diagnostic imaging techniques
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
the production and interpretation of images for medical diagnosis purposes
define diagnostic imaging
non invasive
is diagnostic imaging an invasive or noninvasive method to achieve a diagnosis?
determine the cause of the injury/illness and guide the diagnosis along with other tests and follow up
what is the goal of diagnostic imaging?
radiology (xray)
computed tomography (CT)
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
ultrasonography
nuclear medicine
what are the different types of imaging?
radiopaque
in radiology, an image that appears white is called...
the image appears black because there is a very low amount of matter
in radiology, what does radiolucent mean?
2 or more images at different angles
we need to perform this in radiology because it is a 2D image, so to accurately view the subject, we must have 2 or more images
what does "orthogonal views" mean?
radiopaque; radiolucent
in radiology, a structure that appears white is called ________, while a structure that appears black is called __________
black
a radiolucent structure appears what color?
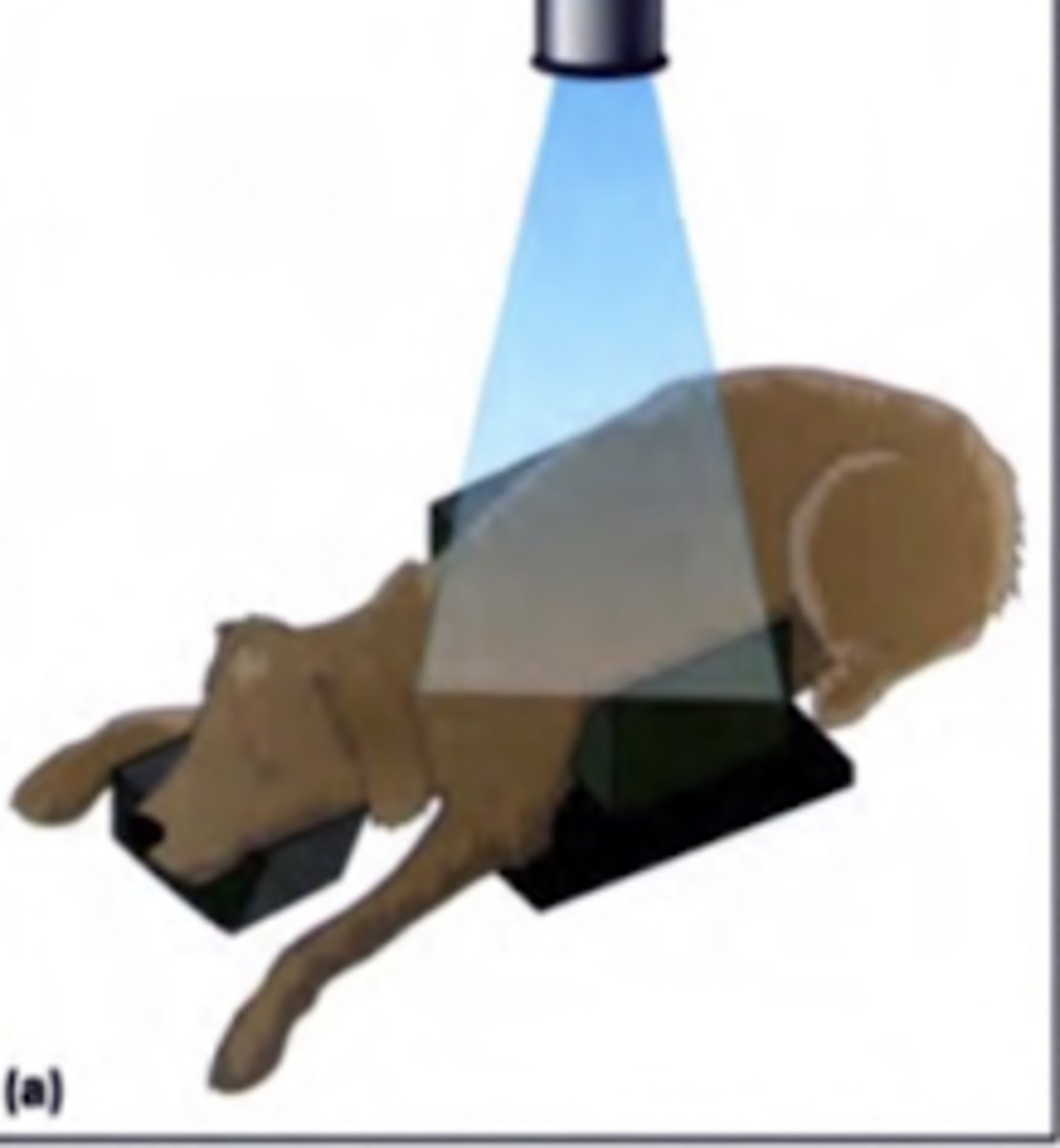
dorsoventral
this view is called...

ventrodorsal
this view is called:
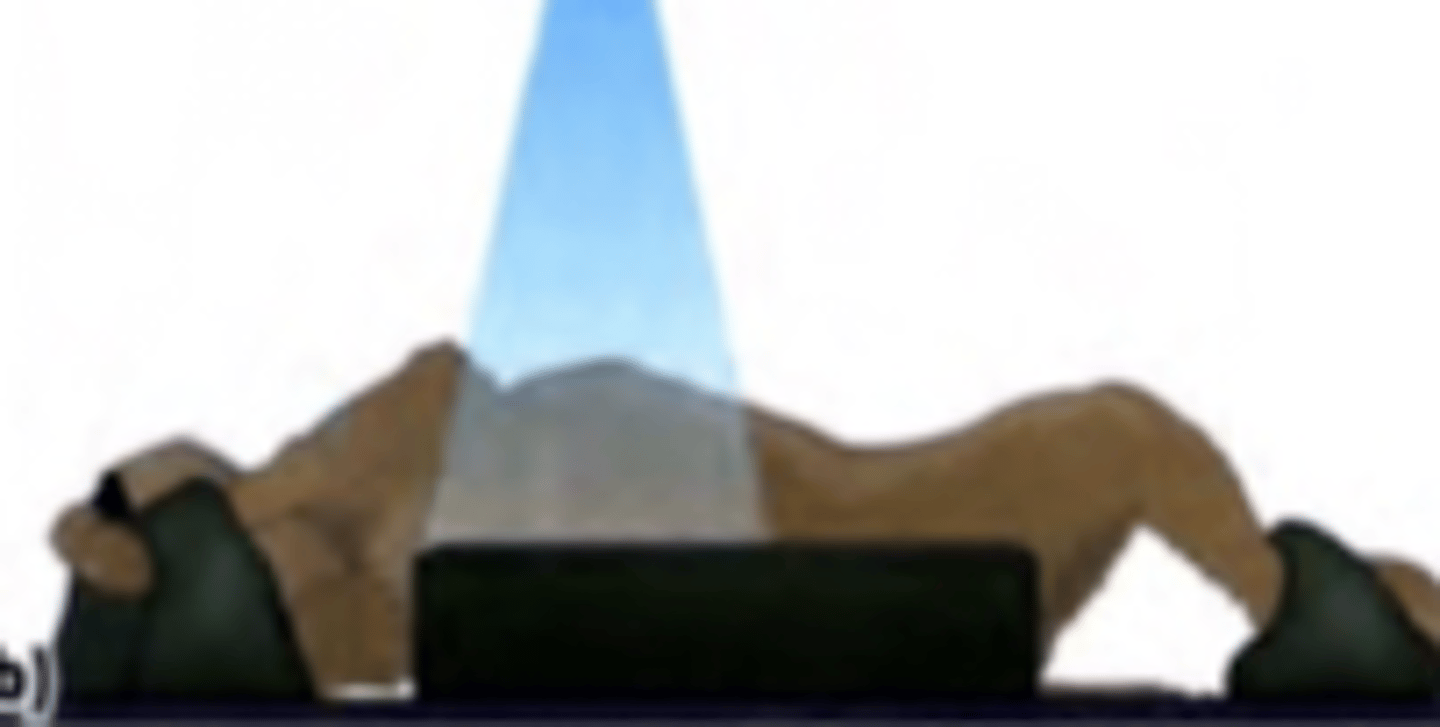

ventrodorsal
what is the name for this view?
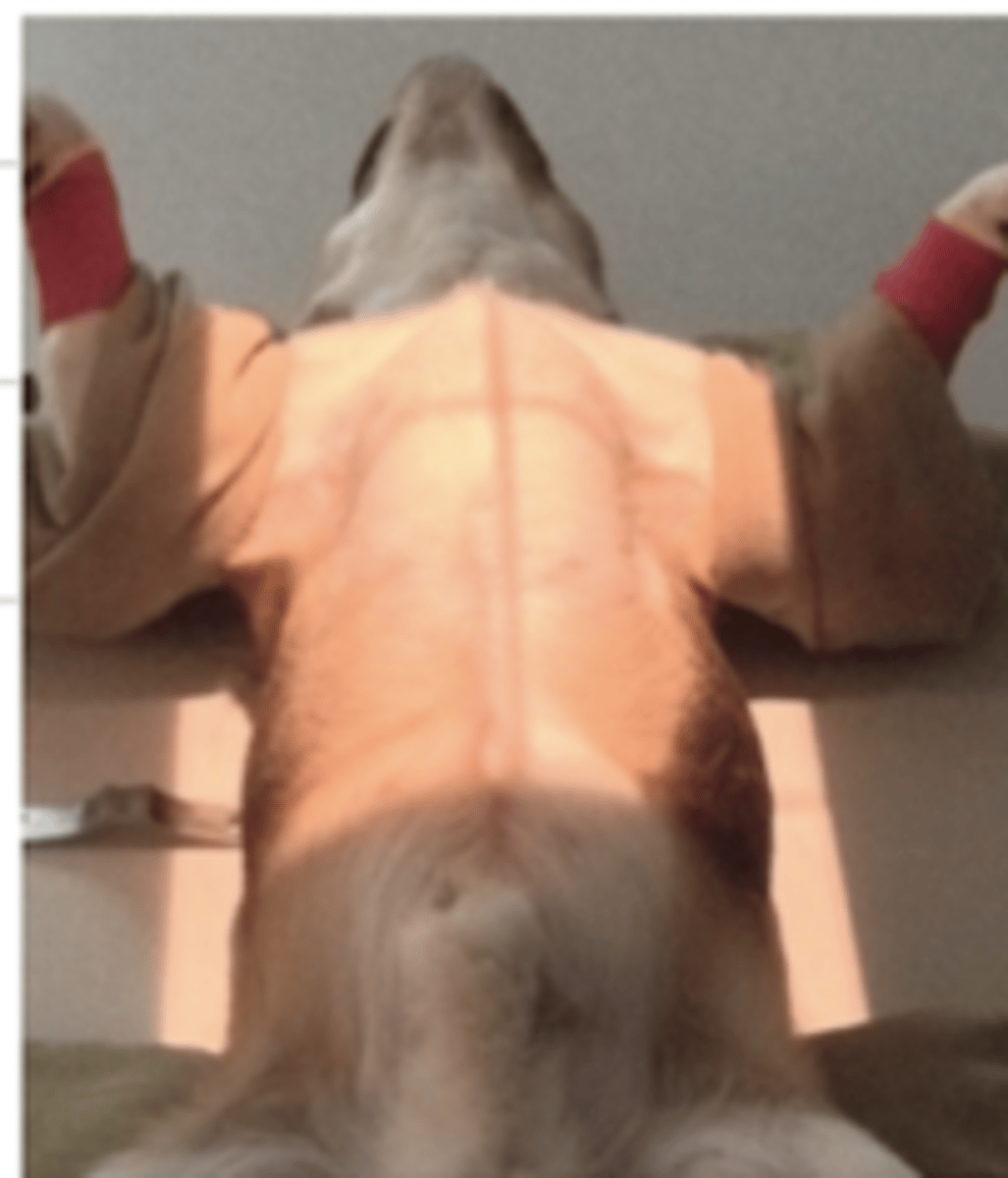

right lateral
this view is called.....
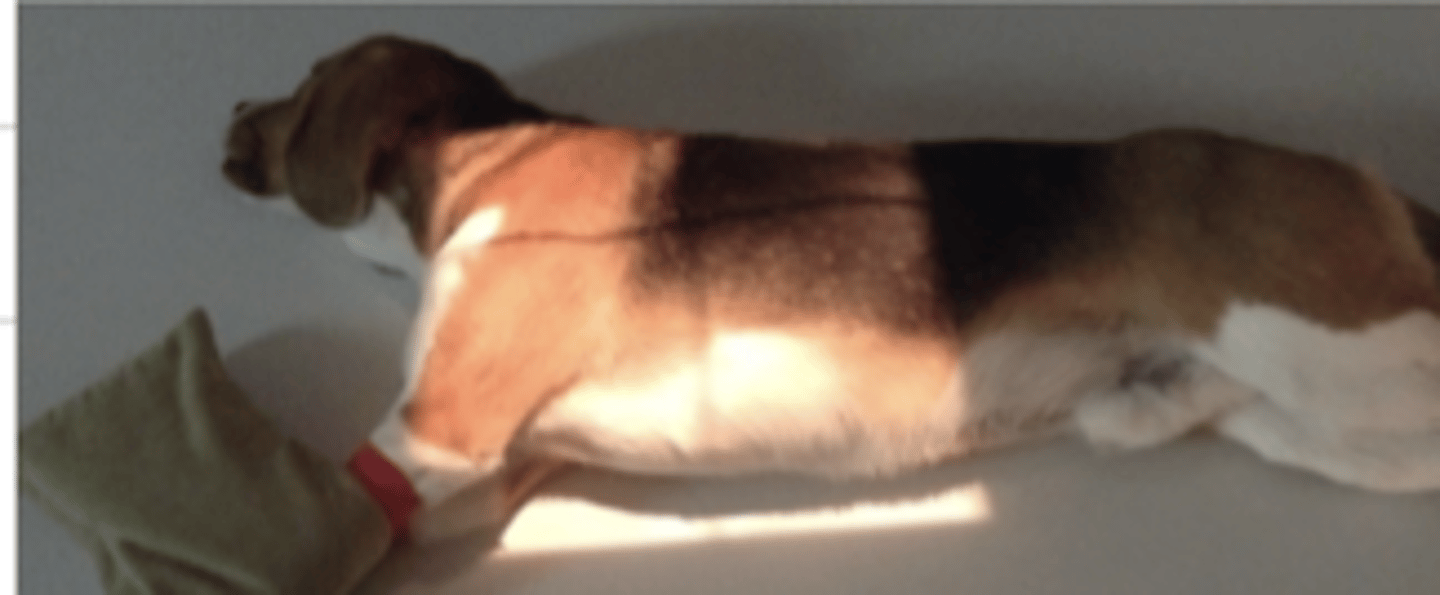

left lateral
if the animal is laying on its left side, the radiology view is called?
by the side that is resting on the table
lateral radiographs are named how?
cranial/rostral on the left
caudal on the right
how do we place lateral xrays on the screen?
cranial/rostral; caudal
lateral xrays should always be placed on the screen with _____ on the left and _____ on the right
left side of the animal; cranial/rostal
ventrodorsal/dorsoventral xrays should always be placed on the screen with _____ on the right and _____ up.
cranial/rostral part up
left side of the animal on the right
how do we place VD/DV xrays on the screen?
-increased mutation rate
-increased rate of miscarriage or fetal anomalies
-increased susceptibility to disease
-increased risk of cancer
-increased risk of cataracts
what are the different biological effects of xrays on the patient and operator?
radiography
because xrays have lots of biological effects (increased risk of disease and cancer, mutation rate, cataracts, miscarriage, etc)
for which type of imaging must the operator wear this? why?

a type of contrast radiography used to visualize the GI tract. we mix contrast with the patient's food so that when they eat it, it goes through their GI tract and in a radiograph, we can see it very well
what is a Barrium GI tract study?
Barrium GI tract study
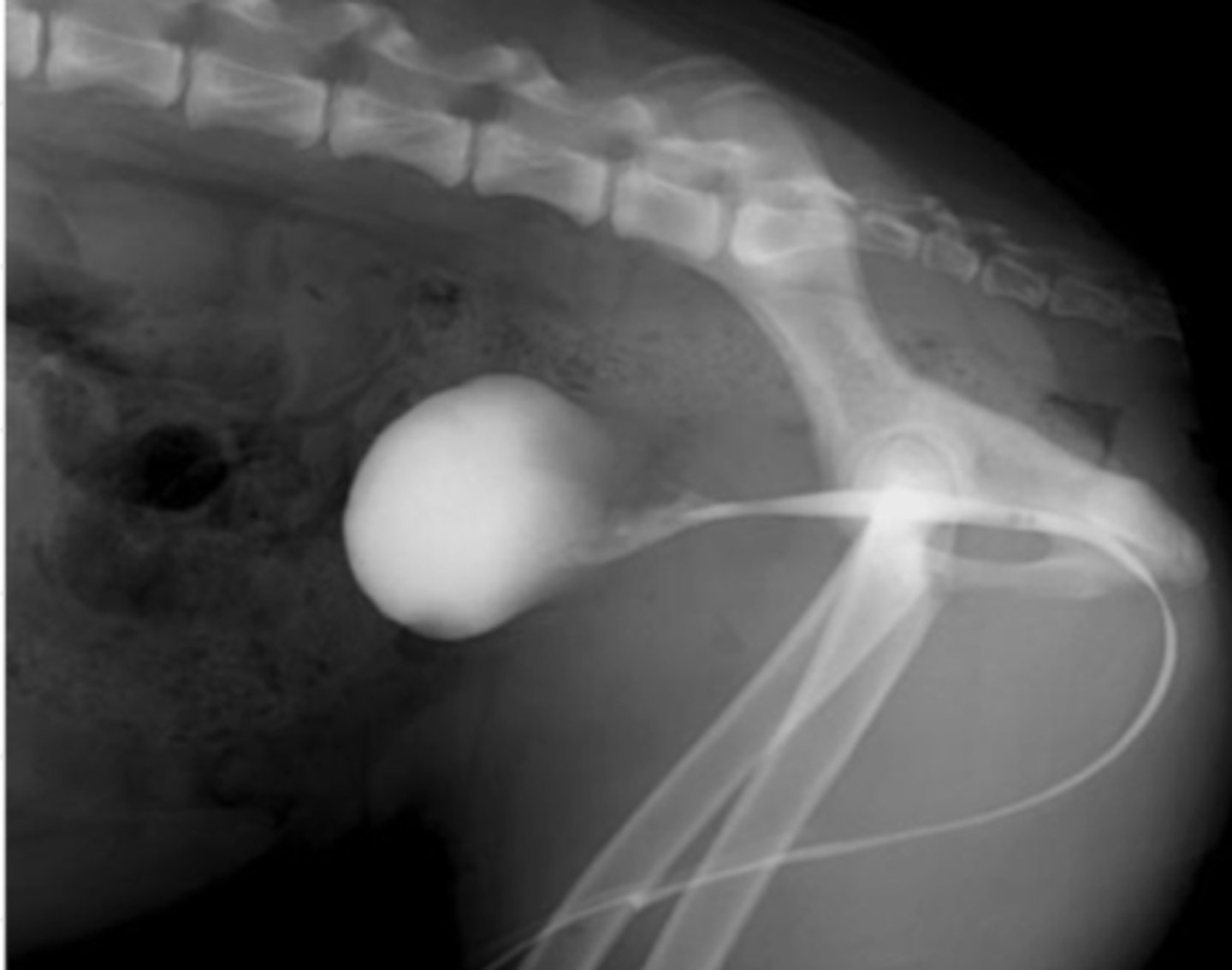
what contrast method is used in this radiograph?
excretory urogram
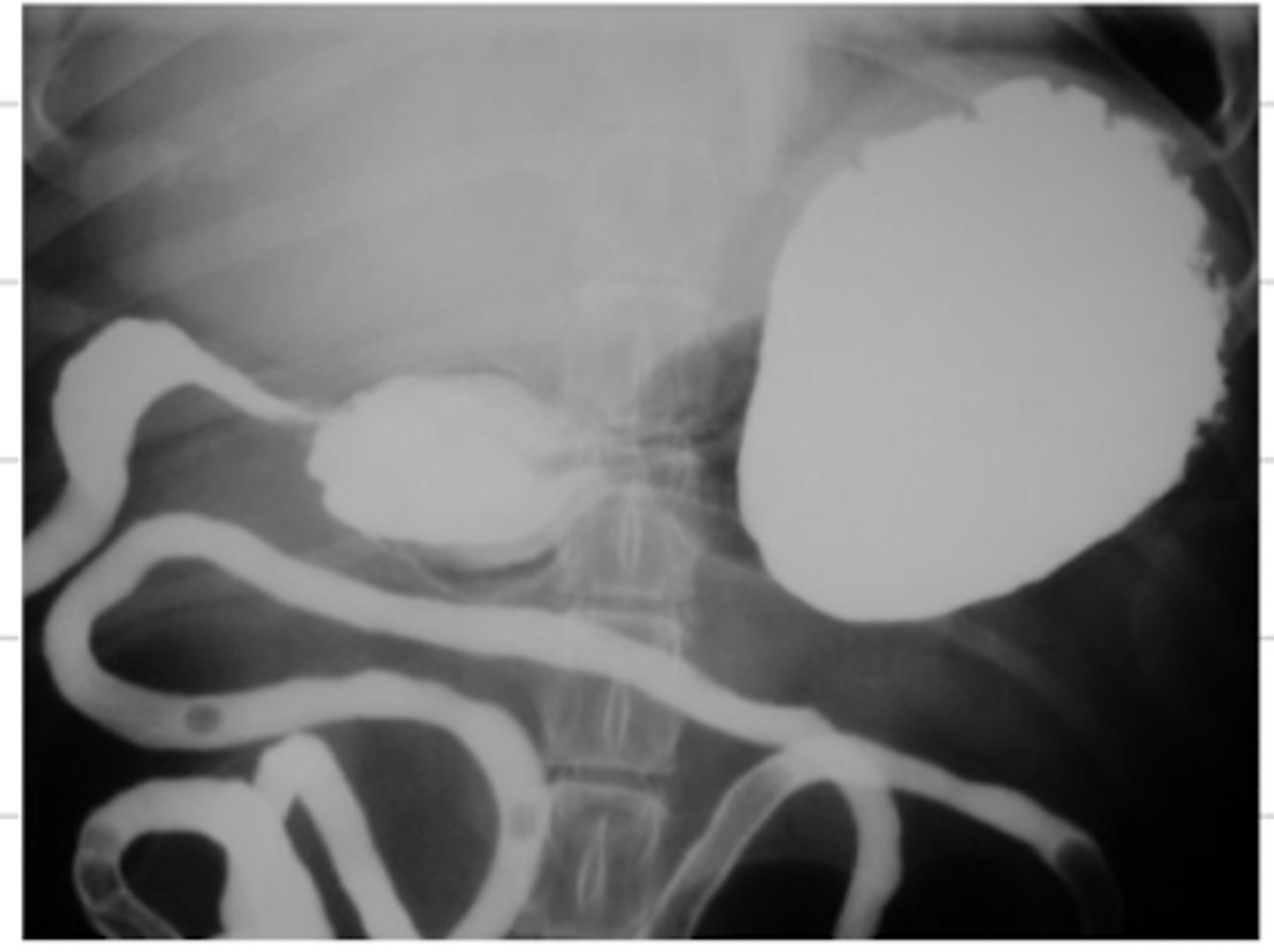
what contrast method is used in this radiograph?
a type of contrast radiograph used to visualize the urinary system- where we put contrast in the patient's IV, so that it goes with the blood to the kidneys and out through the ureters to the rest of the urinary tract
what is an excretory urogram?
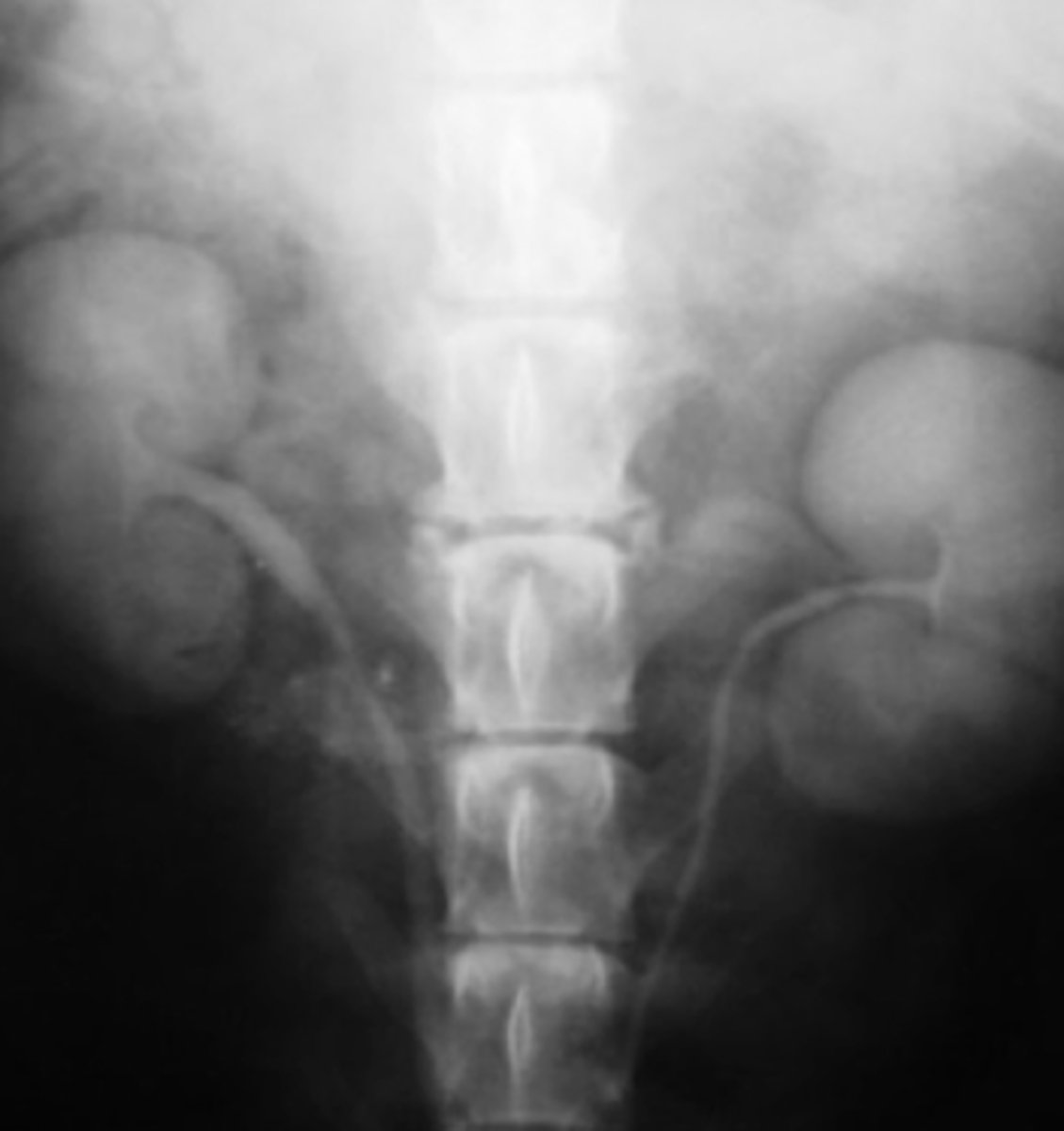
retrograde urogram
what contrast method is used in this radiograph?
a type of contrast radiograph used to visualize the lower urinary system- we put contrast in the urinary catheter so it goes directly to the bladder and urethra
what is a retrograde urogram?
myelography
what type of radiograph is used to visualize the spinal cord?
a type of contrast radiograph used to visualize the spinal cord- we inject contrast into the spinal cord
what is myelography?
myelography
what type of radiograph method was used here?
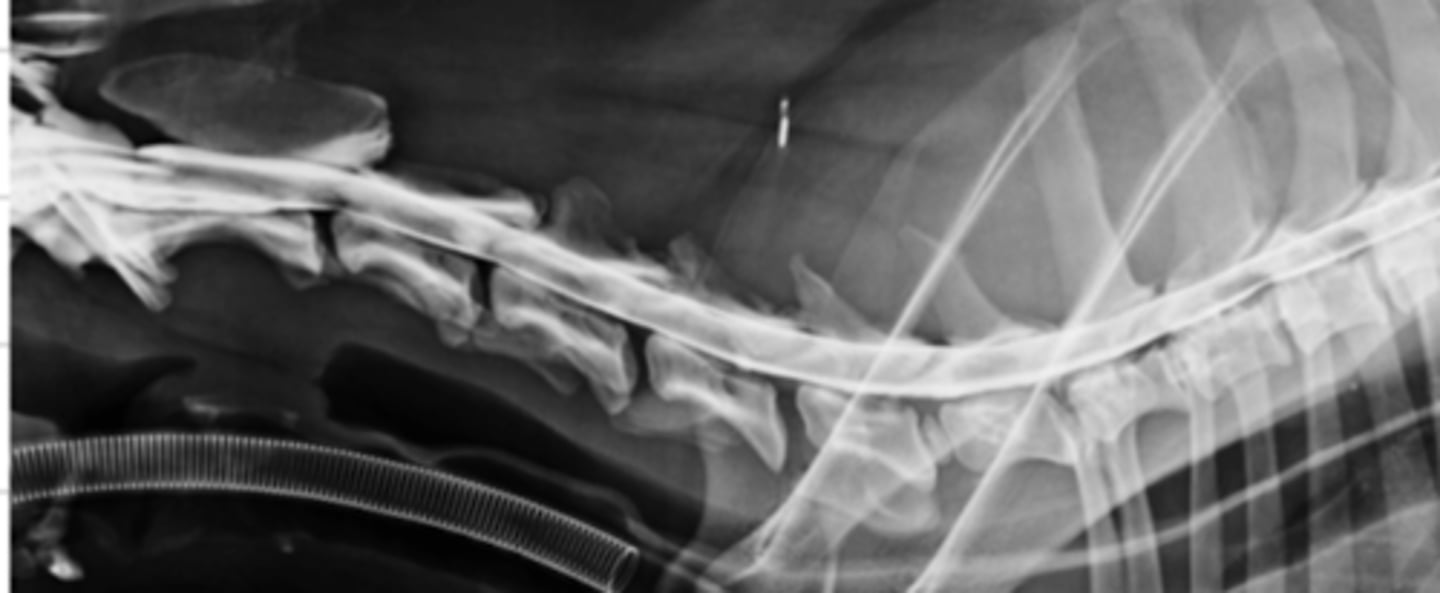
a radiograph contrast method used to visualize the arteries- we inject contrast into the arteries
what is arteriography?
an xray video (dynamic image).
what is fluoroscopy?
fluoroscopy
what is an xray video called?
yes, it is an xray video, so has the same biological effects as an xray
is a fluoroscopy dangerous?
a type of diagnostic imaging where the Xray tube rotates around the patient, generating multiple transverse images of the patient as it rotates.
what is a computed tomography (CT)?
a sequence of 2D images, creating a 3D image- produced in CT
what are "tomographic images"?
bones and lungs
CT is most useful to visualize what structures?
CT
which is more useful to visualize the lungs- radiographs or CT scans?
hyperdense/hyperattenuated
in computed tomography- a white structure is called....
black
in computed tomography- a hypodense/hypoattenuated structure appears in what color?
hyperdense/hyperattenuated;
hypodense/hypoattenuated
in computed tomography- a structure appearing white is called ____________, while a structure appearing black is called ______________
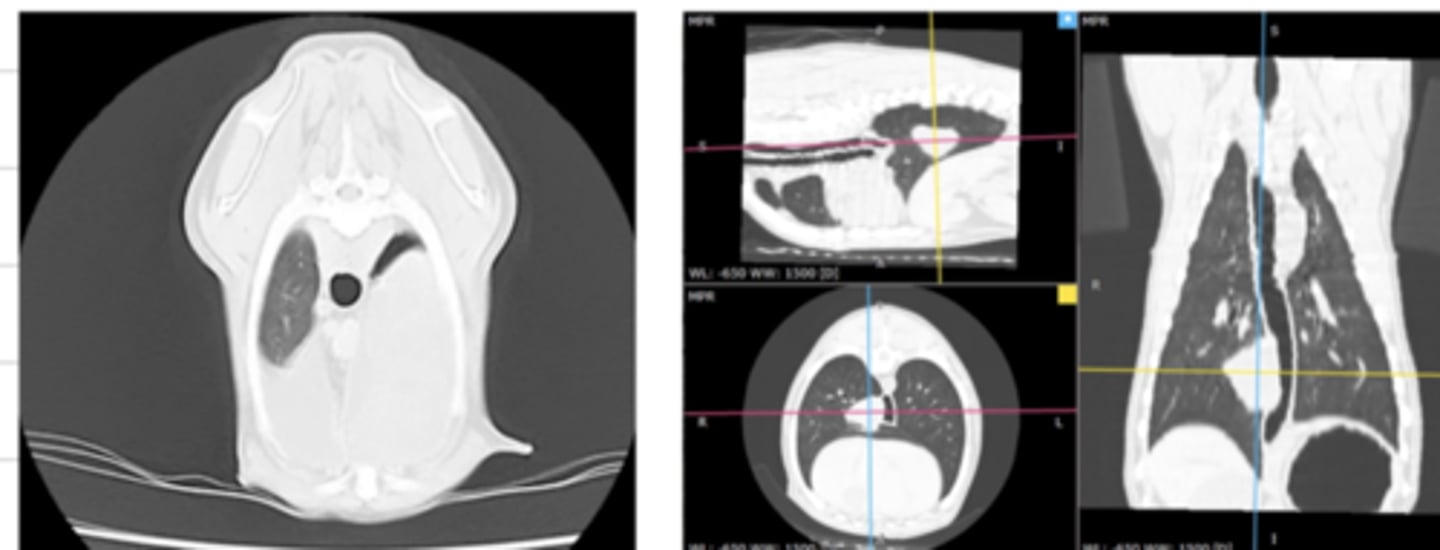
computed tomography (CT)
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create these images?
advantages: creates images without overlapping or reconstructions needed
disadvantages: needs sedation/anesthesia, expensive
what are the advantages and disadvantages of using computed tomography (CT) to produce images?
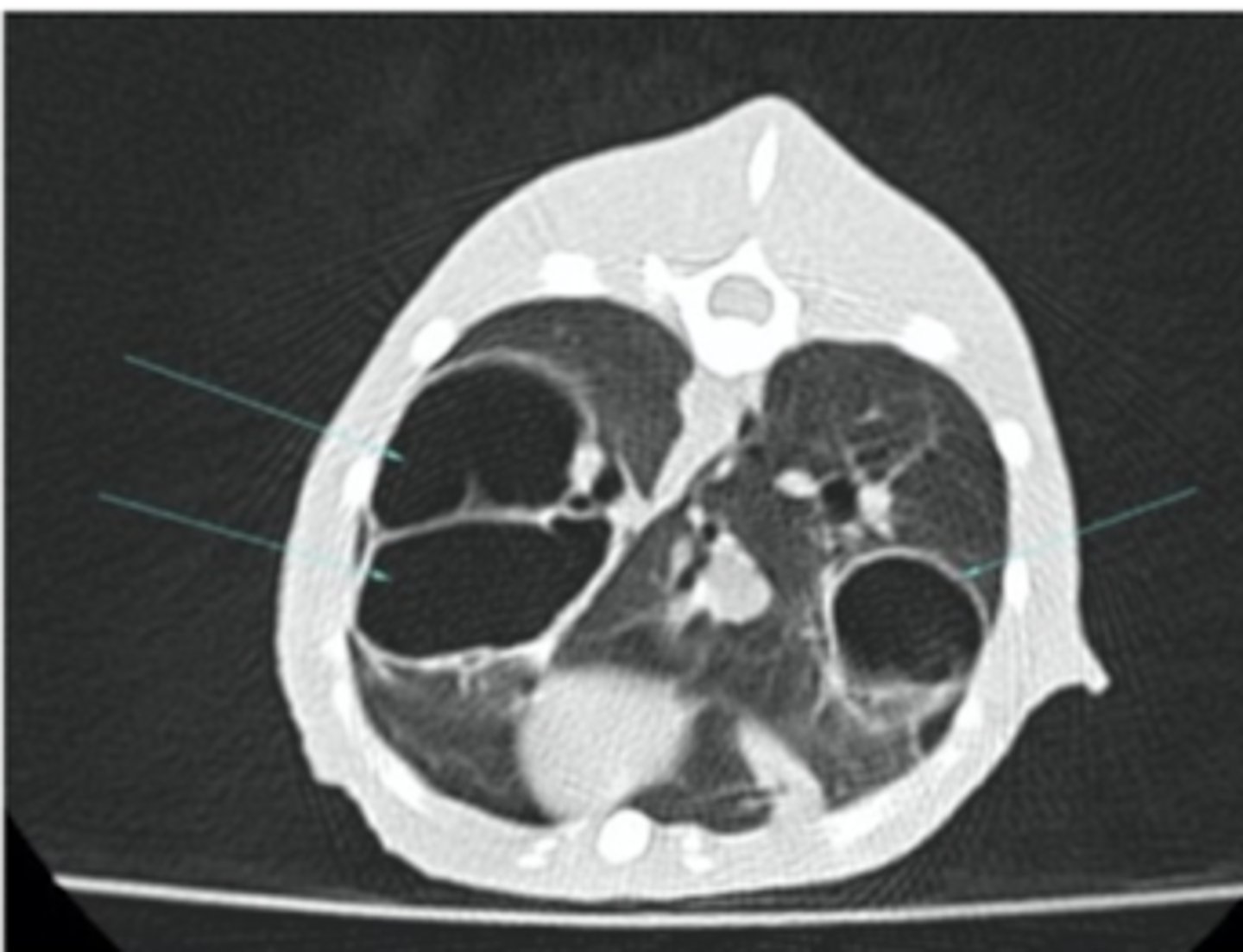
computed tomography (CT)
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create this image?
computed tomography (CT)
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create these images?
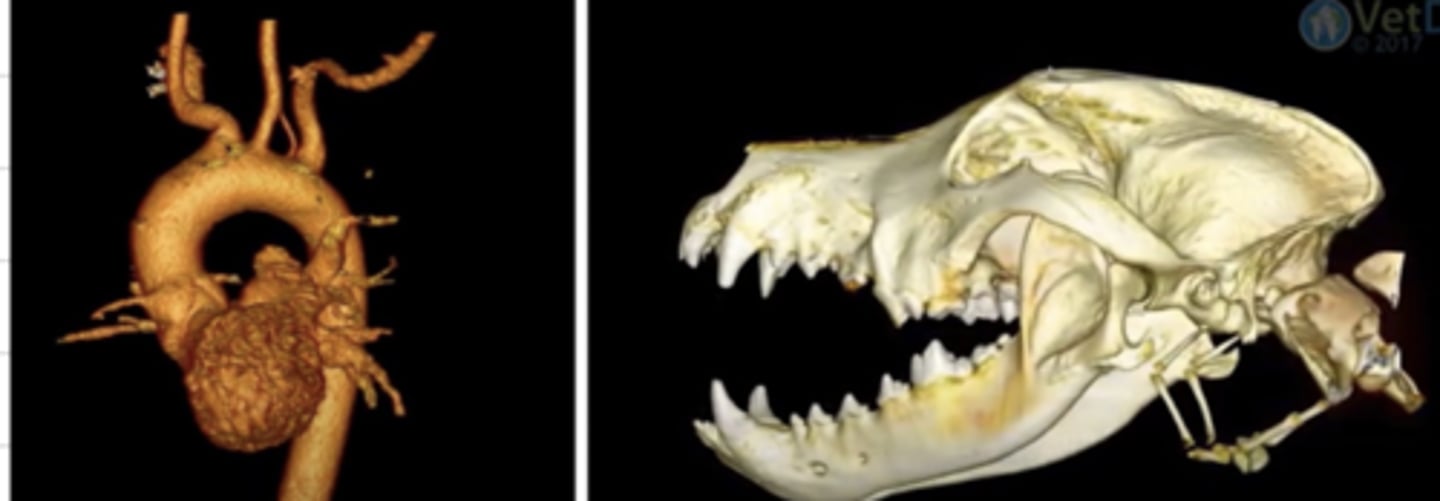
computed tomography (CT)
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create this image?
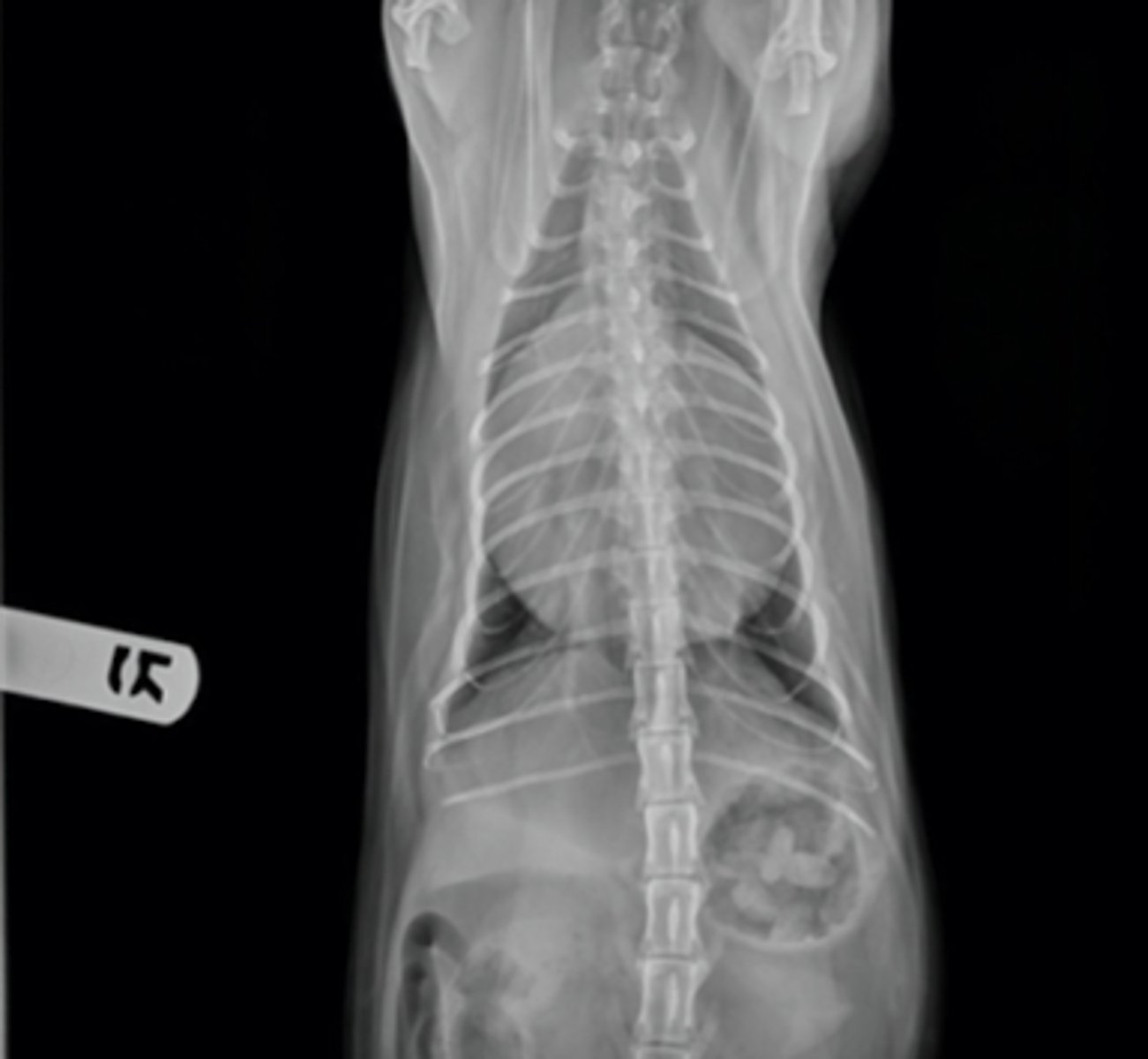
radiography (xray)
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create this image?
computed tomography (CT)
which is more expensive- radiography or computed tomography?
a type of imaging that uses a high power magnetic field that interacts with the body's hydrogen atoms to produce detailed images of internal body structures
what is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
MRI
which type of imaging uses magnetic resonance to produce detailed images of the body's internal structures?
soft tissues, brain, spinal cord
what structures is MRI most useful for?
MRI
what type of imaging is best for visualizing the brain?
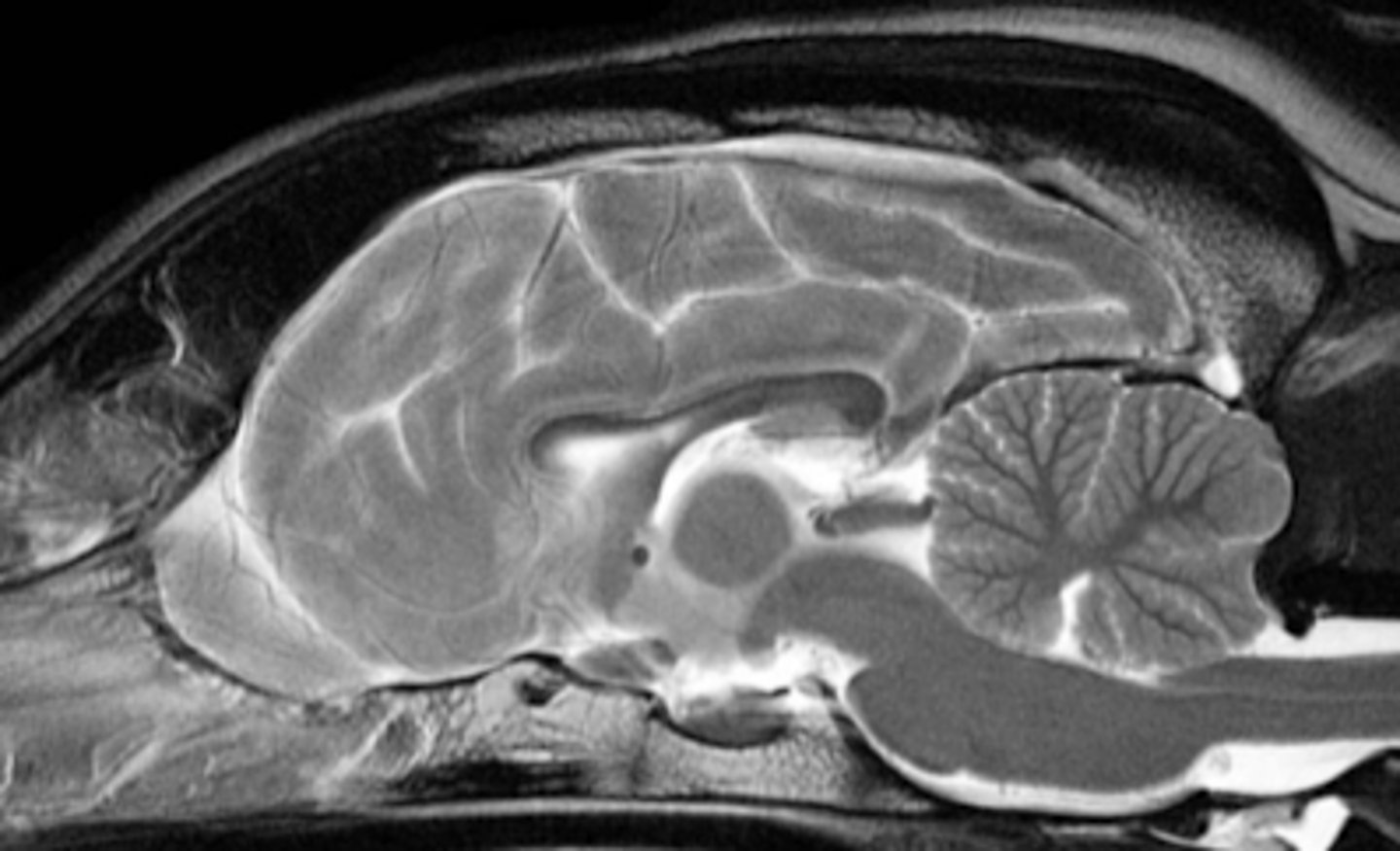
MRI
what diagnostic imaging technique was used to create this image?
CT- it uses xrays.
MRI has NO biological effects
which is more dangerous for the body- CT or MRI?
NONE
what biological effects does MRI have?
-cannot be used in animals with any metal inside of them- even a microchip needs to be removed first
-requires 100% immobility of the patient (anesthesia)
-expensive
-takes a long time to receive the images
what are the disadvantages of using an MRI?
MRI
which type of imaging can we NOT use for an animal with any metal inside of them (even a microchip)?
yes, 100%
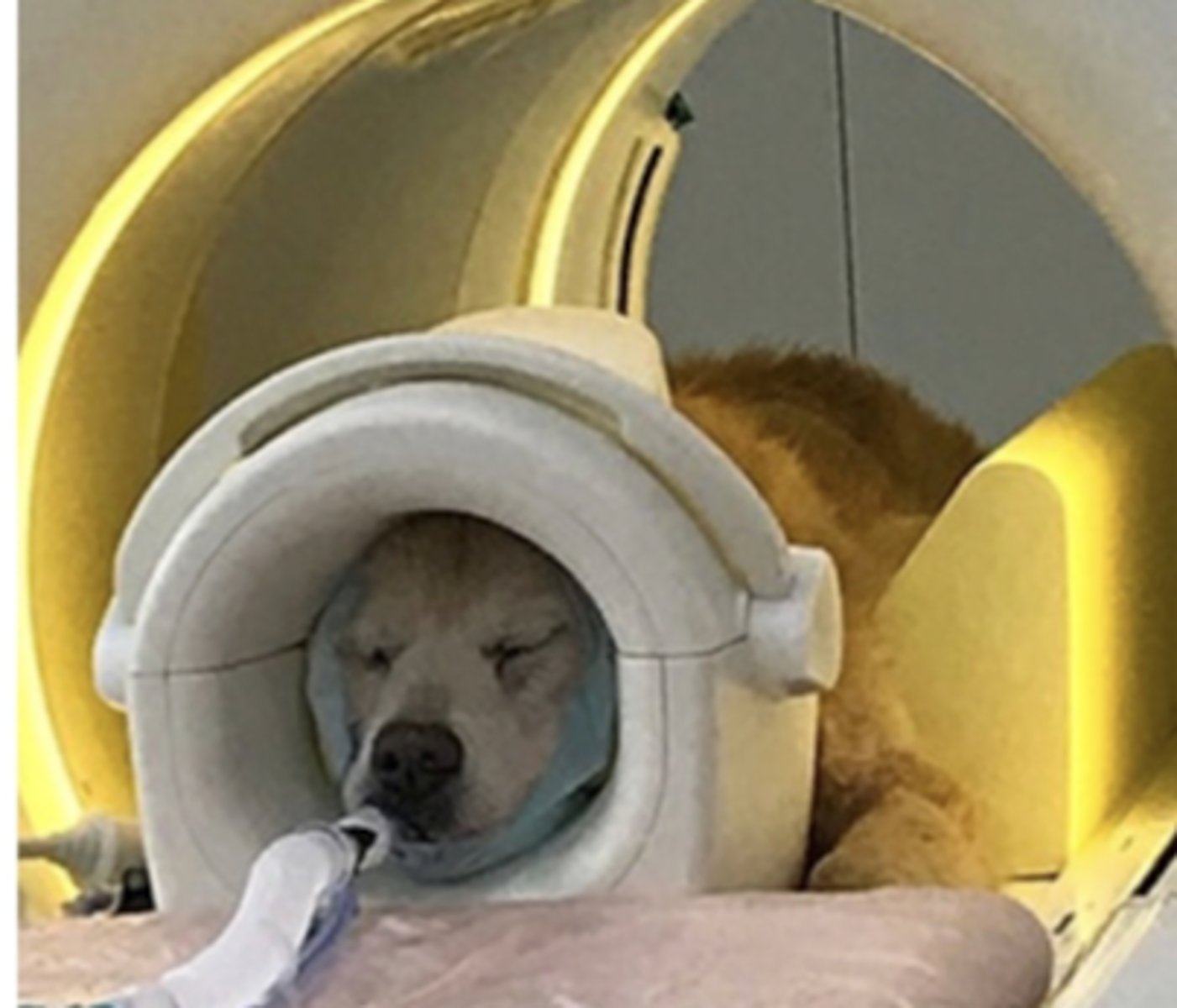
must we anesthetize the patient for an MRI?
sometimes, but usually just sedation is good
must we anesthetize the patient for a CT?
sometimes, but usually just sedation is good
must we anesthetize the patient for a radiograph?
hyperintense
for an MRI, a structure that appears white is called...
grey
in MRI, an isointense structure appears in what color?
hypointense
in an MRI, a black structure is called....
MRI
what is this type of imaging called?
a type of diagnostic imaging that uses ultrasound waves to pass through different structures. these waves are reflected back to the probe depending on the tissue density, and the probe collects the echoes and transmits them into an image.
what is ultrasonography?
soft tissues
movement
what is ultrasound useful to visualize?
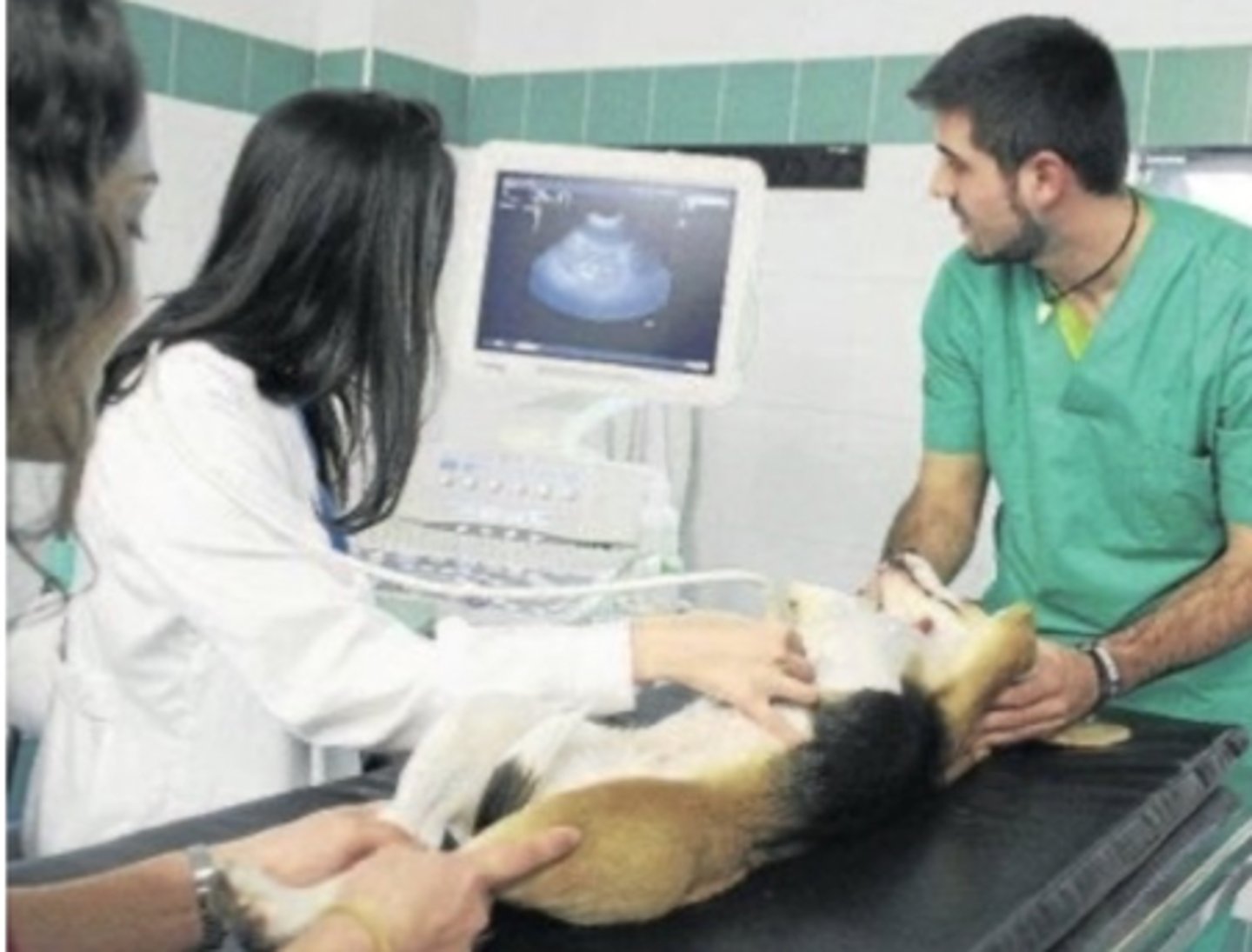
ultrasonography
what imaging technique is being used?
ultrasonography
fluoroscopy
which type of imaging is a dynamic study?
no. but sometimes requires sedation
does ultrasonography require anesthesia?
none- it is safe
what are the biological effects of ultrasounds on the patient/operator?
ultrasonography
these images were produced with what type of imaging?
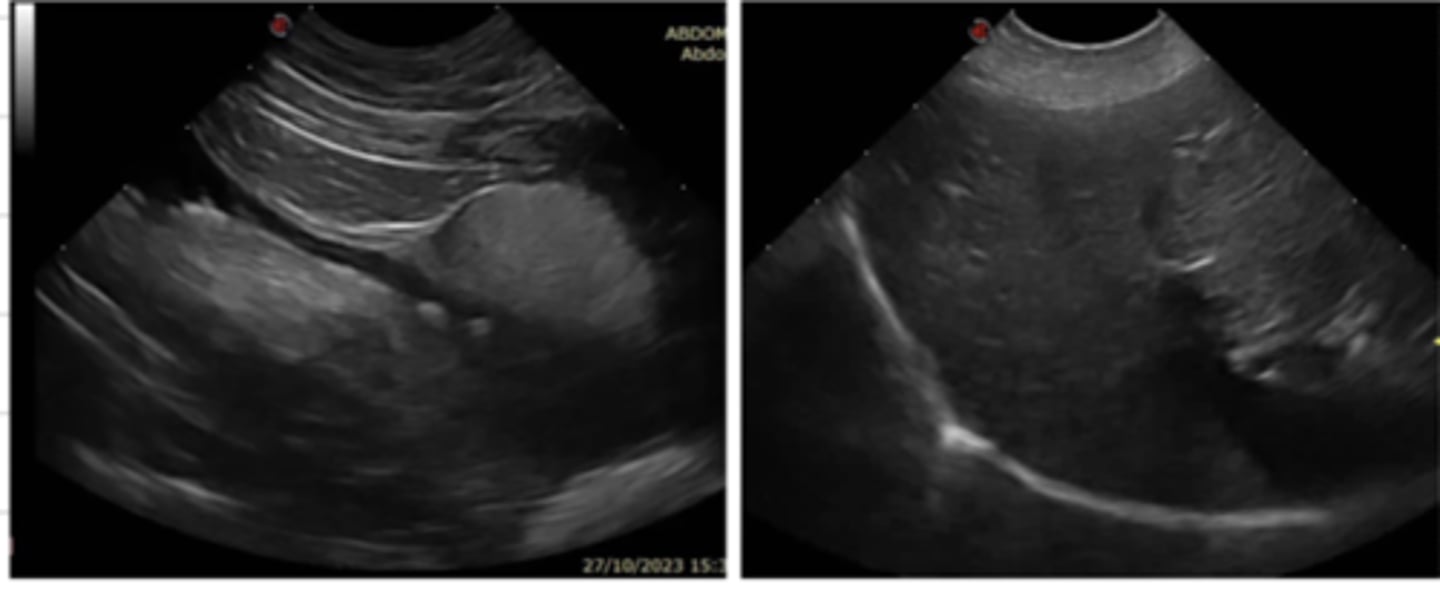
ultrasonography
this terminology is used for what type of imaging technique?
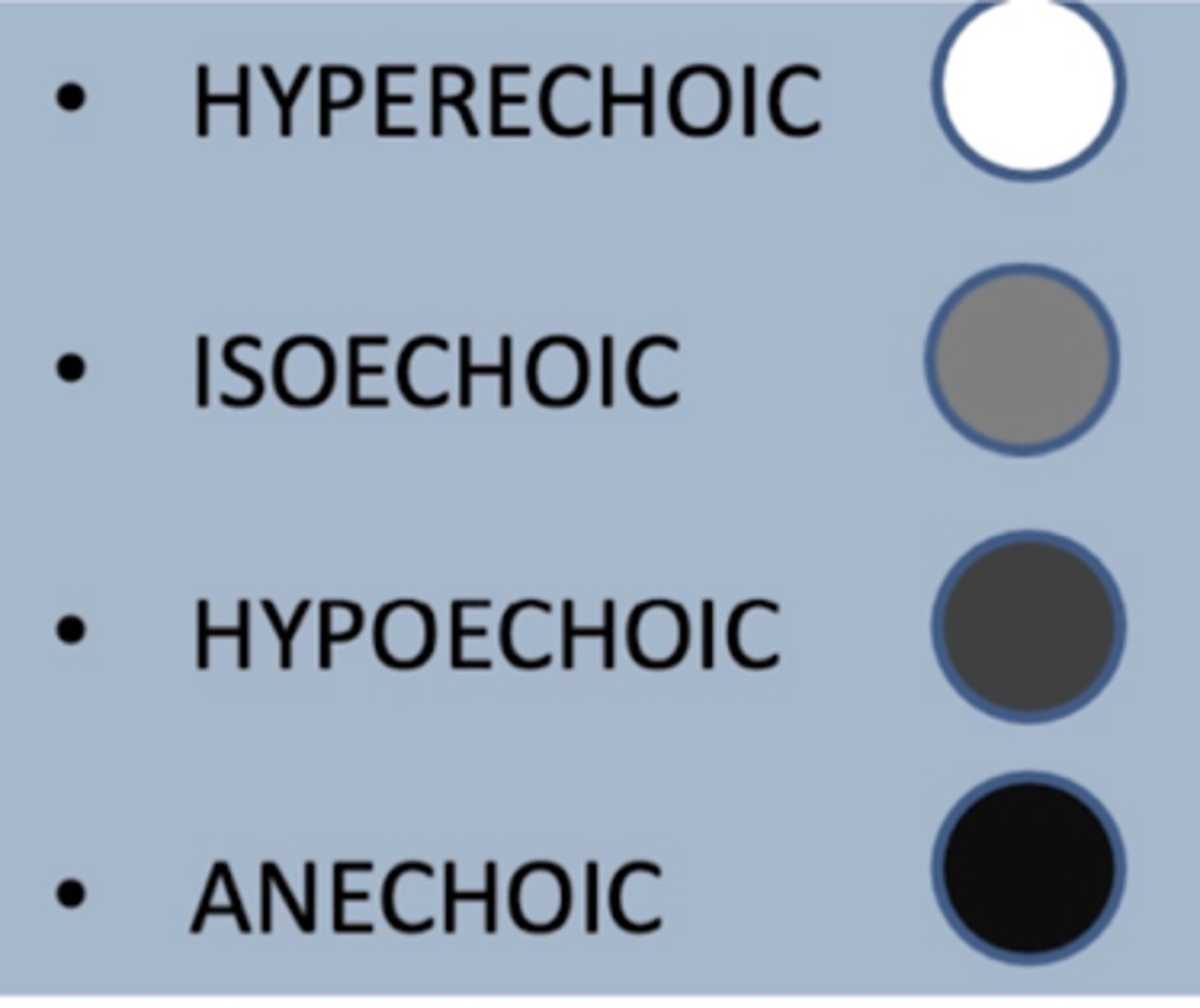
anechoic
in an ultrasound, a structure that appears black is called...
isoechoic
in an ultrasound, a structure that appears light grey is called...
dark grey
in an ultrasound, a structure that is hypoechoic appears in what color...
hyperechoic
in an ultrasound, a structure that appears white is called...
ultrasonography
radiography is complementary with what other imaging technique? (frequently performed together)
radiography
ultrasounds are frequently performed with what other imaging technique?
-abdominal ultrasounds
-pregnancy diagnosis
-echocardiography
-noncardiac chest ultrasounds
-ocular ultrasounds
-superficial tissues (neck, mammary glands, subcutaneous tissue)
-musculoskeletal ultrasounds
-fine needle aspirations/biopsies
what are the frequent uses of ultrasonography?
ultrasonography
what imaging technique is commonly used for pregnancy diagnosis?
ultrasonography
what imaging technique is commonly used to guide the vet for a fine needle aspiration or biopsy?
administering small amounts of radioactive materials, known as radioisotopes or radiotracers, via injection into the bloodstream, swallowing, or inhalation. They accumulate in specific organs or tissues in the body. The radiation emitted by these materials is detected by a gamma camera. it is used for detecting the functionality of specific tissues/organs
what is nuclear medicine?
nuclear medicine+ gammagraphy
what type of imaging is used to detect the functionality of different tissues/organs?
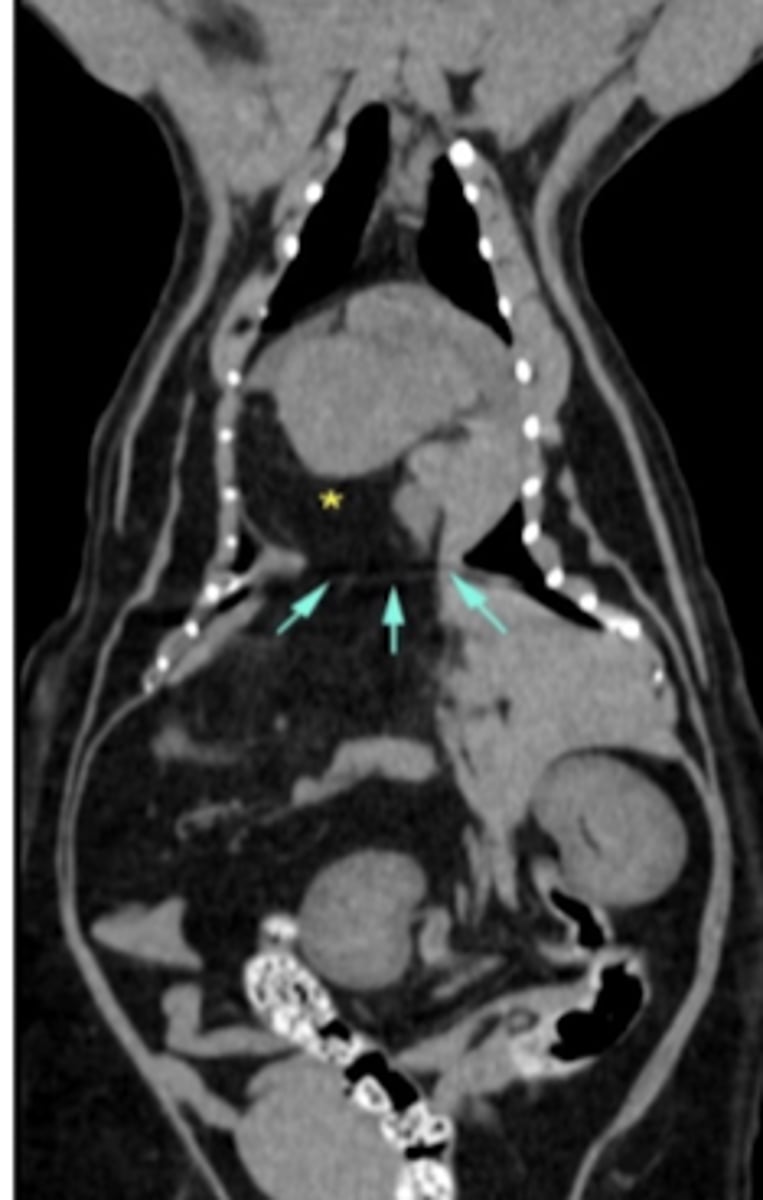
nuclear medicine+ gammagraphy
what type of imaging was used to produce these images?
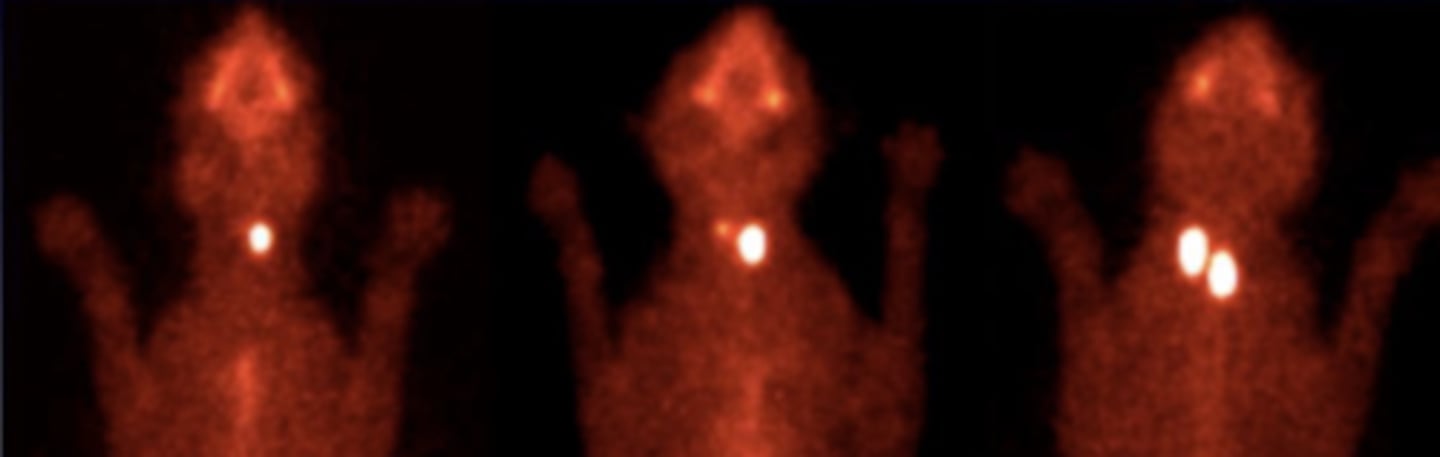
CT
MRI- most useful
which 2 imaging techniques are useful for visualizing the brain?
radiology (with contrast)
CT
MRI- best
which imaging techniques could we choose if we wanted to see the spinal cord?
radiology
CT- most useful
MRI
if we want to assess bone structures, what imaging techniques are the best?
radiology
ultrasound
CT- most useful
MRI
if we want to assess the respiratory tract, what imaging techniques are the best?
radiology
ultrasounds- most useful
CT
MRI
which imaging techniques could we choose if we wanted to see the heart/vessels?
radiology
ultrasounds
CT
MRI- most useful
which imaging techniques could we choose if we wanted to see the ligaments/tendons?
MRI
which is the best imaging technique for seeing ligaments or tendons?
CT
which is the best imaging technique for seeing the respiratory tract?
CT
which is the best imaging technique for seeing the skeleton?
ultrasound
(can also see with xrays, CT, MRI)
which is the best imaging technique for seeing the abdomen?
ultrasound
which is the best imaging technique for seeing the eye?
what is arteriography?