Pathophysiology Final Exam
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
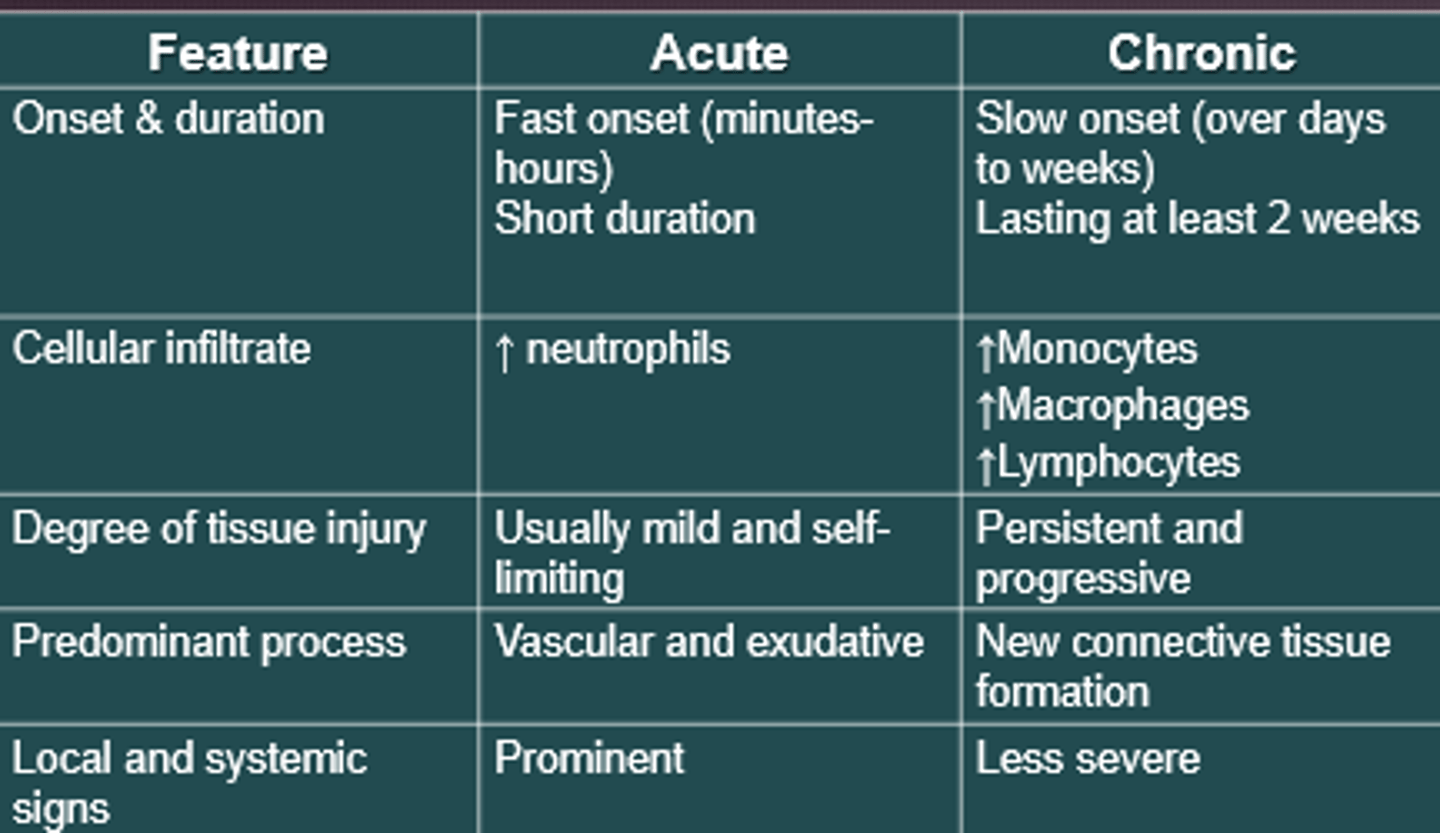
Acute
- Illness develops suddenly and doesn't last long; a few days or weeks
- Pneumonia, if treated appropriately, will go away quicke
Chronic
- Illness develops slowly and may worsen over time; a few months or years
- Asthma, diabetes, hypertension
Sign
Can be observed by others
Symptom
Only what the patient feels
Iatrogenic
Disease or problem caused by medical treatment or a doctor
Etiologic Factors
- Biological agents (bacteria, viruses)
- Physical forces (trauma, burns, radiation)
- Chemical agents (poison, alcohol)
- Genetic inheritance
- Nutritional excesses or deficits (Immune system is impaired)
- Nosocomial infections: Healthcare associated/hospital acquired infections
- Iatrogenic events: Ex. Radiation therapy, urinary catheter
- Idiopathic disease: Idiot doesn't know
- Protozoa causes malaria
- Most illnesses are multifactorial
Nosocomial infections
- Patient comes into the hospital for one thing and ends up developing a disease from the hospital
- Insurance doesn't pay for disease from the hospital- Wound infections, pneumonia (ventilator)
- Wash hands often- Urinary catheters, central lines
Apoptosis
- Programmed cell death
- Genetic mutations, fetal development, cells in endometrial lining when our period occurs
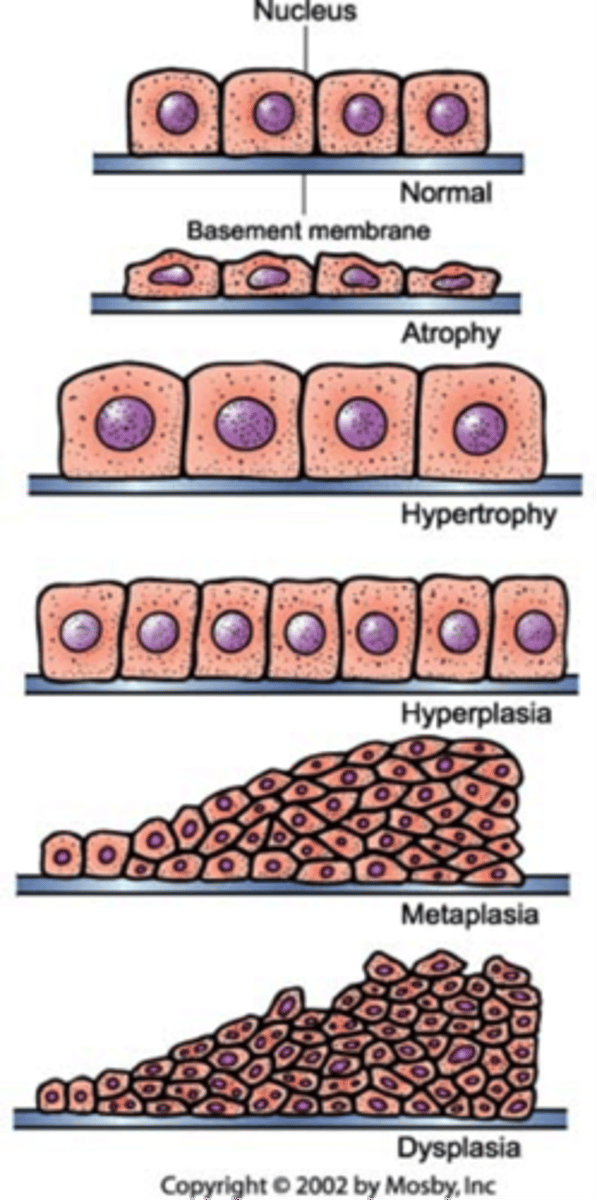
Atrophy
Cells, tissues, or organs decrease in size and function
Dysplasia
Abnormal change in size, shape, and organization
Hyperplasia
Abnormal increase of normal cells in a body part
Hypertrophy
Enlargement of an organ due to the increase in the size of cells, not the amount of cells
Hypoxia
Inadequate oxygen supply to tissues below physiologic levels despite adequate perfusion of the tissue by blood
Metaplasia
Reversible replacement of one cell type for another, change in type of adult cells in a tissue to a form that is not normal for that tissue
Hypoxia
- Most common and important case of cell injury!!
- Less than normal oxygen levels
- After about 3-5 minutes, we go from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism
- When a cell doesn't get enough oxygen, ATP can't be made, cell damage or death will occur
- Oxidative phosphorylation can't be finished without oxygen
- The sodium-potassium pump needs ATP; if there's no ATP, sodium will continue to rush into the cell and water will follow causing the cell to swell
- When the cell swells up
- Anaerobic glycolysis
- Calcium pump
- Causes of hypoxia
- Higher in mountains = lower oxygen
Causes of hypoxia
- Insufficient oxygen in the air
- Respiratory disease (COPD, asthma)
- Anemia (decreased blood cells): Decrease oxygen carrying capacity of cells
- Ischemia (decreased blood flow)
- Inability of cells to use oxygen
Cellular adaptation
- Mechanism used to prevent cellular and tissue harm due to stressors
- Change in size: Atrophy and hypertrophy
- Change in number: Hyperplasia
- Change in form: Metaplasia and dysplasia
- Responses also include intracellular accumulations and storage of products in abnormal amounts
- Genes can be operating genes needed for normal cell function or genes that determine specialized function (differentiation)
- Usually the differentiation genes are altered- Normal adaptive responses occur in response to need and an appropriate stimulus
Atrophy
- Cells that are atrophied reduce oxygen consumption and other cell functions by decreasing size of organelles and other structures
- Cells are not getting what they need
- When many cells are involved, the entire tissue or muscle atrophies
- These cells aren't dead, capacity is just reduced
- Cells may return to normal in time
- A: Without
- Trophy: Nourishment
Causes of atrophy
- Disuse: Reduction in skeletal muscle use, usually occurs when in a cast but can be restored once the cast is removed
- Denervation: Occurs in muscles of paralyzed limbs
- Inadequate nutrition: Tissues aren't getting fed correctly
- Loss of endocrine stimulation: Loss of estrogen stimulation during menopause results in atrophy in reproductive organs
- Ischemia (decreased blood flow): Cells decrease size and energy requirements for survival
Hypertrophy
- Increase in cell size and tissue mass
- Results from increased workload on an organ or body part, normally seen in cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue
- Hyper: Exceeding- Trophy: Nourishment
Physiologic Hypertrophy
- Increase in muscle mass r/t exercise
- Uterine and breast enlargement during pregnancy
Pathologic Hypertrophy
- Urinary bladder r/t obstruction
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Caused by hypertension, left ventricle has less volume because hypertrophic cells are taking up space
Compensatory Hypertrophy
Enlargement of a remaining organ or tissue after a portion has been surgically removed or becomes inactive
Hyperplasia
- Increase in number of cells in an organ or tissue
- Occurs in tissues with cells capable of mitotic division
- Activation of genes controlling cell division and intracellular messengers that control replication and growth
- Hyperplasia and hypertrophy can happen together
- Hyper: Exceeding
- Plasia: Growth
Physiologic (hormonal) Hyperplasia
- Breast enlargement during puberty
- Uterine and breast enlargement during pregnancy
- Increase in uterine lining during menstrual cycle
Pathologic Hyperplasia
- Skin warts
- Endometrial hyperplasia (abnormal uterine lining growth)
- Atypical hyperplasia of the breast
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Prostate gland increases in size and squeezes and can obstruct urine
Compensatory Hyperplasia
- Regeneration of liver tissue
- Wound healing
- Hyperkeratosis (ex. callus)
Metaplasia
- Reversible replacement of one type of cell for another
- Cell type remains with the primary tissue
- Usually fully reversible when irritant is removed
- Meta: Change beyond
- Plasia: Growth/development
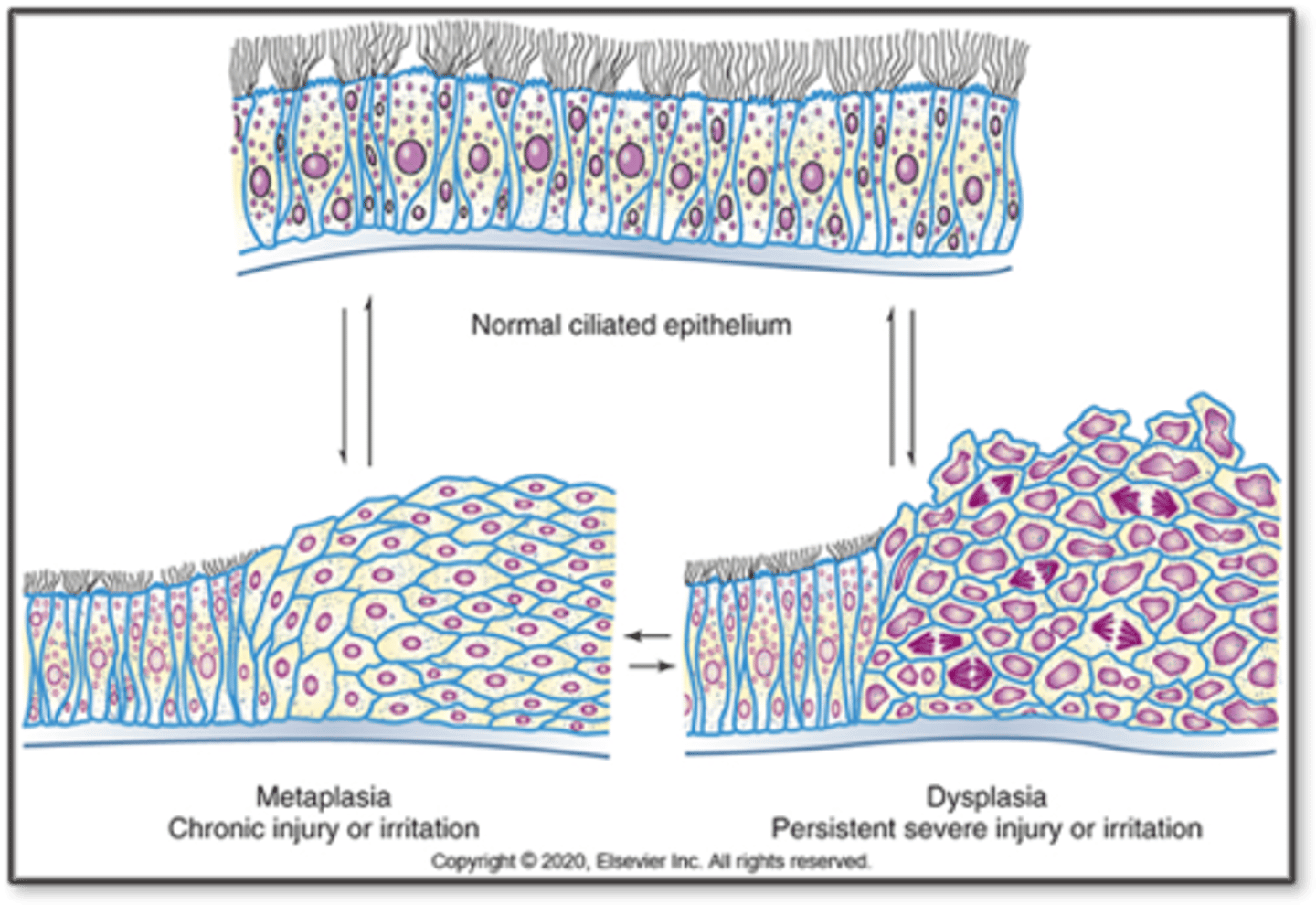
Metaplasia Examples
- Adaptive substitution of stratified squamous epithelial cells for the ciliated columnar epithelial cells in the trachea and large airways of a habitual cigarette smoker
- Continuous GERD can cause metaplasia because of excessive acid, columnar cells handle this acidic environment better
Dysplasia
- Abnormal change in size, shape, and organization of cells- Minor degrees may cause chronic irritation or inflammation
- Mostly of metaplastic squamous epithelium in respiratory tract and uterine cervix
- Potentially reversible after irritation is removed
- May/may not develop into cancer
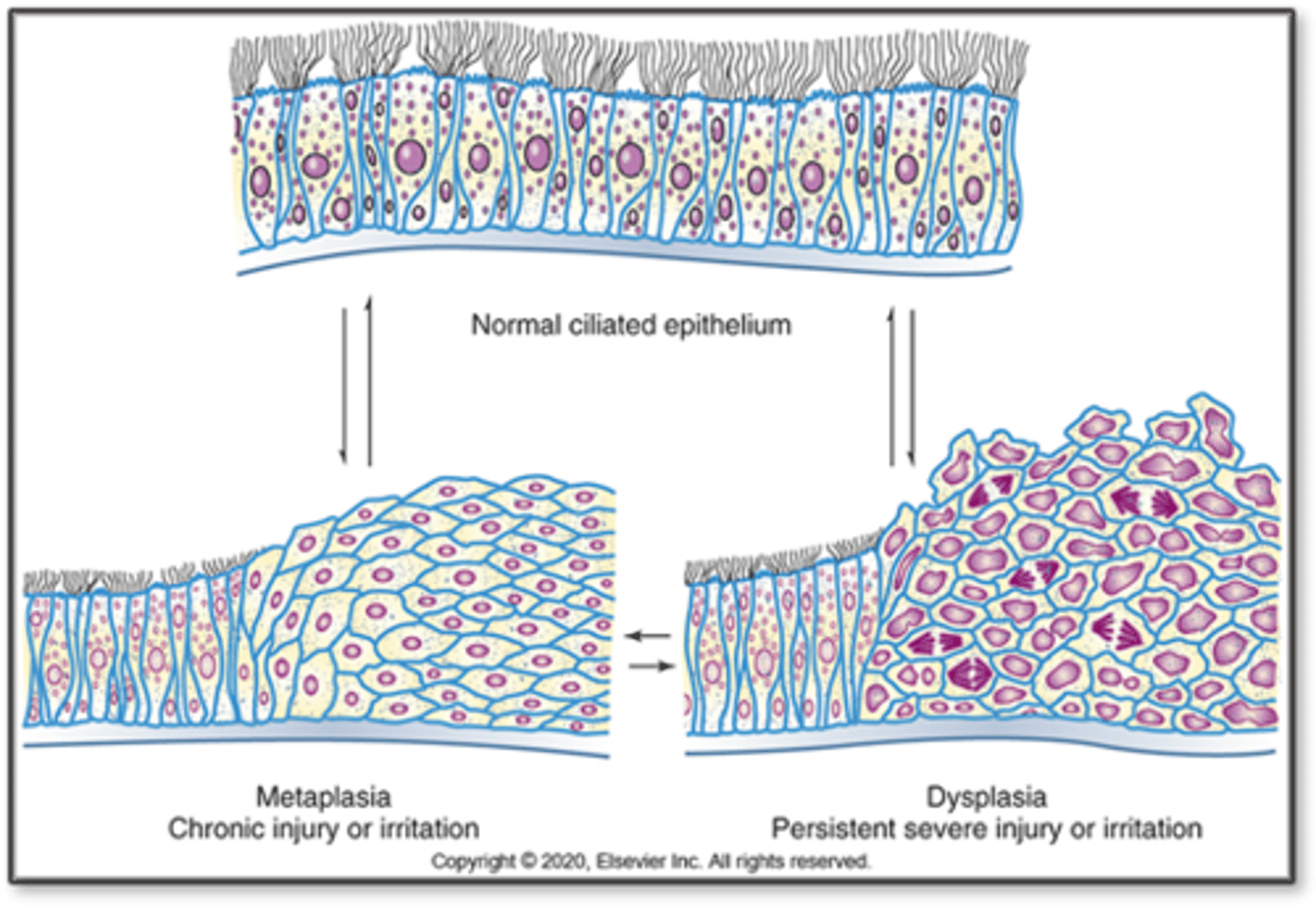
Dysplasia Examples
Pap smears can show mild dysplasia
Cellular injury
- Physical injury
- Cellular injury
- Chemical injury
- Biologic agents
- Nutritional imbalances
Physical injury
- Mechanical forces: Body impact with another object; split and tear tissue, fracture bones, injure blood vessels, and disrupt blood flow
- Temperature extremes: Damage cell, organelles, and enzyme systems; coagulation can occur with more intense heat; blood viscosity increases in intense cold and induces vasoconstriction; edema results from increased capillary permeability; frostbite
- Electrical injuries: Alternating current is more dangerous; there's an entry and exit point
Cellular injury
- Non Ionizing: Infrared light, ultrasound, microwaves, and laser energy; causes atoms and molecules to vibrate and rotate; mainly thermal injuries; dermal and subcutaneous injury; very low frequency, causes vibrations; generates heat energy
- Ultraviolet: Increases skin cancer risk, damages DNA, depends on intensity of rays, amount of melanin protects against UV rays
- Ionizing: Directly breaks chemical bonds, free radicals are released that destroy cells; rapidly dividing cells of bone marrow and intestines are more vulnerable; initial response includes swelling, disruption of organelles, alterations of cell membrane, and changes in the nucleus; genetic mutations, skin burns can occur; intestines, heart, blood vessels, brain, etc
Chemical injury
- Drugs
- Lead
- Mercury
Drugs
- Ethyl alcohol: harms gastric mucosa, liver, a developing fetus, and other organs
- Antineoplastic and immunosuppressant drugs: Directly injure cells; Other drugs: Produce metabolic end products that are toxic to cells
- Acetaminophen (tylenol): Detoxified in the liver where it can become highly toxic metabolite, keep daily intake to less than 4 grams for adults
- Performance enhancing steroids
Lead
- Small amounts can accumulate and become toxic
- Can cause cognitive and intellectual deficits and neurobehavioral problems
- Absorbed from GI tract or lungs into the blood
- Calcium, iron, or zinc deficiency increases lead absorption
- Major targets are RBCs, GI tract, kidneys, and nervous system
- Anemia can occur affecting RBCs
- In the GI tract, "lead colic" can occur which is a form of abdominal pain
- In the Kidneys, it can cause damage and hypertension
- In the nervous system, Demyelination and death of cortical cells, effects neural development
- Inhaled or ingested
- In paint, some toys
- Can be permanent decline in child's intellectual abilities
- Lead competes with hemoglobin which can cause anemia (fatigue, paleness), calcium (bone dysfunction), nerve transmission and brain development
Mercury
- Mercury vapor, inorganic divalent mercury, methyl mercury, and ethyl mercury
- Toxicity involving the CNS and kidneys can occur depending on the type of exposure
- The bigger the fish, the more potential exposure the fish has had
- Children and pregnant women are most vulnerable
Biologic agents
- Bacteria: Interfere with cellular production of ATP, cell slowly starves
- Viruses: Enter cell and become incorporated into its DNA
- Parasites
Nutritional imbalances
- Obesity and diets high in fats may predispose people to atherosclerosis
- Starvation: Deficiency of all nutrients and vitamins
- Selective deficiency: Single nutrient or vitamin
- Scurvy: Vitamin c deficiency; weakness, gum disease
- Rickets: Vitamin d deficiency in children; weakness, bowed legs; colder environments
Hypoxia and ATP depletion
- Hypoxia deprives the cell of oxygen
- Caused by inadequate oxygen, respiratory disease, ischemia, anemia, edema, or inability of cells to use oxygen
- Causes power failure in the cell
- As lactic acid accumulates, pH lowers; this can then cause cell membranes to be altered and chromatin clumping and cell shrinkage
- Reduced ATP causes cell swelling and failure of the sodium/potassium pump
Hypercalcemia
Too much calcium in the blood
Hyperkalemia
Too much potassium in the blood
Hypocalcemia
Too little calcium in the blood
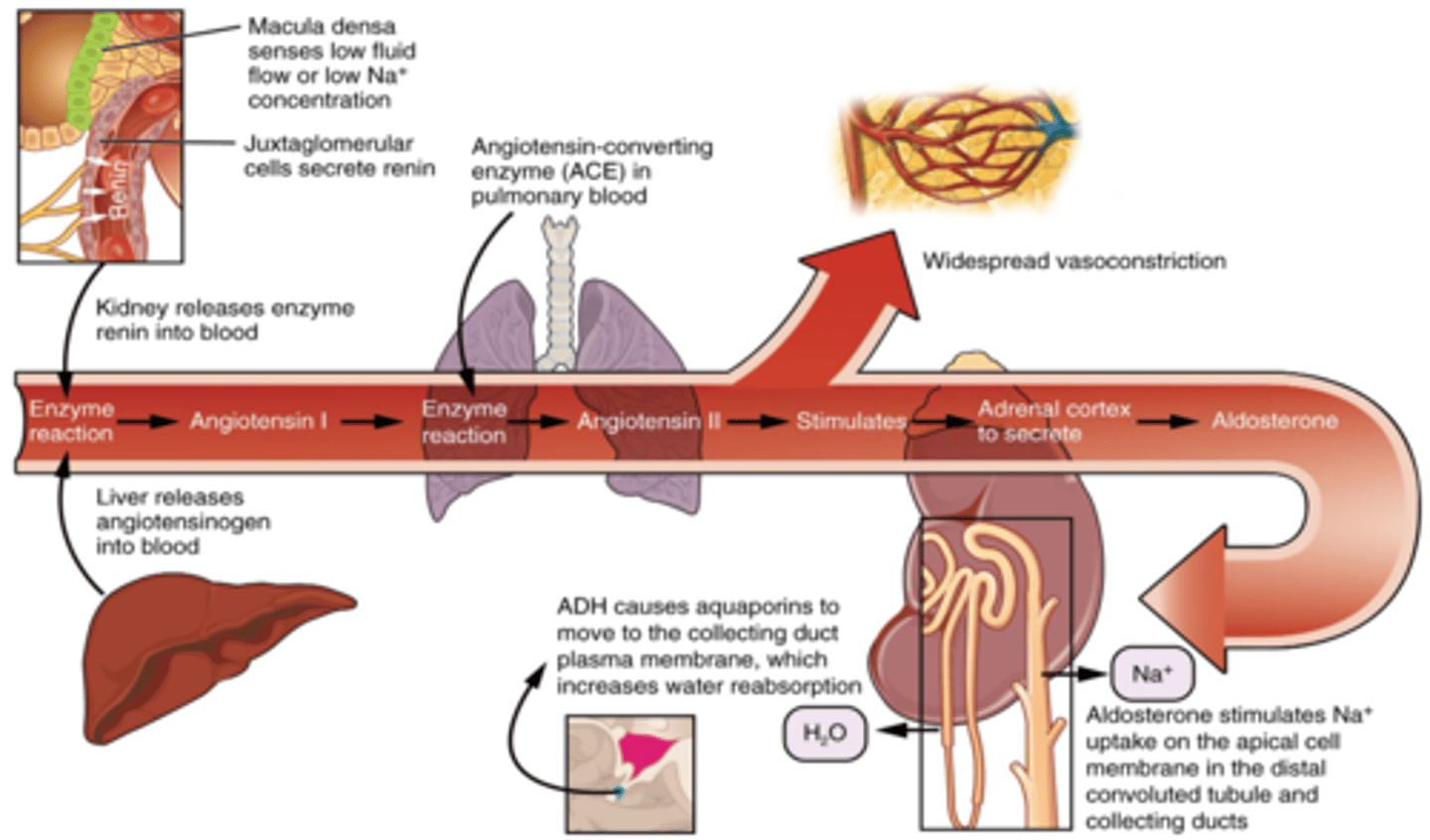
Renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS)
- When active and dehydrated, juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin and liver releases angiotensinogen
- Angiotensin 2 is most potent vasoconstrictor, acts in hypothalamus to stimulate thirst along with ADH
Hyperkalemia: Major causes
- Decreased renal elimination (renal dysfunction, decreased urine output)
- Excessive intake
- Movement from ICF to ECF
- Patients who are acidotic
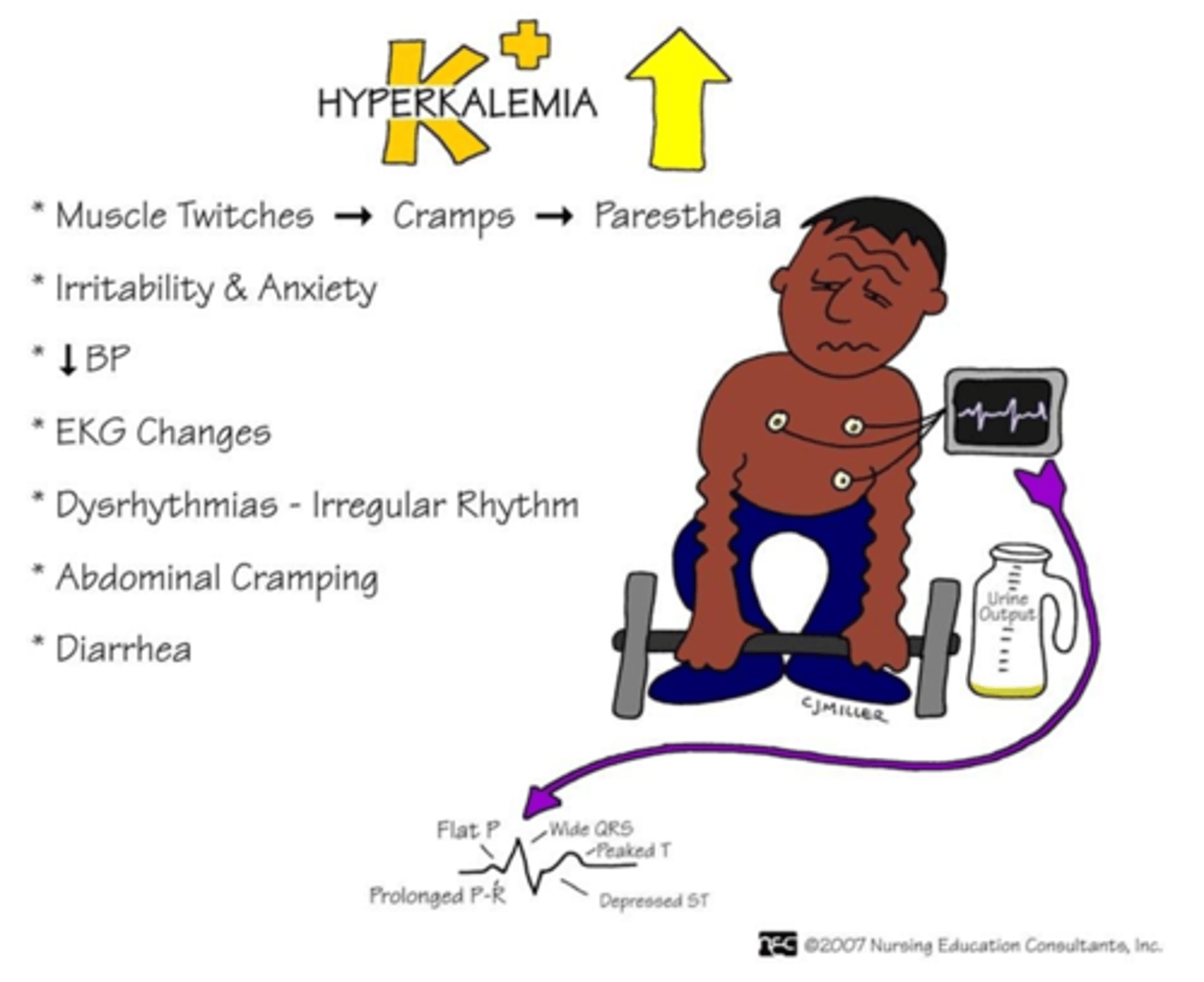
Hyperkalemia: Manifestations
Heart
- Arrhythmias: Cardiac standstill
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Tall T waves on EKG
Neuromuscular
- Paresthesia (pins and needles)
- Weakness/dizziness
- Muscle cramps
GI
- Abdominal cramping
- Increased motility (hyperactive bowel sounds)
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
Hypocalcemia: Major causes
- Kidney disease
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Hypoparathyroidism: Not releasing enough PTH
- Inadequate intake/absorption
- Excess alcohol intake
- GI diseases: Crohn's, celiac disease
- Calcium is bound to protein so low albumin can affect calcium levels
- Causes increased neuromuscular excitability because it increases the threshold, involuntary muscle contraction
- Tetany: Locked jaw
- Deadly dysrhythmias

Hypercalcemia
Major causes:
- Hyperparathyroidism (too much PTH)
- Cancer
Less common:
- Excessive intake (too much vitamin D or calcium in diet or vitamins, GERD)
Acid base balance
Body acids exist in 2 forms
- Volatile
- Nonvolatile
Acids are by-products
Normal serum pH: 7.35-7.45
- Decrease pH = acidosis
- Increase pH = alkalosis
Regulated by:
- Chemical buffer systems
- Lungs
- Kidneys
- Hydrogen ion excretion or absorption
Acid-base regulation
- Buffer system is the first to respond
- Respiratory mechanism is 2nd to respond
- Metabolic is 3rd to respond
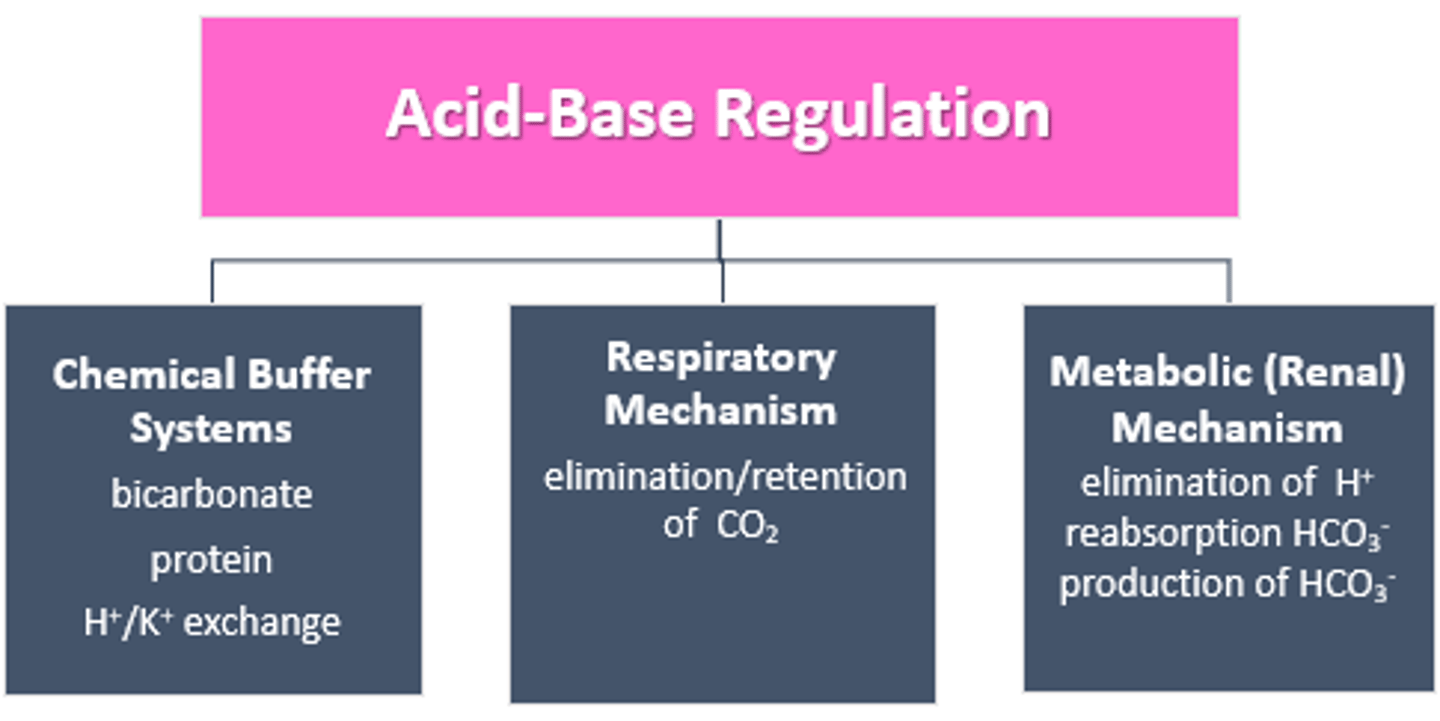
Respiratory acidosis
Excess CO2 in the blood d/t bradypnea
- CO2: Rise
- pH: Drops
How do the kidneys compensate?
- Hold on to the bicarb to make it more basic
- Get rid of hydrogen ions
- Urine is more acidic
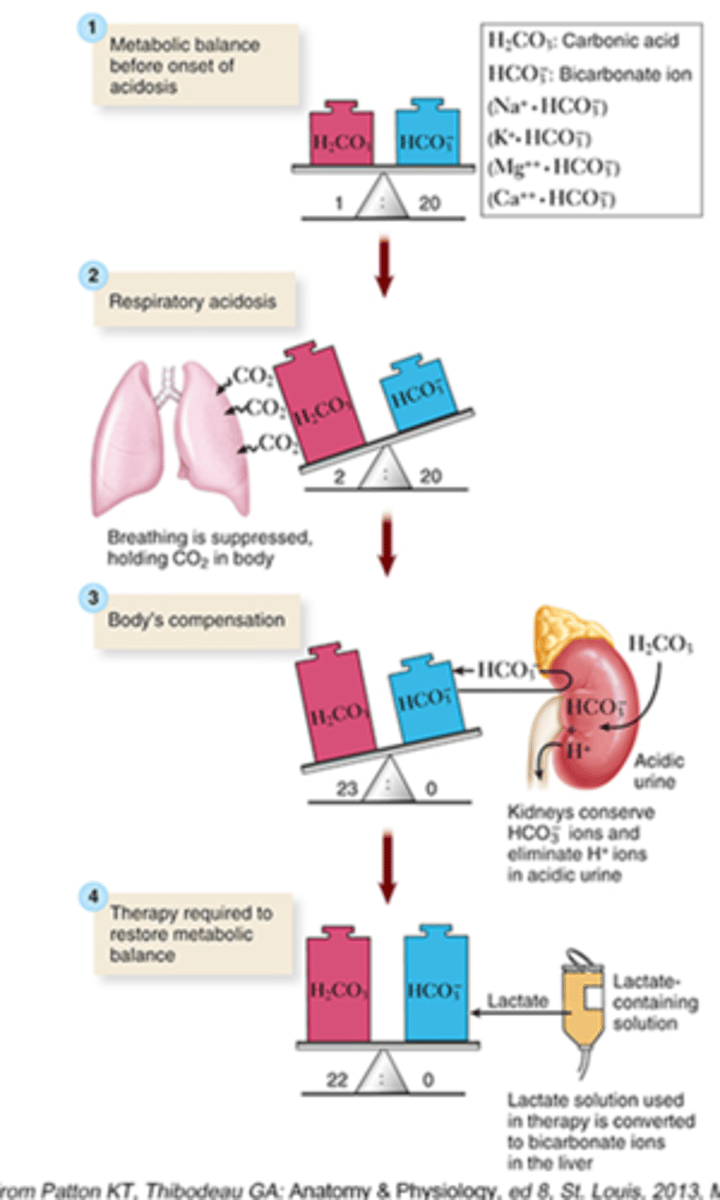
Causes of Respiratory acidosis: "DEPRESS" breathing
- D: Drugs (opiates, sedatives) diseases of neuromuscular system
- E: Edema
- P: Pneumonia
- R: Respiratory center in brain (brain injury)
- E: Emboli
- S: Spasms of bronchial tubes d/t asthma
- S: Sac (alveolar) elasticity d/COPD
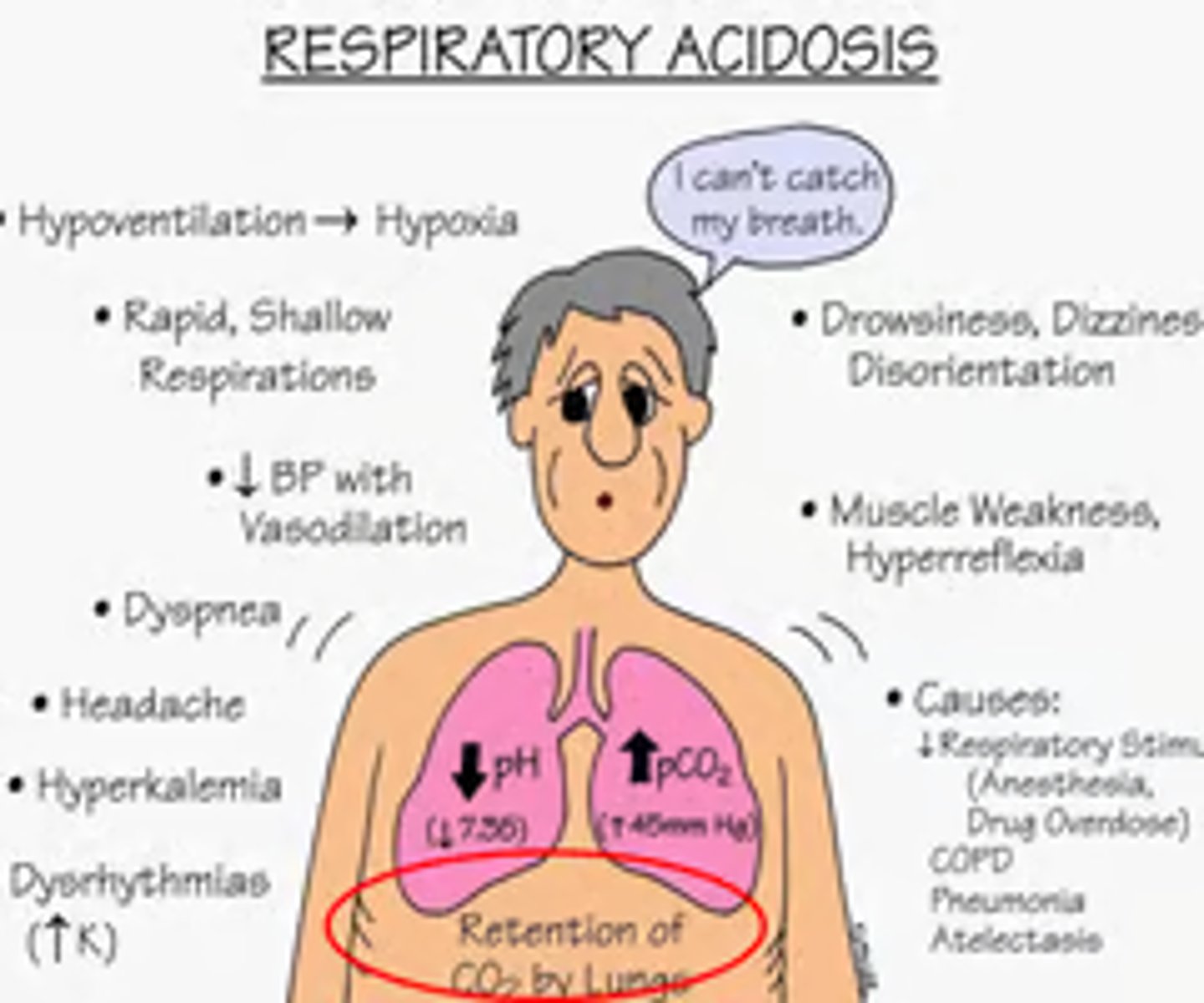
Hypoventilation
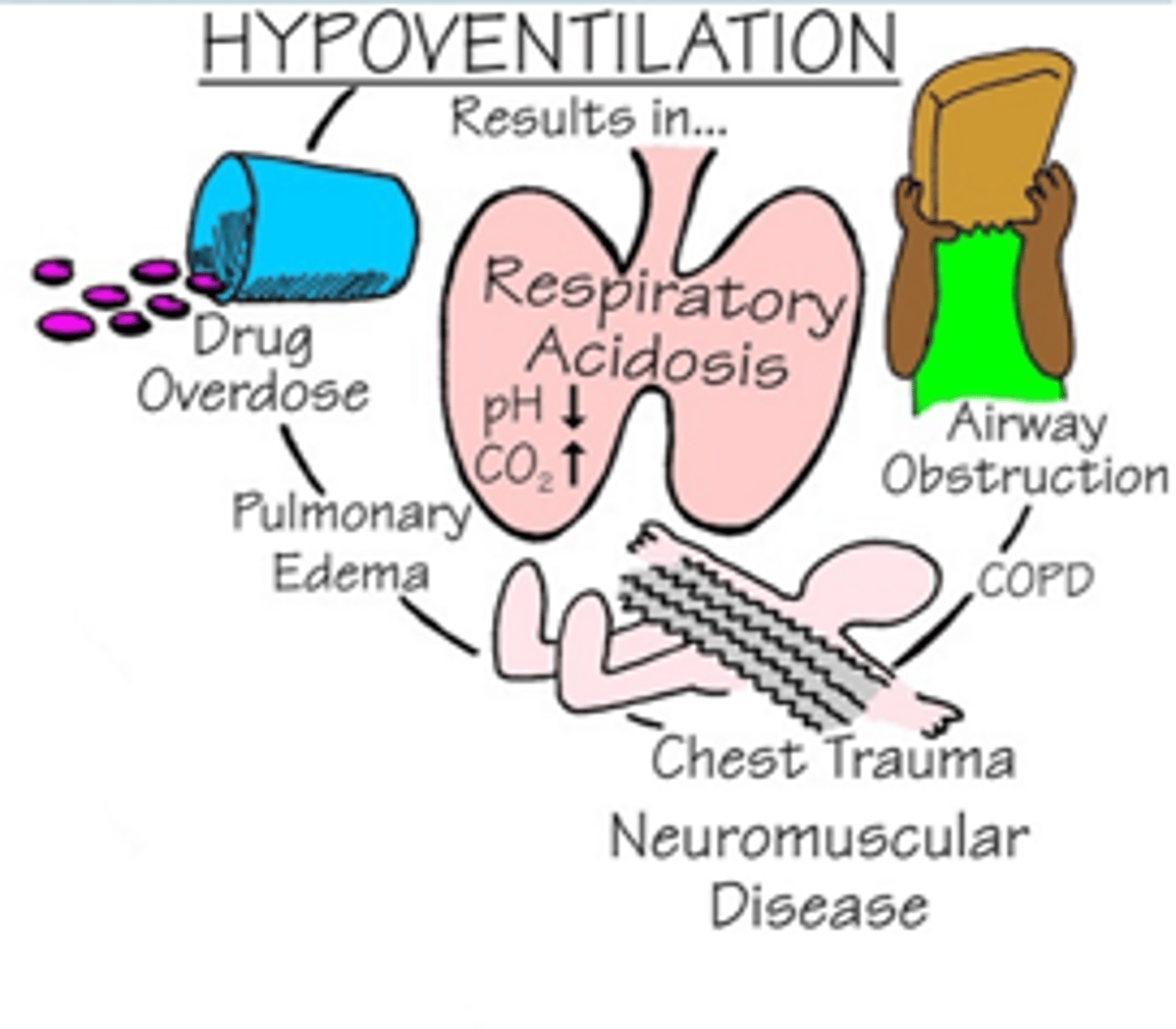
Respiratory acidosis: Treatment
- Breathing treatments
- Antibiotics
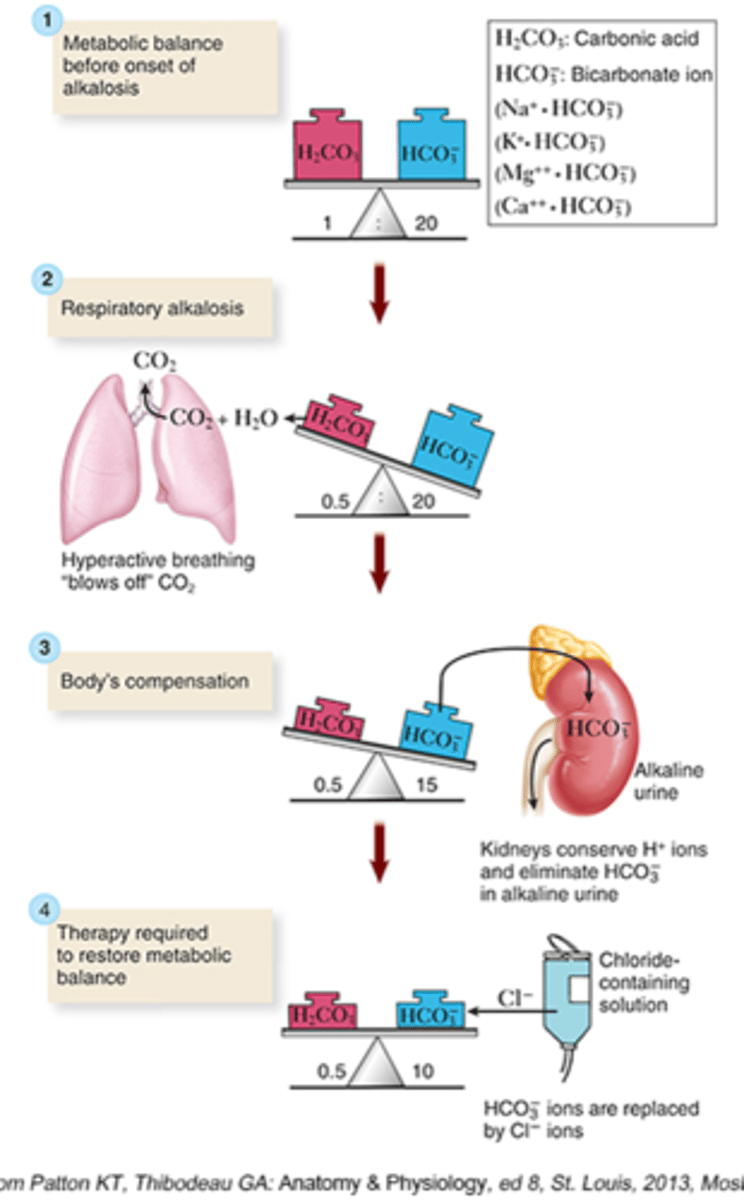
Respiratory alkalosis
Expelling too much CO2 d/t tachypnea
- CO2: Drops
- pH: Rises
How do the kidneys compensate?
- Increase elimination of bicarb
- Hold on to hydrogen ions
- Causes protein to bind with calcium
- Can cause hypocalcemia and hypokalemia
- Headache, tingling, dizziness
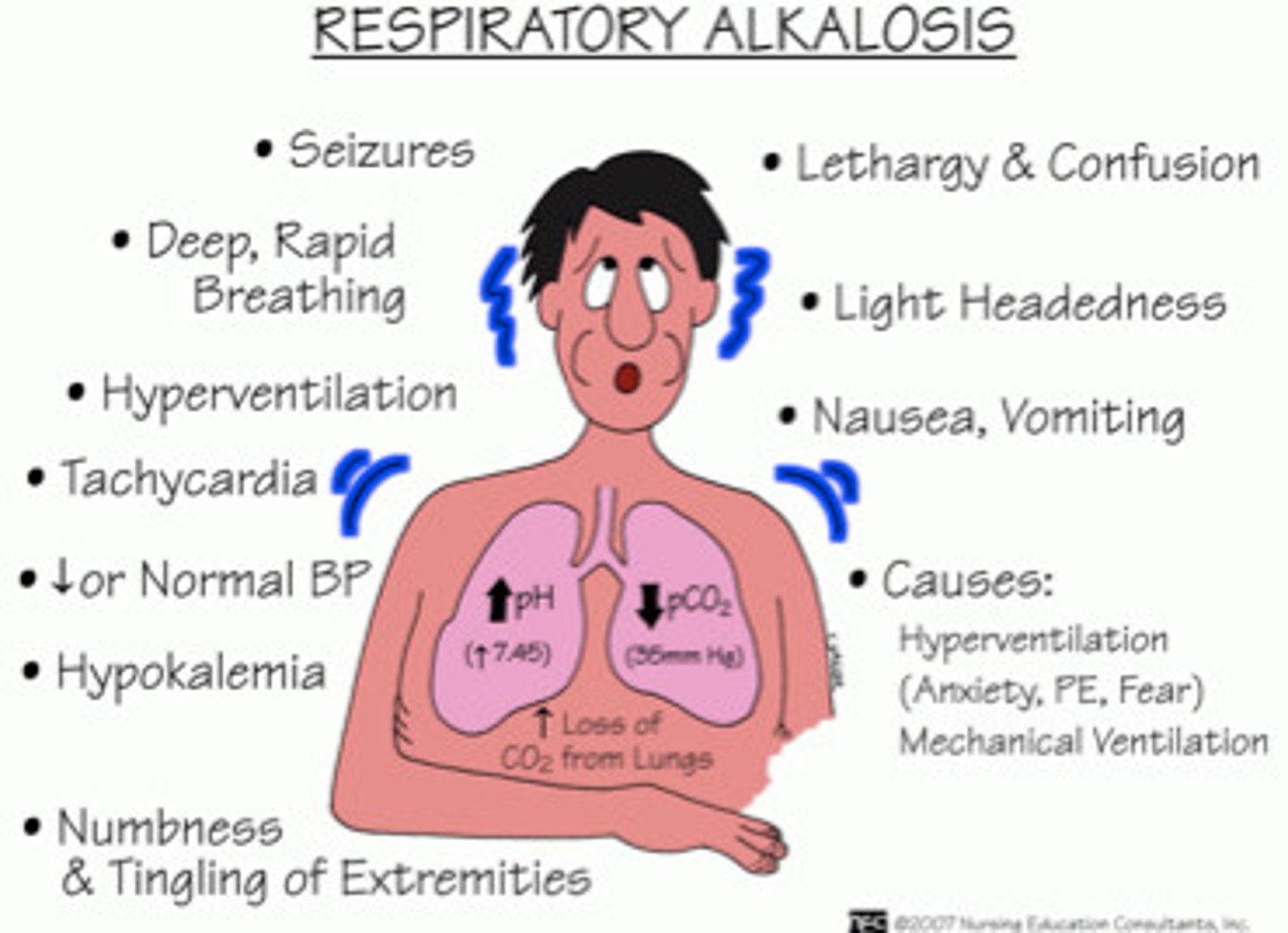
Causes of Respiratory alkalosis: "TACHYPNEA"
- T: Raised temperature
- A: Aspirin toxicity
- C: Controlled mechanical breathing
- H: Hyperventilation
- Y: HYsteria (anxietY)
- P: Pain
- N: Neurological injuries
- E: Emboli & edema (pulmonary)
- A: Asthma d/t hyperventilation
Hyperventilation
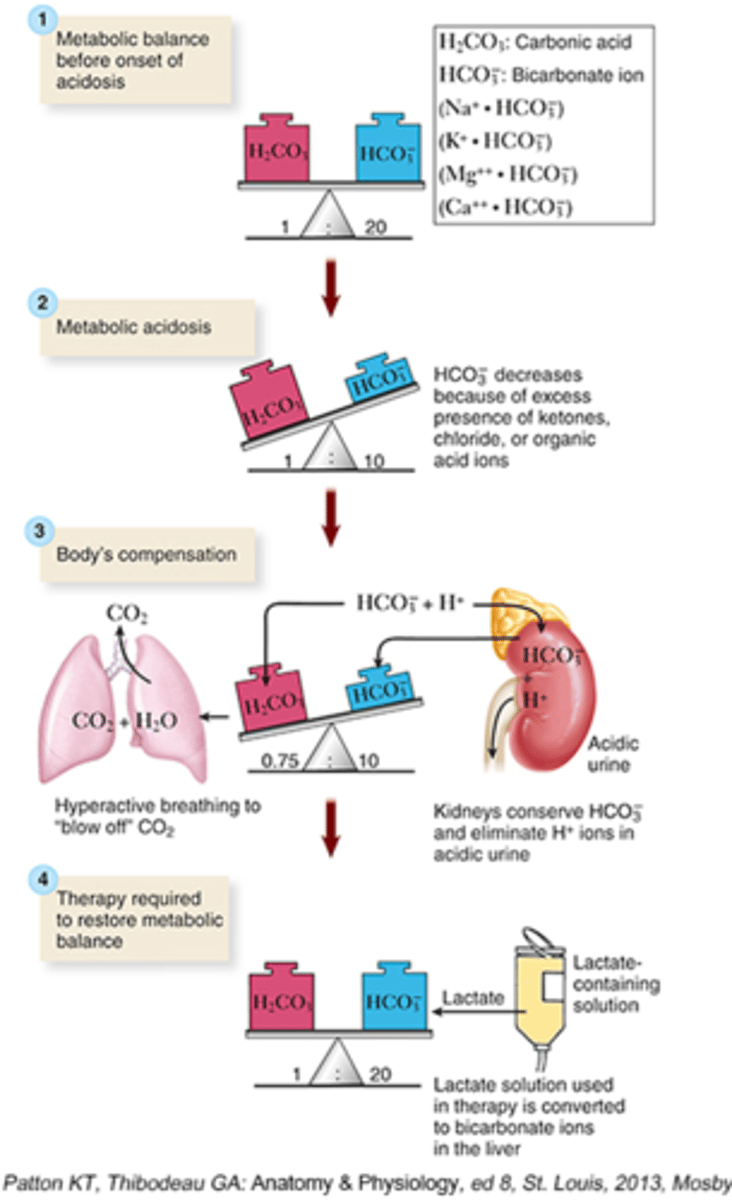
Metabolic acidosis
Increase build up of acid or excessive loss of HCO3-
- HCO3-: Decrease
- pH: Decrease
How do the lungs compensate?
- Blow more CO2 off
- Breathe deeper
Causes: "ACIDODIC"
- A: Aspirin toxicity
- C: Carbs not metabolized (increased production of ketoacids)
- I: Insufficient kidney function
- D: Diarrhea
- Starvation, diarrhea, alcoholic ketoacidosis
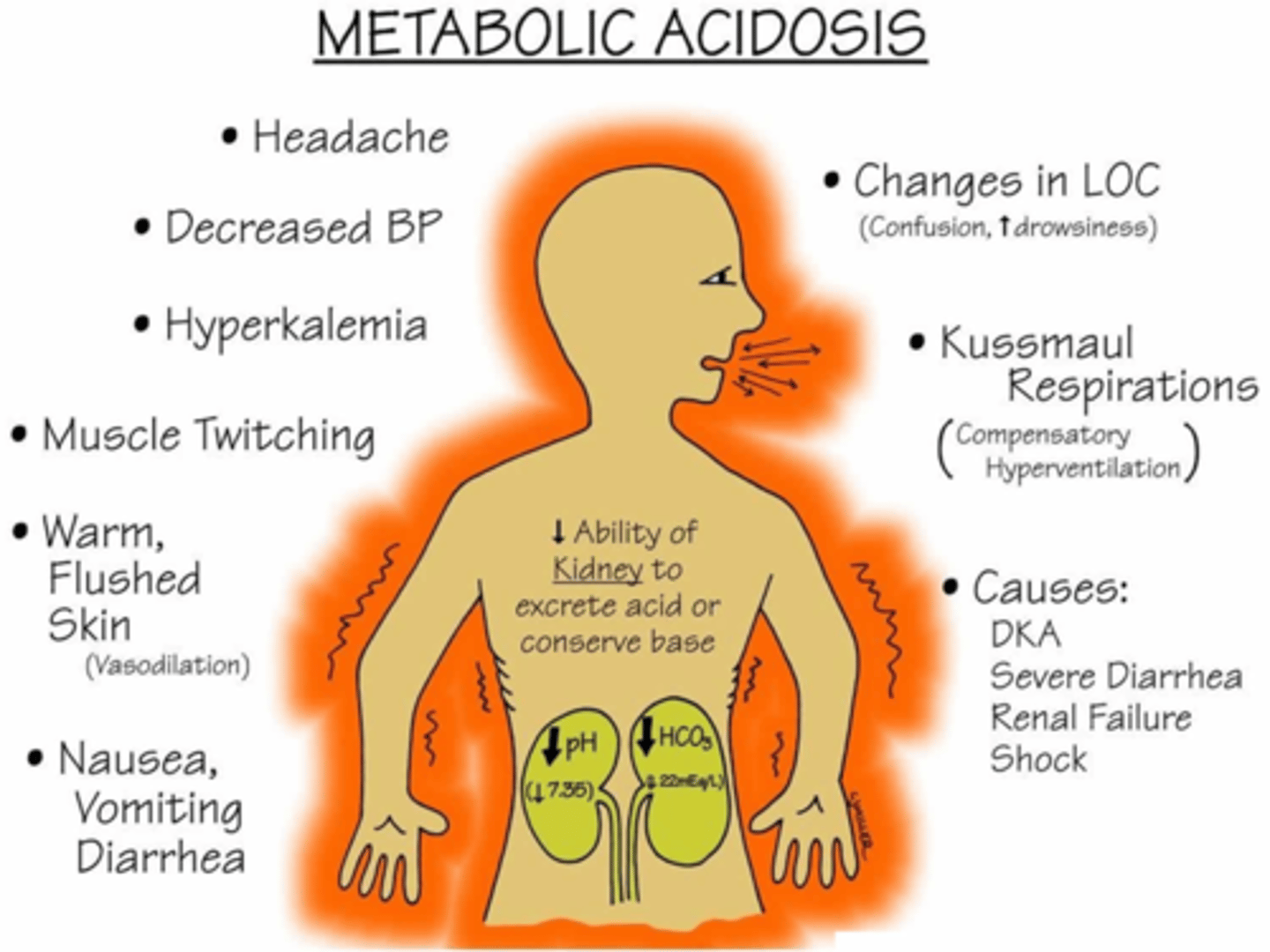
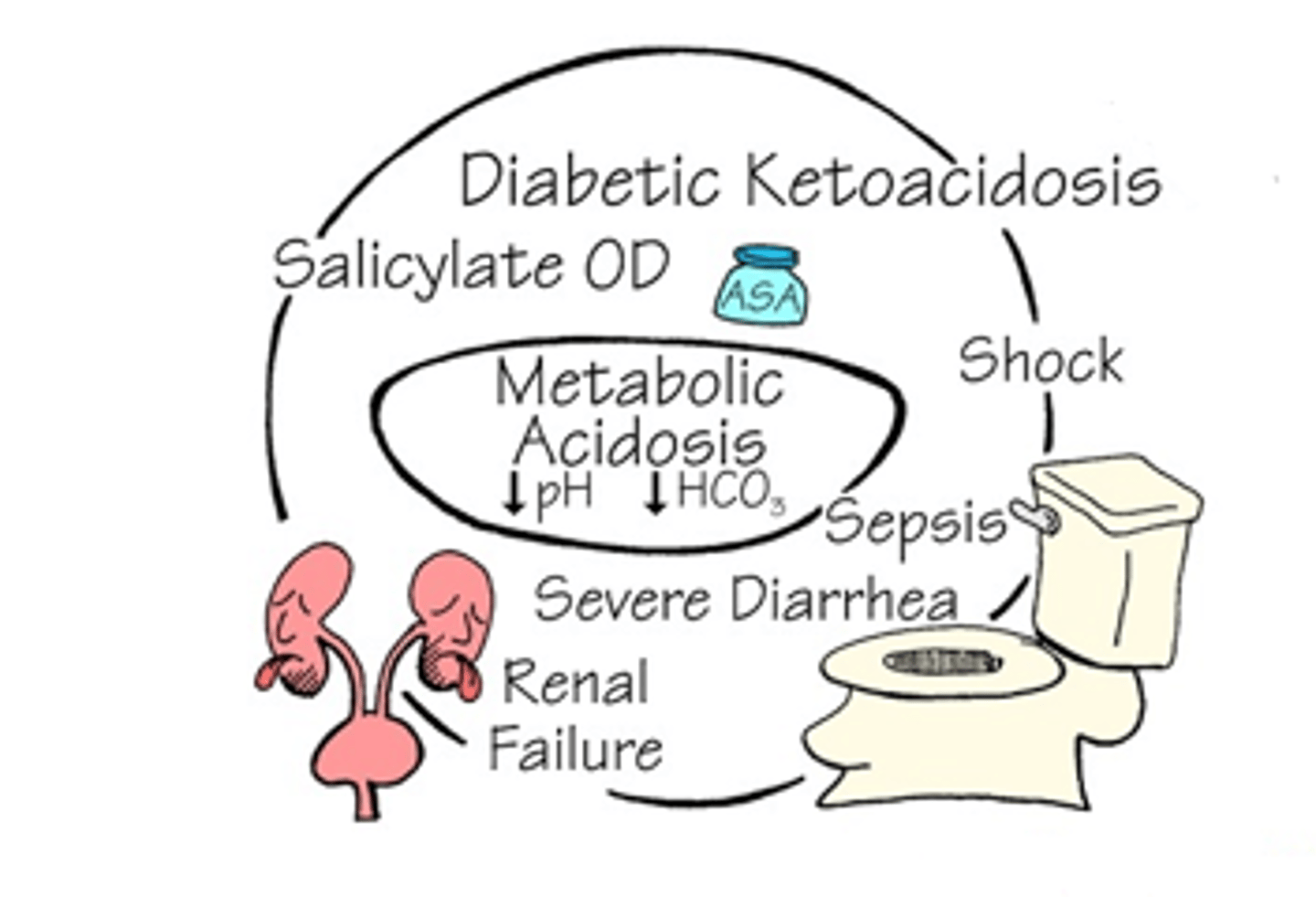
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
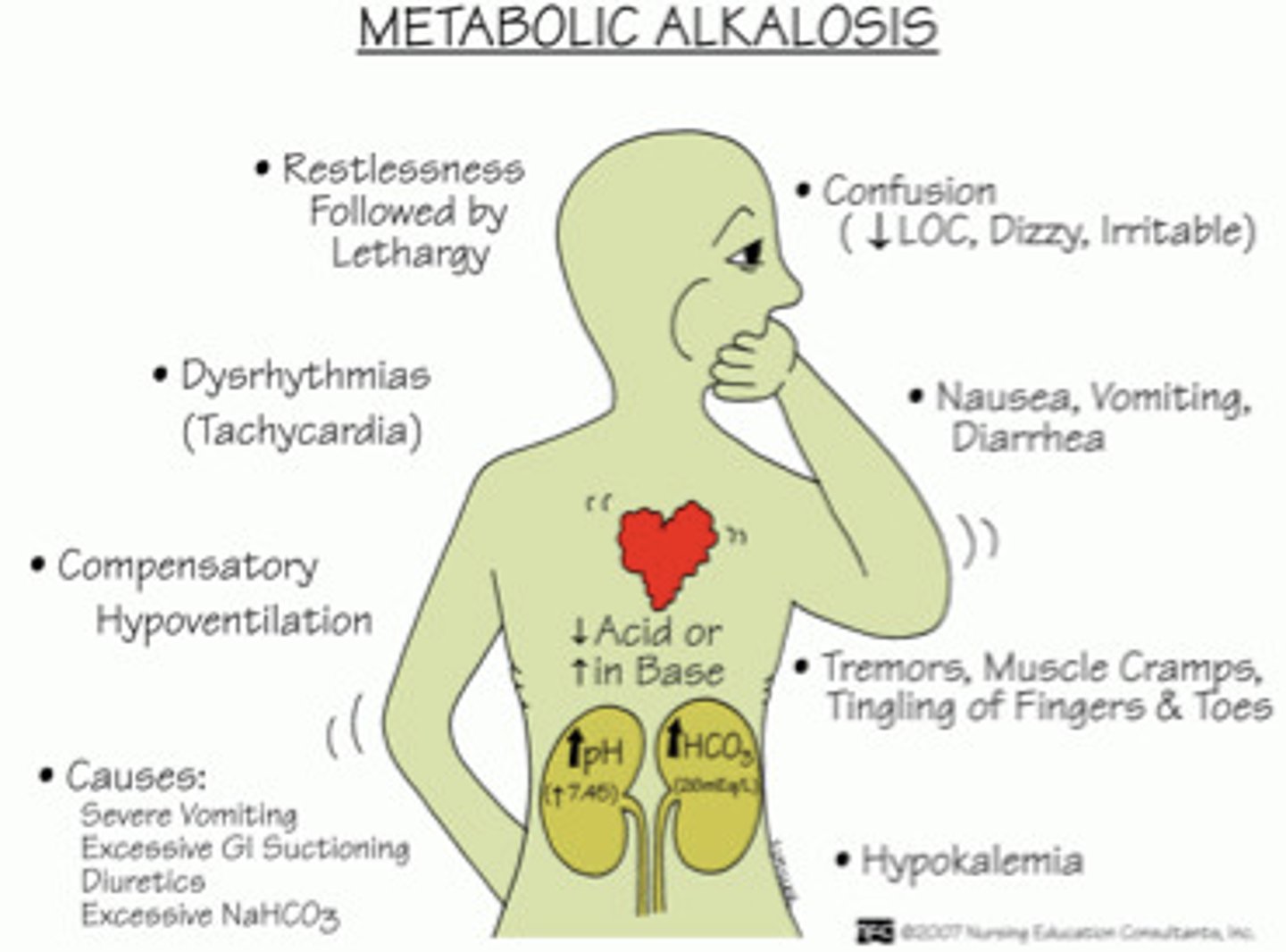
Metabolic alkalosis
- Increase loss of acids (H+)
- Increase amount of HCO3- in the body
Both can also happen
- HCO3-: Increase
- pH: Increase
How do the lungs compensate?
- Holds on to CO2
- Breathing slows
Causes of Metabolic alkalosis
- Diuretic therapy
- Severe vomiting
- Excessive gastric suctioning
- Overuse of antacids
Lines of defense
- 1st: Natural barriers (innate, nonspecific)
- 2nd: Inflammatory response (innate, nonspecific)
- 3rd: Immune response
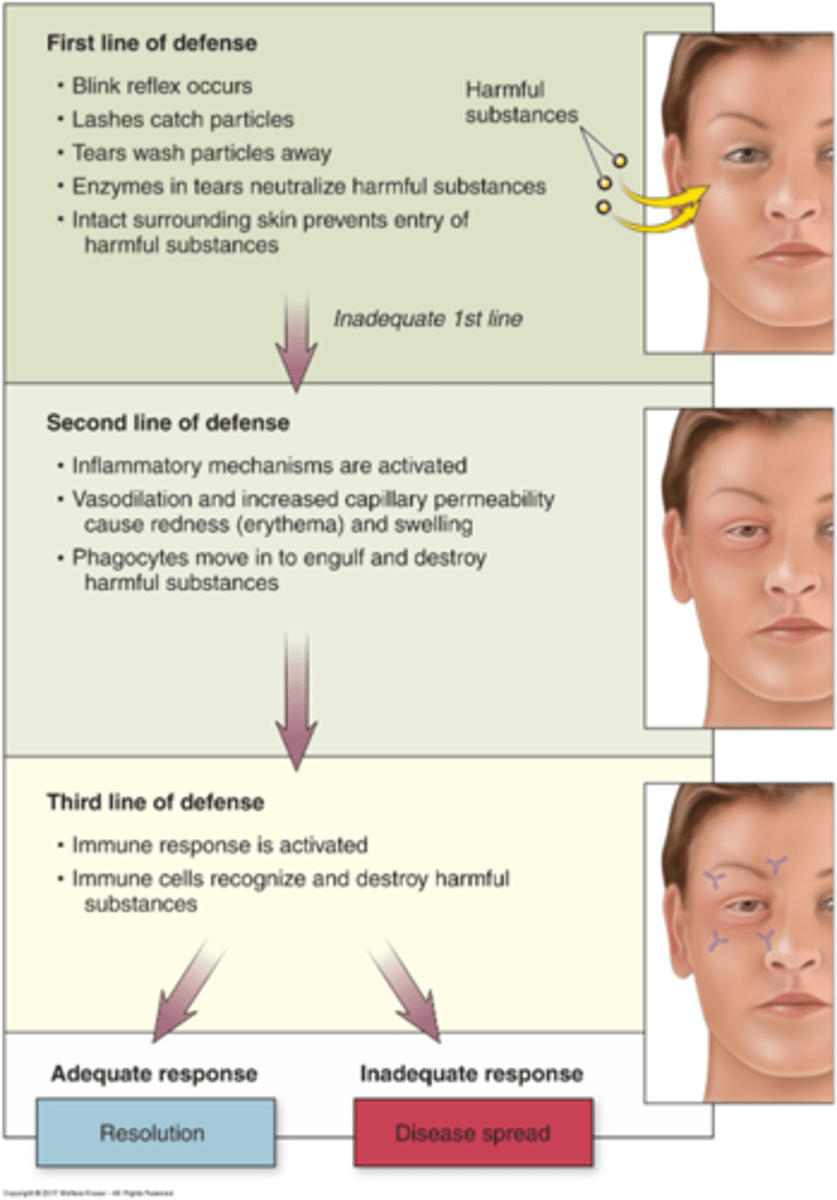
1st line of defense: Natural barriers
Physical
- Skin
- Mucous membranes: Line tracts, mucus, cilia
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Chemical
- Contain enzymes capable of killing bacteria, has acidic environments
- Sweat and oils
- Mucus
- Tears
- Saliva
- Stomach acid
- Urine
- Interferons: Proteins, inhibit replication of viruses
- Normal bacterial flora: Compete with other organisms that could cause harm; gut flora is very important (vitamin K and B synthesis, antibacterial substances)
To strengthen these:
- Prevent disruption
- Use antibiotics to prevent destruction of normal flora
- Lotion
- Washing hands

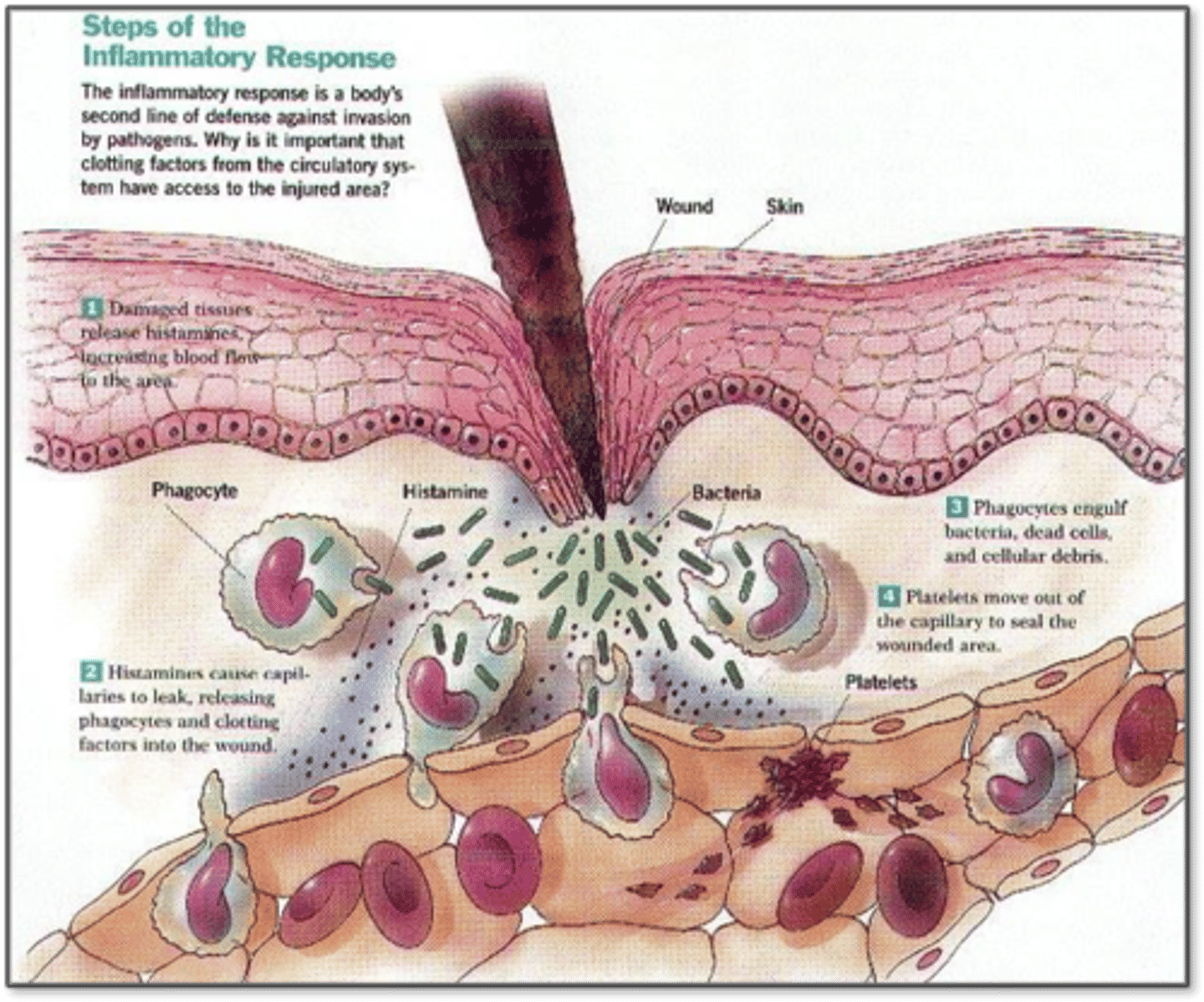
2nd line of defense: Inflammation
- Triggered by tissue injury
- Same response every time
Inflammation: Goals
- Increase blood flow to site (vascular response); more O2, nutrients, important WBCs
- Increase healing cells at the sight (cellular response)
- Prepare for tissue repair (cellular and chemical)
Inflammation: Vascular response
Facilitated by chemical mediators causing
- Vasodilation (at or near sight of injury), dilute toxins
- Increase vascular permeability (stuff will leak into interstitial space), edema
Objective: Get more blood flowing to injured area
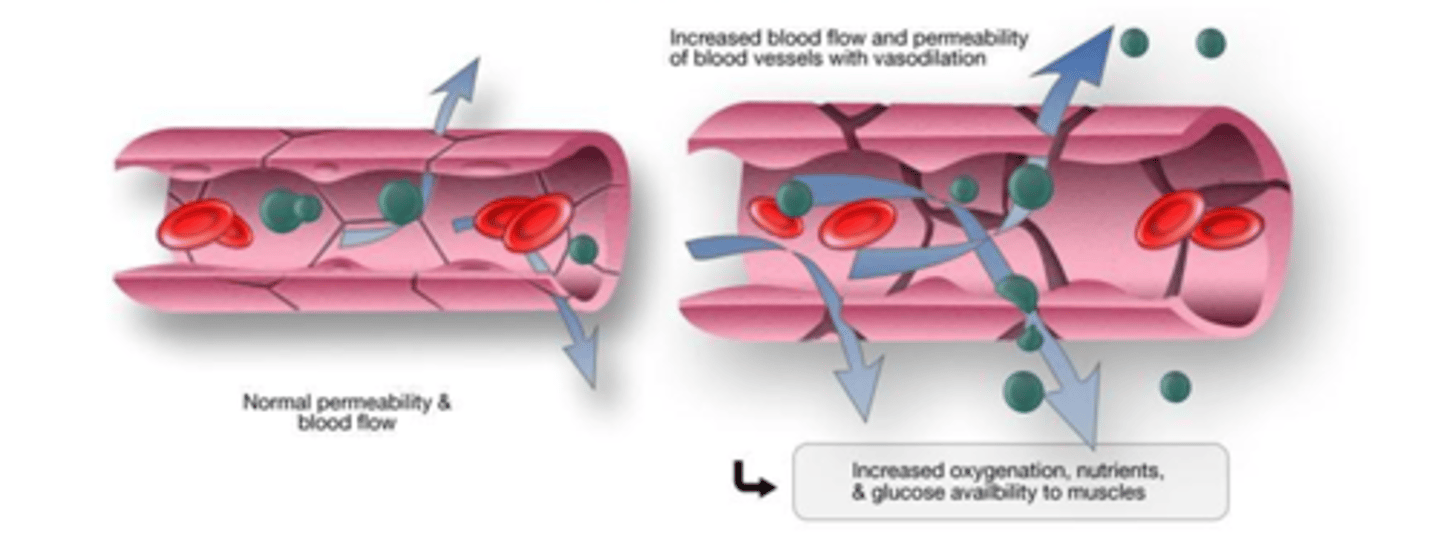
Inflammation: Cellular response
- Margination: Leukocytes gather on wall, accumulate
- Adhesion: Adhere strongly to intracellular adhesion molecules, attaching on endothelium
- Transmigration: Adhesion will cause endothelial cells to separate and allow leukocytes to extend
- Chemotaxis: Leukocytes extend according to these factors
- Leukocyte activation: So leukocytes can get in
- Leukocyte phagocytosis: Cellular debris removed, platelets help clot
- Cytokines: Call in the troops, causes endothelial cells lining vessels to express cell adhesion molecules
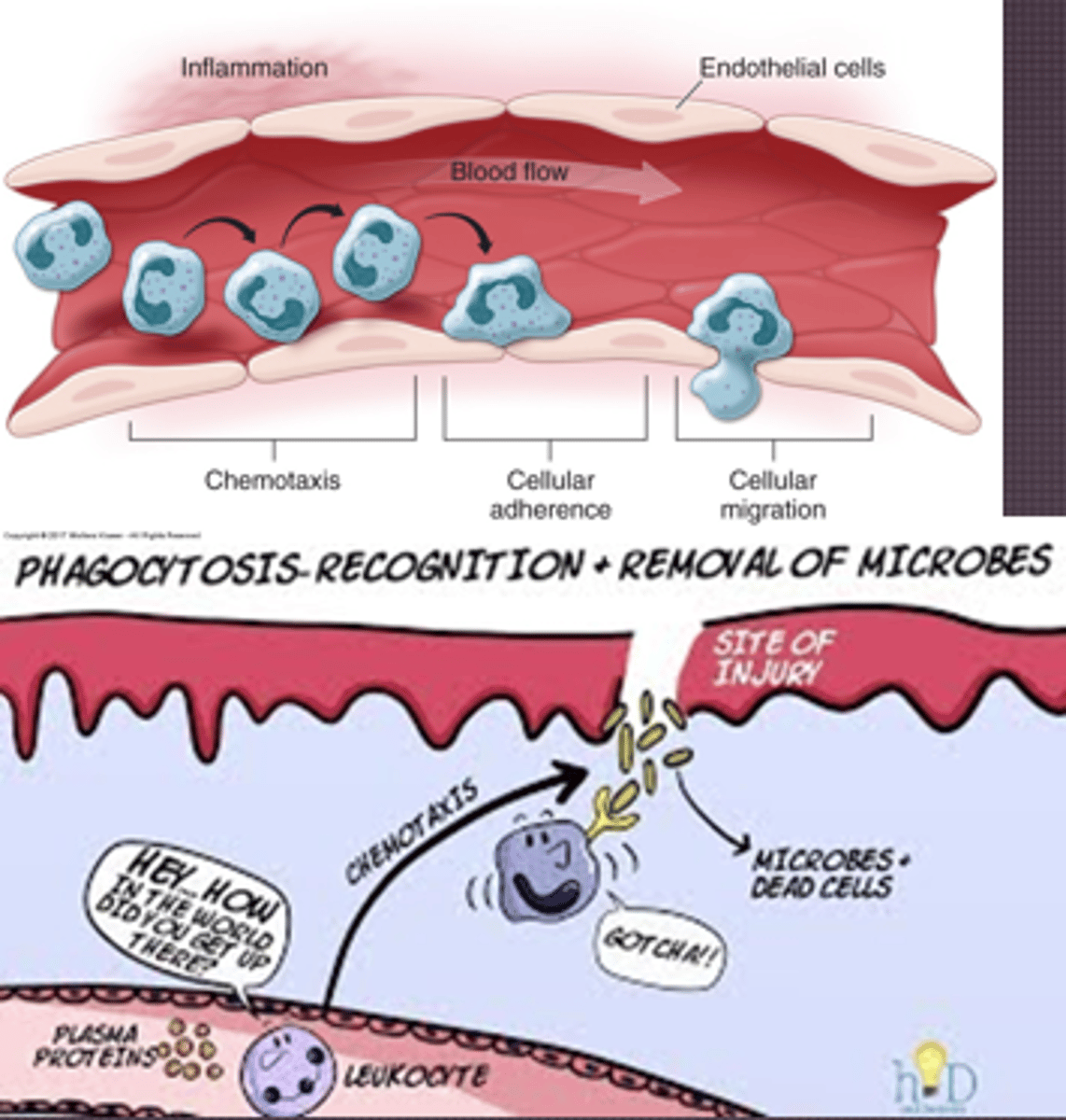
Inflammation: Factors
- Duration
- Type of foreign agent
- Degree of injury
Tissue injury
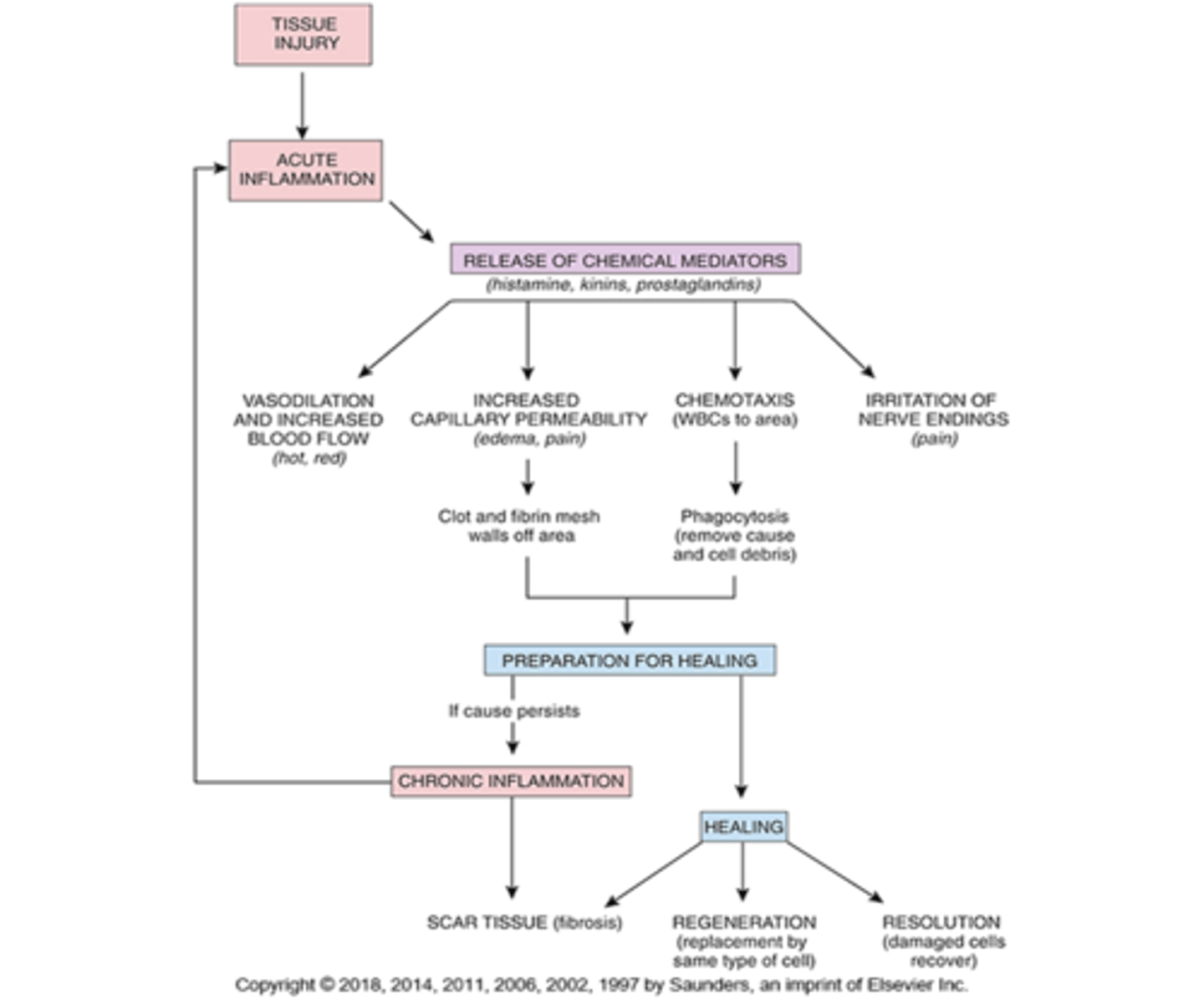
Stages of inflammatory response
Inflammation: Local manifestations
- Redness
- Heat
- Swelling (edema)
- Pain
- Loss of function (acute or chronic)
- Obstruction, decreased blood supply, ischemia

Exudate
- Serous: Blister; fluid leaked out, watery, proteins and WBCs
- Hemorrhagic: Damaged capillary or vessel, blood
- Fibrinous: Thick and sticky; a lot of cells, seen in lungs with pneumonia, wounds/burns
- Membranous: On mucous membranes, thicker drainage
- Purulent: Bacterial, thick, yellow/green, leukocytes, cellular debris
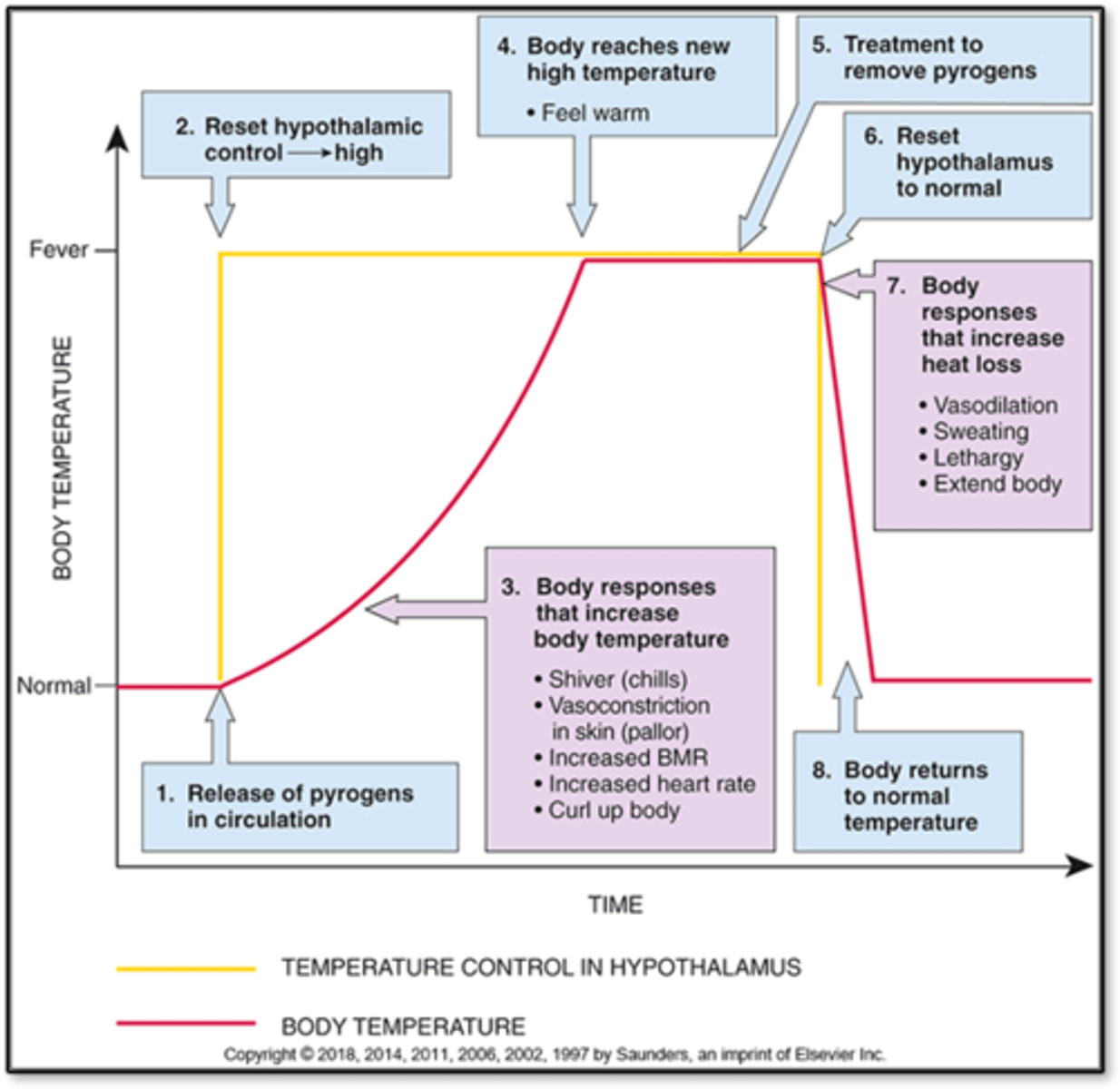
Inflammation: Systemic effects
- Fever
- Sleepiness
- Lethargy
- Malaise: Feel bad
- Anorexia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Increased release of serotonin
- Melatonin increase
- Lowers pain threshold
- Medications: Cold: Antihistamines, aspirin (inhibit prostaglandin production, fever), tylenol
Chronic inflammation
- Persistent, lasts many weeks to years
- Monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes are more involved
- Formation of granulomas and scarring: Wall it off
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation
Wound healing
- First Intention: Sealing a wound by sutures, staples, etc.
- Secondary intention: Cells fill in the gap, more at risk for developing infections, letting a wound heal naturally
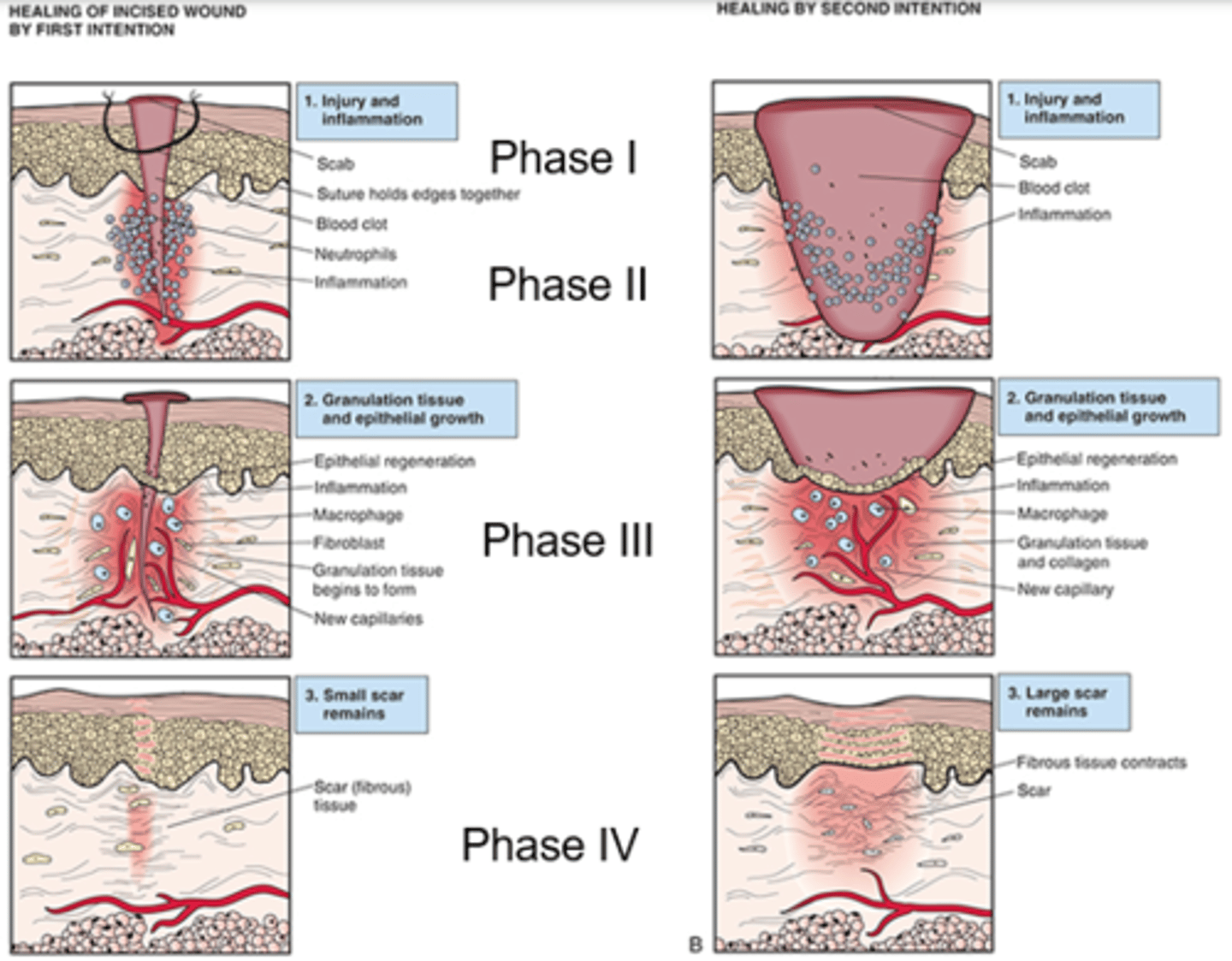
Factors affecting wound healing
- Malnutrition
- Blood flow and oxygen delivery (increases infection risk)
- Impaired inflammatory and immune response
- Infection, wound separation, and foreign bodies
Dysfunctional wound healing
- Dysfunctional collagen synthesis: Can develop keloids, buildup over scar area
- Wound disruption: Dehiscence
- Contracture: Wounds draw up tendons when they heal
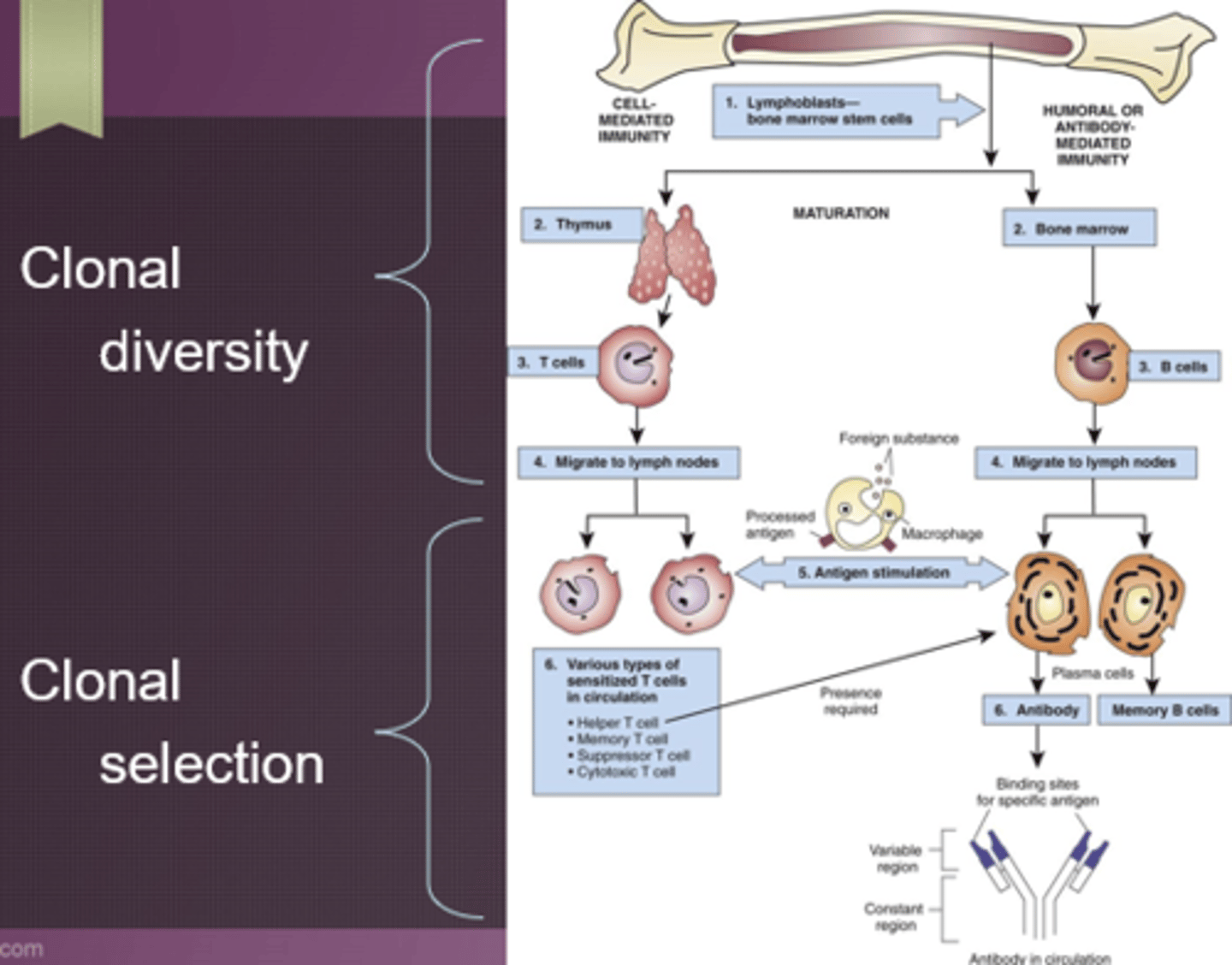
Clonal diversity and selection
- Humoral/antibody mediated: B cells (mature in bone marrow); plasma B cells (antibodies) and memory B cells
- Cell-mediated: T cells (mature in thymus); cytotoxic T cells, regulatory T cells (don't allow adaptive immune system to become overabundant), memory T cells; active in blood tissue
- Still naive at this point- Not exposed to anything, nonspecific
- Waiting for their match, make soldiers specific to a certain antigen
- Response will be quicker with memory cells
- Bacteria, infection, viruses, etc.
Lymphocytes
"The helper"
- Most important cell in adaptive immunity
- Identify foreign antigens, signal activation of B cells and T cells
- If they aren't working properly there will be a decreased immune response (Ex. HIV, AIDS), could be virally infected, these cells may become hijacked
- Signal activation of: B-cells, Killer T-cells
"The Killer"
- Seek and destroy: Viral-infected cells, Some cancer cells
- Release chemicals and enzymes that destroys the cell membrane and causes an inflammatory response that attracts macrophages and more lymphocytes to the site
- Replicate to make memory cells

Regulatory T-cell
- Regulate or suppress other cells in the immune system, so we don't become damaged
- Autoimmune can affect these

B-cells: Activated to form
- Plasma B cells: Secrete proteins (antibodies) specific to certain antigens, release a lot, antibodies neutralize and pull in phagocytes, activate complement system, supplements innate system
- Memory B cells: Replicate and wait for exposure to that antigen, response will be quicker
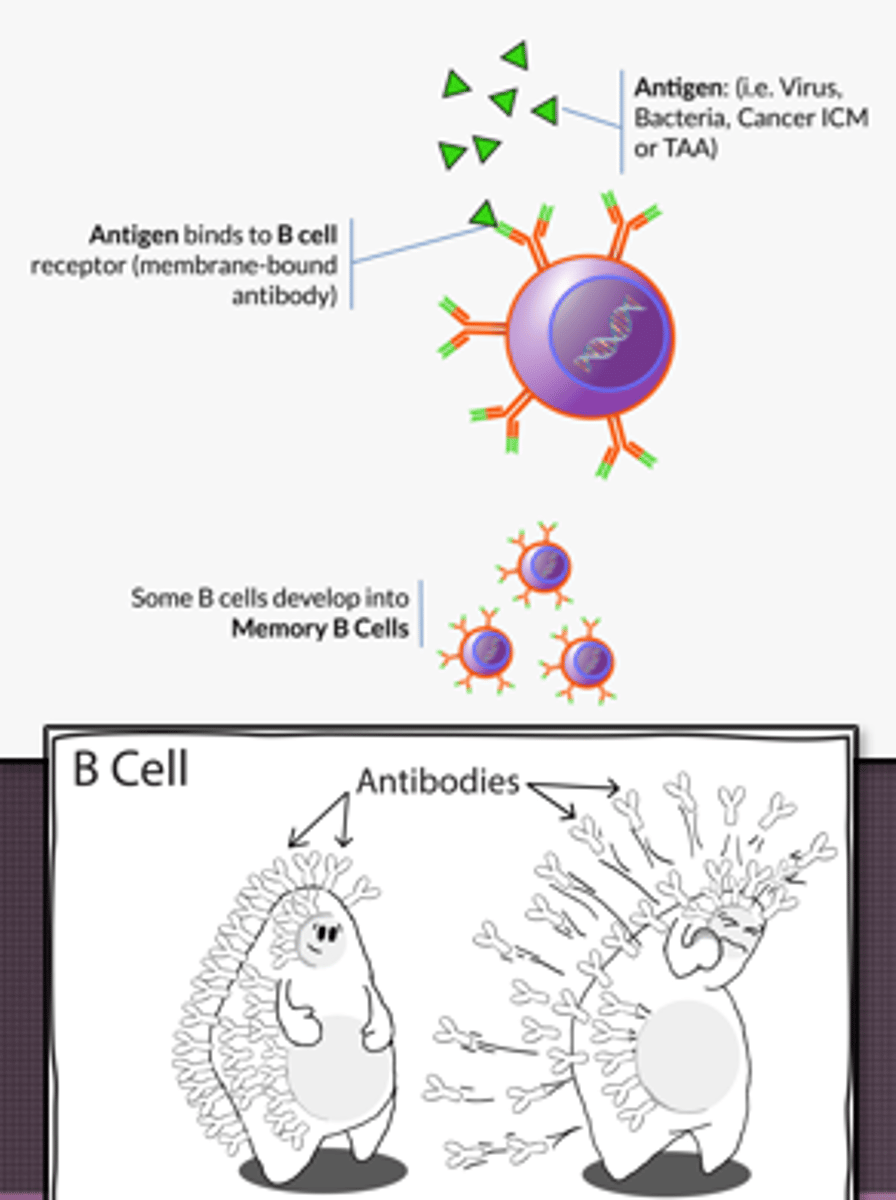
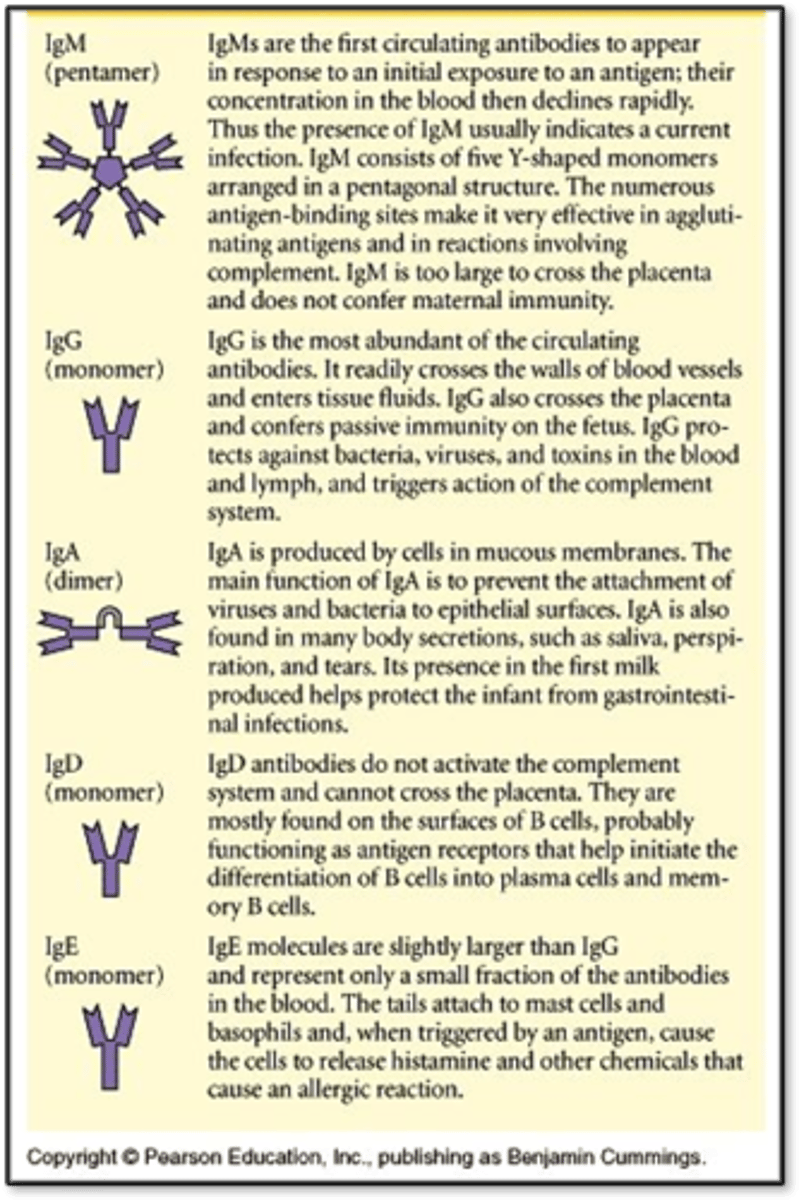
Immunoglobulins (antibodies) and their functions
- IgG: Most abundant, long-term immunity, crosses placenta and passes to fetus, triggers complement; protects against bacteria, viruses, and toxins
- IgA: Second most abundant, found in mucosal areas, prevent attachment of bacteria and viruses to epithelial surfaces, produced in colostrum (first milk) and protects infant from GI infections
- IgM: Largest, active infection, first antibody produced during infection, agglutinate antigens
- IgE: Allergic reactions, parasite defense, cause histamine and other chemicals to release
- IgD: Helps B cells activate and differentiate into plasma and memory B cells
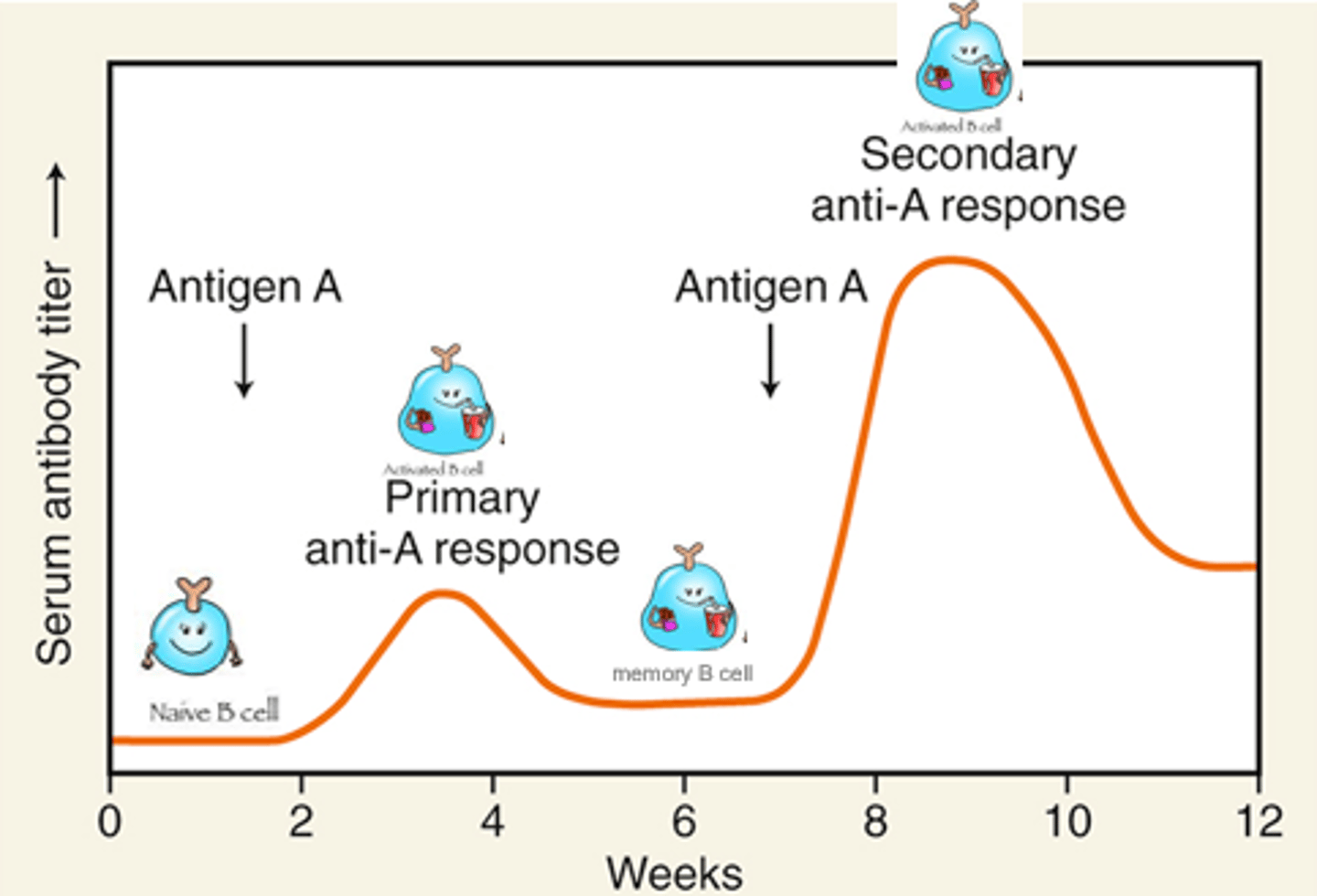
Acquiring immunity: Primary and secondary response
- Helper T cell launches immune response
- Hypersensitivity could be a bad thing on second exposure
- Takes about 2-3 weeks for our adaptive immune system to identify an antigen to launch attack
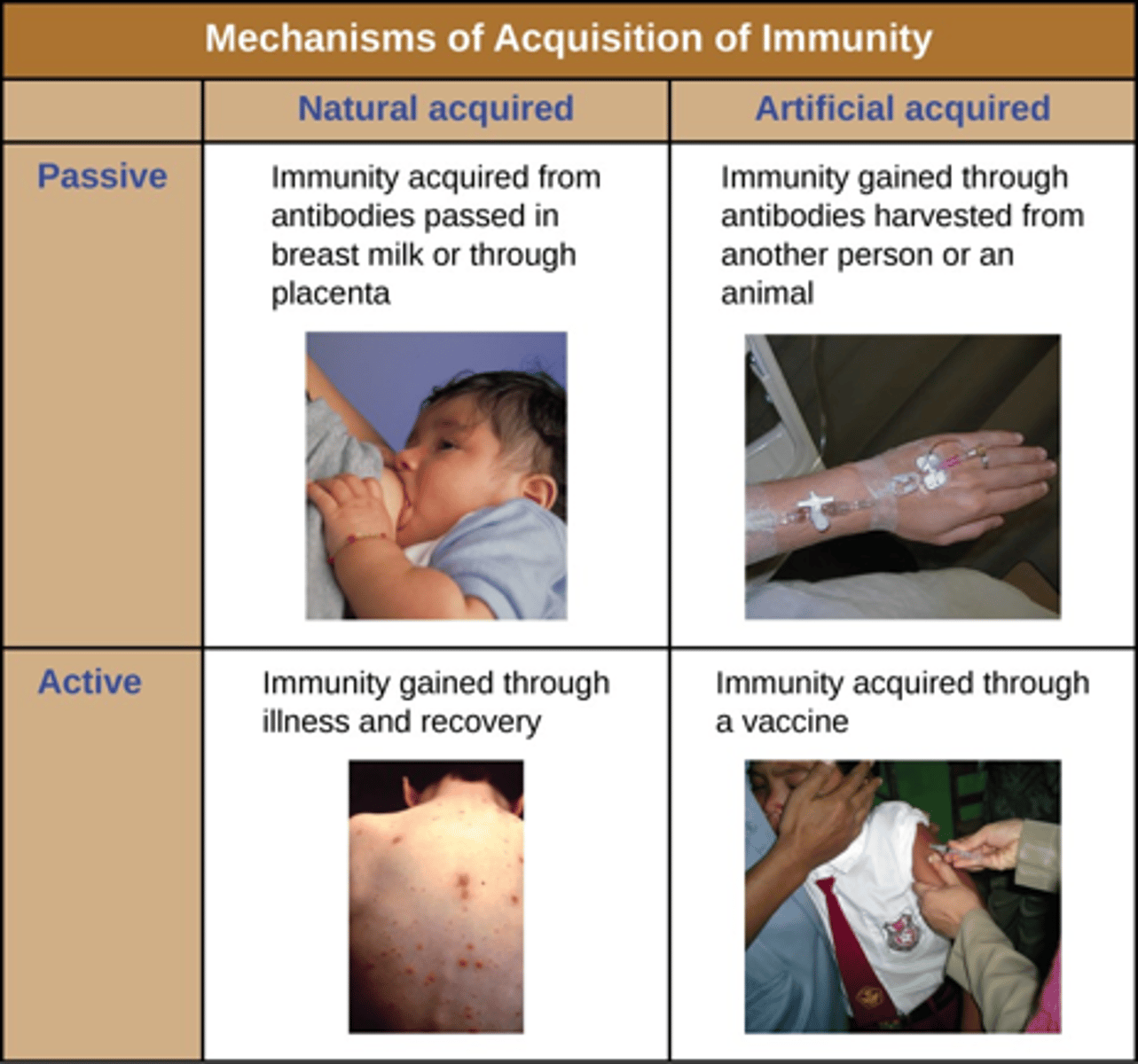
Acquiring immunity: Passive
- Immunity transfer from host to recipient
- Effective immediately but only temporary
- No memory cells
- Natural: IgG, IgA
- Artificial: Rabies vaccine, snake venom; giving someone another person's antibodies (someone who has already been exposed and has recovered)
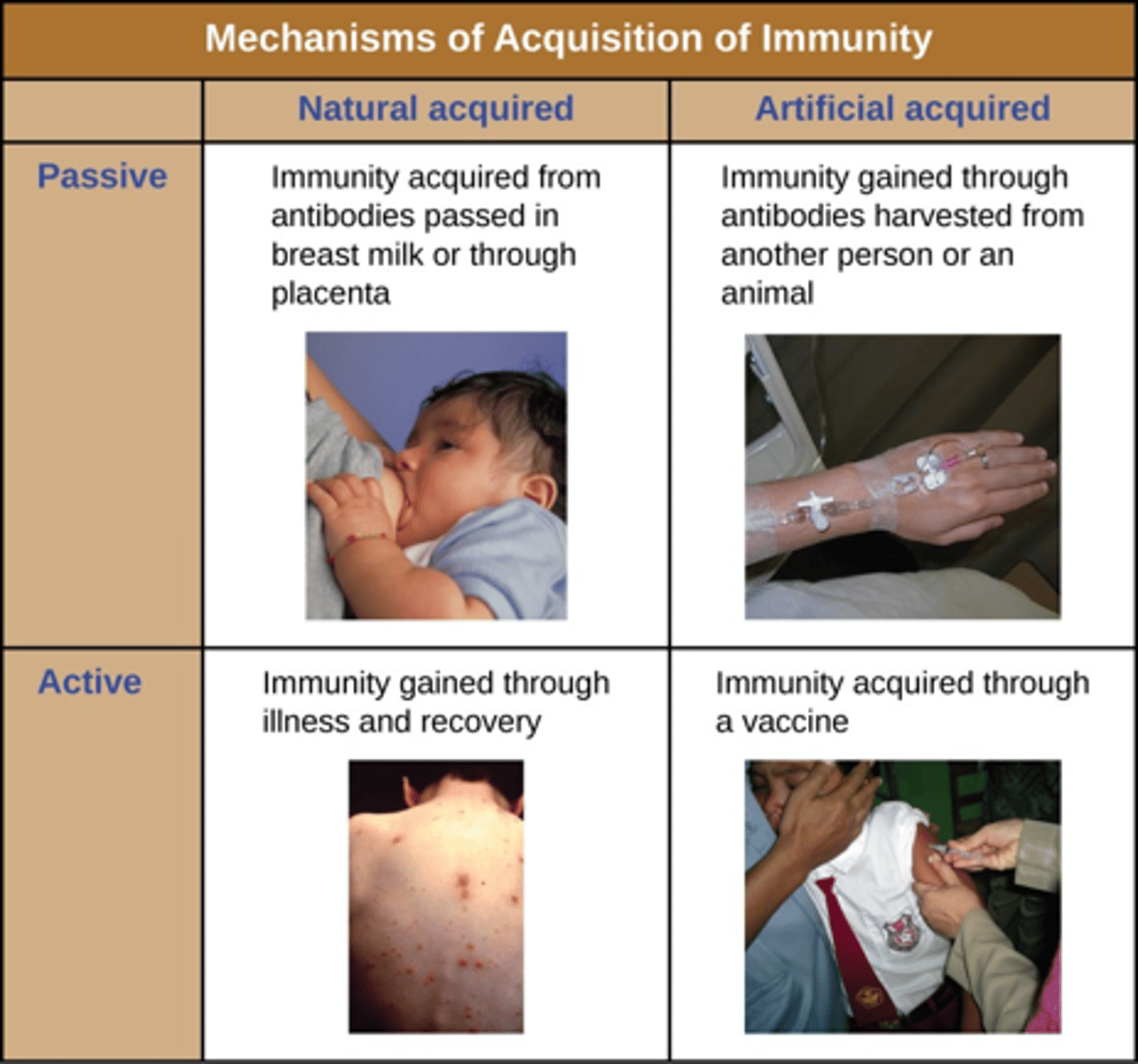
Acquiring immunity: Active
- Development of antibodies
- Effective after several weeks but lasts years
- Natural: Direct exposure to antigen
- Artificial: Vaccinations
Hypersensitivity reactions
- Inflated or inappropriate response to an antigen resulting in inflammation & destruction of healthy tissue
- Appear after reexposure
- May be immediate (min or hr) (antibodies) or delayed (after several hours) (T cells)
- First response probably won't be that bad, but the second response will be more aggressive and rapid
Hypersensitivity reaction types
- Type 1: Immediate hypersensitivity
- Type 2: Cytotoxic hypersensitivity
- Type 3: Immune complex hypersensitivity
- Type 4: Cell-mediated or delayed hypersensitivity
Type 1
- Immediate hypersensitivity
- Immune system reacted too well, secondary response is higher
- IgE bind to mast cells and basophils
- Cause release of histamine and other chemical mediators
- Effects: Immediate inflammation and itching (pruritus)
- Seasonal allergies
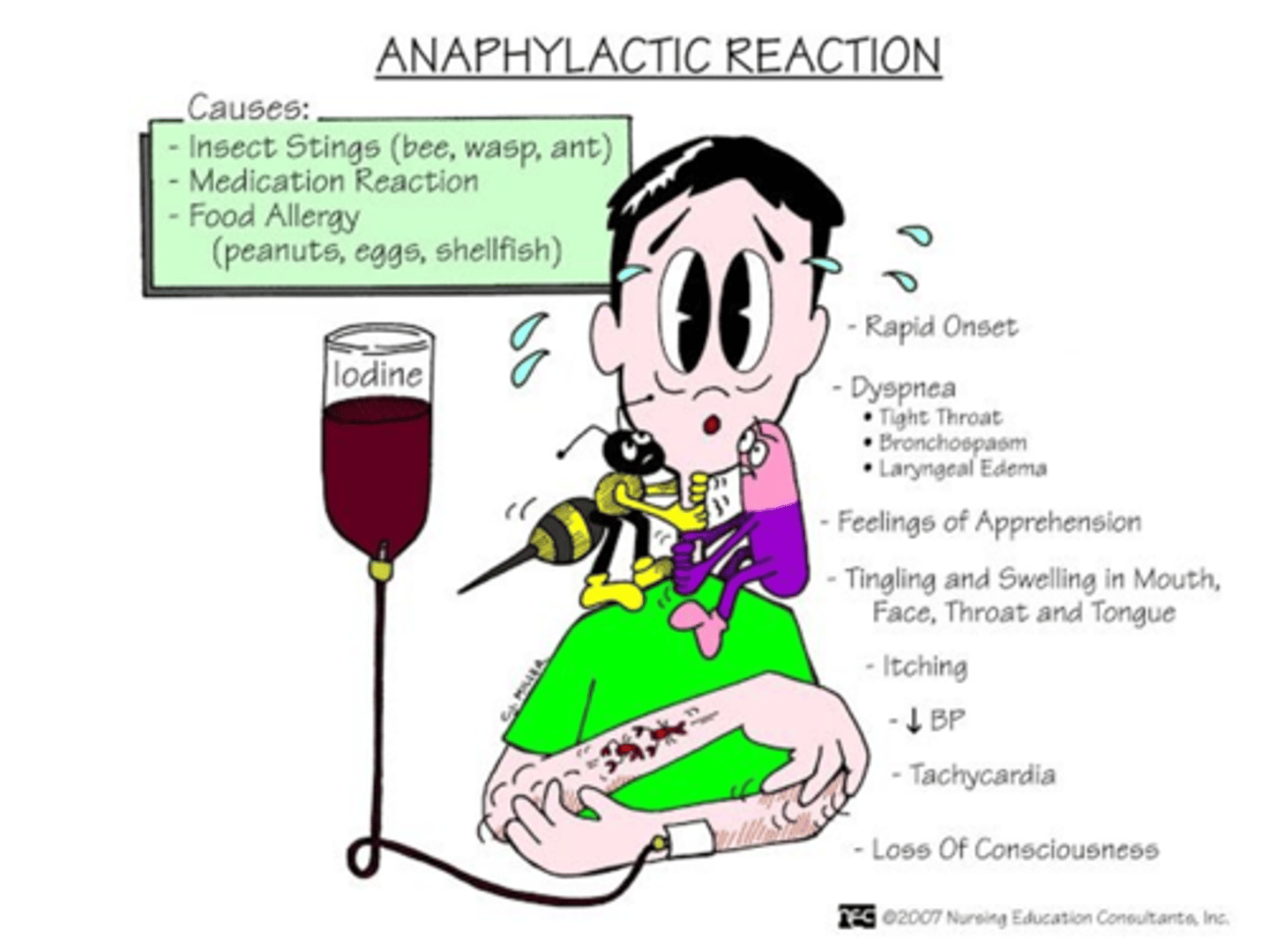
Anaphylactic reaction (Type 1)
Treatment
- Epipen (epinephrine): Bronchodilation, increase in BP
- Benadryl
- Glucocorticosteroids
Second exposure is much worse
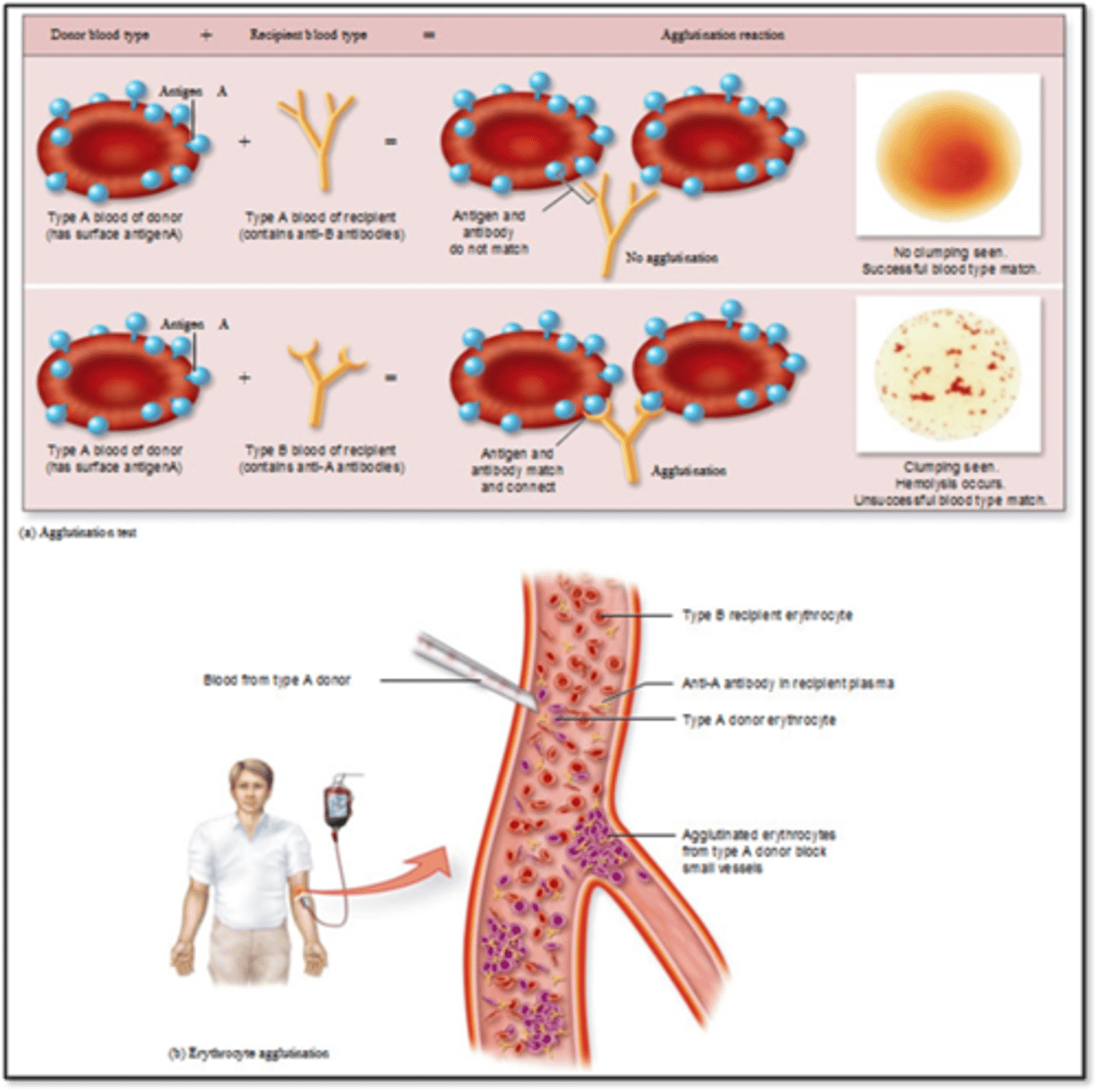
Type 2: Cytotoxic hypersensitivity
- Too robust response
- IgG or IgM binds with an antigen on person's own cell
- Tissue specific (usually blood cells)
- Effects: Phagocytosis, cell lysis
- Incompatible blood transfusion
- Erythroblastosis fetalis: RH negative mom with RH positive child
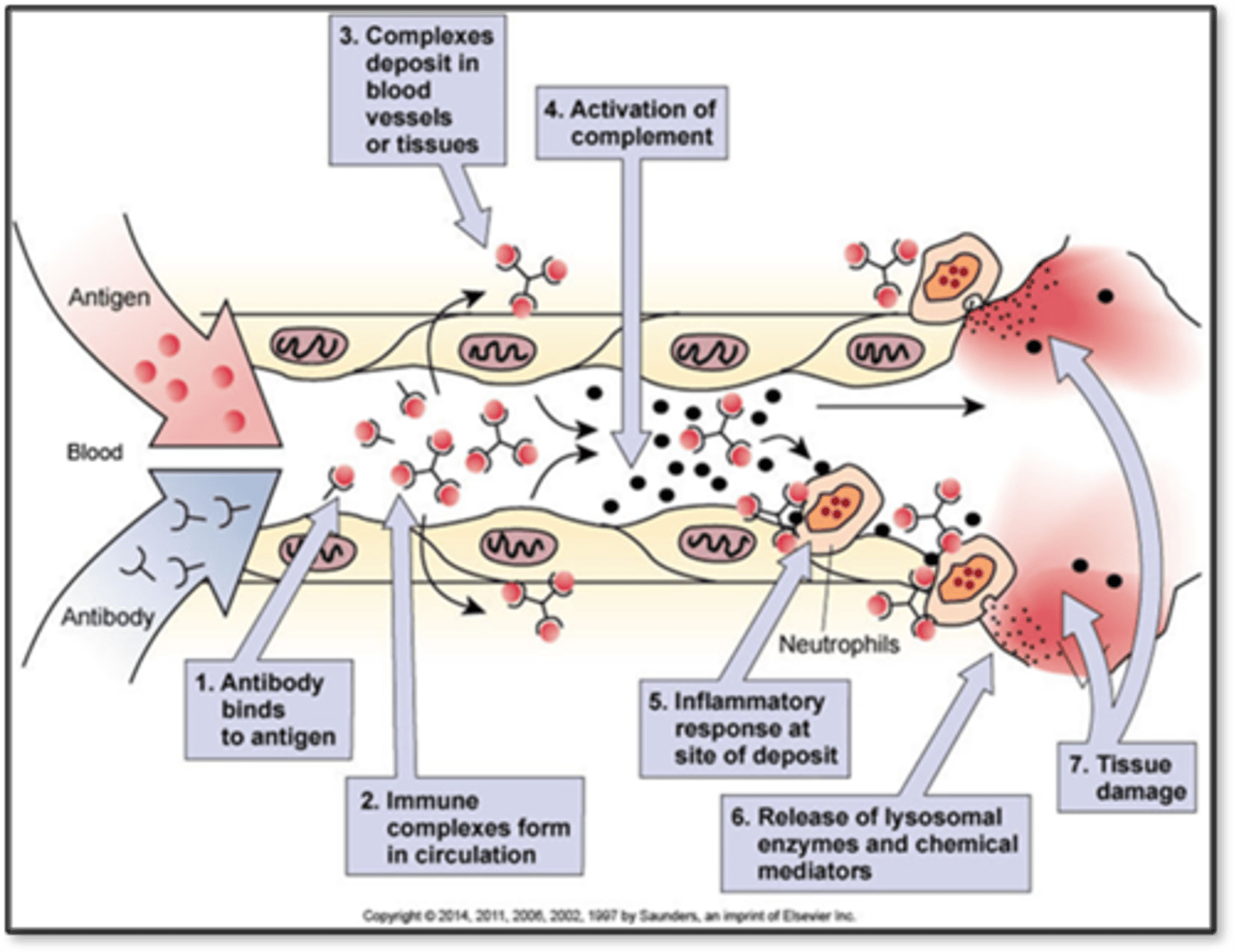
Type 3
- Immune complex hypersensitivity
- Antigen-antibody complexes deposit in tissue
- Complement system activated, inflammation occurs
- Immune system becomes confused
- Maybe failure of regulatory T cells
- Can attack heart muscle, can deposit into kidneys, renal failure after strep
- Heart, kidneys, joints, blood vessels
- Effects: Inflammation, increased vascular permeability
Type 4
- Cell-mediated or delayed hypersensitivity
- Delayed response by sensitized T-cells
- Usually 48-72 hours after exposure
- Ex. TB skin test is checked a few days after it is given
- Effects: Delayed inflammation and tissue damage
- Poison ivy
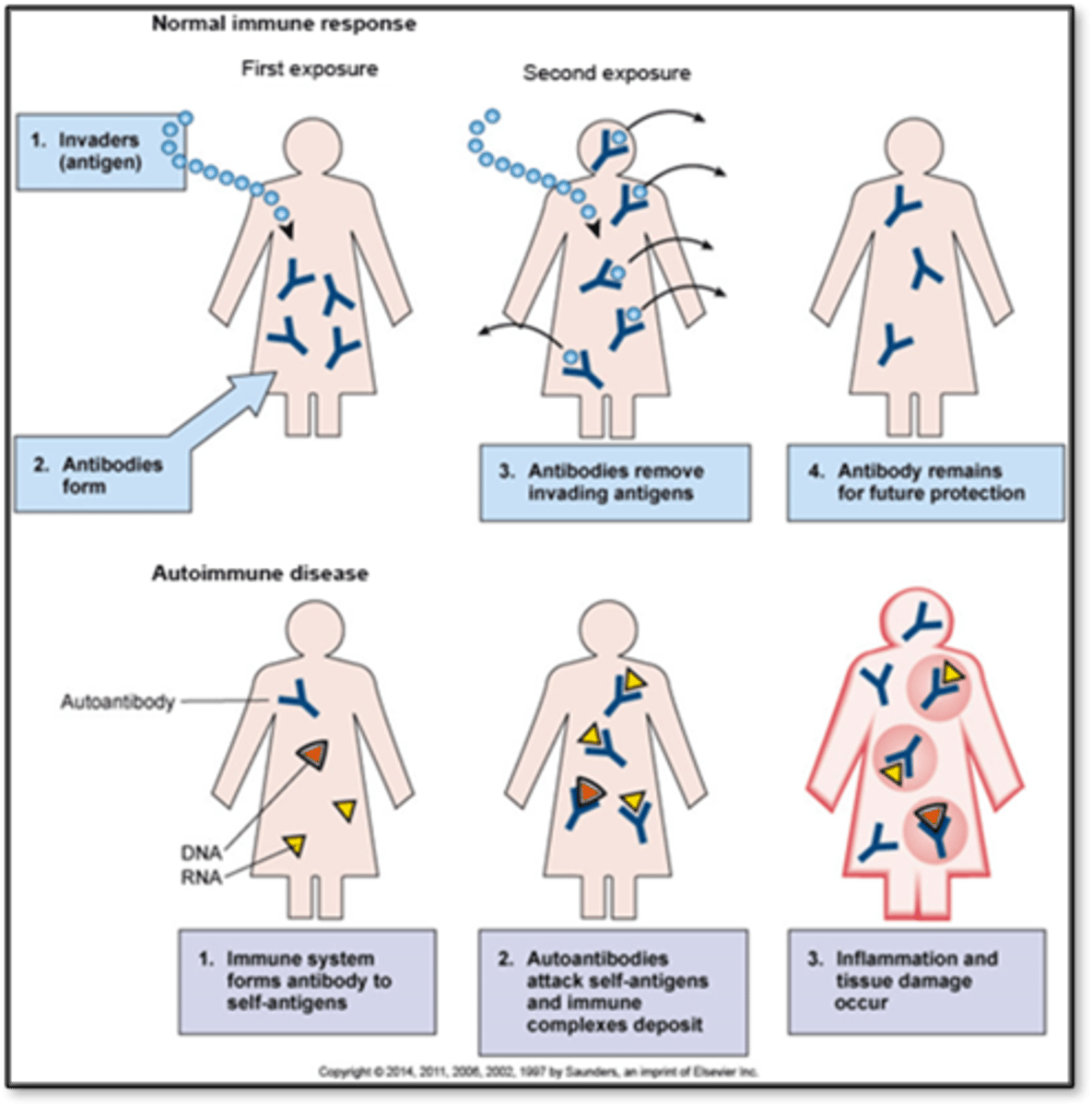
Autoimmune disorders
- Overreaction and confusion of immune system
- Development of autoantibodies, don't recognize our own tissue
- Effects: Inflammation, tissue damage
- Immune system can't distinguish between self and non self
- More common in women
- Genetic predisposition, something in the environment could activate it
- Type 1 diabetes: Born with tendency then something triggers it along the way; ex. Puberty, viral triggers
General adaptation syndrome
- Physiological process the body undergoes when there's prolonged stress, has 3 stages
- General because the effect was a general systemic reaction
- Adaptive because the response was in reaction to a stressor
- Syndrome because the physical manifestations were coordinated and dependent on each other
Types of stress
- Eustress
- Distress