Amino Acids
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YOU MUST KNOW THESE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
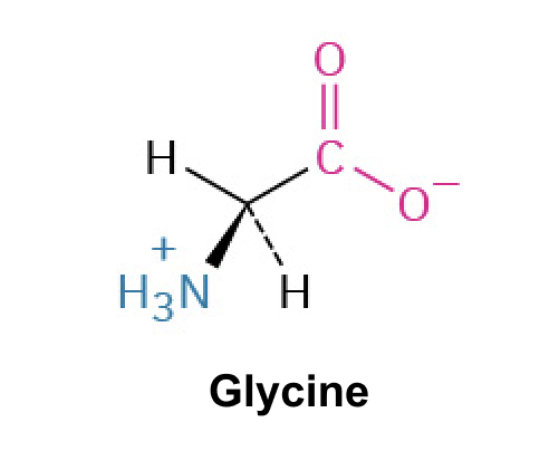
Glycine (Gly,G)*
Side Chain: H- hydrogen
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar
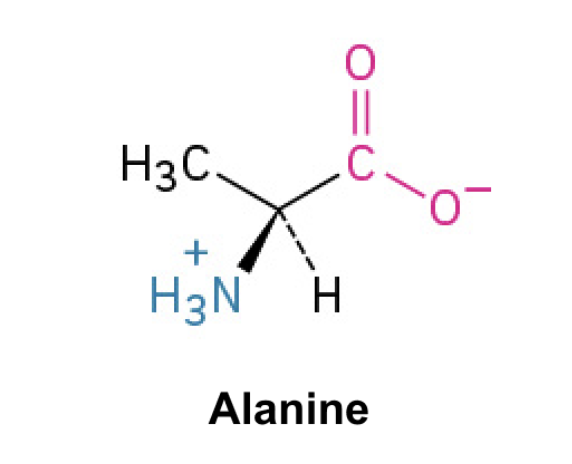
Alanine (Ala, A)
Side Chain: CH3- methyl, hydrophobic, nonpolar
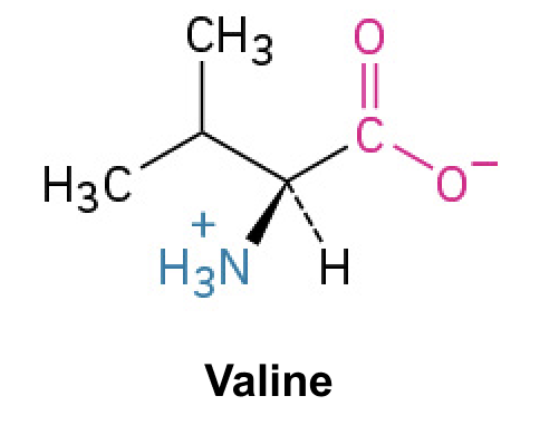
Valine (Val, V)
Side Chain: (CH(CH3)2)- isopropyl, hydrophobic, nonpolar
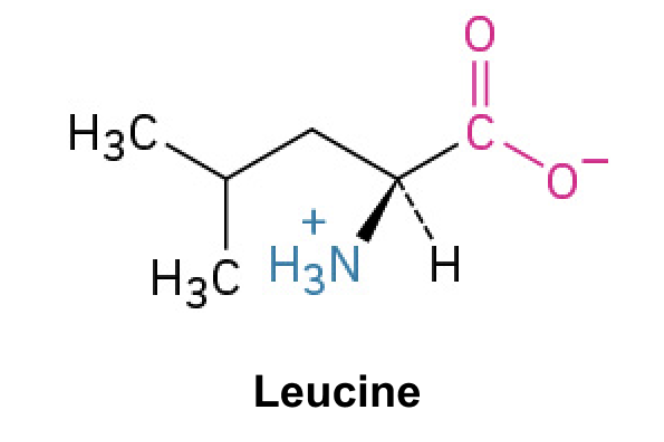
Leucine (Leu, L)
Side Chain: (CH2CH(CH3)2)- isobutyl, hydrophobic, nonpolar
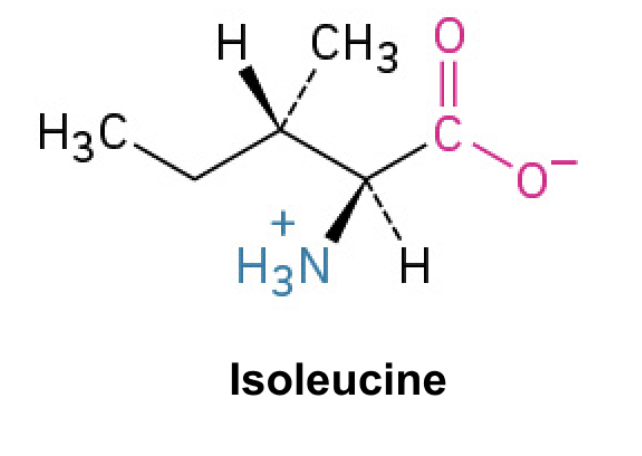
Isoleucine (Ile, I)
Side Chain: (CHCH(CH3)CH2- sec-butyl, hydrophobic, nonpolar
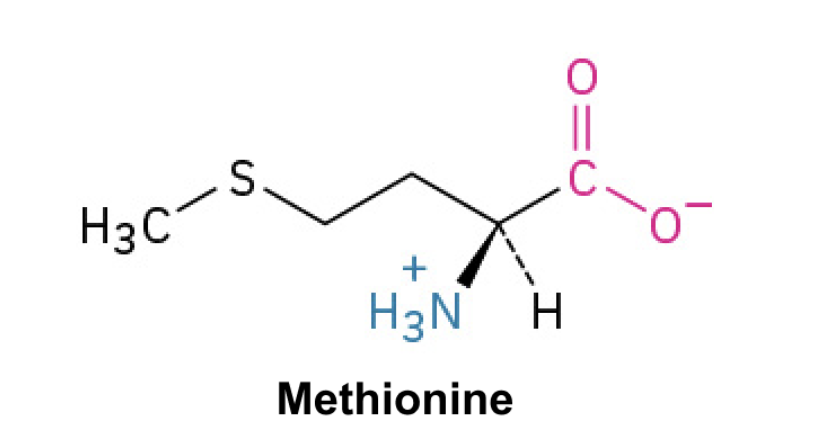
Methionine (Met, M)
Side Chain: (CH2CH2SCH3)- thioether, hydrophobic, Van Der Waals, nonpolar amino acid essential for protein synthesis, contains sulfur.
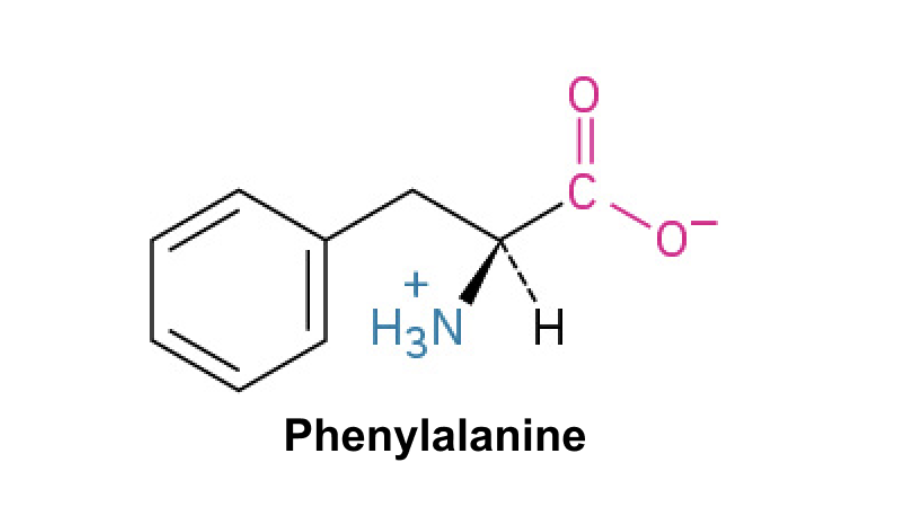
Phenylalanine (Phe, F)+
Side Chain: (C6H5CH2)- phenyl(benzene ring), hydrophobic, π-π interactions, nonpolar amino acid with aromatic ring
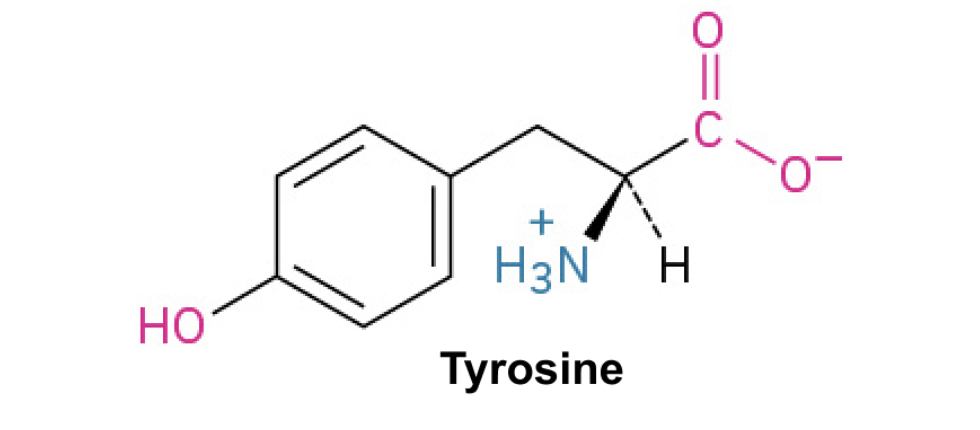
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y)+
Side Chain: (C6H4OHCH2)- phenol, π-π interactions , hydrogen bonding, polar with hydroxyl group, slightly hydrophilic.
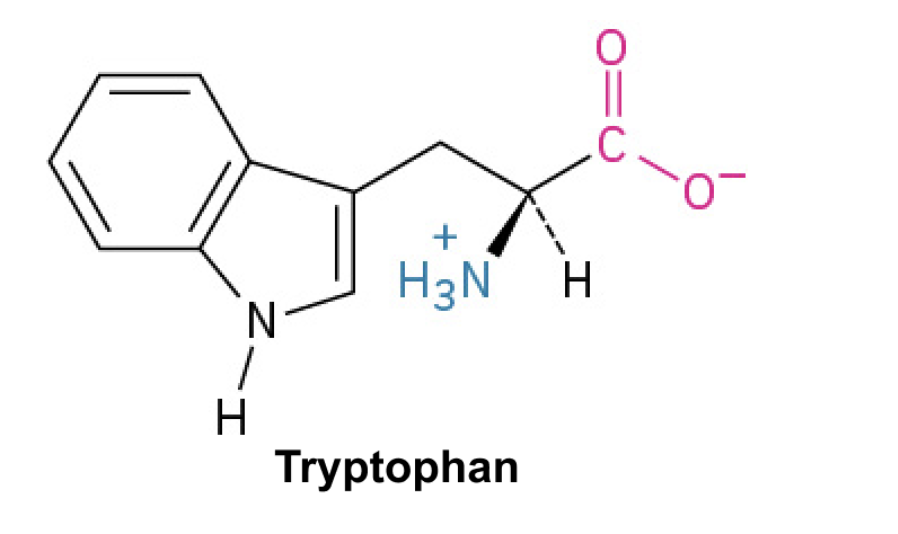
Tryptophan (Trp, W)+
Side Chain: (C8H6N)- indole, hydrophobic, π-π interactions, nonpolar. Has a nitrogen atom and important for protein-protein interaction
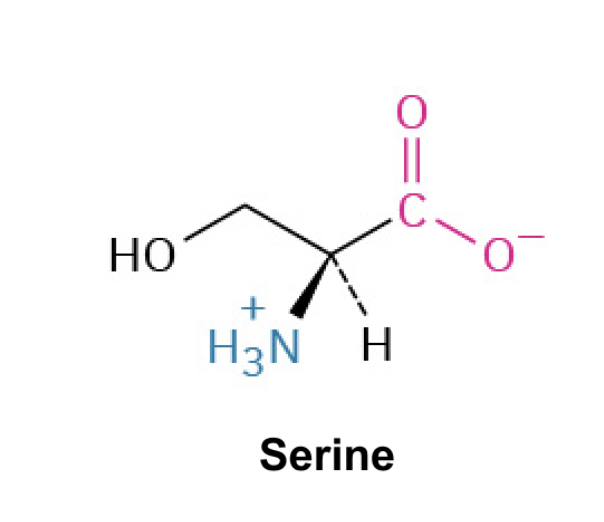
Serine(Ser, S)
Side Chain: (CH2OH)- hydroxymethyl, forms hydrogen bonds, polar and hydrophilic, plays a role in enzyme active sites.
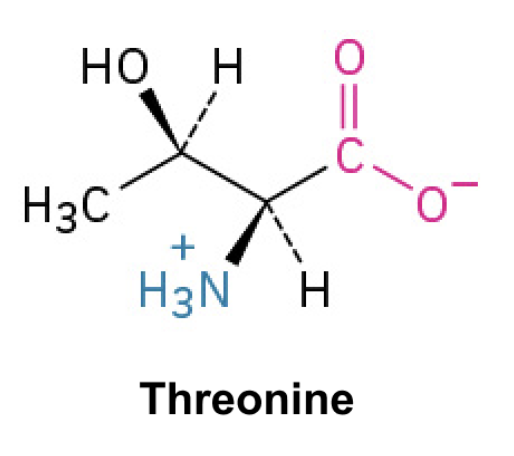
Threonine(Thr, T)
Side Chain: (CH(OH)CH3)- hydroxyl, forms hydrogen bonds, polar essential amino acid, involved in protein synthesis
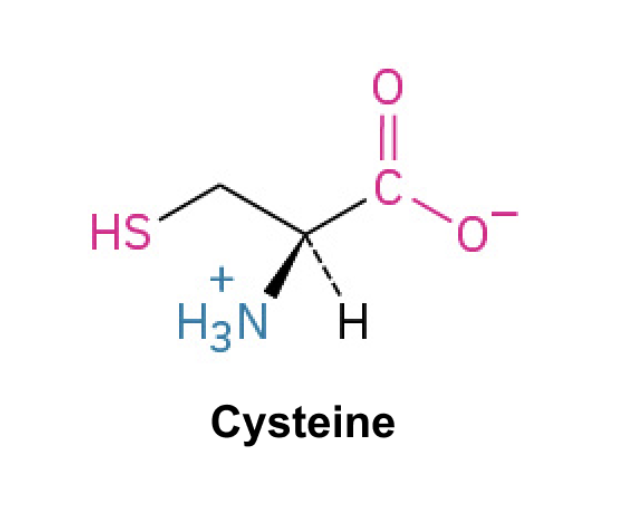
Cysteine(Cys, C)
Side Chain: (CH2SH)- thiol, forms disulfide bonds, hydrogen bonding, polar and nonpolar properties(via the disulfide bonds). Cysteine is an amino acid with a side chain containing a thiol group, which allows it to form disulfide bonds that stabilize protein structure.
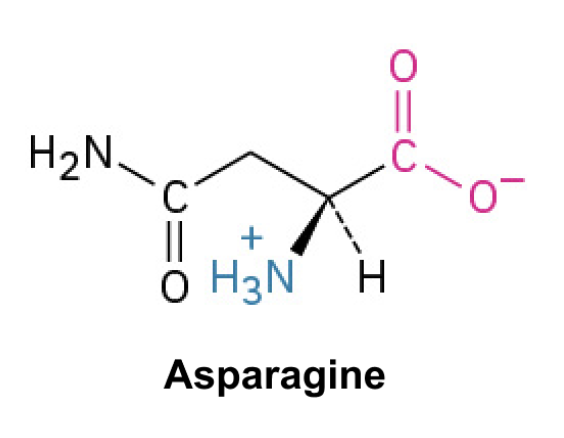
Asparagine (Asn, N)
Side Chain: (CH2CONH2)- amide, forms hydrogen bonds, polar and participates in protein interactions
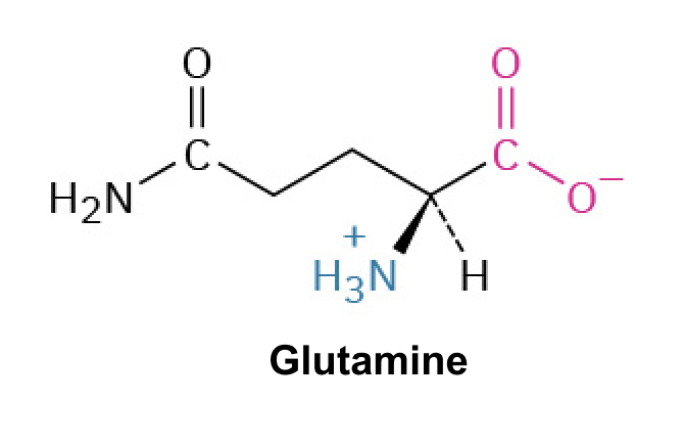
Glutamine (Gln, Q)
Side Chain: (CH2CONH2)- amide, forms hydrogen bonds, polar (similar to asparagine but with an additional methylene group)
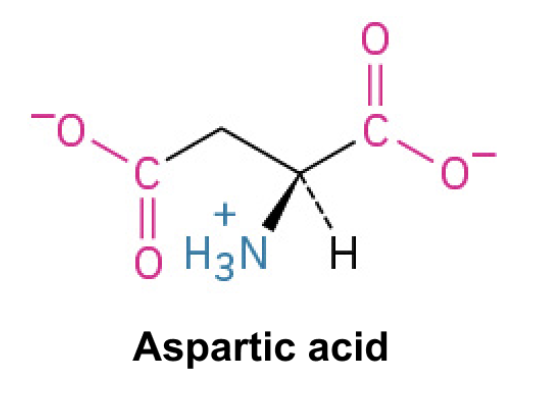
Aspartate (Asp, D)
Side Chain: (CH2COO-)- carboxylic acid, negatively charged, polar, ionic interactions, hydrogen bonding (commonly involved in enzyme active sites and protein interactions)
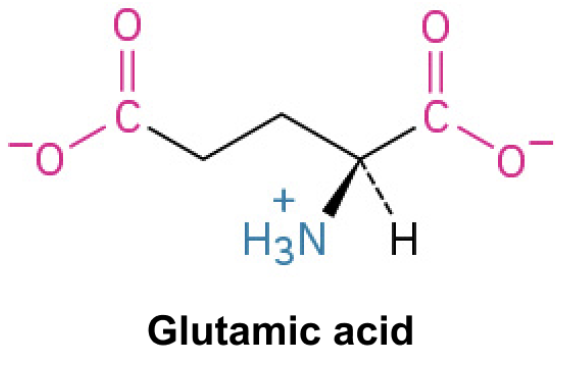
Glutamate (Glu, E)
Side Chain: (CH2COO-)- carboxylic acid, negatively charged, polar, involved in neurotransmission and protein interactions. Involved in active sites of enzymes
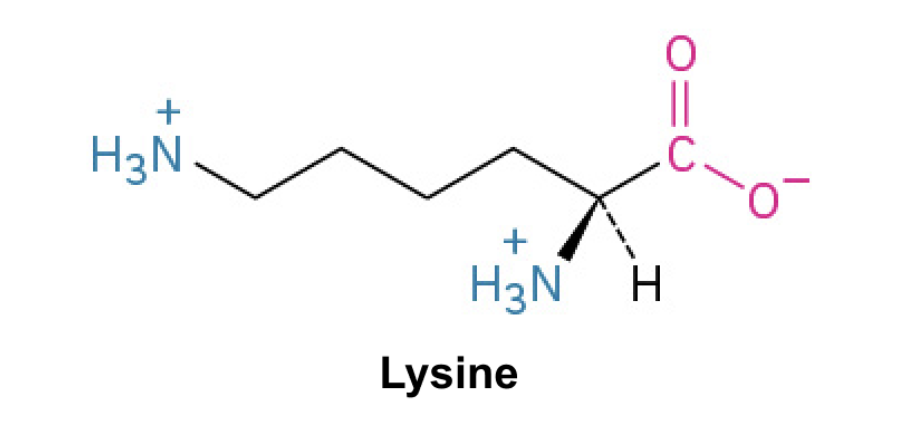
Lysine (Lys, K)
Side Chain: (CH2CH2CH2CH2NH3+)- amine, positively charged (3+), ionic interactions, and hydrogen bonding
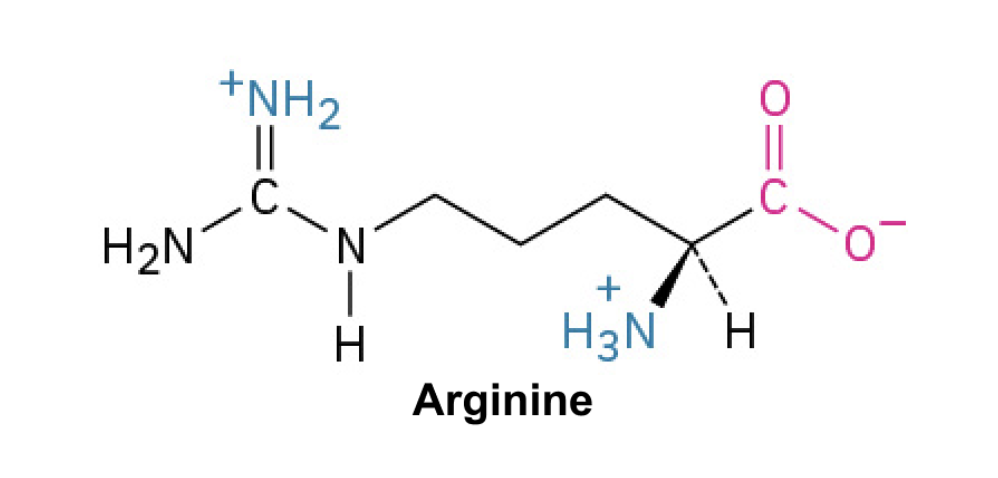
Arginine (Arg, R)
Side Chain: (CH2CH2CH2NHC(NH2)2⁺)- guanidinium, positively charged (2+), ionic interactions, and hydrogen bonding
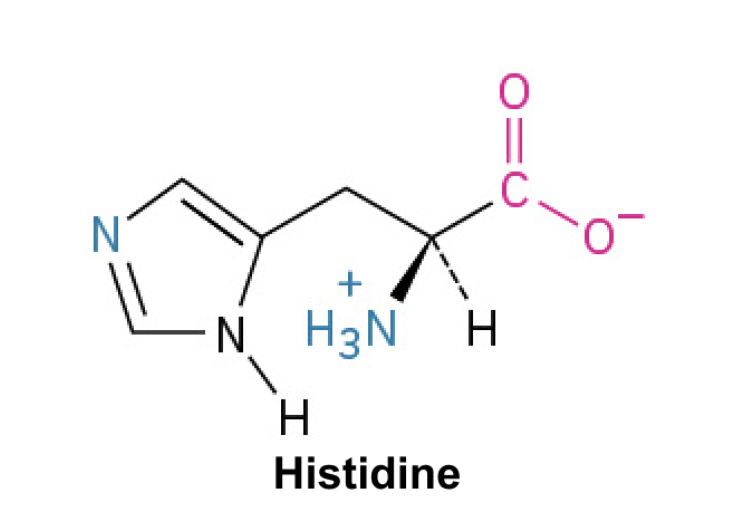
Histidine (His, H)
Side Chain: (CH2-CH3H3N2)- imidazole, which can shuttle protons, playing an important role in enzyme active sites and buffering
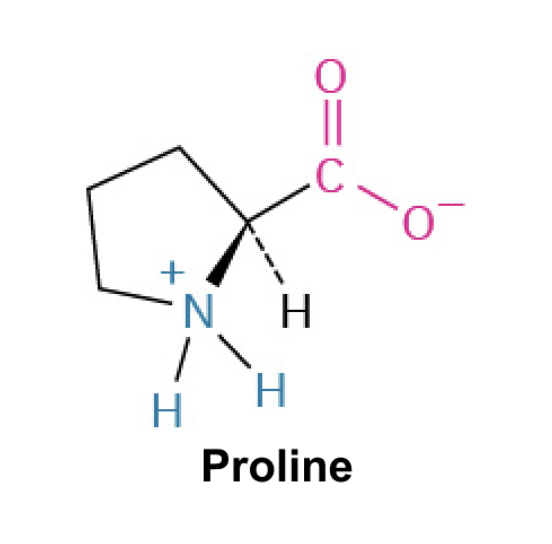
Proline (Pro, P)
Side Chain: (CH2CH2CH2-NH-)- pyrrolidine ring, hydrophobic interactions, structural constraints, weak hydrogen bonding(less flexible due to the rigid ring). Typically found in turns and loops of proteins