Introductory Economics: Lesson 3-6
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
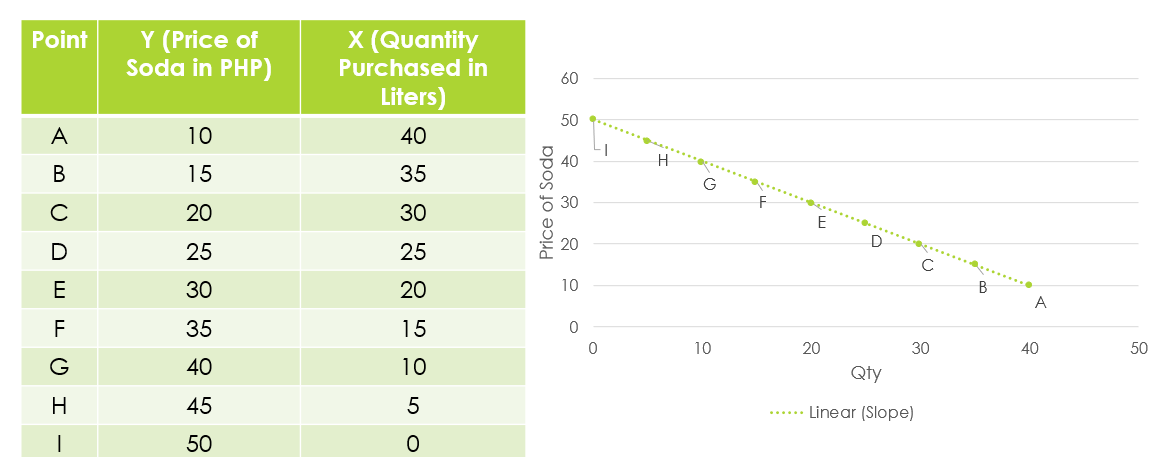
Law of Demand
The concept that there is an opposite relationship between process for goods and services and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase in a specific time.
Law of Demand
Can be shown as a downward sloping due to the inverse relationship of variables, say prices and quantity.
Changes in demand
An increase or decrease in the quantity demanded at each possible price.
Change in quantity demanded
A movement between points along a stationary demand curve.
Decrease in Price
Increase in quantity demanded
Change in nonprice determinant
Increase in Demand
What are the Nonprice determinants of demand?
Number of Buyers
Tastes and Preferences
Income
Expectation of Buyers
Prices of Related Goods
Income
Normal and Inferior good
Prices of Related Goods
Prices of related good and complementary good
Law of Supply
The concept that there is a positive relationship between prices for goods and services and the quantity the suppliers are willing to produce in a specific time.
Law of Supply
Can be shown as an upward sloping curve due to the positive relationship of variables, say prices and quantity.
Changes in supply
An increase or decrease in the quantity supplied at each possible price.
Change in quantity supplied
A movement between points along a stationary supply curve.
What are the nonprice determinants of supply?
Number of Seller
Technology
Resource Prices
Taxes and Subsidies
Expectation of producers
Prices of other goods the firm could produce
Inverse Relationship
Law of Demand: Individual buyer’s curve
Law of Demand: Market demand curve
Inverse Relationship
Equilibrium
A market condition that occurs in any price and quantity where the quantity of demanded and quantity of supply meets.
Equilibrium Points
Signifies the most ideal price of a certain goods and services.
Equilibrium of Supply and Demand
Occurs normally in a competitive type of market where there are several sellers of the same good or services.
Equilibrium
No agent in the market dictates the price of a good or a service.
Price System
A rationing role that uses the forces of supply and demand to establish an equilibrium of desirable price.
Consumer Surplus
It is the value of the difference between the price the consumers are willing to pay and the actual price of the product.
Consumer Surplus
The volume of surplus is equal to the product of prices and the quantity purchased.
Producer Surplus
It is the value of the difference between the price the consumers are willing to sell and the actual selling price of the price of the product.
Producer Surplus
The volume of surplus is equal to the product of prices and the quantity produced.
Market Efficiency
Maximize the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
Market Efficiency
Net benefit is equals to consumer and producer surplus.
Deadweight Loss
In market efficiency, it is the net loss of consumer and producer surplus due to underproduction or overproduction.
Deadweight Loss
The area in the triangle where the demand or production is not implemented.
Deadweight loss
An opportunity cost/lost.
Changes in Market Equilibrium
Caused by the changes of supply and demand.
Changes in Market Equilibrium
The shift of demand or supply from its original conditions either a shift to the left or right.
Changes in Market Equilibrium
The causes of shifts can be due to the price or nonprice factors.
Repealing Laws of Supply and Demand
Government interventions to control and prevent prices from rising or falling to the equilibrium price.
Price Ceilings
In price control, it is the legal maximum price established per product by the government
Price Floors
In price controls, it is the legal minimum price established per product by the government.
Price Ceiling
In ceiling price, this causes limiting of production.
Price
In ceiling price, this is forced to increase since demand is higher than the supply.
Ceiling Price
Shortage of product
Price Floor
In floor price, this encourage production.
Price
In floor price, this is forced to decrease since the demand is lesser than the supply.
Floor Price
Surplus of product.
Market Failure
A condition in which there is too few or too many resources used in the production of goods and services.
Market Failure
Lack of competition and externalities
Wealth of the Nations, Adam Smith
People of the same trade seldom meet together even for merriment or diversion, but the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the public, or in some diversion to raise prices.
Market Failure: Lack of Competition
Seller collusion, government intervention, and restrictions
Promotes artificial scarcity that decreased supply.
Increases the price of a product
Own Price Demand Elasticity (E = d/p)
It is the responsiveness of the quantity demanded in the changes in the own product.
Income Elasticity (E1)
Refers to the sensitivity of the quantity demanded for a particular good to change in the real income of consumers who buy this good.
Cross Price Elasticity (Epr)
Refers to the sensitivity of the quantity demanded for the changes in the price of one good or another.
Own Price Demand Elasticities Factors
Number of suitable substitutes
Number of uses of the product
Expenditure share of the products
Relative location of price in the demand curve
E > 1
The established price in the higher demand curve is elastic. Quantity demanded is responsive to the changes in the price of the product itself.
E < 1
The established price in the lower demand curve is inelastic. Quantity demanded is not responsive.
Arc and Point Elasticity
Two ways of computing elasticities.
Arc Elasticity
Given two points in the curve.
Point Elasticity
Given the demand function. At least one point is given.
E = 1
Unitary Elasticity - we cannot say that it is responsive or not.