Abstract Data Types
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
The facilities and functionality of an Abstract Data Type (ADT) - What it does
As users of an ADT, it is important to understand what the functionality is and how we can access that functionality
The data structure employed by the ADT - How it does what it does
As programmers of an ADT, we need to understand what options are available to implement an ADT, evaluate them and pick the best one
The implementation of the data structure - How it is stored and manipulated
As Computer Scientists, we should understand the basics of the data structure
Why ‘Abstract’
The definition of an ADT only mentions what operations can be performed but not how these operations will be implemented
The ADT does not specify how the data will be organised in memory, or the algorithms to be used for implementing the operations
Abstract because it is an implementation independent view
The process of providing only the necessary information and hiding the internal details is known as abstraction
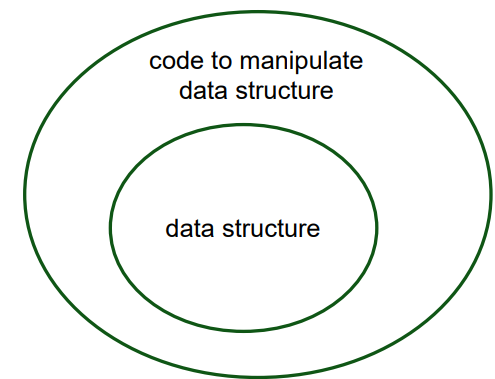
Difference between Data Structures and an ADT
A data structure is the physical representation of the structure of the data being stored in memory
An abstract data type is both the data structure and the procedures/functions which manipulate that data structure
Level of Support for ADTs
The level of support for ADTs differs among programming languages
Most languages will allow us to introduce data structures as user-defined types
this is a minimal level of support
Some languages will allow us to encapsulate the data structure and offer operations as part of the definition of the ADT
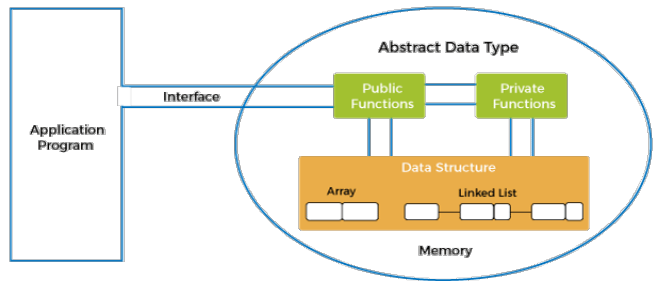
Encapsulation
The only way the user can interact with a variable of that ADT is through an interface, a set of procedures that operate on the data structure
The user cannot directly manipulate the physical stored data structure
‘Strong’ Encapsulation
If the encapsulation is “strong” then details of how the data structure is actually stored can be completely hidden from the user
The user will have a conceptual (or “abstract”) understanding of what the ADT does, not how it does it