Lecture #2: Atoms to organisms
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
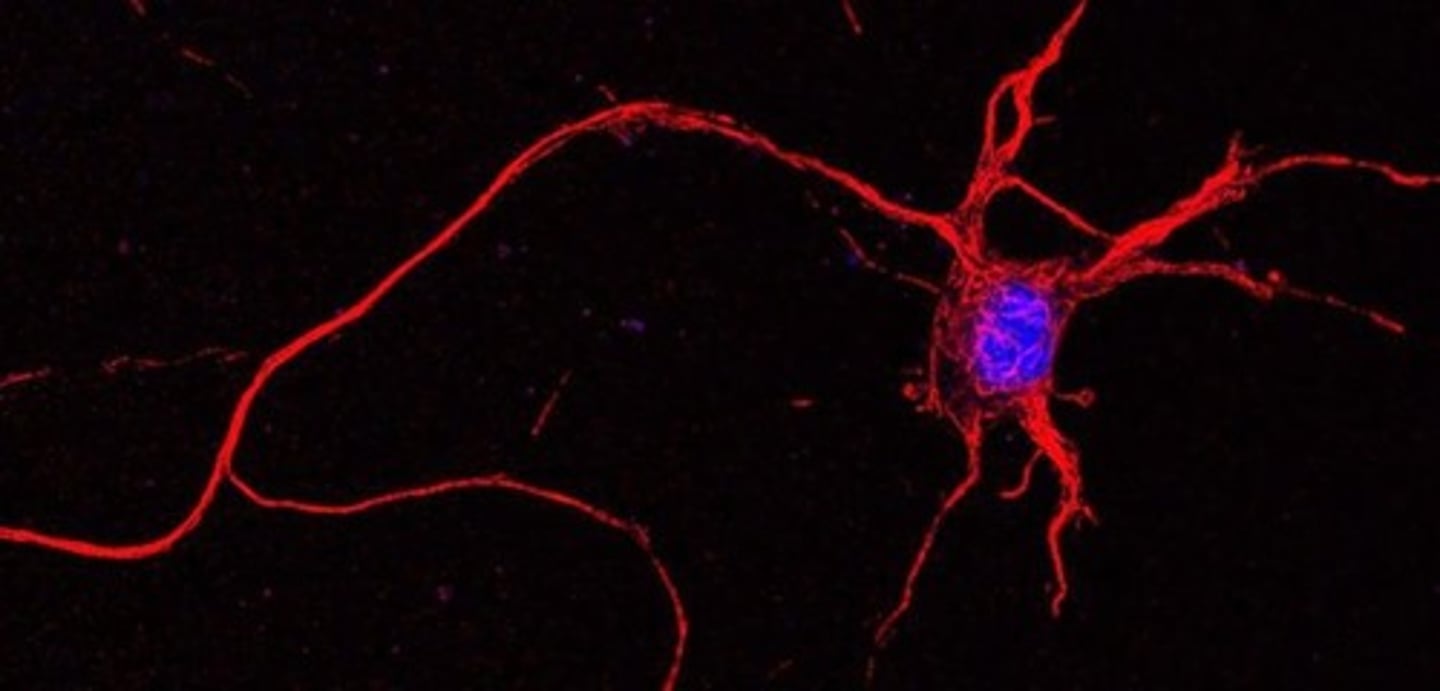
Neuron
The longest cells in an animal body, with some spanning over a meter in length.
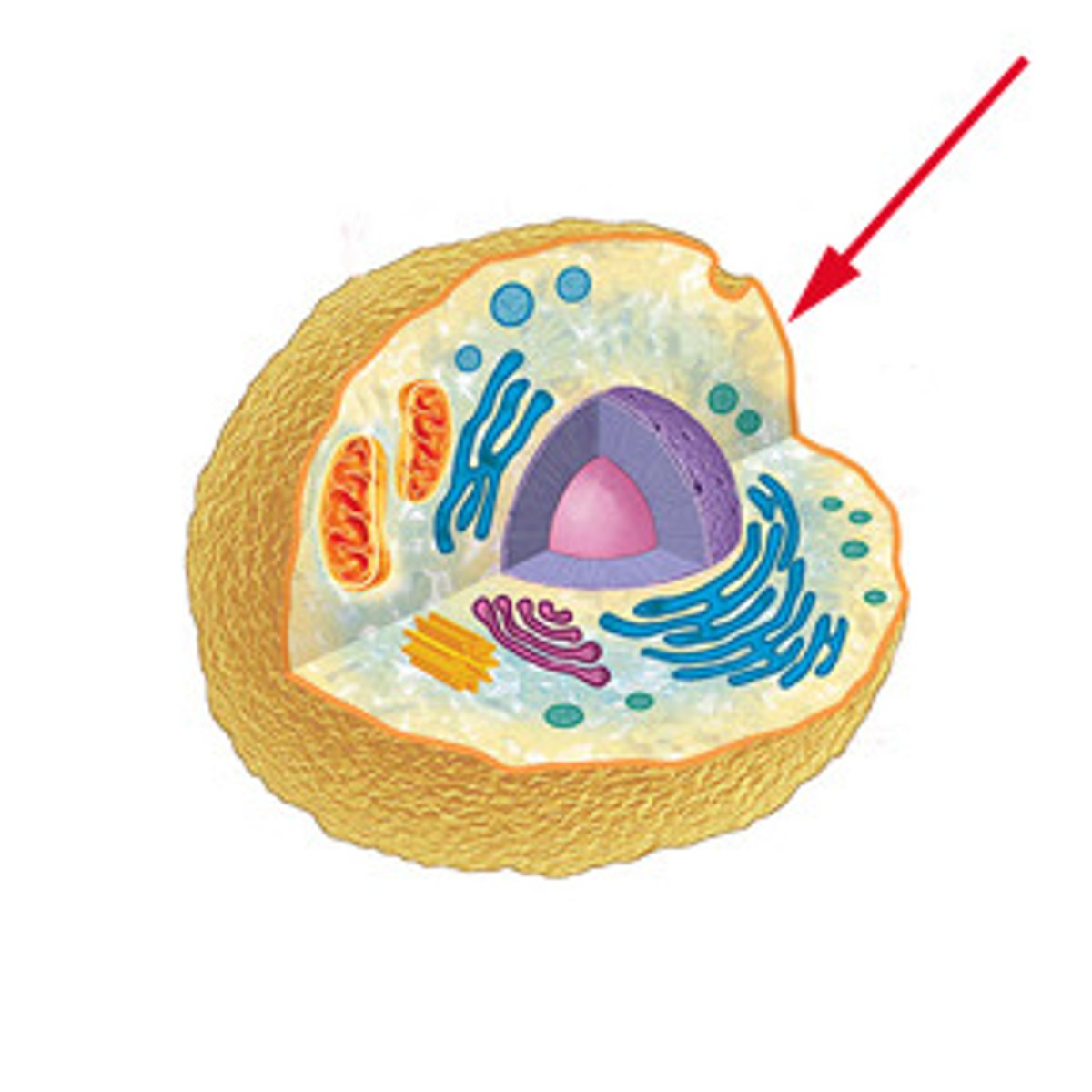
Cell
The basic unit of life.
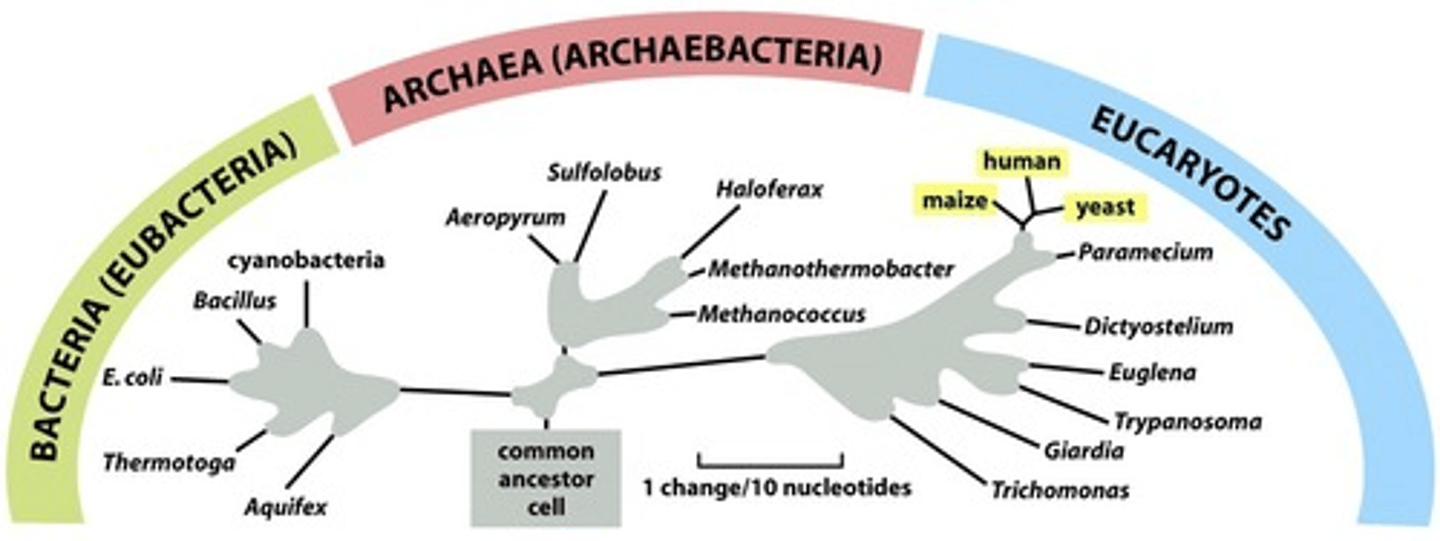
Life is cellular
Organisms are composed of cells, including Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Plants, and Animals, but not viruses or prions.
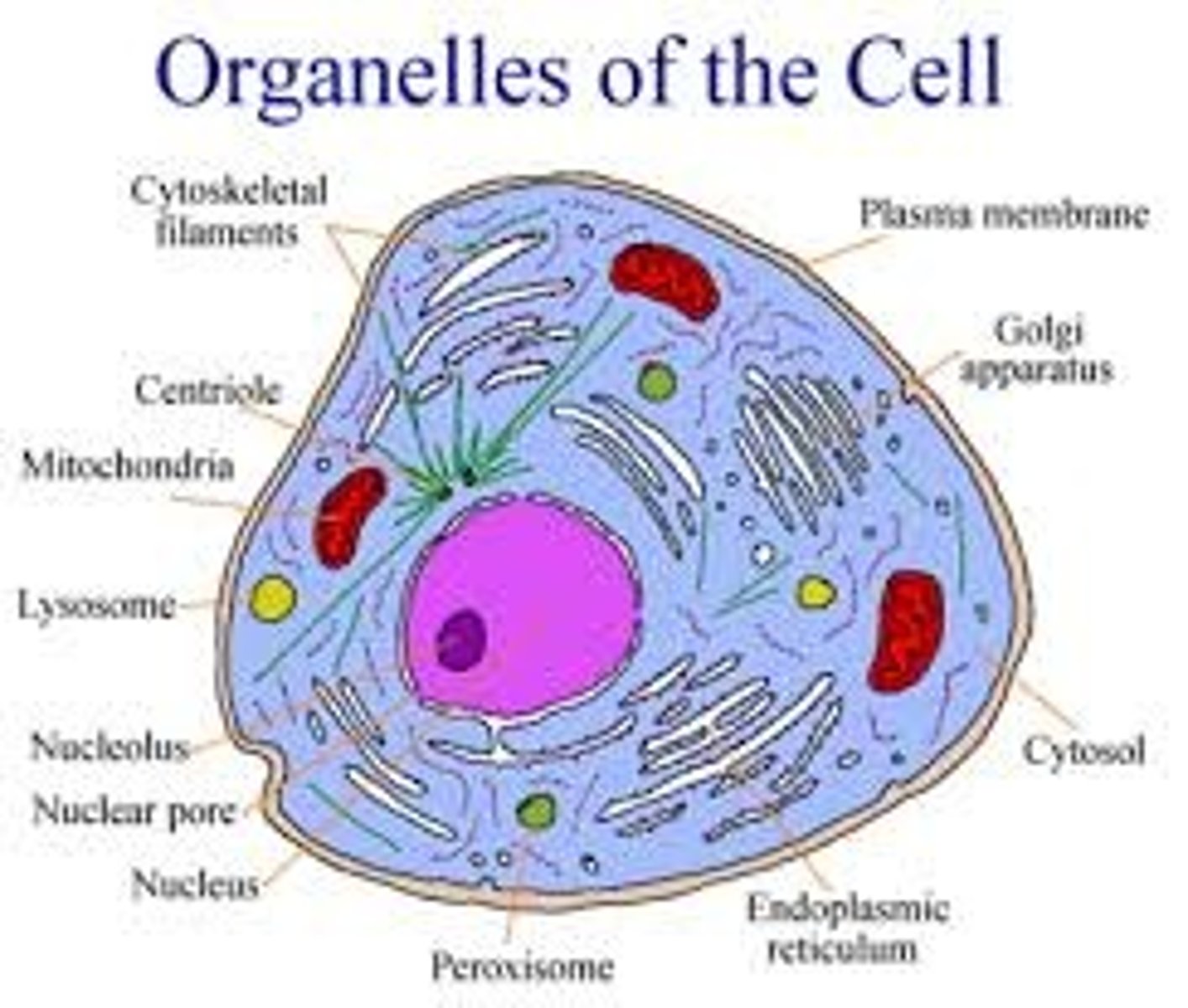
Organelles
Compartmentalized structures within cells that perform specific tasks.
Macromolecules
Polymers composed of monomers,
Ex. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids.
Monomer
The basic building block of macromolecules.
Polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units (monomers).
Carbohydrates
Biological molecules made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen, including Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides.
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates, which polymerize to form larger carbohydrates.
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate formed from two monosaccharides.
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate formed from multiple monosaccharides.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins.
Proteins
Macromolecules that perform a variety of functions in the body, including catalyzing biochemical reactions.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules that carry genetic information, including DNA and RNA.
Transporter
A type of protein that moves substances across cell membranes.
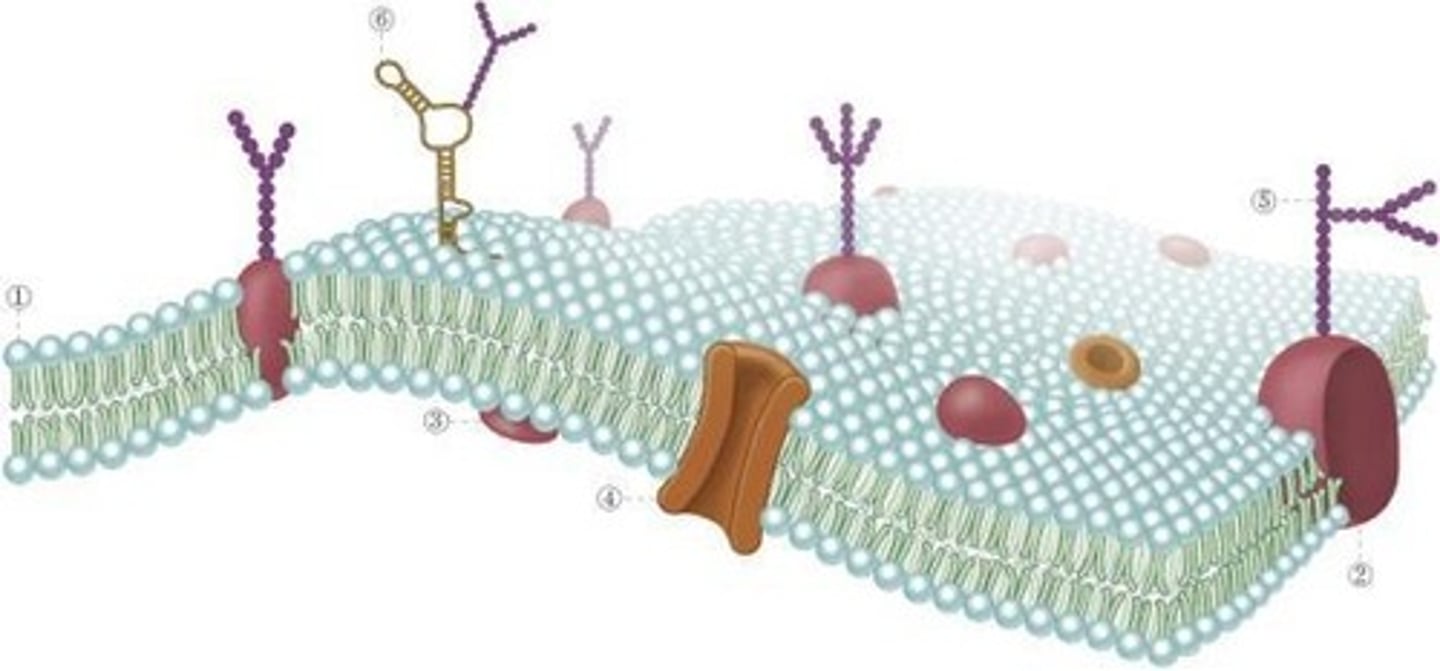
Membrane
A barrier that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment.
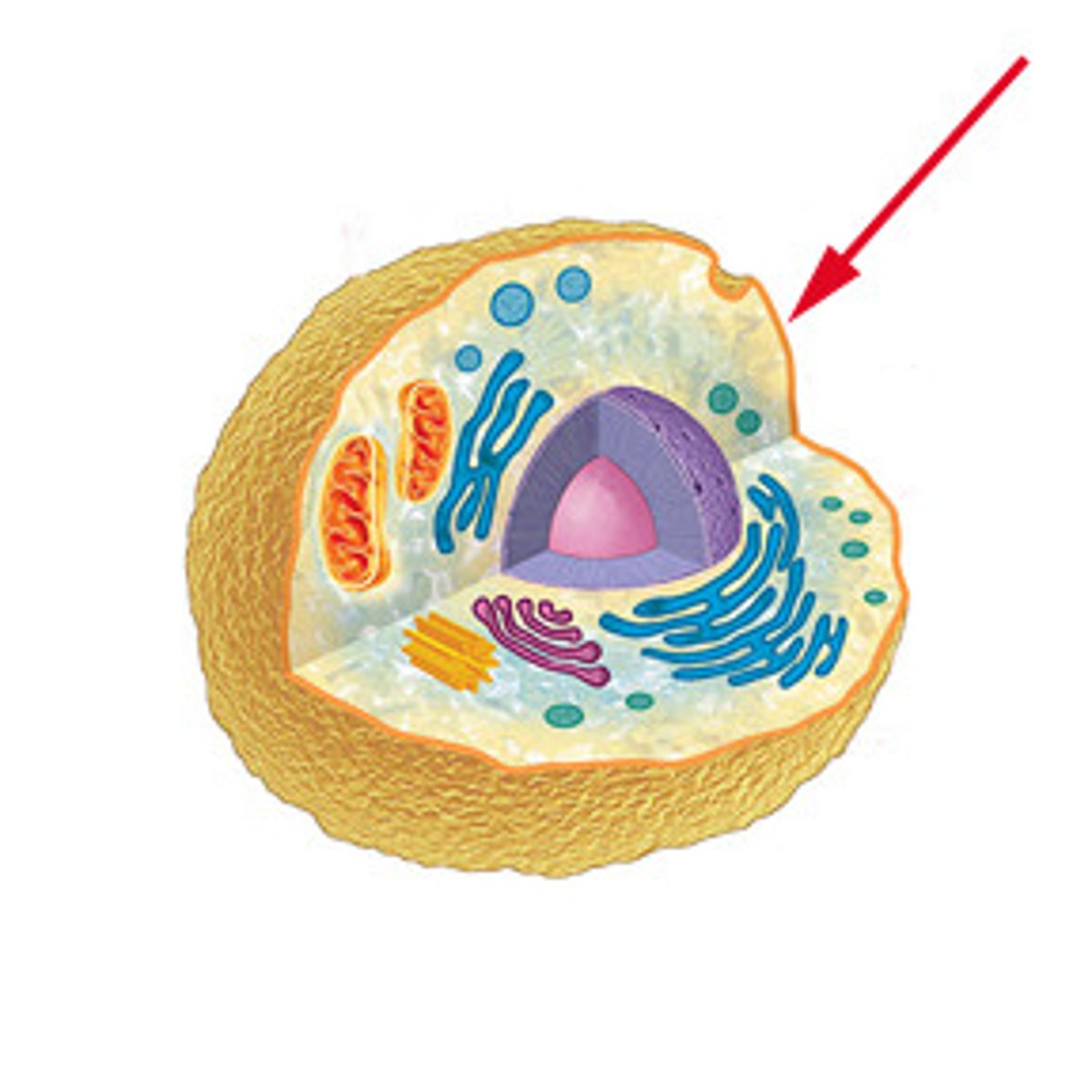
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance within a cell that contains organelles.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that provides structural support to the cell.
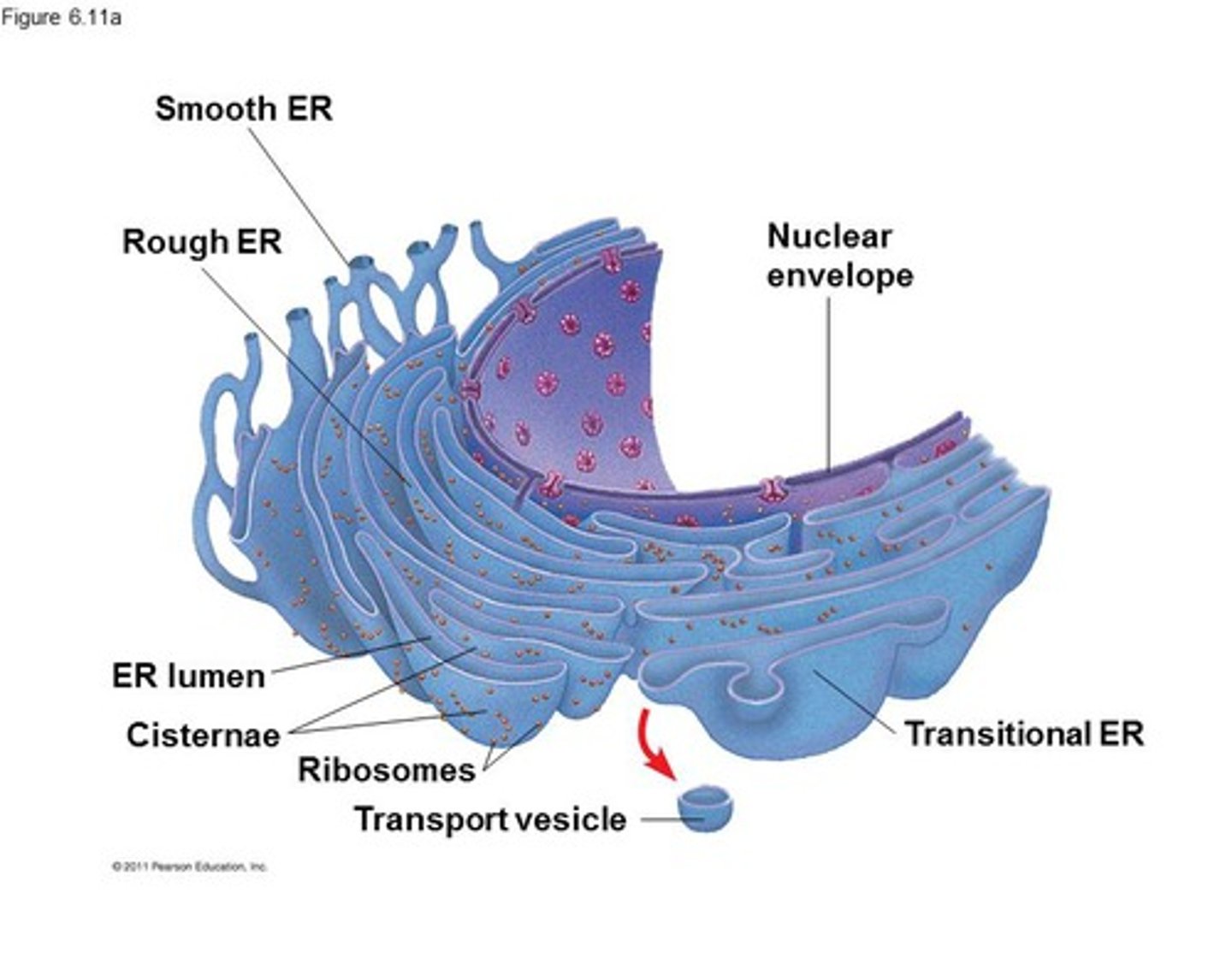
Rough ER
Endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes, involved in protein synthesis.
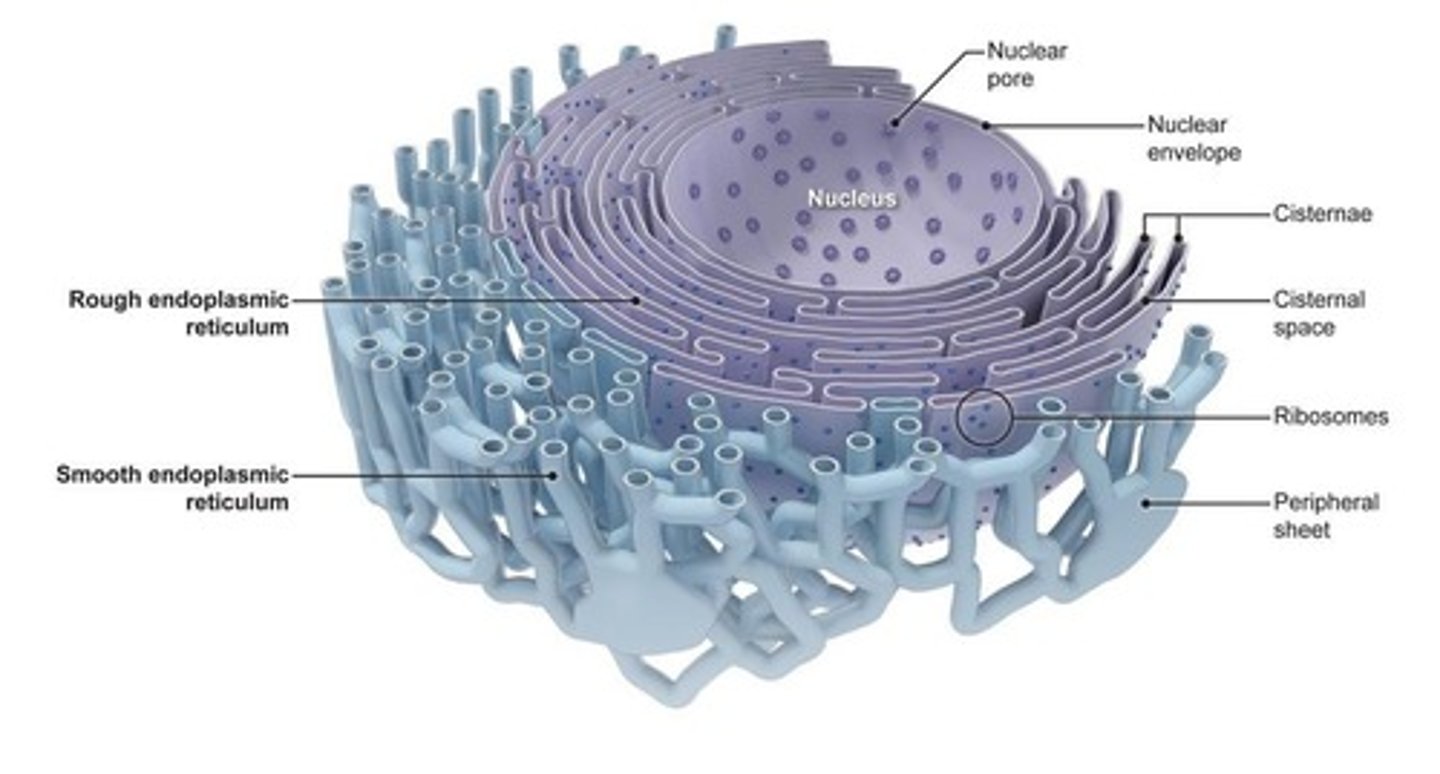
Smooth ER
Endoplasmic reticulum without ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis.
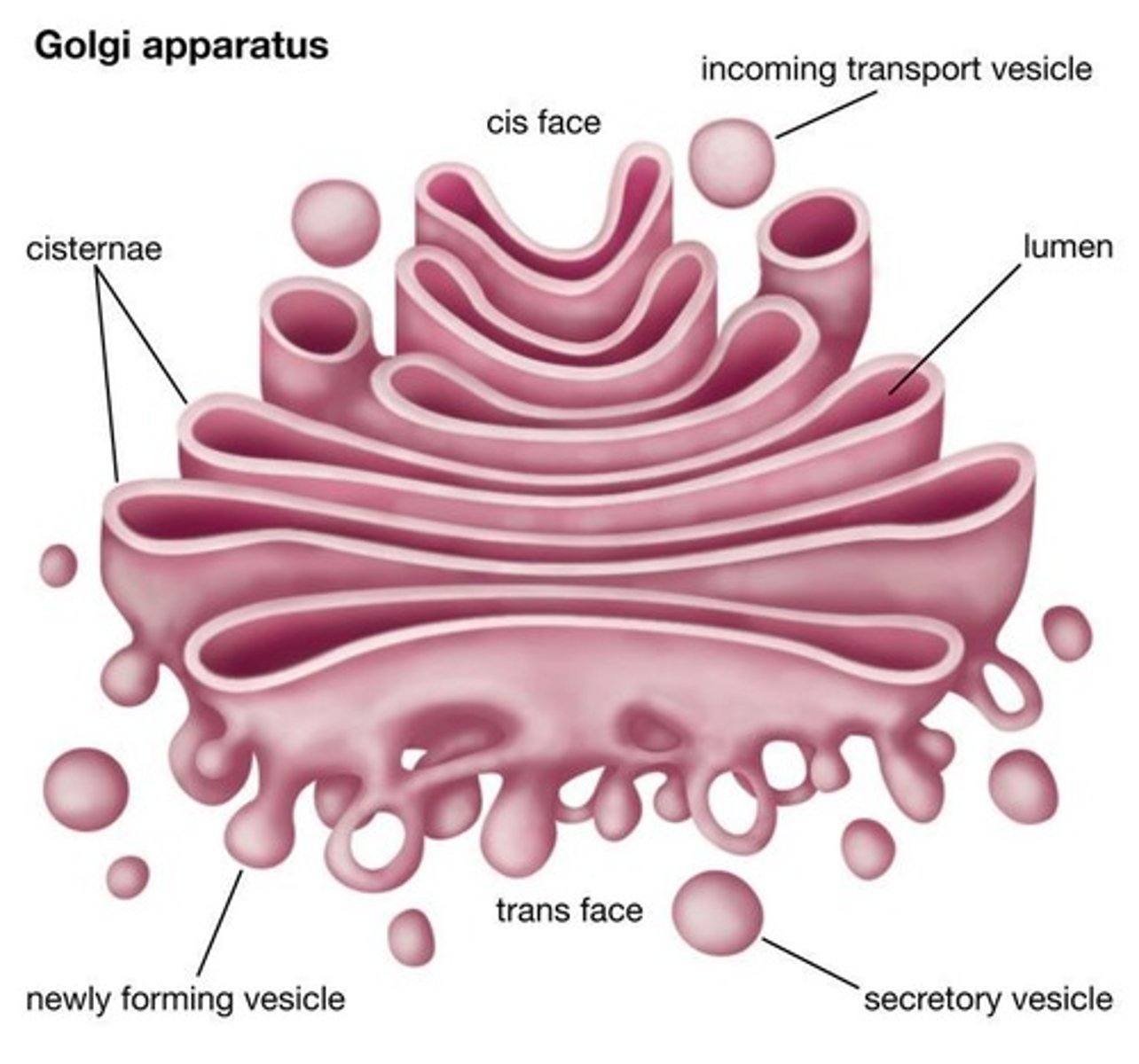
Golgi
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
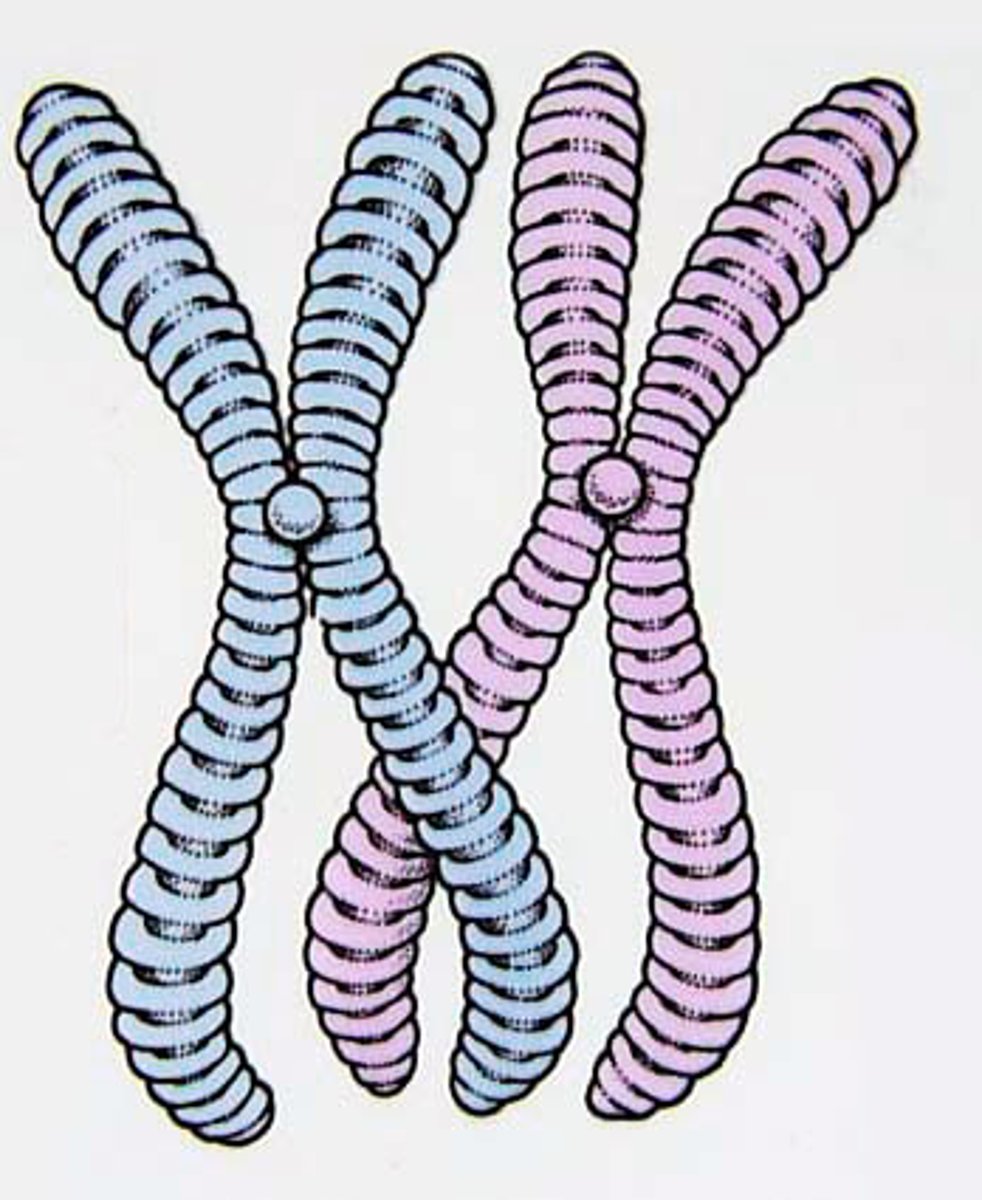
Chromosomes
Structures within cells that contain genetic information.
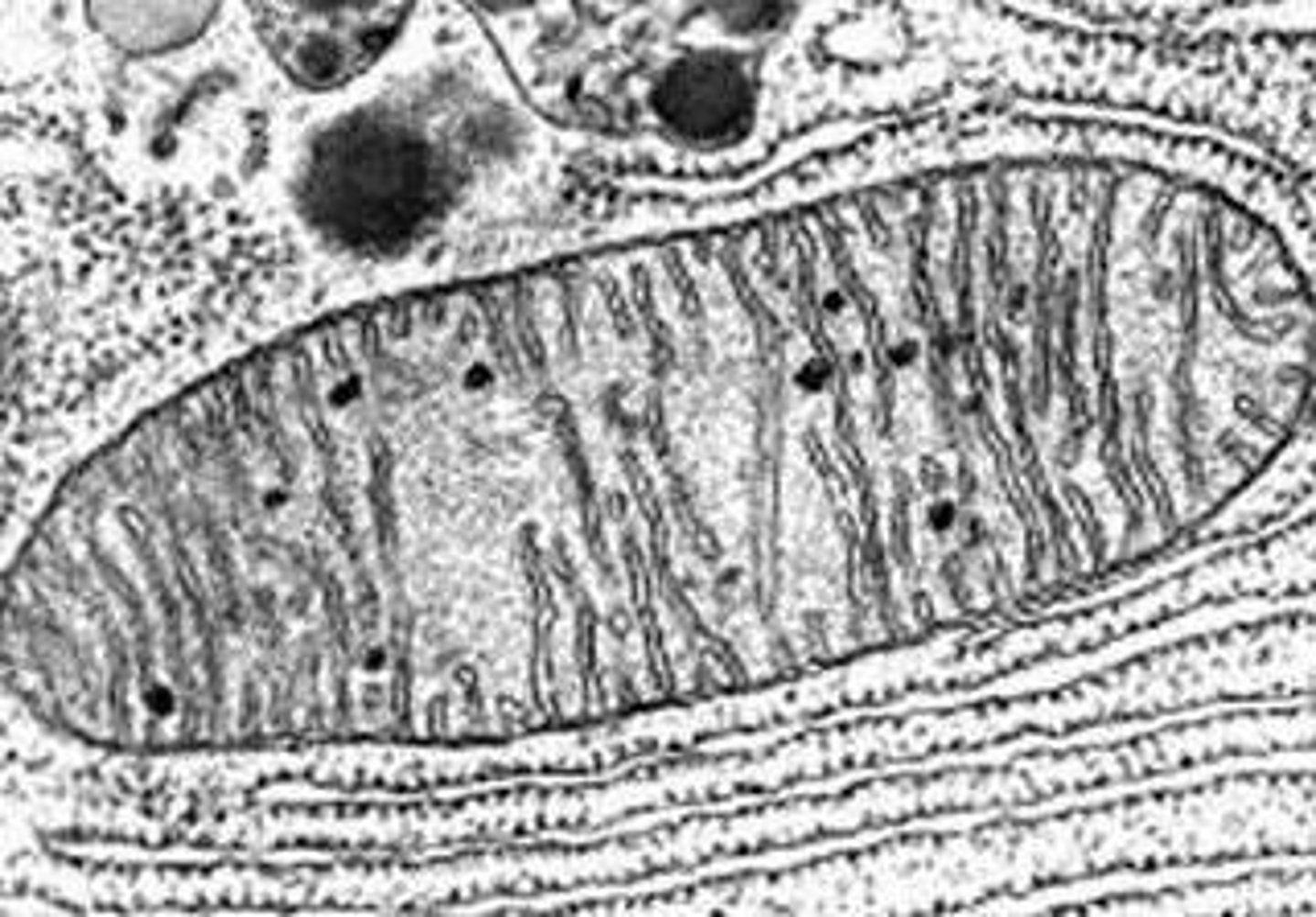
Mitochondria
Organelles that produce energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
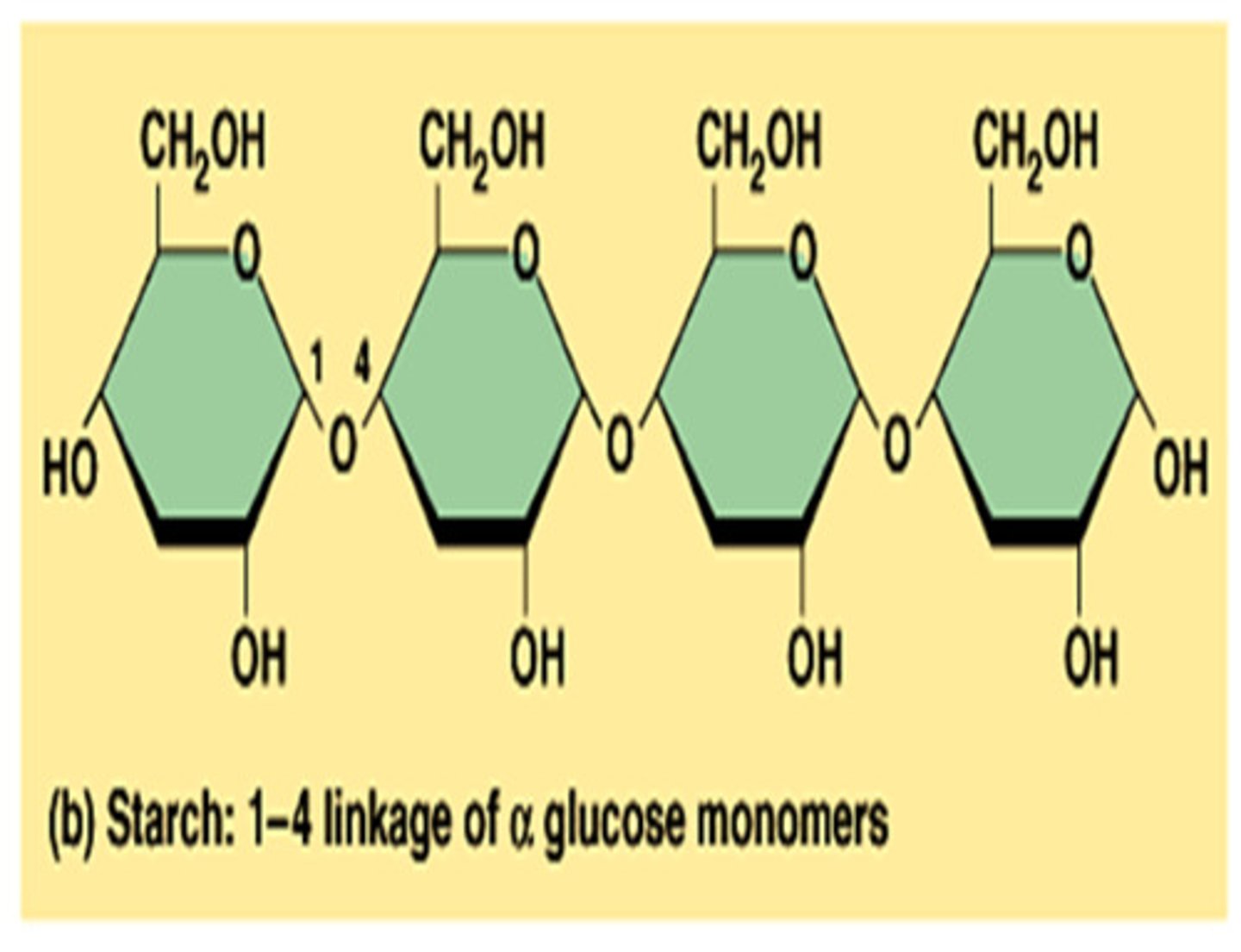
Polysaccharides
Each polysaccharide type has unique sense (chemical bonds) and unique monomers.
Properties of Proteins
Proteins have sense and informational properties.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids linked together.
Dipeptide
A molecule formed from two amino acids.
Nucleotides
The basic building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA/RNA).
Lipids
A diverse class of biological molecules consisting of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and many others.
Enzymes
Protein and sometimes nucleic acid catalysts that enhance the rate of biochemical reactions.
Membranes
Conglomeration of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that regulate the entry and exit of molecules.
Ribosome
Cellular structures that synthesize proteins.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membranous tubules (cisternae) with diverse metabolic roles.
Nucleus
Stores, copies, and transmits genetic information for the rest of the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
Combination of cisternae and vesicles in which biological molecules are processed and packed.
Mitochondrion
Performs respiratory metabolism to capture energy for the cell.
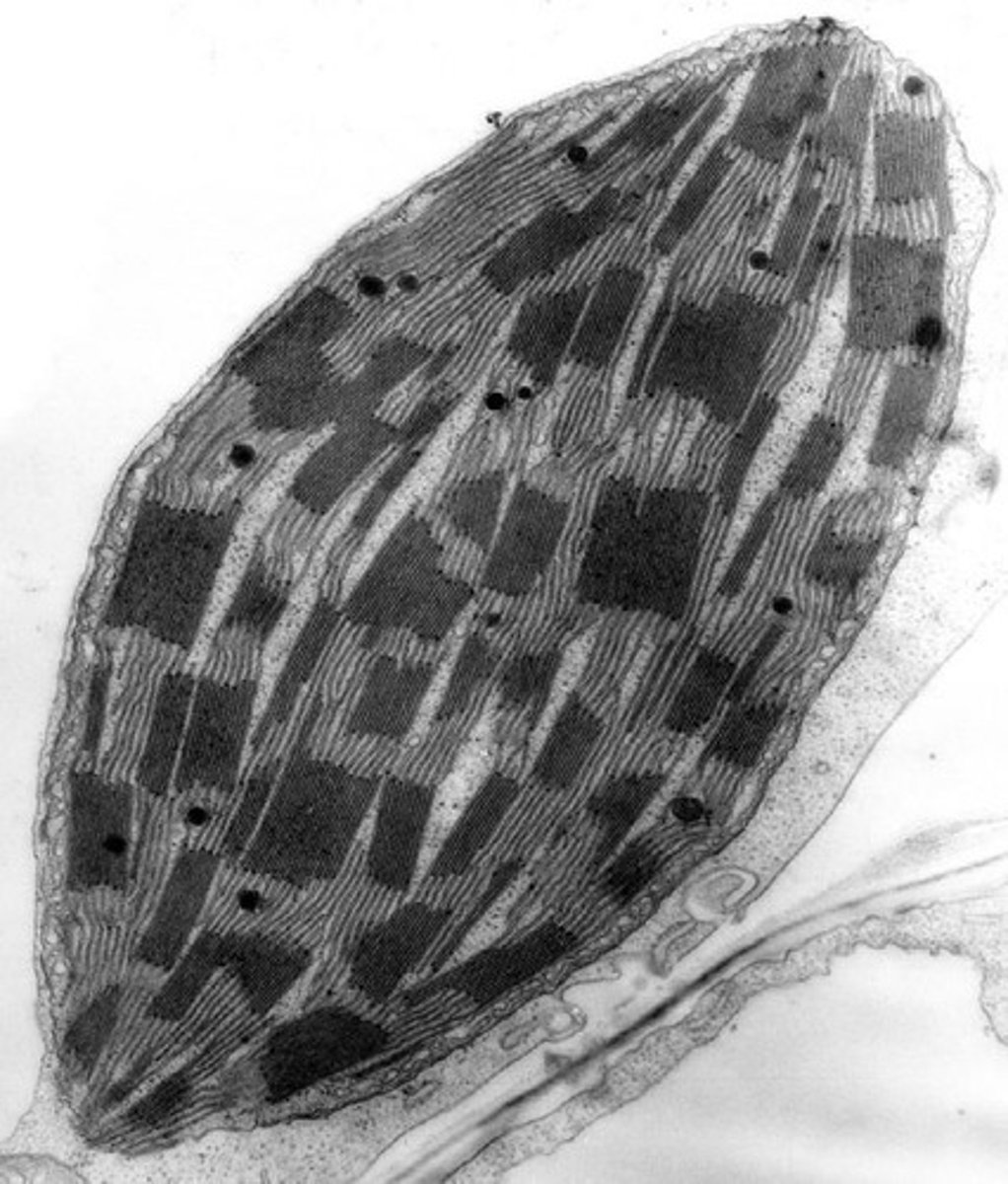
Chloroplast
Performs photosynthetic metabolism to synthesize sugars for the cell.

Tree of Life
Has many unique clades (groups of evolutionarily-related organisms).
Taxonomy
An organism's place or name within the organization of life.
Domains
The largest functional clades, which include Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota.
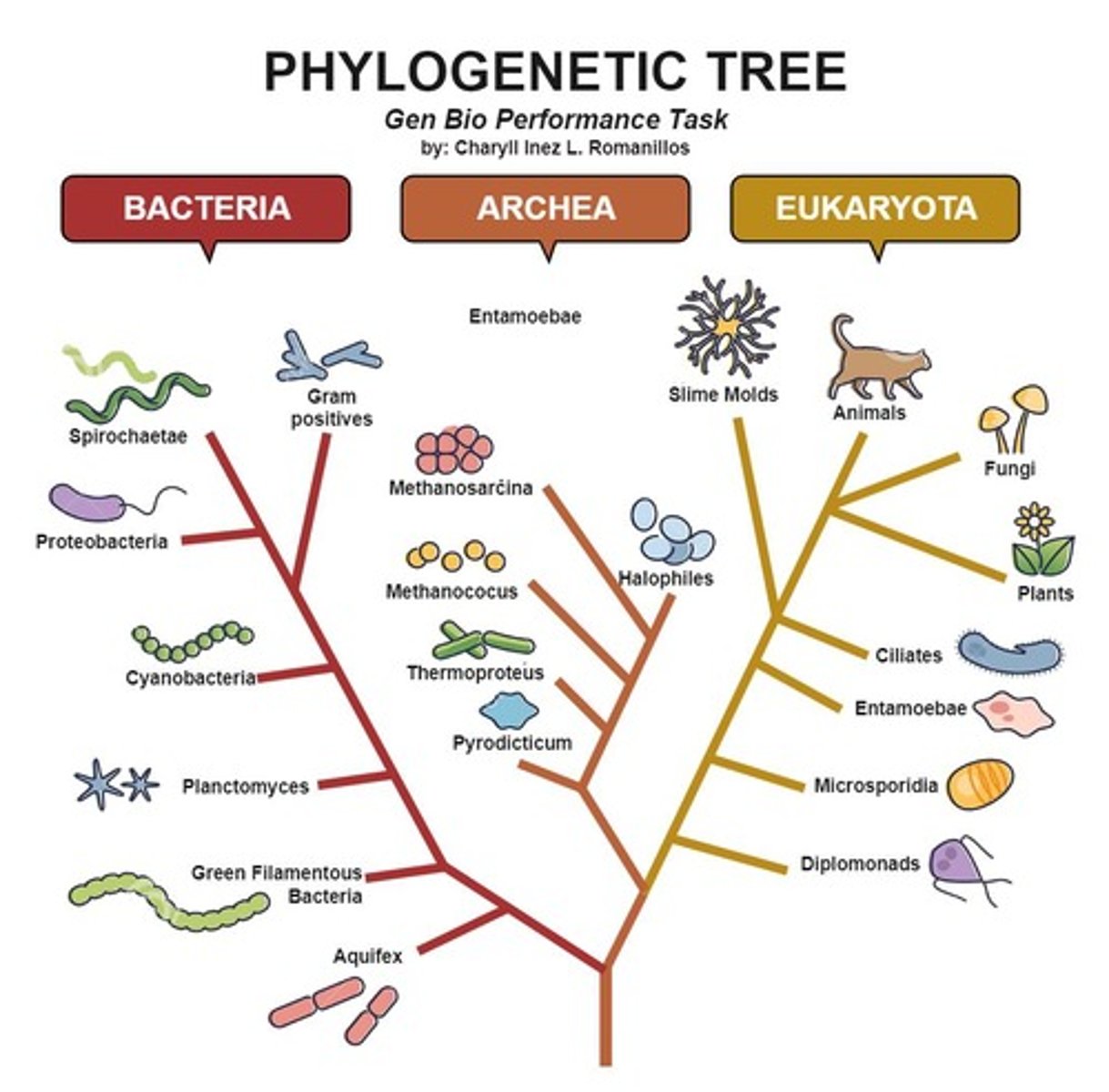
Prokaryotes
Organisms like Bacteria and Archaea that are unicellular and lack membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes
Organisms like Fungi, Plants, and Animals that can be unicellular or multicellular and have membrane-bound organelles.
Life Organization
Life is organized from atoms to organisms, including atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, and organisms.