Anatomy and Physiology II - Section 4, Lesson 4
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Term: Excretion
Definition: The process of removing waste products from metabolism, whereas secretion involves moving materials with a purpose within the body.
Term: Micturition
Definition: The action of urinating or voiding, involving involuntary and voluntary actions of the internal and external urethral sphincters.
Term: Voluntary Control of Urination
Definition: Consciously preventing the relaxation of the external urethral sphincter to maintain urinary continence.
Term: Bladder Volume and Urge to Void
Definition: An urge to void occurs when bladder volume reaches about 150 mL but can be easily overridden. Incontinence may occur as the volume approaches 300-400 mL.
Term: Normal Micturition Reflex
Definition: Stretch receptors in the bladder wall trigger nerve impulses that cause contraction of the detrusor muscle and relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter.
Flashcard 5:
Term: Spinal Reflex and Micturition
Definition: The spinal reflex generates micturition and is active in infants, becoming modifiable with maturity (potty training).
Term: Micturition and Spinal Cord Injury
Definition: The micturition reflex can remain even after spinal cord injury, but external sphincter relaxation may be impaired, requiring catheterization.
Term: Nerves Involved in Micturition
Definition: The hypogastric, pelvic, and pudendal nerves control urination, with voluntary micturition requiring an intact spinal cord and functional pudendal nerve.
Term: Cholinergic Neurons and Urinary Continence
Definition: Cholinergic neurons maintain contraction of the external sphincter during bladder filling, preventing urination.
Term: Sympathetic Nervous System in Micturition
Definition: Sympathetic activity via hypogastric nerves inhibits detrusor muscle contraction, promoting bladder filling.
Term: Parasympathetic Nervous System in Micturition
Definition: Parasympathetic activity stimulates detrusor muscle contraction and internal sphincter relaxation for bladder emptying.
Term: Micturition Process Step 1
Description: As the bladder fills, distension activates stretch receptors, triggering nerve impulses.
Term: Micturition Process Step 2
Description: Stretch receptors send signals to the brain, creating the urge to urinate.
Term: Micturition Process Step 3
Description: Sensory nerve impulses are relayed to the brainstem and higher brain centers, allowing conscious control.
Term: Micturition Process Step 4
Description: If bladder volume is low, the pontine storage center is activated, suppressing parasympathetic activity and promoting continued filling. If volume is high, the pontine micturition center is activated, allowing micturition.
Term: Micturition Process Step 5
Description: The pontine micturition center activates parasympathetic fibers, inhibiting sympathetic fibers, and relaxing the external sphincter.
Term: Micturition Process Step 6
Description: Parasympathetic stimulation causes the detrusor muscle to contract and the internal sphincter to relax, allowing urine passage.
Term: Spinal Reflex in Infants
Definition: Micturition is controlled by a spinal reflex in infants, making urination involuntary until they gain voluntary control through potty training.
Term: Incontinence
Definition: Loss of the ability to control micturition, often occurring when voluntary control fails.
Term: Sacral Micturition Center
Definition: A group of neurons in the sacral spinal cord that controls urination, acting reflexively unless modified by higher brain centers.
Term: Pontine Storage Center
Definition: A collection of neurons that regulate micturition at a supraspinal level, suppressing parasympathetic activity and enhancing sympathetic activity during bladder filling.
Term: Sympathetic Innervation
Definition: Part of the nervous system that increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and pupil size.
Term: Parasympathetic Fibers
Definition: Nerve fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system involved in bladder contraction and relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter.
Term: Spinal Reflex
Definition: An involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus, involved in micturition.
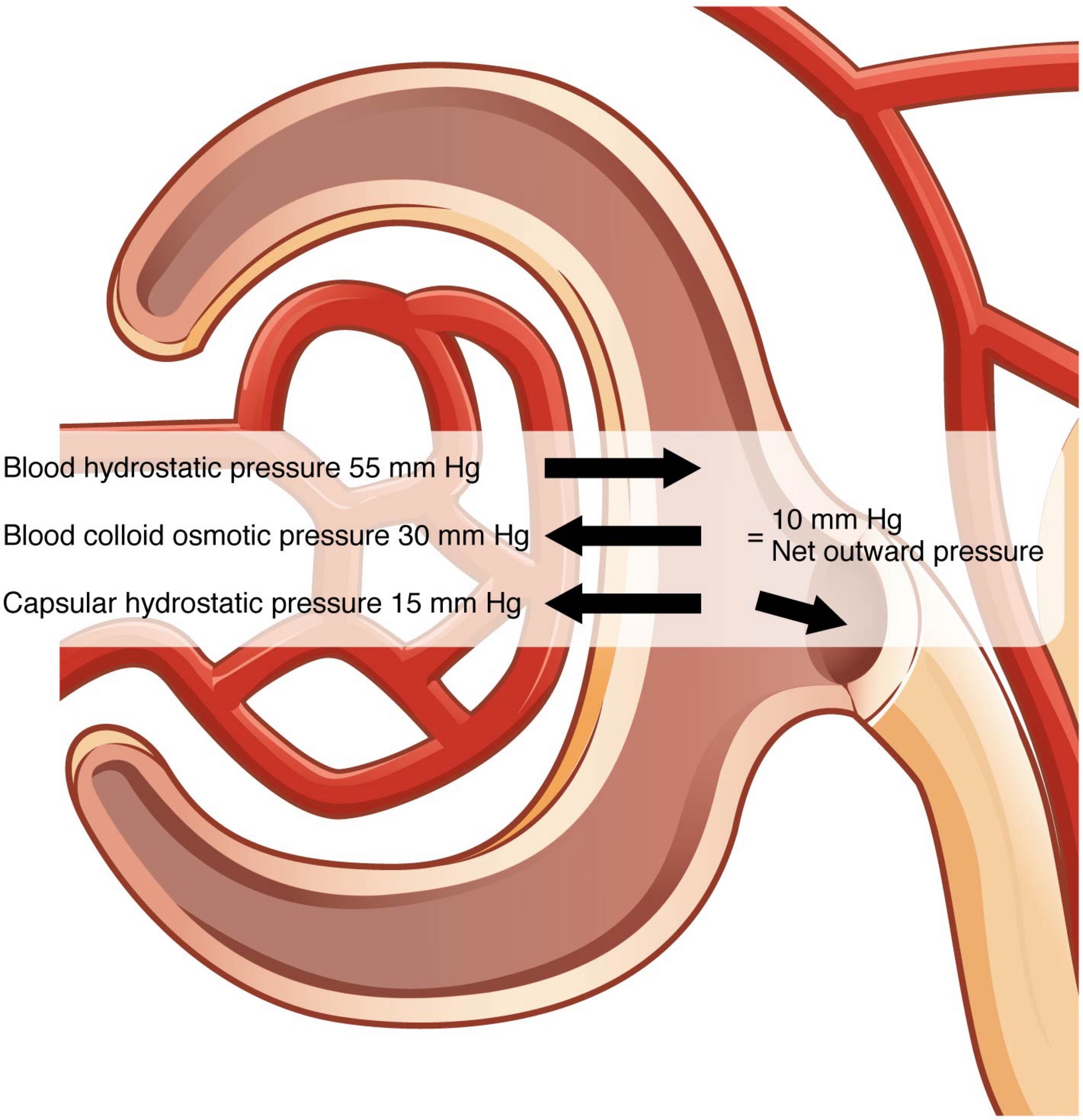
Term: Glomerular Filtration
Definition: Blood flows from the afferent arteriole into the glomerulus for filtration, where pressure forces fluids and specific solutes to leave the blood and enter the glomerular capsule.
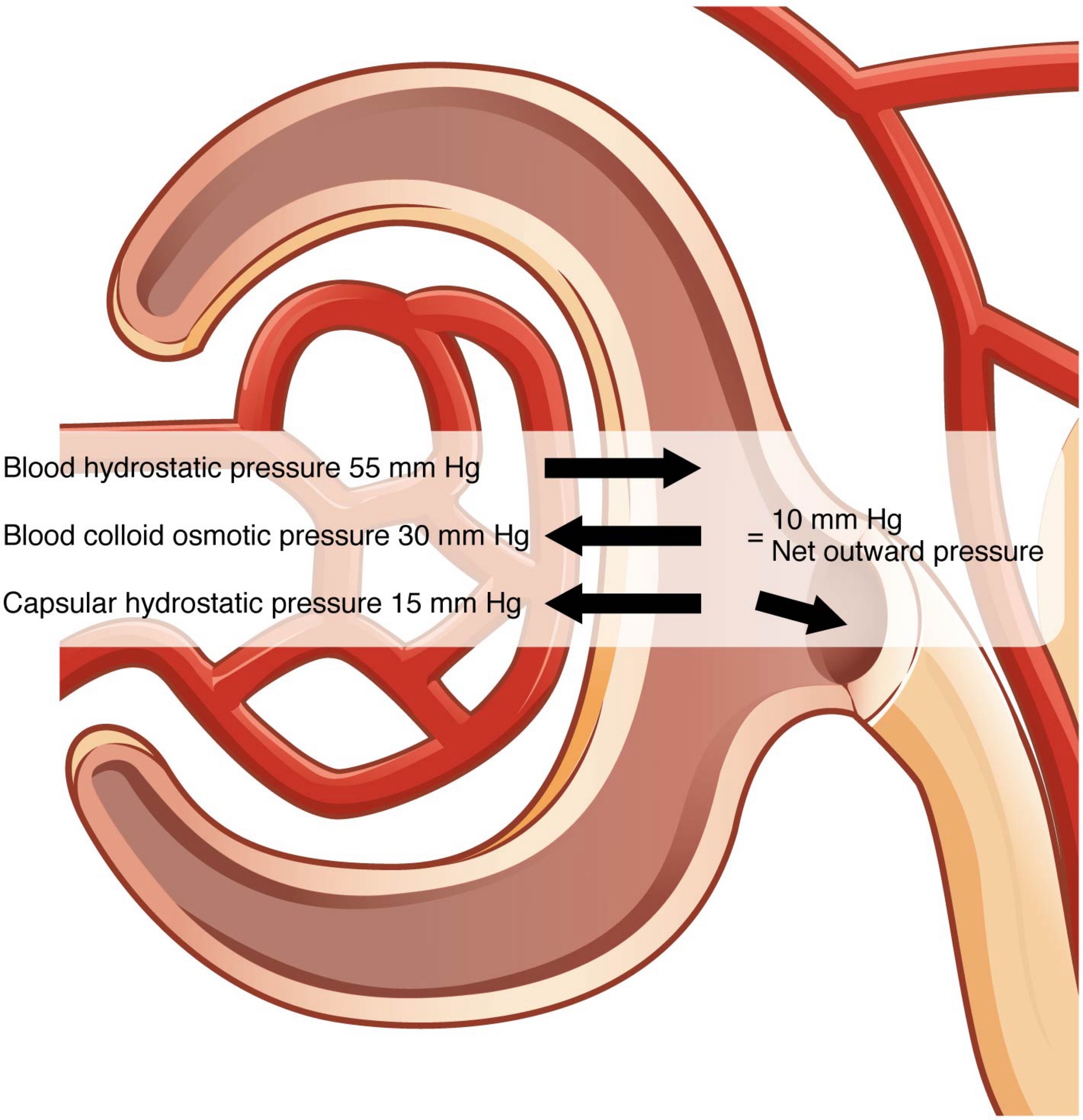
Term: Glomerular Filtrate
Definition: The fluid that leaves the glomerulus and enters the glomerular capsule.
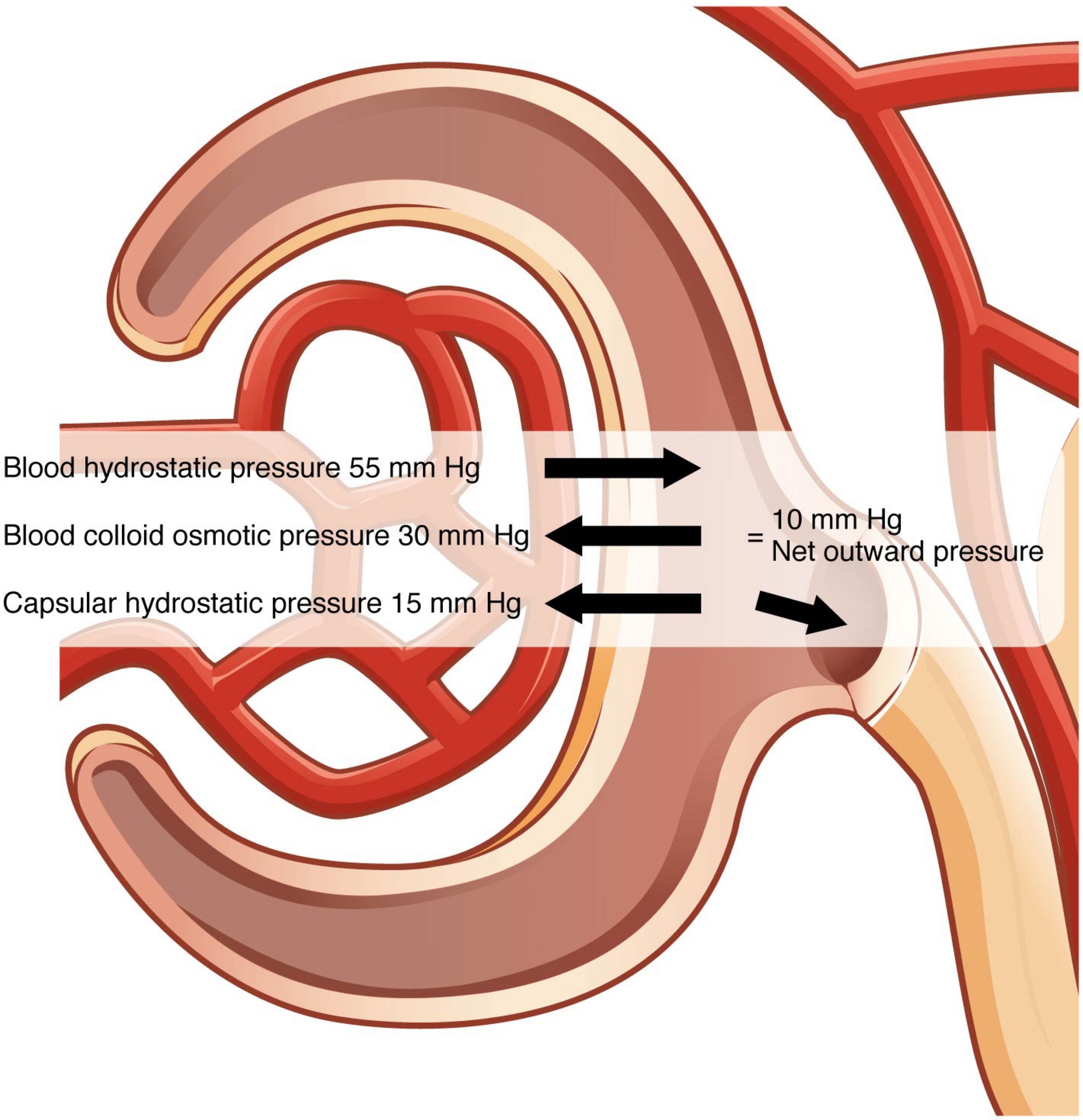
Term: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Definition: The rate of renal filtration; typically around 125 mL/min in males and 105 mL/min in females.

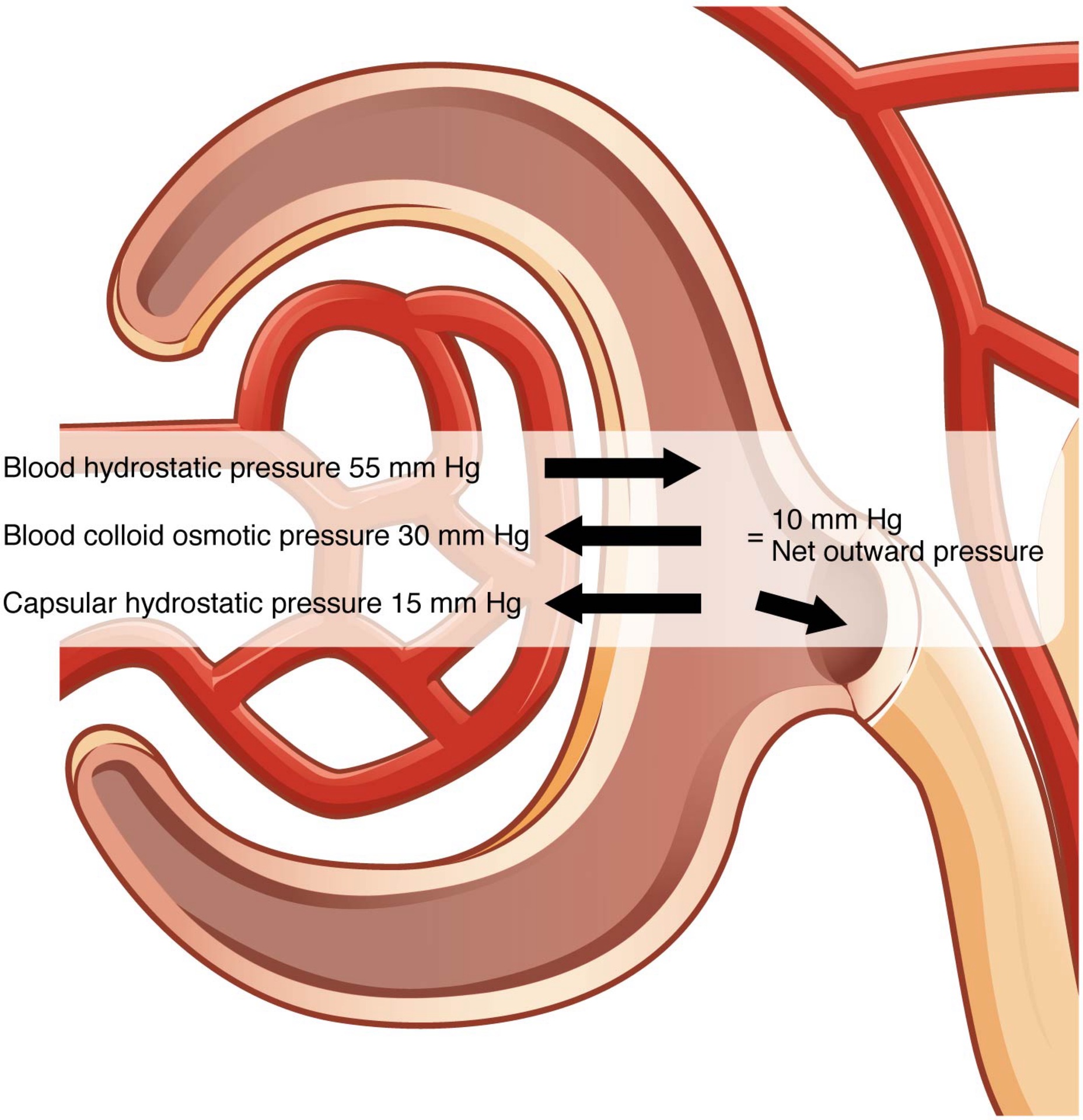
Term: Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Definition: The pressure of fluid across the glomerulus, calculated by taking the hydrostatic pressure of the capillary and subtracting the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood and the hydrostatic pressure of Bowman’s capsule.
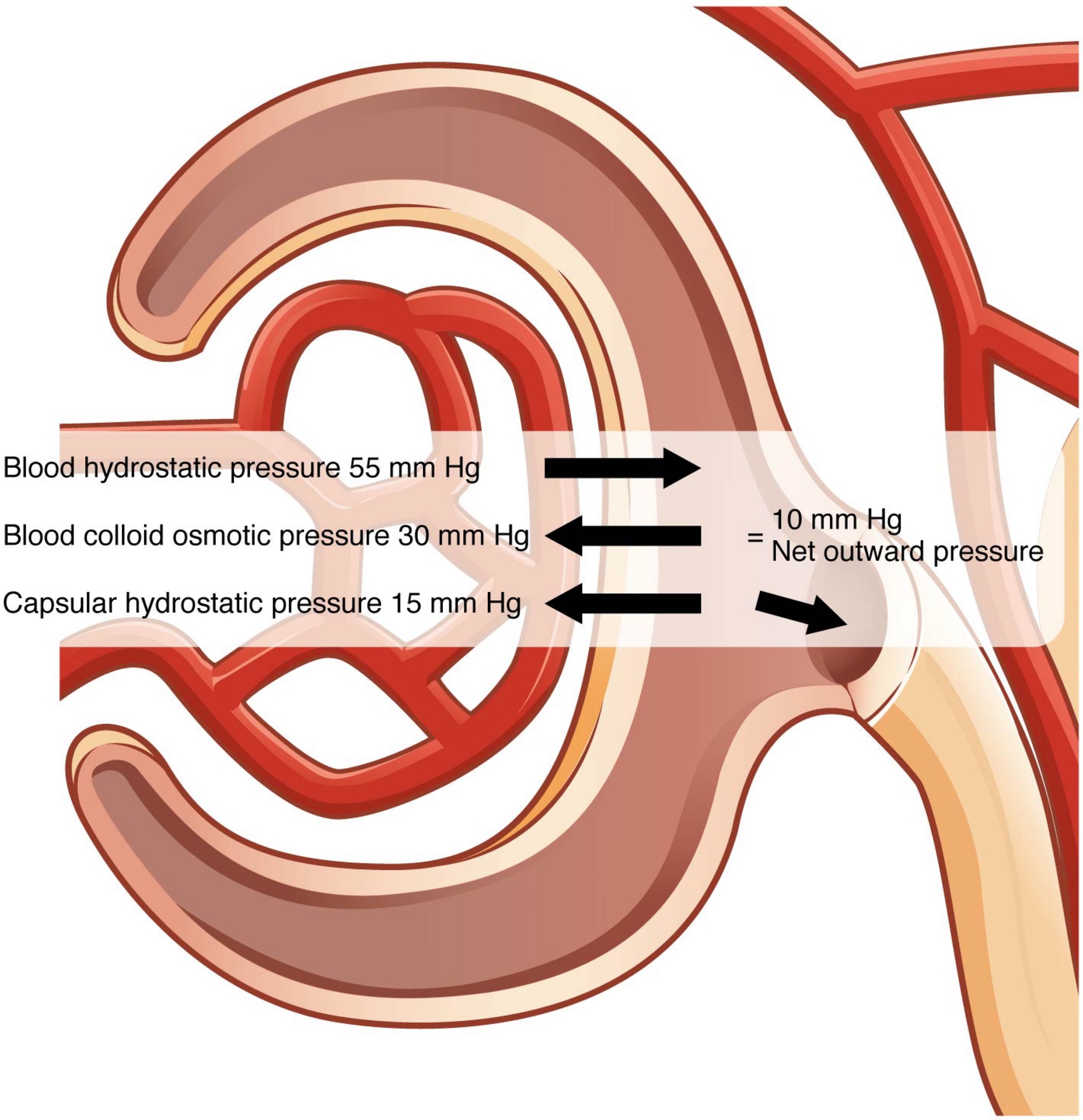
Term: Glomerular Filtration
Definition: Blood flows from the afferent arteriole into the glomerulus for filtration, where pressure forces fluids and specific solutes to leave the blood and enter the glomerular capsule.
Term: Glomerular Filtrate
Definition: The fluid that leaves the glomerulus and enters the glomerular capsule.
Term: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Definition: The rate of renal filtration; typically about 125 mL/min in males and 105 mL/min in females.
Term: Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Definition: The pressure of fluid across the glomerulus, calculated by taking the hydrostatic pressure of the capillary and subtracting the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood and the hydrostatic pressure of Bowman’s capsule.