Module 3- Exchange and Transport
1/273
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Section 1: Exchange and Transport S
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
274 Terms
What do cells exchange with their environment?
Oxygen
Glucose
Carbon Dioxide
Urea
Do smaller animals have a higher or lower surface area?
Higher
How does diffusion happen in a single celled organism?
Directly across the cell surface membrane
Why is diffusion faster in single celled organisms?
Small distances to travel
How would you describe the surface area to volume ratio of a larger animal?
Low
Whay is it difficult to exchange enough substances in a animal?
They have a higher metabolic rate and use up oxygen and glucose faster
What are the features of most exchange surfaces?
Large Surface Area
Thin
Good Blood Supply and Ventilation
How are root hair cells adapted for function?
Have long hairs which stick out into the soil with each branch covered in millions of microscopic hairs
What do root hair cells microscopic hairs do?
The roots have a large surface area which increases the rate of absorption of water and mineral ions
How is the Alveoli adapted to its function?
A thin layer of alveolur epithelium cells
Surrounded by a large capillary network
Why is the thin layer of alveolur epithelium cells in beneficial?
Decreases the distance which O2 and CO2 diffuse over
How does gas exchange work?
O2 Diffuses out of the alveolur space into the blood and Co2 diffuses in the opposite direction
How is the large capillary network beneficial to the alveolus?
Each alveolus has its own blood supply which constantly takes oxygen away from the alveoli and brings more carbon dioxide
What do the good supply of blood and vetilation help maintain in the lungs?
Maintain concentration gradient of O2 and Co2
How are fish gills adapted to its function?
Large network of capillaries
Well ventilated
How are fish well ventilated and how does this increase rate of reaction?
Constant flow of water
Maintains a concentration gradient of oxygen
What is the pathway of air in mammals?
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Alveoli
What work together to move air in and out of mammals?
Ribcage
Intercostal muscles
Diaphragm
What is the function of Goblet cells?
Secret mucus
Where are goblet cells found?
Line the airways
What do the goblet cells mucus do?
Traps microorganisms and dust particles in the inhaled air stopping them reaching the alveoli
What do the cillia do?
Moves mucus upward away from the alveoli towards the throat
Where are cillia found
Surface of cells lining the airways
What do cillia prevent?
Lung infections
What is the function of elastic fibres in the walls of the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli?
Help the process of breathing out
What happens to the elastic fibres when breathing in?
They stretch and recoil to help push air out
What do smooth muscle in the walls of the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli do?
Allows their diameter to be controlled
What happens to the smooth muscle during excercise?
Relaxes making the tubes wider
What do rings of cartilage in the walls of the trachea do?
Provide support
Prevent collapsing when the pressure drops
What shape cartilage does the trachea have?
Large C shaped pieces
Does the trachea have Smooth muscle ?
YES
Does the trachea have elastic fibres?
YES
Does the trachea have Goblet cells
YES
What is the epithelium like in the trachea?
Cilliated
What is the bronchi cartilage like?
Smaller pieces
Does the bronchi have smooth muscle?
YES
Does the larger bronchiole have smooth muscle?
YES
Does the smaller bronchiole have smooth muscle?
YES
Does the smaller bronchiole have smooth muscle?
YES
Does the smallest bronchiole have smooth muscle?
NO
Does the alveoli have smooth muscle?
NO
What is the larger bronchiole cartilage like?
Doesnt have any
What is the smaller bronchiole cartilage like?
Doesnt have any
What is the smallest bronchiole cartilage liek?
Doesnt have any
What is the alveoli cartilage like?
Doesnt have any
Do the trachea, bronchi, larger smaller and smaller bronchi and alveoli have elestic fibres?
YES
Does the larger bronchiole have goblet cells?
YES
Does the smaller bronchiole have goblet cells?
NO
Does the smallest bronchiole have goblet cells?
NO
Does the alveoli have goblet cells?
NO
What are the bronchi epithelium cells like?
Cilliated
What are the larger bronchiole epithelium cells like?
Cilliated
What are the smaller bronchiole epithelium cells like?
Cilliayed
What are the smallest bronchiole epithelium cells like?
No cillia
What are the larger alveoli epithelium cells like?
No cillia
What happens to the external intercostal and diapragm during inspiration?
Contract
During inspiration how does the ribcage move?
Upwards and outwards
How does the diaphragm move in inspiration?
Flattens and increases volume
What happens when the thorax volume increases?
The lung pressure decreases
What can inspiration be described as?
An active process requiring energy
What happens to the external intercostal muscles and diaphragm during expiration?
Relax
How does the ribcage move during expiration?
Downwards and inwards
What happens to the diaphragm during expiration?
Becomes curved
What happens to the thorax during expiration what does this do to pressure?
Decreases
Increases the air pressure
What is normal expiration?
A passive procuess
What is tidal volume?
Volume of air in each breath
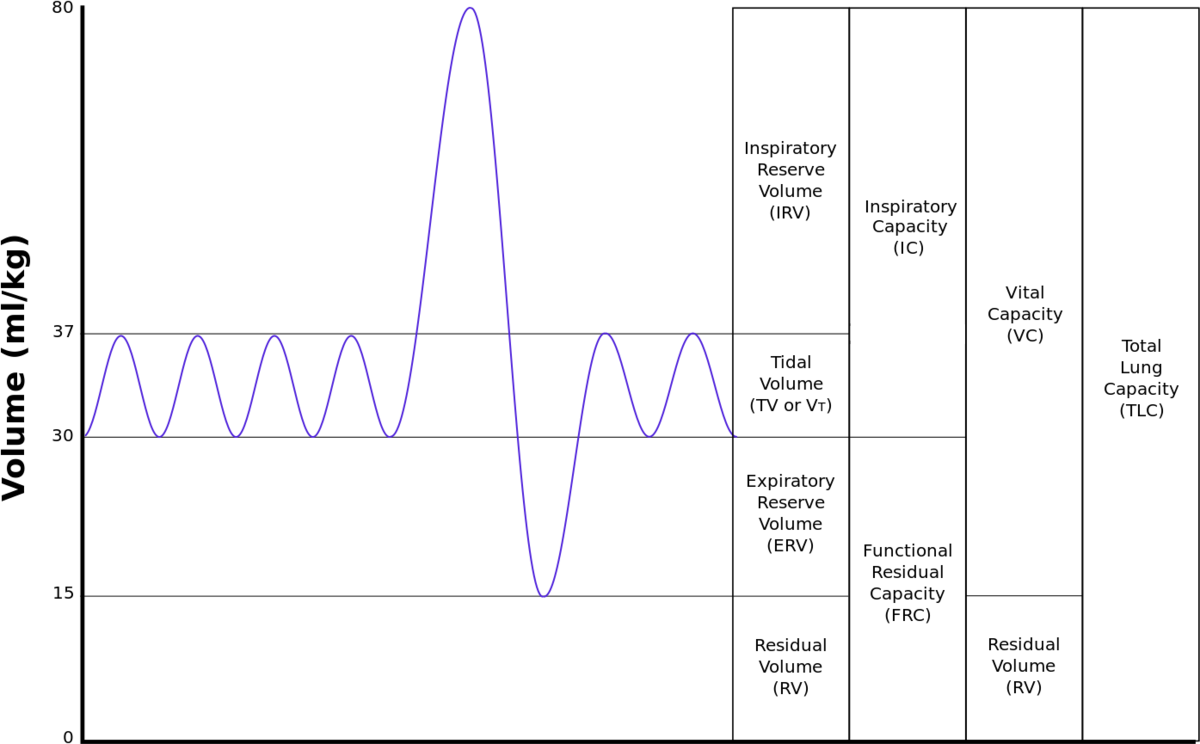
What is the vital capacity?
Maximum volume of air that can be breathed in or out
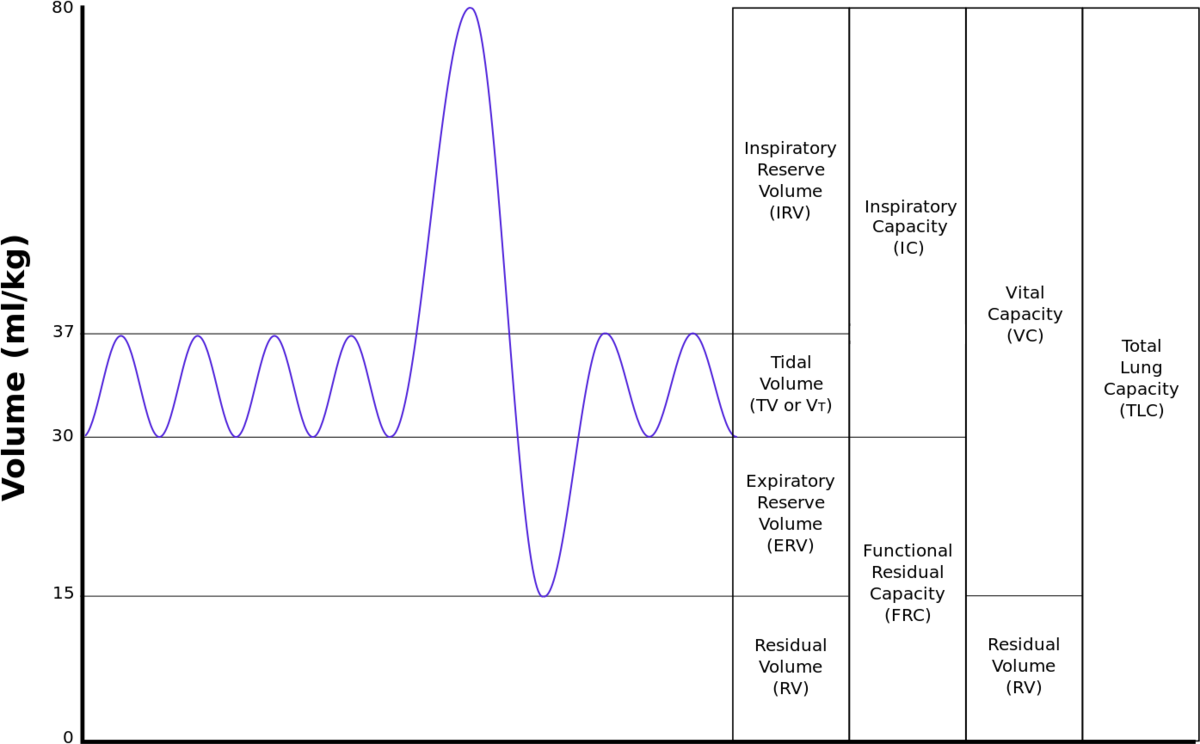
What is breathing rate?
Breaths taken usually in a minute
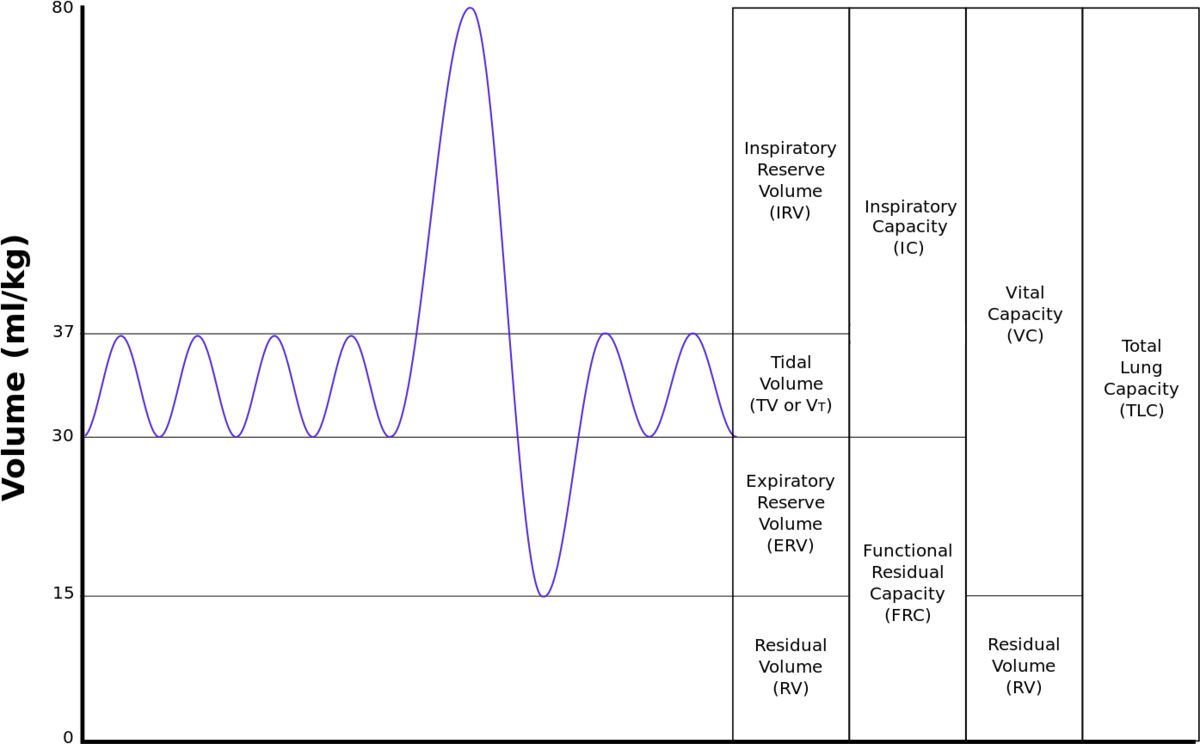
What is oxygen uptake?
Rate at which an organism uses up oxygen
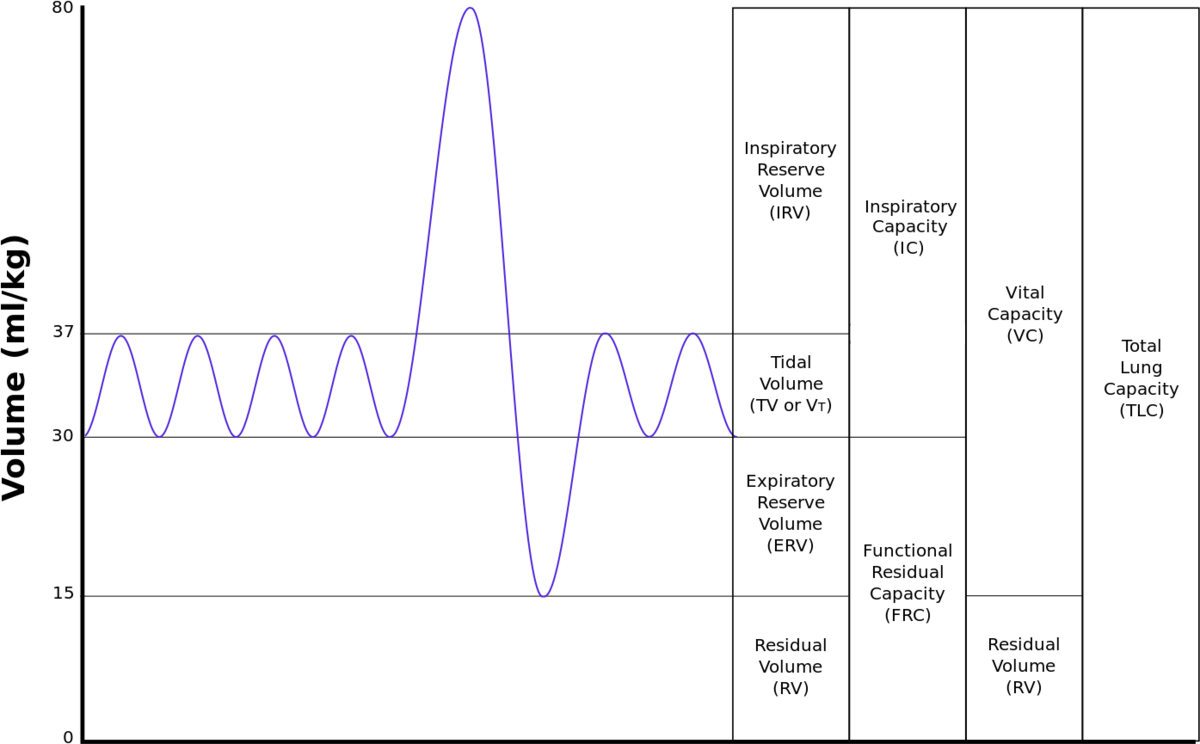
How does a spirometer work?
Oxygen filled chamber with a moving lid
The person breathes through a tube connected to an oxygen chamber
The lid moves up and down
Theres movements can be recorded by a pen attached to the lid which writes on a rotating drum creating the spirometer trace
The soda lime in the tube absorbs the carbon dioxide
What is gaseous exchange in fish?
Water enters through its mouth and passes out through the gills
The gill has gilll filaments or primary lamellae giving a suface area for exchange which is then covered in secondary lamallea
The gill plates have lots of blood capillaries and thin surface area
Blood flows through the gill plates in one direction and water flows opposite direction
What is the gaseous exchange system of a fish known as?
Countercurrent
What is each gill in a fish supported by?
A gill arch
How are gills ventilated?
The fish opens its mouth whihc lowers the floor of the buccal cavity sucking water in
when its mouth is closed the floor of buccal caivty is raised focing water out across gill filaments
The operculum is forced open allowing water to leave the gills
What happens to the pressure when a fish opens its mouth?
The volume of the buccal cavity increases decreasing pressure in cavity
What happens to the pressure when a fish closes its mouth?
The volume of the buccal cavity decreases increasing pressure in cavity
What are insects air filled pipes called?
Tracheae
How does air move through an insect
Air moves into tracheae through spiracles
Oxygen travels down the concentration gradient towards the cells carbon dioxide moves down its own gradient to be releases
The tracheae branches to tracheole which have thin permeable walls and go to individual cells containing fluid for oxygen to dissolve in
Oxygen then dossolves from this fluid into body cells and carbon dioxide diffusing in the opposite direction
How do insects change the volume of their body?
Rhythmic abdominal movements
How can you dissect insects?
Attatch to a dissecting board
Cut and remove exoskeleton
Fill the abdomen with saline solution revealsing the tracheae
Examine under microscope
How can you dissect fish?
Place fish of dissection board
Push back operculum and remove gills
Look closely
What do mammals use to carry nutrients?
Blood
What type of circulatory system do fish have?
Single
What type of circulatory system do mammals have?
Double
How many times does blood pass the heart in a double circulatory system?
Twice
How does blood pass around the body in fish?
Heart pumps blood to the gills
Then through the rest on the body in a single circuit
How does blood pass around the body in mammals?
Right side pumps blood to the lungs
From the lungs it travels to the left of the heart which pumps to the rest of the body
When the blood returns to the heart it enters the right side
What circulatory system do verterbrates have?
Closed
How does blood travel in closed systems?
Heart pumps blood into arteries (branch out in capillaries)
Substances like oxygen and glucose diffuse from blood into capillaries into the body cells leaving the blood in the vessels
Veins take blood back to the heart
What trype of blood system do inverterbrates have?
Open
How does blood travel in an intertebrate
Heart contracts in a wave starting from mthe back and pumping the blood into a single main artery
The artery opens up into the body cavity
The blood flows around the insects organs gradually returning to the heart segments through valves
What does an insects circulatory system not do?
Supply it with blood
What do the hearts valves prevent it from?
Back flow
What do the atrioventricular valve link?
Artia and the Ventricles
What do the semi-lunar vavles link?
Ventricles
Pumonary Artery
How do valves prevent backflow?
Only open one way (open or closed depends on relative pressure)
If higher pressure is behind the valve its forced open
If higher pressure in front on the valve it is forced shut
What is the cardiac sequence?
An ongoing sequence of contraction and relaxation keeping blood continously circulating
What is the first stage of the cardiac cycle?
The ventricles relax and the atria contract
What happens when the ventricles relax and the atria contract?
The volume decreases and the pressure increases pushing blood into the ventricle
Through what valve is blood pushed into the ventricle?
Antrioventricular valve