12 Alkanes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
radical
a species w an unpaired electron
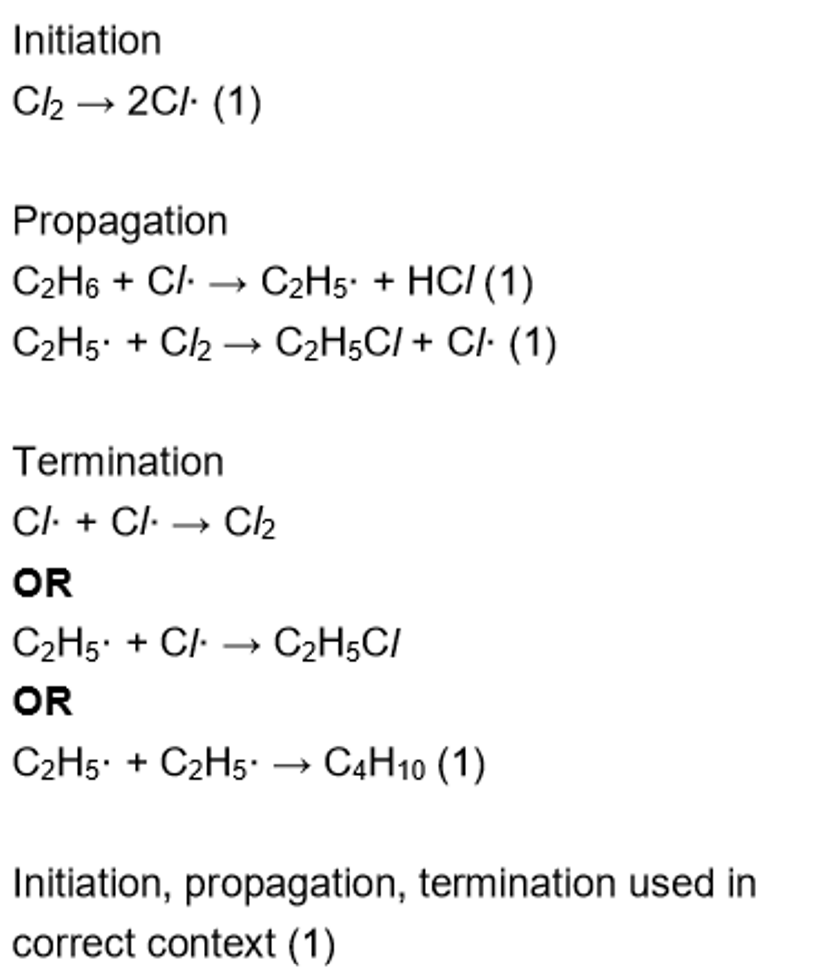
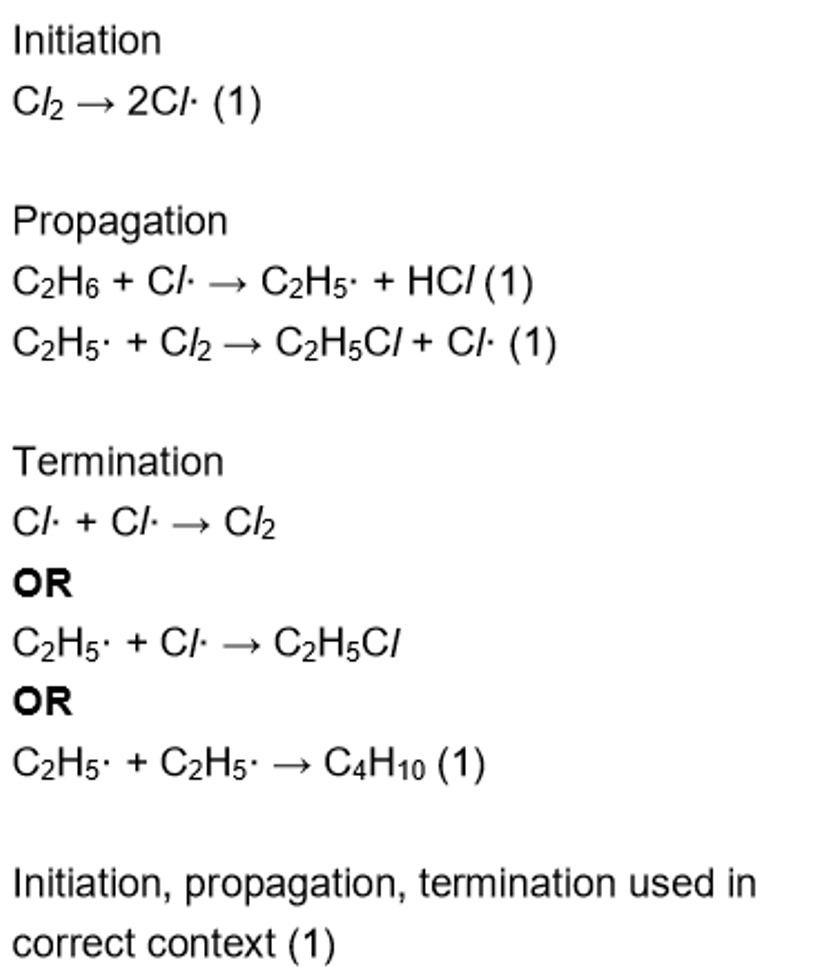
reaction mechanism for chlorine + ethane
alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons, containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms, joined w single convalent bonds
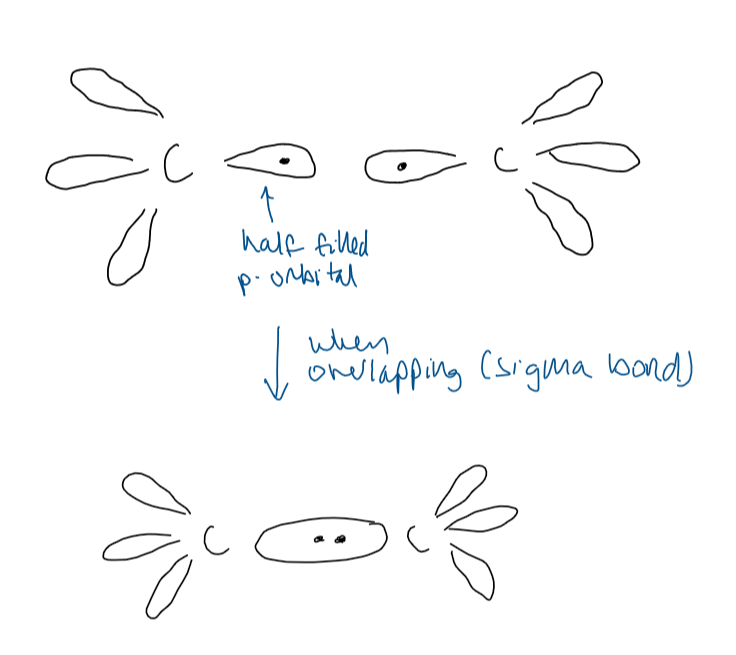
sigma bond σ
the result of the overlap of two orbitals, one from each bonding atom
single bond in alkanes
do σ sigma bonds have rotation
yes, they are not rigid
what shape would u expect around the C atoms in alkanes
tetrahedral
carbon has 4 bonding regions which r filled so 4 bond pairs
equal repulsion
diagram for 3D shape of ethane
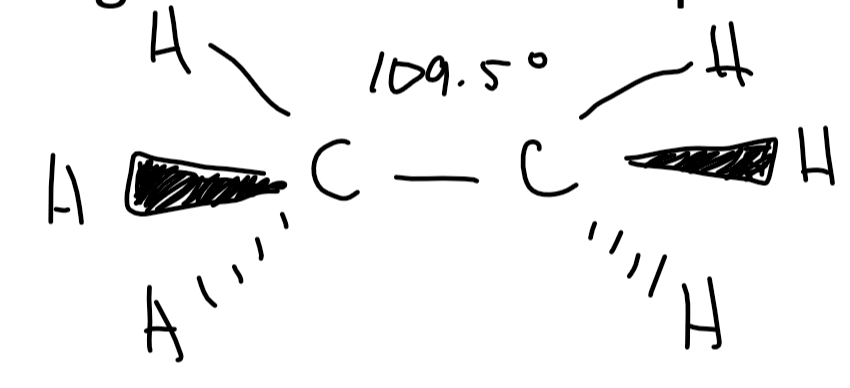
what process does crude oil undergo to extract alkanes
fractional distillation
what r fractions
a mixture of similar length hydrocarbons
where is the fractionating column the hottest
bottom
coldest at top
describe steps of fractional distillation
crude oil fed into column and vaporised (bitumen never vaporises tho)
rises and condenses in trays in fractions when its bpt is reached
cracking
the shortening of longer chained alkanes to make shorter, more useful chains
how does branching have an effect on bpt of alkanes
more branching = lower bpt
less branching means molecules are closer together
higher SA in contact
greater LF and IMF
more energy required to pull molecules apart
characteristics of small alkanes
low bpt
runny, low viscosity
easy to ignite, flammable
burns w clean flame
characteristics of big alkanes
high bpt
viscous
hard to ignite
burns w smoky flame
y do characteristics of alkanes change w increase in chain length
longer chain
more electrons
greater LF
more energy required to overcome LF
combustion tends to be less complete (smoky flame)
y don’t alkanes react w most common reagents
C-C and C-H sigma bonds r v strong
C-C bonds r non polar
electronegativity of C and H is so similar the C-H bond is considered non-polar
y are alkanes used as fuels
readily available
easy to transport
burn in a plentiful supply of oxygen w/out releasing toxic products
what do alkanes need to react w halogens and y
sunlight
the high energy UV radiation present provides the initial activation energy needed for the rxn to take place
what kind of reaction is bromination of alkanes
substitution
photochemical
which halogens will react w alkanes
bromine and chlorine
iodine isn’t reactive enough, fluorine too reactive
what is the mechanism for bromination of alkanes
radical substitution
steps for radical substitution
initiation
propagation
termination
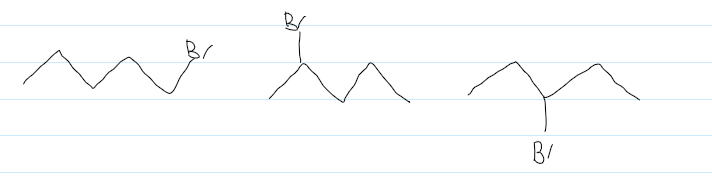
what r the limitations w radical substitution in organic synthesis
multiple organic compounds are formed
if C chain is longer than 2, a mixture of monosubstituted isomers will be made
reactions of alkanes
combustion
cracking
alkanes + halogens in sunlight

radical
what is a reactive intermediate that acts as a catalyst in alkanes + halogens in UV
radical
features of homologous series
each successive member differs by a CH2 group
similar chemical properties, gradually differing physical properties
same general formula
same functional group
describe how a sigma bond forms
overlap of orbitals directly between the bonding atoms