Final Exam -- Freshwater Systems
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Collector
Organisms that are designated by their use of adaptive features to filter and catch organic matter
Grazer
Organisms that feed off of periphyton that accumulates on larger structures such as stones, wood, or large aquatic plants
Shredder
Organisms that feed off of coarse particulate organic matter such as small sections of leaves. They ingest the organic matter along with volunteer organisms (fungi, microorganisms) attached to the source; shredders break it up into a finer particulate matter.
Periphyton
Complex mixture of algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes, fungi, and detritus, that are attached to submerged surfaces in most aquatic environments
Discuss the importance of the River Continuum Concept—include stream order, BMI assemblage [from a functional feeding standpoint], role of the riparian based on stream size
RCC describes how rivers change as they flow from headwaters to end waters. As stream size increases, the assemblage of BMI shifts from shredders and collectors in headwaters to collectors and predators in larger river systems. The riparian zone is important to headwater systems because much of the food consumed by shredders and collectors is from fallen leaves.
Stream order and size affect temperature in streams. True/ False
True
How does the riparian zone affect BMI?
In order for a healthy stream flow, different BMIs have different functions. In a riparian zone, many shredders and collectors are needed to break down nutrients for predators and collectors in larger river systems.
The riparian zone also provides protection/shelter for BMIs from predators.
Explain nutrient spiraling [include an illustration in your response].
S = Sw + Sp
Sw = uptake length; average distance a nutrient molecule travels downstream in dissolved form
Sp = turnover length; average distance a nutrient molecule travels downstream in particulate form
What are the three ways benthic macroinvertebrates feed off organic material and why is this important for the RCC?
Shredders feed on small sections of leaves, in which they break up the leaf into a finer particulate matter.
Collectors use adaptive features to filter and catch organic matter.
Grazers feed off of periphyton that accumulates on large structures.
This is important for the RCC because each BMI has a specific task that helps the stream flow be healthy.
Describe the leaf processing sequence after it enters the streambed as litterfall.
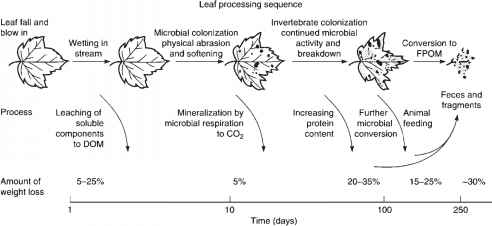
What is a functional feeding group and how are individuals in this group categorized?
Functional feeding groups are a classification approach that is based on behavioral mechanisms of food acquisition rather than taxonomic group. Individuals are categorized based on their mechanisms for obtaining food and the particle size of the food, and not specifically on what they are eating.
Define the relationships between light, algae, polysaccharide matrix, substratum.
Light exposure triggers physiological processes in the algae cells.
Discuss and define DOM/POM/COM/CPOM [provide the relative particle size of each group].
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is transported from the watershed into aquatic systems.
Particulate Organic Material (POM)
Coarse Organic Material (COM)
Course Particulate Organic Material (CPOM) are small sections of leaves (1 mm-10 cm)
ISC
Impervious Surface Cover
CSO [include effects on urbanization on water quality]
Combined Sewer Overflows
Chemical effects depend on:
extent and type of urbanization
presence of wastewater treatment plant effluent
Geomorphology
A branch of geology that is concerned with the structure, origin, and development of the topographical features of the earth’s surface
With ISC, how does it affect the water penetrating into the ground?
Water penetrates into the ground faster when ISC is present
Floods peak faster and are shorter in duration with more ISC. True/False
True
The water table declines and groundwater recharge is increased with ISC. True/False
False, groundwater recharge is reduced and water table declines
Know how the different percentages of imperviousness affect evapotranspiration and runoff.
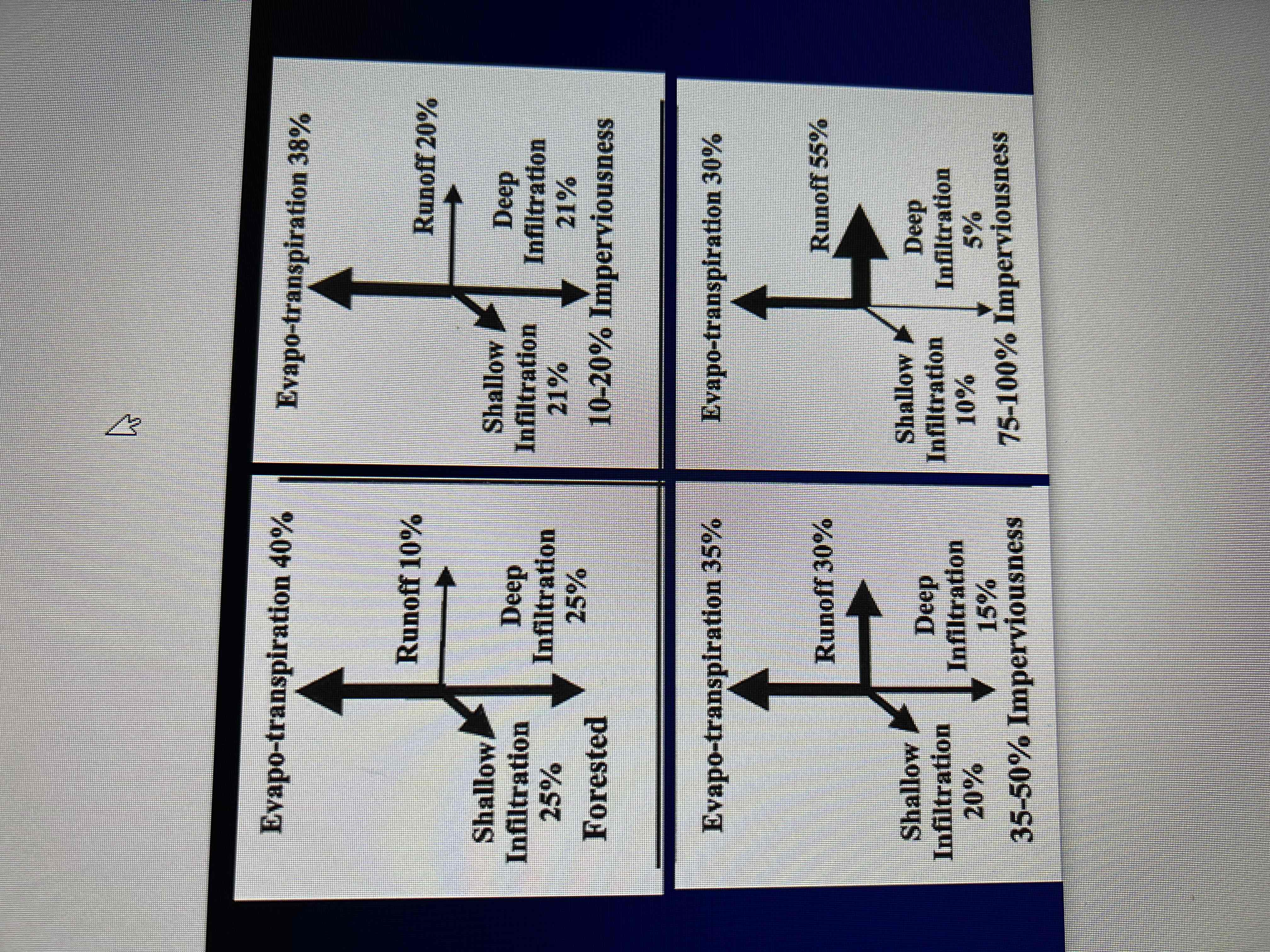
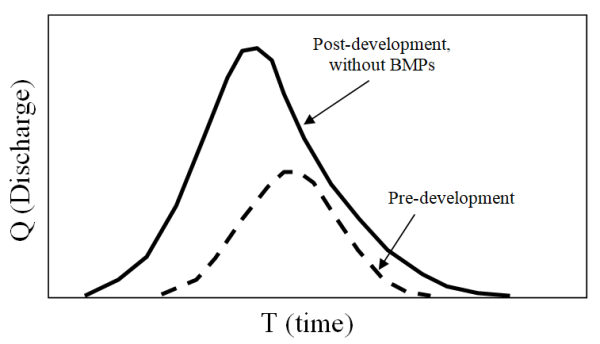
How does ISC affect discharge and baseflow from a pre-development and post-development standpoint?
As ISC increases:
Culverts, canals, and pipes alter the distribution of water
Floods peak faster and are shorter duration
Flood peaks increase
A 2-year flood in an urban stream is equivalent to a 10-year flood in a forested stream
What are some geomorphic effects of urbanization?
Alters drainage density
decreases natural channel densities
Increases overall drainage density
It affects sediment supply and discharge
Stream widening and incision - begins between 2-6% ISC
Decreased channel stability
Loss of pool-riffle structure
Alters sediment texture - less fines, more coarse substrate
Less large woody debris
What effects does land aggregation and removal of trees have on streambeds?
Increased stream temperature
Decreased groundwater recharge
“Heat island” effect
Briefly describe how wastewater systems work/where the water comes from and travels to.
Wastewater systems work by collecting wastewater from homes, businesses, and industries. The water then travels through pipes to a septic tank or a wastewater-treatment plant. The treatment plants clean the wastewater for discharge into streams or other receiving waters, or for reuse.
What is a stormwater hotspot? Provide examples.
An area of land that produces higher concentrations of pollutants; normally found in urban runoff
Commercial parking lots
Fleet storage areas
Industrial areas
Gas stations/vehicle service areas
Landscape nurseries
What is the ecological role of microbes and algae in a body of water?
Microbes
Bacterial densities increased in urban streams
Increased antibiotic resistance
Algae
Reduced species diversity
Reduced biomass
How does urbanization impact benthic macroinvertebrate populations?
Decreased diversity
Decreased abundance (toxins) or increased abundance (nutrients)
Shifts in species composition
Relative increase of tolerant species
Community “health” declines
Increased suspended solids in water (turbidity) heightens the effects of erosion. True/False
True
Provide 4 ways that urbanization impacts the fish community.
Fish diversity declines
Fish abundance declines
Tolerant taxa increase
Increased % of contaminated fishes'
Sensitive taxa decline
Increased abundance of exotics
Overall community “health” declines
What percent ISC can you generally find a degradation threshold?
10-20%
What do endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) do to aquatic organisms?
Mimic or block natural hormones
What type of land use is most impactful on FW systems?
Urban land use
What components may increase levels of effluent in aquatic systems?
Sewage - pharmaceuticals
Industry - pulp and paper chemicals
Diel
involving a period of 24 hours
DVM
(Diel vertical migration) of zooplankton to potentially avoided fish predation
DHM
(Diel horizontal migration) zooplankton aggregate in macrophytes beds during daylight hours and migrate to the pelagic zone to avoid predators
YOY fishes
Young-of-the-year fishes (defined as larval/juvenile fish produced in the current year’s spawn)
Infochemicals
Organisms who live in an “odor world”; they depend strongly on chemical stimuli to learn about the biotic and abiotic environment
Cyclomorphomsis
A phenomenon in cladocerans that involves a regular seasonal and/or induced change in body allometry… evidence is equivocal if temperature, predation, or a combination of these factors induces morphological changes
How does size selective grazing affect the size and composition of the zooplankton community?
Predation (fish) influenced the size and composition of the zooplankton community— large-bodied zooplankton were rapidly consumed, resulting in zooplankters which tend to be smaller in size
How does zooplankton biomass correlate to total phosphorus levels?
Zooplankton biomass is higher when total phosphorus levels are higher
The interaction between larval fishes and cladocerean abundance is typically a _______ relationship.
Negative
In tropical systems, zooplankton still exhibit the same vertical migration as they do in stratified lakes. True/False
True
Typically, during day light hours, where are Daphnia found?
In the sediments or in the aphotic zone
What is the most abiotic factor in transparent lakes that is most consequential in regulating Daphnia survivorship?
Seasonal phosphorus availability
Lakes where zooplankton tend to show very limited vertical migration are typically eutrophic and/or minimal populations of zooplanktivorous fish. True/False
False, typically oligotrophic
Baseflow
Streamflow which results from precipitation that infiltrates into the soil and eventually moves through the soil to the stream channel
Riparian zone
Pertaining to, situated or dwelling on the margin of a river… including banks on water bodies where sufficient soil moisture supports the growth of vegetation
Delta
Flat plane of alluvial deposits between the branches at the mouth of a river, stream, or creek
Incised channel
A stream that, through degradation, cut its channel into the bed of a valley
Backwater
A pool formed by water backing upstream from an obstruction or a secondary channel that is connected to the active main channel
Lotic
Aquatic system with rapidly flowing water (e.g. brook, stream, or river) where net flow of water from headwaters to the mouth is unidirectional
Glide
A shallow stream reach with a maximum depth that is ~ 5% or less than average stream width and velocity < 20 cm/sec
Alliuvium
Deposits resulting from sediment transport that is deposited in streambeds, floodplains, lakes, and/or estuaries
Battureland
Strip of land between low water and the edge of a levee
Headwaters
The source of a stream
Meander
A curved portion of a sinuous winding stream— consisting of two consecutive loops; one clockwise, one counterclockwise
Suspended load
Sediment moved by a stream in suspension
Percolation
The movement of water through the soil (influenced by gravity)
Epilithic/Epipelic/Epiphytic/Epizootic
Epilithic - algae on rock or stones
Epipelic - algae growing on sediments
Epiphytic - algae on plants
Epizootic - algae growing on animals
Sublimation
Transition of a substance from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase
Evapotransporation
Describes the sum of evaporation and plant transporation from the Earth’s land surface to the atmosphere
Explain how a headcut is generated—include an illustration in your response.
A headcut is upstream migration or deepening of a stream channel created by erosion
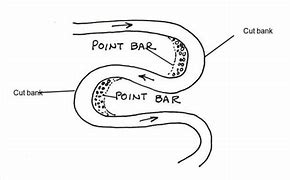
Contrast and draw a cutbank vs. a point bar.
Cutbank - streambank that has been eroded and has a steep face
Point bar - located on the inside of meander bends
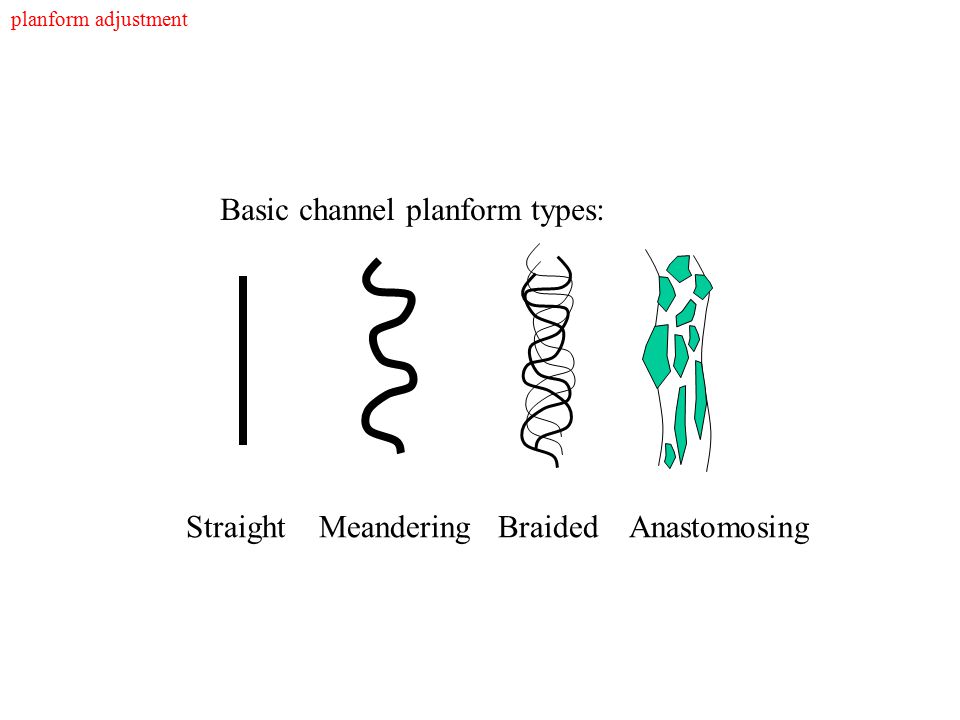
Draw a braided, straight, meandering and anatomizing channels.
Headwaters typically have coarse sand and laminar flow. True/False
False, they have coarse gravel and turbulent flow
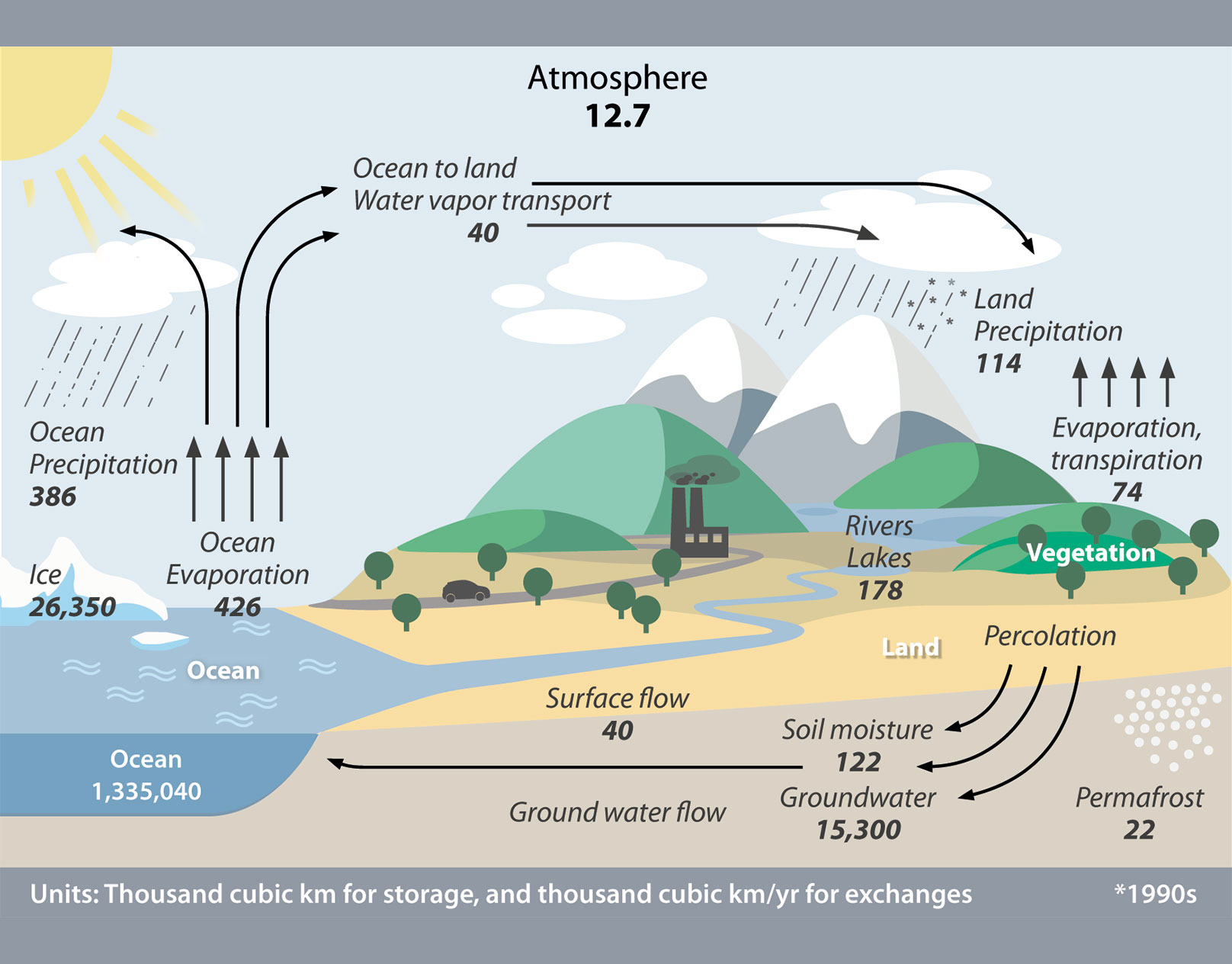
Explain and draw the global hydrological cycle.
The global hydrologic cycle is a continuous exchange of moisture between the oceans, the atmosphere, and the land.
Explain ENSO—include the movement of water in the southern ocean, location of various land masses, turnover, planktonic productivity, wind direction, location of various oceanic water masses, and the overall effects of both El Nino and La Nina on worldwide precipitation---especially as it pertains to North America.
Relatively predictable oscillations in the Southern Pacific Ocean influence global rainfall/snowfall
Upwelling off the Peruvian coast brings cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface —> triggering elevated primary production that sustains robust marine systems (usually water temps are ~ 8 degrees C warmer in the west) … water is about 0.5 m higher in Indonesia than Ecuador
However, ~ every 5-7 years westward trade winds dissipate allowing warmer central/west waters to shift towards the east; this disrupts the intensity of near-continent upwelling
As El Nino sets in, climatological conditions then depart from “normal”— specifically southwest U.S. receives increased precipitation and colder winters conversely the AK, Canada, and much of the northern U.S. states have warmer winters
El Nino is “climatologically counterbalanced” by La Nina in the southern Pacific Ocean
Following the El Nino period—that regulates the movement of warm water—trade winds reverse and blow west (with higher-than-normal intensity and duration) resulting in a pronounced increase in upwelling off the South American coast that usually extends far out from the coast along the equator
Elevated trade wind activity in La Nina results in conditions then depart from “normal”—specifically southwest U.S. receives almost no precipitation; conversely the AK and Canada are extremely cold and flooding plaques southeast Asia