Chapter 12: The Endomembrane System and Peroxisomes
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Sites for protein synthesis, processing, and sorting; lipid synthesis, and drug detoxification
Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus
Carry and sort material brought into the cell
Endosomes
Digest ingested material and unneeded cellular components
Lysosomes
Houses hydrogen peroxide degradation reactions. Perform diverse metabolic functions. Contains catalase specific for hydrogen peroxide
Peroxisomes
Continuous network of flattened sacs, tubules, and vesicles through the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER consists of membrane-bound tubular and flattened sacs called?
cisternae
The internal space of the ER is called?
lumen
Contains ER exit sites. Areas where the transport vesicles that contain lipids and proteins made in the ER, detach from the ER, and start moving to the Golgi Apparatus
Transitional ER
Formed using the ER material. Will contain the protein that was being built and synthesize in the rough ER. Bud off from the ER
Transport vesicle
Functions of ER
protein and lipid synthesis
A type of ER that form large flattened sheets
Rough ER
A type of ER that form tubular structures
Smooth ER
Flow of genetic information in a cell. Final output is protein
Central Dogma
Most of the genes associated with eye color are related to the production, transport, and storage of the pigment protein called?
melanin
amount and quality of melanin in the front layers of the iris
eye color
TRUE OR FALSE:
Brown eyes have less melanin and blue eyes have more melanin
False
Carries the genetic code for protein synthesis to the cytoplasm
mRNA
Serves as the site for protein synthesis
rRNA
Reads the code (mRNA) and carries the amino acid to be incorporated to the developing protein
tRNA
TRUE OR FALSE:
Ribosomes on the cytosolic side of the rough ER membrane synthesize both membrane-bound and soluble proteins for the endomembrane system
True
Newly synthesized proteins enter the endomembrane system how?
cotranslationally
Proteins are inserted through this in the ER membrane into the rough ER lumen as the polypeptide is synthesized by the ER bound ribosome
pore complex
The site for the initial steps of addition of carbohydrates to glycoproteins. Assembly of multimeric protein complexes. A membrane factory for the cell
Rough ER
Quality control proteins that are incorrectly folded modified or assembled are exported for degradation
ER associated degradation
What step is this statement in the protein synthesis?
As the protein elongates, the end of the polypeptide enters the ER. As the amino acid gets longer, it penetrates inside the lumen of the ER
Step 2
What step is this statement in the protein synthesis?
Addition of sugar units (glycoproteins)
Step 3
What step is this statement in the protein synthesis?
Semi completed length of the polypeptide, there would also be a budding of vesicle which will transport the molecule that buds of in the Golgi Apparatus where everything else happens before secretion [release] happens
Step 4
It started in the cytoplasm then entered in the RER and synthesized
Cotranslational protein synthesis
Has no role in protein synthesis. Involved in the synthesis of lipids and steroids such as cholesterol and its derivatives. Responsible for inactivating and detoxifying potentially harmful substances
Smooth ER
Critical functions in muscle contraction. Can store calcium in the SER
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Drug detoxification often involves
hydroxylation
Adding hydroxyl groups to hydrophobic drugs increases their solubility
hydroxylation
TRUE OR FALSE:
When drug is less soluble, it can easily release (detoxify)
False
The elimination of barbiturate drugs is enhanced by what enzymes in the smooth ER
hydroxylation
Hydroxylation is catalyzed by a member of what family of proteins?
cytochrome P-450
Prominent in the liver for detoxification
Smooth ER
TRUE OR FALSE:
The more cytochrome P-450 a patient have, the faster detoxification is.
True
The study of the differences in the presence or activity of particular cytochrome P—450 genes in different patients
Pharmacogenetics
This stores glucose as glycogen in granules associated with smooth ER
liver
When glucose is needed by the body, glycogen is broken down to glucose-6-phosphate by an enzyme called? (This is unique to SER)
Glucose-6-Phosphatase
If a patient can’t breakdown glycogen, what part of the endomembrane system is responsible for that?
Smooth ER
TRUE OR FALSE:
The SER and Glycogen are near to each other in terms of proximity.
True
Smooth ER that specializes in calcium storage
sarcoplasmic reticulum
It is released when needed for muscle contraction
Calcium
The SER lumen contains high concentrations of
calcium-binding proteins
A membranous structure surrounding each myofibril (like ER). Responds to the action potential. Stores and release Ca2+ when an action potential is received
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains this chambers that is attached to T tubules
Terminal cisternae
If a patient found to have malfunctioning ineffective muscle contraction, who is the culprit and why?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum can’t store or release calcium
Smooth ER in some cells is the site of
steroid biosynthesis
If a patient has high cholesterol, it can be due to unhealthy diet or?
hyperactive SER
TRUE OR FALSE:
Smooth ER has also been found associated with plastids in some plants, and may be involved in plant hormone synthesis
True
Part of protein synthesis wherein it is partially finishing the structure of the protein. Adding sugars/carbohydrates to polypeptides
Glycosylation
Start of protein synthesis is in the
cytosol
As the polypeptide elongates, it penetrates the
lumen
Using the membrane of the ER, it will bud off forming this, a vehicle that transports the partially finish polypeptide to the Golgi Apparatus for packaging and release
vesicle
TRUE OR FALSE:
Polypeptide synthesis beings in the cytosol but takes one of three alternative routes when the polypeptide is approx. 30 amino acids long
False
the primary source of membrane lipids with a few exceptions
ER
Mitochondria synthesize
phosphatidylethanolamine
Peroxisomes synthesize
cholesterol
Chloroplasts contain enzymes for
chloroplast-specific lipids
Type of diffusion that is flip-flop and changes postion
transverse diffusion
The rotation of the ER
own axis
Type of diffusion that is neighboring
lateral diffusion
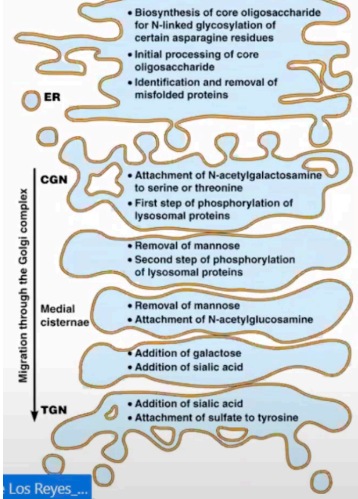
It plays an important role in processing and packaging secretory proteins, and in complex polysaccharide synthesis. Here, glycoproteins and membrane lipids from the ER undergo further processing and are sorted and packaged for transport thru transport vesicles
Golgi Complex
The Golgi complex consists of flattened membranous sacs called
cisternae
A series of cisterna, usually 3-8, is called
Golgi stack
the cis face is oriented towards the ER, the Golgi compartment on this side is called the (receiving end)
cis-Golgi network (CGN)
The opposite side is called the trans face and the compartment on this side is called the (shipping side)
trans-Golgi network (TGN)
Has plasma membrane because they are only bud off of the ER. Received by the CGN
Vesicles
Movement of material towards the plasma membrane (left to right)
anterograde transport
The flow of vesicles from Golgi cisternae back to the ER (right to left)
retrograde transport
What is the composition of a vesicle?
Phospholipid bilayer
TRUE OR FALSE:
Through the antegrade transport, the lipids that compose the vesicle are disappearing. Through the retrograde transport, it ensures that there’s a supply of materials to form new vesicle
True
As a secretory granule fuses with the plasma membrane and discharges its contents (exocytosis), a bit of membrane from the ER becomes part of the plasma membrane. This flow of lipid toward the plasma membrane must be balanced
Anterograde
This allows the cell to balance the flow of lipids toward the plasma membrane. It also ensures a supply of materials for forming new vesicles
Retrograde
Are carbohydrate chains containing 3-10 sugar units
Oligosaccharides
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions involving the resulting ______ then modify the oligosaccharide side chain
glycoproteins
The initial steps of N-glycosylation take place on the
cytosol
What is the core oligosaccharide complex ratio of a carbohydrate?
2N:9M:3G
used in the formation of sugar units start in the cytosol where they are attached to the (carrier of oligosaccharides unit for glycosylation)
Dolichol phosphate
Needs to be transported and will be transported by the (translocator)
Flippase
A protein is expected to have sugar units is not functional as it doesn’t have sugar units. The culprit is?
Flippase
Proteins in a vesicle are released to the exterior of the cell as the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
exocytosis
Secrete hormones, mucus, milk proteins, and digestive enzymes through exocytosis
animal cells
Secrete enzyme and structural proteins for the cell wall
Plants and fungal cells
ARRANGE THE PROCESS OF EXOCYTOSIS
A. Fusion with the plasma membrane discharges the contents of the vesicle
B. Vesicles containing products for secretion move to the cell surface
C. The membrane of the vesicle becomes part of the cell membrane
D. The membrane of the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
B, D, A, C
The cell will receive molecules inside the cell
Endocytosis
ARRANGE THE PROCESS OF ENDOCYTOSIS:
A. A small segment of the plasma membrane folds inward
B. It pinches off to form an endocytic vesicle containing ingested substances or particles
A, B
The ingestion of large particles up to and including whole cells or microorganisms
phagocytosis
For more complex organisms, phagocytosis is usually restricted to specialized cells called
phagocytes
In humans, WBC cells use phagocytosis as a means of
defense
Detoxify hydrogen peroxide which can be reactive oxygen species which we don’t like to accumulate in our body
Peroxisomes