Pathophysiology Exam #4: An In-Depth Review of Pulmonary Function Alterations
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
Tidal volume
Volume of air exhaled after normal inspirations (500 mL)
Residual volume
Volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximum respiration (1200 mL)
Vital capacity
Maximal amount of air that can be moved in and out of the lungs with a single forced inspiration and expiration (4800 mL)
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)
Volume exhaled in the first second after deep inspiration and forced expiration
Forced vital capacity (FVC)
Total volume of air that the patient can forcibly exhale in one breath
The values of ____________ and ____________ are expressed as a percentage of the predicted normal for a person of the same sex, age, and height.
FEV1 and FVC (expressed as FEV1/FVC)
Describe how FEV1 and FVC (and their ratio) are affected in an obstructive pattern
- Reduced FEV1 (<80% of the predicted normal)
- Reduced FVC (but to a lesser extent than FEV1)
- FEV1/FVC ratio is reduced (<0.7)
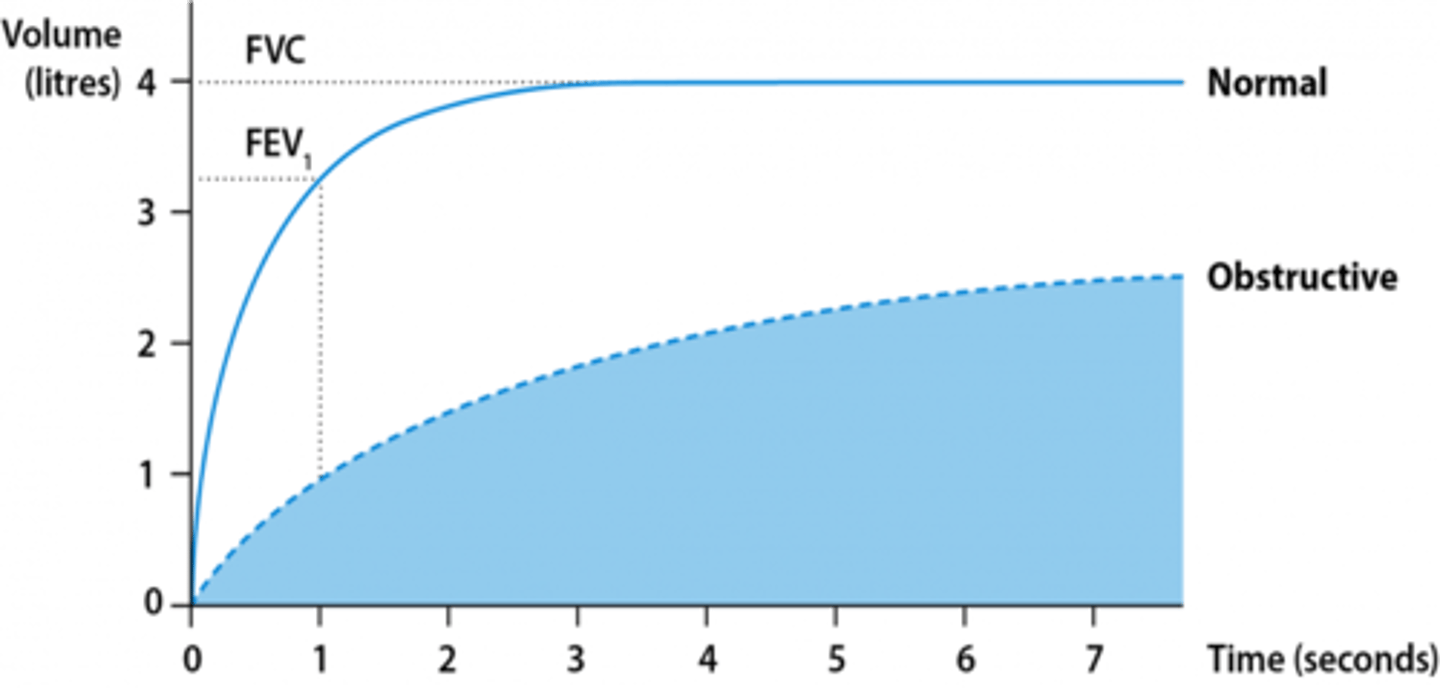
Mild obstruction
- FEV1 is 80% or more of the predicted value
- If you have mild COPD, your spirometry test results can be normal after you take medication.
Moderate obstruction
FEV1 is 50-79% of the predicted value after medication
Severe obstruction
FEV1 is 30-49% of the predicted value after medication
Very severe obstruction
FEV1 is below 30% of the predicted value after medication
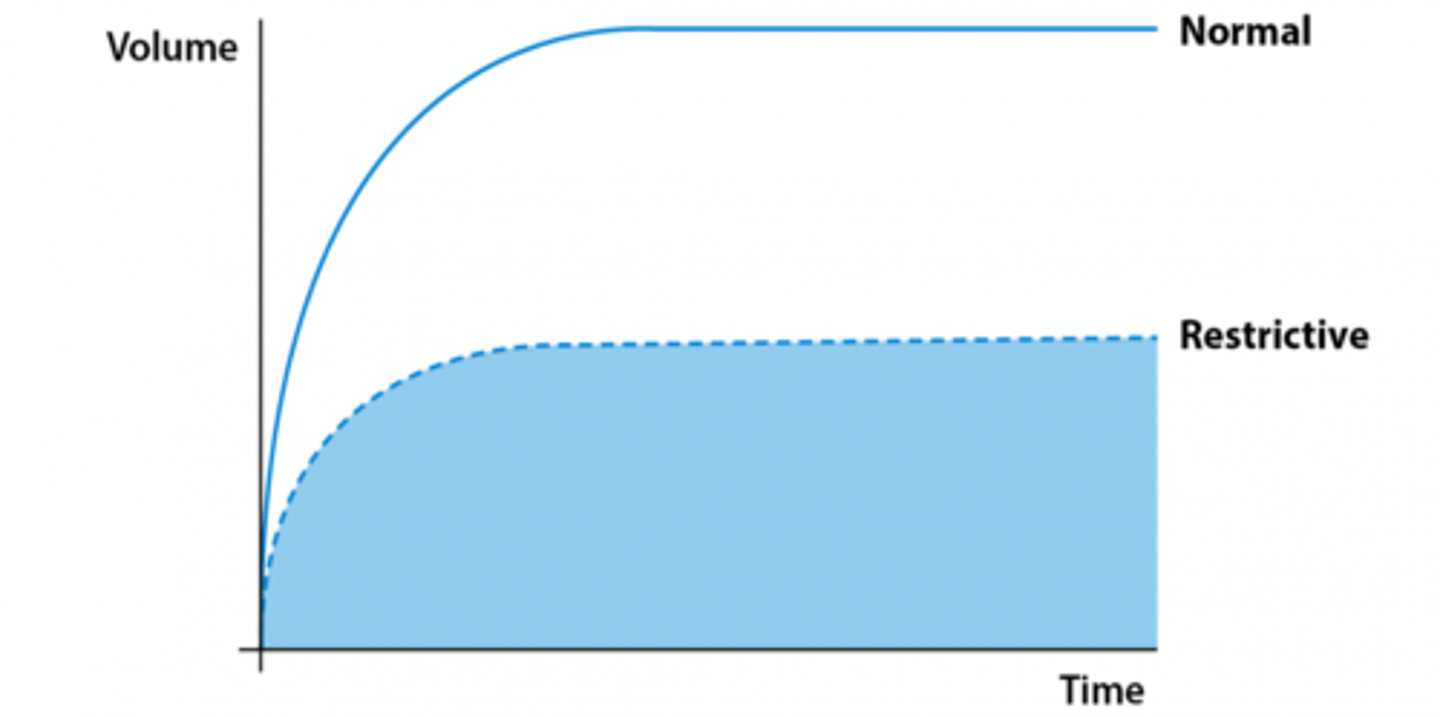
Describe how FEV1 and FVC (and their ratio) are affected in a restrictive pattern
- Reduced FEV1 (<80% of predicted normal)
- Reduced FVC (<80% of predicted normal)
- FEV1/FVC ratio is normal (>0.7)
Dyspnea
- Subjective sensation of uncomfortable breathing
- May not correlate with underlying disease
- Due to diffuse or focal disturbances in ventilation, gas exchange, or ventilation-perfusion
Severe dyspnea
- Flaring of the nostrils
- Use of accessory muscles of respiration
- Retraction of the intercostal spaces
Dyspnea on exertion
Shortness of breath with activity
Orthopnea
Dyspnea when lying down
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND)
- Awakening at night and gasping for air, must sit or stand up
- Heart failure and pulmonary disease
What is a cough?
Protective reflex that helps clear the upper airways; an explosive respiration
Irritant receptors in the airway are stimulated by...
- Particles
- Mucous
- Inflammation
- Foreign body
There are very _________ (few, many) irritant receptors in the distal airways (distal bronchi/alveaoli)
few; so we may have significant secretions in the distal airway without any cough initaited
Steps of the cough reflex
1.) Inspiration
2.) Closure of glottis and vocal cords
3.) Contraction of expiratory muscles
4.) Reopening of glottis
5.) Sudden forceful expiration (ideally removing particles/fb/mucous)
Effectiveness of a cough is depend on what 2 things?
- Depth of inspiration
- Degree of airway narrowing (more narrow = more velocity)
Stimulation of irritant receptors is transmitted to the CNS via the __________________ to the __________________.
vagus nerve; medulla
The cough reflex can be inhibited by...
- Opiates (codeine)
- Serotonergic agents (dextromethorphan)
Acute cough (time and causes)
Resolves in 2-3 weeks
Causes:
- URI, allergic rhinitis, acute bronchitis, pneumonia, CHF, PE, aspiration
Chronic cough (time and causes)
More than 3 weeks (>7-8 weeks)
Causes:
- Smoker: chronic bronchitis, cancer
- Nonsmoker: postnasal drip, non-asthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis, asthma, GERD, heightened cough reflex sensitivity, vocal cord dysfunction, medications
What does yellowish-green, cloudy, thick mucous indicate?
Bacterial infection
What does rusty or dark-colored sputum indicate?
Pneumococcal pneumonia
What does very large amounts of purulent sputum with foul odor indicate?
Bronchiectasis
What does thick, tenacious mucus indicate?
Asthma or cystic fibrosis
Blood-tinged sputum may result from ________________________ and may also be a sign of ______________ or ____________________________.
chronic cough; tumor; tuberculosis
Hemoptysis
- Coughing up bright red blood
- Frothy
- Alkaline pH
Eupnea
- Normal and effortless breathing
- 8-15 breaths per minute
- Tidal volume = 400-800 mL
Labored breathing is present if airway is...
obstructed
Large airway obstruction
- Slow ventilatory rate
- Increased effort
- Prolonged inspiration and expiration (stridor or wheeze)
Small airway obstruction
- Rapid ventilatory rate
- Small tidal volume
- Increased effort
- Prolonged expiration (wheezing)
- Asthma/COPD
Characteristics of restricted breathing
- Disorders that stiffen the lungs or chest wall and decrease compliance (fibrosis)
- Small tidal volumes
- Rapid ventilation rate
Tachypnea
Increased respiratory rate
Bradypnea
Decreased respiratory rate
Apnea
Absence of breathing
Hyperpnea
Normal rate, but deep respirations
Cheyne-Stokes
Gradual increases and decreases in respirations with periods of apnea
Biot's
Rapid, deep respirations (gasps) with short pauses between sets
Kussmaul's
Tachypnea and hyperpnea
Apneustic
Prolonged inspiratory phase with shortened expiratory phase
Minute ventilation =
tidal volume x respiratory rate
When alveolar ventilation is normal, CO2 is removed from the lungs _____________________________ as it is produced by cellular metabolism.
at the same rate
Normal arterial pressure of CO2
40 mmHg
Characteristics of hypoventilation
- Alveolar ventilation is inadequate in relationship to metabolic demands
- Leads to respiratory acidosis from hypercapnia (PaCO2 > 44 mmHg)
- Caused by airway obstruction, chest wall restriction, or altered neurologic control of breathing
- May be overlooked until severe
Characteristics of hyperventilation
- Alveolar ventilation exceeds the metabolic demands.
- Leads to respiratory alkalosis from hypocapnia (PaCO2 < 36 mmHg)
- Caused by anxiety, head injury, or severe hypoxemia
Cyanosis
- Bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes
- 5g/dL of desaturated hemoglobin regardless of concentration
Characteristics of peripheral cyanosis
- Most often caused by poor circulation
- Best observed in the nail beds
- Ex: Reynauds
Characteristics of central cyanosis
- Caused by decreased arterial oxygenation (low partial pressure of oxygen)
- Best observed in buccal mucous membranes and lips
- Ex: pulmonary or cardiac disease (right to left shunts)
Clubbing is due to...
chronic hypoxia
Characteristics of pleural pain
- Usually sharp or stabbing in character
- Infection or inflammation of parietal pleura (pleuritis or pleurisy)
- Can cause pain when the pleura stretch during inspiration and are accompanied by a pleural friction rub (auscultation)
Characteristics of chest wall pain
- Muscle or rib pain (rib fracture)
- Costochondritis: inflammation of the costo-chondral junction
- Reproducible
Hypercapnia
- Increased carbon dioxide (CO2) in the arterial blood
(increased PaCO2) = respiratory acidosis
- Due to hypoventilation of alveoli
- CO2 easily diffuses from blood into alveolar space
- Occurs from decreased drive to breathe or an inadequate ability to respond to ventilatory stimulation
- Easily overlooked as breathing pattern and ventilation may appear normal
Hypoxemia
- Reduced oxygenation of arterial blood (reduced PaO2)
- Can lead to HYPOXIA – reduced oxygen of cells in tissues
Due to problems with:
- Oxygen delivery to alveoli
- Ventilation of alveoli
- Diffusion of oxygen from alveoli into blood
- Perfusion of pulmonary capillaries
Hypoxemia causes widespread ____________________________ and when severe leads to __________________________________.
tissue dysfunction; organ infarction
Hypoxemia due to decrease in oxygen delivery
- Depends on amount of oxygen in inspired air
Common clinical causes:
- High altitude
- Low oxygen content of gas mixture
- Enclosed breathing space (suffocation)
Hypoxemia due to hypoventilation of alveoli
- Hypoventilation causes increase in PaCO2 and decrease in PaO2
- Less oxygen available to diffuse into blood
- Can be corrected easily if alveolar ventilation is improved by increases in RATE and DEPTH of BREATHING
Hypoxemia due to diffusion of oxygen from alveoli into blood
Dependent on 2 factors:
1.) Balance between alveolar ventilation and perfusion (V/Q)
2.) Diffusion of oxygen across the alveolarcapillary membrane (impaired if membrane is thickened or if there is a decrease in SA)
V/Q Mismatch
Abnormal ventilation-perfusion ratio
Most common cause of hypoxemia
V/Q mismatch
Normally, the alveolar-capillary lung units receive ______________ amounts of ventilation and perfusion
equal
Normal VQ
0.8-0.9
- Perfusion is greater than ventilation in lung base
- Blood is normally shunted to bronchial circulation
Low V/Q
- Inadequate ventilation occurs to well perfused areas of the lung
- Atelectasis
- Asthma
- Pulmonary edema
- Pneumonia
Very low V/Q
SHUNTING
- Blood passes through portions of the pulmonary capillary bed that gets no ventilation
High V/Q
- Poor perfusion to well ventilated portions of the lung
- Wasted ventilation (alveolar dead space)
- PE
Hypoxemia due to poor perfusion of pulmonary capillaries
- Diffusion impaired due to thickening of the surface (edema, fibrosis)
- Surface area is decreased
- Emphysema (destruction of alveoli)
Characteristics of acute respiratory failure
- Gas exchange is inadequate (hypoxemia)
- PaO2 is ≤50 mm Hg.
- Hypercapnia occurs, during which partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is ≥50 mm Hg
- pH is ≤7.25
-Requires ventilatory support, oxygen, or both.
-Often mix of hypercapnia and hypoxemia
-Complication of any major surgical procedure
- Most common post-op problems: atelectasis, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, PE
Respiratory failure can be due to direct injury to...
- Lungs
- Airway
- Chest wall
- Brain
- Liver
True or False: Only those with a history of pulmonary disease can have respiratory failure
False
Respiratory failure is mostly...
Hypercapnic: d/t poor alveolar ventilation (pt. needs ventilator support)
Hypoxemic: d/t poor exchange of oxygen between alveoli and capillaries (pt. needs oxygen therapy)
Early symptoms of hypoxia
Restlessness, anxiety, tachycardia/tachypnea
Late symptoms of hypoxia
Bradycardia, extreme restlessness, dyspnea
Causes of chest wall restriction
- Deformity
- Trauma
- Immobilization (pain, disease, fat tissue)
Work of breathing is increased and ventilation may be compromised d/t a decrease in tidal volume
Diagnosis of chest wall restriction
- Pulmonary function testing (look for reduced FVC)
- ABG (hypercapnia)
- Radiographs
Causes of neuromuscular disease
- Muscular dystrophy
- Myasthenia gravis
- GBS
Can lead to impairment of respiratory muscles d/t chest wall restrictions
____________________________ is the most common cause of hospital admission due to hypoventilation and ______________________.
Respiratory difficulty; hypercapnia
_________________________ is the instability of a portion of the chest wall from rib or sternal fracture.
Flail chest
Flail chest can cause ________________________________ of the chest with breathing, which can then lead to...
paradoxical movement; hypoxemia and hypoventilation
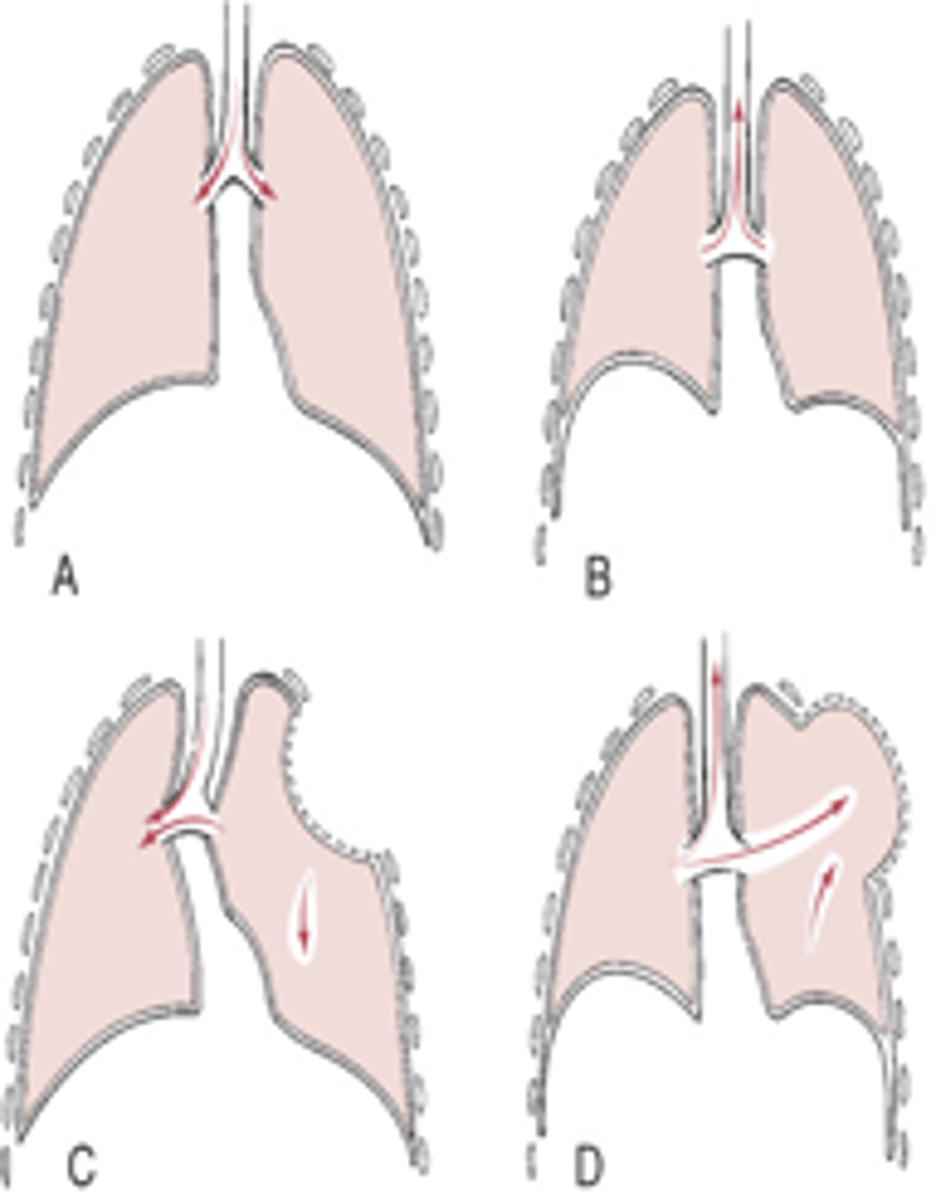
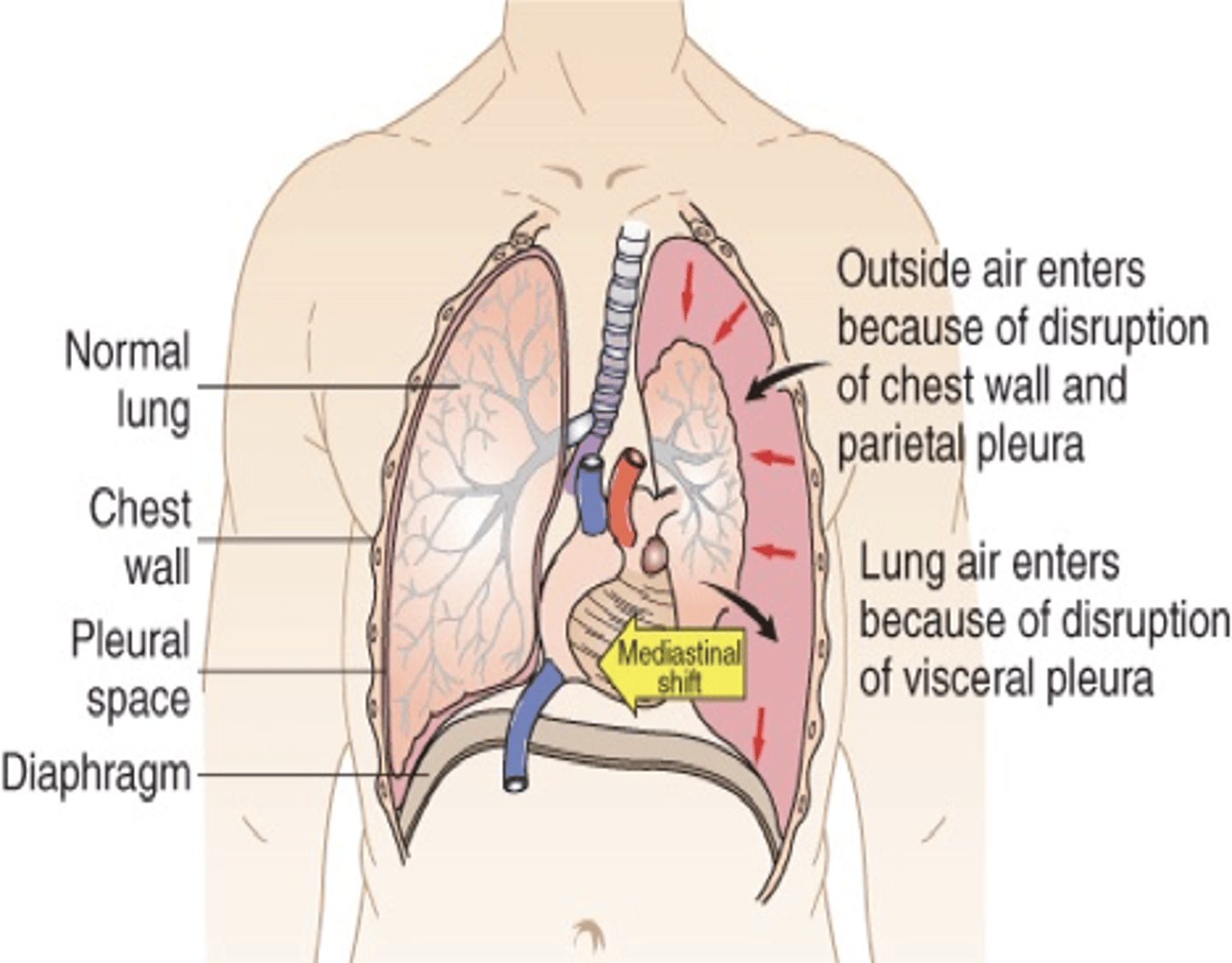
Pneumothorax
Presence of air or gas in the pleural space caused by a rupture in the visceral pleura or the parietal pleura and the chest wall
Primary (spontaneous) pneumothorax
Occurs unexpectedly in healthy individuals (men, 20-40 yoa)
Secondary pneumothorax
Caused by disease (COPD), trauma, injury (mechanical ventilation), or condition
Iatrogenic pneumothorax
Caused by medical treatments (transthoracic needle aspiration)
Open pneumothorax
Air pressure in the pleural space equals barometric pressure, because air that is drawn into the pleural space during inspiration is forced back out during expiration
Tension pneumothorax
- Site of pleural rupture acts as a one-way valve, permitting air to enter on inspiration but preventing its escape by closing up during expiration
- As more air enters, air pressure exceeds barometric pressure
- Air pressure pushes against the recoiled lung causing compression atelectasis, pushes against the mediastinum compressing and displacing the heart
LIFE THREATENING
Clinical manifestations of pneumothorax
- Sudden pleural pain, tachypnea, and possible mild dyspnea
- Severe hypoxemia, tracheal deviation away from the affected lung, and hypotension
- Absent or decreased breath sounds, hyper-resonance to percussion on affected side
Treatment: chest tube
Pleural effusion
Presence of fluid in the pleural space from blood vessels or lymphatics
Transudative effusion
Watery and diffuses out of the capillaries (CHF)
Exudative effusion
High concentrations of white blood cells and plasma proteins (inflammation/infection/CA)
Chylothorax
Milky fluid of lymph/fat (injury/infection/disorder)
Hemothorax
Blood exudate
Empyema
Pus (infection, inflammation, abcess)
Clinical manifestations of pleural effusion
- Dyspnea and pleural pain
- Small pleural effusions may be undetected and DO NOT affect lung function
Treatment: thoracocentesis, chest tube, surgery
Clinical manifestations of empyema
Cyanosis, fever, tachycardia, cough, and pleural pain
Treatment
-Administration of antimicrobial medications (Staph aureus, E.coli, anaerobic bacteria and Klebsiella pneumoniae)
- Drainage of the pleural space with a chest tube
Characteristics of restrictive lung disorders
- Decreased compliance of lung tissue
- Patients complain of dyspnea, have increased RR, decreased TV
- Decreased FVC; FEV1/FVC normal (<0.7)
- Low V/Q = hypoxemia
_________________________ is the passage of fluid and solid particles into the lungs.
Aspiration
Most frequent site affected by aspiration
Right lower lobe