Water Pollution
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
What is mercury pollution?
Mercury is a persistent, bioaccumulative, toxic pollutant.

Mercury Properties
• Neurotoxicity.
• Liposolubility.
• Bioaccumulation.
• Biomagnification
How is mercury released into the environment?
- Disposal of items containing mercury, like batteries, thermometers, etc
- Chemical plants that produce chlorine using mercury electrodes
- Combustion of coal
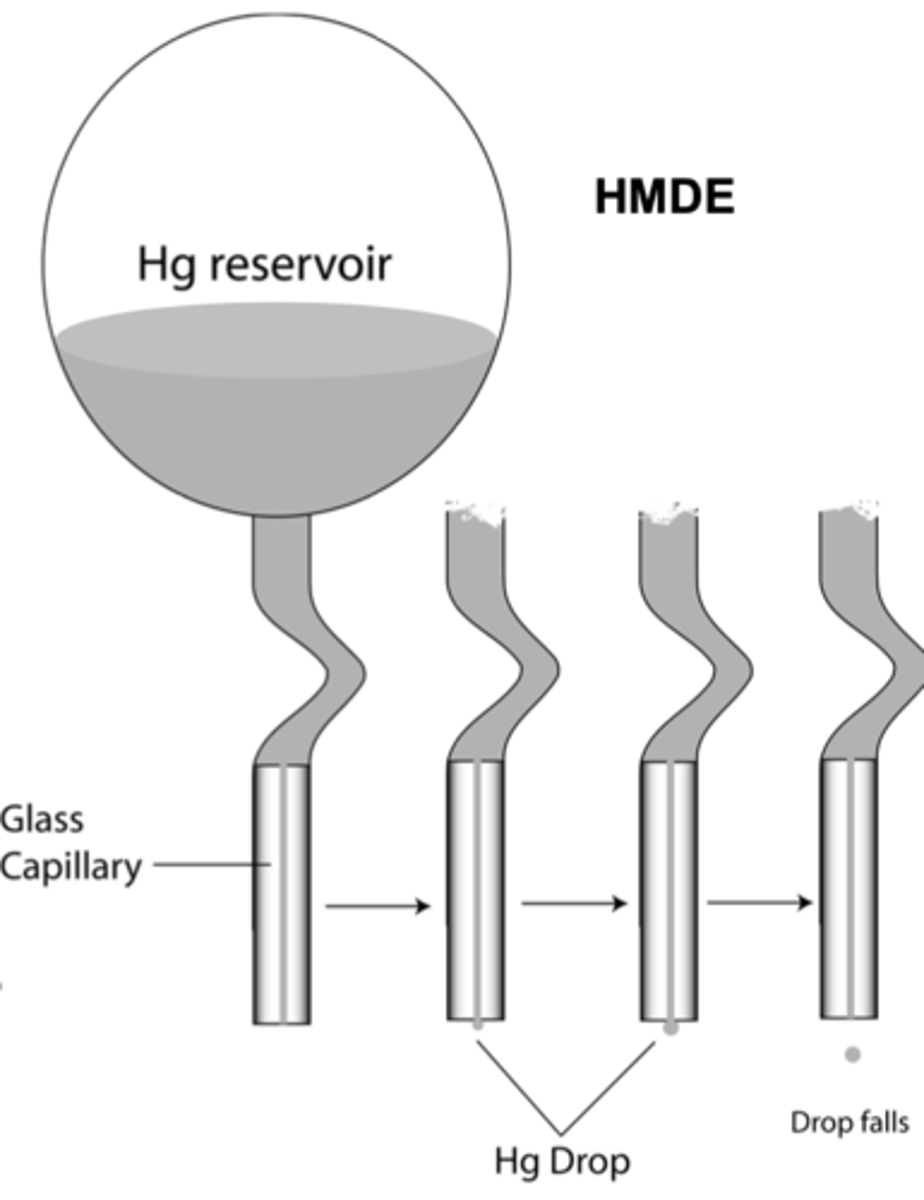
Types of Chemical forms of Mercury
- Elemental mercury
- Inorganic mercury
- Organic mercury
Example of an Inorganic Mercury compound
Mercury Oxide
Example of an Organic Mercury compound
Methyl Mercury
Liquid (elemental) Mercury
- It is not easily absorbed through the skin or gut
- Vapours may be absorbed in the lungs if they are inhaled

Inorganic Mercury Compounds
- An example would be Mercury Oxide (HgO)
- They are absorbed moderately well in the gut

Organic Mercury Compounds
Example: Methyl Mercury (CH₃Hg)
Easily absorbed through the skin, by the gut, and as vapours if inhaled
Why are organic mercury compounds dangerous?
They are liposoluble, so can pass through cell membranes easily, including through the blood-brain barrier into the brain, where the impacts can be more serious.
It can also cross the placenta and harm unborn babies.
Also causes kidney damage.
Why are even low toxicity inorganic mercury compounds still having severe pollution impacts?
1) Relatively low toxicity inorganic mercury compounds enter anaerobic sediments in lakes or the sea
2) They may then be changed into organic compounds (such as methyl mercury) by anaerobic microbes.
3) The mercury then bioaccumulated and biomagnifies along food chains
4) It often reaches concentrations that are much higher than when it was released into the environment.
How to control mercury pollution?
Replacing mercury thermometers with electronic thermometers
Using reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters to remove mercury from effluents
Ion exchange filters
Disposal at high pH to reduce solubility
What are heavy metals?
Metals with toxic effects on the body, including lead and mercury.
Why are heavy metals dangerous?
Heavy metals inhibit enzyme function, especially the enzymes of the nervous system
What properties of heavy metals causes pollution?
- Liposolubility
- Synergism
- Solubility
Liposolubility of Heavy Metals
It means they can be stored in fat droplets in living cells, so that chronic exposure to small doses may eventually lead to toxic concentrations by bioaccumulation.
Passage along the food chain may lead to biomagnification
Synergism of Heavy Metals
They can cause more serious pollution if they act in conjunction with other pollutants. There is synergism between cadmium and zinc, affecting plant growth parameters and their oxidative stress.

Solubility of Heavy Metals
Heavy metals are more soluble at low pH. Therefore pollution caused by heavy metal wastes can be reduced by increasing the pH to reduce solubility.
2 types of Heavy Metals:
- Lead
- Mercury
Lead Properties
- Neurotoxicity
- Liposolubility
- Bioaccumulation
- Biomagnification
What does lead exposure lead to?
Acute exposure to large doses may cause severe symptoms including brain damage, paralysis, and eventually death
Very high doses can kill by causing liver and kidney failure
These problems are only likely in industrial accidents and are prevented by good working practices, like wearing facemasks, using water sprays, or remote operations
Lead Controls
- Discontinued uses of: paint, petrol additives, lead pipes, solder for water pipes, lead fishing weights
- Waste storage at high pH
Discontinued uses of: solder for water pipes
Water pipes used to be made of lead for like 4500 years.
It then lead to lead being dissolved into water, and so people drinking it could suffer from chronic exposure.
In the UK, most piping was replaced in the 20th century with copper pipes.
Lead solder has been replaced with solder based on copper.
Discontinued uses of: lead based paint
When lead based paint got dusty and crackly, it posed a much greater health risk, especially to children, who pick up particles under their fingernails and suck their fingers.
Lead based paints were phased out in the 80s.

- Discontinued uses of: petrol additives
Anti knock agents (like tetra ethyl lead) were added to petrol to smooth the explosion of combustion and reduce engine wear.
However, lead particulates were released into the atmosphere, creating a public health threat.
Since the 80s, lead has been replaced with other chemicals such as benzene
Waste storage at high pH
Reduces lead solubility
What are the named pesticides?
Organochlorines
Organophosphates
Pyrethroids
Neonicotinoids
When were organochlorines introduced?
1940s
What are the properties of organochlorines?
High toxicity
High persistence
High liposolubility
Bioaccumulates and biomagnifies
What are the advantages of organochlorines?
They have high insect toxicity and low vertebrate toxicity.
They were initially used to control pests (like mosquitoes), then were used as an agricultural insecticide.
What are the disadvantages of organochlorine?
High toxicity to insects led to the deaths of many non target insects (bees and butterflies)
High persistence & high liposolubility, so less likely to be washed off fields.
High liposolubility means its can cross the cell membrane. This allows DDT to bioaccumulate and biomagnify up the food chain.
This produced levels that were toxic to predatory vertebrates at the top of the food chain like herons and otters (basically it killed a bunch of top predators)
Why was the bioaccumulation and biomagnification of organochlorines bad?
It produced levels that were toxic to predatory vertebrates at the top of the food chain (like herons and otters)
Are organochlorines banned?
Yes
What are the properties of organophosphates?
Low persistence
Low liposolubility
High water solubility
High toxicity
What are the advantages of organophosphates?
The low persistence and liposolubility mean they don’t bioaccumulate.
What are the disadvantages of organophosphates?
High mammalian toxicity
They are neurotoxins and inactivate the enzyme acetylcholinesterase so nerve function is damaged. It was used in WW2 as a weapon
Why is high mammalian toxicity of organophosphates bad?
Farmworkers can be at risk of acute exposure to doses, possibly causing death
What does chronic exposure to organophosphates lead to?
ADHD, Alzheimer’s
What are the properties of pyrethroids?
Low persistence
Not liposoluble / do not bioaccumulate / biomagnify
High specificity / high insect toxicity / low mammal toxicity
Insoluble in water / low mobility
Not carcinogenic
Why is the low persistence of pyrethroids good?
It means pyrethroids don’t remain in the environment for a long time, as it degrades quickly
What are the properties of neonicotinoids?
High specificity/ high insect toxicity / lower vertebrate toxicity
Relatively persistent
Water soluble
What are the advantages of neonicotinoids?
High insect toxicity
Lower vertebrate toxicity as they cannot cross the cell membrane and blood-brain barrier since they aren’t liposoluble
Neonicotinoids are broken down rapidly in the presence of sunlight and soil microbes.
What are the disadvantages of neonicotinoids?
Neonicotinoids are neurotoxins and inhibit the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Relatively persistent
Water soluble.
Why is neonicotinoids being water soluble bad?
They can leach into rivers and cause harms to fish.
Leaching into water bodies can cause toxicity if consumed.
Leaching allows the dispersal of lower concentrations
What do neonicotinoids do to bees?
Their use has been linked to the decline of many bee populations.
They are very toxic to bees
Since they have neurotoxic effects, they reduce the bees’ ability to navigate. Also reduces their immunity to disease.
When does neonicotinoid's impact on non targeted species appear to be increased?
By a synergist action with some fungicides that may be present at the same time.
Long term impacts of neonicotinoids
Some research suggests that neonicotinoids may build up in aquifers, which may cause issues in the future.
What is the most widely used pesticide?
Neonicotinoids
What are the named controls of pesticides?
Restrictions on use
Use of non-persistent pesticides
Use of more specific pesticides
Use of systemic pesticides
Application timing
Restrictions on use
Some pesticides have been banned, or their use has been restricted where they could cause problems.
Examples of restricted pesticides
Use of organochlorines is banned in most countries (though DDT can be used in some countries for malaria control)
Use of non-persistent pesticides
Non-persistent pesticides will break down rapidly and won’t become concentrated or travel long distances after application
Example of low persistent pesticides
Organophosphates are less persistent than organochlorine
Use of more specific pesticides
Pyrethroid and organochlorine insecticides are both toxic to insects but pyrethroids are less toxic to mammals
Use of systemic pesticides
They are absorbed by the crop and translocated within it.
They do not need to be sprayed onto all surfaces, are not washed off after they have been absorbed, and will protect new growth.
What is the issue with systemic pesticides?
As the systemic pesticides are present within the plant tissue, they may be eaten by humans if they are still present when the crop is eaten.
Application timing
Spraying on not windy days results in less spray drifting to surrounding habitats.
Spraying at night or when crops are not in flower will reduce impact on bees
Newer spraying techniques use smaller droplets to produce a more even coverage which reduces the amount required
The food samples collected were individually wrapped before being sent for analysis of pesticide levels.
Why is this less important for samples containing systemic pesticides than contact pesticides?
Systemic pesticides will be retained within the food
Suggest why pesticide residue levels in samples of a single type of food may show high variability.
Different amounts of pesticides applied because:
Types of pest may vary
Seasonal changes. A species life cycle affect abundance, and therefore different application rates are used
Different application methods
Number of predators vary
Variation after application because:
Rainfall
Time before harvest
Storage method
Food items are collected and analysed for pesticide residues throughout the year.
Suggest other factors that may be considered when selecting food items for testing to ensure that the pesticide residue levels are representative.
Large sample size
Random locations
Samples from different regions
Large range of food items tested
Large range of food from different outlets (suppliers, like supermarkets, wholesalers)
What is acid mine drainage?
Acidic water exiting from a subsurface mine, and it is very detrimental to aquatic ecosystems

Sources
Spoil heaps

What reactions occur in spoil heaps that contribute to acid mine drainage?
Small amounts of sulfide ores and oxygen react in the spaces between waste particles.

What substances are formed from those reactions?
Metal oxides and oxides of sulfur

What do metal oxides and sulfur oxides do?
They dissolve in drainage water, producing sulfuric acid.
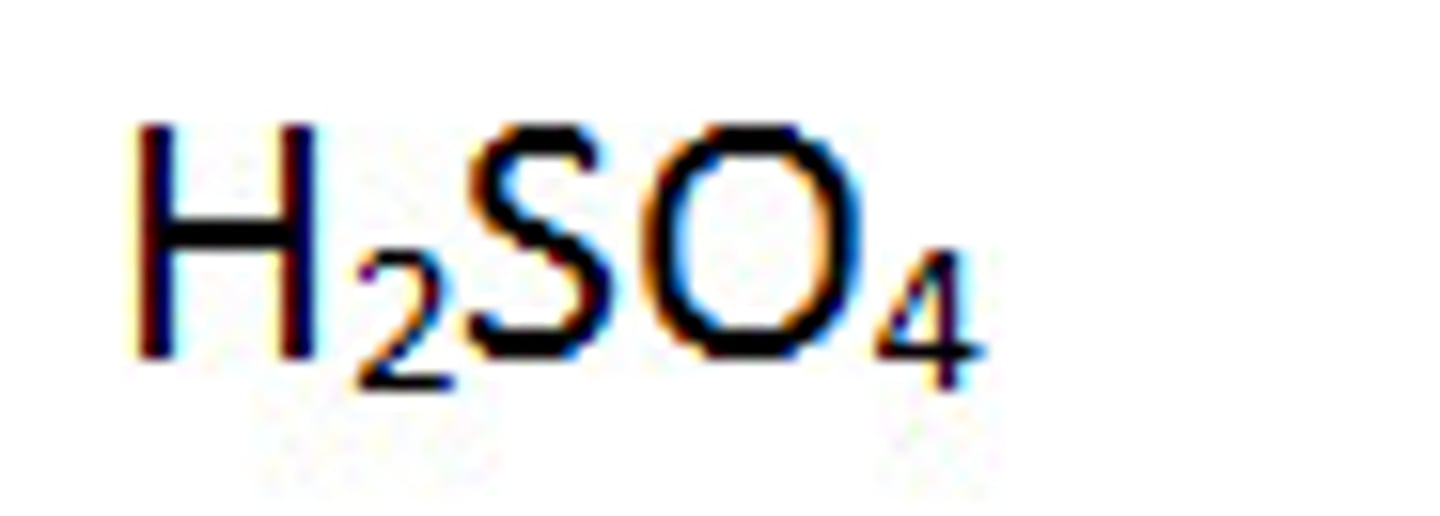
What is the term for drainage water containing sulfuric acid from spoil heaps?
Acid mine drainage
Effects
- The acidic solutions that leach out of the spoil heap have low pH
- Acid mine drainage leads to increased solubility and mobilisation of toxic metals

A change in river pH
It moves the pH of the river water outside of the species' range of tolerance
How does a change in river pH affect enzymes in organisms?
It can denature enzymes, preventing them from performing functions like digestion.
What impact does a change in river pH have on soil health?
It reduces soil health, causes nutrient leaching, and kills detritivores and microorganisms.

How does a change in river pH affect species with calcium-based exoskeletons?
It dissolves calcium based exoskeletons, affecting species like freshwater crayfish
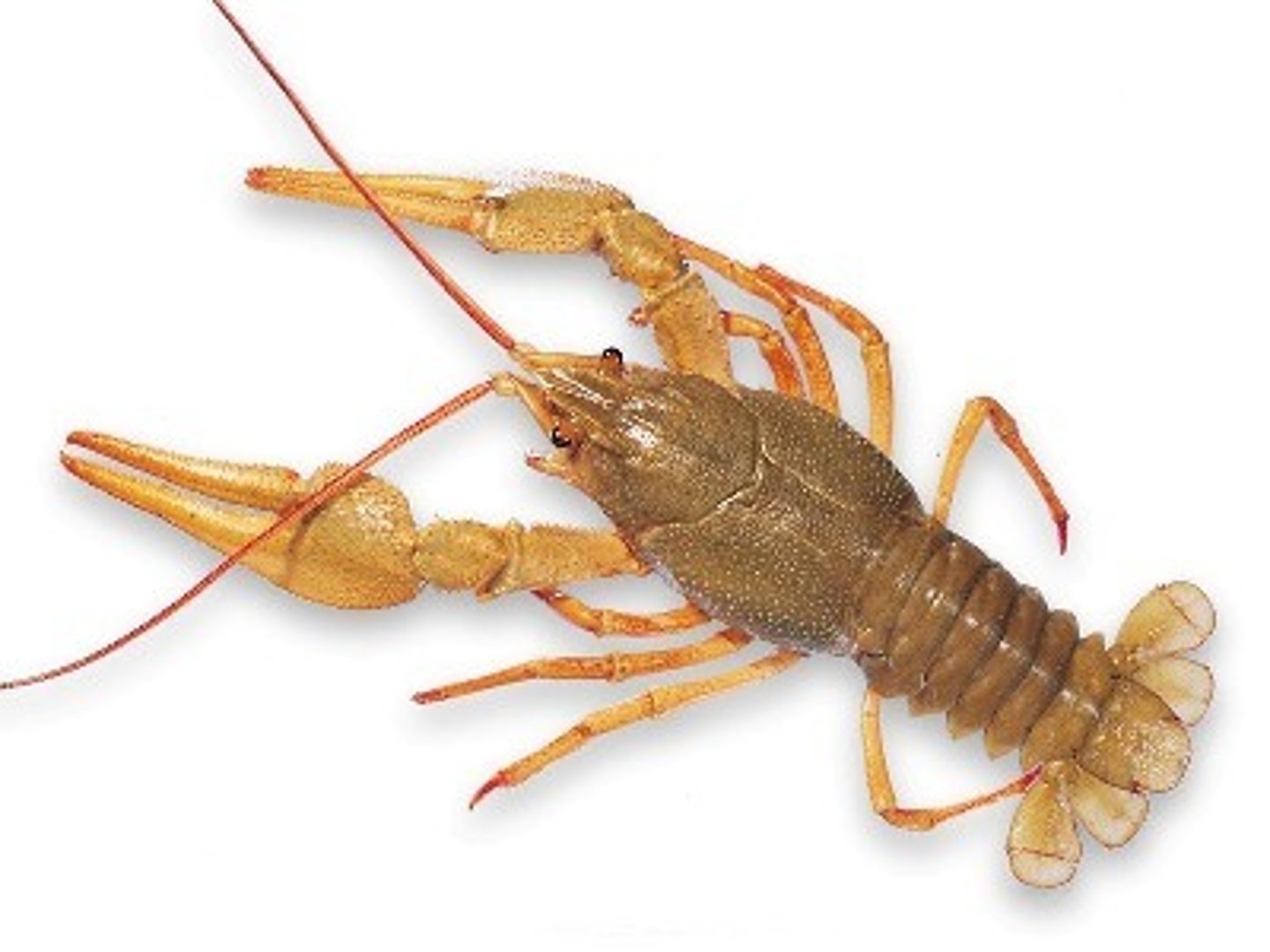

How can drainage mine water acidity be controlled?
By passing it through crushed limestone, neutralising the acidity.

What additional benefit does passing drainage water through crushed limestone provide?
It reduces the solubility of many toxic metals.
What happens to metals in mine water after treatment with crushed limestone?
Since their solubility is reduced, the solid metal precipitate deposits can then be filtered out and removed using techniques such as reverse osmosis.
How are wetland plants used in mine water control?
Wetland plants are often used for bioremediation to help treat mine water.
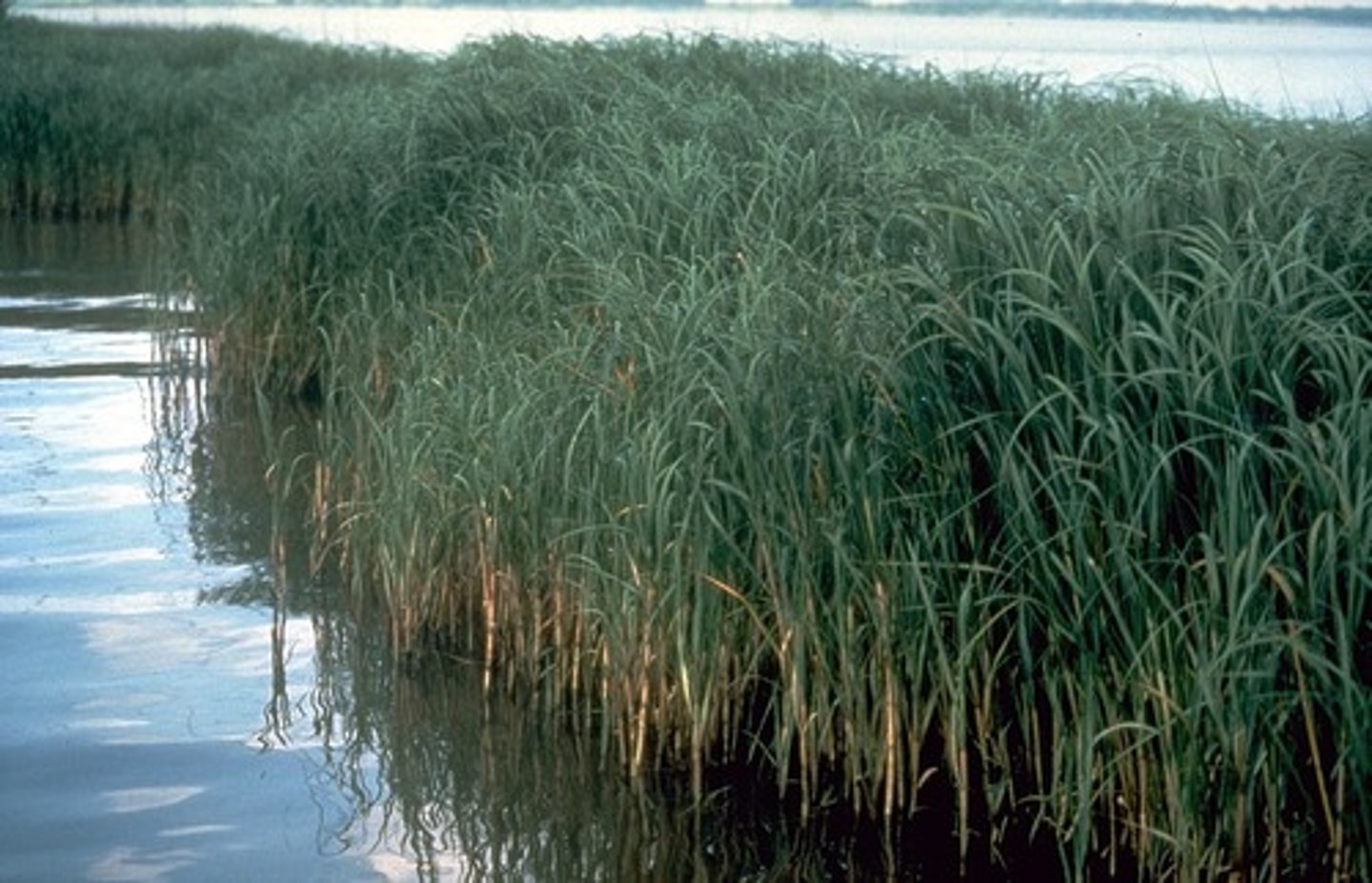

What are organic nutrients?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
Sources
Many processes involving animal and plant products produce liquid effluents. These effluents contain organic nutrients
What kinda processes involving animals and plant products we talkin' 'bout here?
Sewage works
Manure disposal
Paper mills
Food processing plants

Effects
- Deoxygenation
- Pathogens
Deoxygenation
Untreated organic nutrients flow into rivers, providing food for microorganisms. Aerobic digestion from these microorganisms deoxygenates the water and may kill aerobic organisms such as fish
Microorganisms can also cover the river. This prevents light reaching normal water plants and all of photosynthesis is inhibited
Pathogens
Sewage can contain pathogens from infected people
If other people come into contact with these pathogens, either directly or through contaminated food or water, the disease can spread
Diseases spread include cholera, typhoid, and dysentery
Controls
- Pre treatment
- Primary treatment
- Secondary treatment
- Tertiary treatment
- Anaerobic sludge digestion
Why is it important to treat organic effluents?
To prevent deoxygenation of water
Sewage treatment works
Each sewage treatment works is designed to treat specific effluent it receives to a satisfactory standard
The fluids can then be discharged without causing unacceptable pollution
A high standard may be required in more sensitive environments or where it is more urban
Pre treatment
The removal of solid objects, such as paper, plastic
Pre treatment methods:
Screens
Grit traps
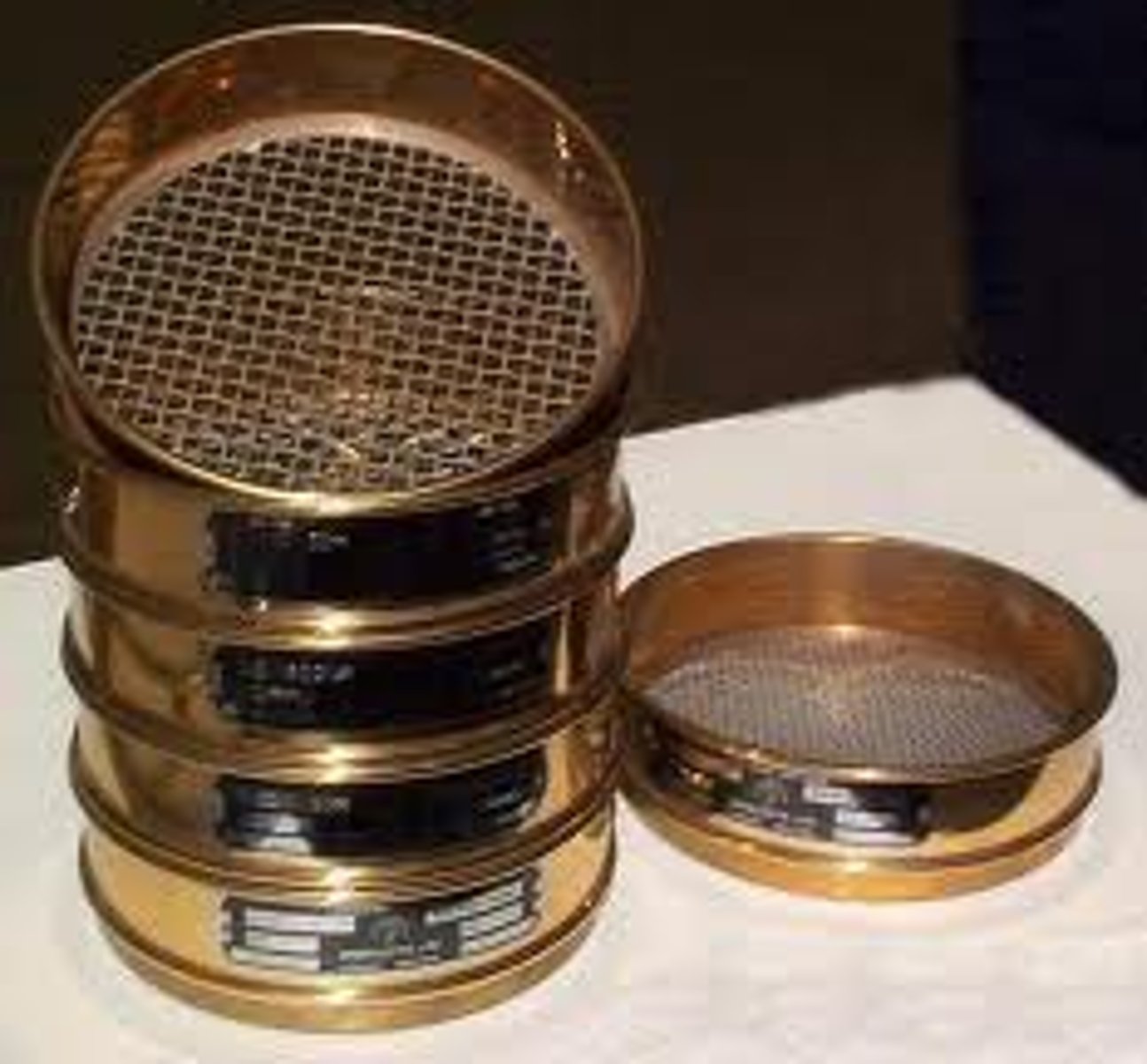
Pre treatment methods - Screens
Metal grills or sieves used to trap floating and suspended items such as plastic and paper items. These are then treated by incineration or disposed of in a landfill site

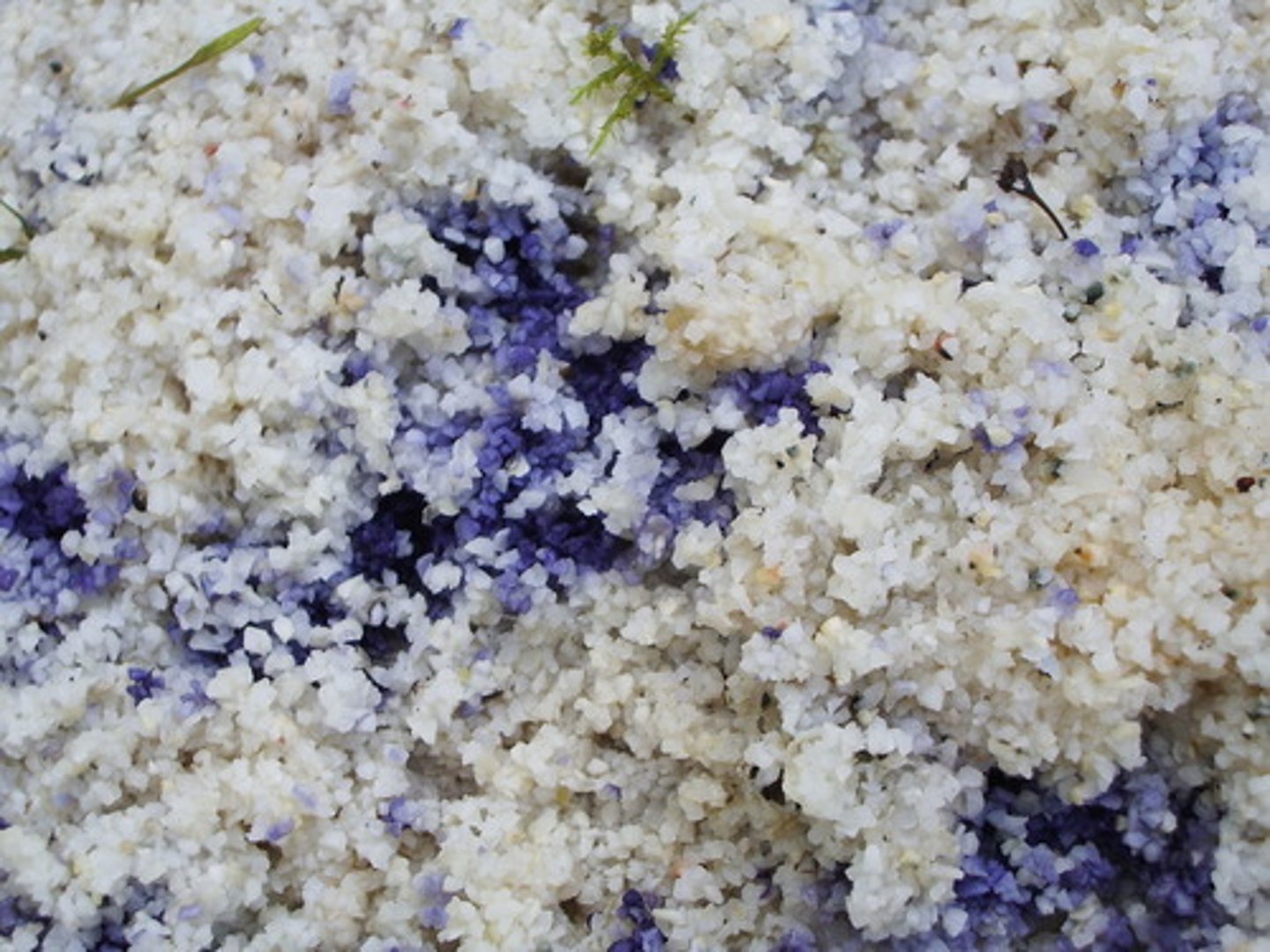
Pre treatment methods - Grit traps
The channel widens out so that the effluent flows more slowly, and the kinetic energy lowers until it’s not enough to carry the grit along, and the grit drops to the bottom.
The grit can later be removed from the tank and then disposed of in a landfill site

Primary treatment
The separation of most organic solids from fluids
Primary treatment methods:
Primary sedimentation
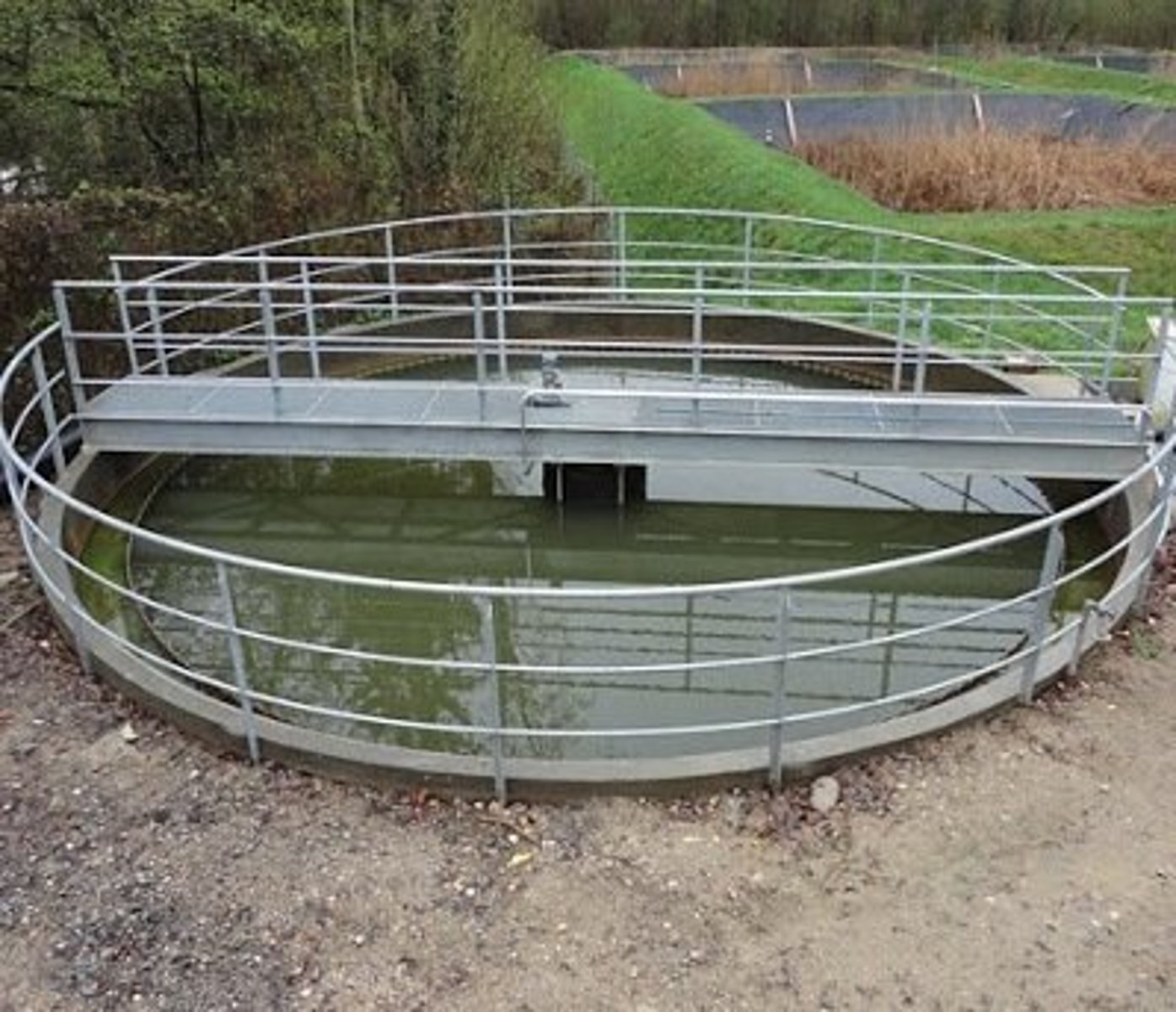

Primary treatment methods - Primary Sedimentation
The effluent is left to stand in large tanks, where the faecal solids sink to the bottom so that they can be removed and treated separately
95% of the organic matter is removed from the fluid effluent
The risk of deoxygenation in the water body is greatly reduced
Secondary treatment
The digestion and breakdown of the remaining organic matter in the fluids
Secondary treatment methods:
- Aeration tanks
- Secondary Sedimentation
- Filter beds
Secondary treatment methods - Aeration tanks
The remaining organic matter in the fluid effluent is broken down by bacteria
Shortage of oxygen can be a limiting factor as it slows down this aerobic process
To prevent this happening, large amounts of air are mixed in by paddle wheels, or air stones
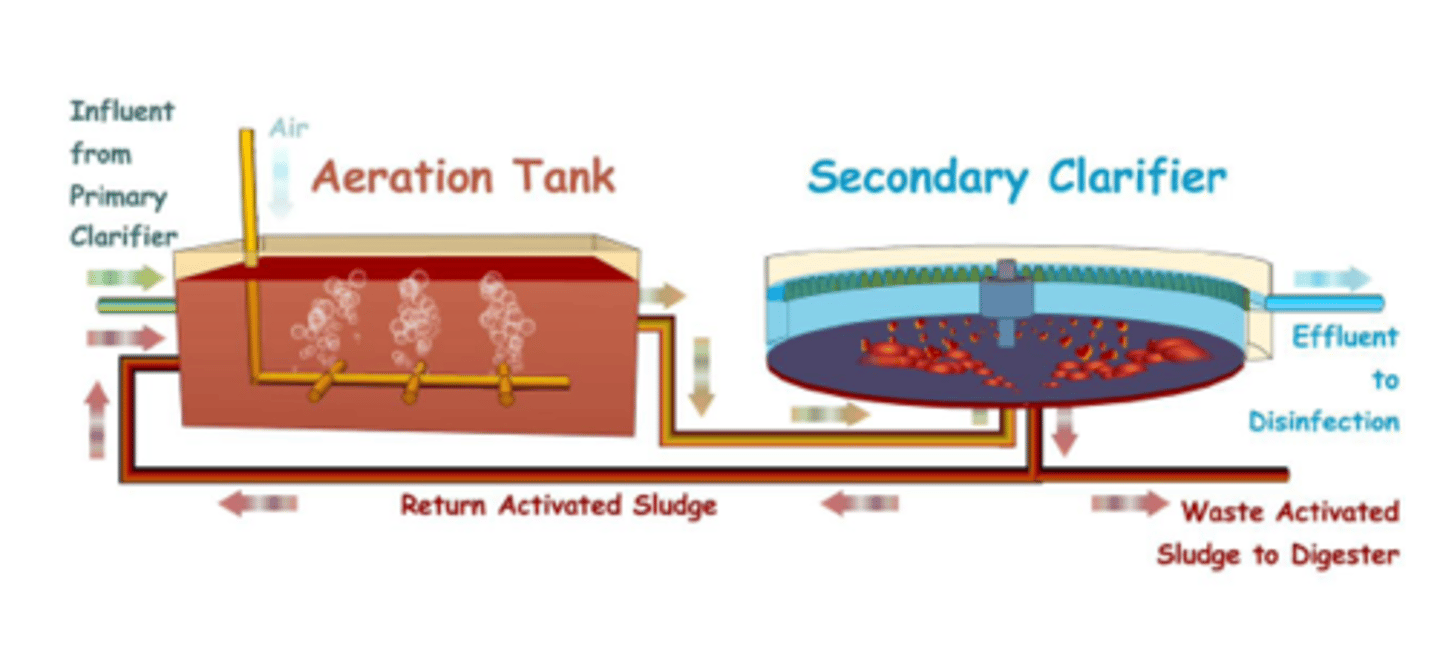
Secondary treatment methods - Secondary sedimentation
The effluent from the aeration tanks contain suspended bacteria
It is collected in the secondary sedimentation tank, and returned to the aeration tank as activated sludge
The clear effluent is then discharged into a river.
This isn't great as it could contain some dissolved inorganic nutrients and could cause cultural eutrophication.
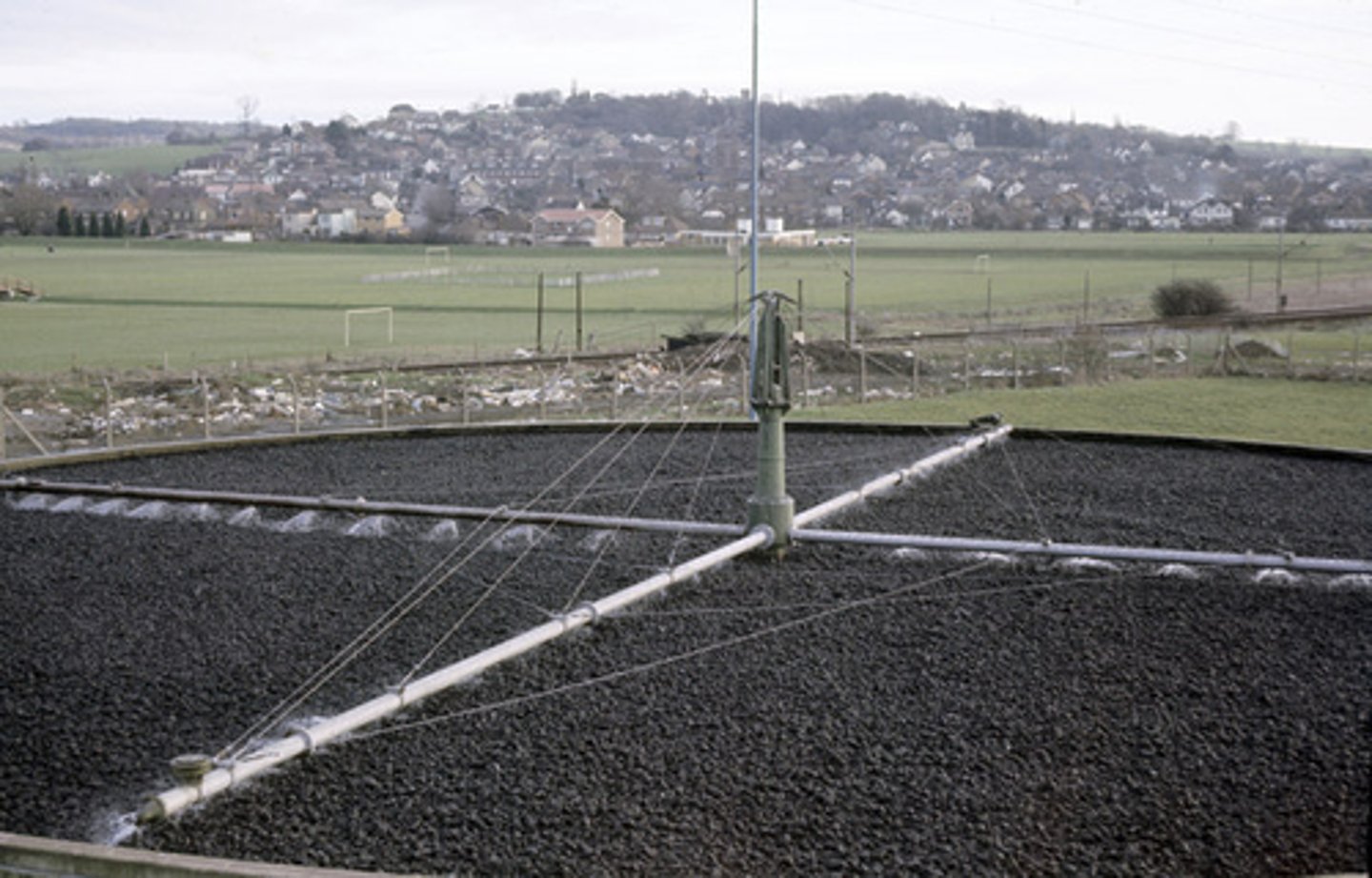
Secondary treatment methods - Filter beds (Alternative to aeration tanks)
Rotating arms spray the liquid effluent over gravel.
The surface area is maximised for microbes (bacteria, fungi, algae, invertebrates) that digest organic matter.
Some bacteria denitrify nitrates, reducing eutrophication.

Tertiary treatment
Additional treatment to remove phosphates or bacteria
Tertiary treatment methods:
- Phosphate removal
- Bacterial microfilters
Tertiary treatment methods - Phosphate removal
Phosphates are removed by adding Fe2(SO4)3, forming insoluble FePO4.
This can be used as an agricultural fertiliser.
Tertiary treatment methods - Bacterial microfilters
Effluent is strained through micro-strainers, and remaining bacteria are killed by UV light or sterilising chemicals like chlorine.