RHS exam prep
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
periapical
radiographic image showing the crown, root tip, & surrounding structures
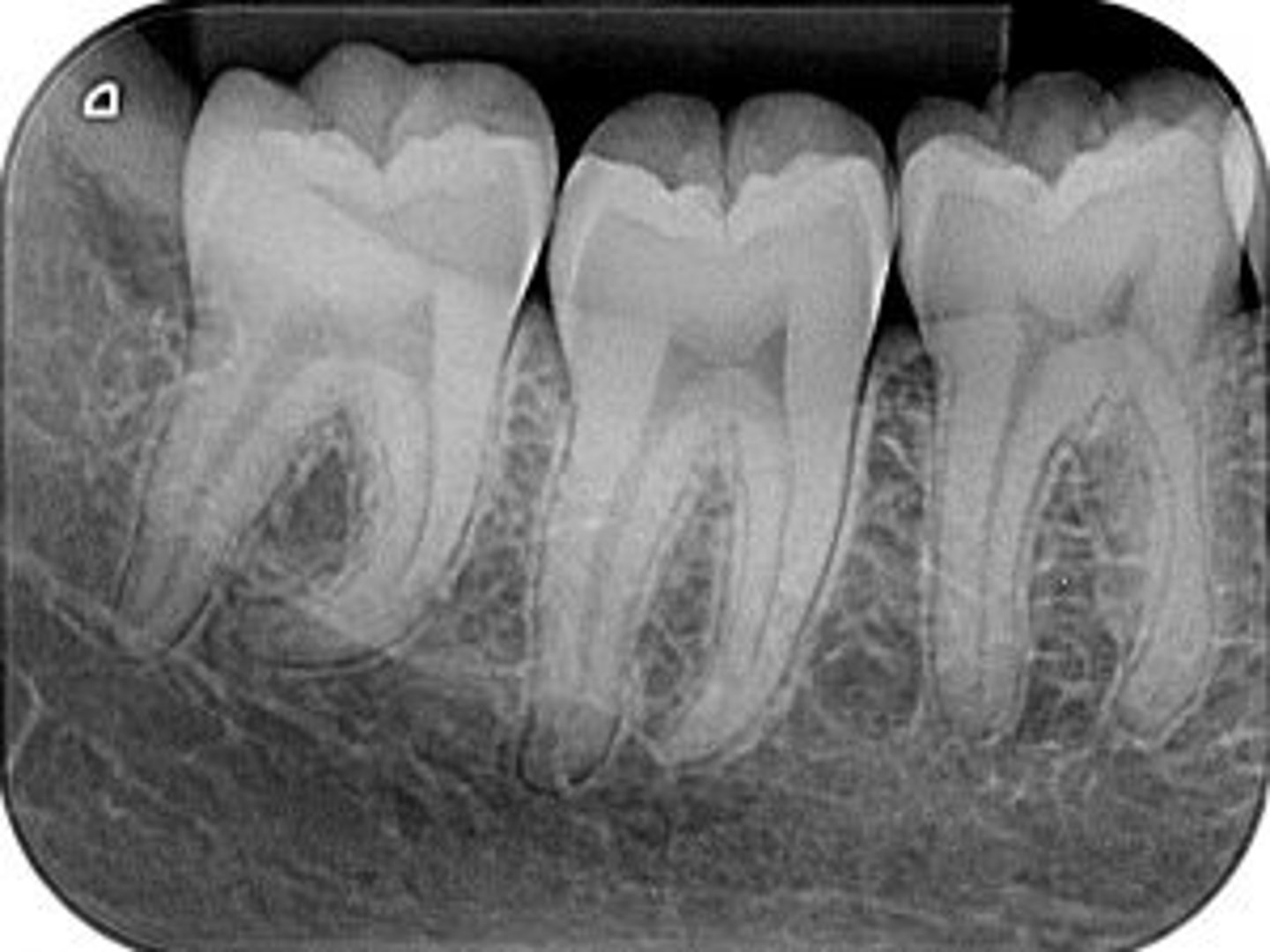
periapical radiographs used to detect:
any abnormalities of the root structure & surrounding bone structure

Bitewing radiograph
image view showing the crowns of both arches on one film
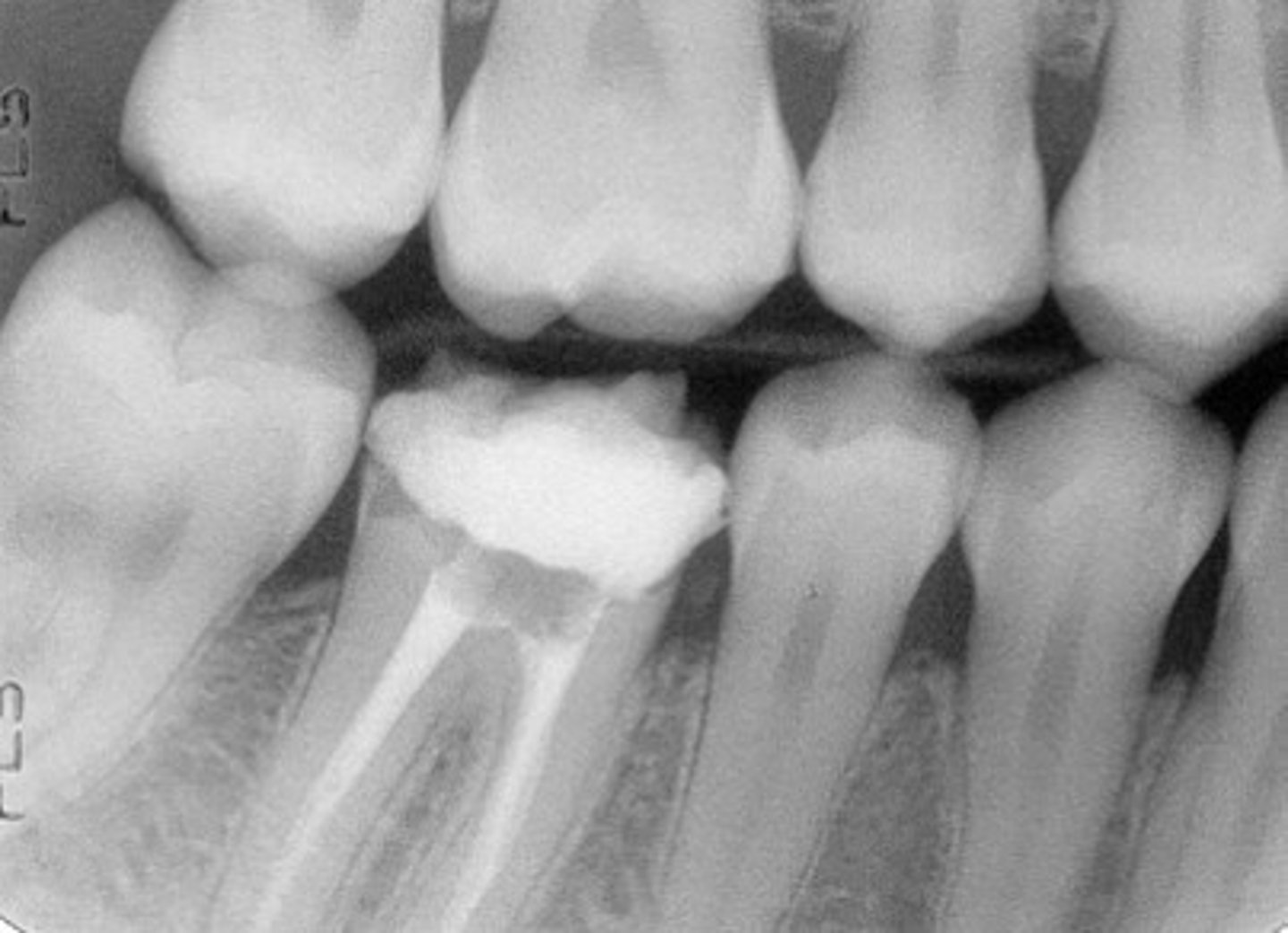
bitewing radiographs used to detect:
or monitor interproximal caries if the proximal surfaces of the teeth cannot be visually tactilely examined
full mouth series radiograph
is composed of a series of individual images, including a combination of bitewing & periapical
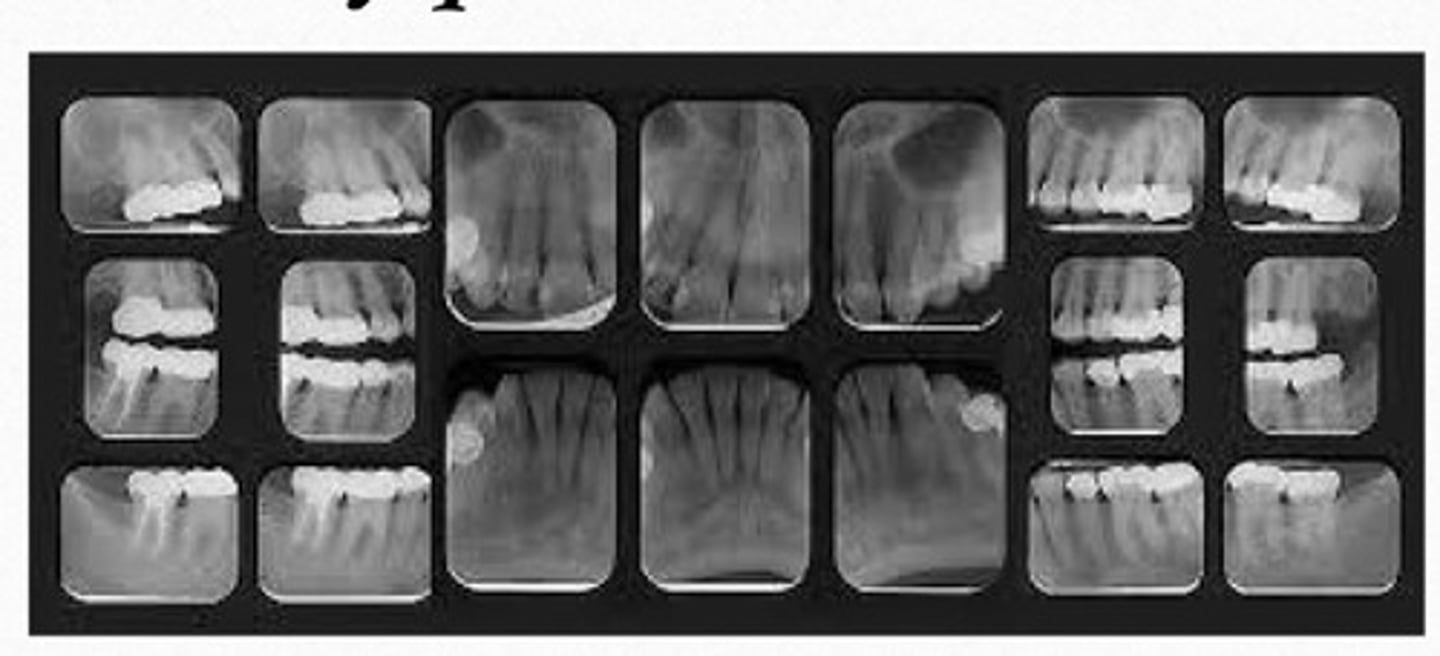
purpose of full mouth series:
as a baseline on the health of your mouth
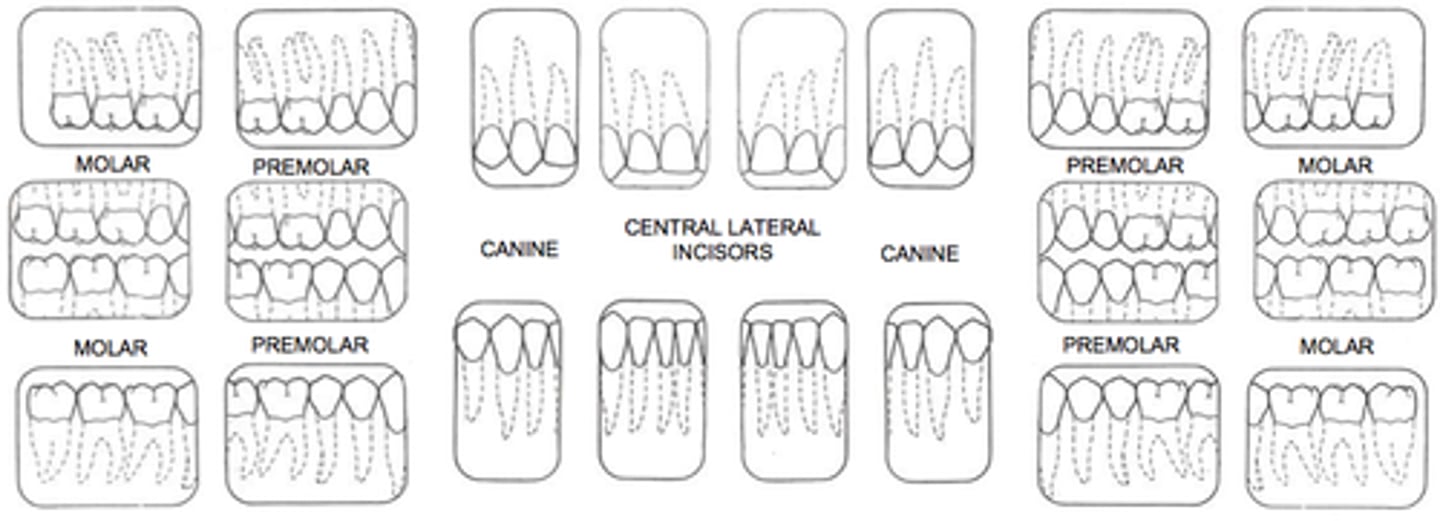
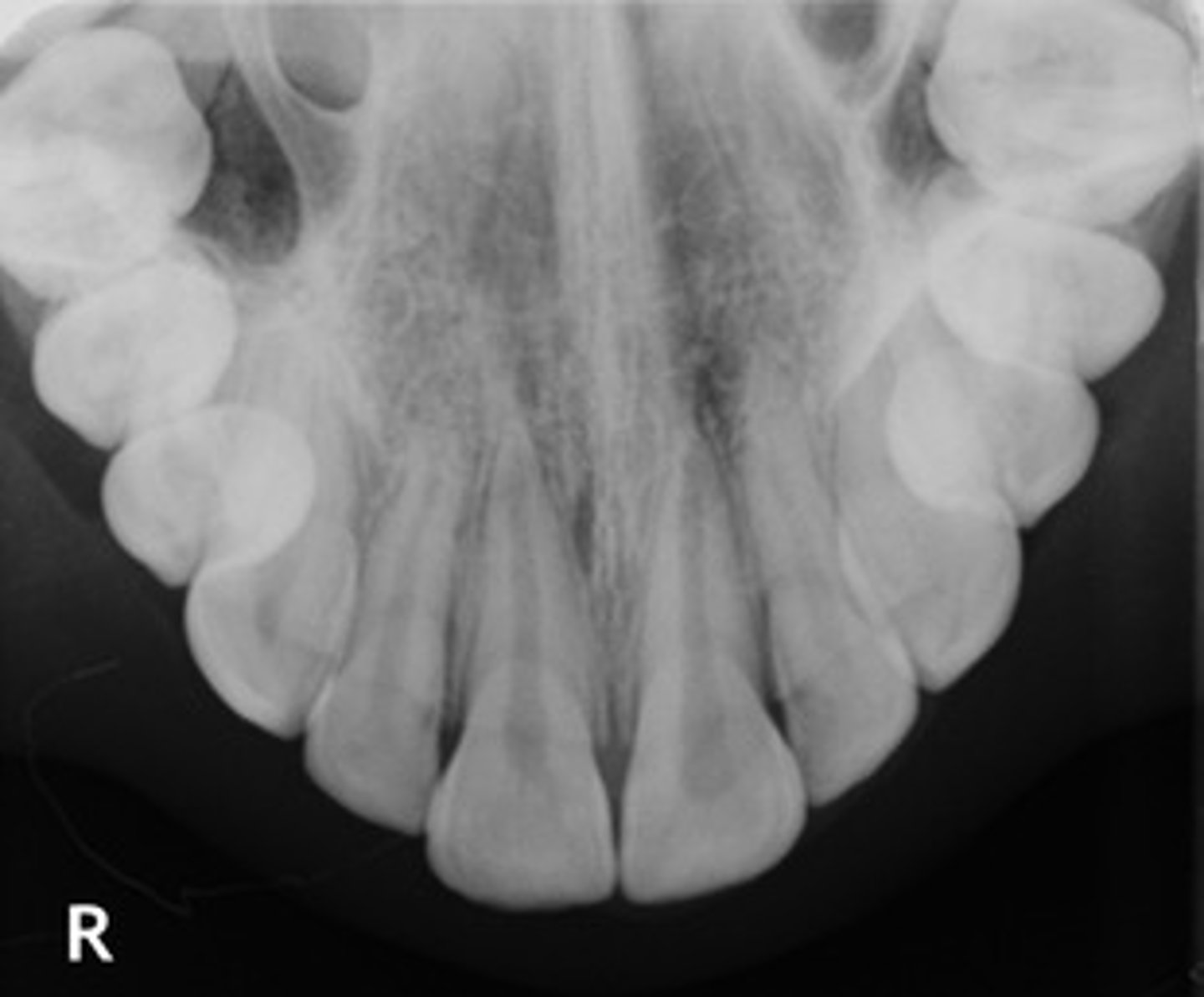
Occlusal radiograph
image that shows large areas of the maxilla or mandible
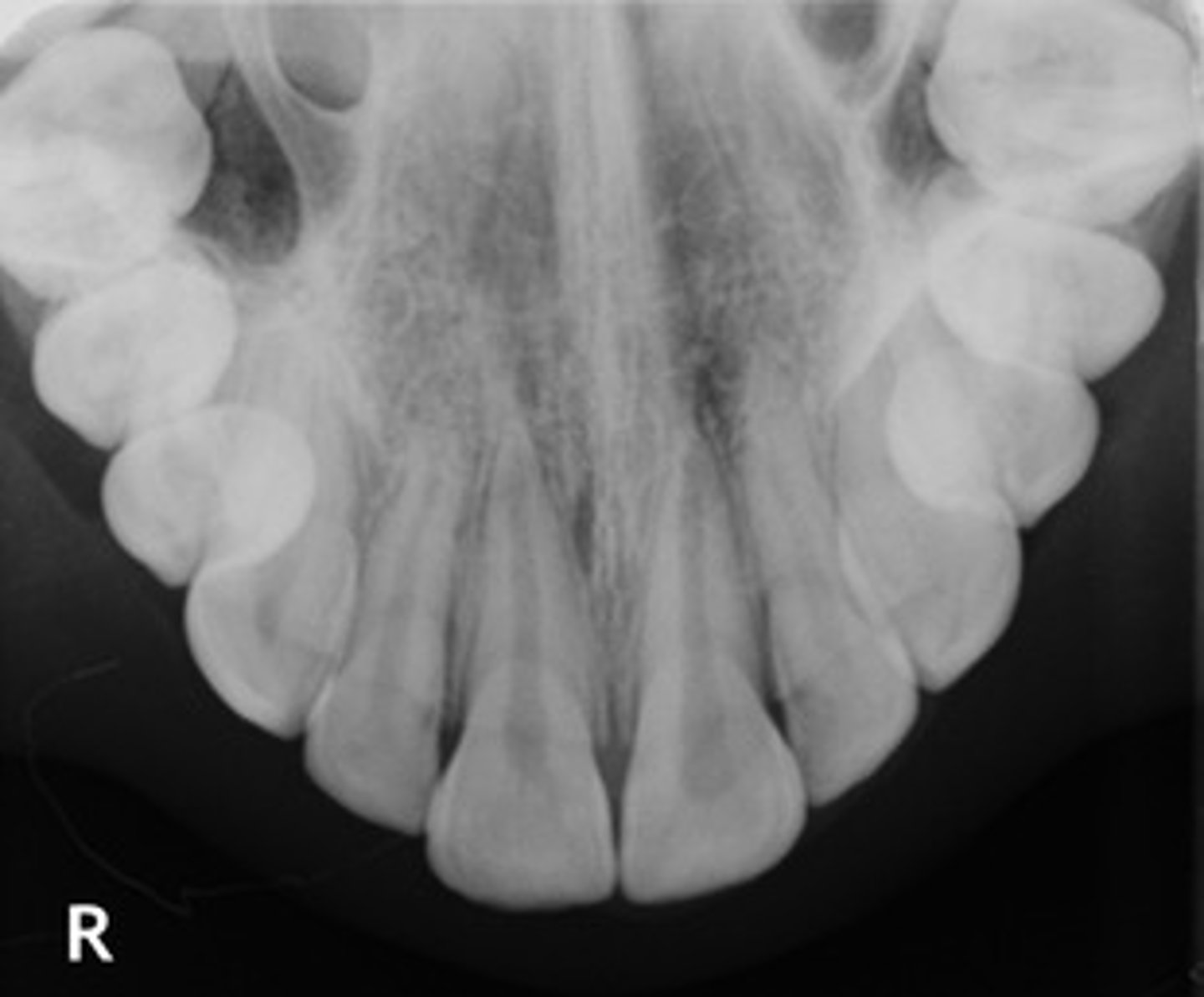
Occlusal radiograph purpose:
help track the development & placement of a section or entire arch of teeth in the upper or lower jaw
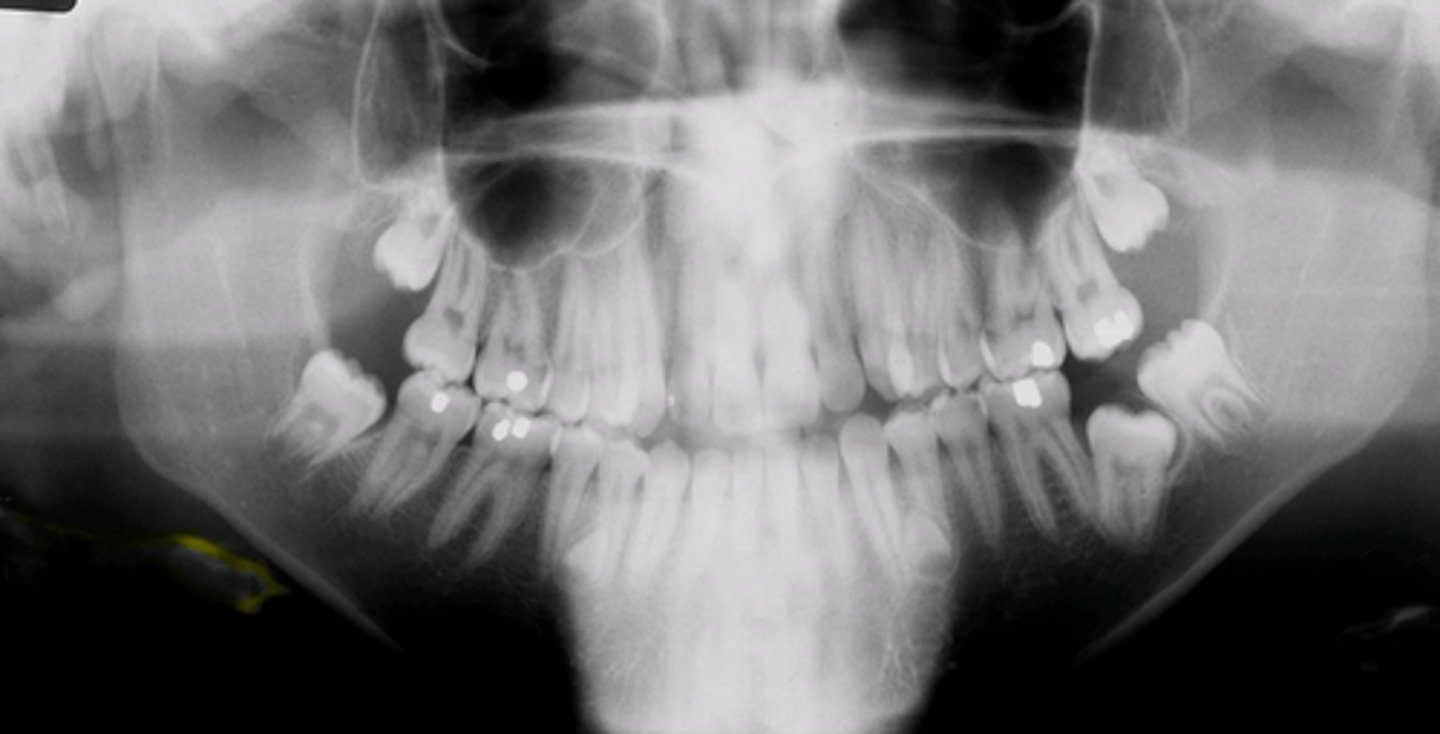
panoramic radiograph
provides full view of the upper & lower jaw
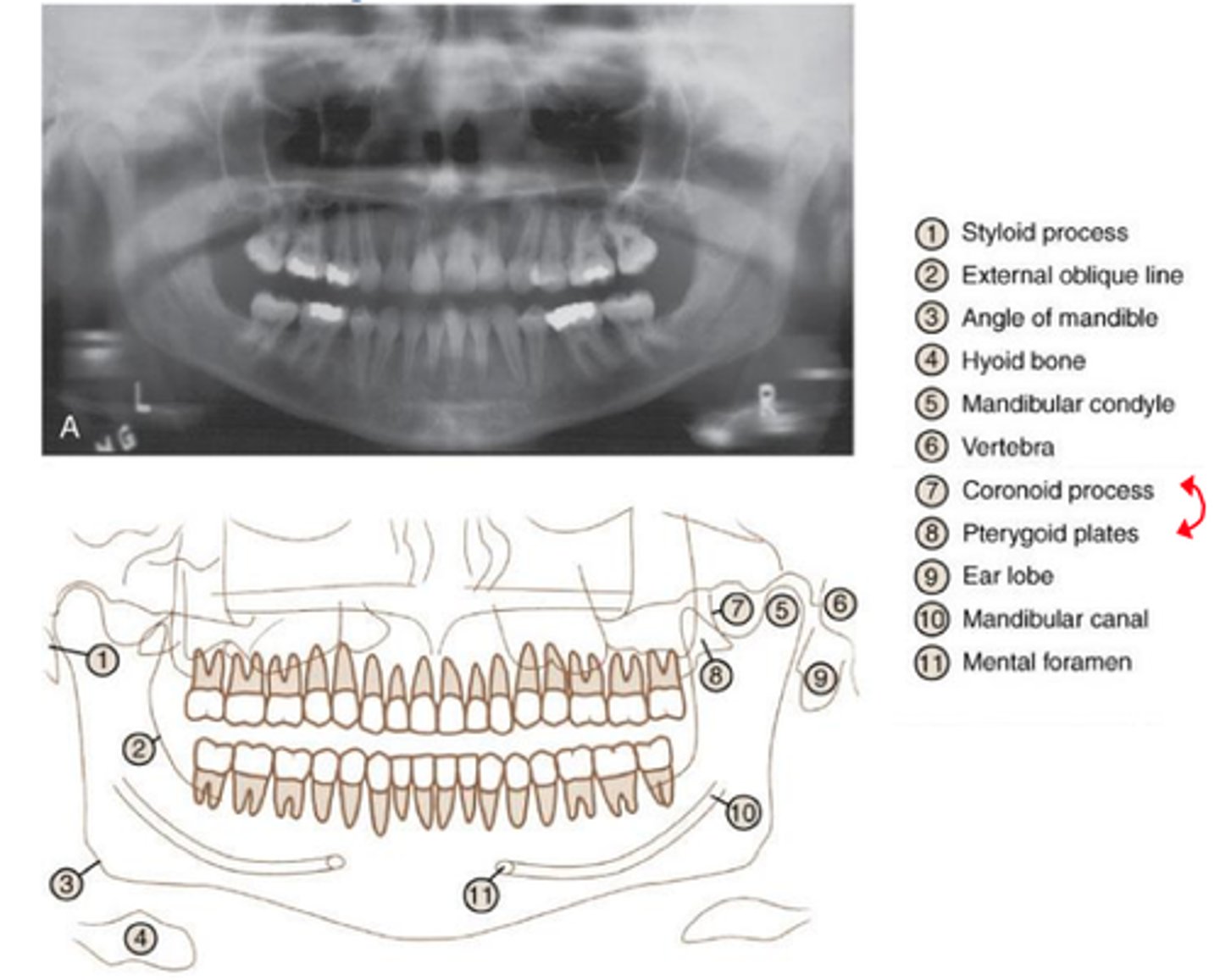
panoramic radiograph purpose
allows us view your head, neck, & jaw, & how they work together as a whole
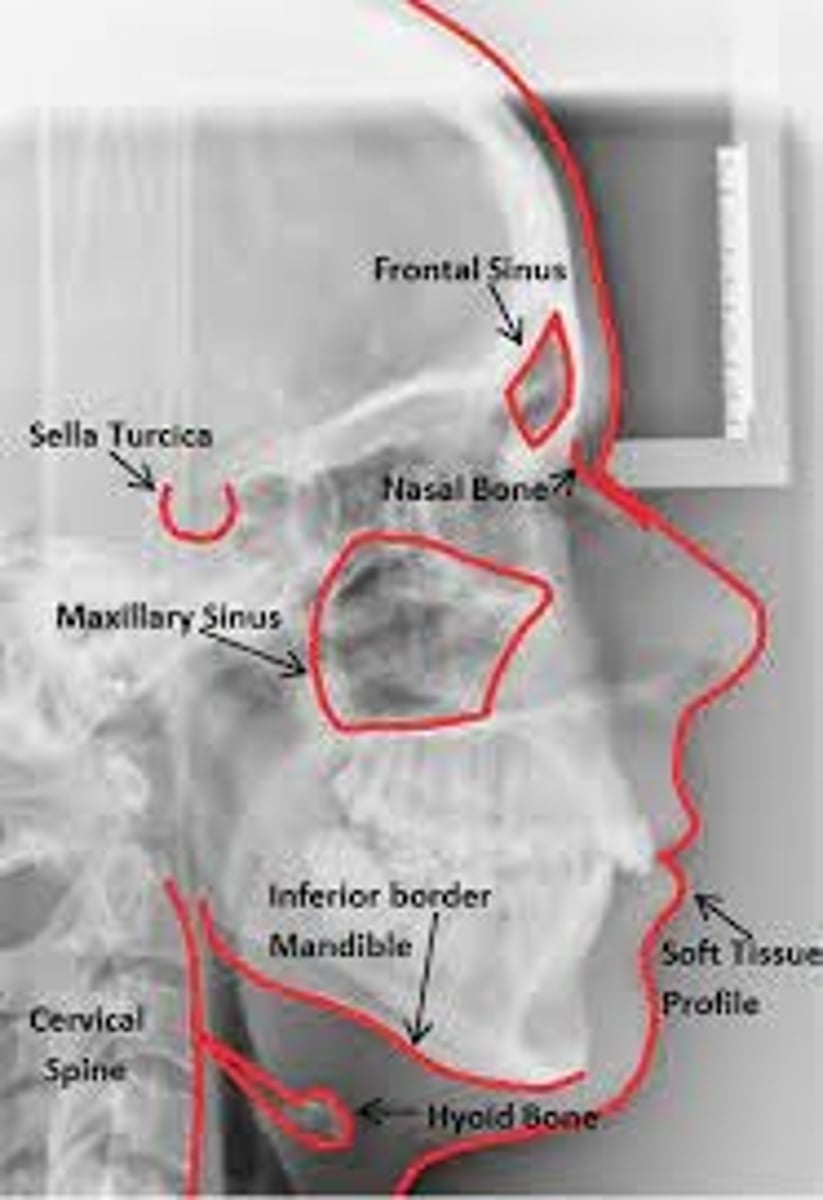
Cephalometric radiograph
extraoral radiograph of the bones & tissues of the head
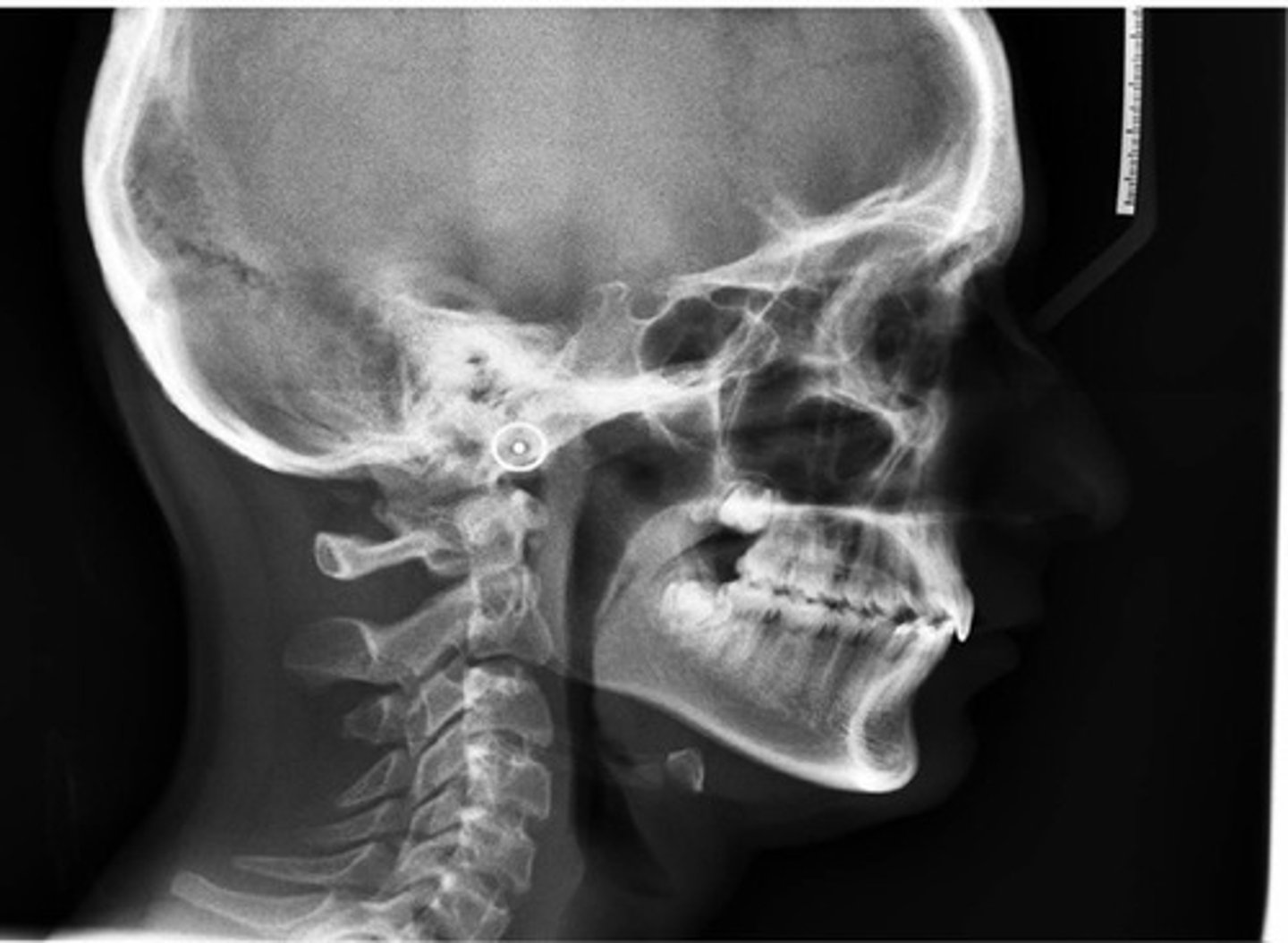
Cephalometric radiograph purpose
enables the dentist to capture a complete radiographic image of the side of the face
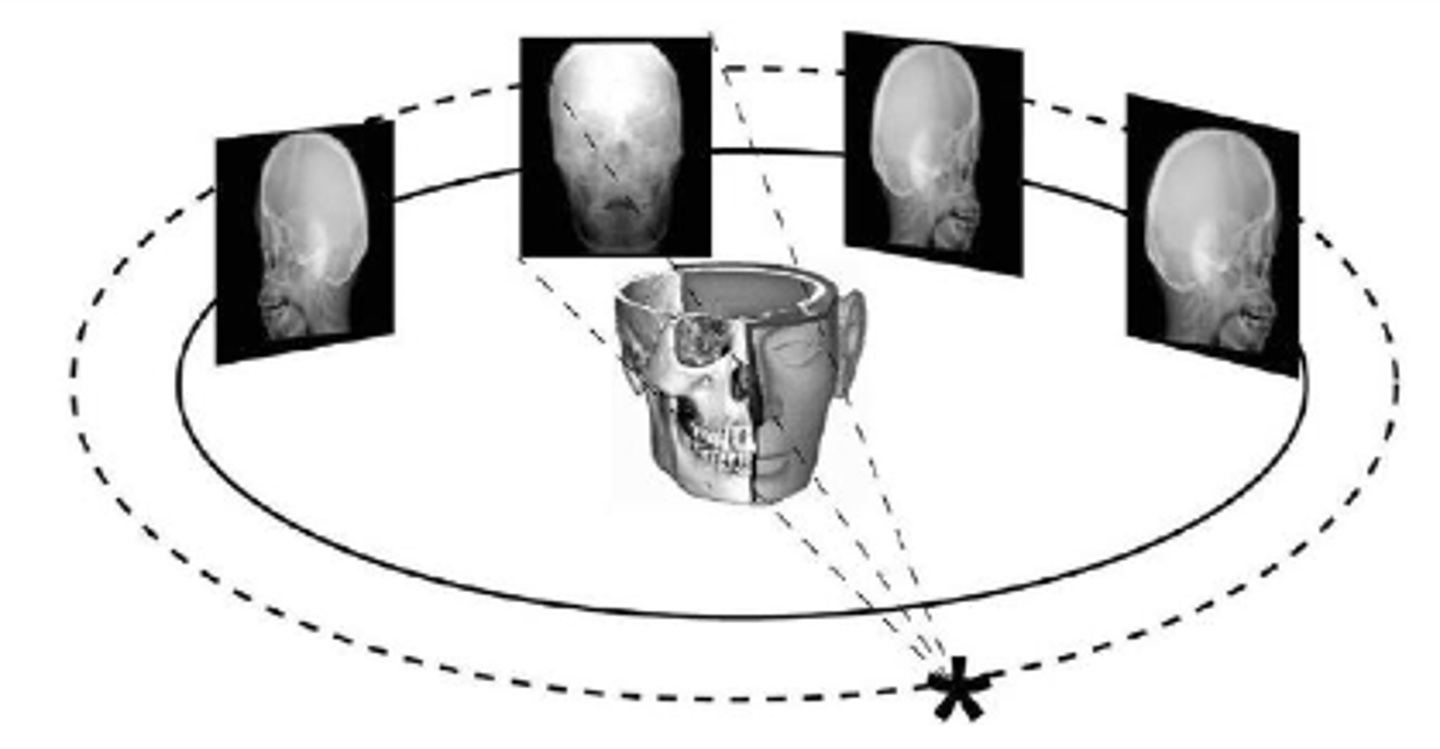
CBCT (cone beam computed tomography)
three dimensional digital imaging method that uses a cone-shaped beam of radiation that rotates around the patient
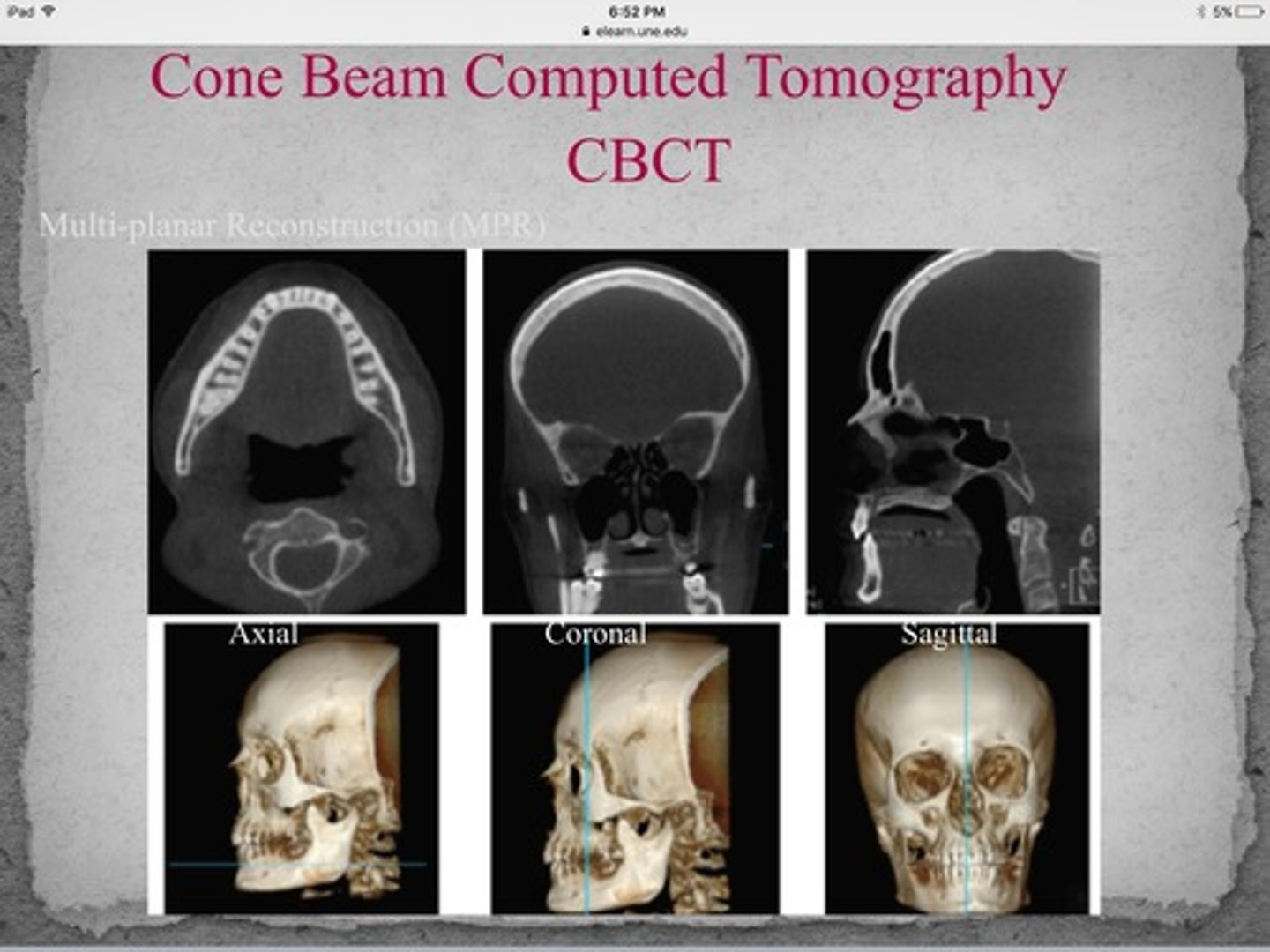
CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) purpose
allows accurate, three dimensional (3D) imaging of hard tissue structures
Radiolucent
- portion of an image that is dark or black;
- the passage of x-rays w/relatively little attenuation by absorption
Radiopaque
- portion of an image that appears light or white
- strongly inhibiting the passage of x-rays
Phosphor plates are processed by using:
laser beam technology
Most bilateral findings in images are considered:
normal anatomic landmarks
Impacted third molars are best seen w/what type of radiograph?
Panoramic
Which of the following is automatically labeled on the computer template for an image?
Date of image
The main purpose of using a lead apron w/a thyroid collar when exposing dental radiographs is to protect the patient from:
scatter radiation
For x-ray machines operating in ranges at or below 70 kVp, the total aluminum equivalent filtration must be a minimum of:
1.5 mm
Foreshortening of the maxillary radiographic image results from:
increased vertical angulation
After a patient has been dismissed, dental unit surfaces & counter tops that may have been contaminated should be cleaned w/an EPA-registered:
intermediate-level disinfectant
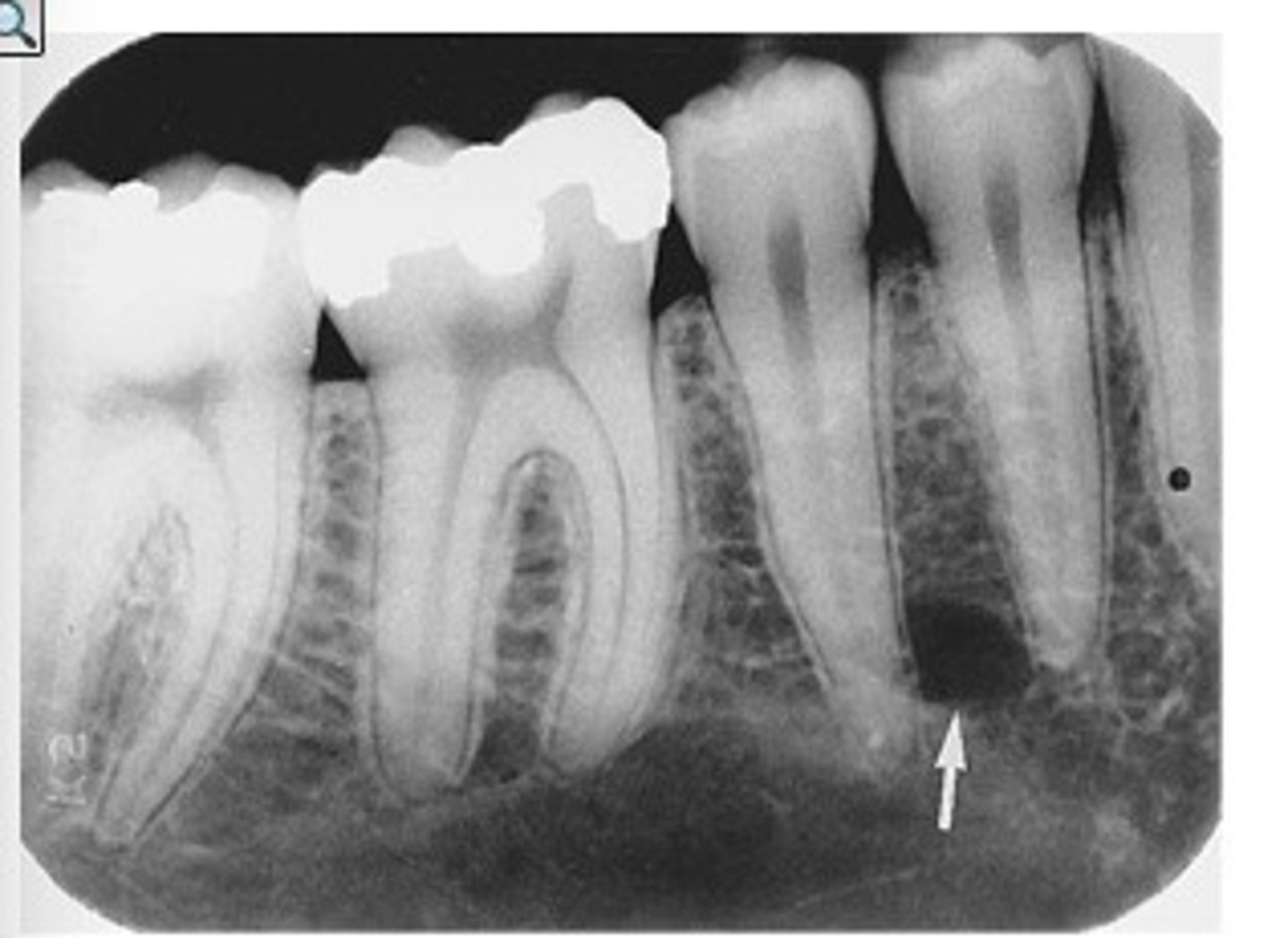
Dilaceration in a radiographic image indicates the:
root shape is abnormally bent or curved
Somatic effects of radiation do NOT have damaging effects on:
offspring
Which of the following will best protect the dental assistant from cross-contamination while exposing radiographs?
Gloves
The time between patient exposure to radiation & the appearance of biological damage is the:
latent period
Which of the following cells exposed to radiation may be associated w/leukemia?
somatic
When documenting a lesion found on an image, all of the following should be described EXCEPT:
severity
A panoramic image appears to have a "reverse smile" when the:
Frankfort plane is angled upward
A cephalometric radiograph is PRIMARILY used to evaluate:
lateral jaw development
Compared to radiopaque structures, radiolucent structures:
appear dark on an image
The radiation that is formed by the interaction of x-rays w/matter is:
secondary radiation
Which of the following anatomical landmarks is NOT normally seen on intraoral radiographs?
Frontal sinus
Compared to a dentulous patient, radiographic exposure time on an edentulous adult patient should:
decrease
According to the inverse square law, when changing the PID length from 8 to 16 inches, the beams intensity is:
1.4 as intense
Which image would be best utilized to see the relationship of the alveolar bone?
vertical bitewing
When using a 16-inch PID compared to an 8-inch PID the exposure time must:
be increased
Which of the following extraoral radiographs is used to evaluate impacted teeth, large lesions & fractures of the mandible?
lateral jaw projection
Dental Healthcare personnel who are pregnant can expose radiographs during the:
entire pregnancy
Which part of the x-ray machine should be covered or disinfected after each patient?
tubehead
Using the ALARA concept as guideline for radiographs includes all of the following EXCEPT:
circular PID
which of the following landmarks useful when mounting images of the mandibular posterior area?
mental foramen
Which of the following should be used to prevent cross-contamination from exposure buttoms?
plastic cover
compared to a dentulous patient, radiographic exposure time on an edentulous adult patient should:
decrease
personnel monitoring for radiation exposure is done by:
wearing a dosimeter
the most common radiographic exposure used to evaluate a dental implant on an adult is:
periapical
on an anterior image, the anterior alveolar crest normally appears:
pointed & sharp
the radiation exposure that poses the greatest hazard to the operator is:
leakage radiation
the population most susceptible to radiation damage is:
infants
when changing the 8-inch PID to a 16-inch PID, which of the following is used to determine the density of the beam?
inverse square law
which of the following causes the inter proximal areas of the teeth to appear overlapped?
improper horizontal angulation
when executing a routine hand wash, the dental assistant should lather & scrub for a minimum of:
20 seconds
When removing a protective barrier after the exposure of radiographs, if a dental assistant touches the surface beneath the barrier the dental assistant must:
disinfect the surface w/an intermediate-level disinfectant
which size image receptor would be used for an adult posterior periapical film?
2
the best way a dental assistant can minimize cross-contamination when exposing radiographs is to:
touch as few surfaces as possible
after using a lead apron on a patient for digital radiograph exposure, it should be:
wiped w/an intermediate disinfectant
if there are no teeth to serve as guides, which of the following landmarks indicates a maxillary molar area radiograph?
tubersosity
what are common uses for a CBCT 3D image?
determining bone structure & tooth orientation
which of the following landmarks is useful when mounting images in the maxillary central area?
anterior nasal spine
the most common reason for taking bitewing radiographs is to evaluate:
interproximal caries
which of the following sequences best describes radiation injury to tissue?
latent period, period of injury, period of recovery
added filtration in the x-ray tubehead protects the:
patient
The Buccal Object Rule is used to determine if a foreign body is located in which direction?
Lingual to Buccal
How is scatter radiation reduced when taking an image?
use of rectangular cone
foreshortening of the maxillary radiographic image results from:
increased vertical angulation
dental x-rays should be prescribed when the:
benefits outweigh the risk of harm
the maximum permissible dose (MDP) of ionizing radiation for occupational exposure is:
5.0 rem per year (0.05 Sv)
which of the following radiograph techniques is recommended for a patient w/a shallow palate?
bisecting
which of the following influences the sharpness of a radiograph?
focal spot size
which of the following affects the speed of the electrons emitted from the tubehead?
kVp
when the tubehead drifts, the first step the dental assistant should take is to:
stop using the machine
if a dental assistant dosimeter badge report indicates exposure to radiation, what should be done first?
evaluate the x-ray equipment & techniques
which of the following pathogens is NOT found in oral or respiratory secretions?
west nile virus
when taking radiographs on a small child who cannot hold the sensor intra-orally, the dental assistant should:
ask a parent or guardian to hold the sensor
which organization regulates disinfectants & chemical sterilants?
EPA
which size image receptor, when placed vertically in the anterior region of the mouth, is the most effective for evaluation caries & periodontal health?
2
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) uses:
3-dimensional technology
when using a 16-inch PID compared to an 8-inch PID the exposure time must:
be increased
what surfaces remain uncovered during digital radiograph exposure & would need to be disinfected between patients?
lead apron & positioning device
which of the following prevents x-rays from escaping the tubehead?
leaded-glass housing
which organ is the most sensitive to radiographic exposure?
thyroid gland
to minimize exposure to the radiographer, the operator should employ the following three types of radiation protection methods:
barrier, monitoring device, operator position
which of the following can help to protect patients from excess radiation to damage to tissues?
high kVp
which of the following extra-oral radiographs is used to evaluate impacted teeth, large lesions & fractures of the mandible?
lateral jaw projection
compared to a round position-indicating device (PID), which of following PIDs reduces patient radiation exposure by up to 70 percent?
rectangular-shaped
an underexposed image will appear:
light
which of the following is a measurement of tissue damage from x-ray energy?
radiation absorbed dose
dental healthcare personnel can BEST shield themselves from radiation during patient exposure by standing behind:
a drywall barrier
the position-indicating device (PID) shape that most effectively reduces patient exposure to radiation is:
rectangular
supernumerary teeth are best detected using what type of image receptor?
panoramic
which of the following affects the quantity of x-rays being emitted from the tubehead?
mA
the BEST radiograph to evaluate a suspected salivary stone in the submandibular gland is a/an:
occlusal
to reduce the patient's anxiety about radiographic exposure the dental assistant should:
take time to explain the procedure
the amount of which of the following is used in determining the degree of radiation injury?
tissue irradiated
which of the following landmarks is useful when mounting images in the maxillary posterior area?
floor of the maxillary sinus
which of the following condition may mimic caries on an intraoral image?
root resorption
radiation injury can be measured by:
dose rate
which of the following would cause elongation on a radiograph?
insufficient vertical angulation