B6: Cell Bio Exam 2 (7-14) FINAL (copy)
1/408
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Why talk it out when your adrenal medulla can just flood you with adrenaline instead?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
409 Terms
hydroxyapatite
what is the main crystalline salt of bone?
bone, kidney, GI
3 tissues responsible for controlling calcium and phosphate levels
Calcitonin, PTH, activated vitamin D
3 hormones responsible for controlling calcium and phosphate levels
bone
acts as a reservoir for 99% of body calcium
calcium and phosphorus
hydroxyapatite contains:
crystal precipitate
in a physiologic fluid, calcium and phosphate form a ________ _________ – we don't want that, so there are mechanisms of exchange
down
in a normal setting, to not have precipitates in the bloodstream, as calcium goes up, phosphate needs to go _____
PTH
What hormone:
acts to increase plasma Ca2+, so there needs to be other mechanisms to ↓ plasma phosphate to not have precipitates in blood stream
increases the number of sodium fast channels, hence easier depolarization
how does low calcium increase excitability of cells?
8.5-10.5
normal calcium range:
hypocalcemia
What disorder:
-<8.5mg/dl
-extracellular Ca2+ → electrical excitability of excitable cells (i.e., sensory and motor nerves and muscle)
-Increases activity of Na fast channels, hence easier depolarization
-Tingling, numbness, muscle twitch/spasms and tetany
hypercalcemia
What disorder:
->10.5mg/dl
-extracellular Ca2+ → excitability of excitable cells
-Constipation, kidney stones, bone pain/loss, polyuria/polydipsia, lethargy, coma
-stones, bones, groans, psychiatric overtones
pregnant women
in ______ ______, a negative calcium balance comes from intestinal calcium absorption being less than calcium excretion, with the deficit coming from the maternal bones
growing children
in _______ ____, a positive calcium balance comes from intestinal calcium absorption exceeding urinary excretion, with the excess is deposited in the growing bones
1,25-dihydroxycholecalcirerol
active form of vitamin D
ionized
the most abundant form of calcium:
-hint: rest is bound to albumin (40%) or complexed with anions (10%)
ionined
only ______ calcium is biologically active
albumin
only calcium bound to _______ (protein bound) cannot be filtered
pH & albumin
factors modifying ionized calcium
albumin
increased H+ binds to ______, raising amount of ionized calcium
-low protein bound calcium
-n/c free ionized calcium
-low total calcium
how does hypoalbuminemia (cirrhosis, critical illness) impact calcium levels?
-high protein bound calcium
-n/c free ionized
-high total calcium
how does hyperalbuminemia (hypovolemia, high protein intake) impact calcium levels?
-inc protein bound
-dec free
-normal total
how does alkalosis alter plasma calcium levels?
-dec protein bound
-inc free
-normal total
how does acidosis alter plasma calcium levels?
-inc protein bound calcium
-normal free ionized calcium
-inc total calcium
how does pregnancy alter plasma calcium levels?
phosphate
What ion:
-major intracellular anion/acid-base buffer
-component of all glycolytic enzymes, ATP/DNA/RNA
-uptake from gut is linear with diet levels
-primary regulation via urinary excretion
hyperphosphatemia
What disorder:
-increased phosphate leads to increased binding of free calcium, therefore there is decreased free calcium
refeeding syndrome
what disorder:
-Insulin promotes phosphorus uptake into peripheral cells
FGF23
aka osteokine
-peptide produced by osteocytes
-negative regulator of serum phosphate via ability to inhibit reabsorption in the kidney, promotes excretion
2.5-4.5
normal serum phosphate level
Ricketts (children) & osteomalacia (adults)
hypophosphatemic disorders associated with excess production of FGF23
FG23 mutation
AD hypophosphatemic rickets is due to:
PHEX mutation
X linked hypophosphatemic rickets is due to excess FGF23 secondary to:
FGF23
sometimes ectopically produced by slow-growing occult mesenchymal tumors, causing a hypophosphatemic paraneoplastic syndrome
bone
-in a constant state of resorption/reformation
-metabolically active tissue, has a good blood supply, etc.
-Hydroxyapatites are most abundant mineral crystals; contain calcium/phosphorous in a molar ratio of about 1.7 to 1 (2.2 to 1 weight ratio), with all the phosphorous as phosphate (PO4-)
-osteoblasts form new bone, Osteoclasts resorb (Breakdown)
hyperphosphatemia & 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D
production of FGF23 is increased by:
FGF23
-inhibits 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, resulting in decreased phosphate absorption intestinally and renally
calcium sensing receptor in the plasma membrane
how do chief cells monitor calcium levels?
chronic hypercalcemia
What disorder:
-decreases transcription of prepro PTH (as well as post translational processing)
C terminal fragment
PTH derived fragment that is most represented in serum, has a longer half life
within seconds!
how fast does PTH respond to calcium levels?
Magnesium
_______ has parallel, but less important, effects on PTH secretion than calcium
directly
PTH works (directly/indirectly) on bone and kidney
indirectly
PTH works (directly/indirectly) on intestine
kidney
effects of PTH on the ______:
-increase 1-OHase, making more active vitamin D
-increase calcium reabsorption in the distal tubule
-decrease PO4 reabsorption in the proximal tubule
intestines
effects of PTH on the ______:
-indirect
-the increased vitamin D from the kidneys increases calcium and phosphate uptake
bone
effects of PTH on the ______:
-increase reabsorption of mineralized bone, with increases serum calcium
-Phosphate will increase initially
increase serum Ca, decrease serum P
overall action of PTH
Bind to osteoblasts, which respond by activating osteoclasts to resorb bone
how does PTH increase bone resorption?
hydroxyproline (collagen fragments)
increased resorption of organic bone matrix is reflected by excretion of:
those in the kidney!
what effect of PTH happens the quickest?
increased urinary cAMP, decreased serum phosphate, increased serum calcium
PTH inhibits renal phosphate reabsorption on the proximal tubule resulting in:
1,25 dihyddroxycholecalciferol
PTH increases intestinal Calcium absorption indirectly by stimulating ________________ in the kidney
NO!
are there PTH receptors in the intestine?
PTH (and Vit D) binds to osteoblasts
Osteoblasts release M-CSF and RANK ligand to promote osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast Activity (Bone Resorption)
Pre-osteoclasts and active osteoclasts express the RANK receptor
Secrete HCl and hydrolytic enzymes
As Osteoclasts go through Apoptotic cell death, newly exposed bone matrix releases growth factors and chemokines attracting preosteoblasts
Newly formed osteoblasts secrete collagen, proteoglycans and growth factors to replace osteoid matrix
Mineralization occurs over weeks once Ca++ becomes available (VitD effect)
how does PTH increase bone resorption?
formation
hormones promoting bone ________:
-androgens, estrogens
-thyroid hormone
-GH, IGF
-calcitonin
-vitamin D
resorption
hormones favoring bone ________:
-PTH
-cortisol
-HIGH thyroid hormone
-inflammatory cytokines
androgens, estrogens, calcitonin
hormones inhibiting bone resorption
increases calcium release
bone resorption's effect on calcium levels
proximal tubule
Actions of PTH on the ________ _________:
-PTH decreases renal phosphate reabsorption in the proximal tubule (i.e., inc phosphate excretion)
-cAMP/PKA activation Phosphorylates NERF proteins which stabilize the Sodium-Phosphate co-transporter (PT) which renders it inactive.
-Phosphate transporters taken out of lumen and degraded via lysosomes
-cAMP generated as a result of the action of PTH on the proximal tubule is excreted in the urine (inc urinary cAMP indicates PTH action)
-PKA activates 1-α-Ohase and CREB which transcribes 1-α-Ohase (converts 25, VitD to 1,25 VitD)
early distal tubule
Actions of PTH on the ___ _____ _____:
-PTH inc Ca2+ reabsorption
-Activates/inserts Ca++ transporters on lumen side
-Activates Ca++ ATPase transporters on interstitial side
NERF
cAMP activation on _____ proteins in the proximal tubule results in decreased reabsorption of phosphate in response to PTH
PTH action
urinary cAMP indicates:
1 alpha hydroxylase
enzyme that converts 25, Vitamin D to its active form
-upregulated by PKA in the distal tubule in response to PTH, increasing calcium reabsorption
enhances mineralization
long term effects of vitamin D on bone
increases bone resorption
short term effects of vitamin D on bone
-nucleus of osteoblasts (binding activates osteoclasts)
-GI tract
where are vitamin D receptors located
increase plasma calcium and PO4- so it can be used to promote bone mineralizaiton
what is the goal of Vit D?
vitamin D
a group of related secosteroids either derived from the diet or from metabolism of cholesterol
Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2)
precursor of vitamin photochemically synthesized in plants
Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3)
form of vitamin D synthesized in skin in response to sunlight
25-OH vitamin D
when we measure vitamin D levels, this is what we measure
-made in the liver by 25-hydroxylase
1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D
the most biologically active form of vitamin D synthesized by 1-alpha hydroxylase in the kidney
7-dehydrocholesterol
precursor to Vitamain D3 (cholecalciferol)
-converted to D3 by UV light
Vitamin D Binding Protein (DBP)3
Vit D3 Binds to ______ __ _____ ______, and transport to the liver.
conversion of calcidiol to calcitriol in the proximal tubules by 1-alpha hydroxylase
primary regulatory step of vitamin D formation
1st: 25-hydroxycholecalciferol on the liver
2nd: 1,25 hydroxycholcalciferol
negative feedback of vitamin D production
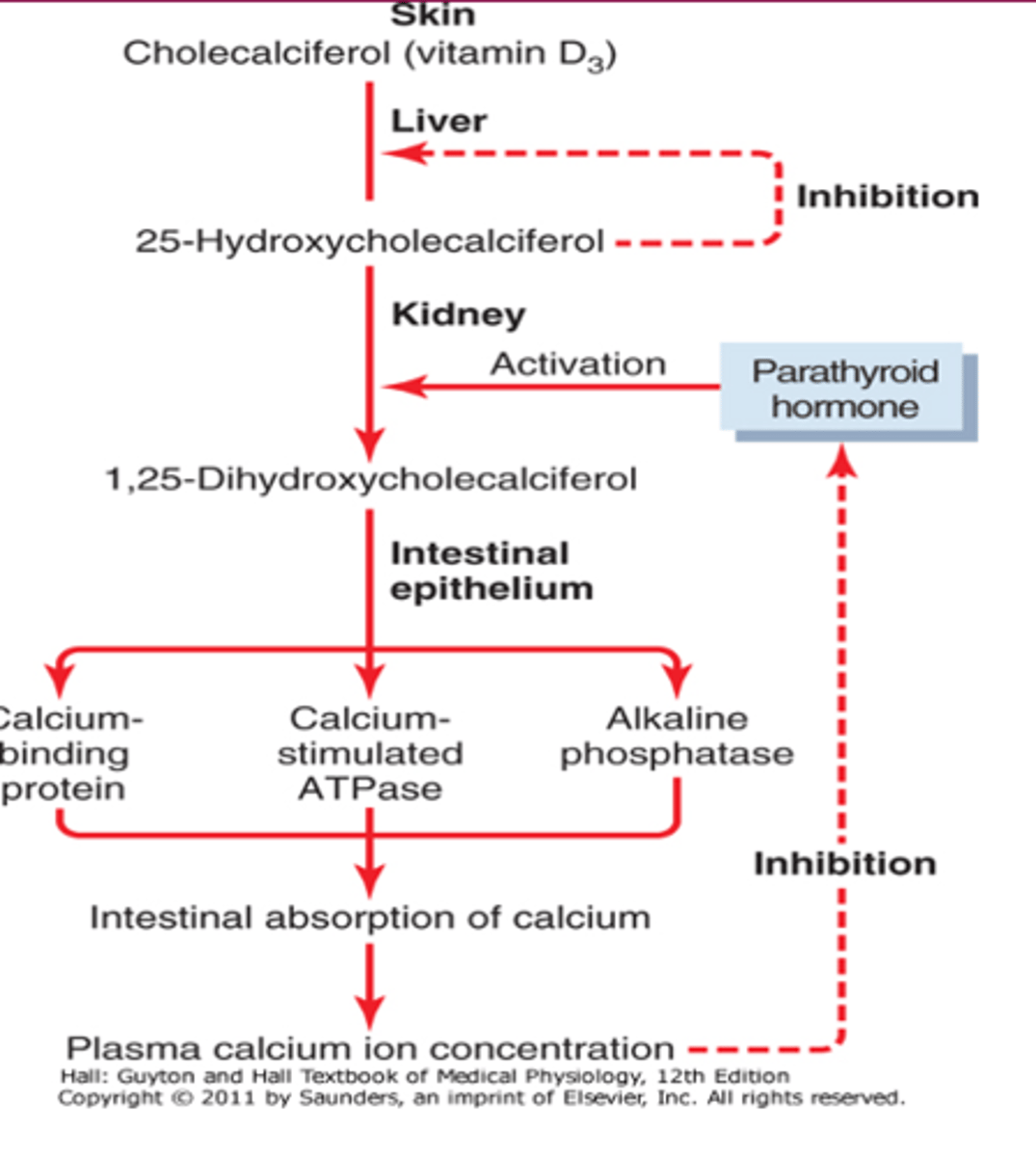
25-hydroxycholecalciferol stays relatively constant, regardless of D3 intake; represents negative feedback
why do we measure 25, Vit D to assess vitamin D status?
-decreased calcium
-increased PTH
-decreased phosphate
1 alpha hydroxylase activity is increased by:
-increased 1,25 Vit D activates 24-OHase, which converts vit D to an inactive form (1,24,25 vitamin D) that can be excreted in bile
negative feedback regulator of 1,25 Vit D
FGF-23
_____________ represses 1a-hydroxylase activity to reduce phosphate absorption
freely enters cells and binds to DNA receptor
signaling of Vit D (a steroid hormone!)
-stimulate calcium and phosphate absorption through intestinal brush border
increases sodium-phosphate transporters in enterocytes
increases epithelial calcium transporters
increases calbindins
major effect of vitamin D on the intestine
calbindins
Protein that transports Ca across osteoblasts to mineralizing (osteoid) side.
slightly increases reabsorption of filtered calcium and phosphate
affect of Vit D on kidney
interacts with osteoblast Vit. D receptors, causing increase in RANKL and M-CSF and hence resorption in the short-term
-BUT, increases availability of both Ca++ and Phosphate, so lots of substrate for mineralization during bone formation
affect of Vit D on Bone
calcitonin
works to lower plasma calcium, beginning only at calcium levels of 9.5 or higher
osteoclasts
what are the target cells of calcitonin
bind up osteoclasts to decrease bone resorption to decrease serum calcium
how does calcitonin target osteoclasts?
vitamin D
increases serum calcium and phosphate
calcium
affect of cortisol on ________:
-cause loss of calcium at the kidney
-reduces calcium absorption in the intestine
bone
long term effects of cortisol on ______:
-decrease bone formation during remodeling
-leads to OSTEOPOROSIS
increased bone turnover
increased alkaline phosphatase is a sign of
yes! due to the increased filtered load of calcium
does PTH increase calcium excretion?
primary hyperparathyroidism
which disorder:
-Elevated PTH!!!
-stones, bones, groans, psychiatric overtones
-↑ serum [Ca2+] (hypercalcemia)
-↓ to normal serum [phosphate] (hypophosphatemia)
-↑ urinary phosphate excretion (phosphaturic effect of PTH)
-↑ urinary Ca2+ excretion (caused by the increased filtered load of Ca2+)
-↑ urinary cAMP
-↑ bone resorption
-Muscle weakness, constipation etc
-decreased production of 1,25-dihyddroxycholecalciferol decreases calcium gut absorption
-kidney failure decreases calcium reabsorption
-causes increased PTH---> increased bone resorption and bone loss (osteomalacia)
-increased serum phosphate complexes free calcium, decreasing calcium
-calcification of arteries
affect of chronic renal failure on calcium and bones
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
high PTH, low calcium, high phosphate, VERY low vitamin D
tertiary hyperparathyroidism due to sustained secondary hyperparathyroidism
ESRD may also be called
tertiary hyperparathyroidism
very high PTH, high calcium, high phosphate, low/normal vitamin D
primary hypoparathyroidism
What disorder:
-often due to thyroid surgery (or congential)
-low PTH, low calcium and tetany , high serum phosphate, low urinary phosphate