OCHEM FINAL
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
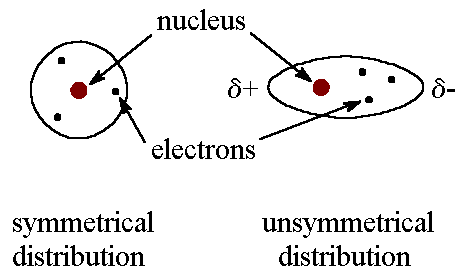
Identify the intermolecular force present
LDF
when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles
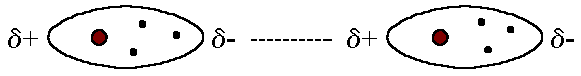
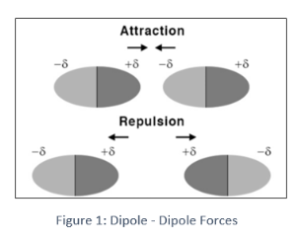
Identify the intermolecular force present
dipole dipole
electrostatic attractions between polar molecules, where the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another
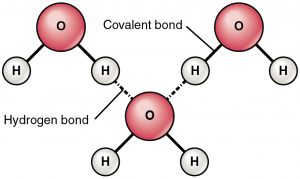
Identify the intermolecular force present
hydrogen bonding
a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom
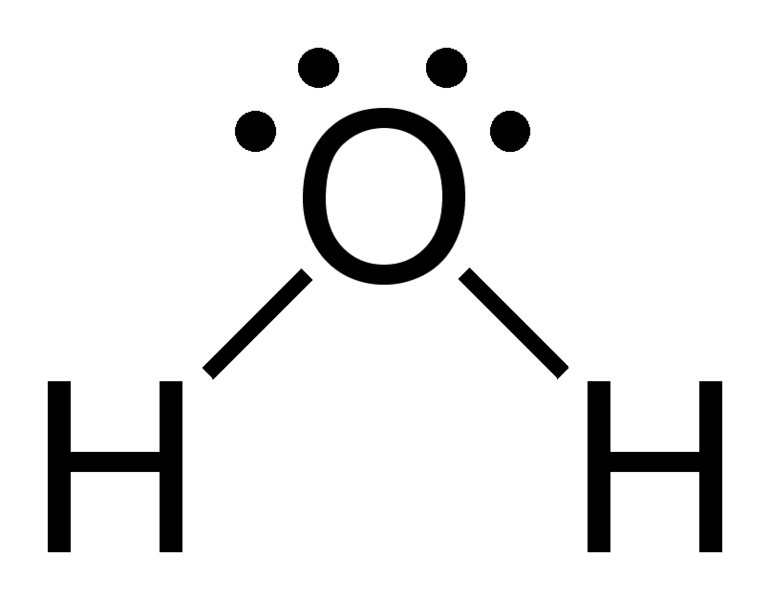
Draw a complete Lewis structure for H2O
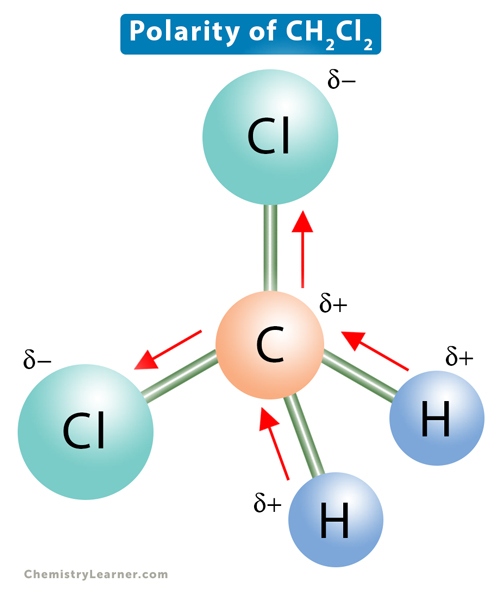
Draw a complete Lewis structure for CH2Cl2
what is the formula for formal charge?
# of valence electrons - # of not bonded electrons - ½ # of bonded electrons
what is the formula for degree of unsaturation?
( 2C + 2 - H + N - X ) / 2
Calculate the degrees of unsaturation for CH2NCl
2
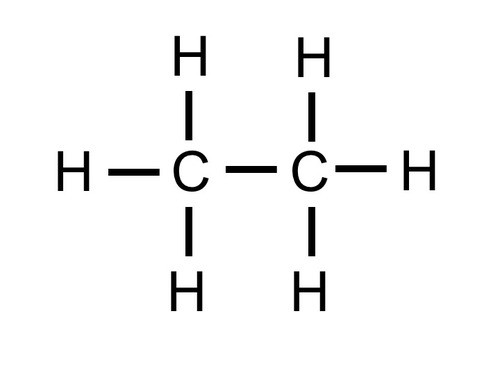
identify the functional group
alkane
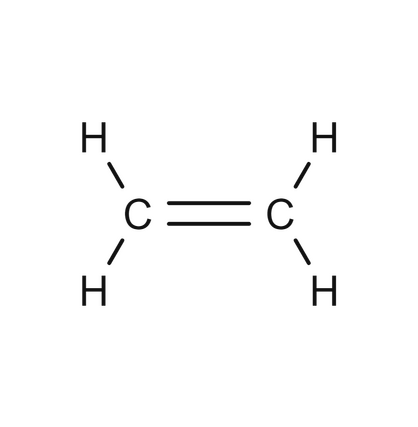
identify the functional group
alkene
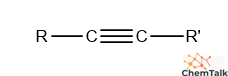
identify the functional group
alkyne
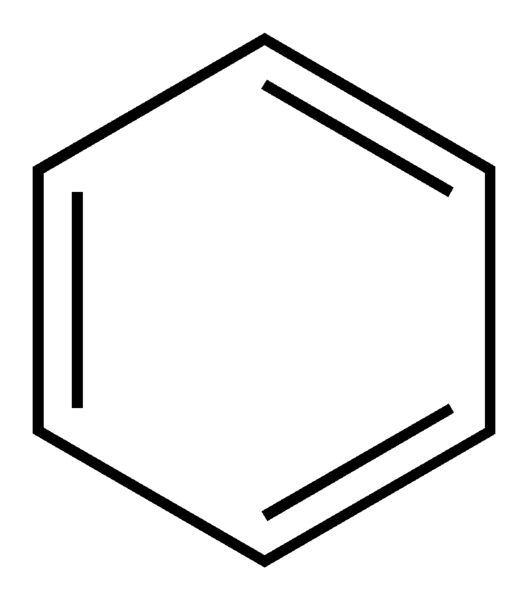
identify the functional group
aromatic ring
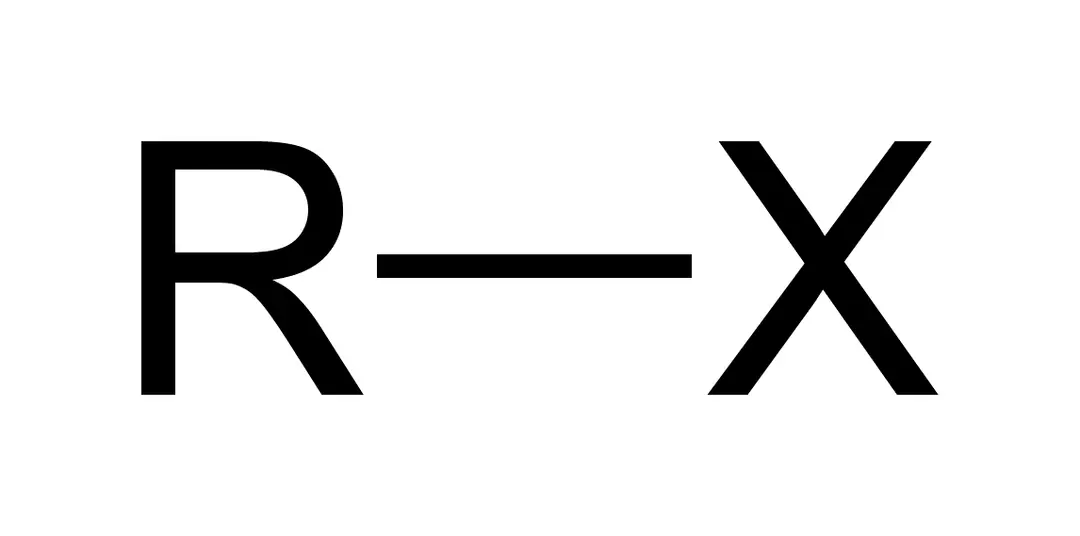
identify the functional group
alkyl halide
identify the functional group
primary alcohol
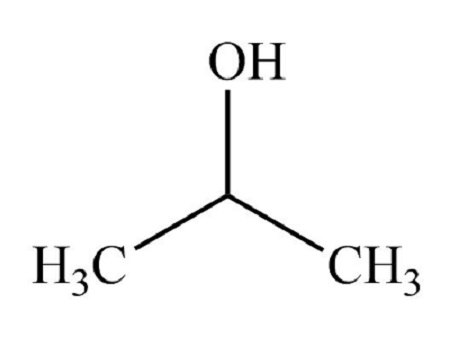
identify the functional group
secondary alcohol
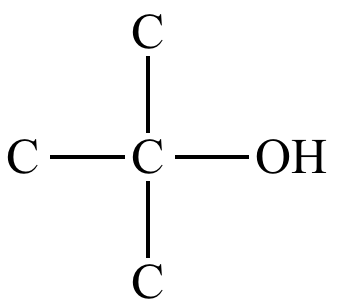
identify the functional group
tertiary alcohol
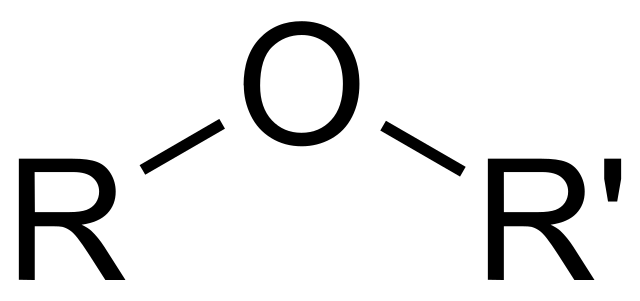
identify the functional group
ether
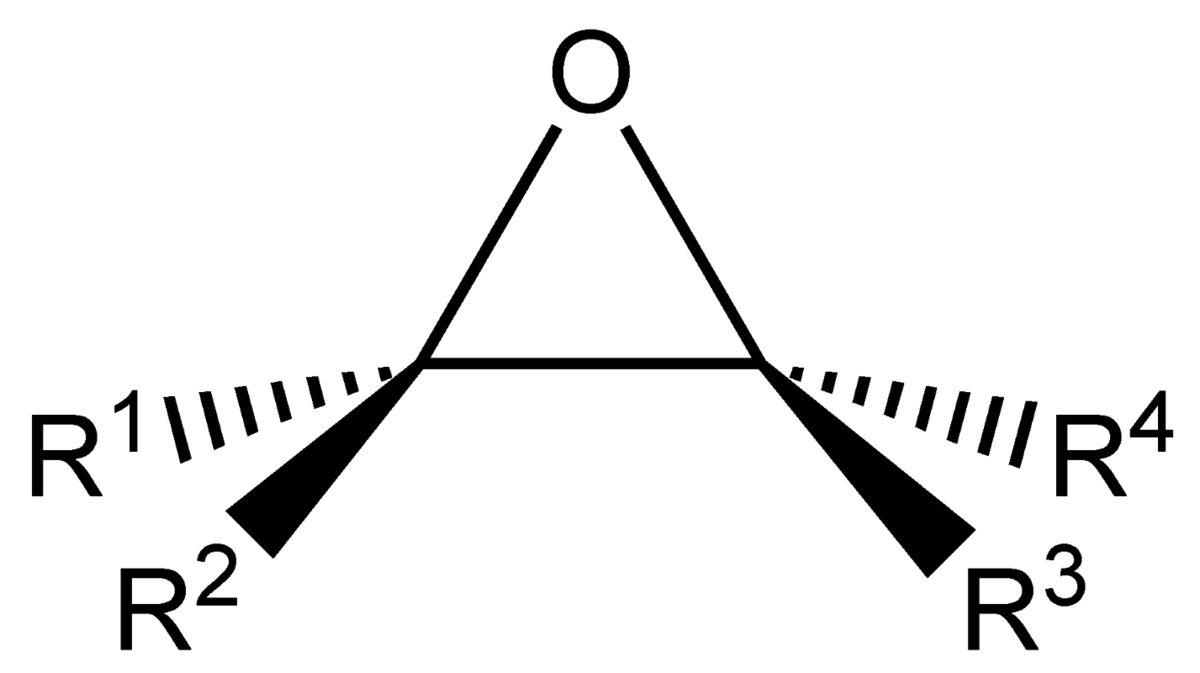
identify the functional group
epoxide

identify the functional group
aldehyde
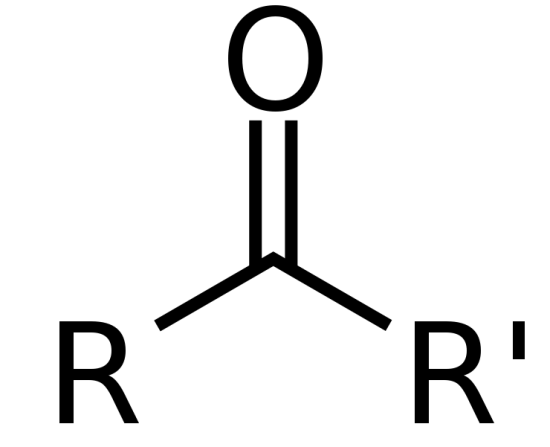
identify the functional group
ketone
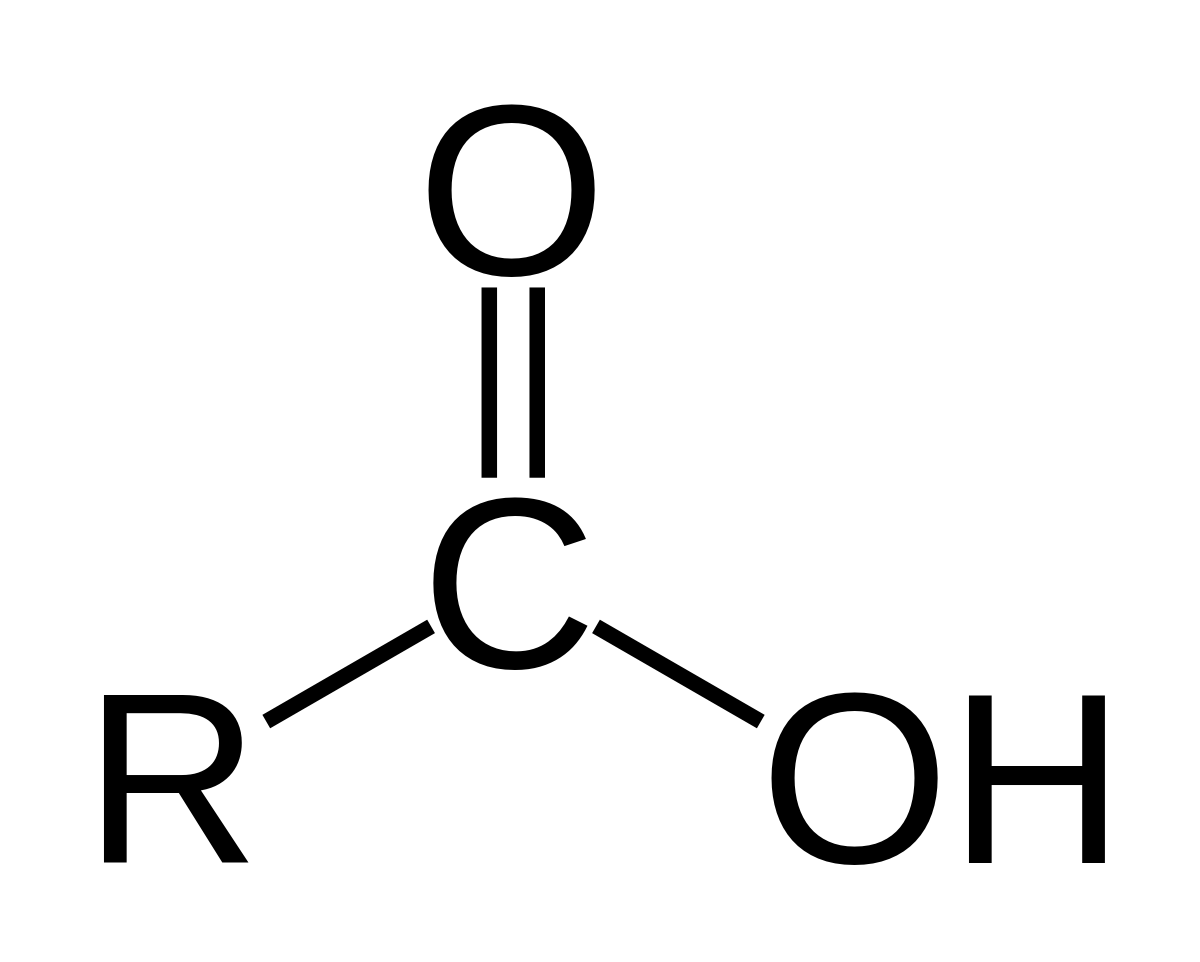
identify the functional group
carboxylic acid
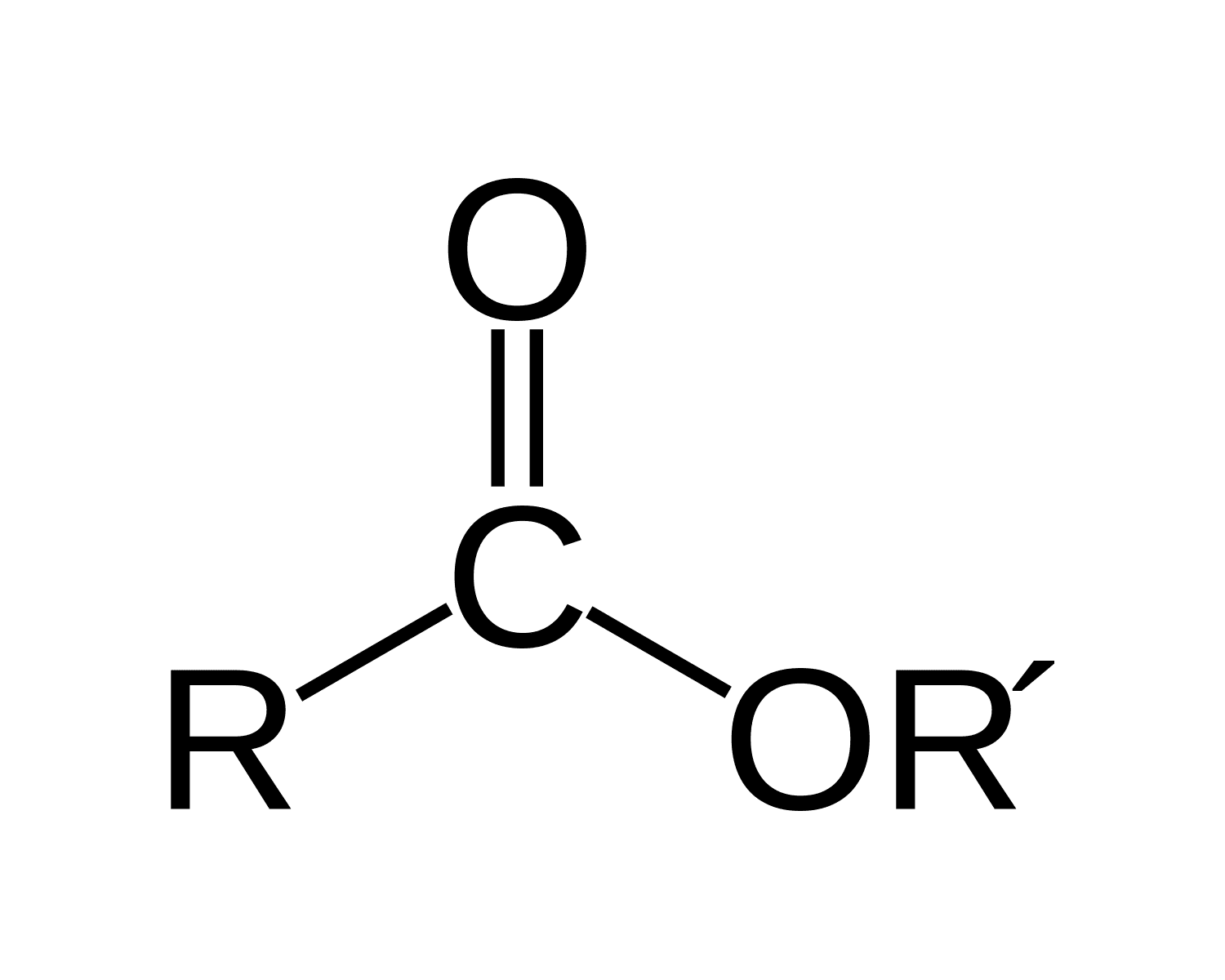
identify the functional group
ester
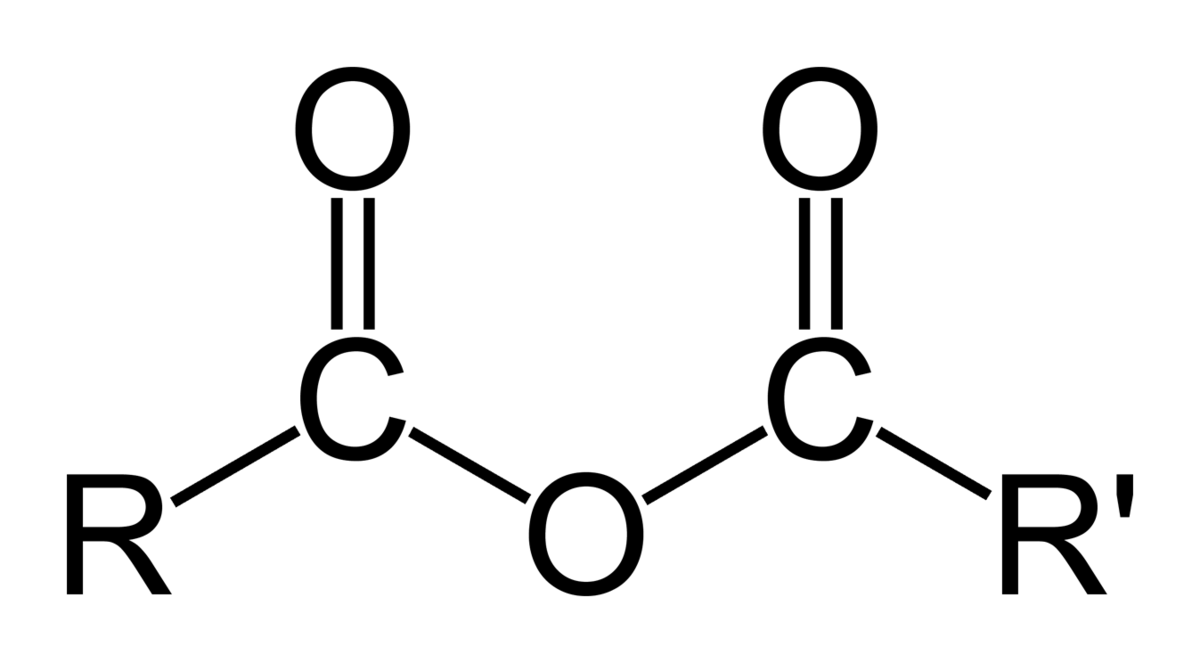
identify the functional group
acid anhydride
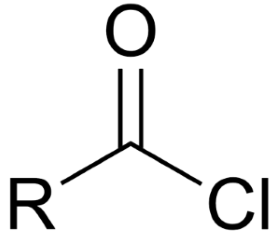
identify the functional group
acid chloride
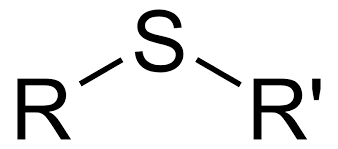
identify the functional group
sulfide
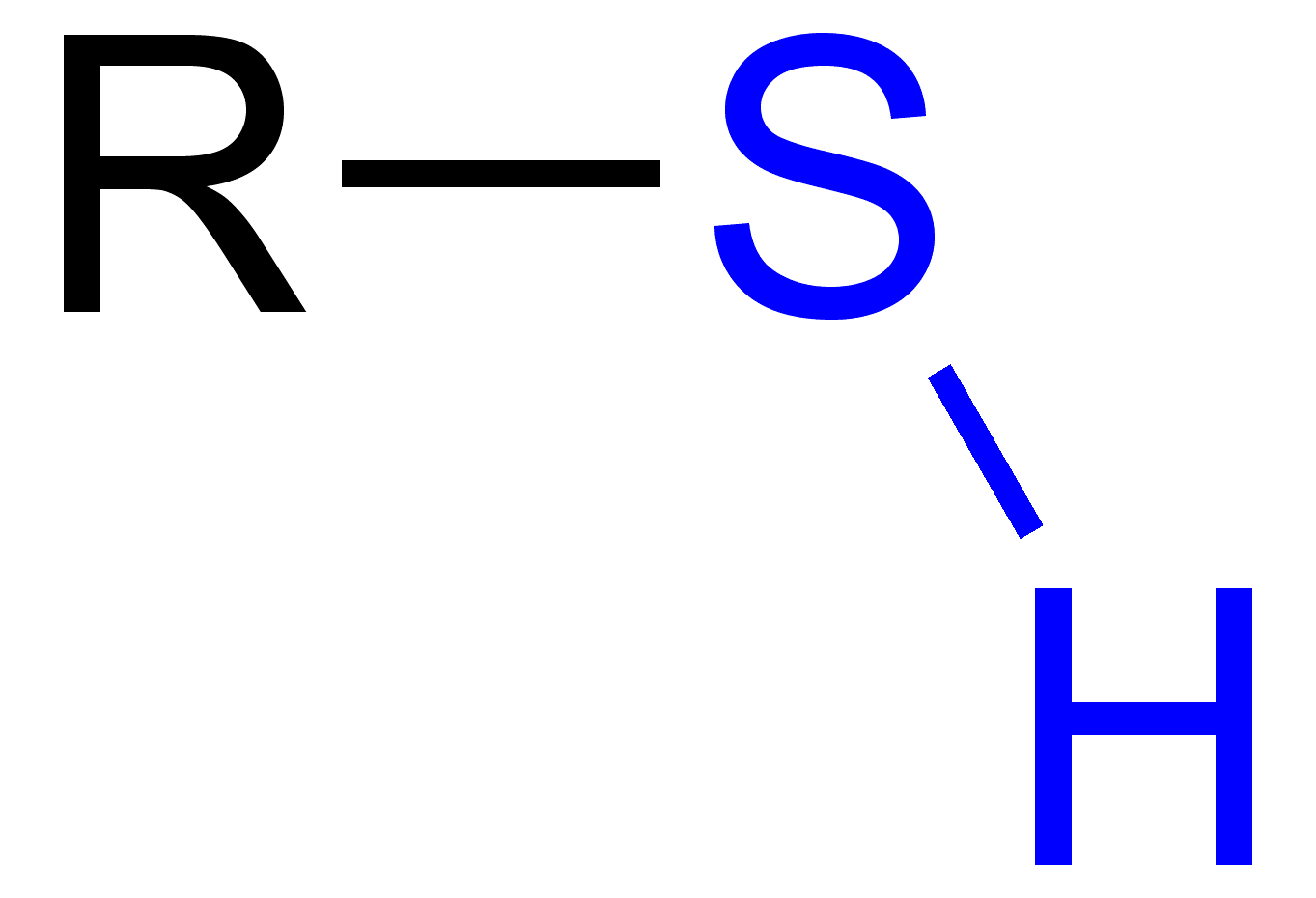
identify the functional group
thiol
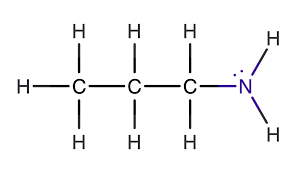
identify the functional group
primary amine
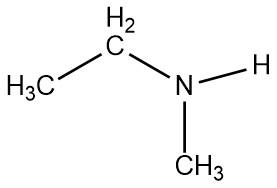
identify the functional group
secondary amine
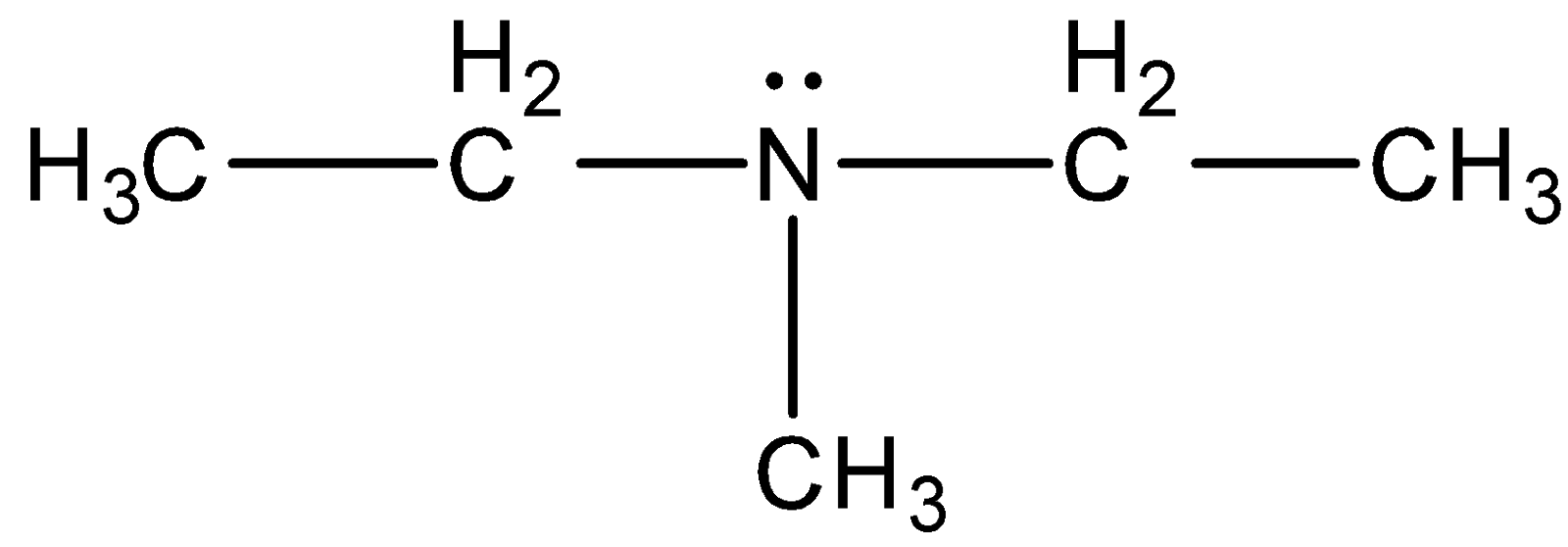
identify the functional group
tertiary amine
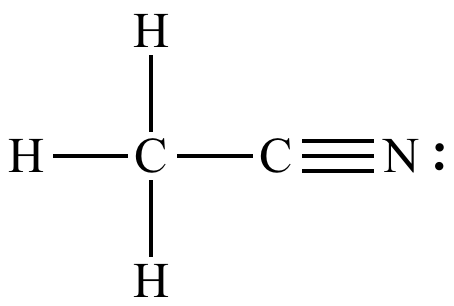
Identify the functional group
nitrile
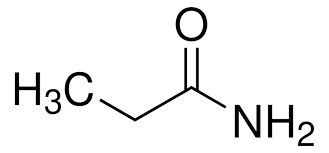
identify the functional group
primary amide
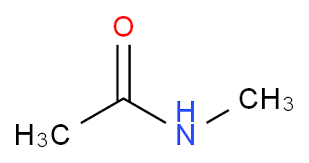
identify the functional group
secondary amide
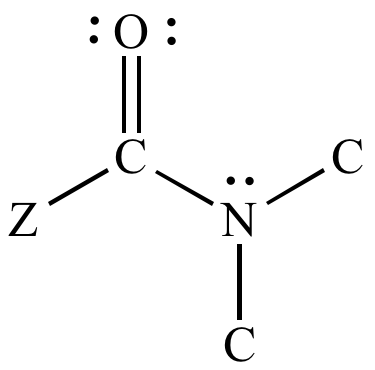
identify the functional group
tertiary amide
what is a proton donor called
bronsted acid
what is a proton acceptor called
bronsted base
what is an electron pair acceptor called
lewis acid
what is an electron pair donor called
lewis base
what is it called when a species is left after a bronsted acid donates a proton
conjugate base
what is is called when a species is formed when a bronsted base picks up a proton
conjugate acid
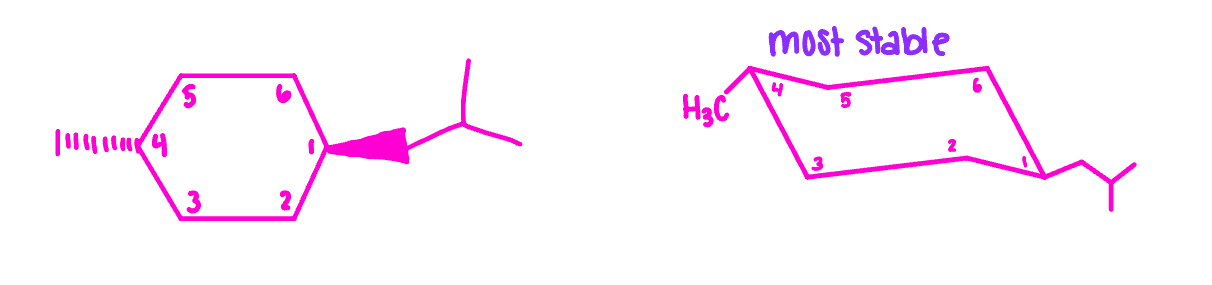
draw the planar structure for trans-1-isobutyl-4-methylcyclohexane
draw the most stable conformation of trans-1-isobutyl-4-methylcyclohexane
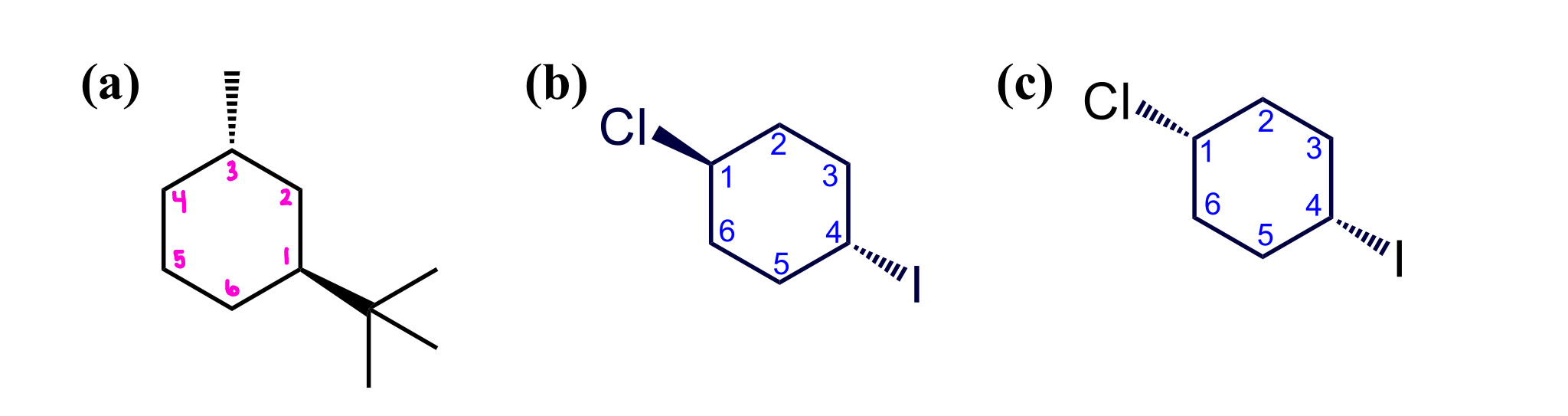
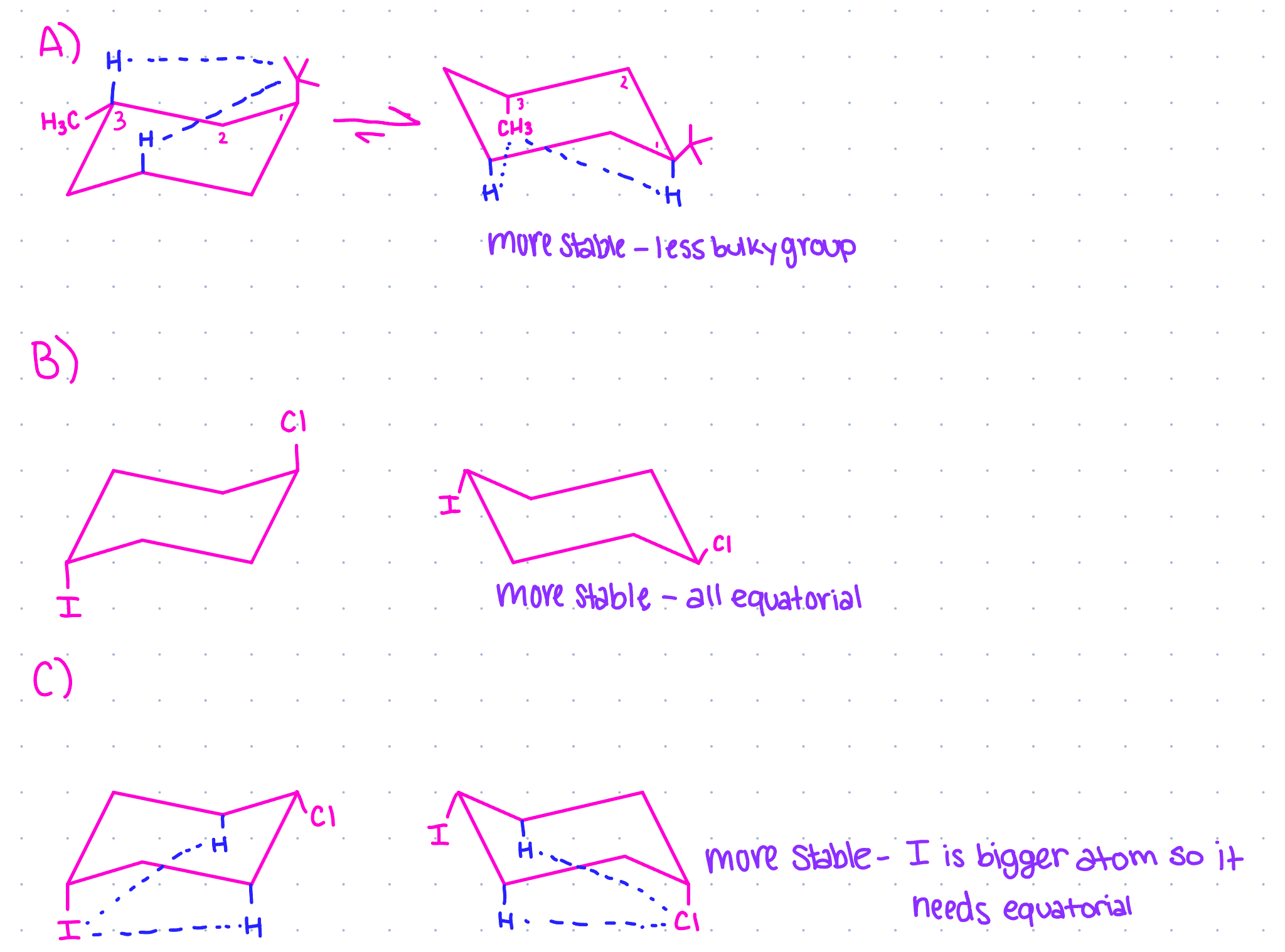
draw both chair conformations for each and identify the more stable conformer for each
what is a chiral molecule
a molecule that cannot be superimposed on it mirror image
what is an achiral molecule
a molecule that is superimposed on its mirror image
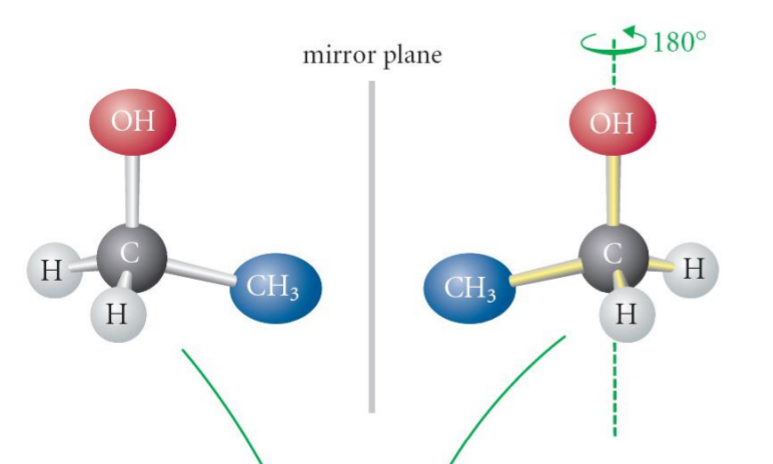
is this molecule chiral or achrial
achrial
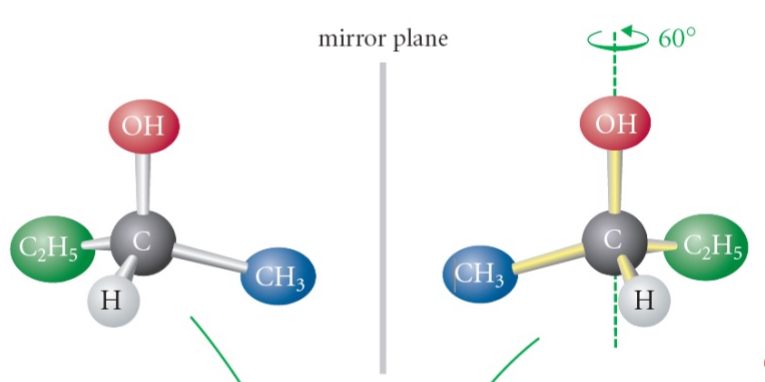
is this molecule chiral or achrial
chiral when the center carbons are aligned
when there molecular formula is the same but there it has a non superimposable mirror image, how are they related
enantiomers
true or false: all enantiomers are chiral
TRUE
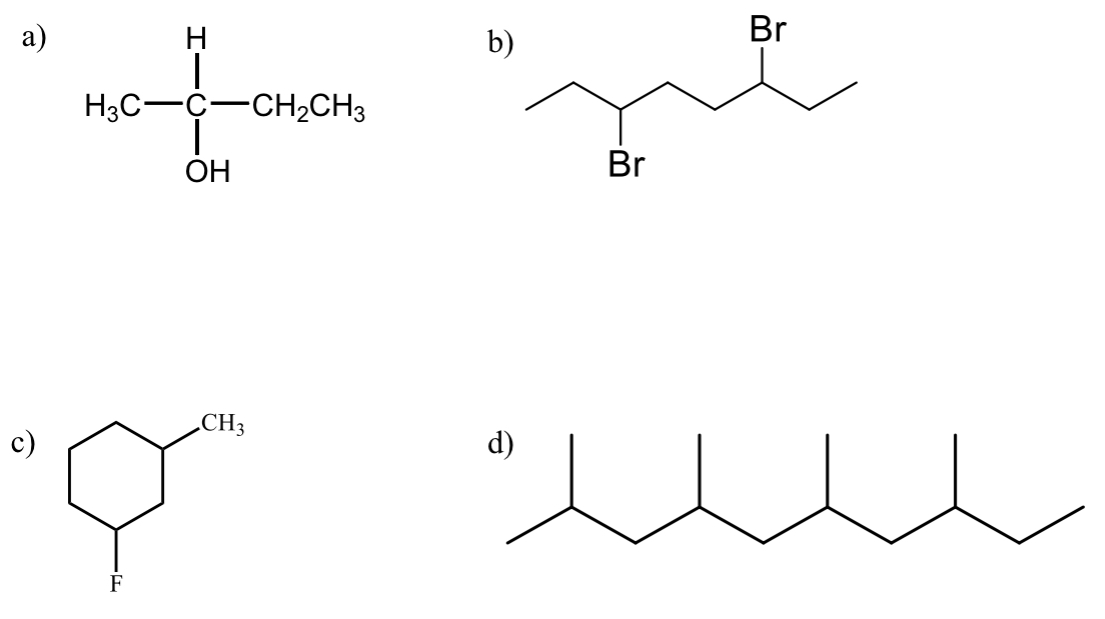
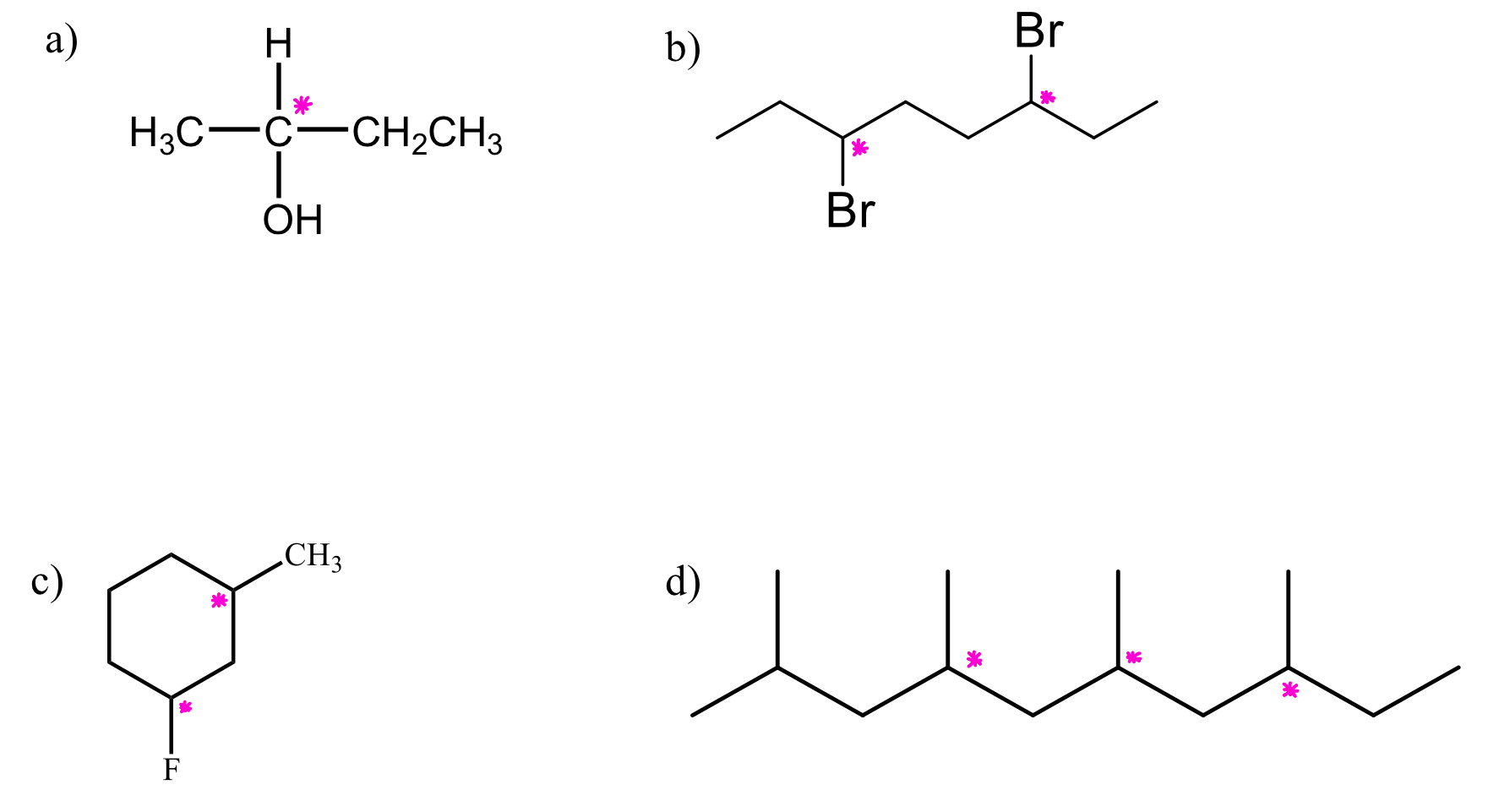
how many stereocenters does each molecule haveand where
what symmetry elements do achiral molecules have
plane of symmetry and/or center of symmetry
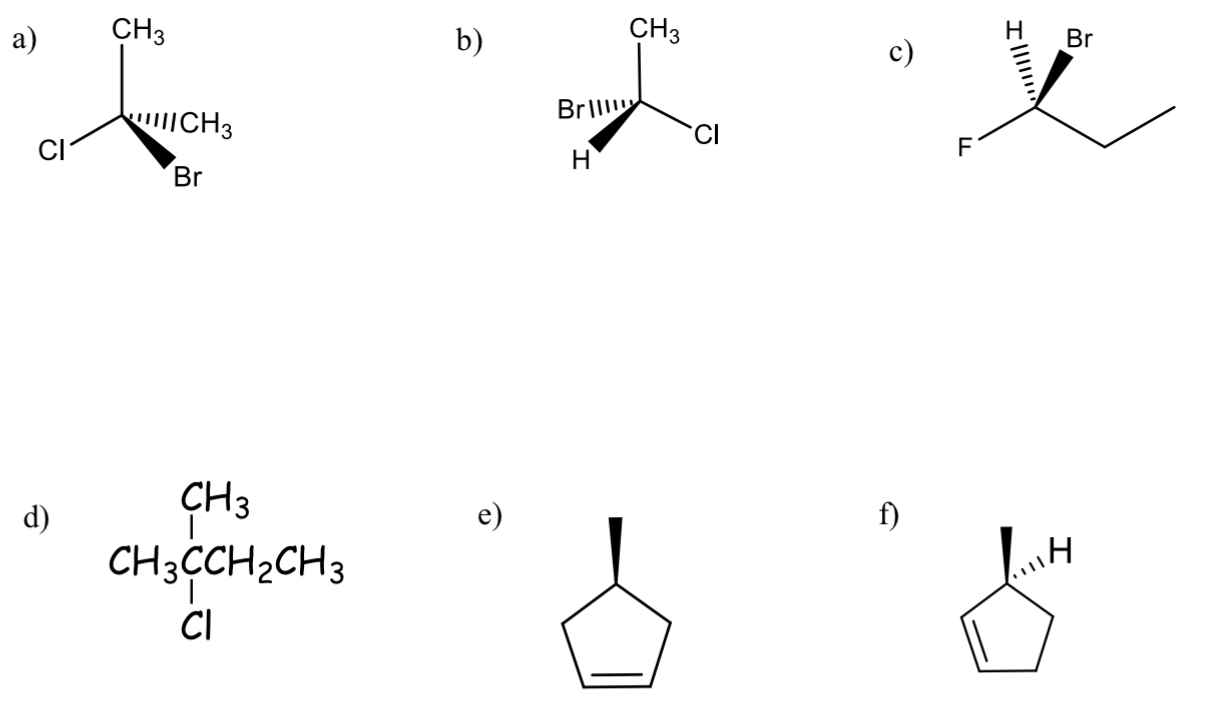
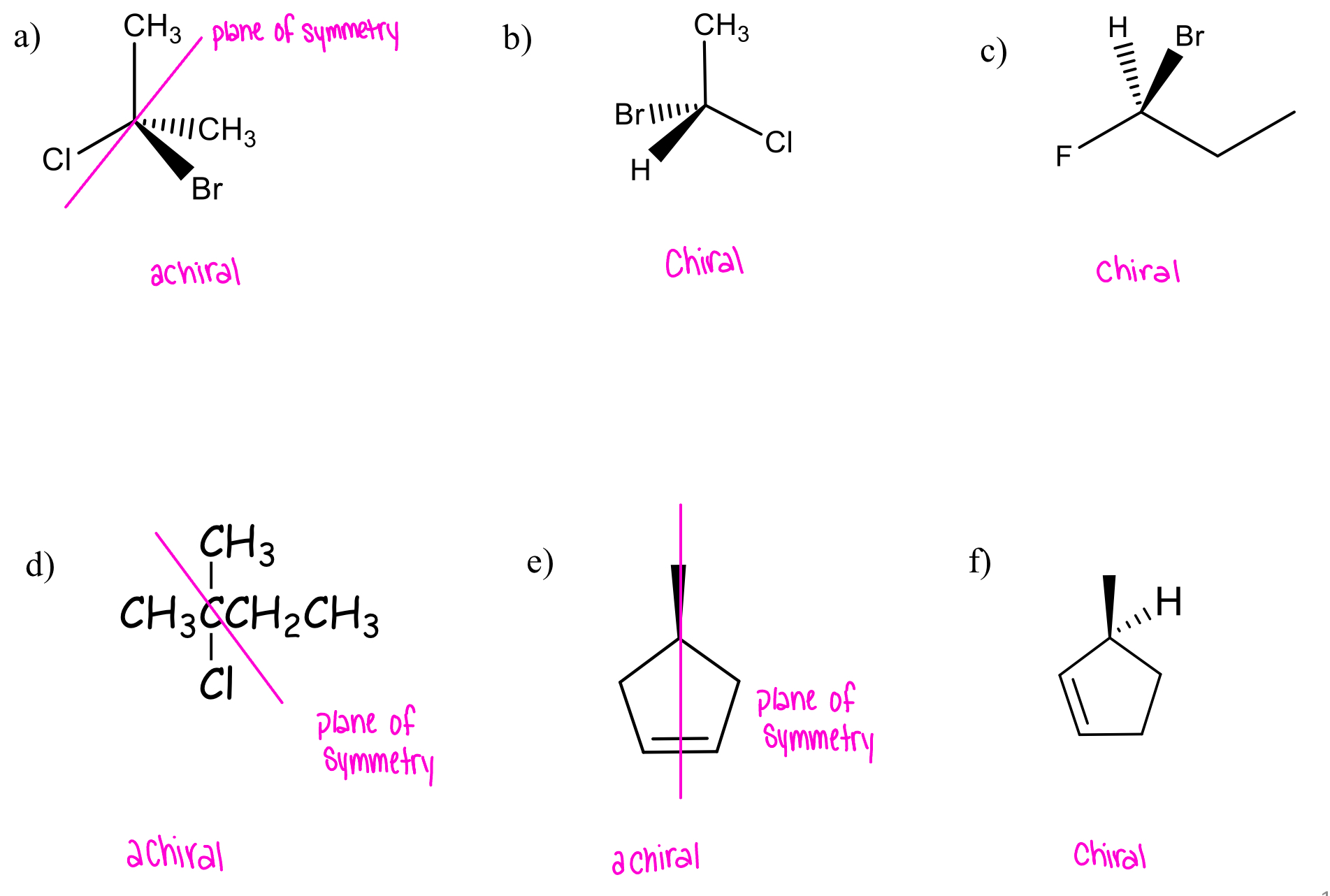
classify each as chiral or achiral

identify all sterocenters and assign absolute confiugurations
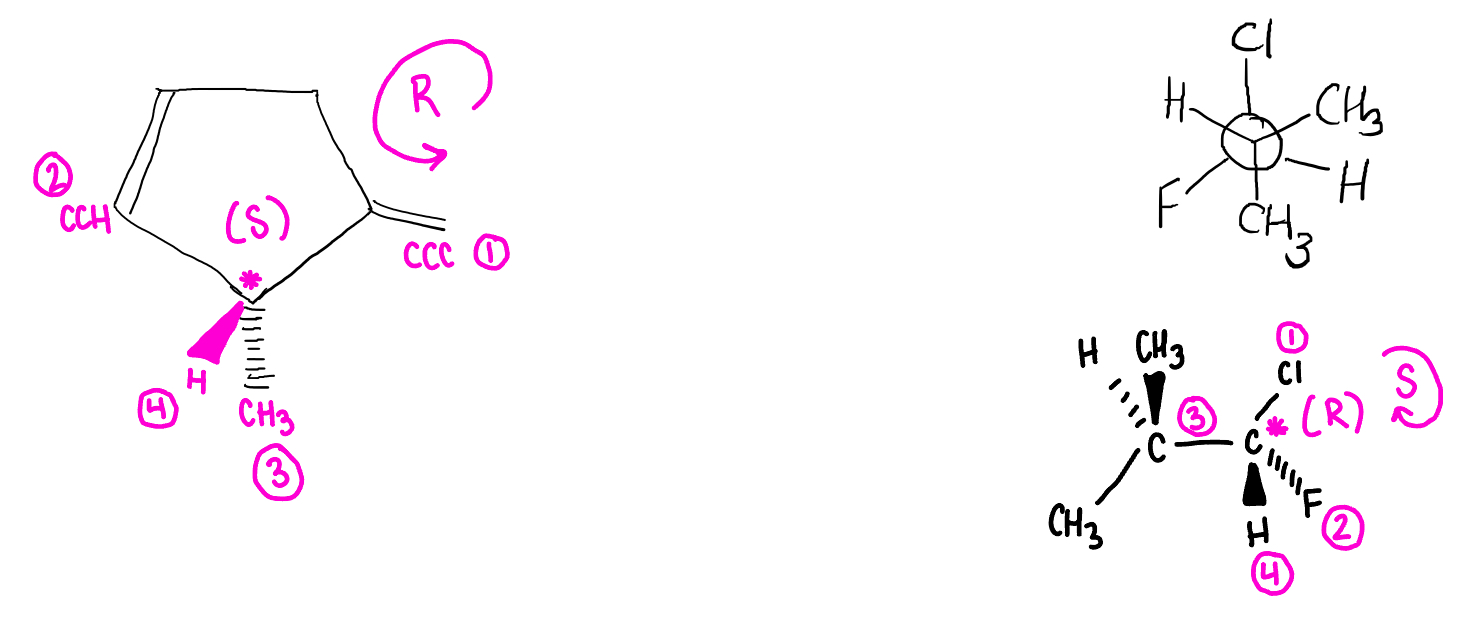
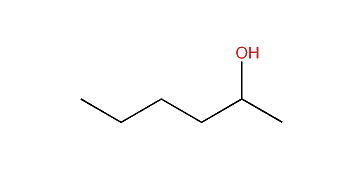
name the following alcohol
hexan-2-ol
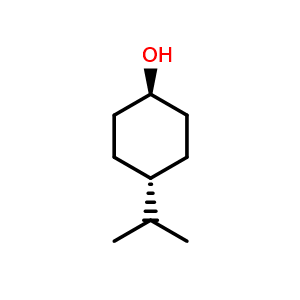
name the following alcohol
trans-4-isopropylcyclohexan-1-ol
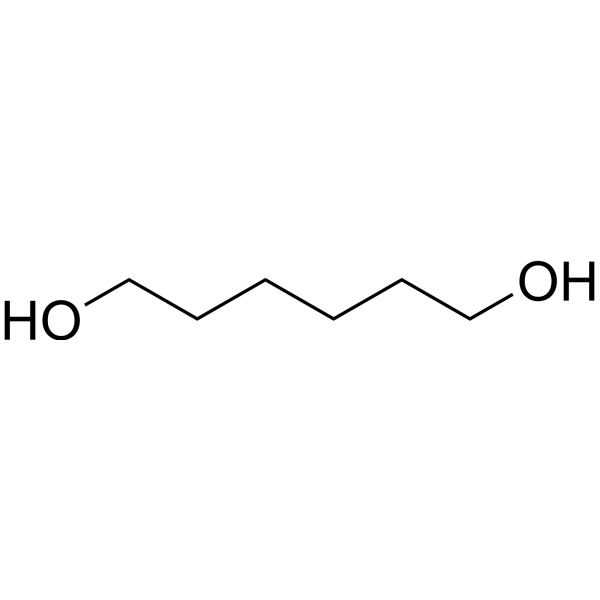
name the following alcohol
hexane-1,6-diol
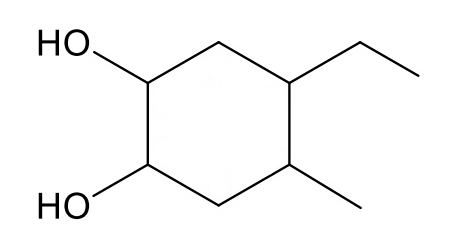
name the following alcohol
4-ethyl-5-methylcyclohexane-1,2-diol
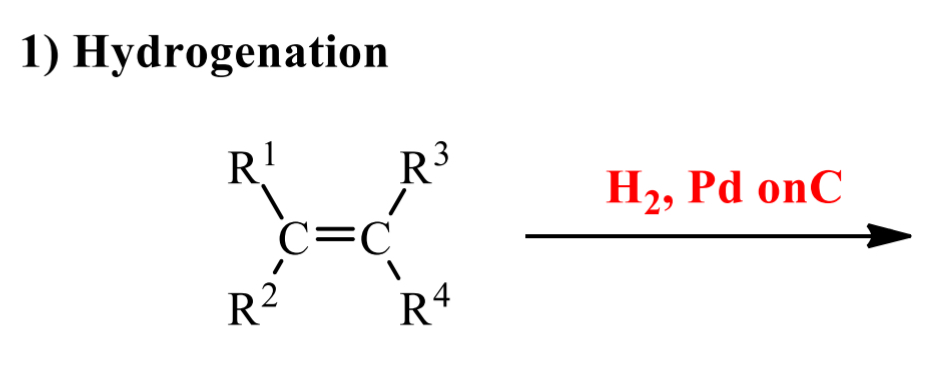
what is the product of this alkene rxn
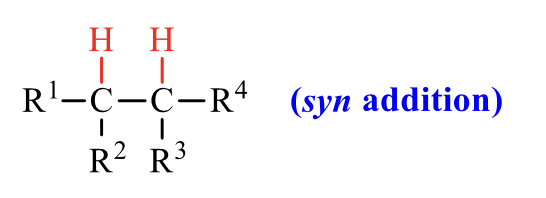
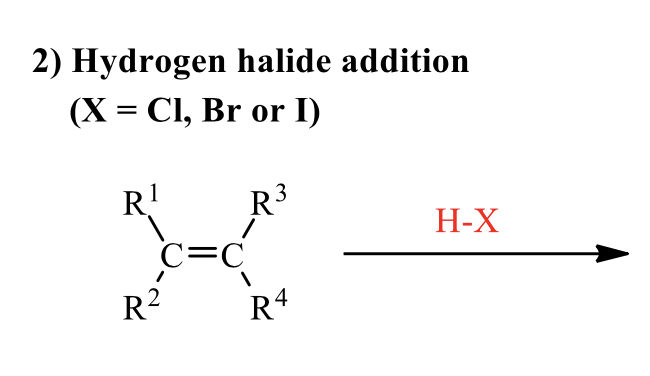
what is the product of this alkene rxn

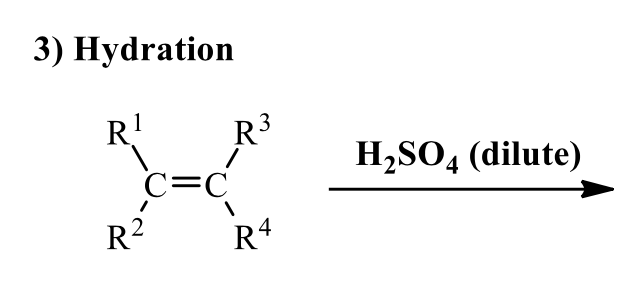
what is the product of this alkene rxn

what is the product of this alkene rxn

what is the product of this alkene rxn
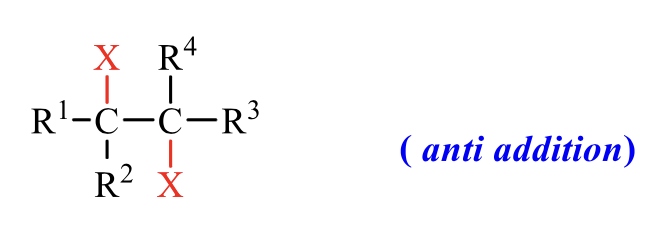
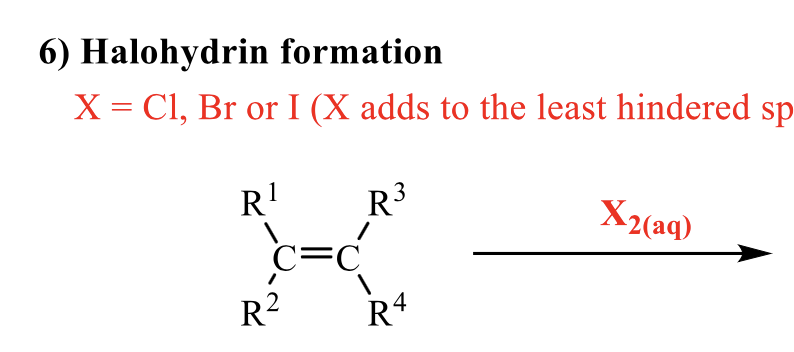
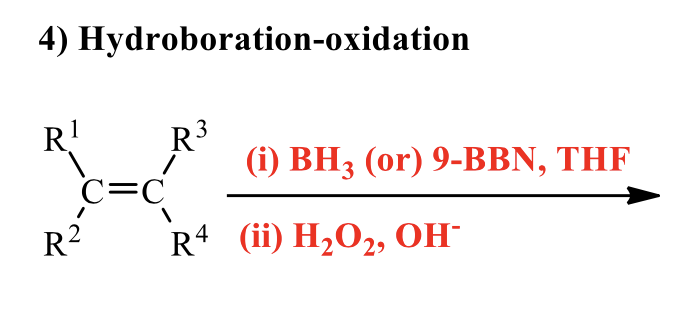
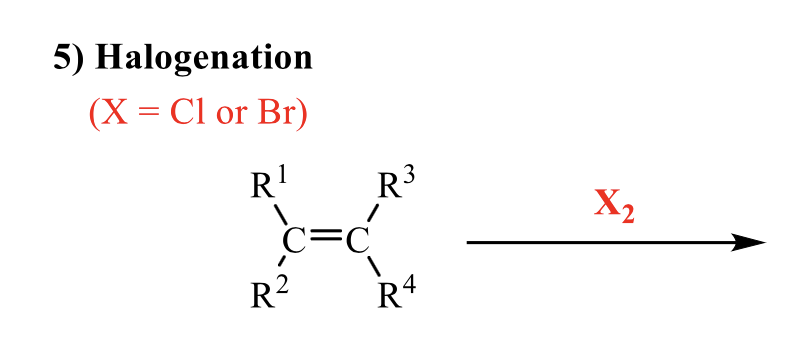
what is the product of this alkene rxn

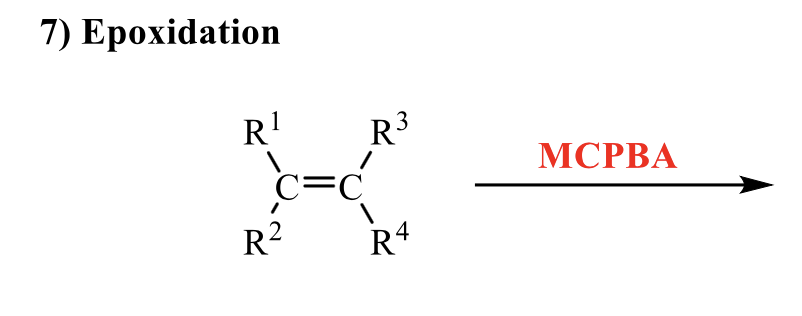
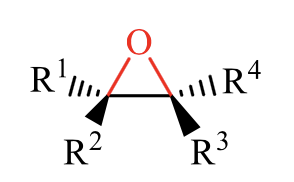
what is the product of this alkene rxn
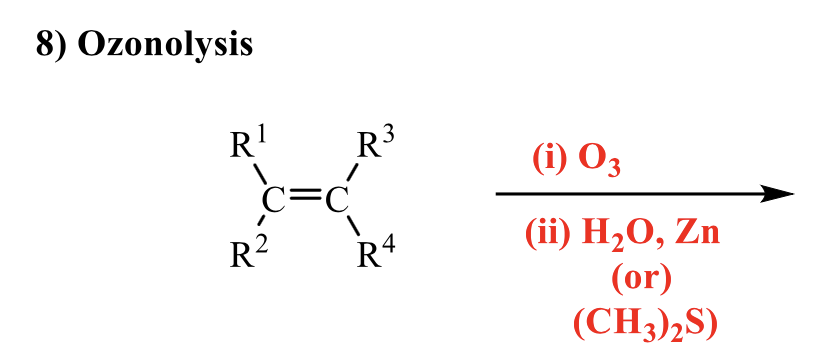
what is the product of this alkene rxn
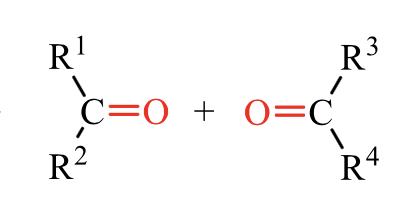
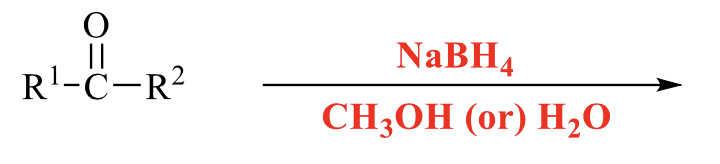
what is the product of this alcohol synthesis
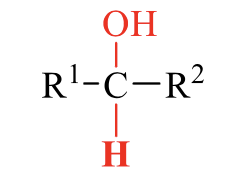
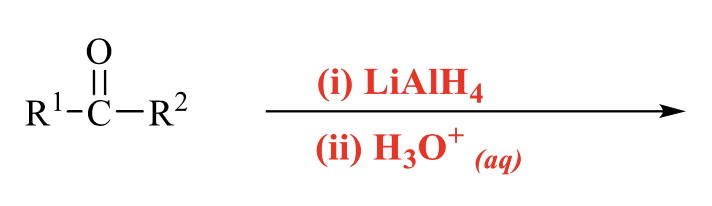
what is the product of this alcohol synthesis
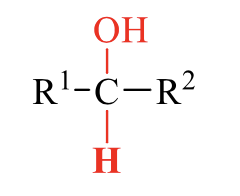
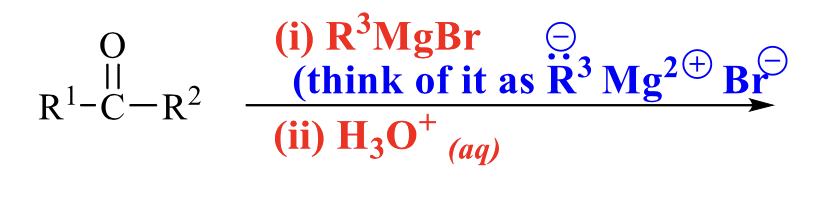
what is the product of this alcohol synthesis
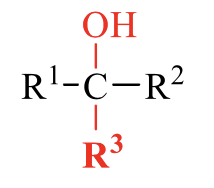
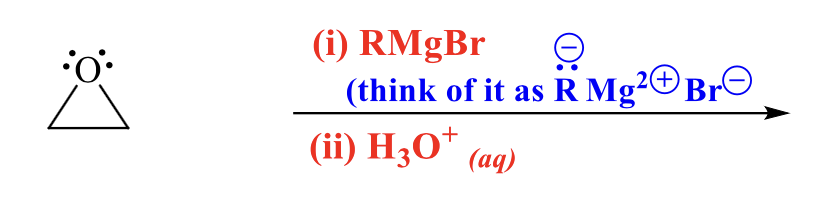
what is the product of this alcohol synthesis
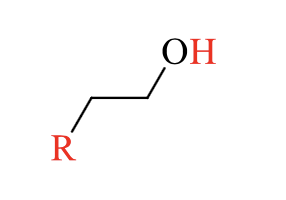
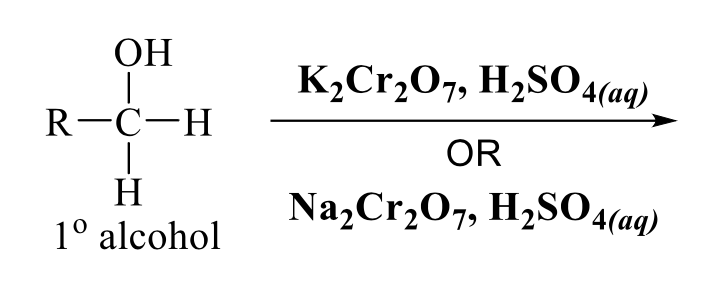
what is the product of this alcohol rxn
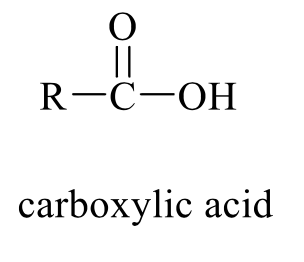
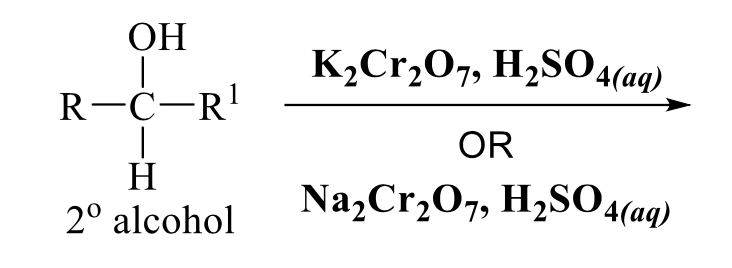
what is the product of this alcohol rxn
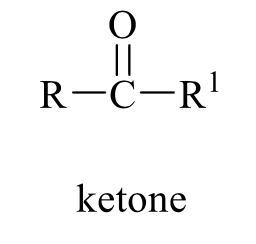
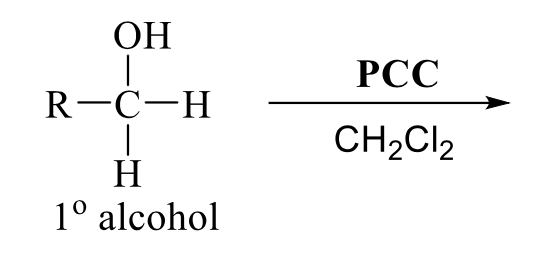
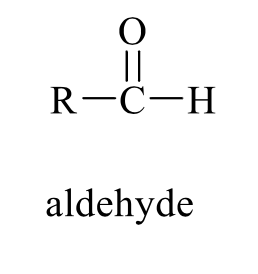
what is the product of this alcohol rxn
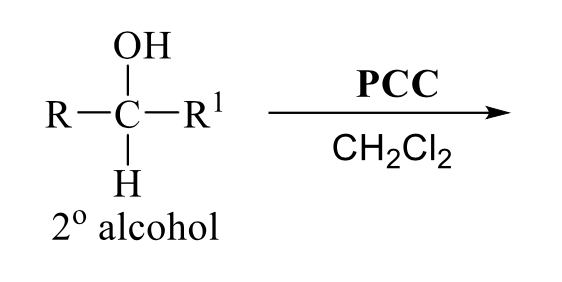
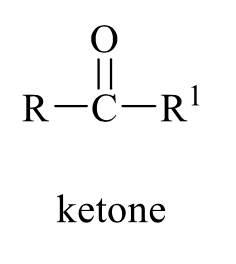
what is the product of this alcohol rxn
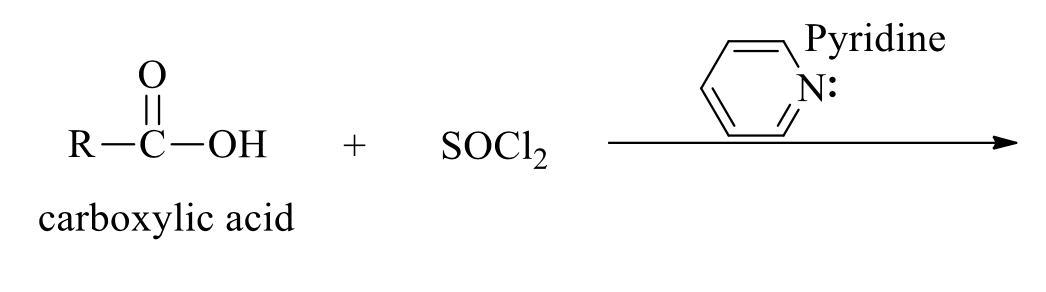
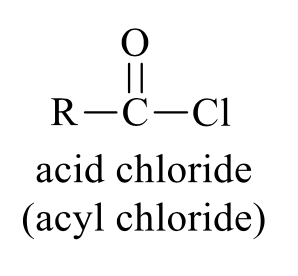
what is the product of this acid chloride synthesis
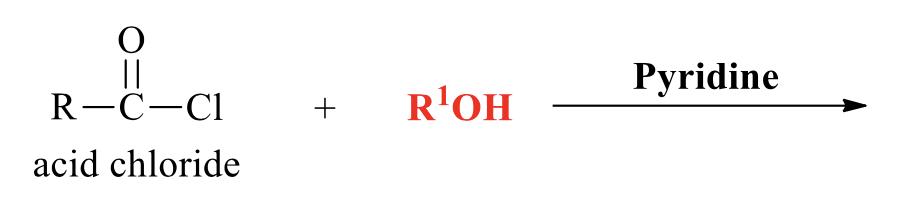
what is the product of this acid chloride rxn
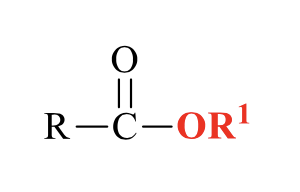
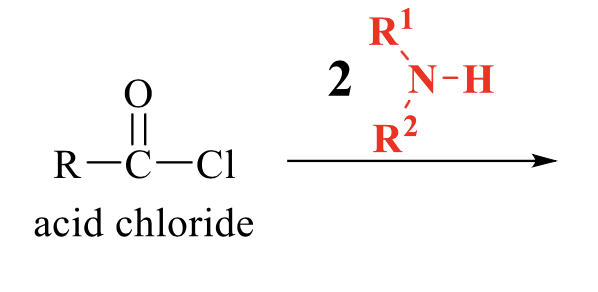
what is the product of this acid chloride rxn
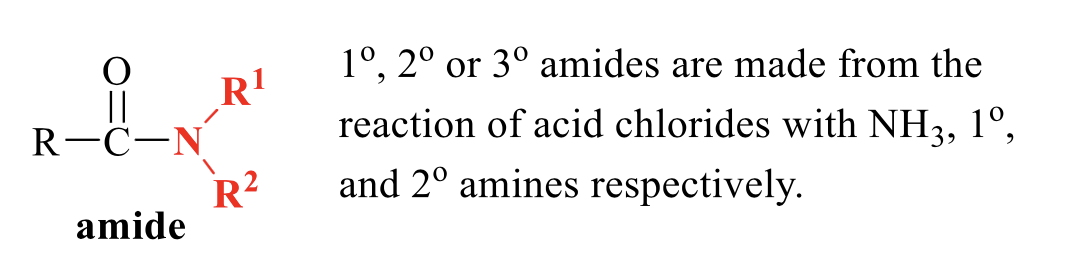

what is the product of this Fischer esterification
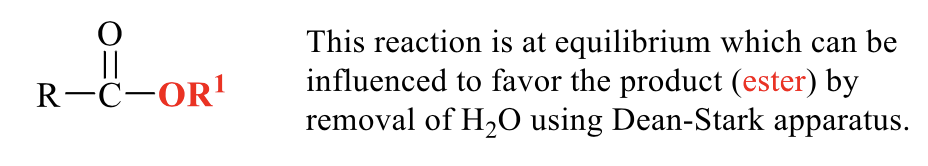

what is the product of this transesterification
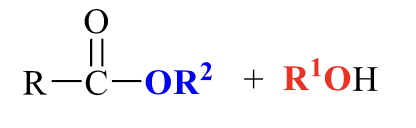
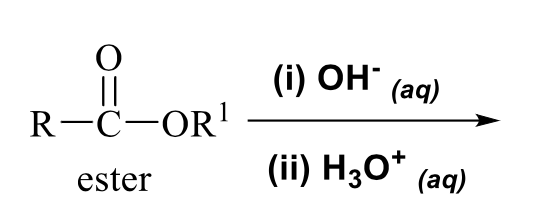
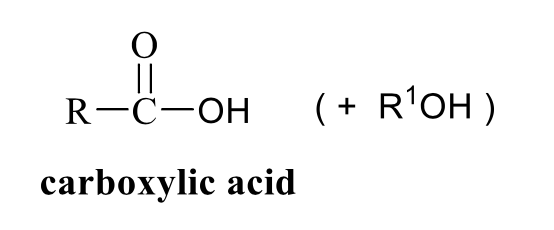
what is the product of this carboxylic acid synthesis
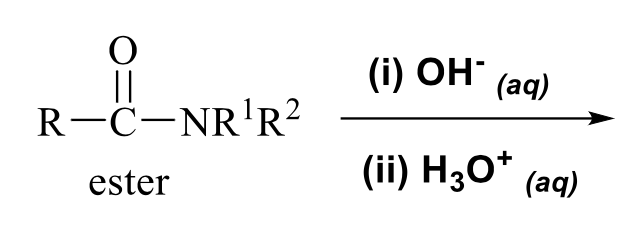
what is the product of this carboxylic acid synthesis
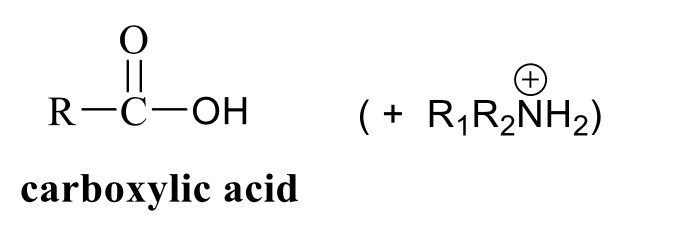
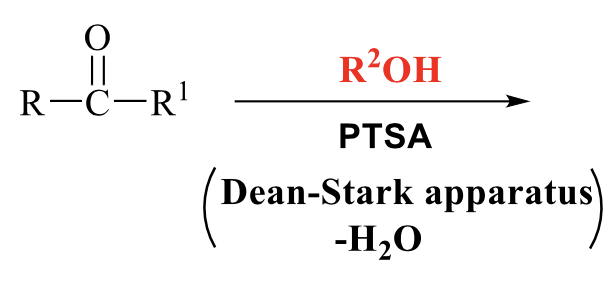
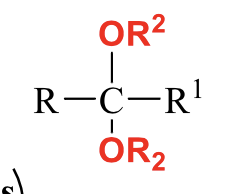
what is the product of this acetal/ketal rxn
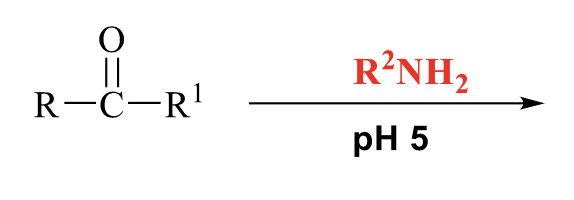
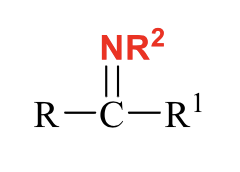
what is the product of this imines formation
what does SN1
3º halides, 1º alcohols, 2º alcohols
what does SN2
methyl halides, 1º halides, 2º halides, methyl alcohols
what does E1
1º alcohols, 2º alcohols, 3º alcohols
what does E2
methyl halides, 1º halides, 2º halides, 3º halides
for halides more nucleophilic nucleophiles do what rxn
SN1 or SN2
for halides more basic nucleophiles such as bulky base, LDA, tBuOK, RO Li/K/Na) do what rxn
E1 or E2
for alcohols rxns with hydrogen halides (HX) do what rxn
SN1 or SN2
for alcohols rxns with conc. H2SO4 do what rxn
E1 or E2
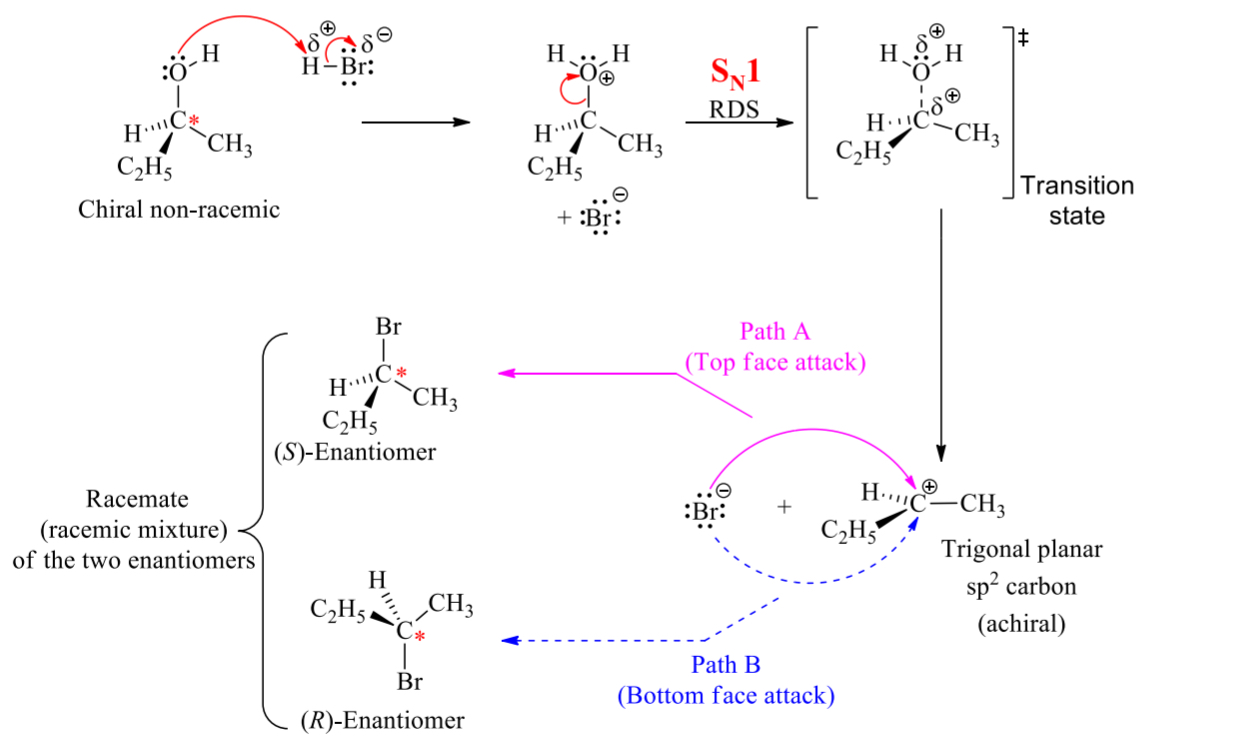
what is the process for a SN1 rxn
RDS
nuclophilic attack on carbocation
if H2O or OH then extra proton transfer step
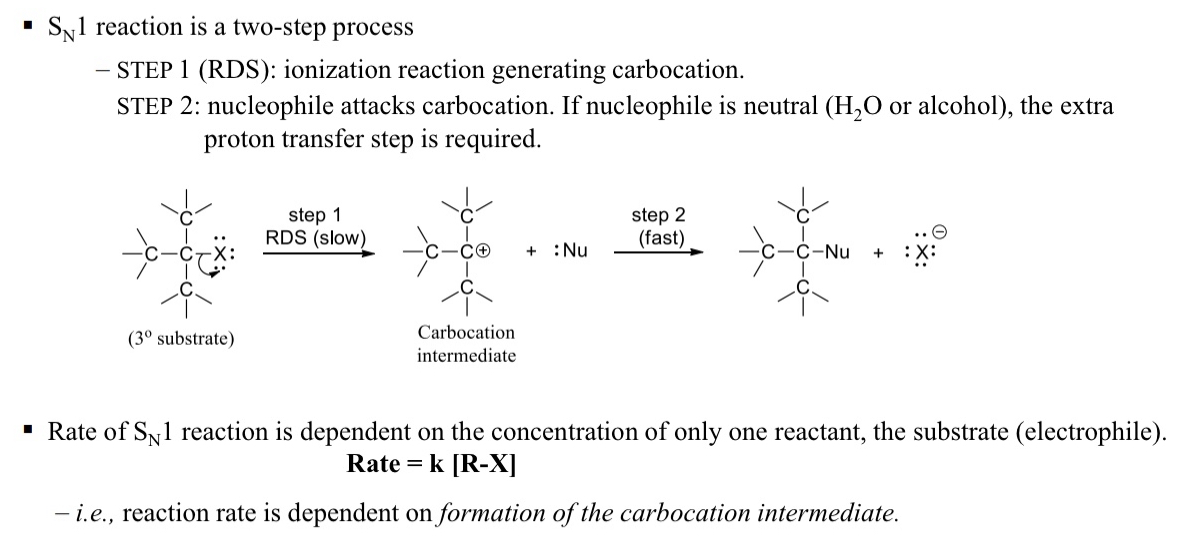
draw the full curved arrow mechanism for this SN1 rxn
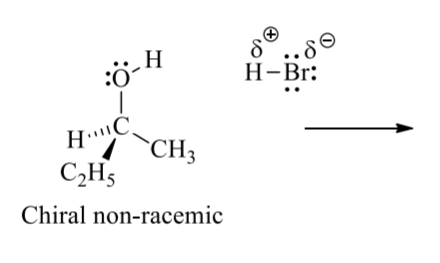
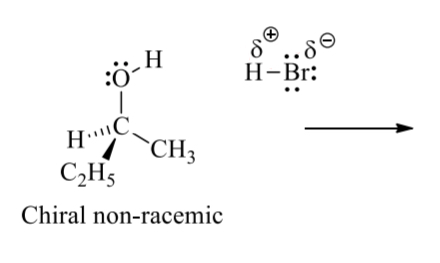
what is the process for a SN2 rxn
nucleophilic backside attack
if chiral carbon give opposite configuration
what is the product for the following SN1 and SN2 halide rxns
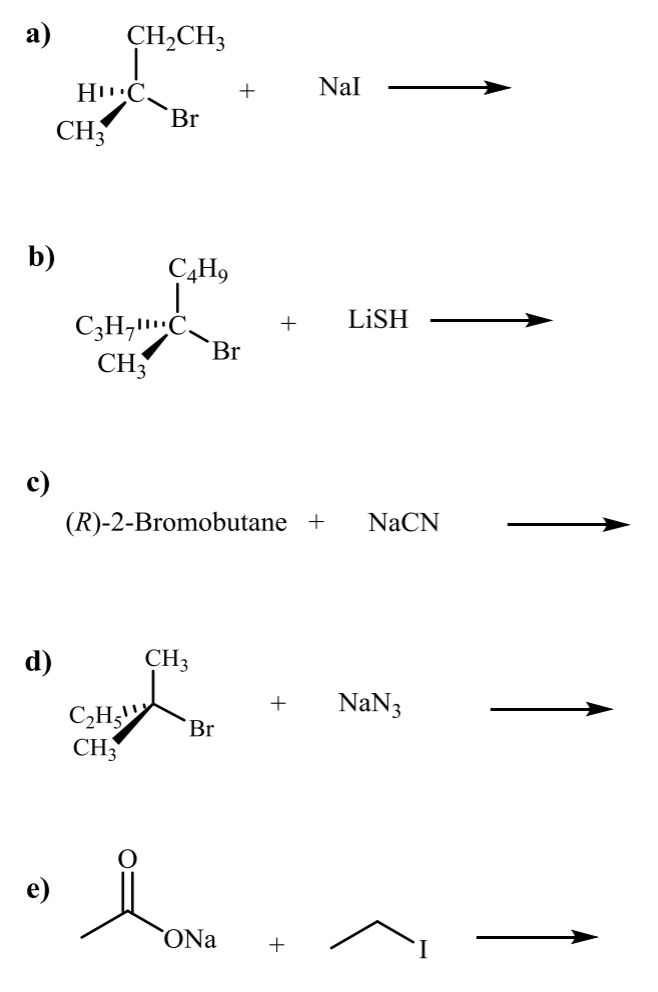
what is the product for the following SN1 and SN2 alcohol rxns
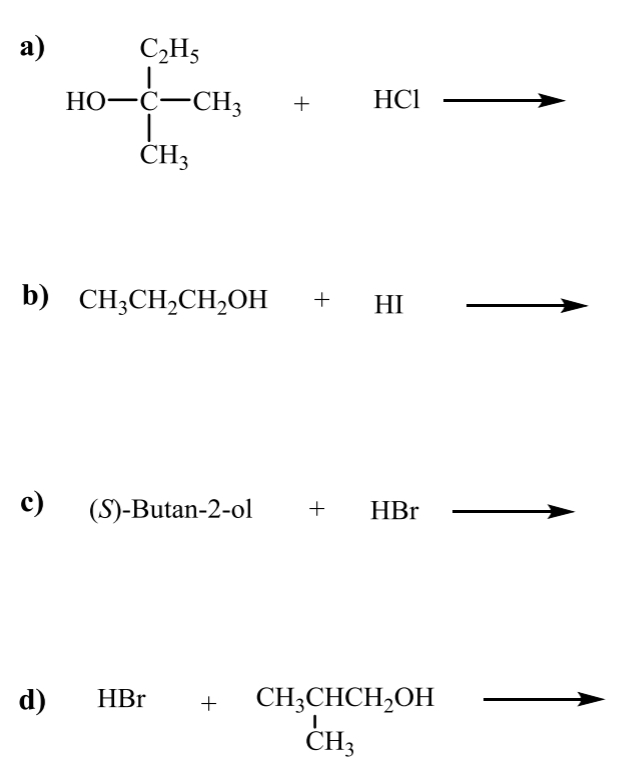
what is the product for the following SN1 and SN2 alcohol rxns
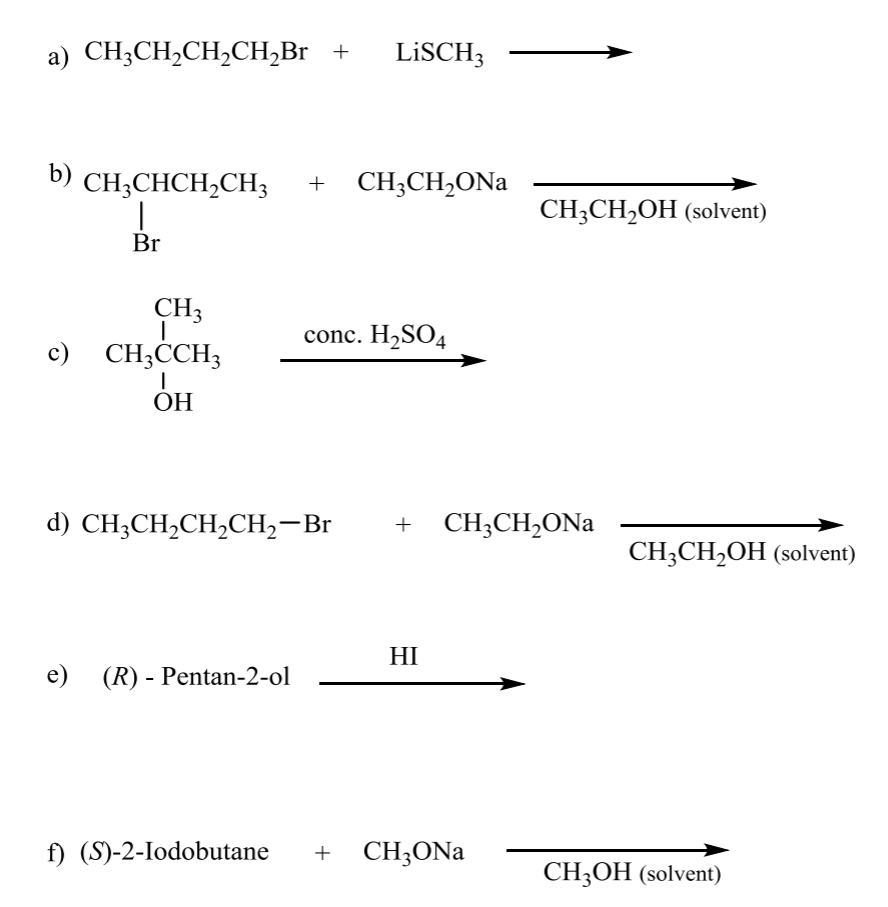
what is the product for the following E1 and E2 rxns
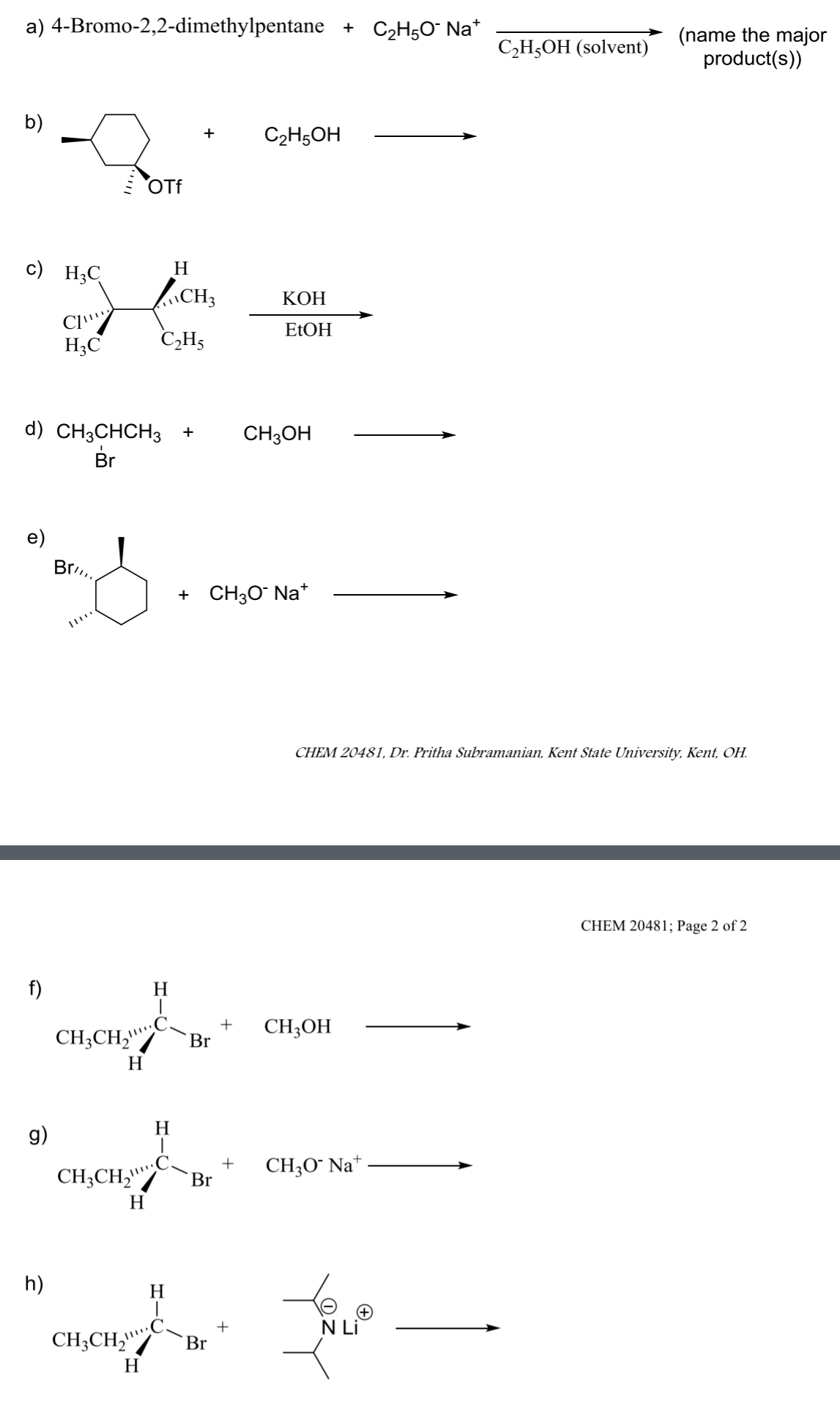
what is the product for the following E1 and E2 rxns
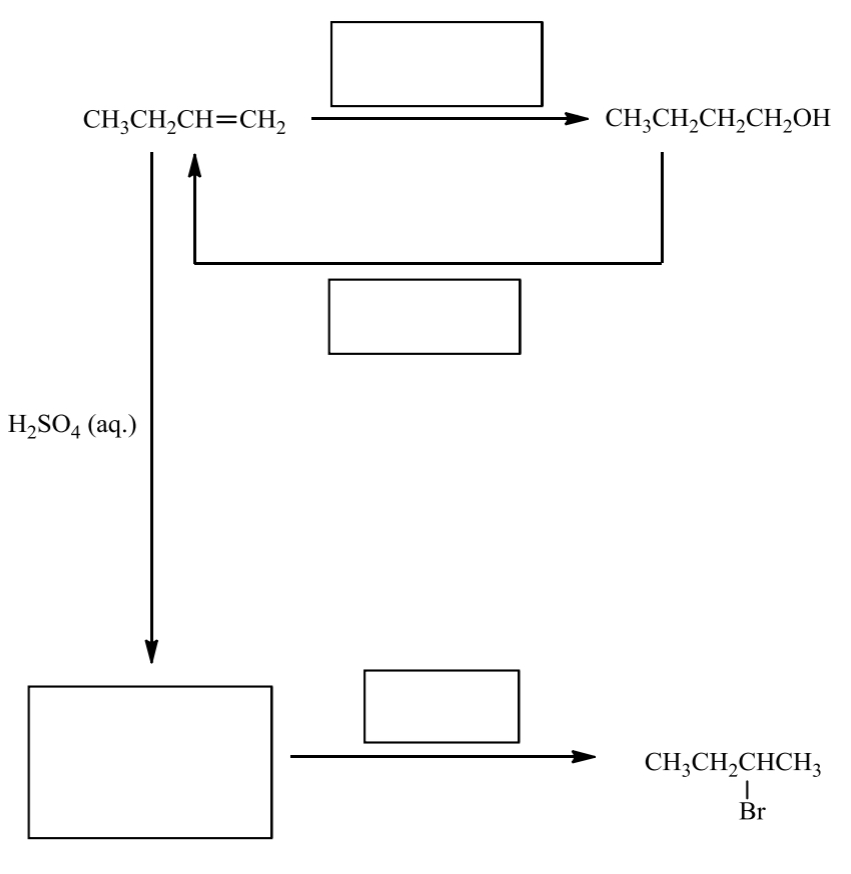
fill in the following route map
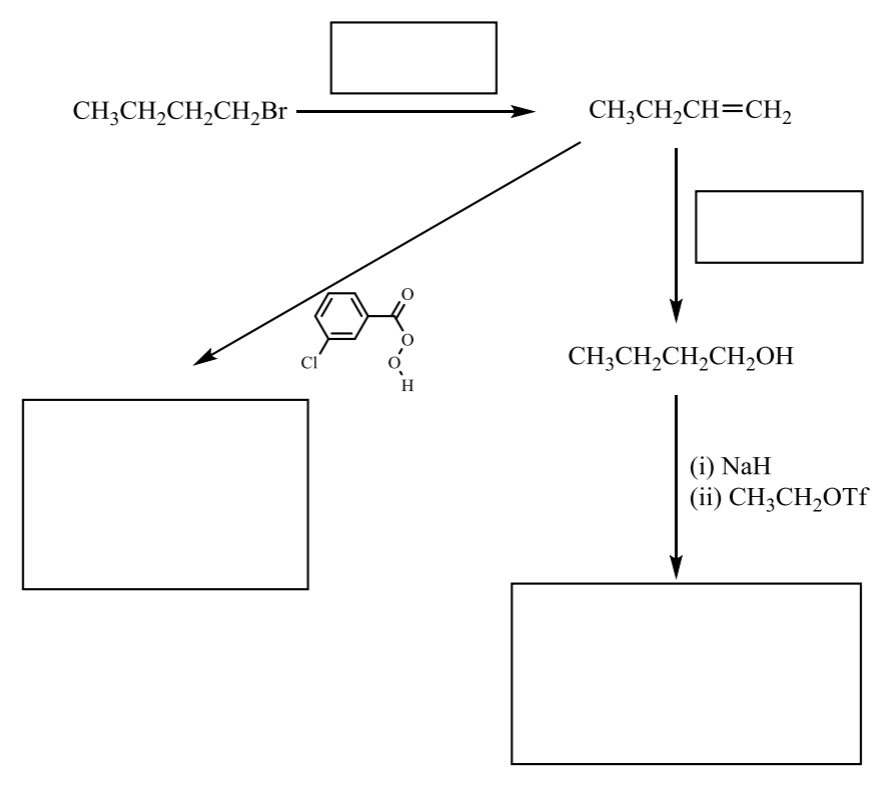
fill in the following route map
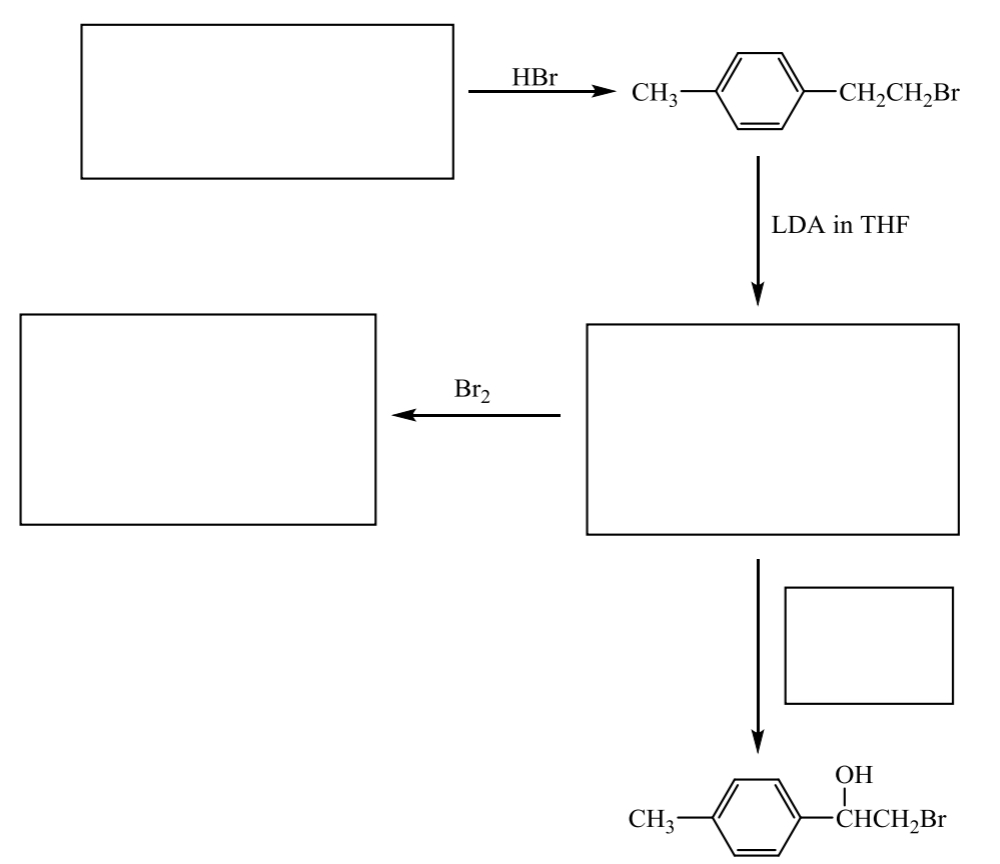
fill in the following route map
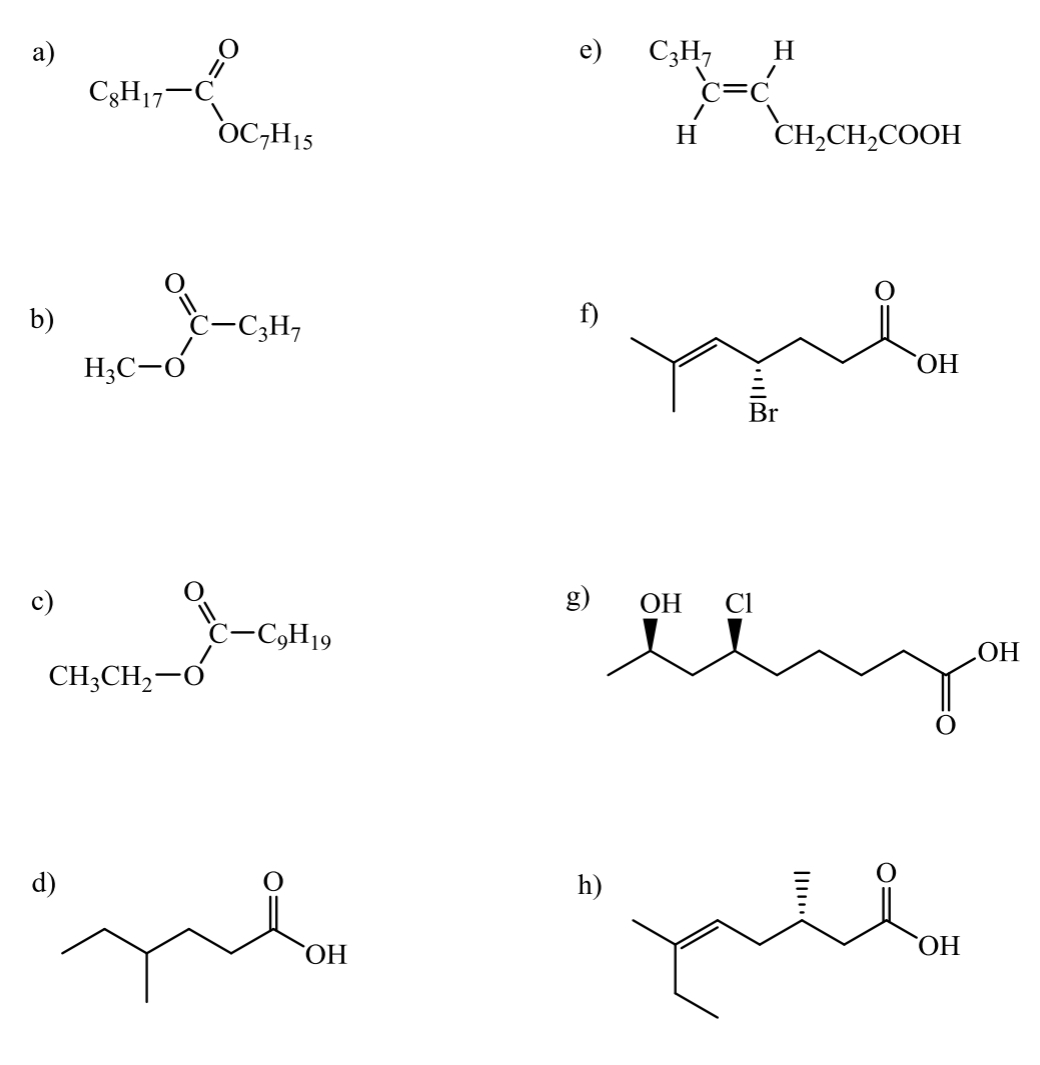
give the IUPAC names for each of the following