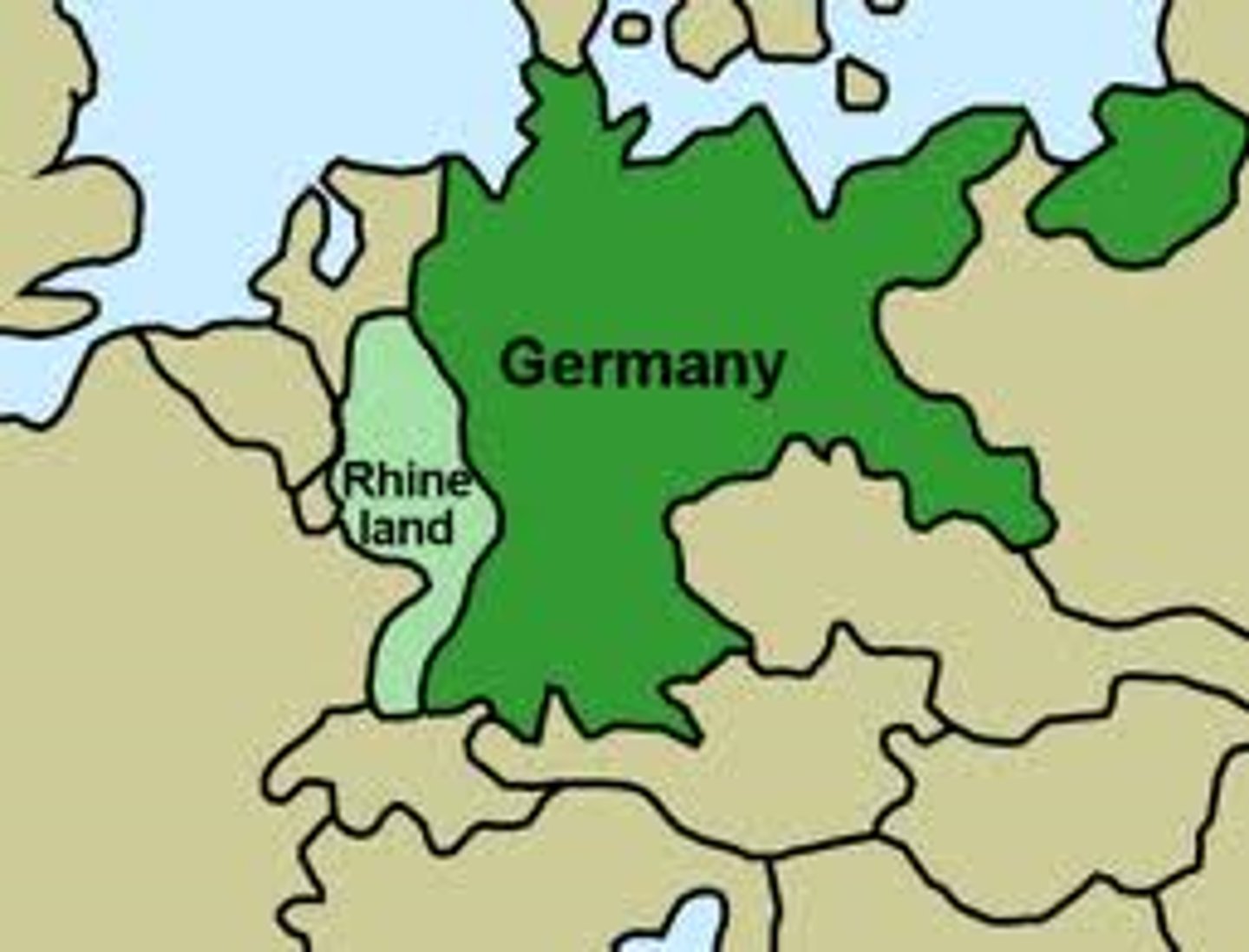
Rhineland
A region in Germany designated a demilitarized zone by the Treaty of Versailles; Hitler violated the treaty and sent German troops there in 1936
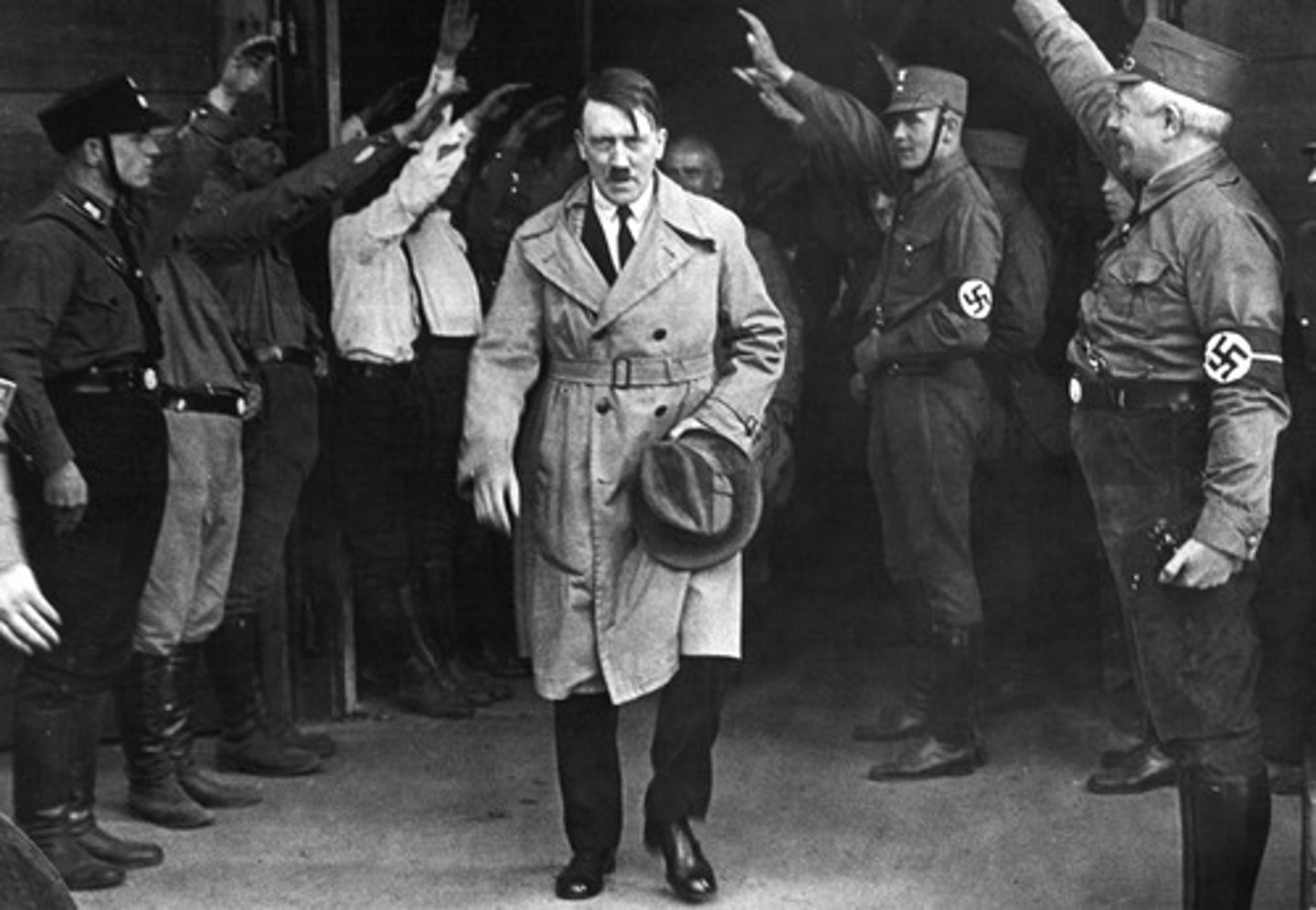
Adolf Hitler
German Nazi dictator during World War II

Scored Earth
Strategy used in Soviet Union to destroy land and food sources to slow invading German forces and buy time for counter attack
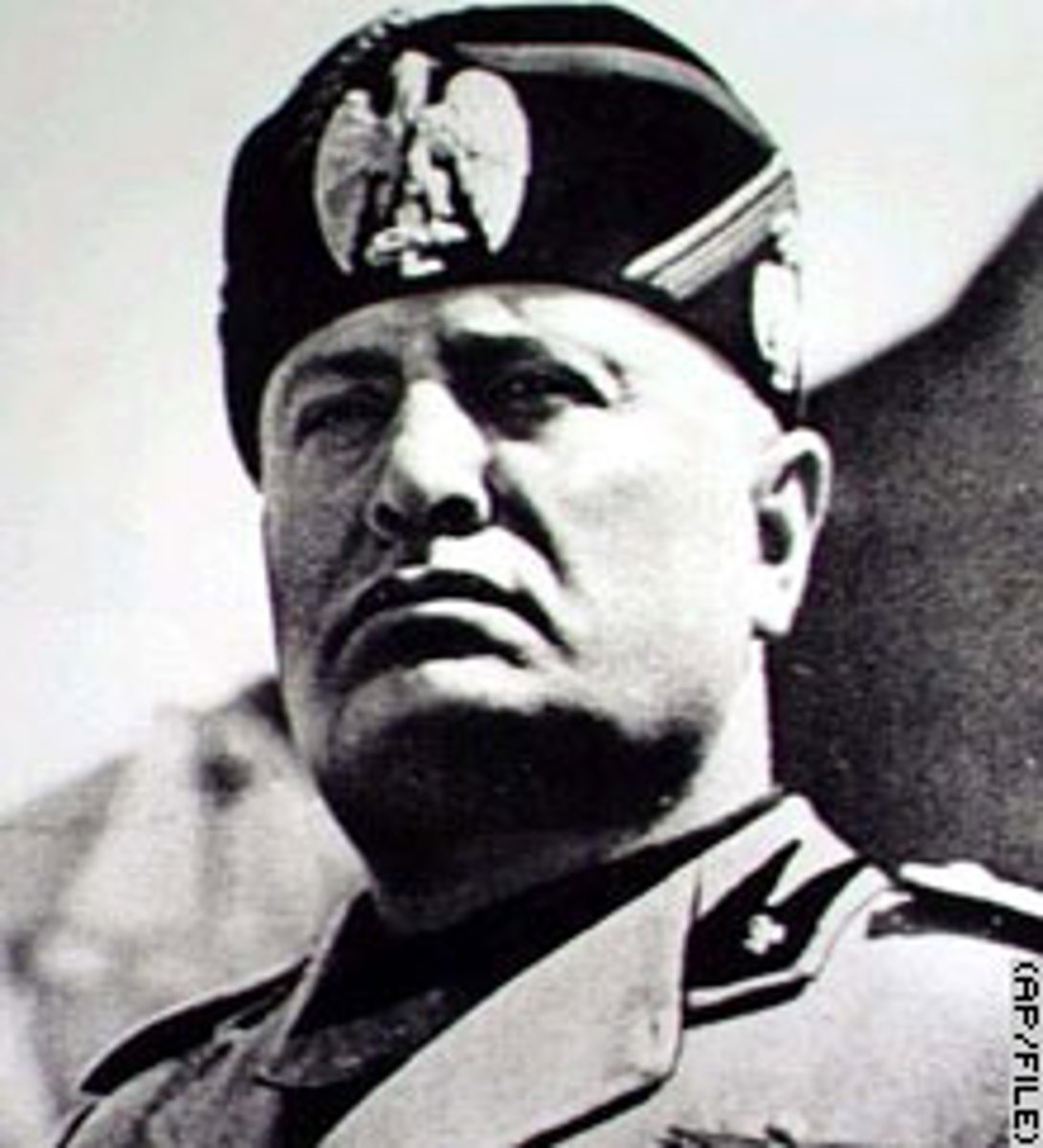
Benito Mussolini
Italian fascist dictator during World War II

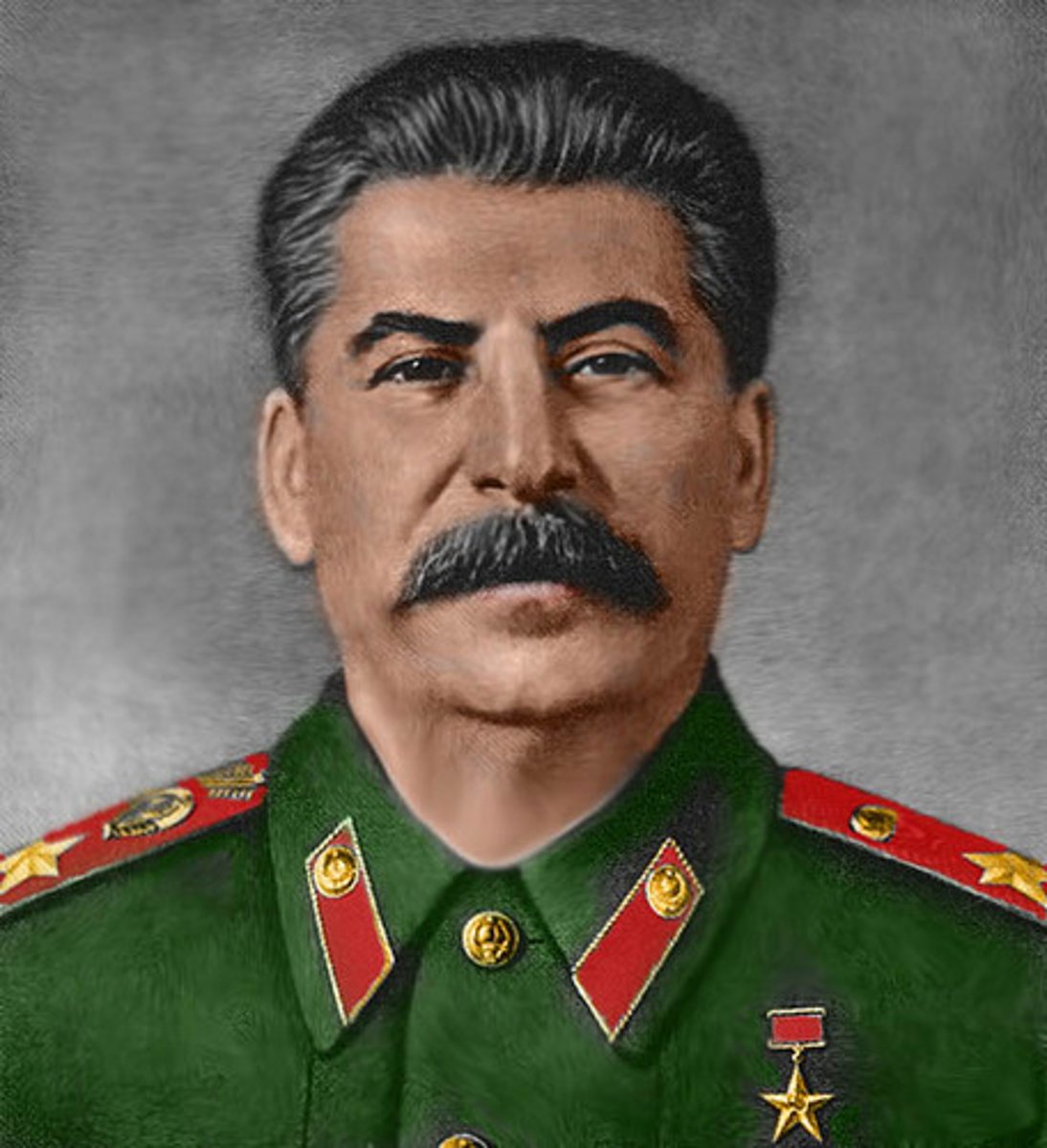
Joseph Stalin
Leader of Soviet Union during World War II; purged millions of people who opposed communism

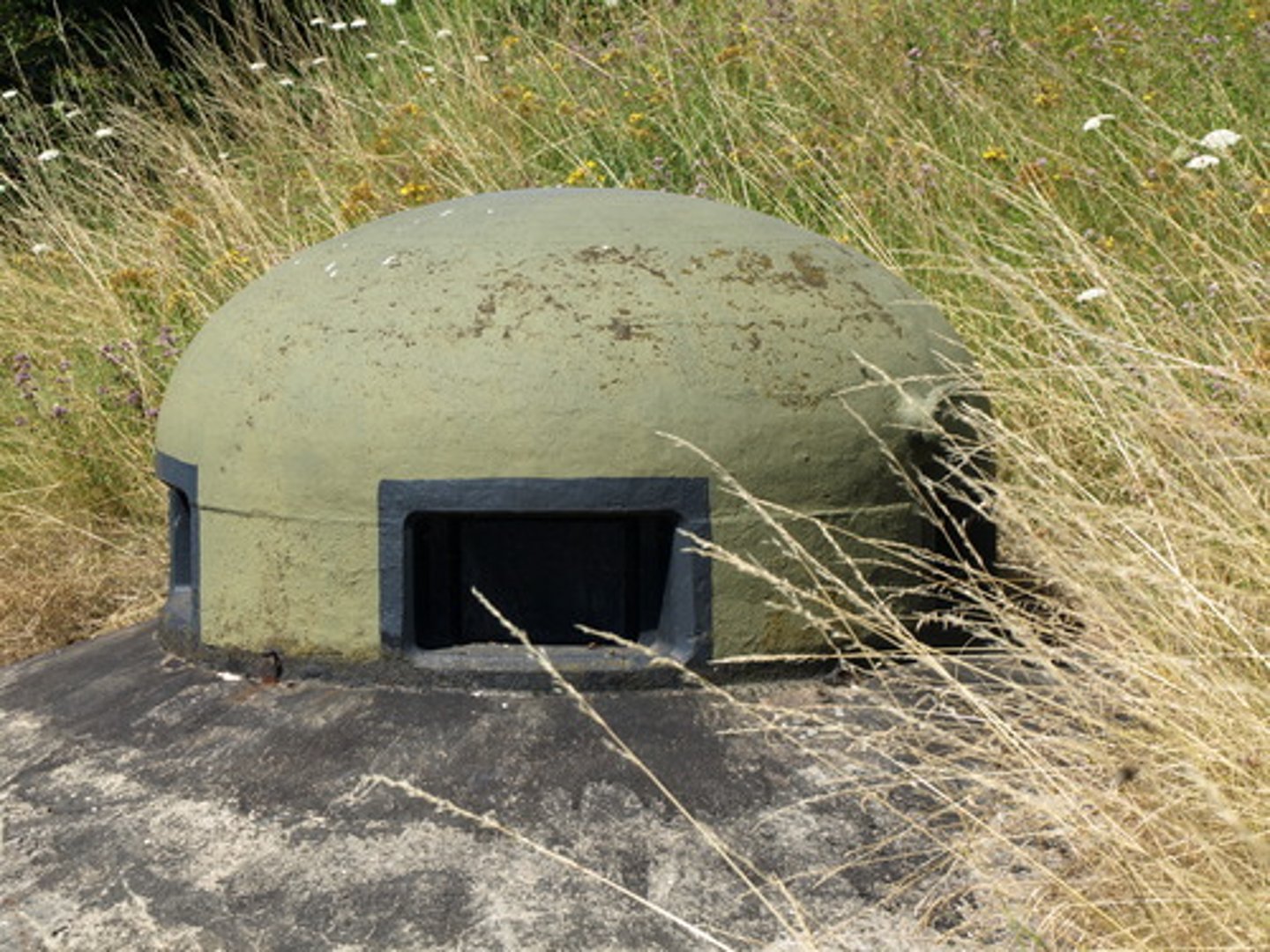
Maginot Line
Created by France after WW1, this fortifications along their eastern border was unsuccessful as Germans flew over and went around this defense system

The Battle of Britain
air campaign waged by the Luftwaffe against the United Kingdom during the summer and autumn of 1940.

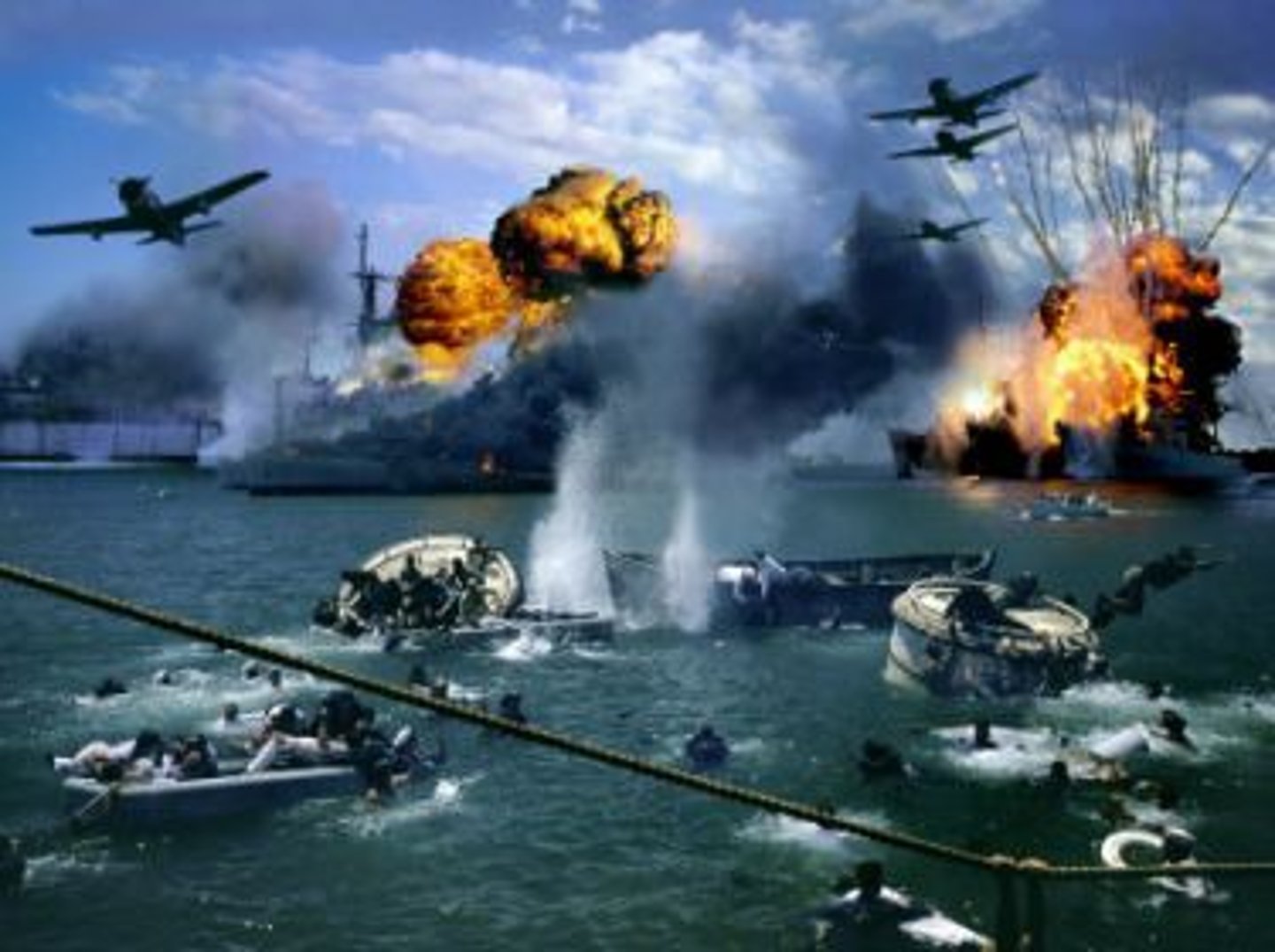
Pearl Harbor
Base in Hawaii that was bombed by Japan on December 7, 1941, which led to America to entering the war

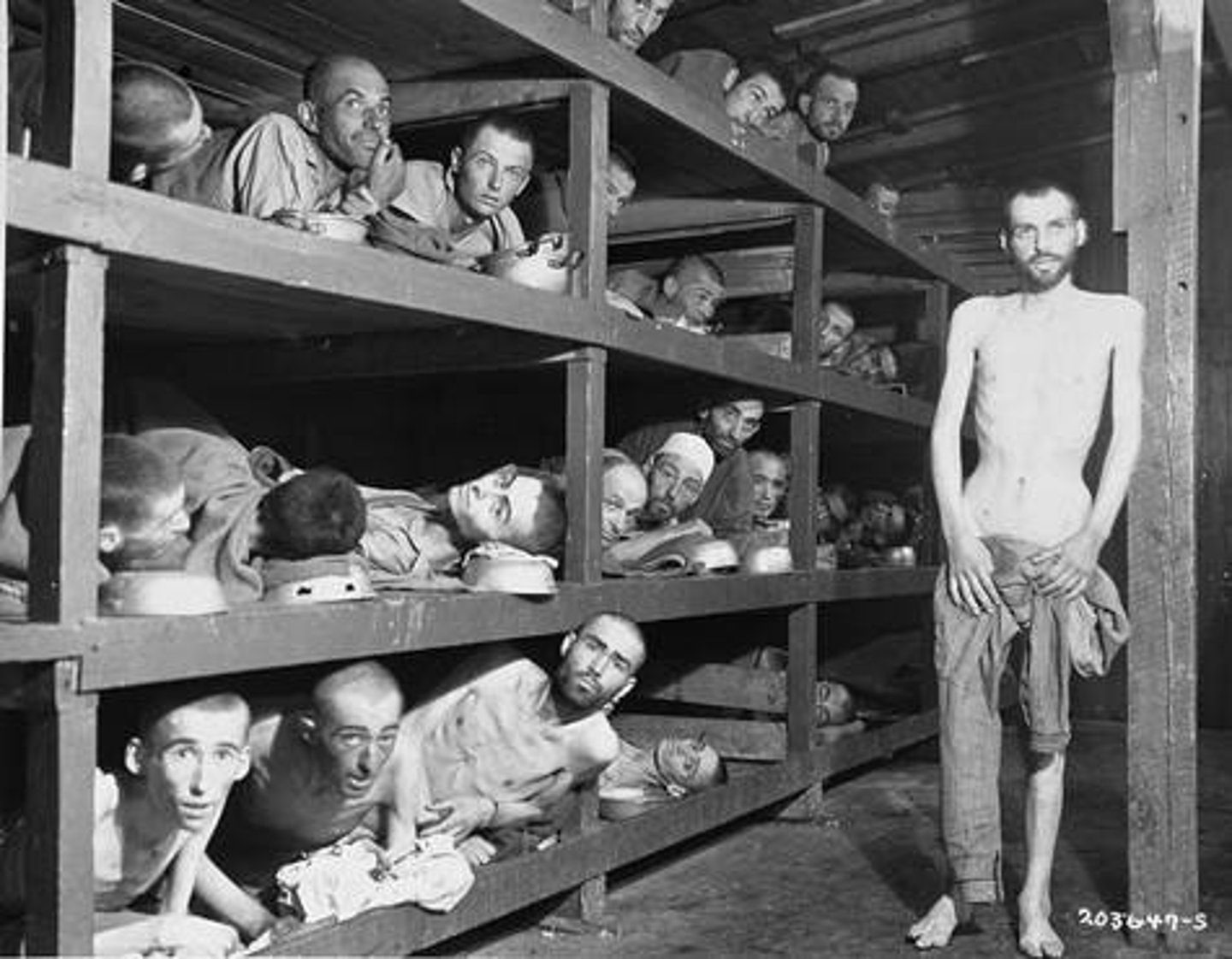
Holocaust
the organized killing of European Jews and others by the Nazis during WWII

Dwight Eisenhower
Supreme Allied Commander in Europe
Leader of the D-Day invasion

The Manhattan Project
A secret research and development project of the US to develop the atomic bomb. Its success granted the US the bombs that ended the war with Japan as well as ushering the country into the atomic era
Normandy
Region in France where D-Day invasion took place

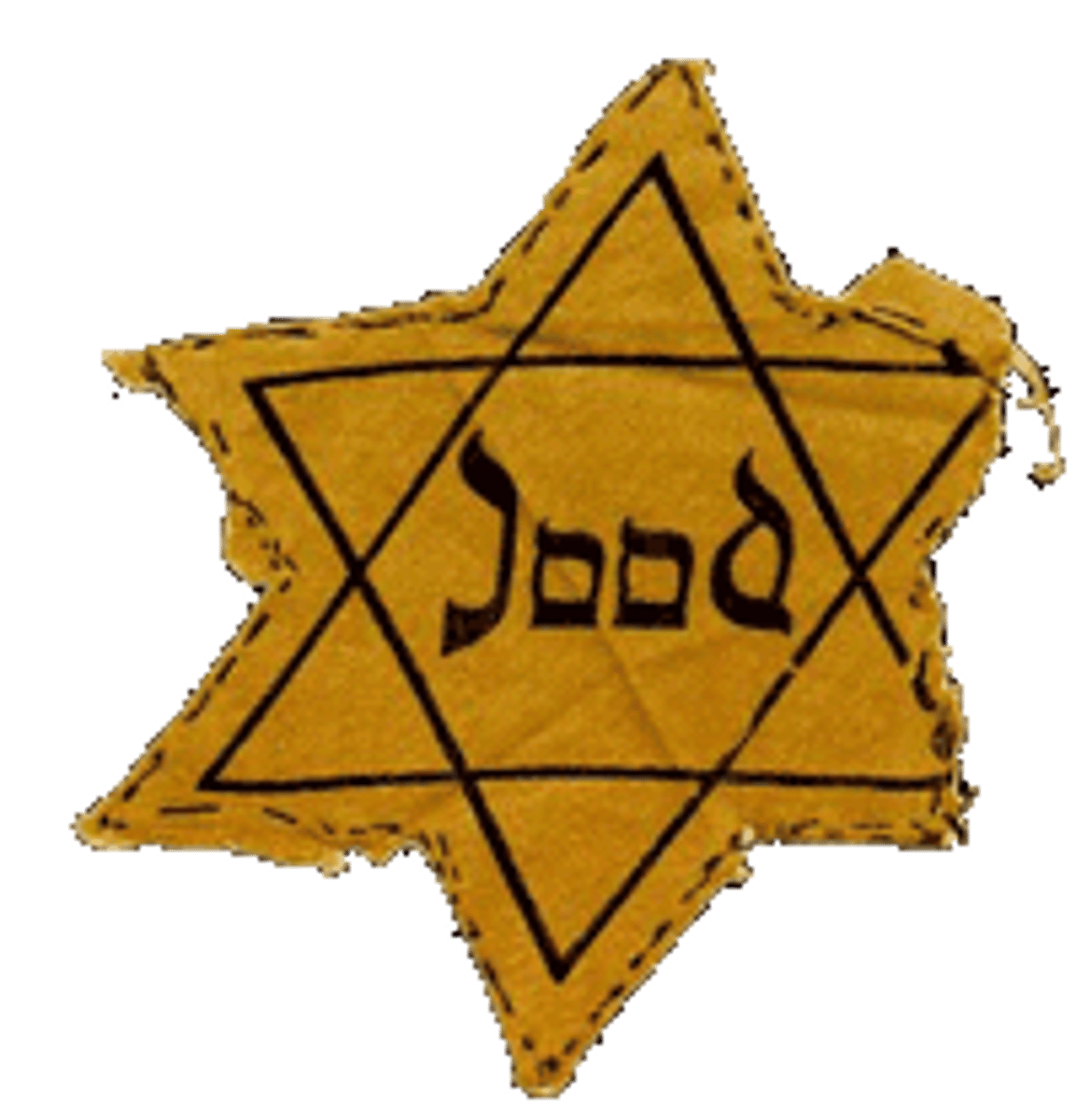
Nuremberg Laws
Placed severe restrictions of Jews, prohibited from marrying non- Jews, attending schools or universities, holding government jobs, practicing law or medicine or publishing books.

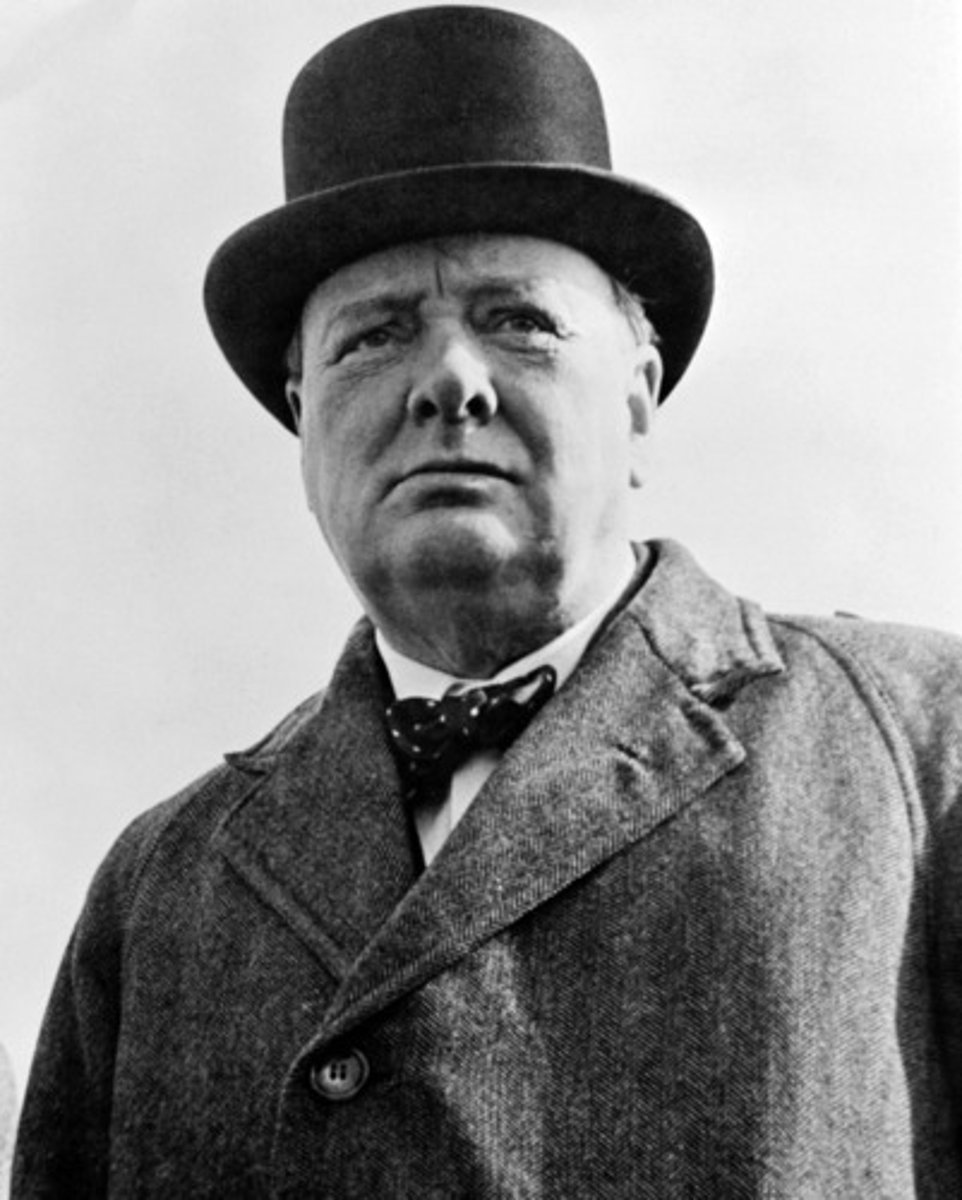
Winston Churchill
Prime Minister of Great Britain during WWII

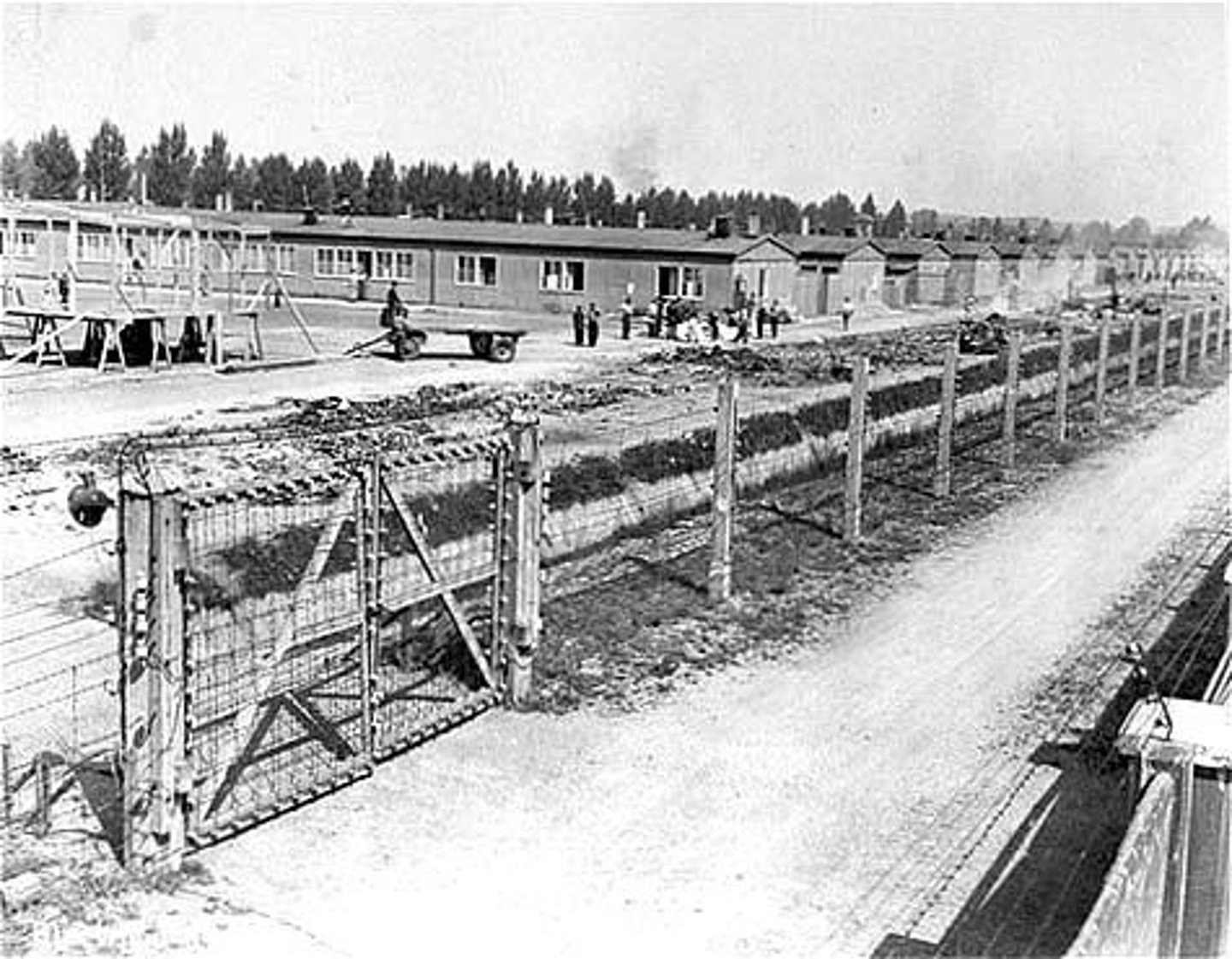
Concentration Camps
prison camps used under the rule of Hitler in Nazi Germany. Conditions were inhuman, and prisoners, mostly Jewish people, were generally starved or worked to death, or killed immediately.

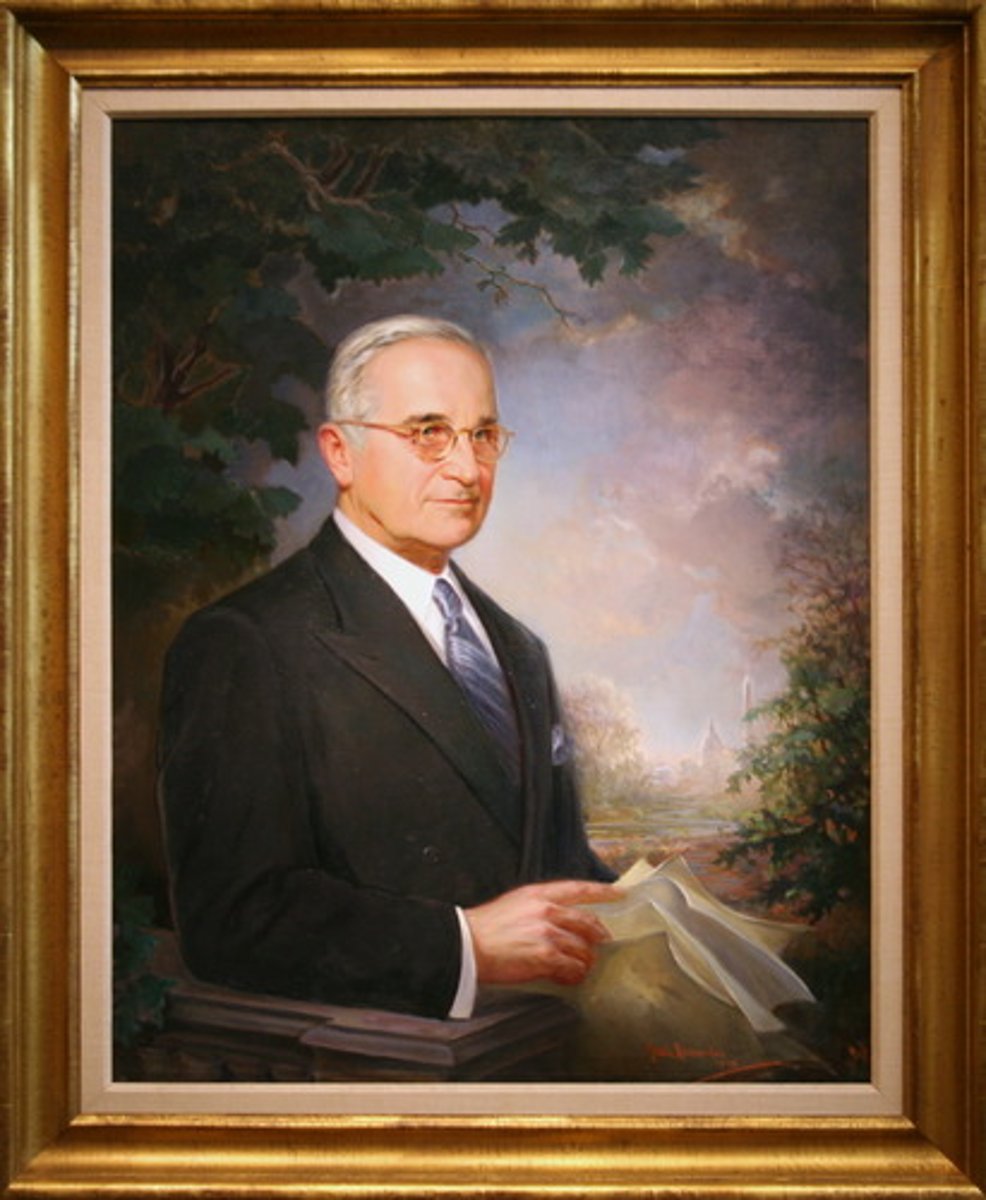
Harry Truman
Became president when FDR died in 1945; public was largely unfamiliar with him

V-E Day
May 8, 1945; victory in Europe Day when the Germans surrendered

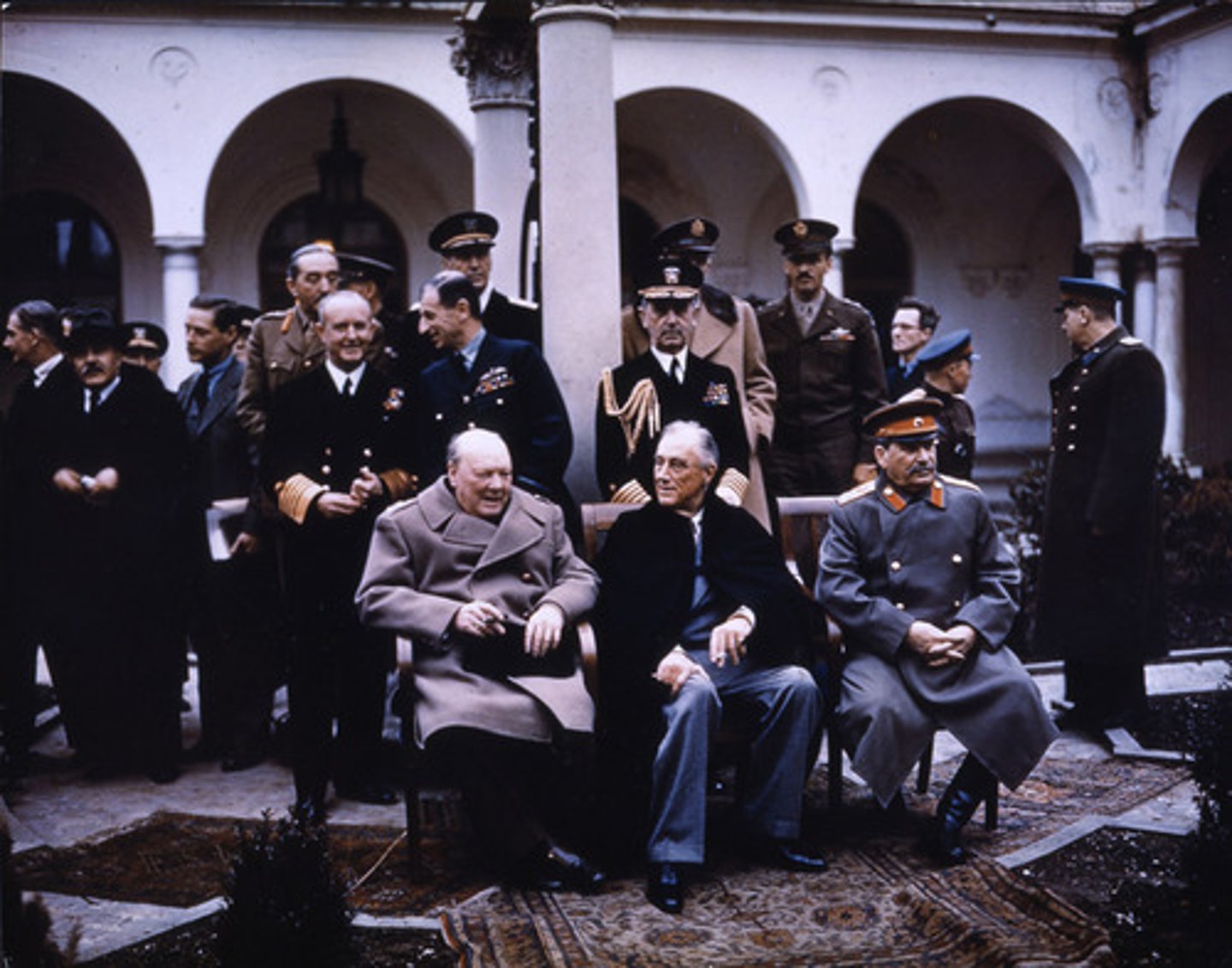
Yalta Conference
meeting at which the Allies agreed to form a United Nations organization

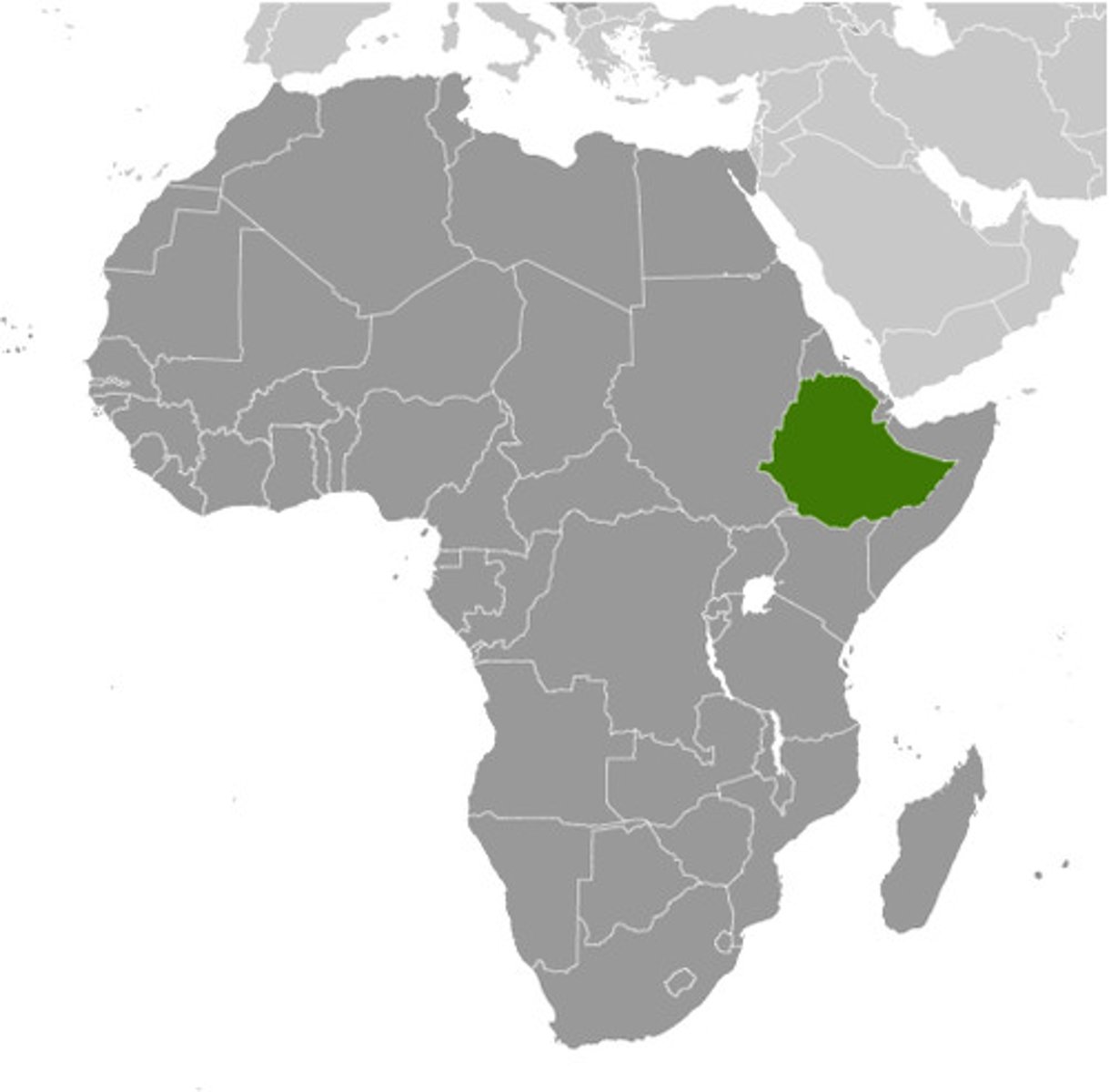
Ethiopia
African nation invaded by fascist Italy in 1935 led by Halie Selassie
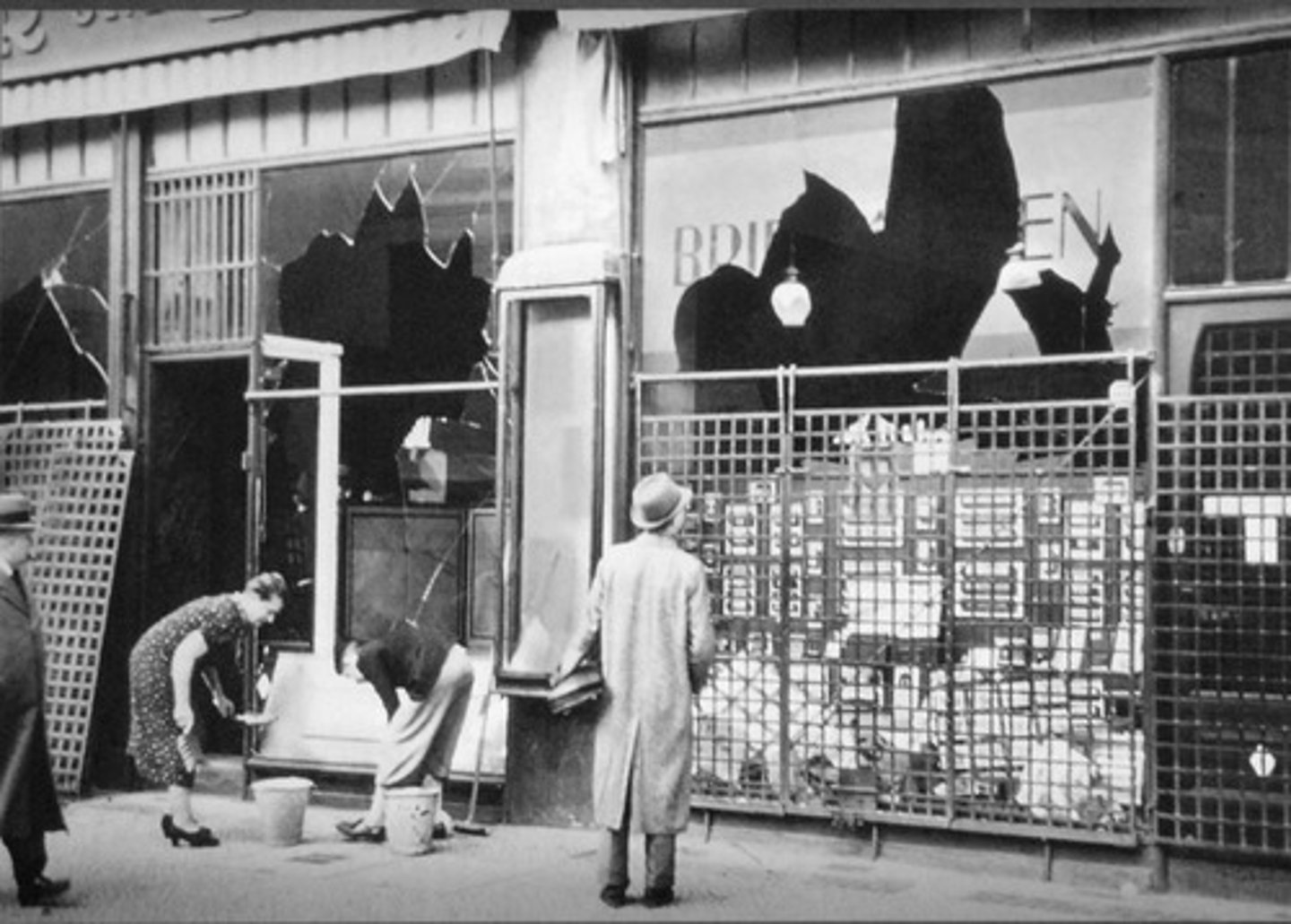
Kristallnacht
(Night of the Broken Glass) November 9, 1938, when mobs throughout Germany destroyed Jewish property and terrorized Jews.

Atlantic Charter
Declaration of principles issued by Winston Churchill and Franklin D. Roosevelt in August 1941

League of Nations
An international association formed after World War I with the goal of keeping peace among nations. US never joined.

Operation Barbarossa
Code name for plan used by Hitler to invade the Soviet Union in search of more living space. Broke the Molotov-Ribbentrop pact

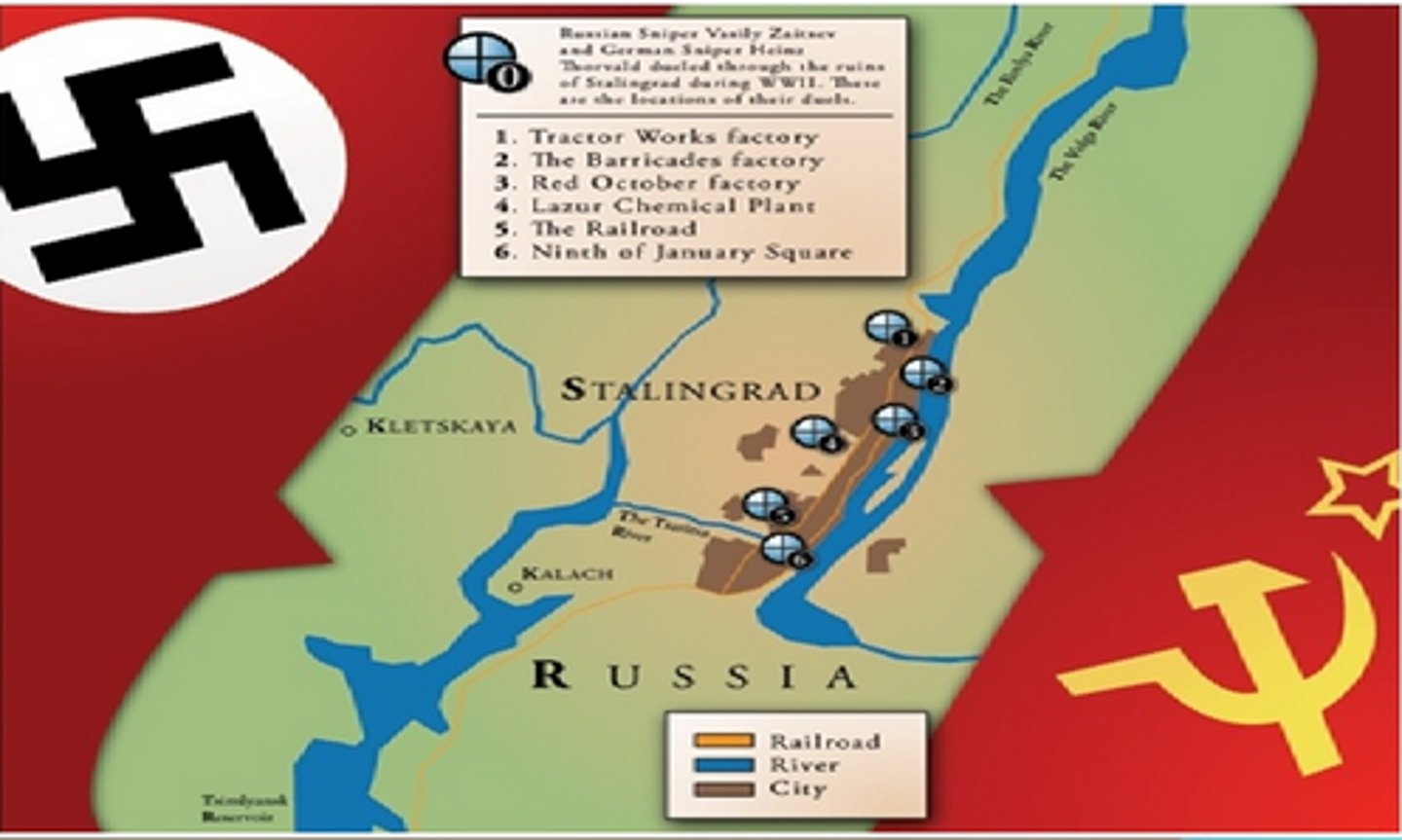
Battle of Stalingrad
Unsuccessful German attack on Soviet city from 1942 to 1943, that was the furthest extent of German advance into the Soviet Union.
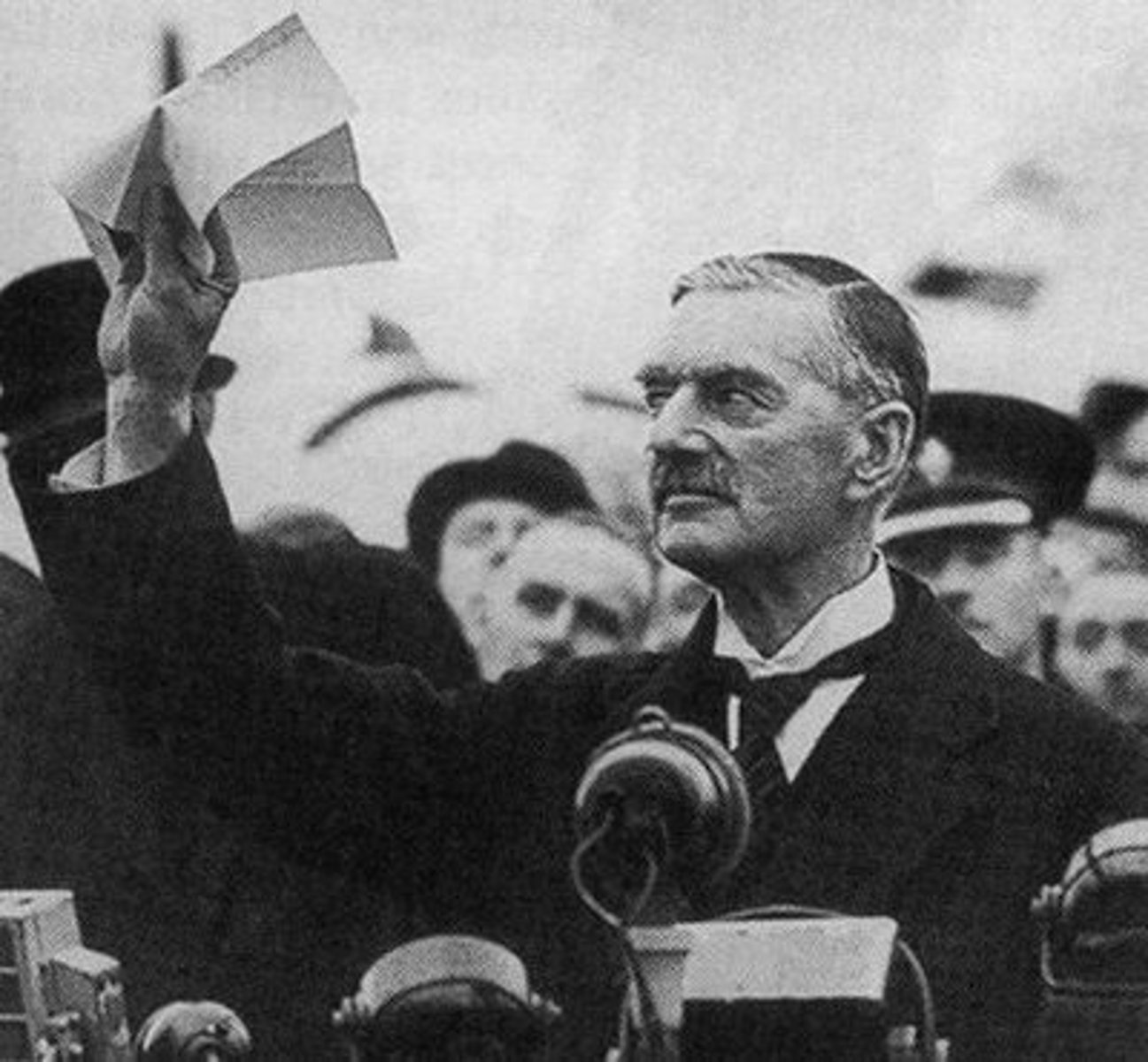
Neville Chamberlain
Prime Minister of Great Britain from -1940. Famous for appeasing Hitler at the Munich Conference; replaced by Churchill

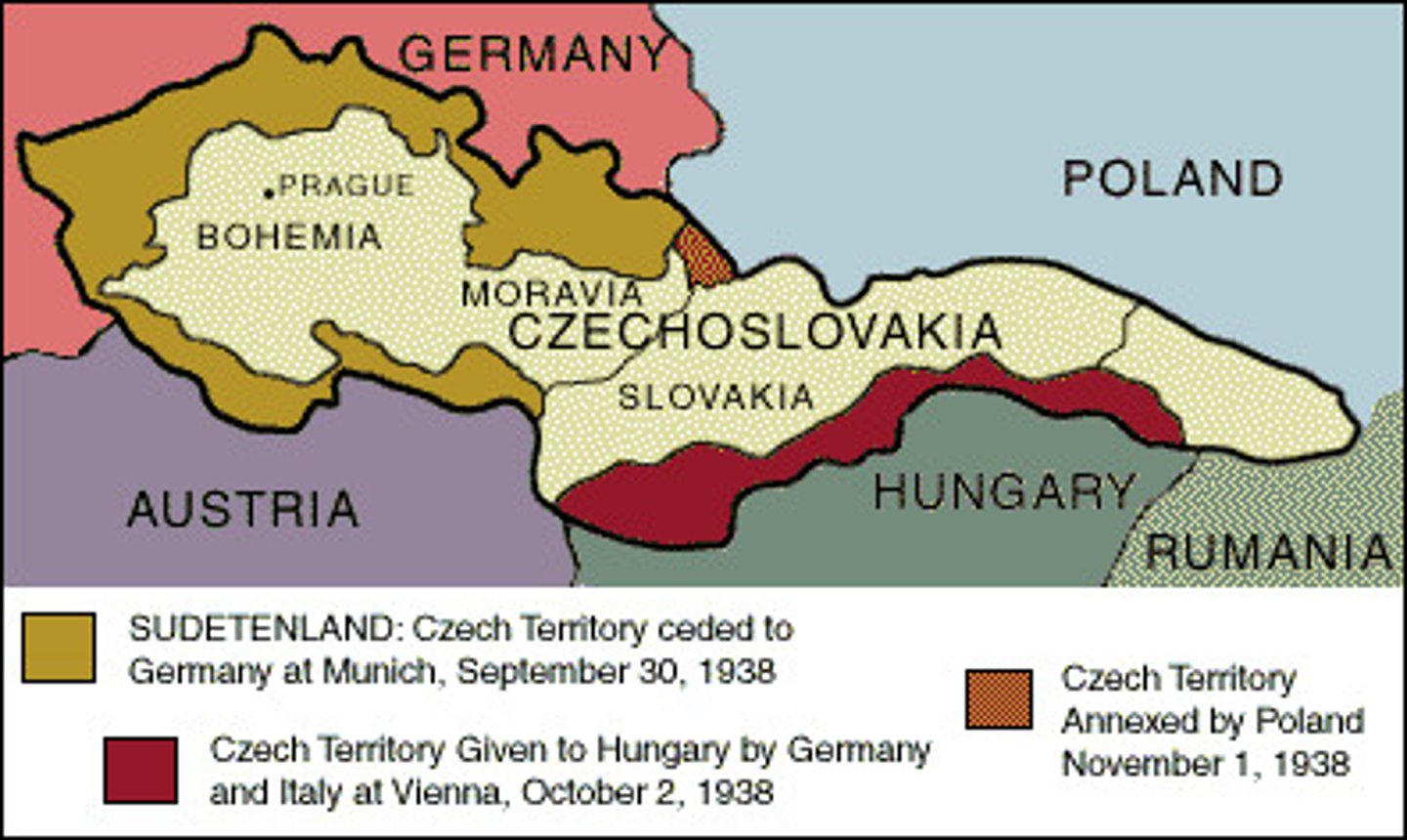
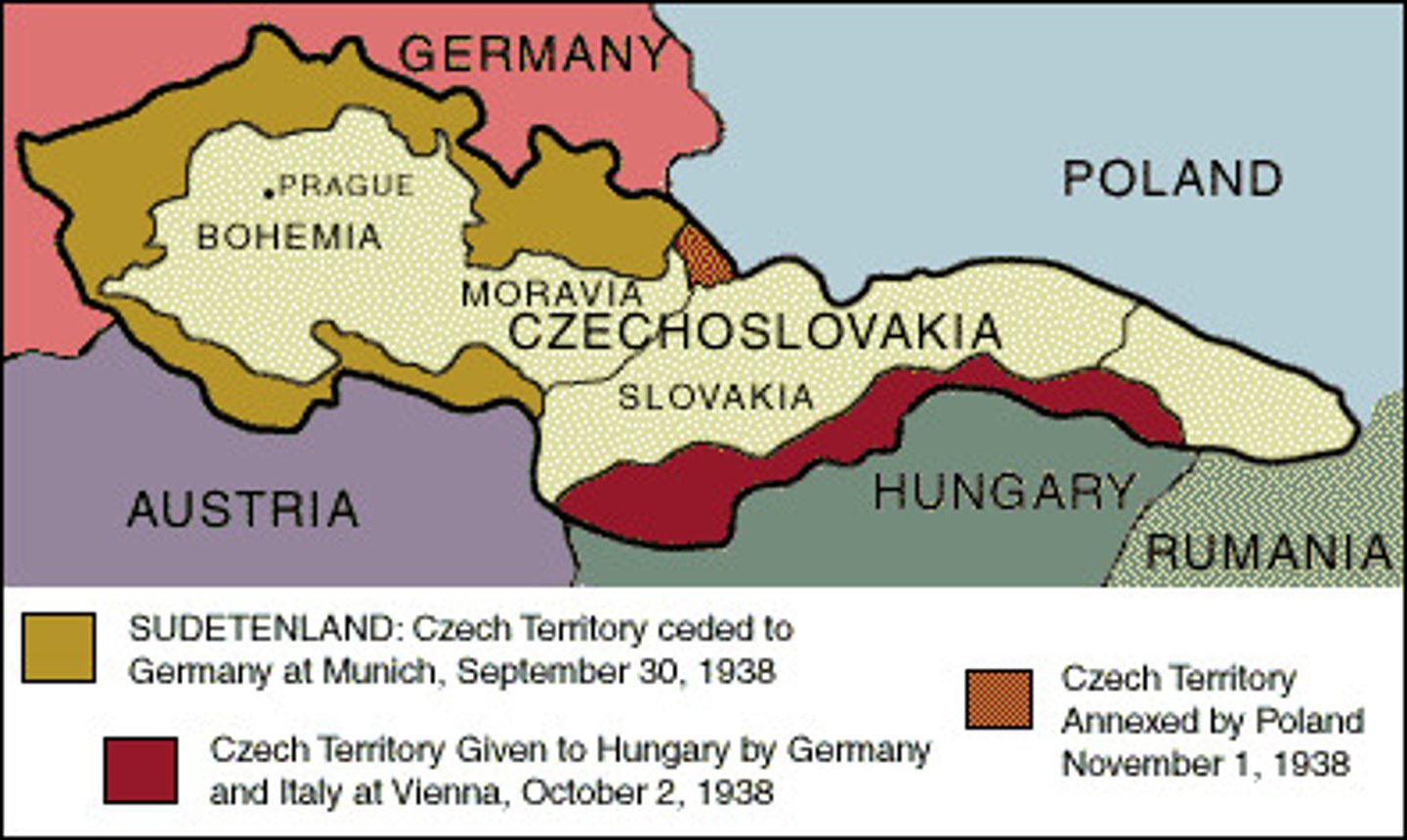
Czechoslovakia
the country that Hitler took over---breaking the Munich Pact
Phony War
period after the collapse of Poland, until Hitler attacked Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, and Belgium

Germany
Humiliation and hyperinflation after WW1 helped Hitler rise to power in this country
Radar
New technology that allows the Allies to detect incoming enemy aircraft
Mein Kampf
Influential book Written by Adolf Hitler describing his life and ideology.

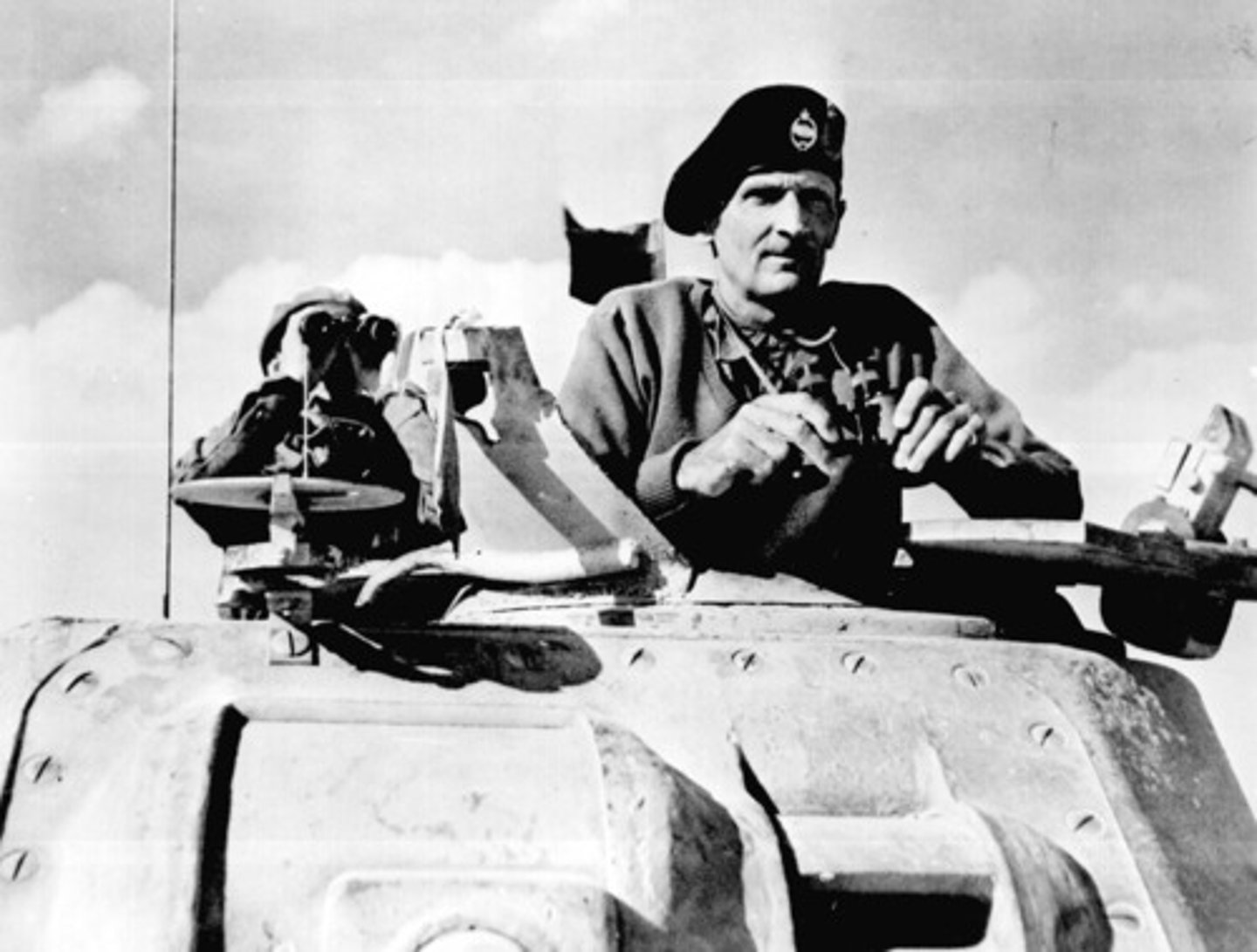
Bernard Montgomery
British General who stopped the Germans at El Alemain

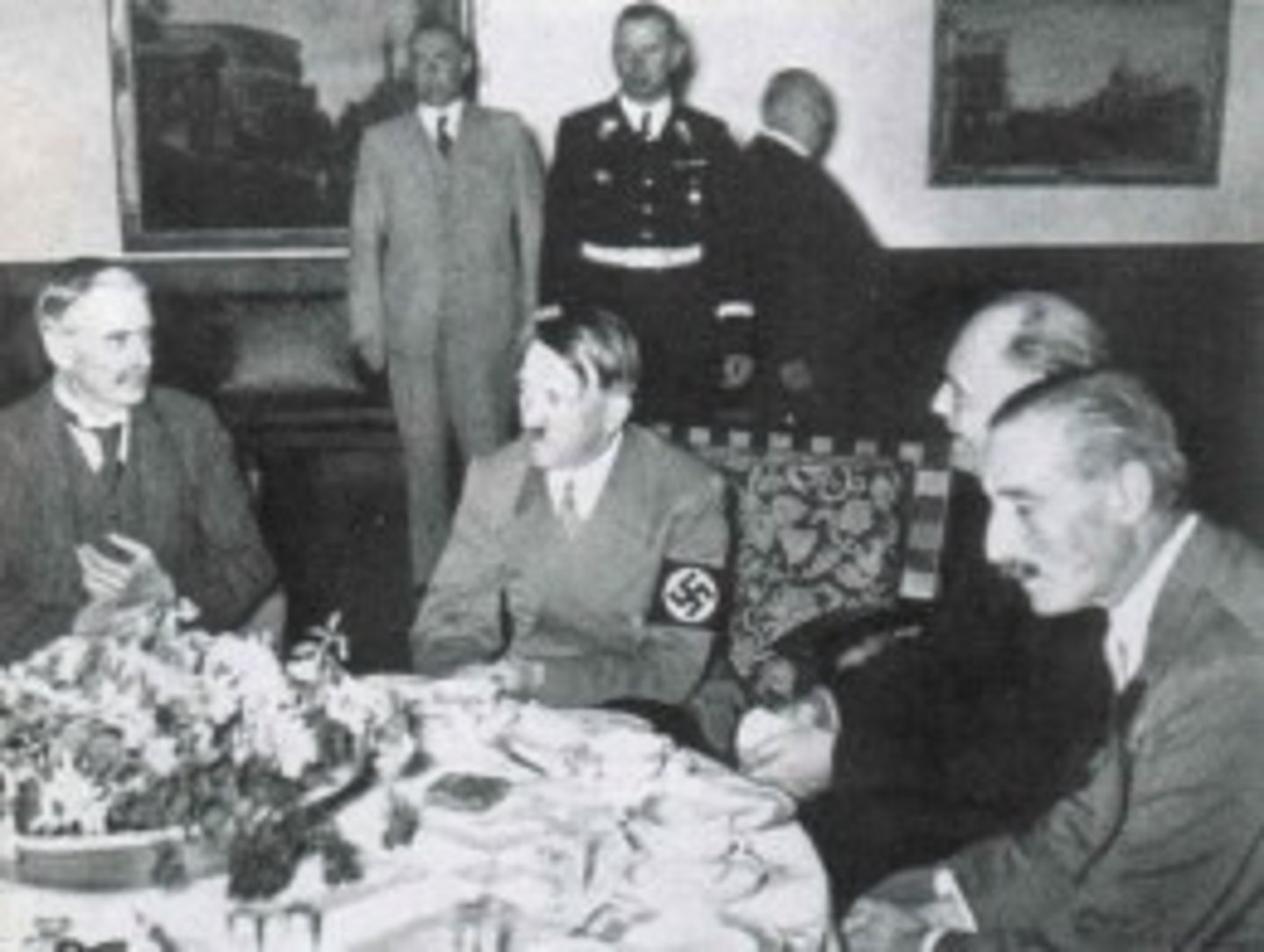
Munich Conference
a 1938 meeting of representatives from Britain, France, Italy, and Germany, at which Britain and France agreed to allow Nazi Germany to annex part of Czechoslovakia in return for Adolf Hitler's pledge to respect Czechoslovakia's new borders

Sudetenland
an area in western Czechoslovakia that was coveted by Hitler; comprised of German speaking people that once belonged to Germany
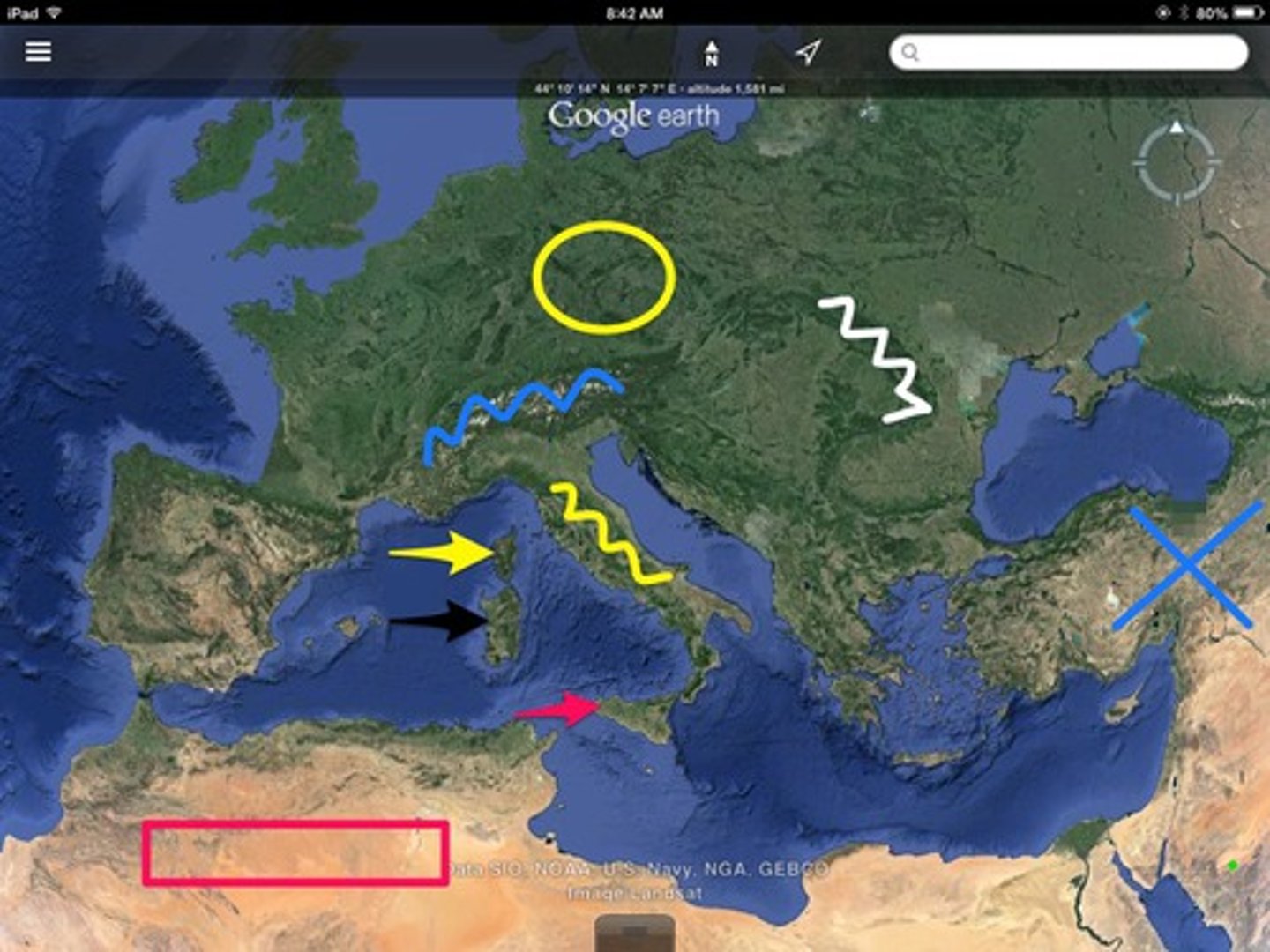
Soft Underbelly
Instead of the Allies invading Nazi-held France, they attacked the German's in North Africa and then Italy.
Lend-Lease Act
1941 law that authorized the president to aid any nation whose defense he believed was vital to American security

Battle of the Bulge
December, 1944-January, 1945 - After recapturing France, the Allied advance became stalled along the German border. In the winter of 1944, Germany staged a massive counterattack in Belgium and Luxembourg which pushed a 30 mile "bulge" into the Allied lines. The Allies stopped the German advance and threw them back across the Rhine with heavy losses.

Island Hopping Strategy
WWII strategy of conquering only certain Pacific islands that were important to the Allied advance toward Japan
Douglas MacArthur
American general, who commanded allied troops in the Pacific during World War II.
Hideki Tojo
This general was premier of Japan during World War II while this man was dictator of the country. He gave his approval for the attack on Pearl Harbor and played a major role in Japan's military decisions until he resigned in 1944
Isoroku Yamamoto
Japanese admiral who planned the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 (1884-1943)
Baatan Death March
In 1942, the Japanese marched 70,000 Filipino and American soldiers 60 miles to a prison camp
Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Two Japanese cities on which the U.S. dropped the atomic bombs to end World War II.
Internment Camps
Detention centers where more than 100,000 Japanese Americans were relocated during World War II by order of the President.
Axis Powers (WWII)
Germany, Italy, Japan
Battle of Midway (1942)
In this battle the US destroyed Japanese aircraft carriers and ended Japanese offensive in the Pacific Theater; turning point
Manchuria
Province in northeast China invaded by Japan in September 1931
Operation Overlord
the code name for the Allied invasion of Europe at Normandy on June 6, 1944; also known as D-Day
Executive Order 9066
FDR's order to place all Japanese Americans in Internment Camps in the western interior of the country.
Sitzkrieg
"Phony War" with Hitler in 1939-1940 where Hitler prepared for his attack
Hirohito
Emperor of Japan during WWII. Remained emperor after WWII but just figure head not really in charge
V-J Day
"Victory over Japan day" is the celebration of the Surrender of Japan, which was initially announced on August 15, 1945
Robert J. Oppenheimer
Scientist; his research led to the development of the atomic bomb.
Non-Aggression Pact
1939-Secret agreement between German leader Hitler and Soviet Leader Stalin not to attack one another and to divide Poland
Final Solution
Hitler's program of systematically killing the entire Jewish people
Battle of Iwo Jima and Okinawa
two great Japanese battles; Two successful battles fought and won by Allied forces in the Pacific.
Vichy France
Southern Pro-Nazi French; govern themselves as loyal to nazis; traitors to the Free French in N. France
Charles de Gaulle
French general and statesman who became very popular during World War II as the leader of the Free French forces in exile (1890-1970)
Kamikaze
Japanese suicide pilots
Anschluss
Union of Austria and Germany
Anti-Semitism
Prejudice against Jews
genocide
Deliberate extermination of a racial or cultural group
Luftwaffe
German Air Force
Haavara Agreement (1933)
Agreement was designed to help facilitate the emigration of German Jews to Palestine.
crimes against humanity
a category of activities, made illegal at the Nuremberg war crime trials, condemning states that abuse human rights
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
As announced in 1940 by Japan's prime minister, the area extending from Manchuria to the Dutch East Indies in which Japan would expand its influence
Auschwitz-Birkenau
The largest and most notorious concentration, labor and death camp where 1.6 million died; located near Oswiecim, Poland.
Unit 731
infamous Japanese army unit that conducted medical experiments on the Chinese
UN Security Council
A 15-member panel which bears the UN's major responsibility for keeping international peace.
Postdam Conference
This is the conference where Stalin, Truman, and Churchill came together to decide how Germany would be administered. Their goals were to establish order, settle peace treaty issues, and deal with the effects of WWII.
Rome-Berlin Axis
the alliance between Italy and Germany (Mussolini and Hitler)
Arms Race (Cold War)
America and USSR competed for superiority in the development and accumulation of weapons after dropping the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki