BCH210: Biochemistry
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Indole
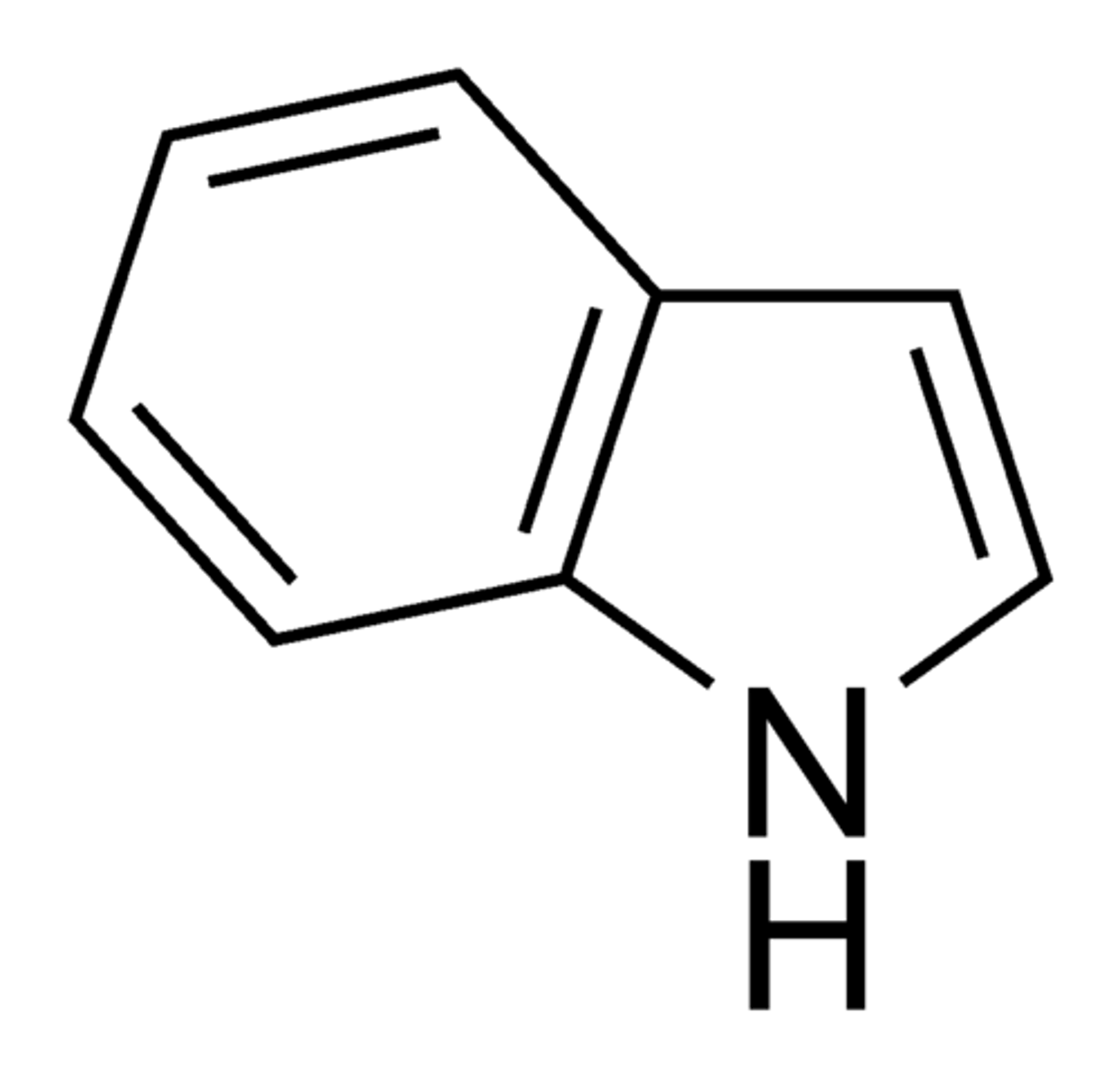
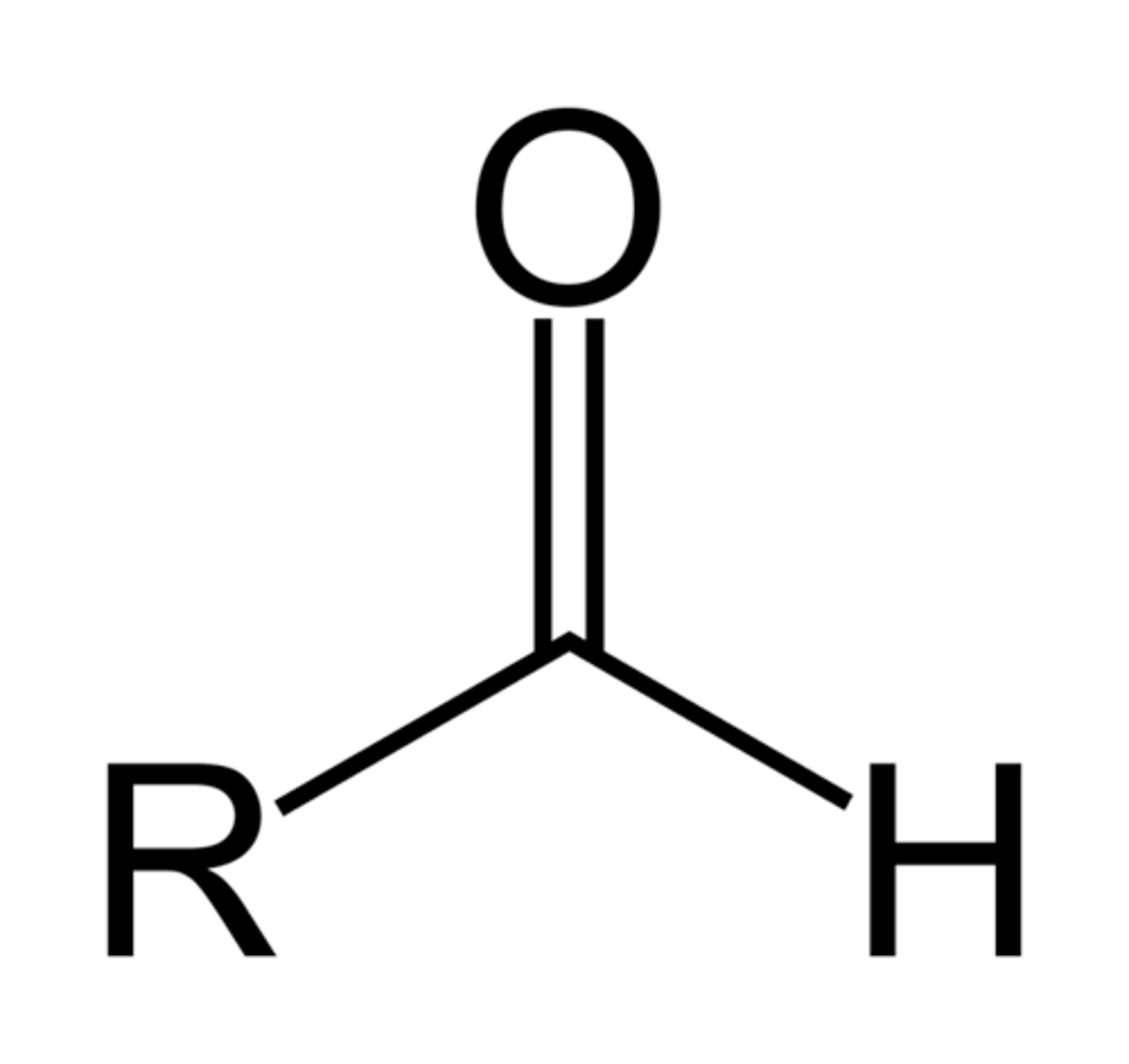
Aldehyde
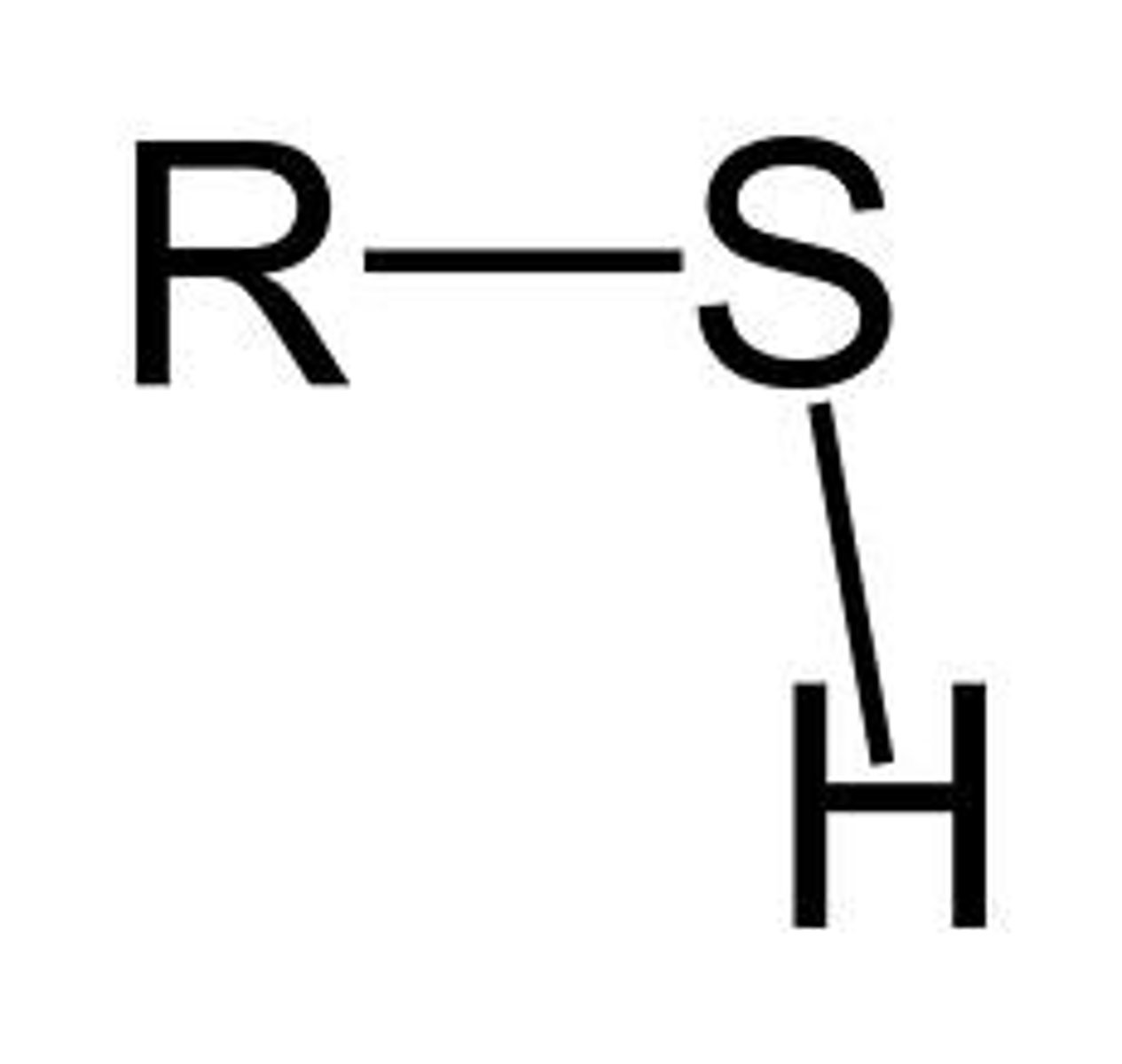
Thiol / Sulfhydryl
Proton Donor
A substance that releases hydrogen ions in detectable amounts; an acid. H+ can be easily removed.
Proton Acceptor
A substance that takes up hydrogen ions in detectable amounts; a base. Lone pair can bond with proton.
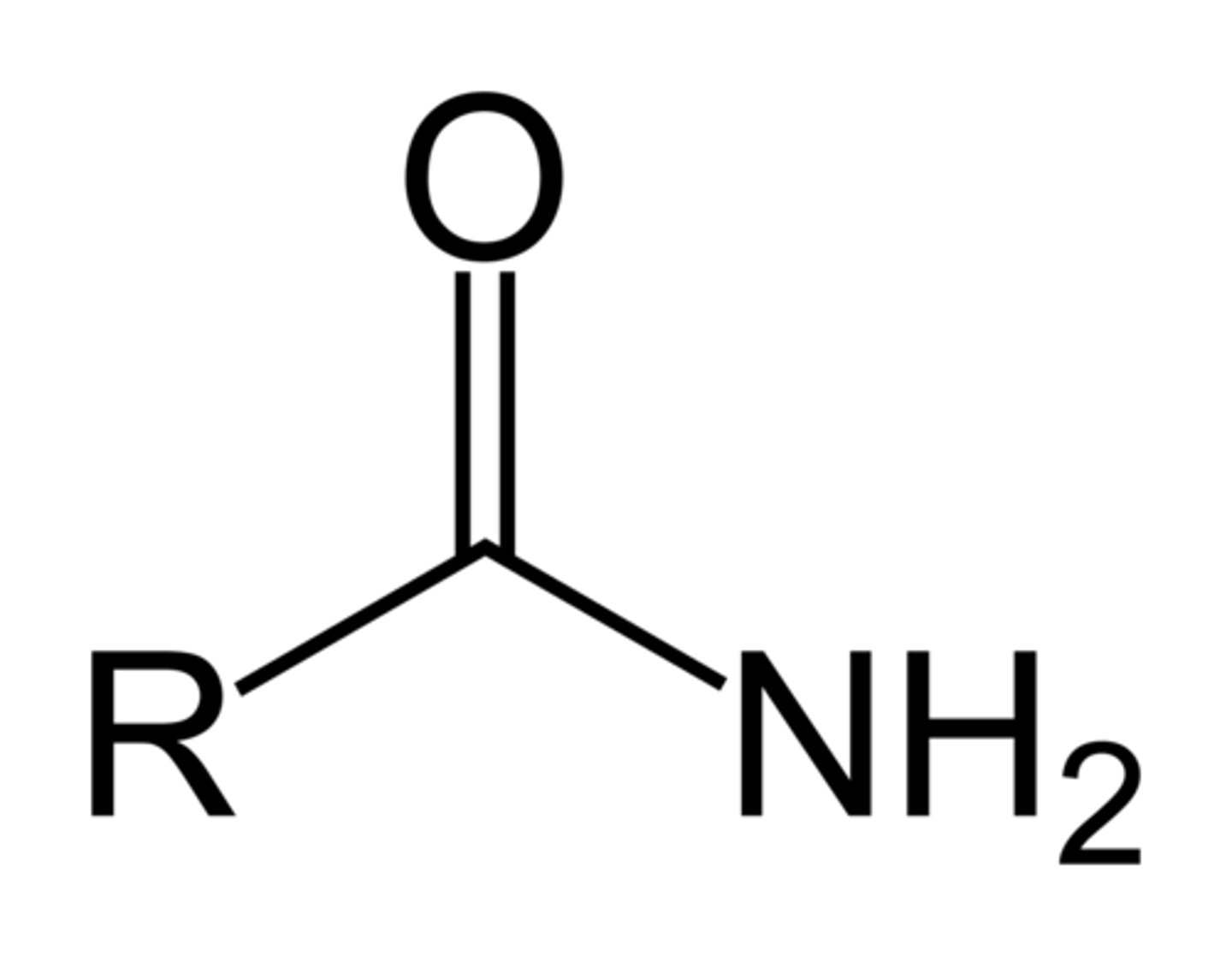
Amide
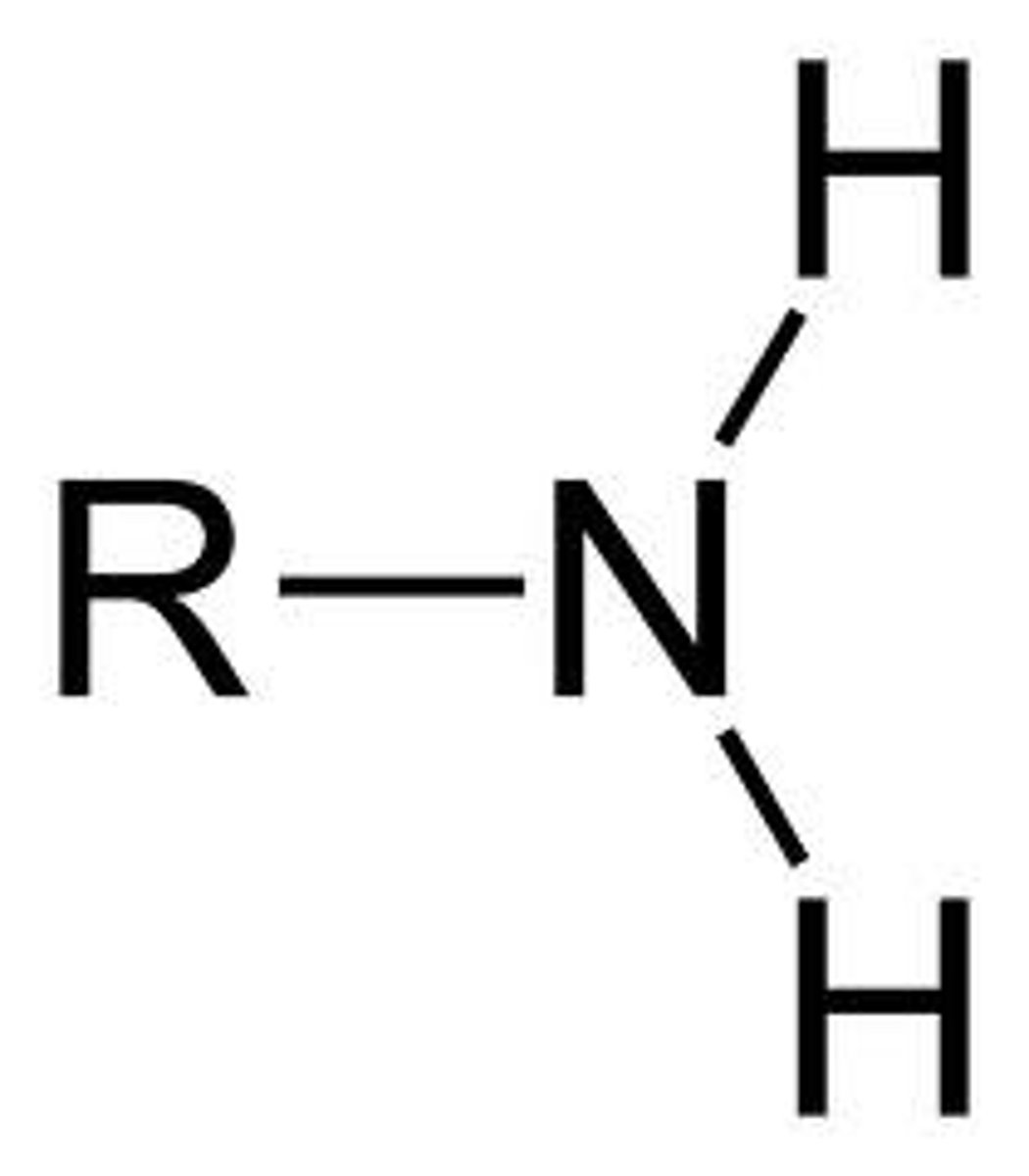
Amine
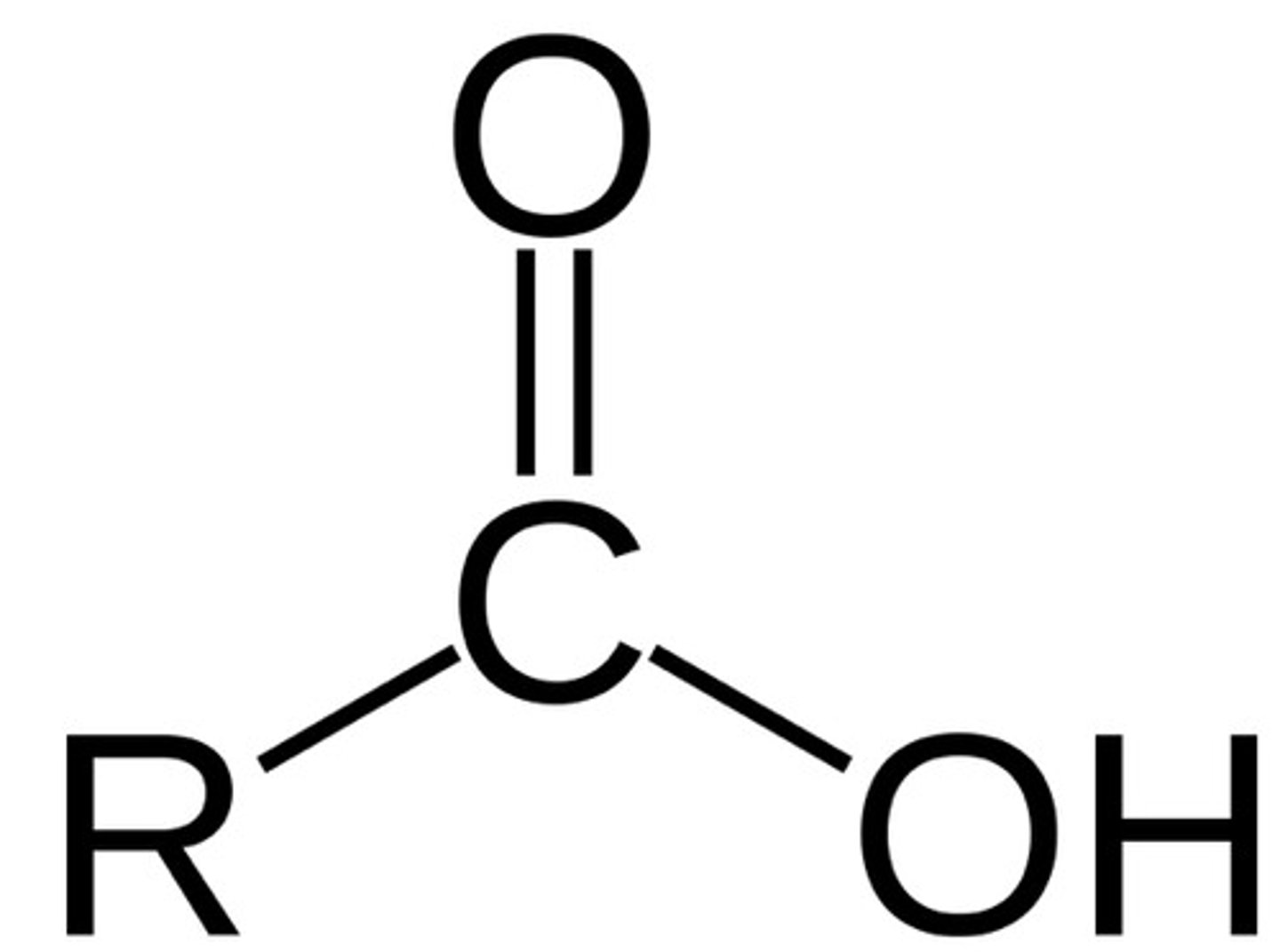
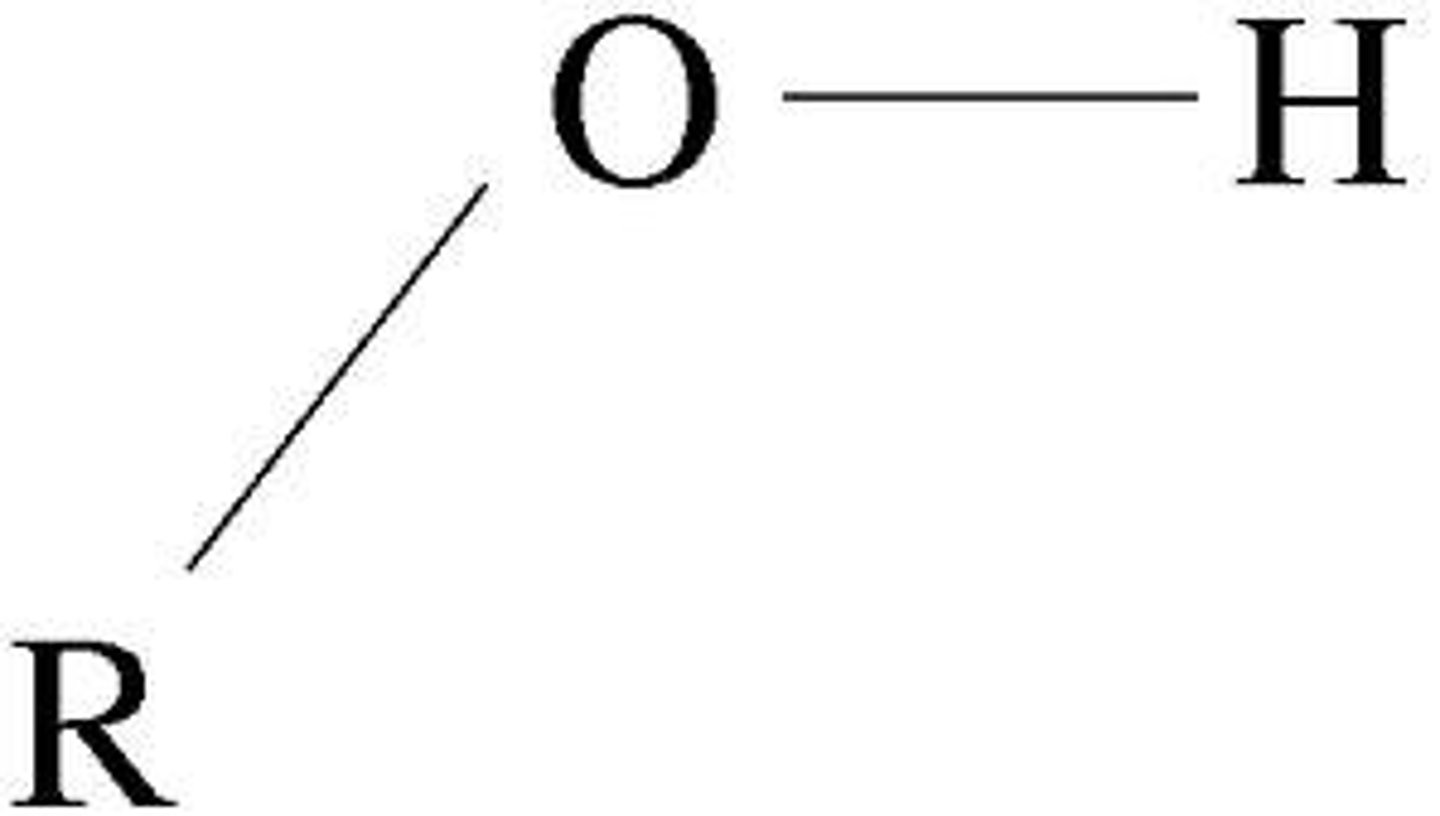
Carboxyl
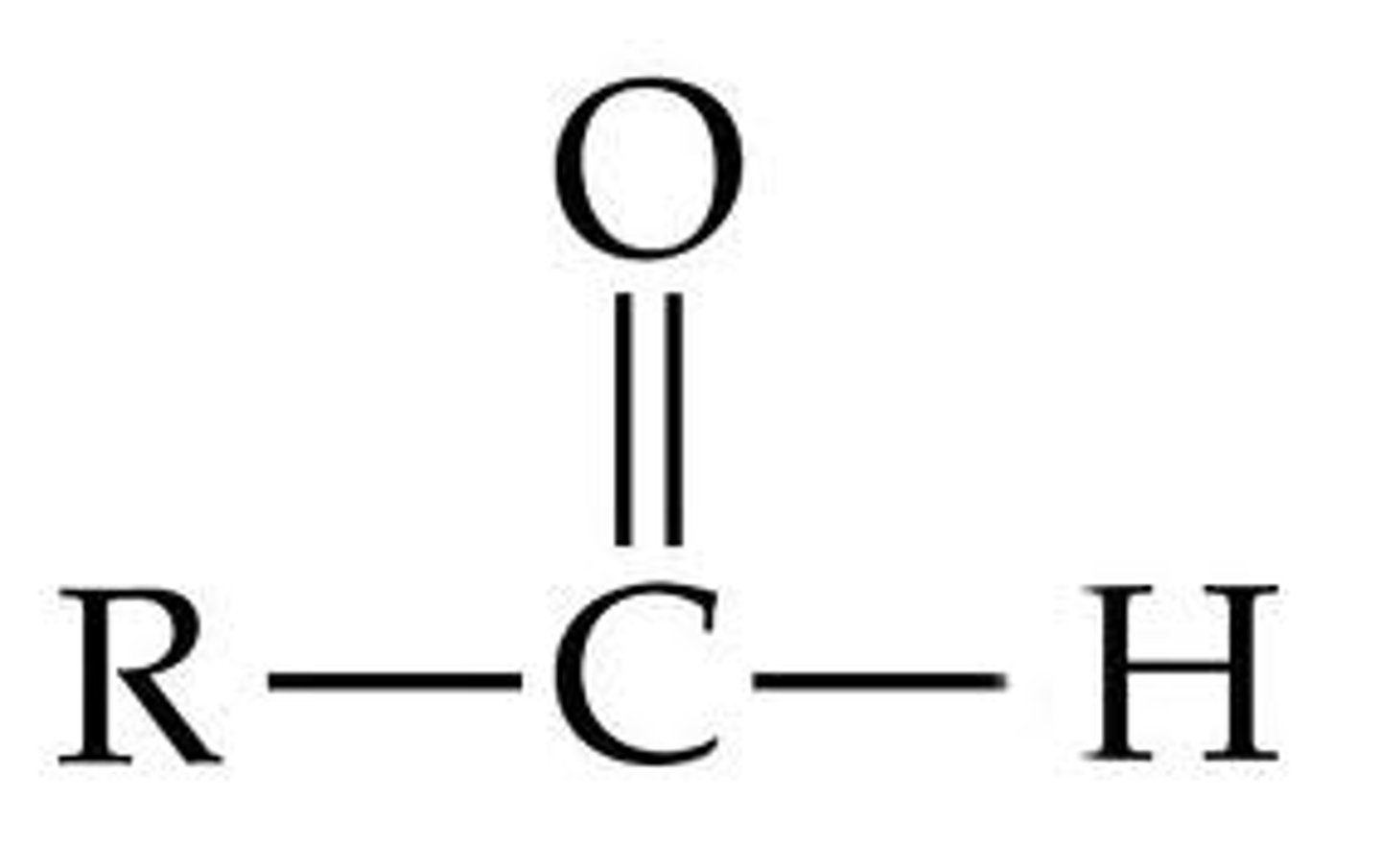
Carbonyl
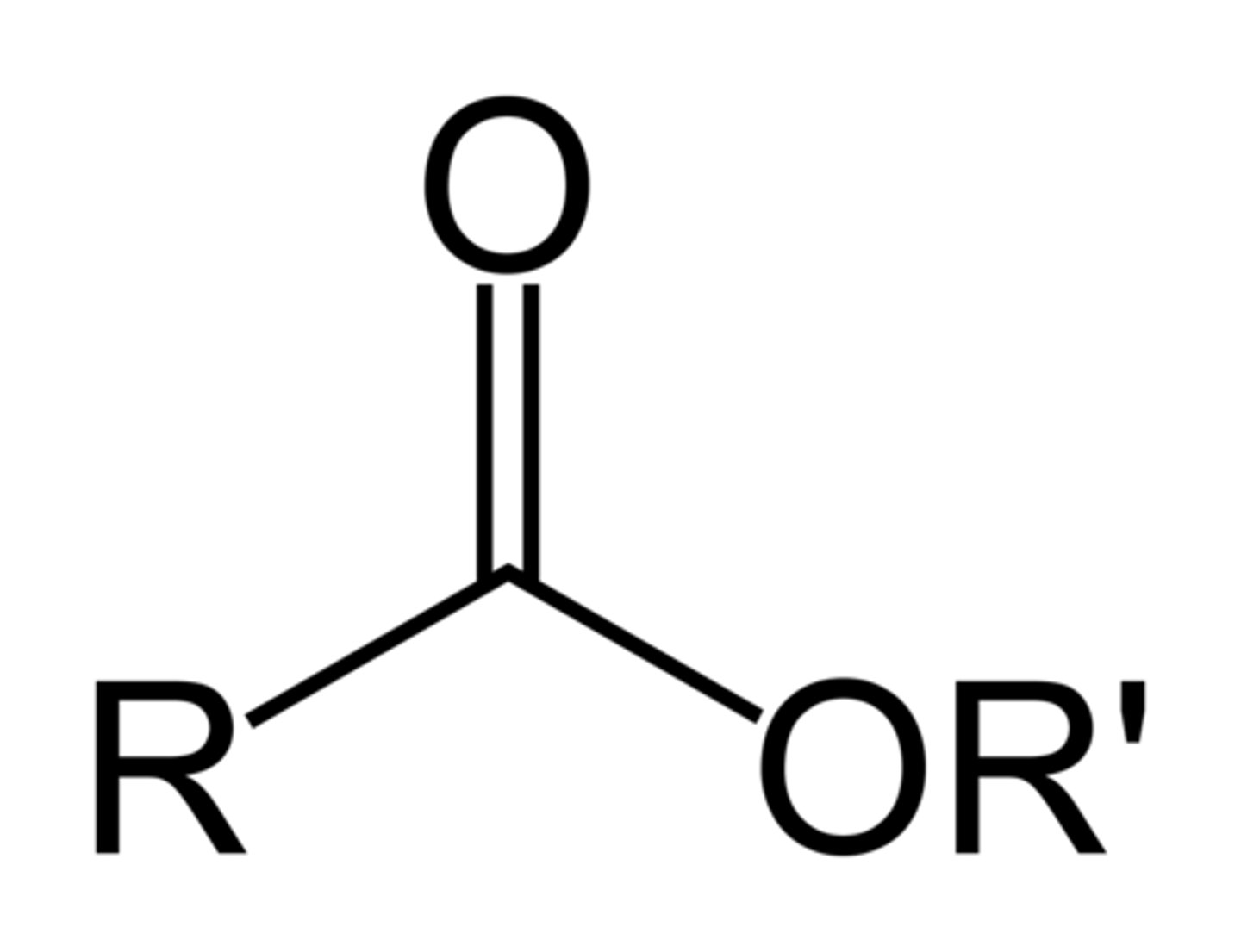
Ester
Ether
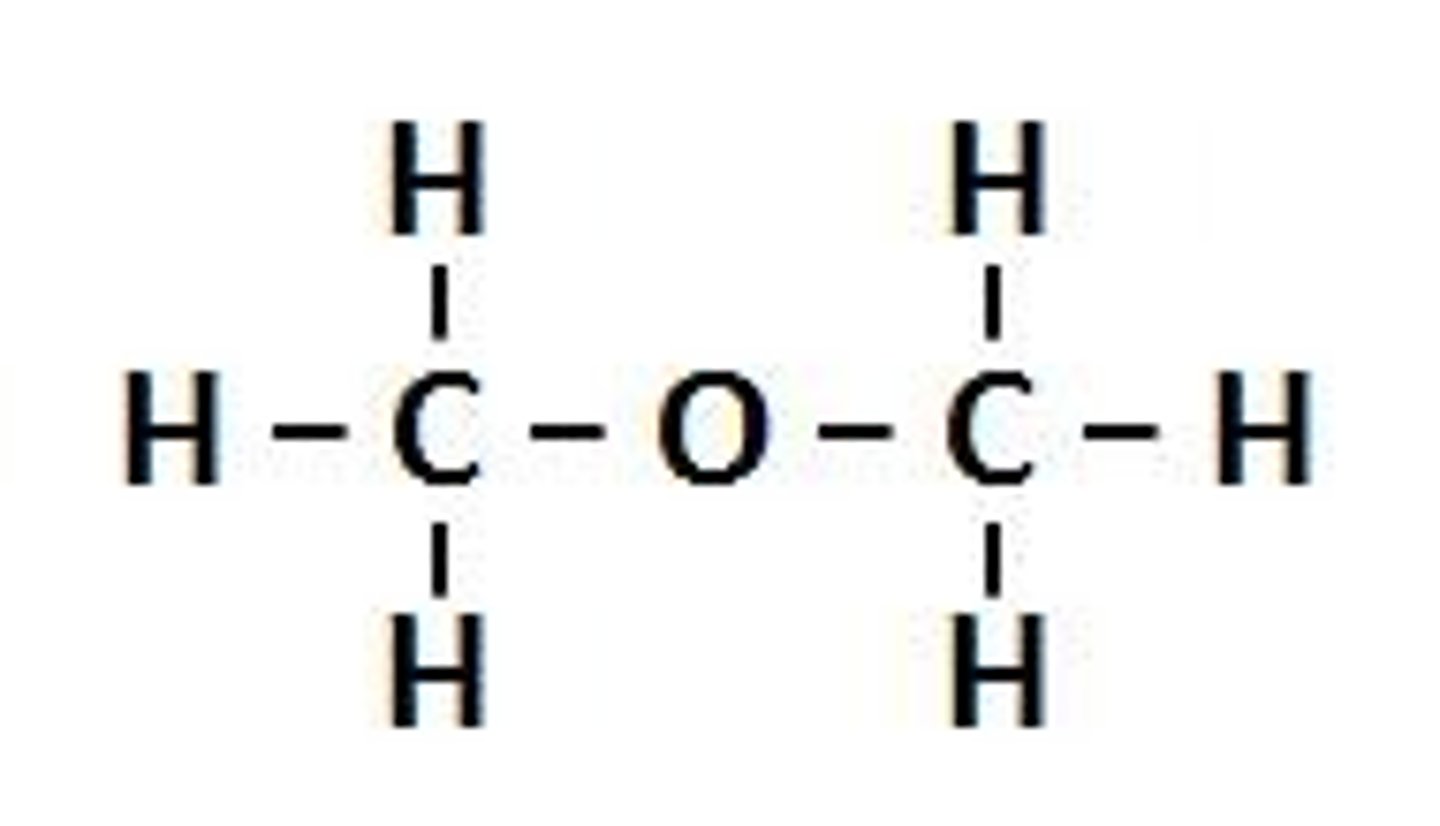
Hydroxyl
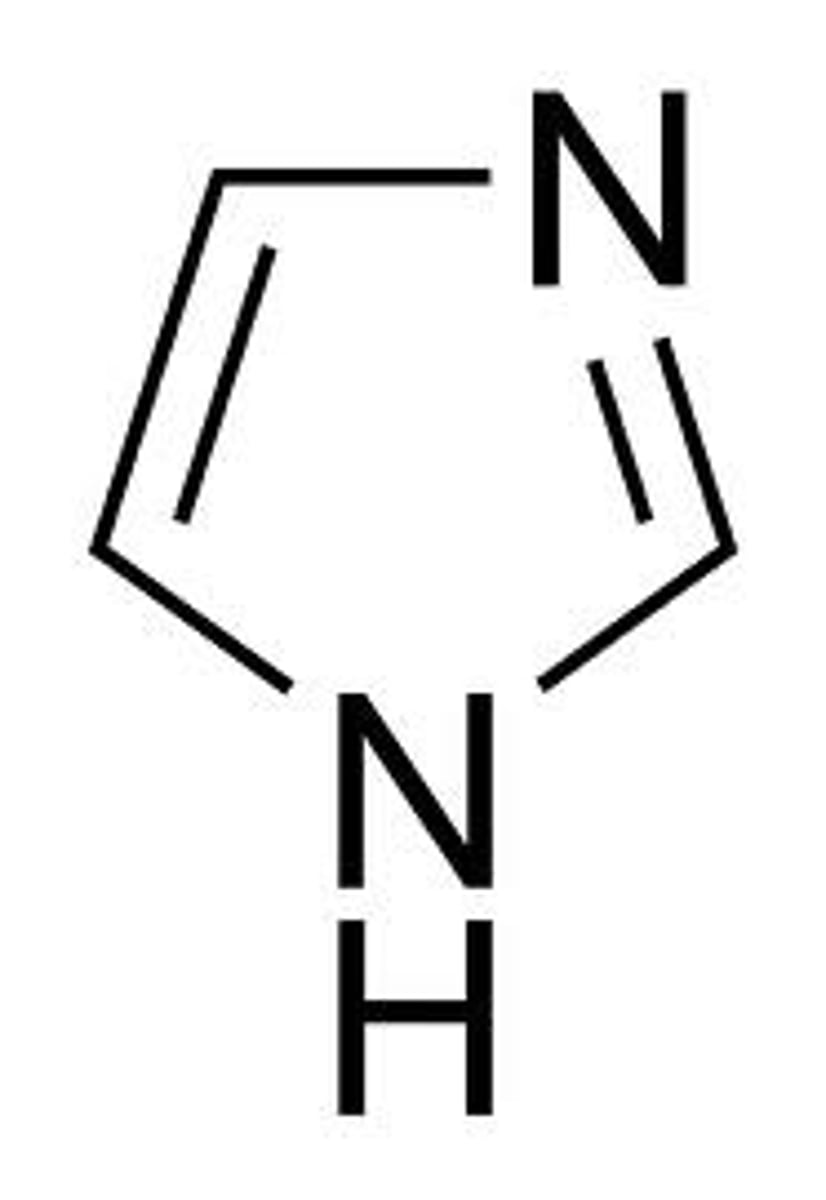
Imidazole
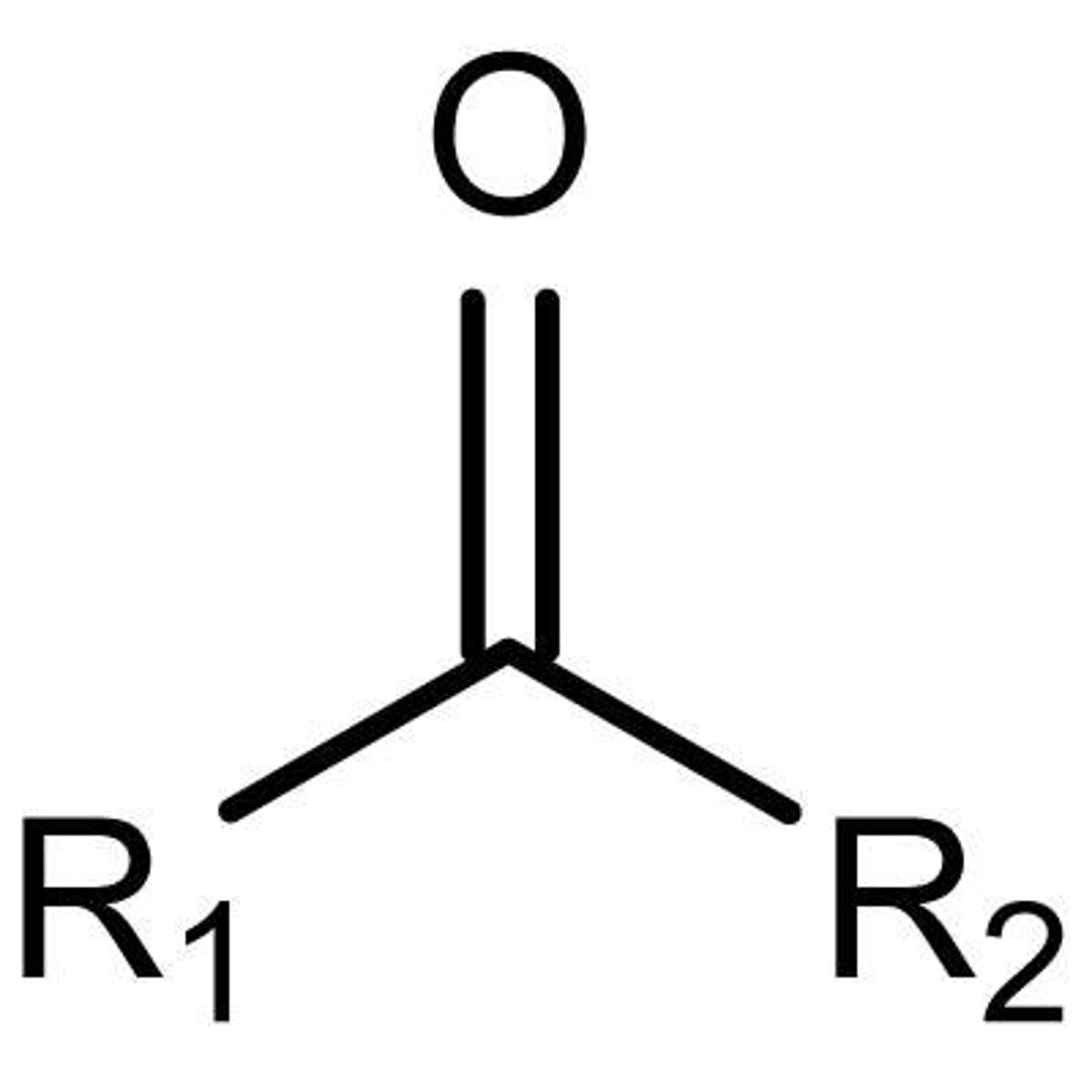
Ketone
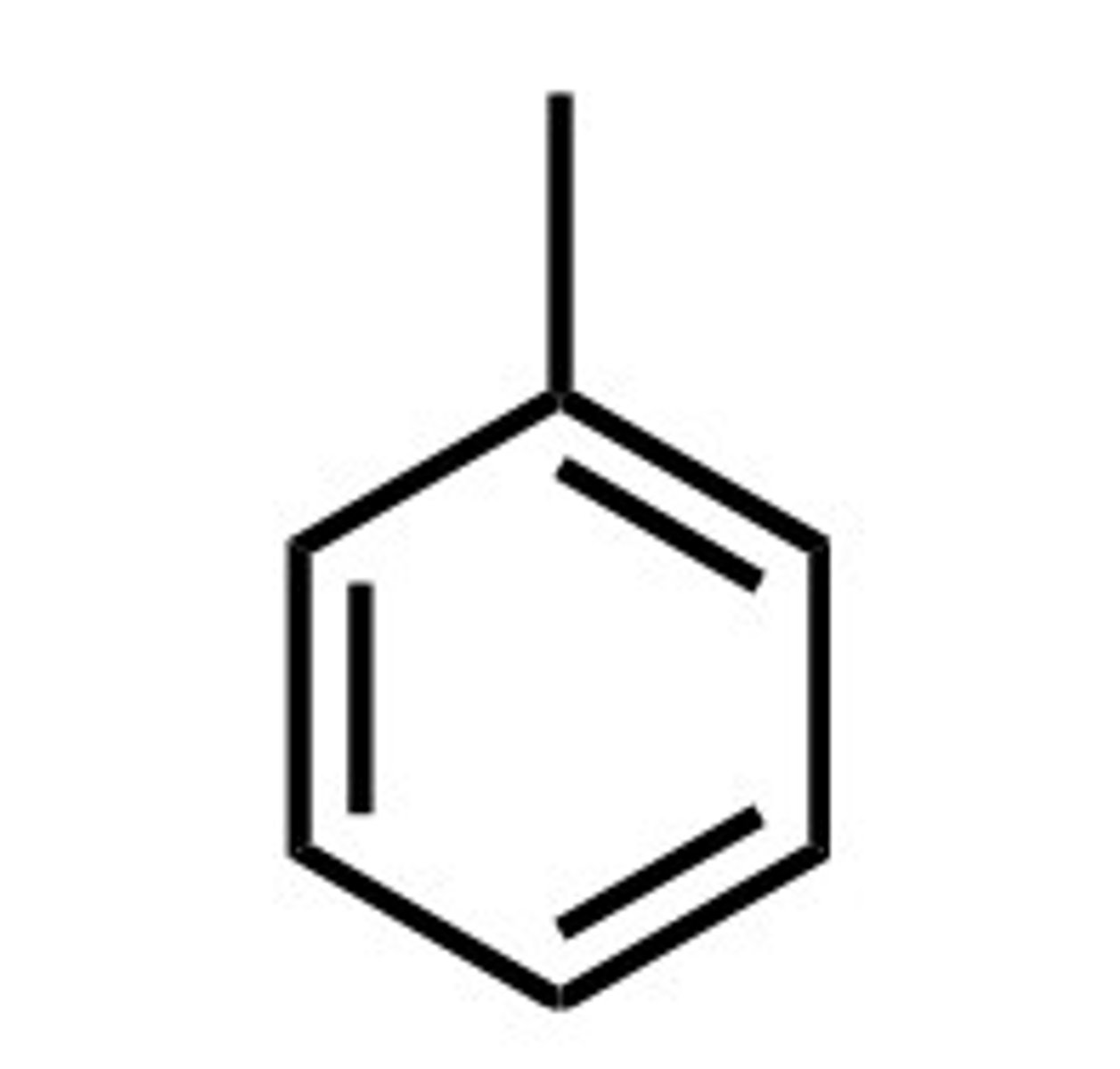
Phenyl
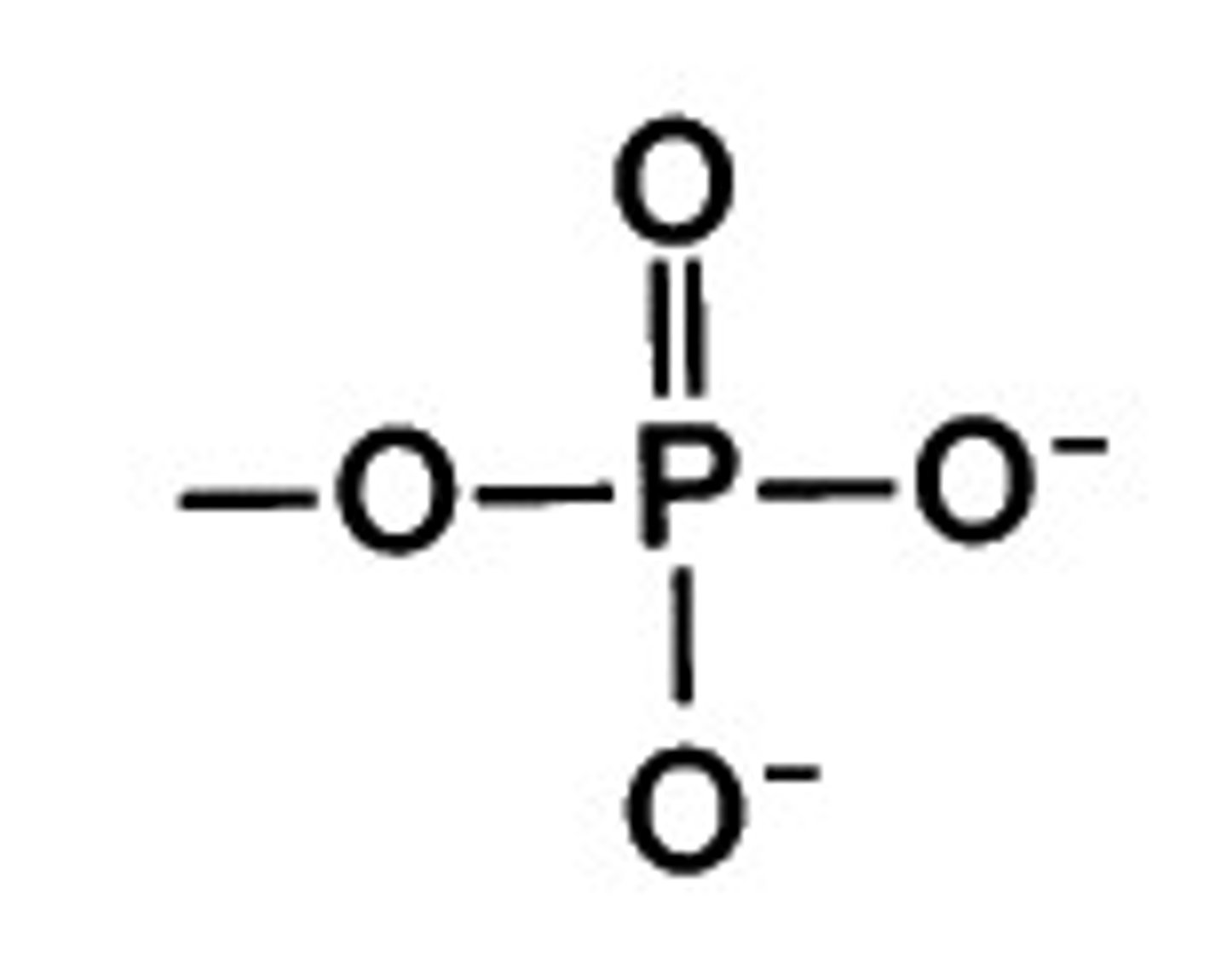
Phosphate
Covalent Bonding
Electron sharing between two adjacent atoms. Highest strength and lowest distance.
Ionic interactions
Salt bridges, strength dependent on interaction
Hydrogen Bonds
Strength is proportional to the polarity of the H bond donor & acceptor.
Hydrophobic interactions
Depends on the entropy of water being released, causing hydrophobic regions to come together.
Van der Waals
Relatively weak and depends on the size of the atoms and the distance between them.
Cofactors
Non-protein compound assisting activity
Coenzymes
Organic cofactor
Co-substrate
Temporary coenzyme
Ligand
Reversible binding molecule
Metal Ion
Inorganic cofactor
Prosthetic Group
Permanently bound cofactor
Silent Mutation
mutation with no effect on polypeptide
Non-Conservative mutation
mutation that creates a different polypeptide
Conservative mutation
mutation that creates a similar(ish) polypeptide
Chromotography
Differential partitioning of a molecule between mobile (buffer) and stationary (column) phase.
Size or Shape
Size-Exclusion/Gel Filtration chromatography
Charge
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Binding Interactions
Affinity chromatography
Hydrophobicity
RP-HPLC (Reverse Phase High Pressure Liquid Chromatography)
CM
cation exchange resin, attracts CATs, is AN
DEAE
anion exchange resin, attracts ANs, is CAT
alpha helix
wavelengths 1650-1660
beta sheet
wavelengths 1620 - 1640
beta turns
wavelengths 1675-1695
random coils
wavelengths 1670-1680
alpha helices
CD wavelength 222nm, 208nm (neg) , 195nm (pos)
beta turns
CD wavelength 217nm (neg)
random coil
CD wavelength 198 nm (neg)
Zymogen
inactive precursor of an enzyme
Irreversible Activation Example
Zymogen cleavage
Irreversible Inhibtion Example
Aspirin & COX1
Competitive
the inhibitor binds to the active site, Km up and Vmax the same
Un-Competitive
inhibitor can only bind to the ES complex, Km and Vmax both down
Non-Competitive
inhibitor binds to the enzyme or ES complex, Km is unchanged and Vmax is down
Oxidoreductases
Oxidation-reduction reactions (NADH, NADPH, FADH2 , O2). Examples: Diamine oxidase, lactate dehydrogenase
Hydrolases
Hydrolysis reaction (transfer of fx group to water) Examples: ATPases, Trypsin
Lysases
Addition or cleavage reactions. Usually involves double bonds and/or cyclization. Ex: Carbonic anhydrase, Adenylyl Cyclase
Isomerases
Group transfer within a molecule. Ex: Phosphoglucomutase
Ligases
Joining 2 molecules using nucleotides (ATP/GTP etc.), Ex: Biotin protein ligase
Translocases
Movement of ions or molecules across a membrane, Ex: Flipases, Ca2+-ATPas
Transferases
Functional group transfer between molecules. Examples: PKA