Grade 8 Science Unit 5-Fresh and Salt Water Systems
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Evaporation, Condesation, Precipitation, Groundwater, Run-off
Name the five stages of the water cycle in order starting from evaporation.
Groundwater: 0.63%
Rivers, lakes, ponds: 0.02%
Glaciers and icebergs: 2.15%
Oceans and Sea: 97.20%
Starting from the top name the water supplies that corresponds to the right percentage.
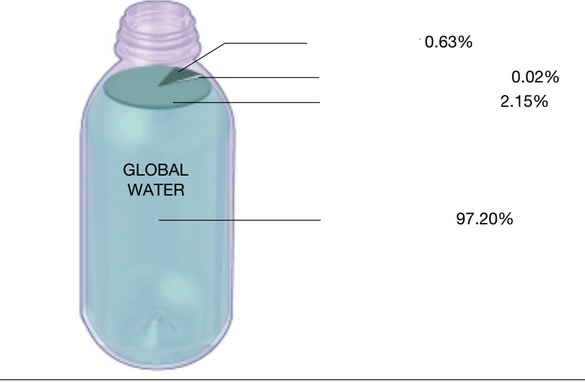
97%
What percent of Earth’s Water is salt?
0.5 percent of Earth’s water is found as liquid fresh water.
What percent of Earth’s water is liquid fresh water.
the characteristics of a water resource that make it
suitable or unsuitable for various uses.
What’s water quality?
the amount of water
What’s water quantity
This moving mass of
ice and snow is called a glacier.
What’s a glacier?
a large dome-shaped glacier that flows outwards from its centre and covers a large area, especially of land.
What’s an iceberg?
an area that feeds two or
more glaciers
What’s an icefield?
a frozen waterfall made
when a glacier flows over a steep
cliff
What’s an icefall?
Glaciers form when snow accumulates, and the weight of new layers compresses the snow below. Snowflakes gradually turn into rounded grains, then ice crystals, and finally solid ice. As the glacier melts and refreezes, air is squeezed out and the snow becomes denser. At least 30 meters of snow must build up for pressure to turn it into glacial ice.
How Does a Glacier Form?
Valley glaciers are found in mountainous regions, are smaller and flow down mountains, while continental glaciers are massive ice sheets that cover large areas of land.
What’s the difference between a valley and a continental glacier?
A crevasse
is a fissure, or crack, in the ice,
What’s crevasse?
Both move and flow, shape the land, both carry materials
How are glaciers and rivers similar?
An advancing glacier is growing and flowing downhill but a retreating glacier is shrinking and seems like its moving uphill.
What’s the difference between an advancing and retreating glacier?
a floating sheet of ice
rarely more than 5 m thick that
breaks easily]
What is pack ice?
Icebergs are large chunks of ice that
break loose, or calve, from continental
glaciers as the glaciers flow downslope
into the ocean
What are icebergs?
Glaciers erode land as they move, acting like bulldozers by pushing and picking up loose material. Meltwater seeps into rock cracks, refreezes, and breaks the rock apart. Glaciers carry the broken rocks, which scrape the ground beneath, causing more erosion.
How goes glacial erosion work?
striations,
are parallel scars or scratches. Striations show in which direction the
glacier moved.
What are striations?
bowl-shaped basins
What is a cirque?
Sometimes two or more glaciers erode a mountain
summit from several directions. This can form a ridge called an arête.
What is an arête?
sharpened peak form from two glaciers eroding a mountain in different directions.
What is a horn?
because a glacier
plucks and scrapes soil and rock from the sides as well as from the
bottom
Why are valleys eroded by glaciers U-shaped and not V-shaped?
As glaciers melt and slow down, they drop the sediment they were carrying. This mixed material, called till, includes boulders, sand, silt, and clay. When till piles up at the front of a glacier, it forms a moraine, a ridge or hill-like deposit. Outwash is sediment carried by meltwater and laid down in layers. If meltwater flows beneath the glacier, it can leave behind a winding ridge of sand and gravel called an esker.
Explain how the terms moraine, esker, and outwash happen.
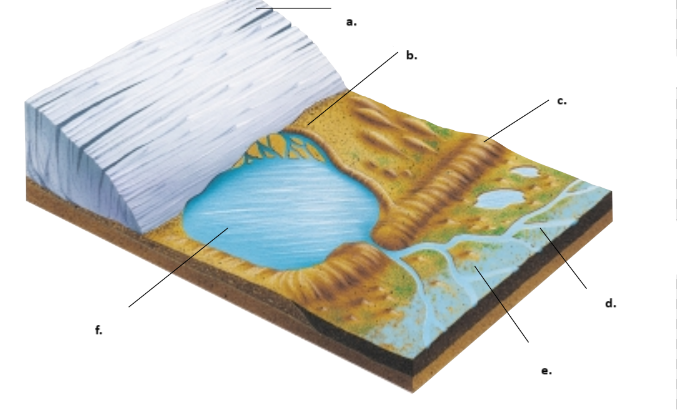
a. -retreating glacier
b. -esker
c. -moraine
d. -glacial stream'
e. -outwash plain
f. -moraine damned lake
Label each one.
meltwater — water formed by the melting of snow and ice
— carves channels in and through glaciers.
millwell. This is a rounded drain in the ice chis-
elled by a stream as it plunges downward.
What is millwell and meltwater?
-They store a significant amount of earth’s fresh water
-They can provide info about the past including ice ages
-They slow down the water cycle
Why are glaciers important?
Seven
At least how many ice ages had earth had?
11,000 years ago.
How long ago did the most recent ice age end?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where gases like carbon dioxide trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere, making life possible. Global warming refers to the recent rise in Earth's average temperature, possibly caused by an increase in greenhouse gases. This warming may lead to melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and more flooding in low-lying areas.
Tell me about the greenhouse effect and global warming.
In a pond, sunlight reaches all the way to the bot-
tom. In a lake, sunlight does not reach the bottom.
What’s the difference between a lake and pond?
a measure of how clear
something is, including water;
determined by the amount of
matter suspended in it
What’s clarity?
the area of land that drains into a body of water
What is a watershed?
Water that doesn’t soak into the ground or evaporate but
instead flows across Earth’s surface is called run-off.
What’s run-off?
The Continental Divide is a line of high land that separates the flow of rivers.
Water on one side flows toward the Pacific Ocean.
Water on the other side flows toward the Atlantic Ocean (or Arctic Ocean in some areas).
In North America, the Continental Divide runs along the Rocky Mountains.
What is the Continental Divide?
The upstream
areas of a watershed are called the
headwaters. The end point of the
water flowing through a watershed
is called the outflow.
What is the headwaters and outflow?
Run-off in cities is usually much higher than in natural areas like wetlands, forests, or prairies, where water can soak into the ground.
Why is the more run-off in the cities?
Slope of land, amount of rainfall, how fast the rain falls, and vegetation.
What effects run-off if it will flow down or soak into the ground?
When the river is less steep or slower-flowing Sediment is deposited on the riverbed or along the banks.
Why does deposition happen in a river?
Streamflow is the amount of water dis-
charged by a watershed. measuring the amount of water
(volume) that flows past a certain point over a period of time
What’s streamflow?
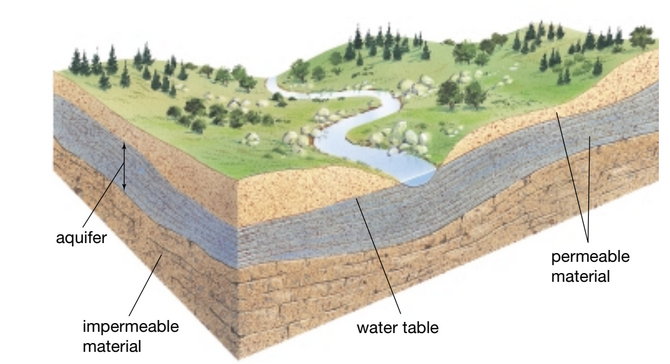
Aquifer: system of water flowing through
porous rock
Water table: The layer of porous rock
in which all pores are full of water
Permeable Material: Part of the ground where water can sink and pass through
Impermeable Material: Water can’t sink through.
Describe the parts listed here.
Point sources are
those where the source of a pollutant is from a small, defined area.
Non-point sources
are those where a pollutant comes from a wide area.
What’s the difference between point and non-point sources?
The measure of the amount of salts
dissolved in a liquid is known as salinity.
What’s salinity?
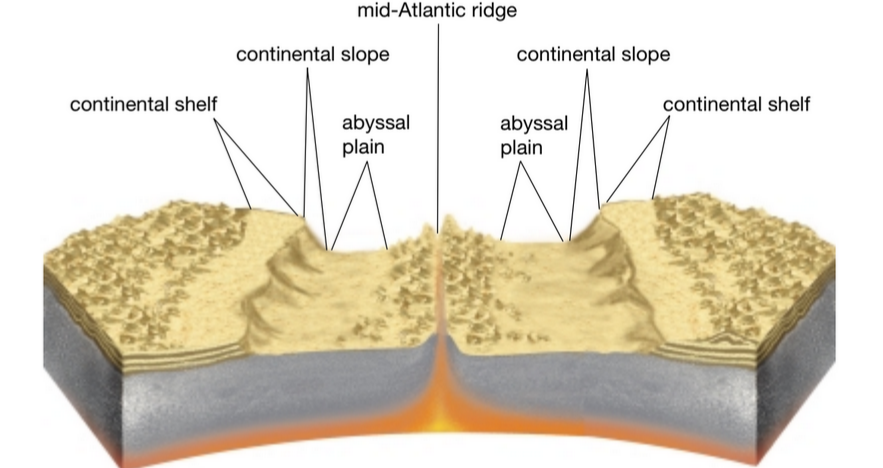
Abyssal Plains: Wide, flat open plains formed of thick deposits of sediments
Continental Shelf: Continental shelves slope gradually away from the land before dropping steeply downward at the shelf edge.
Continental Slope: The steep and fast drop after the shelf.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge- Chain of underwater mountains specifically in the Atlantic Ocean
Describe the features you see here
narrow, steep-sided
canyons
What are trenches?
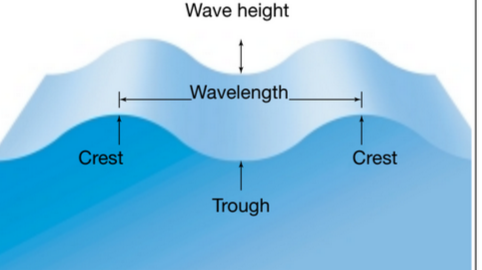
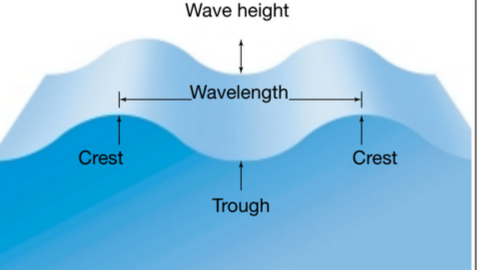
Large ripples in the water set in motion by the wind.
What are waves?
Smooth waves near the shore
What are swells?
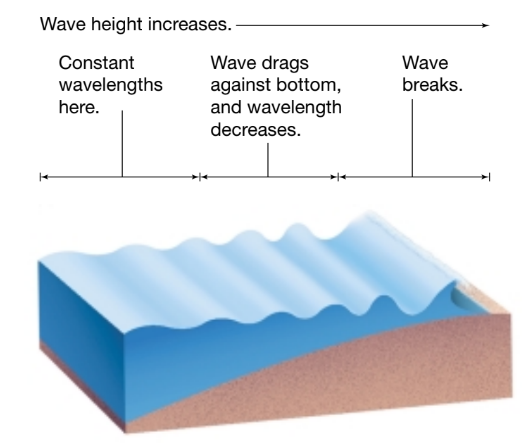
What happens in a breaker wave?
Types of walls to protect against waves.
What are jetties and groins?
Beaches form when rock fragments carried by waves are ground into smaller pieces like sand and pebbles.
How are beaches formed?
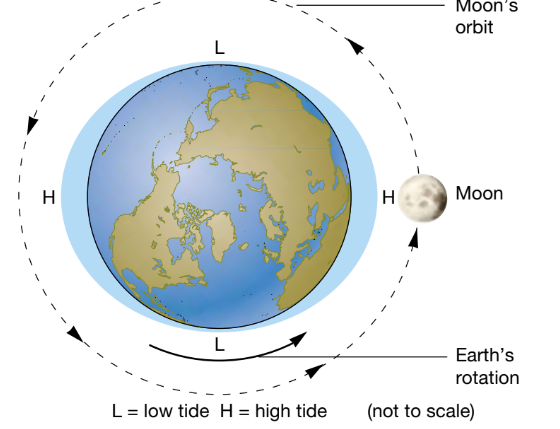
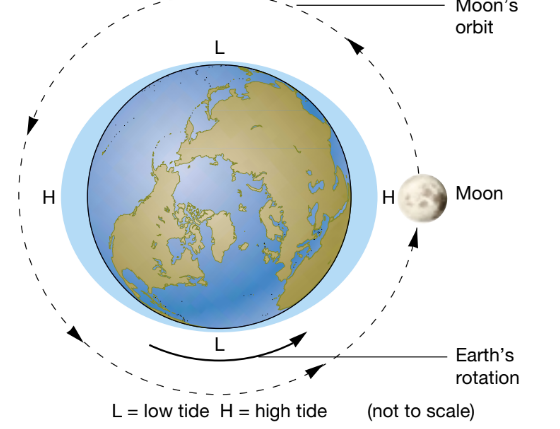
The largest tidal movements (called
spring tides) occur when Earth, Moon, and Sun are in a line. At these times, tides are extra high and extra low.
What happens to the earth moon and sun during spring times. And what are spring tides?
At these times, tides are extra high and extra low. The
smallest tidal movements (called neap tides) occur when the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other. On these days, there is little difference in depth between high and low tides.
What happens to the earth moon and sun during neap tides. And what are neap tides?
Tidal movements
result mainly from the pull of the Moon’s gravity on the ocean.
What celestial body influences the tides?
These winds, called trade winds,
push ocean currents toward the west. Toward the polar regions, westerly winds drive currents the opposite way, from west to east,
What is the difference between trade and westerly winds?
Uneven heating of the atmosphere; rotation of Earth; and the continents.
What three factors influence surface currents?
The thermocline
What is the layer of the ocean called when the temperature starts to rapidly decrease?
the thermal energy
needed to raise the temperature of
1 kg of a substance, such as water,
by 1°C
What is heat capacity?
Wind speed – Stronger winds create taller waves.
Wind duration – The longer the wind blows, the higher the waves can grow.
Fetch – The distance over open water that the wind blows; a longer fetch allows waves to build up more height.
Three things that make up a waves height
The Coriolis effect is the way Earth’s rotation causes moving air and water to curve instead of moving in a straight line
What is The Coriolis effect?
tiny, plant-like organisms that live in water. they are the base of the aquatic food chain because there are so many of them and zooplankton feed off them. they produce oxygen so organisms can live.
What are phytoplankton?
A root-like structure that will anchor seaweed under water so they don’t drift away and can gather nutrients from the soil and water.
What is Holdfast?
detritus—
the decaying bodies of dead plants and animals.
What is detrius?
When there is extra nutrients in the water more algae will grow and when the plants die they sink to the bottom and decay and decomposing and will take up a lot of oxygen so other organisms will begin to die.
What is algal bloom?
Biomagnification: concentration of
a toxin as it moves up through the
food chain
What is biomagnification?
Organisms deep in the ocean use these vents to survive from the chemicals that flow through the cracks.
What is the importance of sea-floor vents?
Water that contains lots of dissolved calcium and magnesium and sodium.
What is hard water?
treated sewage, urban and agricultural run-off, air pollution etc.
what are some human activities that effect water quality
a organism that is sensitive to changes in it’s environment
What’s a Bioindicator Species?
Drinkable
If water is potable then its..?

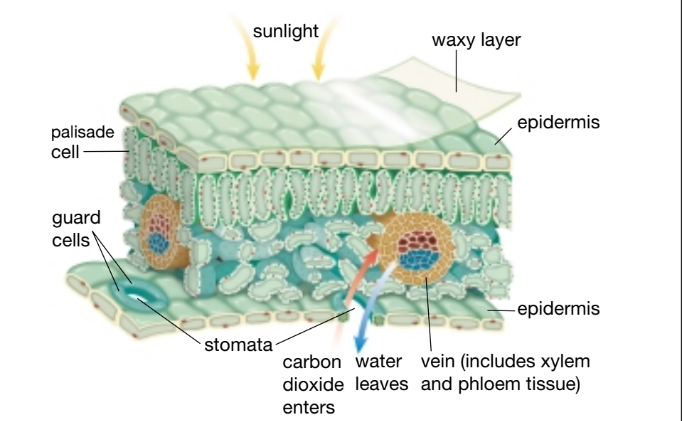
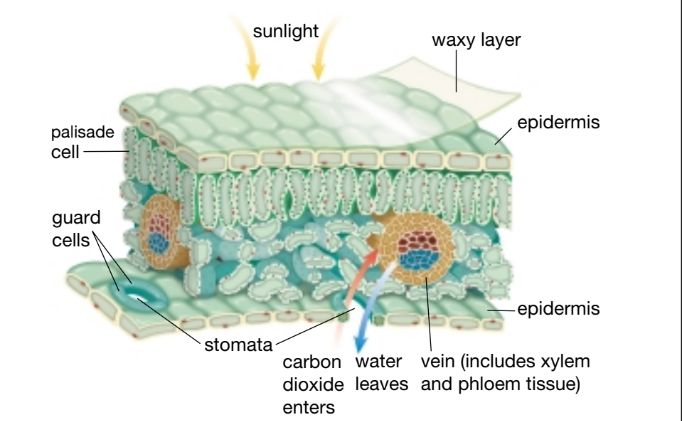
Phloeum tissues transport sugar and xylem transports water and minerals.
What are the two types of vascular tissues and what do they do.
This loss of water from a plant through
evaporation is called transpiration.
What’s transpiration