Blood, Erythrocytes, & Hemoglobin / Erythropoiesis & Hemoglobin Recycling
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What form of CO2 is transferred through the blood?
bicarbonate
What can occur when an animal ingest nitrates or breathe in chlorates?
methemoglobinemia
H+ “push” O2 from the heme group of hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
True
CO2“pushes” O2 from the heme group of hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
False → H+ pushes O2 from the heme group of hemoglobin
Why does chicken’s RBC turnover rate faster?
higher metabolic/oxygen demands
nucleated, less-flexible RBCs
increased oxidative damage
If you have an increase of erythrocytes, what can this indicate?
Many options:
anaplasmosis
genetic
What organ is most of erythropoietin formed in?
kidney
Erythropoietin is produced mainly in the liver
a) True
b) False
False
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells can be stimulated to produce:
a) Erythrocytes
b) Platelets
c) Leukocytes
d) Any type of blood cell
d) Any type of blood cell
What does carbonic anhydrase do?
converts carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid which then splits into hydrogen & bicarbonate
How is most of the CO2 in blood transported?
through bicarbonate
Erythropoietin
• Where is it secreted? What does it do? When is it secreted?
mainly from kidneys, some from liver
stimulates erythropoiesis (production of RBCs)
secreted in response to hypoxia
Even though RBC do not have a lot of O2, why does it help to obtain more O2 when more RBC are produced?
More RBC → more opportunity to recieve any type of O2 available
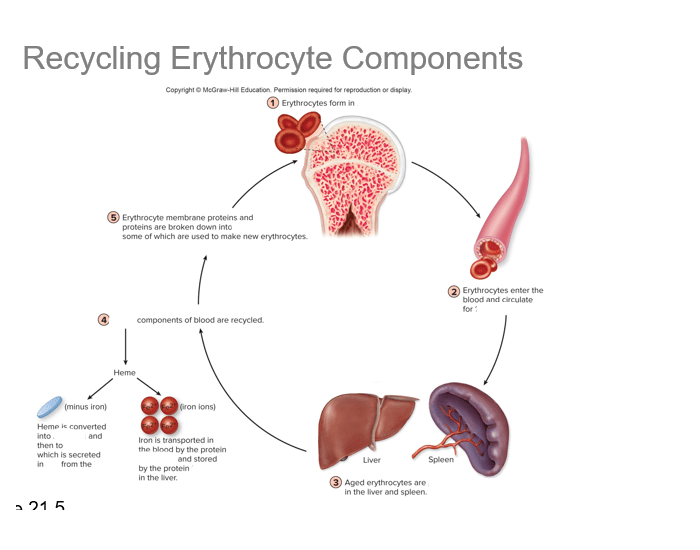
Draw out the Erythrocytes/hemoglobin recycling pathway.
What do RBCs contain a large quantity of?
hemoglobin
How are gases exchanged? What are the different PPs of oxygen in
the alveolar air, lung capillaries, interstitial fluid and inside the
cell?
Gases are exchanged in the lungs via diffusion:
Alveoli (100) → capillary (40) → interstitial fluid (40) → cell <40
Water of the blood transports enormous quantities of CO2 in the form of what?
bicarbonate (HCO-3)
What is carboxyhemoglobin?
a form of hemoglobin that can no longer transport O2
How is carboxyhemoglobin formed?
when carbon monoxide binds almost irreversibly to the heme portion of hemoglobin
List two abnormal forms of hemoglobin.
carboxyhemoglobin
methemoglobin
What is methemoglobin?
hemoglobin that is incapable of binding O2
How does methemoglobin form?
iron oxidized to the ferric form → iron must be in ferrous form to carry O2
RBCs are removed from circulation by ____________ in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow.
macrophages
CO2 is carried in the blood in three forms:
dissolved CO2 -7%
Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) - 70%
Carbaminohemoglobin - 23%
How does a chloride shift occur?
Cl- moves into RBC & HCO3- moves into the plasma
In the lungs, HCO3- is brought back into RBC in exchange for ___________.
Cl-
True or False: CO2 is bound to iron in heme.
False: CO2 is bound to an amino group on the globin portion of Hb
What is erythropoiesis?
the production of new RBCs
Where are all blood cells produced from?
pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells located in the bone marrow
What are metabolites of non-iron heme excreted in?
feces & urine
What is heme transformed into in the macrophages by the removal of globin & iron?
biliverdin
bilirubin
What is bilirubin eliminated by that transports it to the intestine?
liver
What does hematopoiesis mean?
formation of all types of new blood cells
In the reticulocyte stage, the cells pass from the ______1_______ into the ____2______.
bone marrow
blood capillaries
Erythropoiesis negative feedback system is centered in the _________.
kidney
Normally, about ____1_____% of all erythropoietin is formed in the _______2______, and the remainder is formed mainly in the liver.
90%
kidneys
What is anemia?
inability of blood to carry sufficient O2 to the body’s cells
How can a parasitic infection cause anemia?
blood loss
destruction of RBC
bone marrow suppression
What is polycythemia?
excess production of RBCs
What can polycythemia cause?
increased blood viscosity → total peripheral resistance increases → cause increase in HR & increase in RR → vascular system becomes engorged
What is an example of secondary polycythemia?
someone experiencing high altitudes
What are the three main functions of blood?
Transportation → carries O2, CO2, waste products, hormones
Regulation → pH, albumin
Protection → platelets, immune system
Explain the composition of blood.
Packed red blood cells → RBC
WBC → leukocytes
Plasma & serum → clear fluid layer at top
Describe the composition of plasma.
Water - 92%
Solutes - 8%
List the three main elements of blood.
Erythrocytes
Leukocytes
Thrombocytes
What do RBC transport mostly?
O2
Why do RBC not have mitochondria?
to ensure that the O2 they transport is not used by the cell themselves
In general erythrocytes:
a) Contain mitochondria
b) Are bags of hemoglobin
c) Contain many nuclei
d) Are part of the immune system
b) are bags of hemoglobin
2,3 BPG increases O2 binding in hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
b) False
binds less because it wants to let O2 go to the tissues
Increased H+ decrease O2 binding in hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
a) True
H+ will push O2 away from hemoglobin
How does hemoglobin bind oxygen?
Hemoglobin is made up of heme, which contains iron → iron helps with the binding of O2
True or False: Erythrocytes are enucleated.
True: Erythrocytes’ nucleus is lost as the cell matures.
List the two parts that make up hemoglobin.
Globin: protein portion
Heme: iron portion → makes binding to O2 possible
In general erythrocytes:
a) Contain mitochondria
b) Are bags of hemoglobin
c) Contain many nuclei
d) Are part of the immune system
b) Are bags of hemoglobin
Presence of hemoglobin in RBCs substantially ______________ the total O2 carrying capacity of blood.
increases
What occurs with a left shift on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
Left shift: promotes O2 binding to Hb in the lungs (higher affinity)
What occurs with a right shift on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
Right shift: promotes release of O2 from Hb in the tissues (lower affinity)
List the factors affecting Hb affinity for O2.
pH
temperature
2,3-Biphosphoglycerate
2,3 BPG increases O2 binding in hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
False
Increased H+ decrease O2 binding in hemoglobin
a) True
b) False
True
What causes a left shift of the O2-Hb dissociation curve?
decreased temp
decreased 2,3-DPG
decreased H+CO
What causes a right shift of the O2-Hb dissociation curve?
increased temp
increased 2,3-DPG
increased H+