ACYMANS7: Relevant Costing (Differential Cost Analysis)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Incremental analysis would be appropriate for
a. Acceptance of an order at a special price
b. Retain or replace equipment
c. Sell or process further
d. All of these
D
When applying the cost-benefit approach to a decision, the primary criterion is how well management goals will be achieved in relation to costs. Costs include all expected
a. Variable costs for the courses of action but not expected fixed costs because only the expected variable costs are relevant
b. Incremental out-of-pocket costs as well as all expected continuing costs that are common to all the alternative courses of action
c. Future costs that differ among the alternative courses of action plus all qualitative factors that cannot be measured in numerical terms
d. Historical and future costs relative to the courses of action including all qualitative factors that cannot be measured in numerical forms
C
If a firm is at full capacity, the minimum special-order price must cover
a. Variable costs associated with the special order
b. Variable and fixed manufacturing costs associated with the special order
c. Variable and incremental fixed costs associated with the special order
d. Variable costs and incremental fixed costs associated with the special order plus foregone contribution margin on regular units not produced
D
There is a market for both product X and product Y. Which of the following costs and revenues would be most relevant in deciding whether to sell product X or process it further to make product Y?
a. Total cost of making X and the revenue from sale of X and Y
b. Total cost of making Y and the revenue from sale of Y
c. Additional cost of making Y, given the cost of making X, and additional revenue from Y
d. Additional cost of making X, given the cost of making Y, and additional revenue from Y
C
Relevant costs in a make-or-buy decision of a part include
a. Setup overhead for the manufacture of the product using the outsourced part
b. Currently used manufacturing capacity that has alternative uses
c. Annual plant insurance costs that will remain the same
d. Corporate office costs that will be allocated differently
B
What is the opportunity cost of making a component part in a factory given no alternative use of
the capacity?
a. The variable manufacturing cost of the component
b. The total manufacturing cost of the component
c. The total variable cost of the component
d. Zero
D
When a multi-product plant operates at full capacity, quite often decisions must be made as to which products to emphasize. These decisions are frequently made with a short-run focus. In making such decisions, manager should select products with the
a. Highest sales price per unit
b. Highest individual unit contribution margin
c. Highest volume potential
d. Highest contribution margin per unit of the scarce resource
D

Company X is approached by Mr. Y, a new customer, to fulfill a large one-time-only special order for a product similar to one offered to regular customers. The following per unit data apply for sales to regular customers:
The company has excess capacity. Mr. Y wants the cabinets in narra, so direct material costs will increase by P30 per unit.
For the company, what is the minimum acceptable price of this one-time-only special order?
a. P830
b. P930
c. P785
d. P1,440
A
Company X manufactures furniture. The cost accounting system estimates manufacturing costs to be P90 per table, consisting of 80% variable costs and 20% fixed costs. The company has surplus capacity available. It is the company’s policy to add a 50% markup to full costs.
The company is invited to bid on a one-time-only special order to supply 100 tables. What is the lowest price it should bid on this special order?
a. P6,300
b. P7,200
c. P9,000
d. P13,500
B


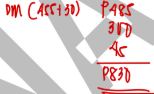
Company X manufactures part X101 used in several of its engine models. Monthly production costs for 1,000 units are as follows:
It is estimated that 10% of the fixed overhead costs assigned to X101 will no longer be incurred if the company purchases it from the outside supplier. Company X has the option of purchasing the part from an outside supplier at P85 per unit.
If the company accepts the offer from the outside supplier, the monthly avoidable costs (costs that will no longer be incurred) total:
a. P82,000
b. P98,000
c. P50,000
d. P100,000
A
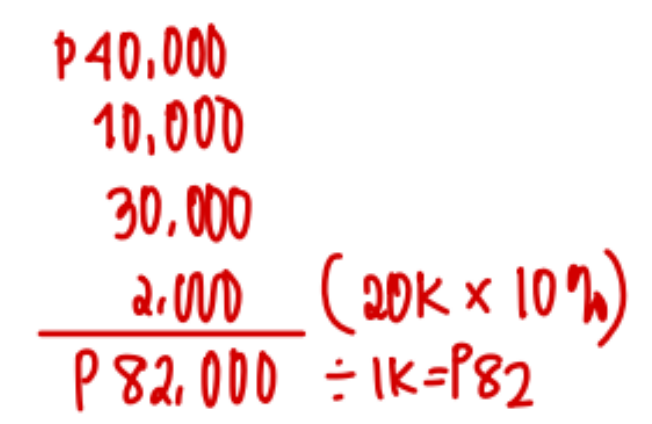

The machine can be operated 7 days a week, for 10 hours per day. How many units should be produced and sold to maximize the weekly contribution margin?
X Y Z
a. 60 40 9
b. 60 40 50
c. 56 28 18
d. 168 0 0
A

Company X produces weekly 15,000 units of Product X9 and 30,000 units of X10 for which P800,000 common variable costs are incurred. These two products can be sold as is or processed further. Further processing of either product does not delay the production of subsequent batches of the joint products. Below are some information:
X9 X10
Unit selling price without further processing P24 P18
Unit selling price with further processing P30 P22
Total separate weekly variable costs of further processing P100,000 P90,000
To maximize the company’s manufacturing contribution margin, the total separate variable costs of further processing that should be incurred each week are
a. P95,000
b. P90,000
c. P100,000
d. P190,000
B


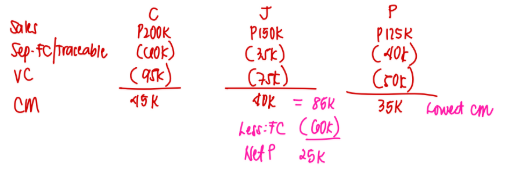
Because the company's objective is to maximize profits, what is its expected net profit after the appropriate product has been discontinued?
a. P10,000
b. P15,000
c. P20,000
d. P25,000
D