History and theory
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer.
The history of computer begins with the birth of ________ which is believed to be the first computer.
Nursing informatics
is a specialization in nursing that focuses on the use of data and information to enhance nursing practice, administration, education, and research
Mother board
is the central circuit board of a computer. Think of it as the backbone that connects all the other components. It houses the CPU, memory, and expansion slots, and it provides the pathways for data to travel between them. It also includes connectors for peripherals like the keyboard, mouse, and monitor.
Monitor
is the visual display screen that allows you to see the output from the computer. It displays images, text, and videos generated by the computer's graphics card.
Keyboard
is an input device that allows you to type text and commands into the computer. It translates keystrokes into signals that the computer can understand.
Mouse
is a pointing device that allows you to interact with the graphical elements on the screen. It controls the cursor, allowing you to select icons, open files, and navigate through menus.
ANA, 1992
A specialty that integrates nursing science, computer science, and information science in identifying, collecting, processing, and managing data and information to support nursing practice, administration, education, and research and to expand nursing knowledge. The purpose of nursing informatics is to analyze information requirements; design, implement and evaluate information systems and data structures that support nursing; and identify and apply computer technologies for nursing.
ANA, 1994).
“Nursing informatics is the specialty that integrates nursing science, computer science, and information science in identifying, collecting, processing, and managing data and information to support nursing practice, administration, education, research, and expansion of nursing knowledge. It supports the practice of all nursing specialties, in all sites and settings, whether at the basic or advanced level. The practice includes the development of applications, tools, processes, and structures that assist nurses with the management of data in taking care of patients or in supporting their practice of nursing.” (
Napier’s bones
It was also the first machine to
use the decimal point.
It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.
It is said that _______ invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.

Abacus
It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with
beads mounted on them.
China, Russia and Japan.
Abacus is still used in some countries like
____________.
NAPIER’S BONES
It was a manually-operated calculating device which was invented by John Napier
Pascaline
also known as Arithmetic Machine
or Adding Machine.
Blaise Pascal.
Pascaline was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician philosopher.
Pascaline
It was a wooden box with a
series of gears and wheels. When a wheel is
rotated one revolution, it rotates the
neighboring wheel.
STEPPED RECKONER OR LEIBNITZ WHEEL
It was a digital mechanical calculator which was
called the stepped reckoner as instead of gears it
was made of fluted drums
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz
STEPPED RECKONER OR LEIBNITZ W was developed by a German mathematician philosopher
DIFFERENCE ENGINE
It was a mechanical computer which
could perform simple calculations. It was a steam
driven calculating machine designed to solve tables
of numbers like logarithm tables.

Charles Babbage
DIFFERENCE ENGINE was designed by ________ who is known as the "Father of Modern Computer".
Analytical Engine
It was a mechanical
computer that used punch-cards as input. It was
capable of solving any mathematical problem and
storing information as a permanent memory
Charles Babbage
This calculating machine was also developed by________________in 1830
TABULATING MACHINE
It was a mechanical tabulator
based on punch cards.
Herman Hollerith
It was invented in 1890, by _____________ , an
American statistician
DIFFERENTIAL ANALYZER
It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It could do 25 calculations in few
minutes.
Vannevar Bush.
It was an analog device
invented by ___________
MARK 1
The next major changes in the history of computer
began in 1937 when Howard Aiken planned to
develop a machine that could perform calculations
involving large numbers.
In 1946, electronic pathways called
circuits were developed to perform the counting.
In 1946, electronic pathways called__________were developed to perform the counting.
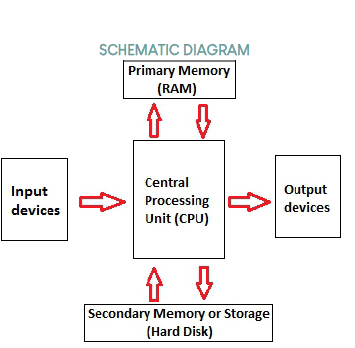
1. Input Devices
2. CPU
3. Output Devices
4. Primary Memory
5. Secondary Memory
There are 5 MAIN computer components
Inputting
Storing
Processing
Outputting
Controlling
THE OPERATIONS OF COMPUTER COMPONENTS
Inputting
It is the process of entering raw
data, instructions and information into the
computer. It is performed with the help of input
devices.
Storing
The computer has primary memory
and secondary storage to store data and
instructions.
Processing
It is the process of converting the
raw data into useful information.
Outputting
It is the process of presenting the
processed data through output devices like
monitor, printer and speakers.
Controlling
The control
unit ensures that all basic operations are
executed in a right manner and sequence.
INPUT DEVICES
enables the user to send data,
information, or control signals to a computer.
OUTPUT DEVICES
The output device displays the result of the
processing of raw data that is entered in the
computer through an input device.
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
also called a processor,
central processor, or microprocessor.
refers to all
physical components of a computer system,
including the devices connected to it.
WHAT IS COMPUTER HARDWARE?
1. Motherboard
2. Monitor
3. Keyboard
4. Mouse
Some of the commonly used hardware in your
computerare described below
Software
Is the general term applied to the instructions that direct the computers’ hardware to perform work
Software
Translate instructions created in human language into machine language. At the machine level, computers can only understand binary numbers, not English, or any other languages
Source Code
Fundamental component of a computer program that is created by a programmer. It can be read and easily understood by a human being
OPEN SOURCE
Any software satisfying the open software initiative’s definition (OSI). ; has access to the source code.
1) Freedom to use
2) Freedom to study
3) Freedom to redistribute
4) Freedom to improve the software in any way they wish
FREE SOFTWARE 4 fs
FREEWARE
software offered free of charge, but without the freedom to modify the source code and redistribute the changes
SHAREWARE
“TRY BEFORE YOU BUY” basis. If a customer continues to use the product after a short trial period, or wishes to use additional features, they are required to pay a specified, usually nominal, license fee
Skype
pidgin
U torrent
Example of freeware
Ardramax keylogger
internet download manager
AVG antivirus
Example of shareware
Concept
An abstract idea; a general idea or understanding of something.
Theory
A scientifically credible general principle that explains a phenomenon.
Concept
Term is used in different fields such as linguistics, sciences, philosophy, etc.
Theory
This term is mainly used in the field of science.
General systems theory
is one of the oldest theories that explain that systems are complex and intricate yet hold commonalities that can be explained and applied to almost any type.
Systems can be physical structures (education, healthcare, financing, etc.), manual (baking a cake, gardening, patient’s hygiene, etc.) or those that are electronic or computerized (electronic medical records, computerized provider order entry, automated medication dispensing, etc.)
Systems can be ________________(education, healthcare, financing, etc.), ____________(baking a cake, gardening, patient’s hygiene, etc.) or those that are _______________ (electronic medical records, computerized provider order entry, automated medication dispensing, etc.)
Von Bertalanffy
Who develop the general system theory
a. All systems must be goal directed
b. A system is more than the sum of its parts
c. A system is everchanging and any change in one part affects the whole
d. Boundaries are implicit and human systems are open and dynamic.
Von Bertalanffy (1969, 1976) developed General System Theory, which has the following assumptions:
Input
The raw materials that are transformed by a system.
Throughput
The activities involved in converting raw materials into a usable product or service.
Output
The final product or service produced by a system.
Input
Money, energy, and individual effort within a system.
Throughput
Thinking, planning, and decision-making processes.
Change theory
It's a framework for understanding how change happens, particularly in social systems, organizations, or even individuals
Kurt lewin
Who develop the change theory
unfreezing-change-refreeze.
Three-stage model of change:
driving forces, restraining forces, and equilibrium.
Change Theory has three major concepts:
Unfreezing is
creating an imbalance or some form of distraction to shake up the status quo between the driving forces (motivators for change) versus the restraining forces (factors that resist change)
The unfreezing stage
is such a crucial step in the change process because it creates some form of conflict that makes the scenario conducive to questioning the status quo. Once the imbalance is created, it is somewhat easier to influence change or to encourage resistors to consider and embrace the change
Moving
is when the actual change occurs, If prior to moving the restraining forces are stronger, at this stage, they have now become susceptible to change.
Refreezing
Change is then adopted and the driving forces become more dominant. However, for change to stick, the third step has to set in _________________, or assuring that change has indeed occurred and has been adopted.
Everett Rogers’ Diffusion of Innovation Theory
is one that is more suitable for unplanned change. It is a more arduous process and can sometimes takes a longer time.
Innovators
-They are quick to embrace change, and no matter the hurdles are, they will face them head on and keep the fight going.
Early Majority
-Most people who are motivated to accept the change fall under this category
Early Adopters
They listen to the change that is being introduced, ask some questions but generally adopts to the change.
Late Majority
-They do not understand or refuse to comprehend the need for change.
Laggard
They are the hard-core resistors. They do not like change. They will do anything to avoid accepting change, e.g., take a leave of absence, resign, retire, sick out, passive aggressive behaviors, etc.
Chaos theory
explores complex, dynamic systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. This sensitivity is often referred to as the "butterfly effect," where a tiny change in starting conditions can lead to drastically different outcomes.
Usable theory
focuses on how easy and efficient it is for users to interact with a system or product.
A _________is one that is effective, efficient, satisfying, and error-free.
Learning Theory
explore how people acquire, retain, and apply knowledge and skills. There are many different learning theories, each with its own perspective on the learning process.
RXBOX
______________ a biomedical device that helps health workers in remote areas consult with medical experts in urban areas. It was originally intended for trauma care at the Philippine General Hospital (PGH).
RXBOX
a telehealth device that helps people in remote areas access medical care
researchers from the University of the Philippines (UP) and the Department of Science and Technology (DOST).
Who developed the rxbox?
Dr. Alvin Marcelo, then NTHC director, and
Dr. Luis Sison of the UP Diliman College of Engineering
Specifically who developed the rxbox
ECG
Pulse oximeter
Thermometer
Sphygmomanometer
Doppler for fetal heart tone
Maternal tocometer
The RxBox sensor suite expanded to include a
Electronic Health Records
Telehealth and remote monitoring
Wearable Technology
Evolving Role of Technology in Nursing
Data Security
Interoperability
Digital Divide
Sociotechnical Challenges to
Digital Health Integration
Data Security
Ensuring patient privacy and
data security is paramount
in the digital health
environment.Data Security
Interoperability
Seamless data exchange
between different
healthcare systems is critical
for effective care
coordination.
Digital Divide
Addressing disparities in digital access and literacy is essential
for equitable healthcare delivery.
Training and Education
Digital Literacy
Access to Technology
Lack of Digital Skills and
Access for Nurses
Training and Education
Nurses require comprehensive
training in using digital tools
effectively.
Digital Literacy
Bridging the gap in digital
literacy among nurses is
essential for successful
implementation of technology.
Access to Technology
Ensuring access to reliable
technology and internet
connectivity for nurses is
critical.
Data breaches can compromise sensitive patient information.
Strong cybersecurity measures and data encryption protocols are essential.
Transparency and patient consent are crucial for
safeguarding privacy.
Patient Privacy and Data
Security Concerns
Fear of the Unknown
Some nurses may resist change and be hesitant to adopt new technologies.
Lack of Support
Providing adequate training, technical support, and resources is crucial for successful adoption.
Focus on User-Friendliness
Designing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces is key for minimizing resistance.
Resistance to Change and
Adapting to New Technologies
Ethical considerations
The ethical implications of emerging technologies require careful consideration.
Data Integrity and bias
Ensuring data accuracy and minimizing bias in AI-powered tools is crucial.
Human centered approach
Technology should augment, not replace, the essential
human connection in nursing.