Lab Quiz #6 Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Physiology BIOL 124 GMU
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
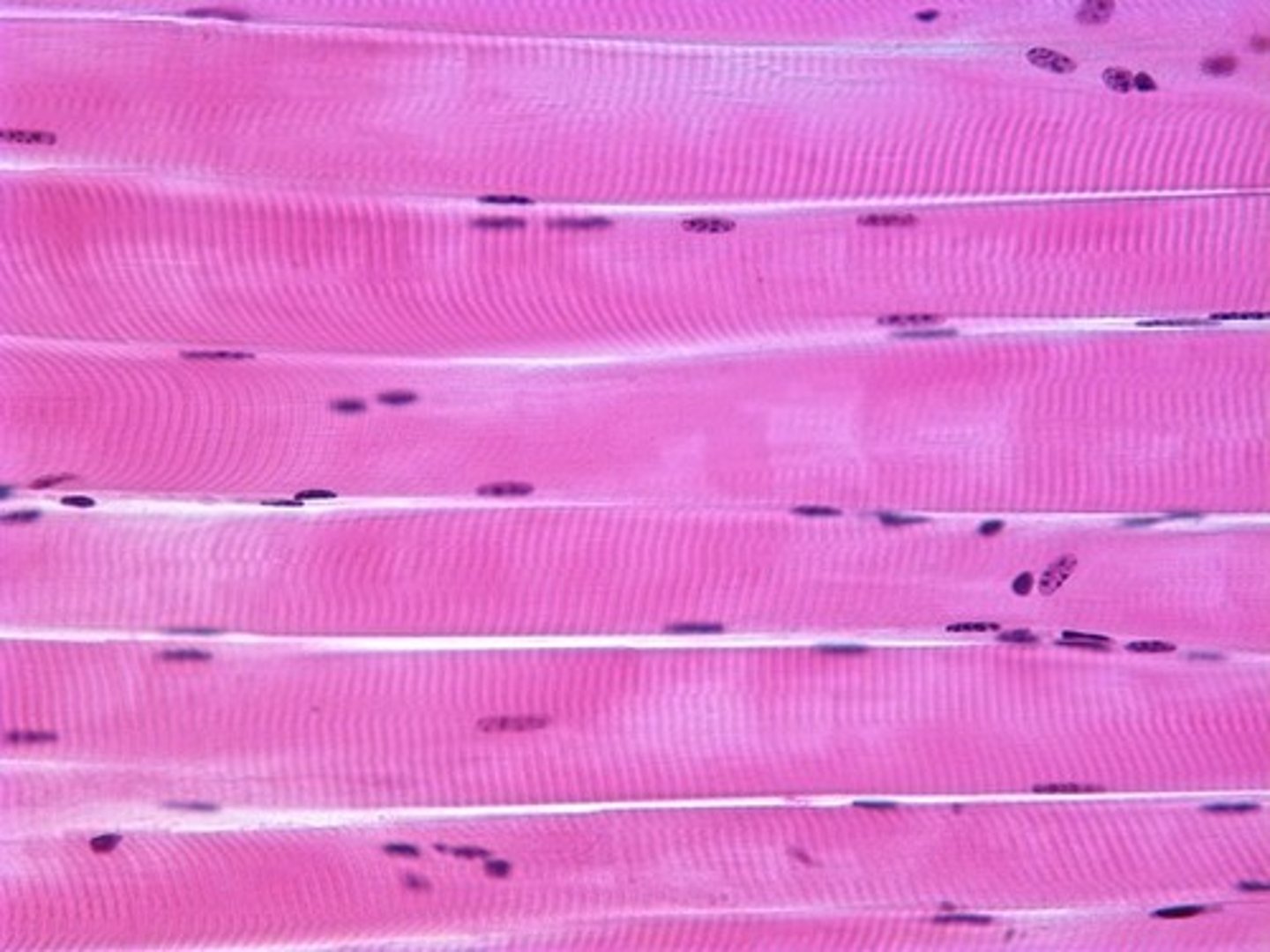
skeletal muscle tissue
structure: long cylindrical striated muscle fibers, cells are multinucleated
location: attached to skeleton
Voluntary
Function: produces movement of the body
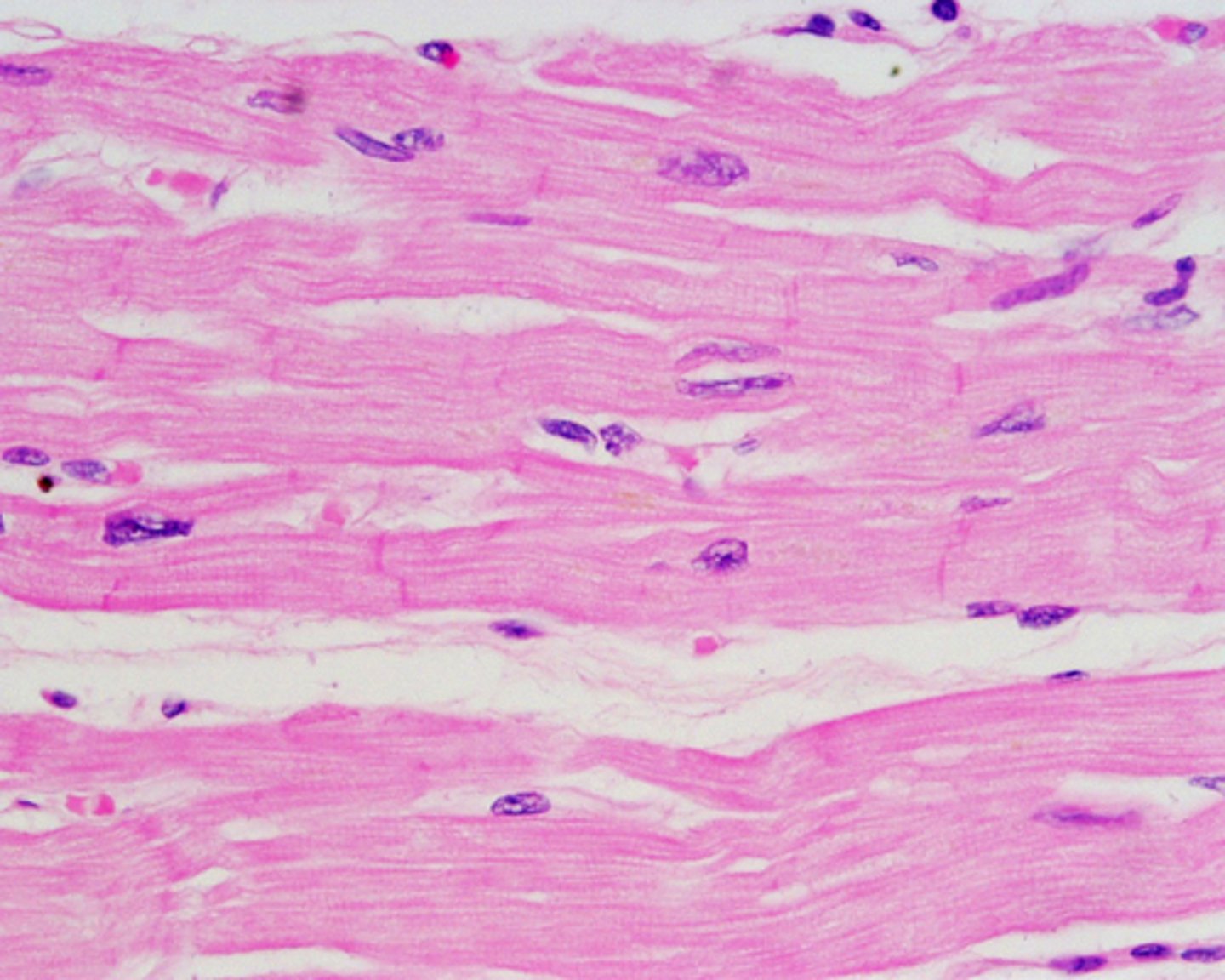
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
structure: short wide branching striated cardiac muscle cells with intercalated discs, cells have a single nucleus or two nuclei
location: heart
involuntary
function: produces beating of the heart
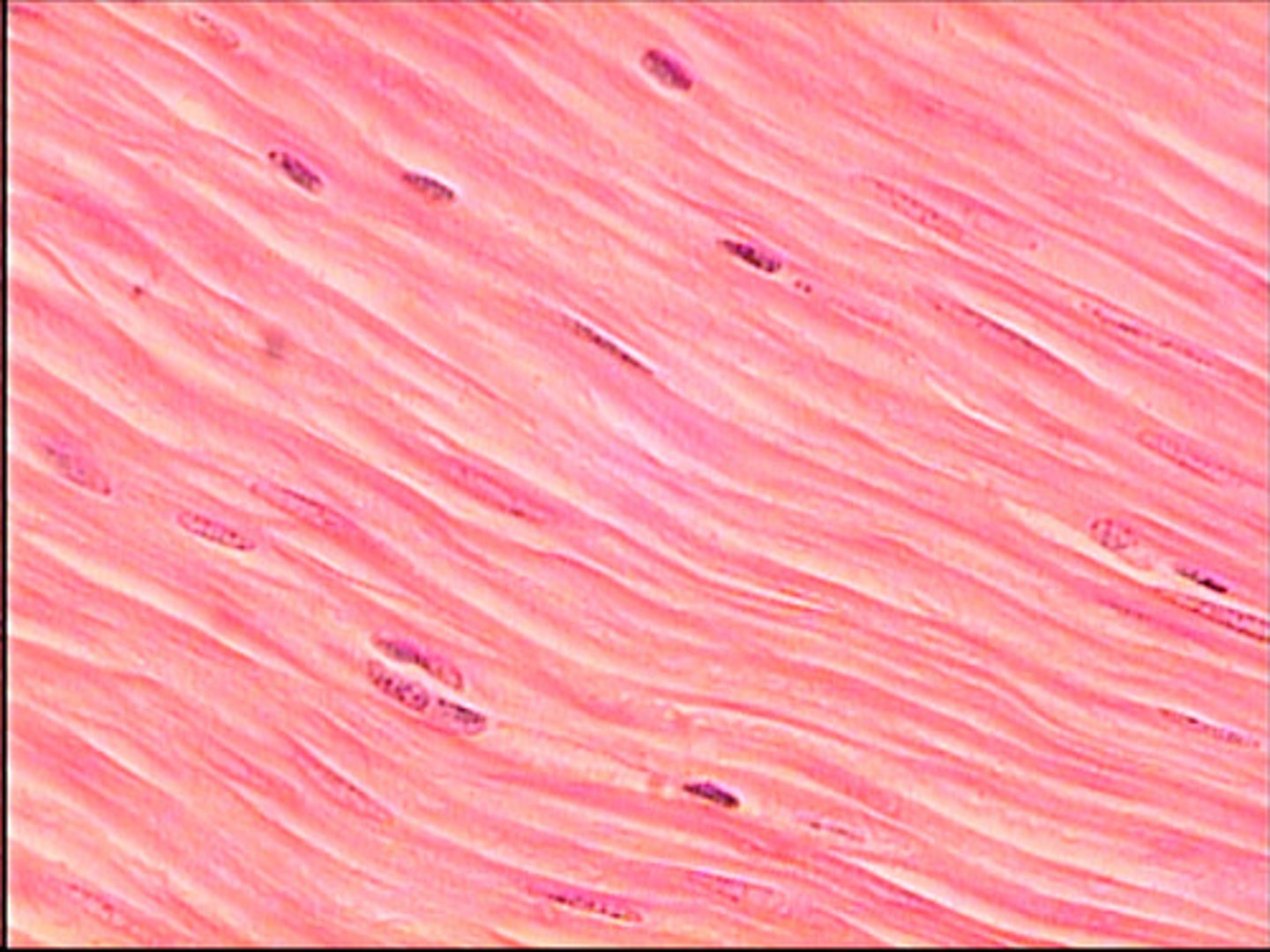
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Structure: thin, smooth muscle cells, generally joined by gap junctions, cells have a single nucleus
location: walls of hollow organs, as well as in the skin and the eyes
involuntary
function: changes diameter of hollow organs causes hairs to stand erect adjusts the shape of the lens and the size of the pupil of the eye
Epimysium
dense irregular connective tissue layer, divides muscle
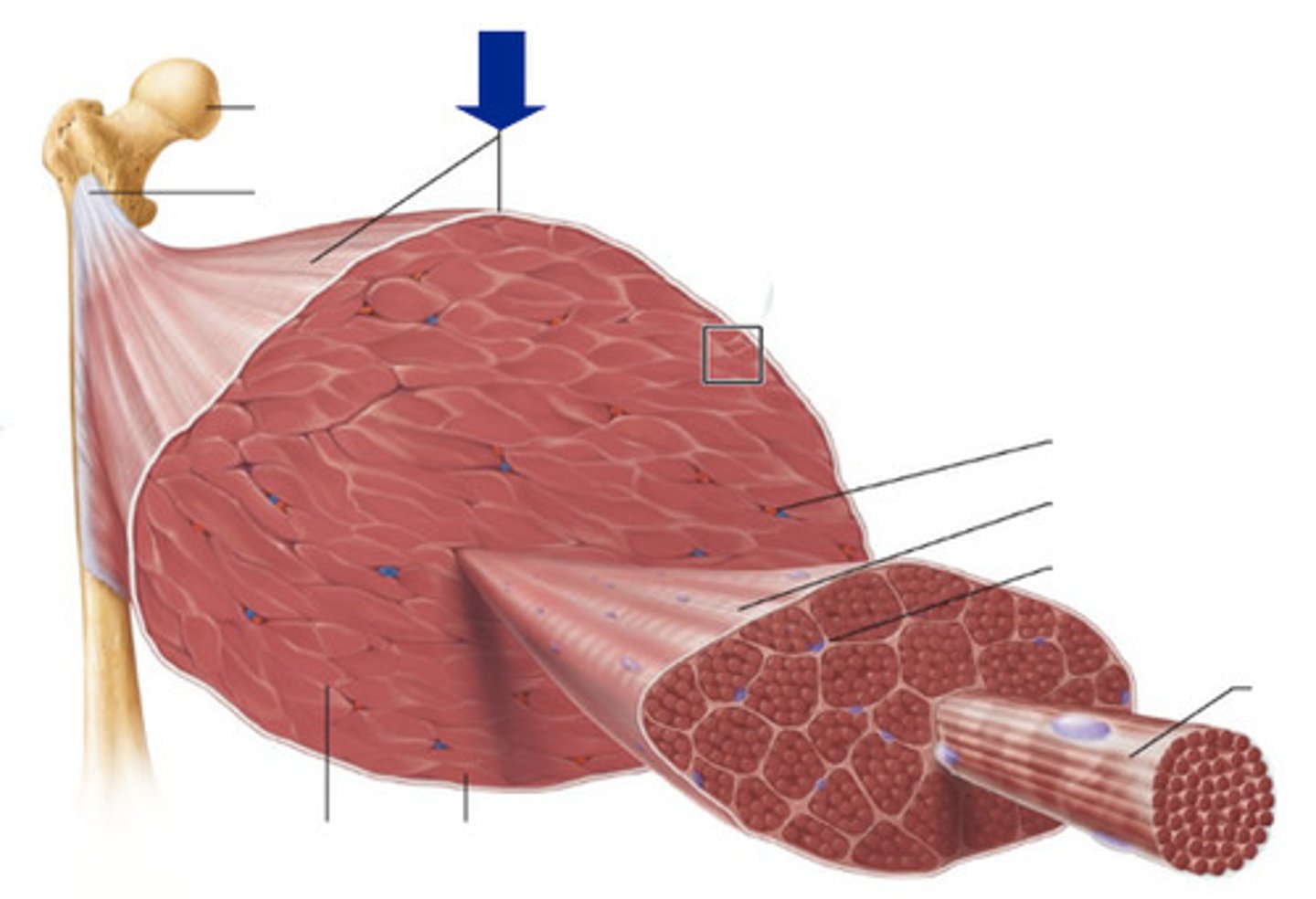
Perimysium
dense irregular connective tissue layer, divides muscle into compartments called fascicles
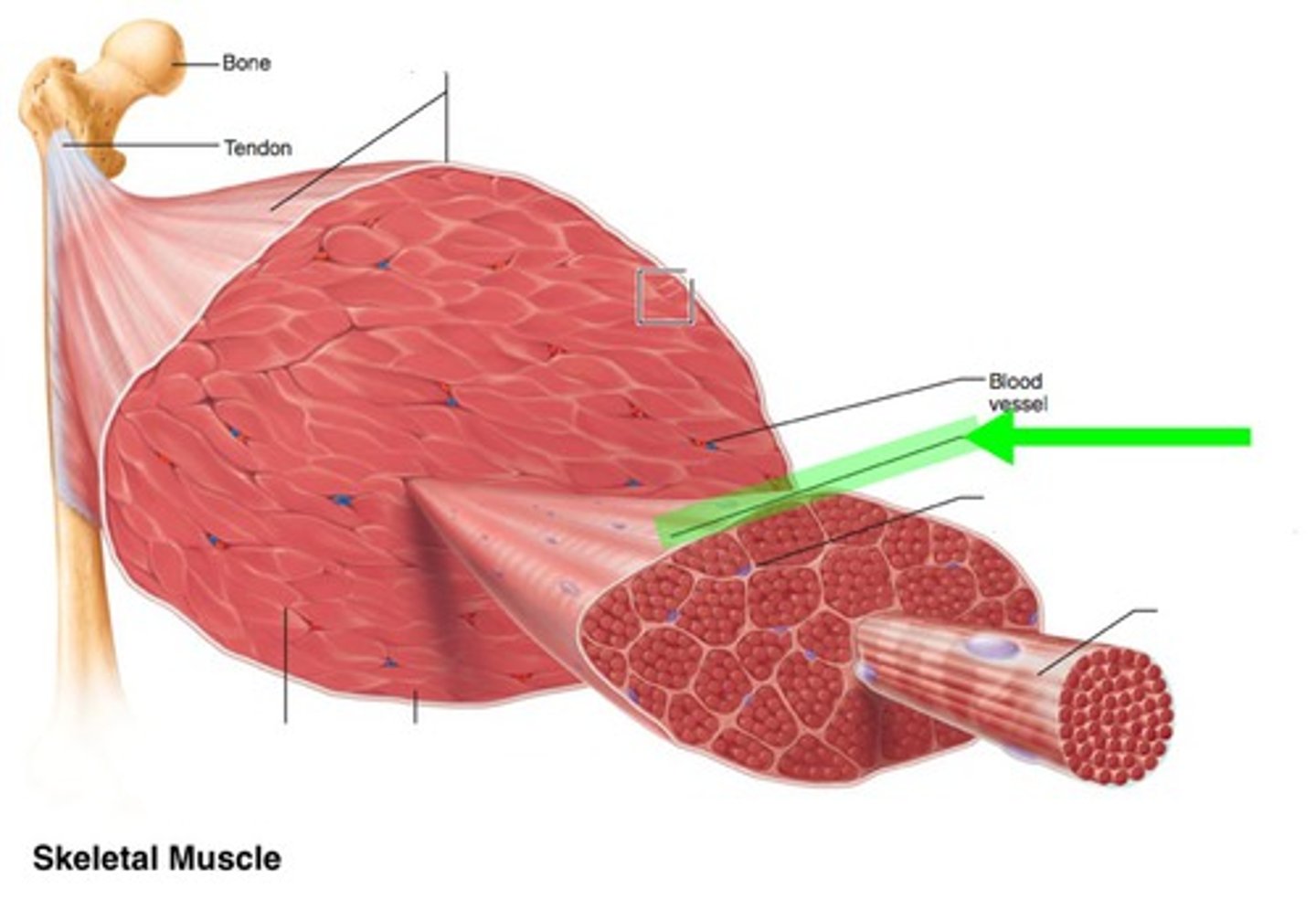
Endomysium
areolar connective tissue layer, surrounds individual muscle fibers
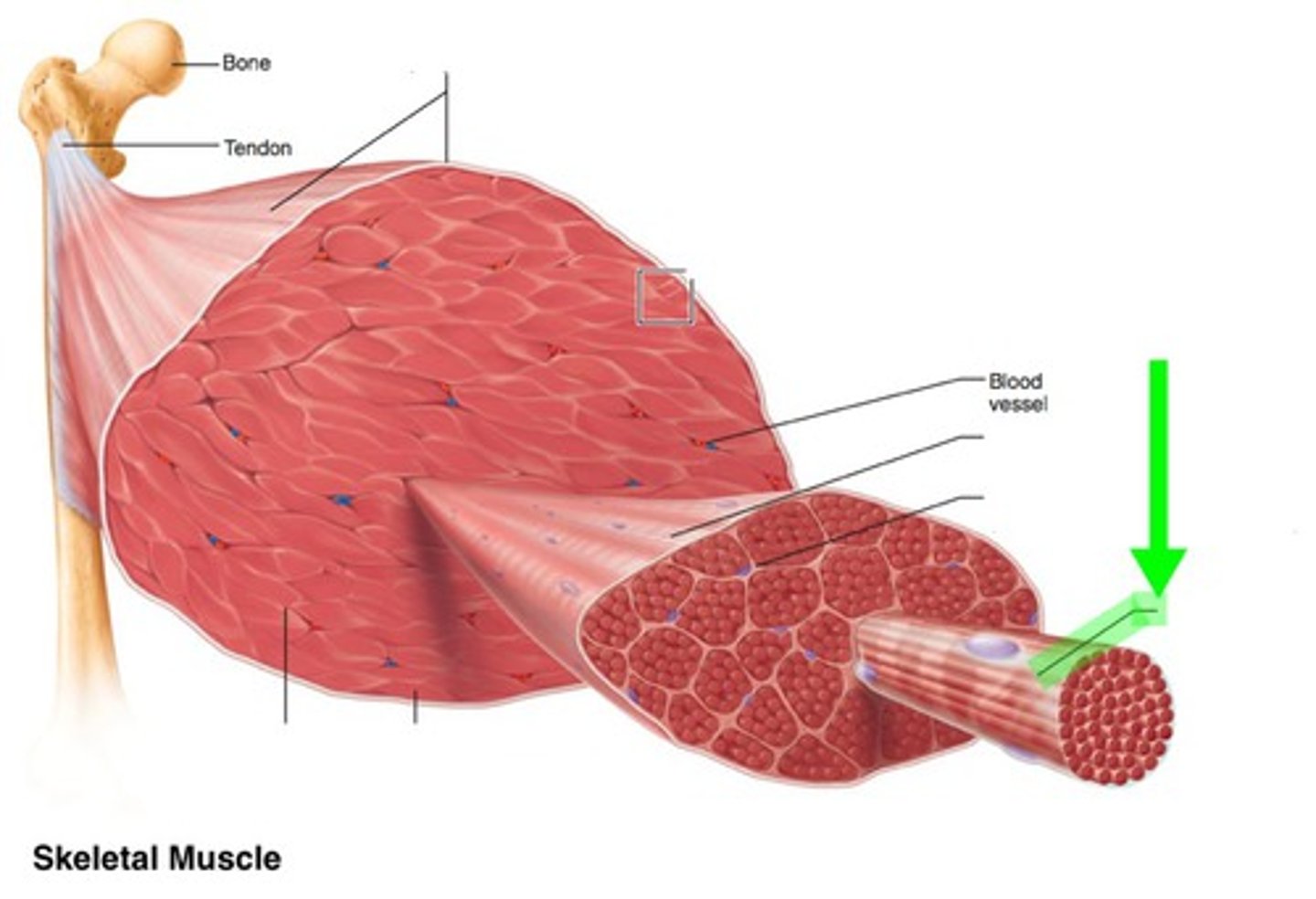
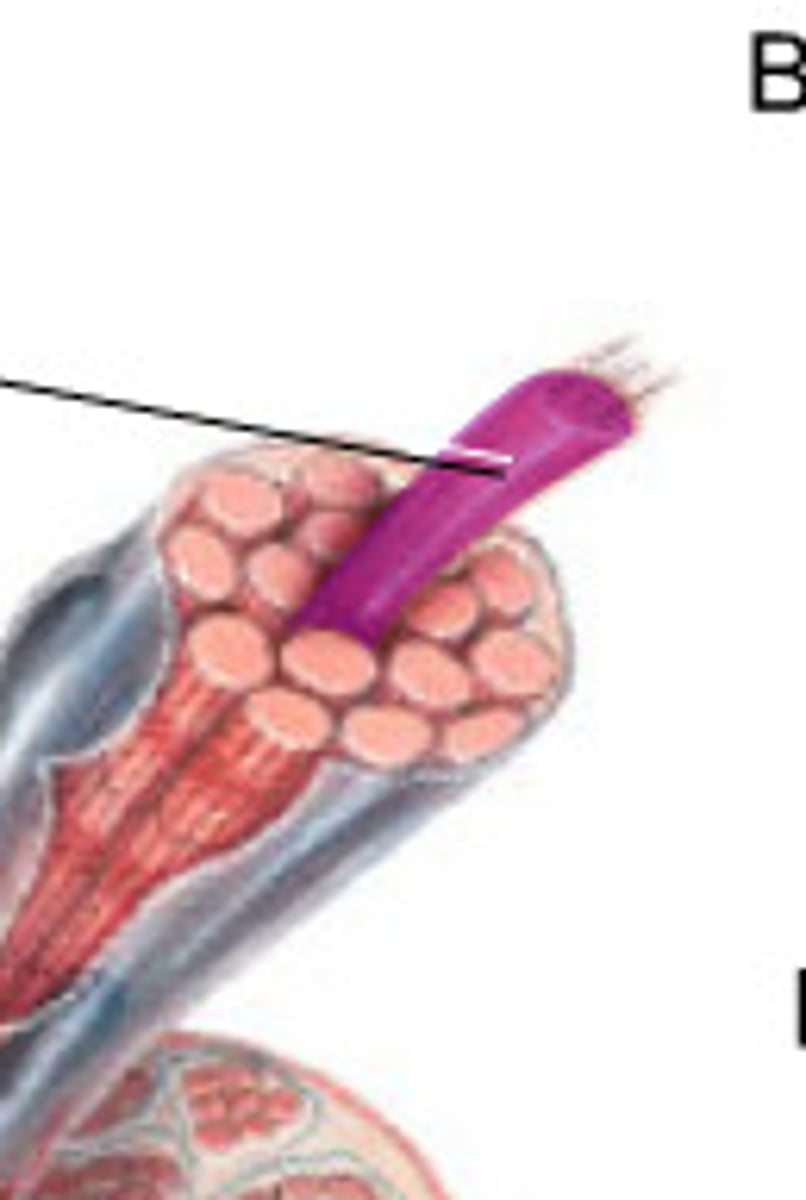
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers, surrounded by perimysium
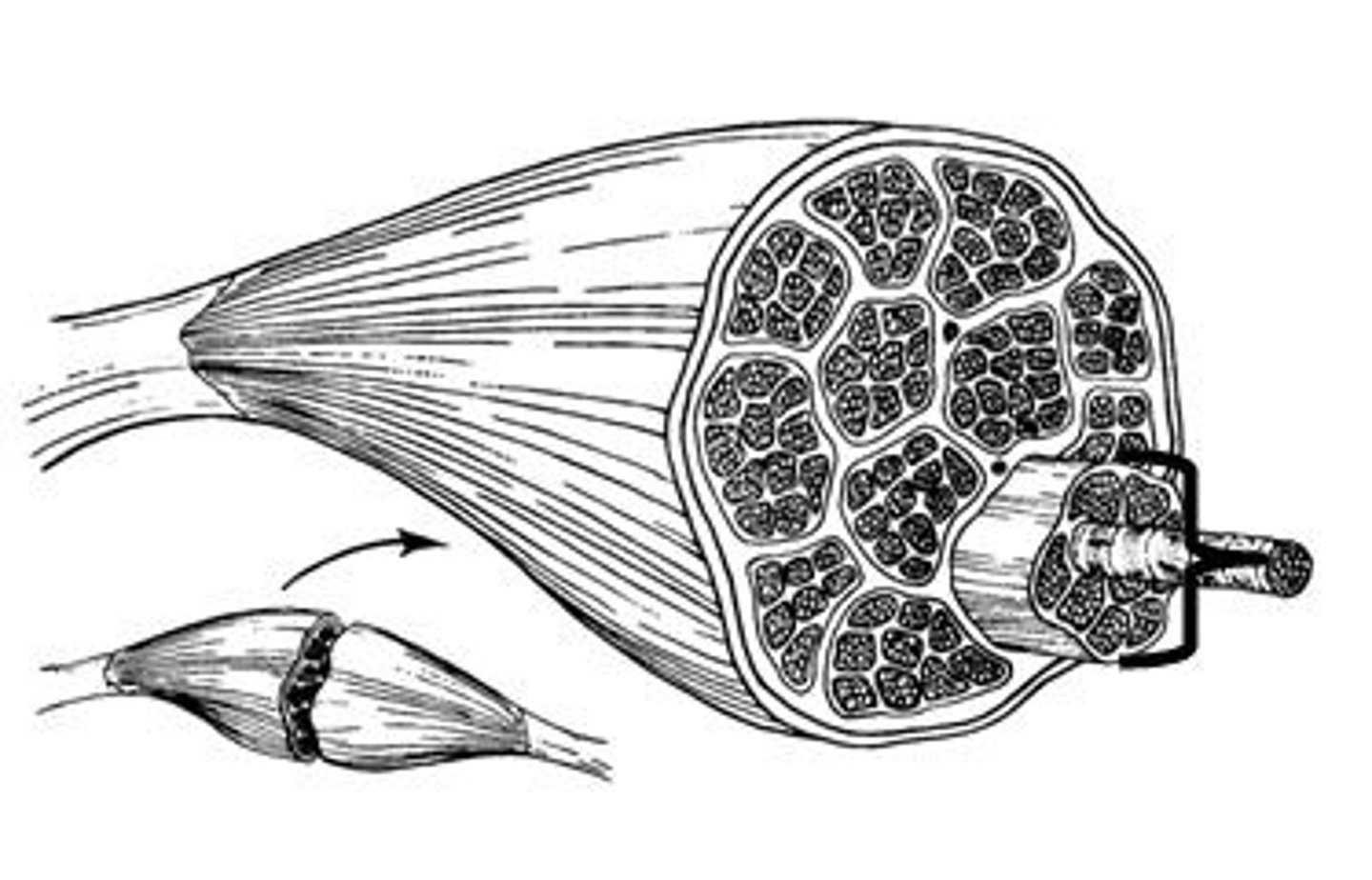
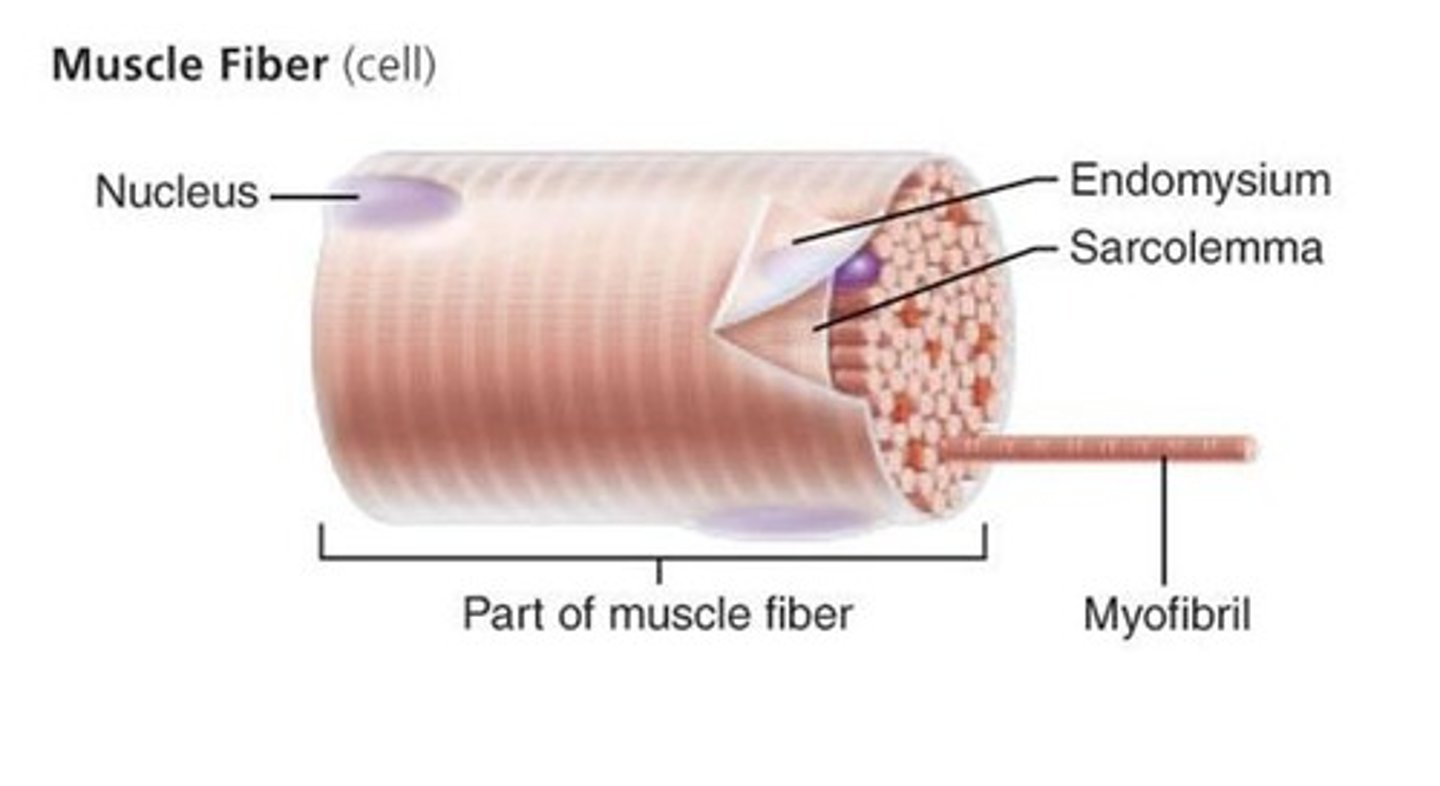
muscle fiber
a single mucleinated muscle cell, wrapped in endomysium
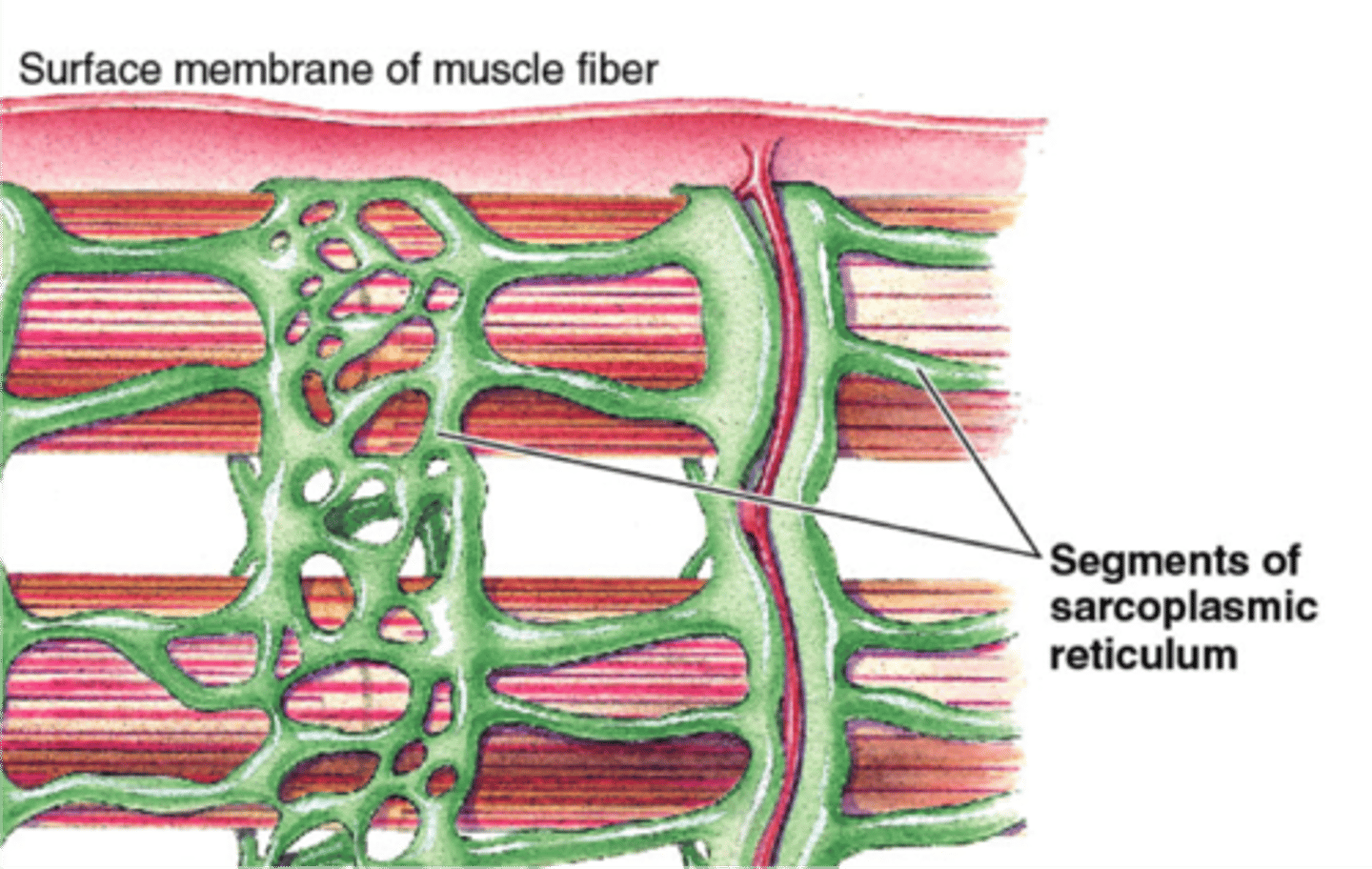
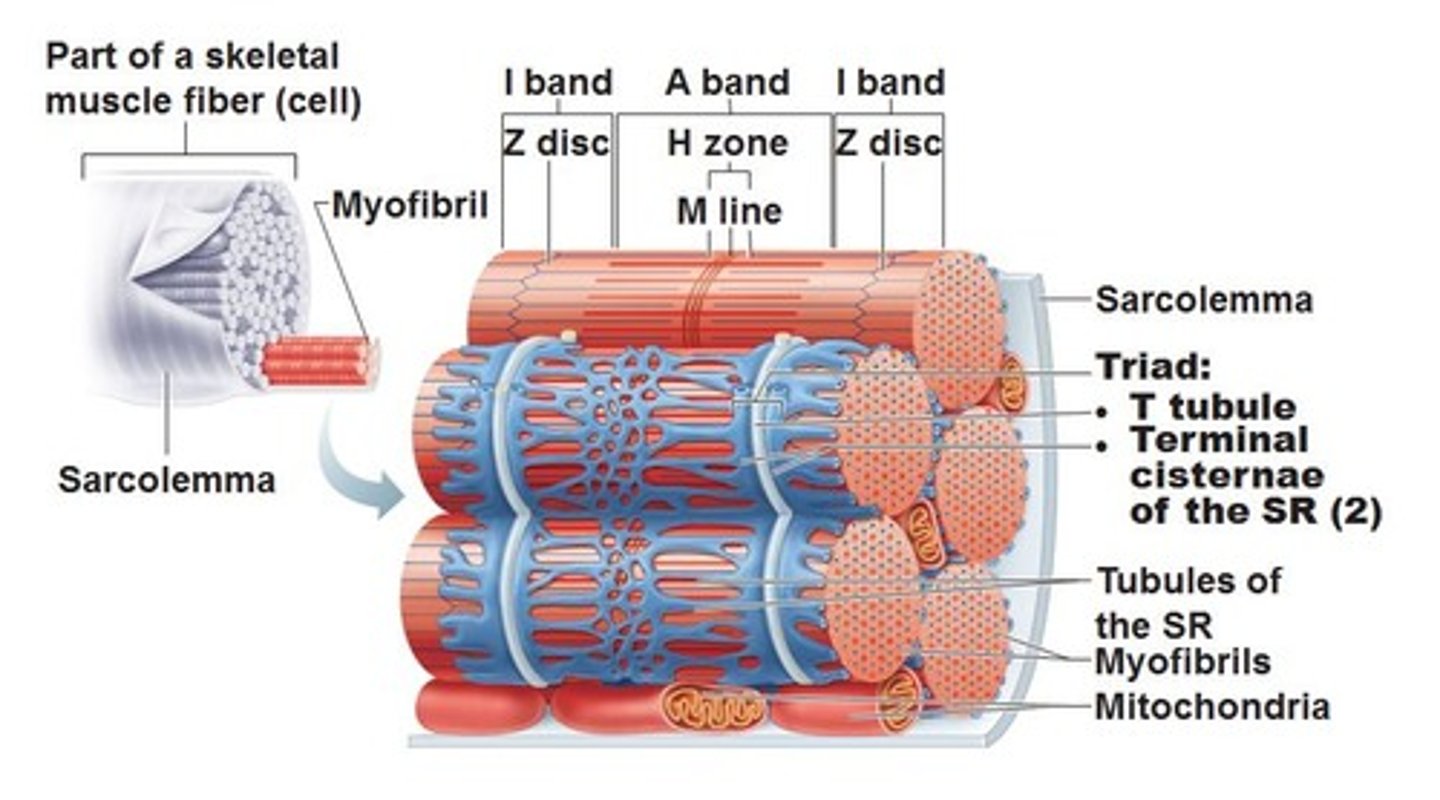
sarcoplasmic reticulum
extensive tubular network that stores ca2+, wraps around myofibrils, enlarged portions are called terminal cisternae
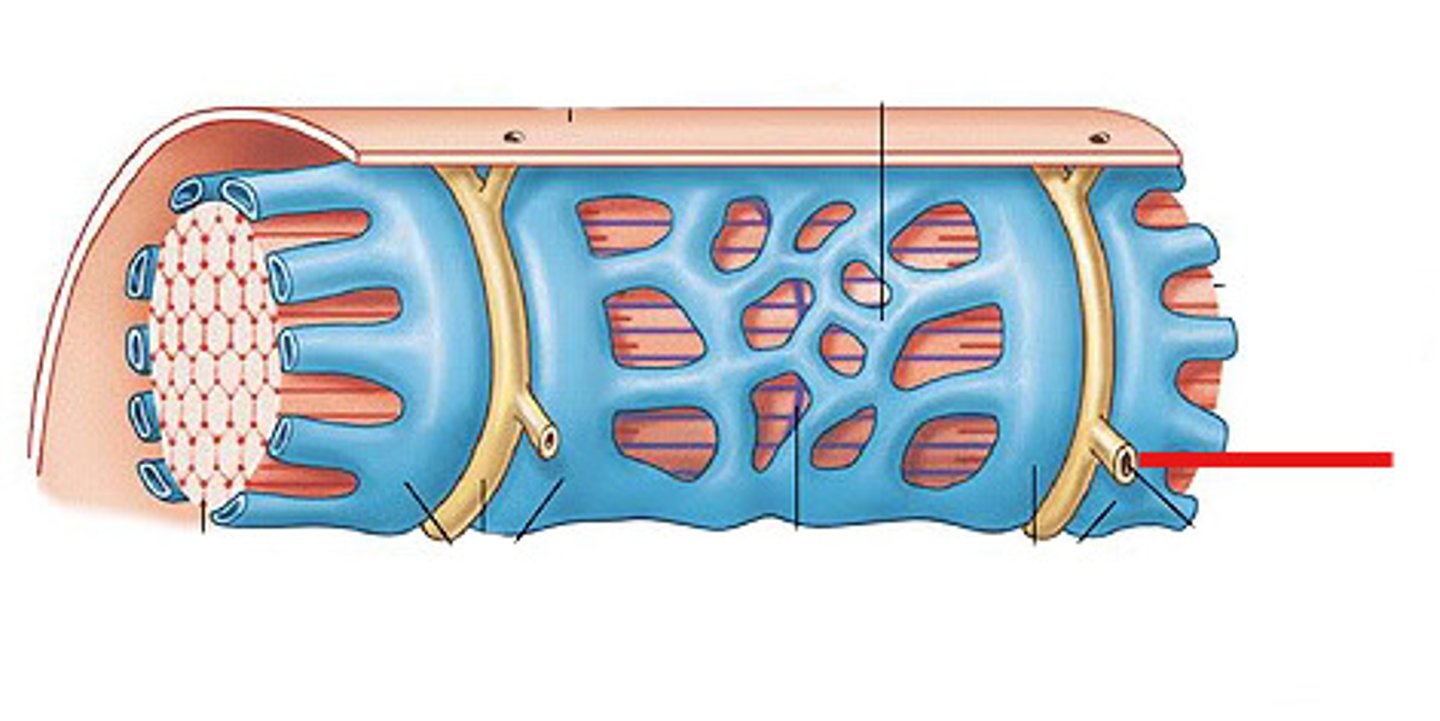
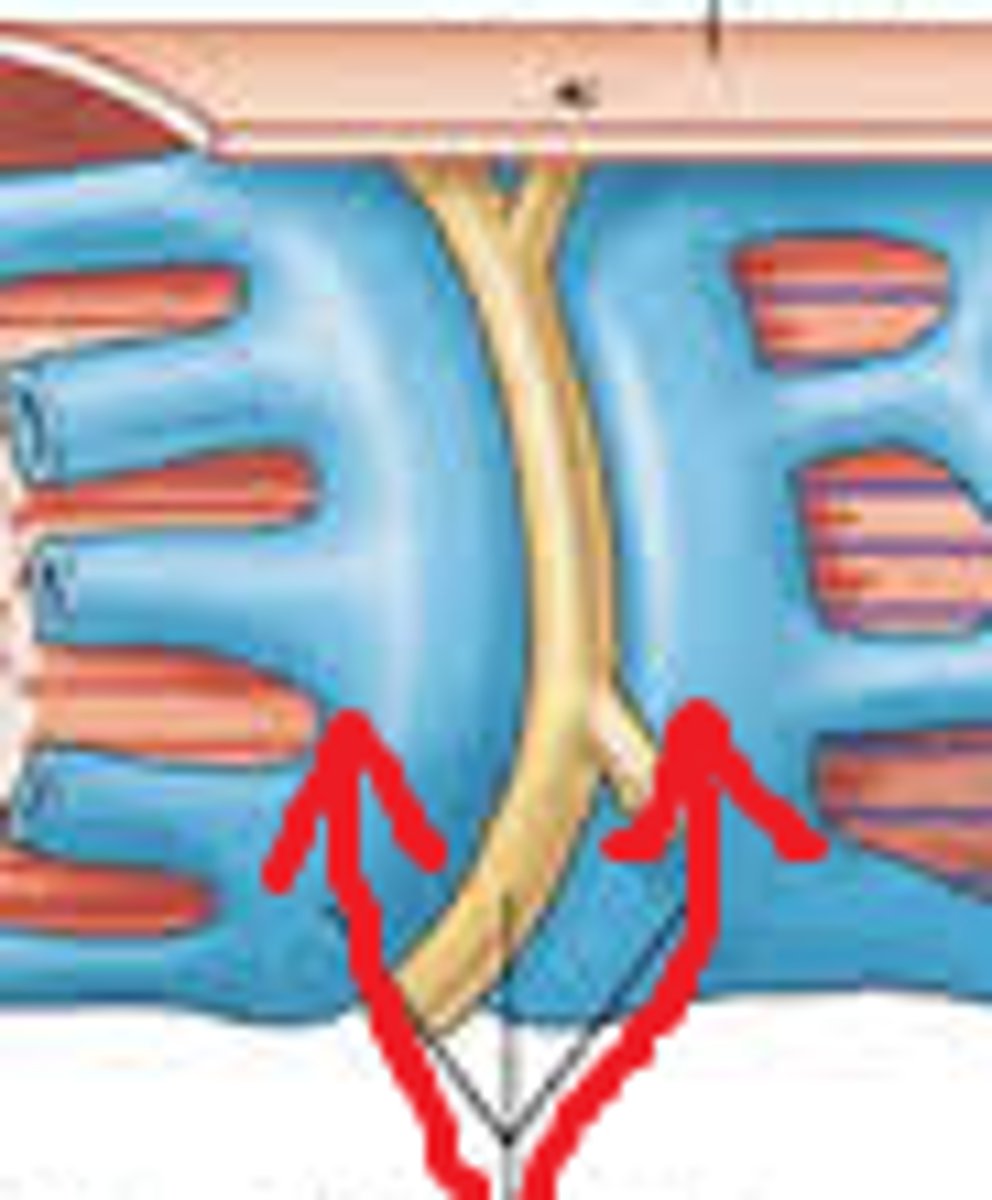
T tubules
invaginations continuous with sarcolemma, forms a network through muscle fiber
terminal cisternae
enlarged areas of the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding the transverse tubules.
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
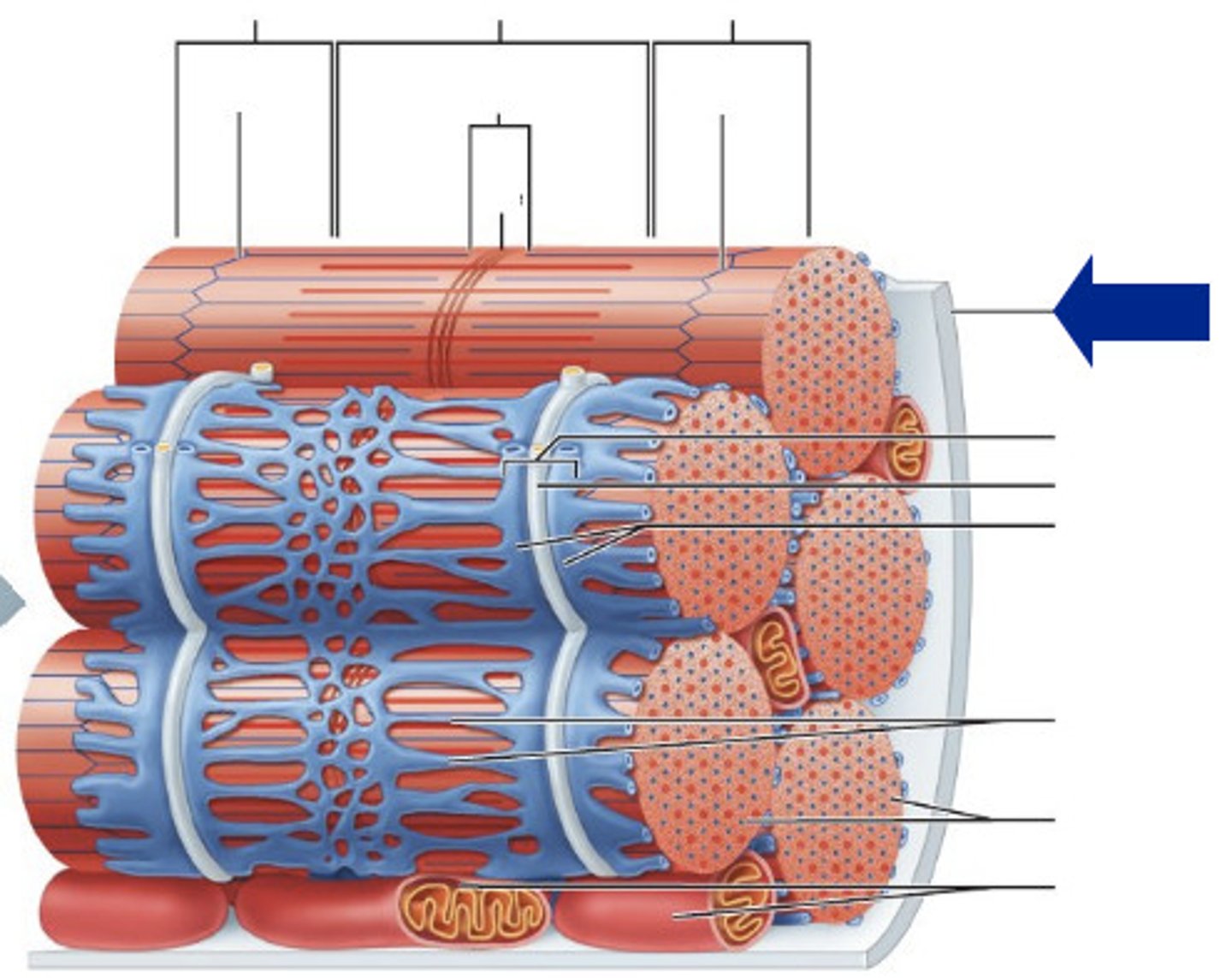
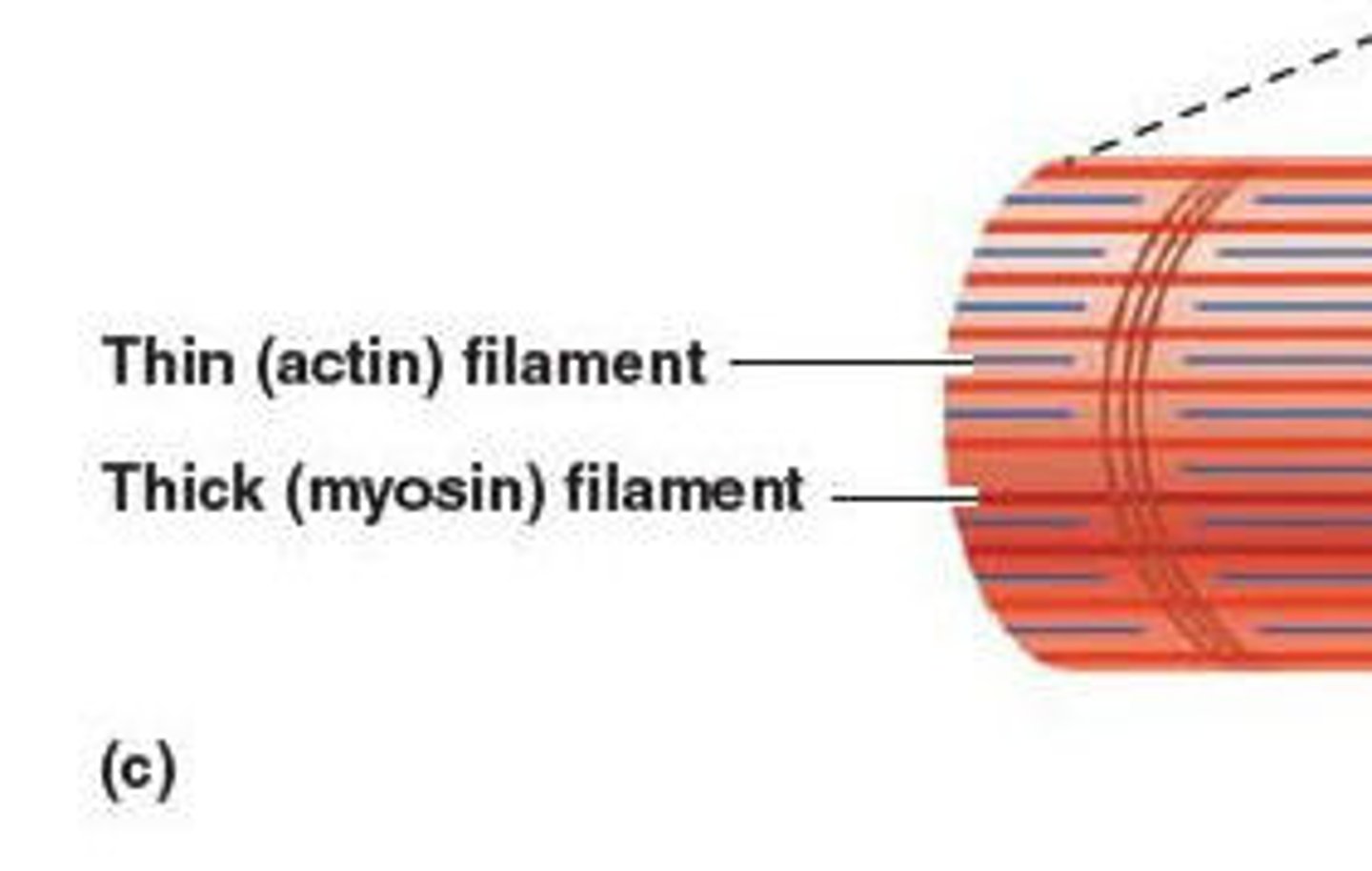
Myofilaments
thick, myosin thin, actin
Myofibrils
cylindrical subunits of muscle fiber, has a banded appearance under microscope due to arrangement of myofilaments, consists of a series of sarcomeres
triad
a T tubule and two terminal cisternae associated with it
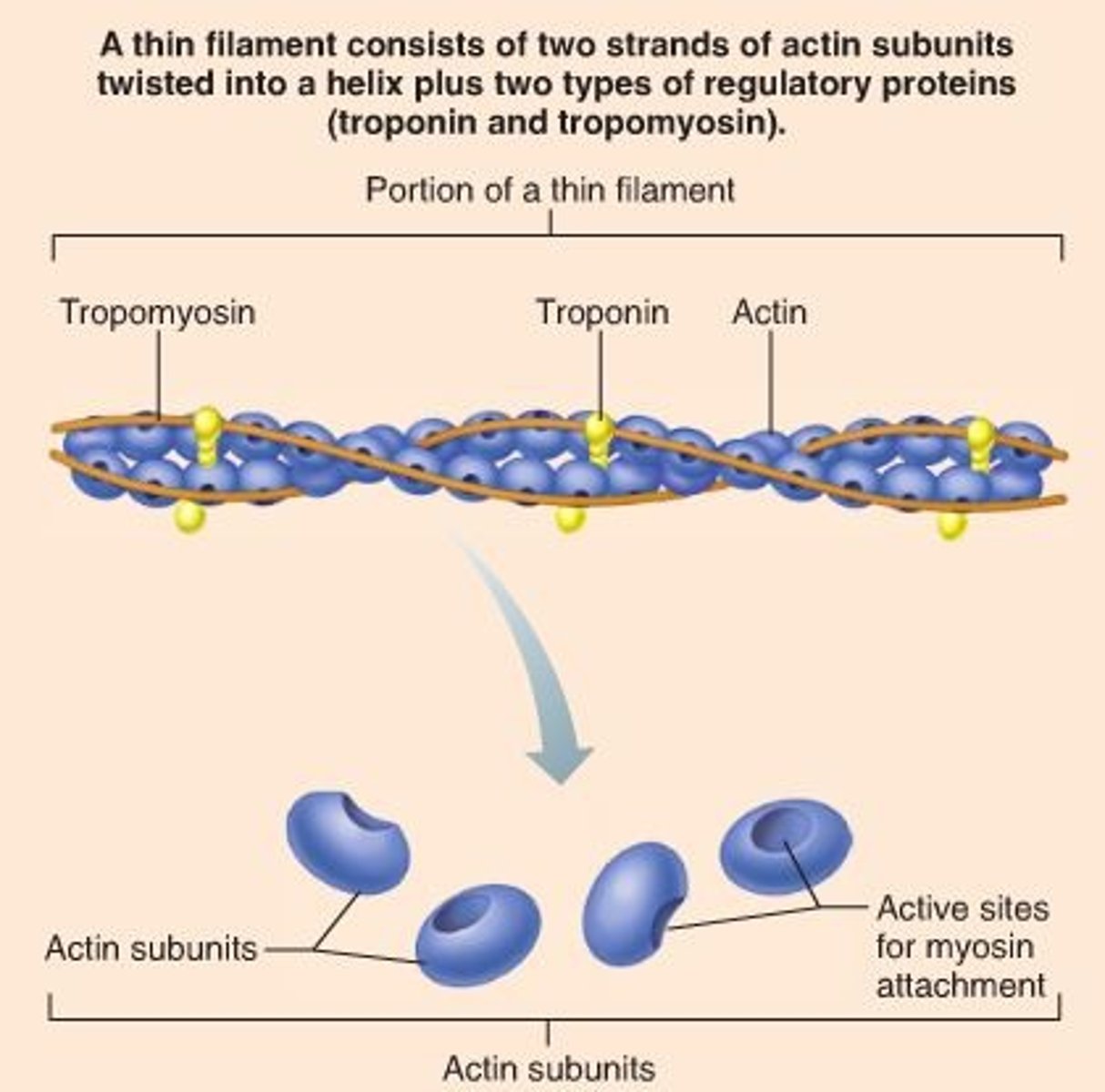
thin filament
actin
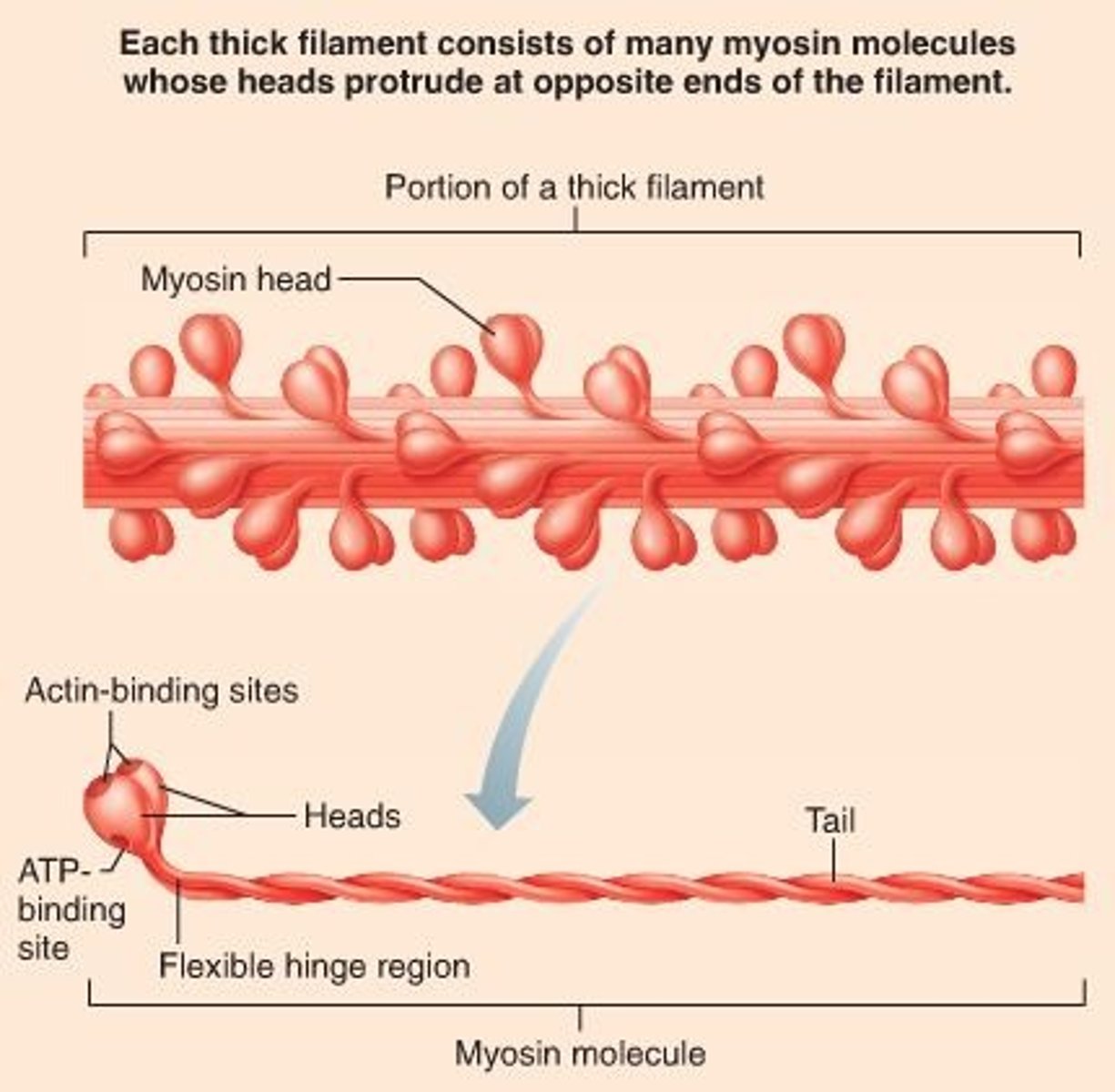
thick filament
myosin
elastic filament
titin
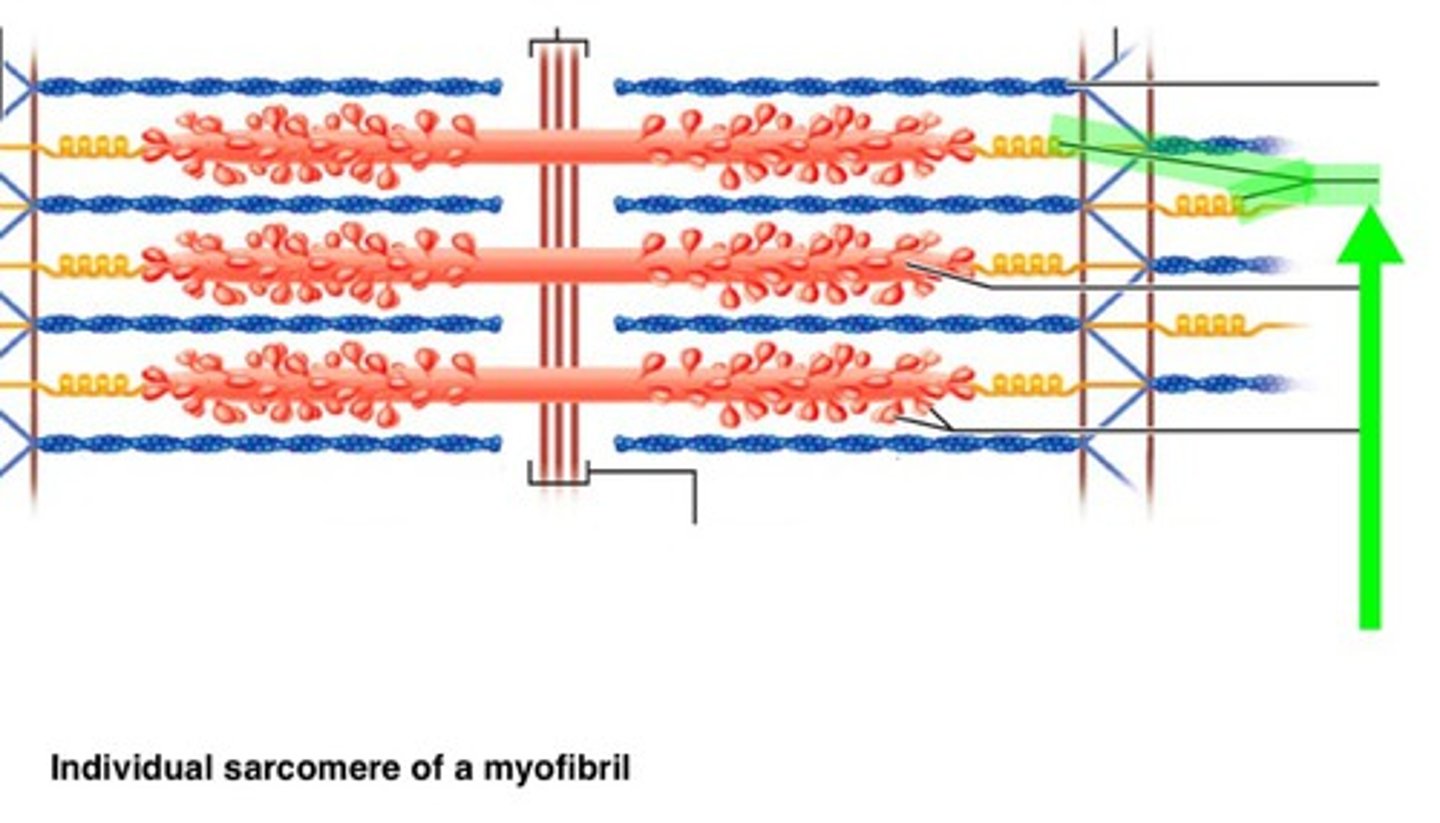
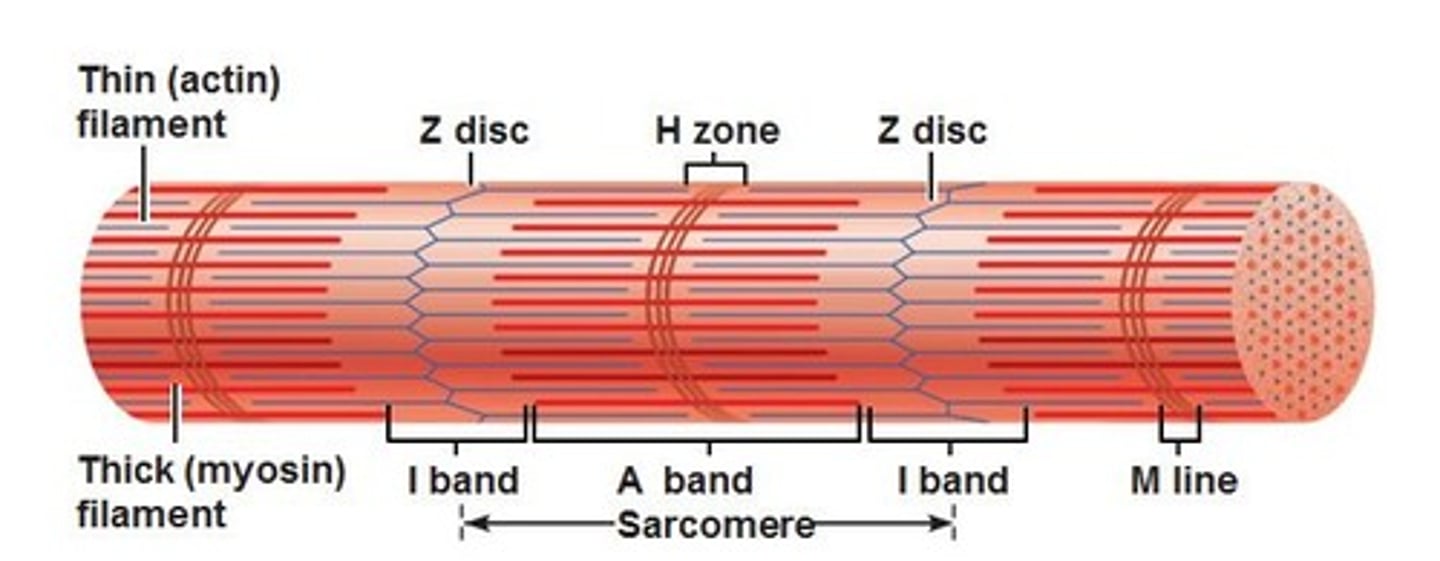
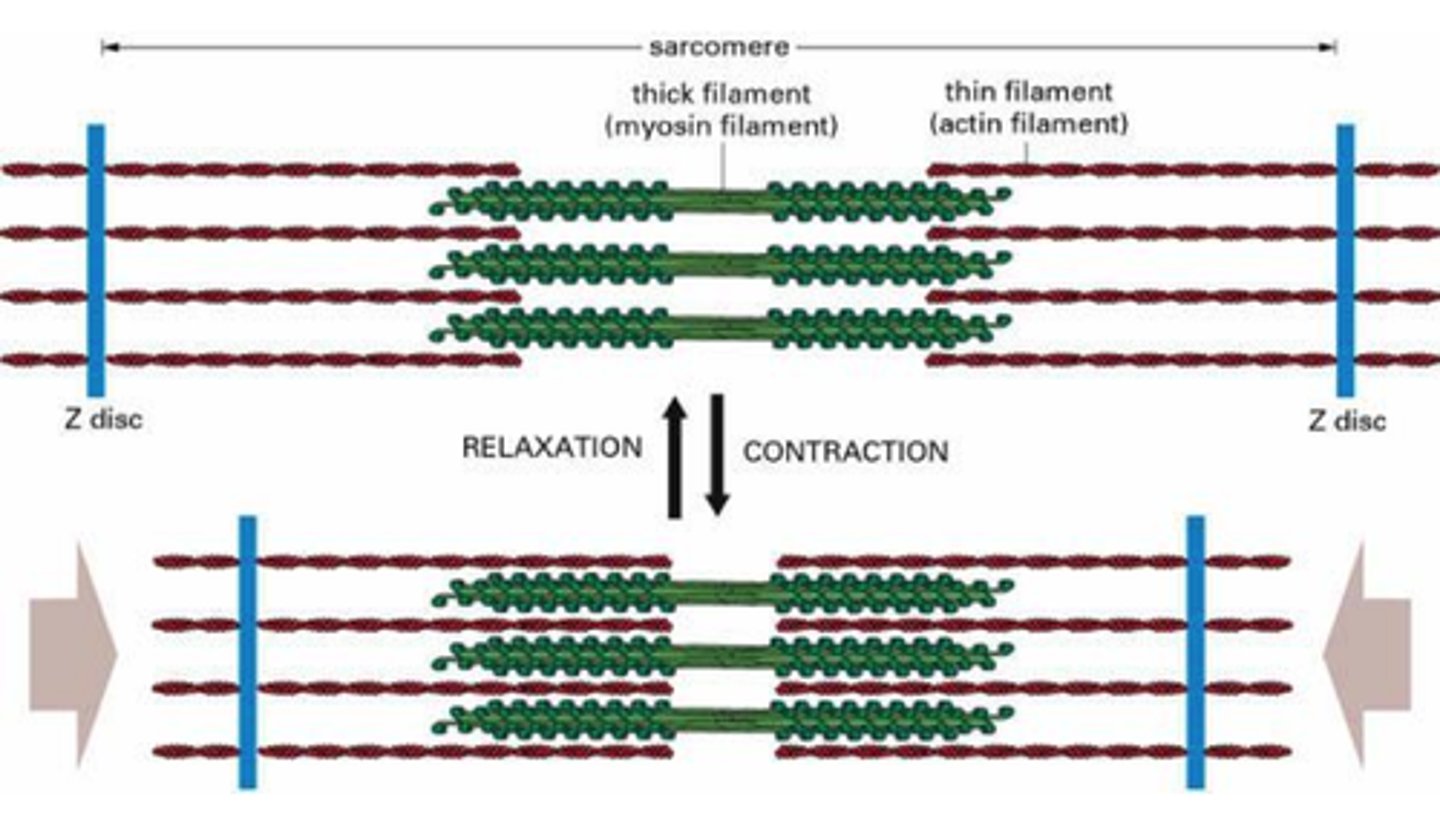
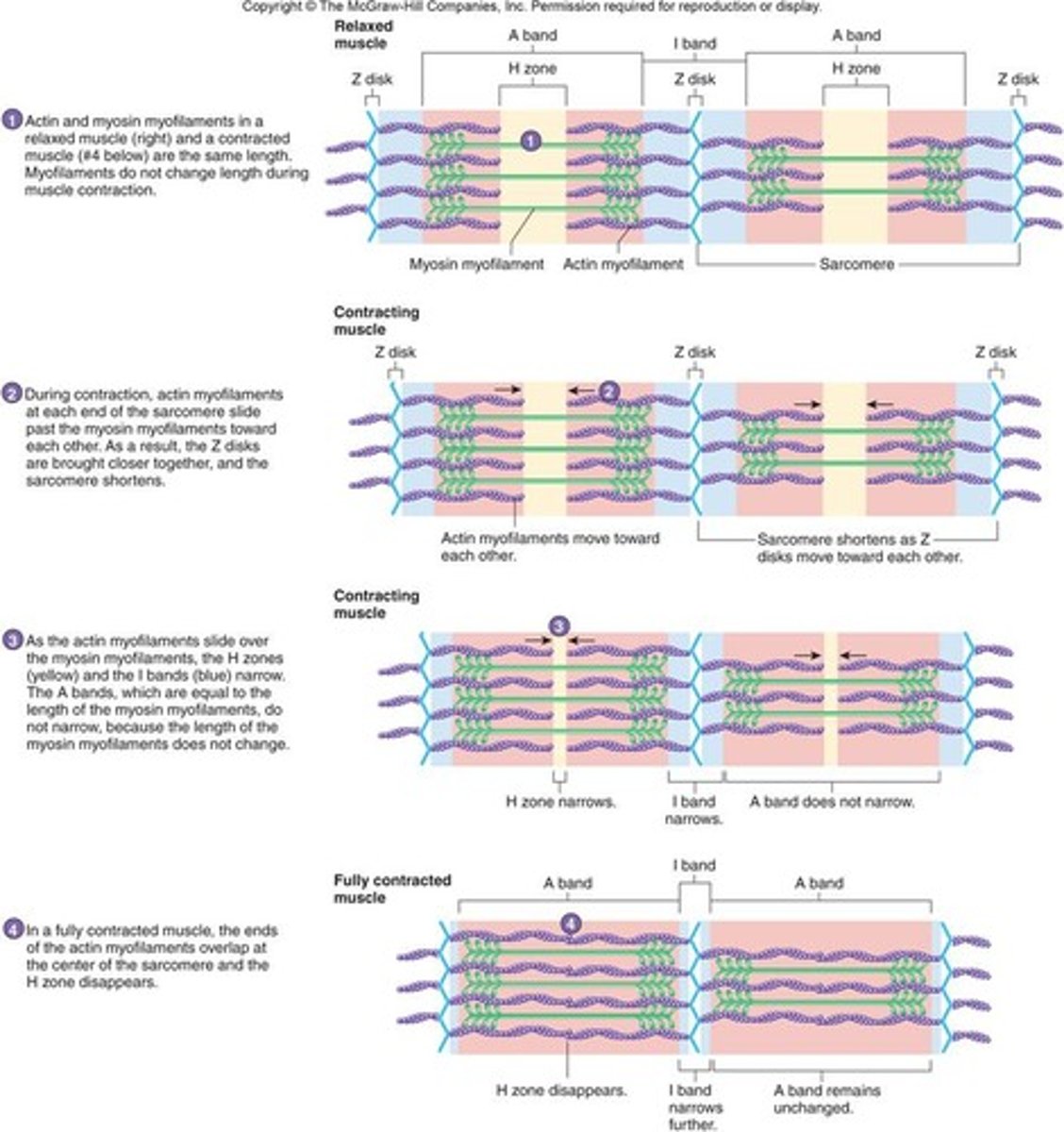
Sarcomere
functional unit of myofibril, extends from one Z disc to the next, specific arrangement of thick and thin myofilaments, z disc, I band, a band, m line, h zone
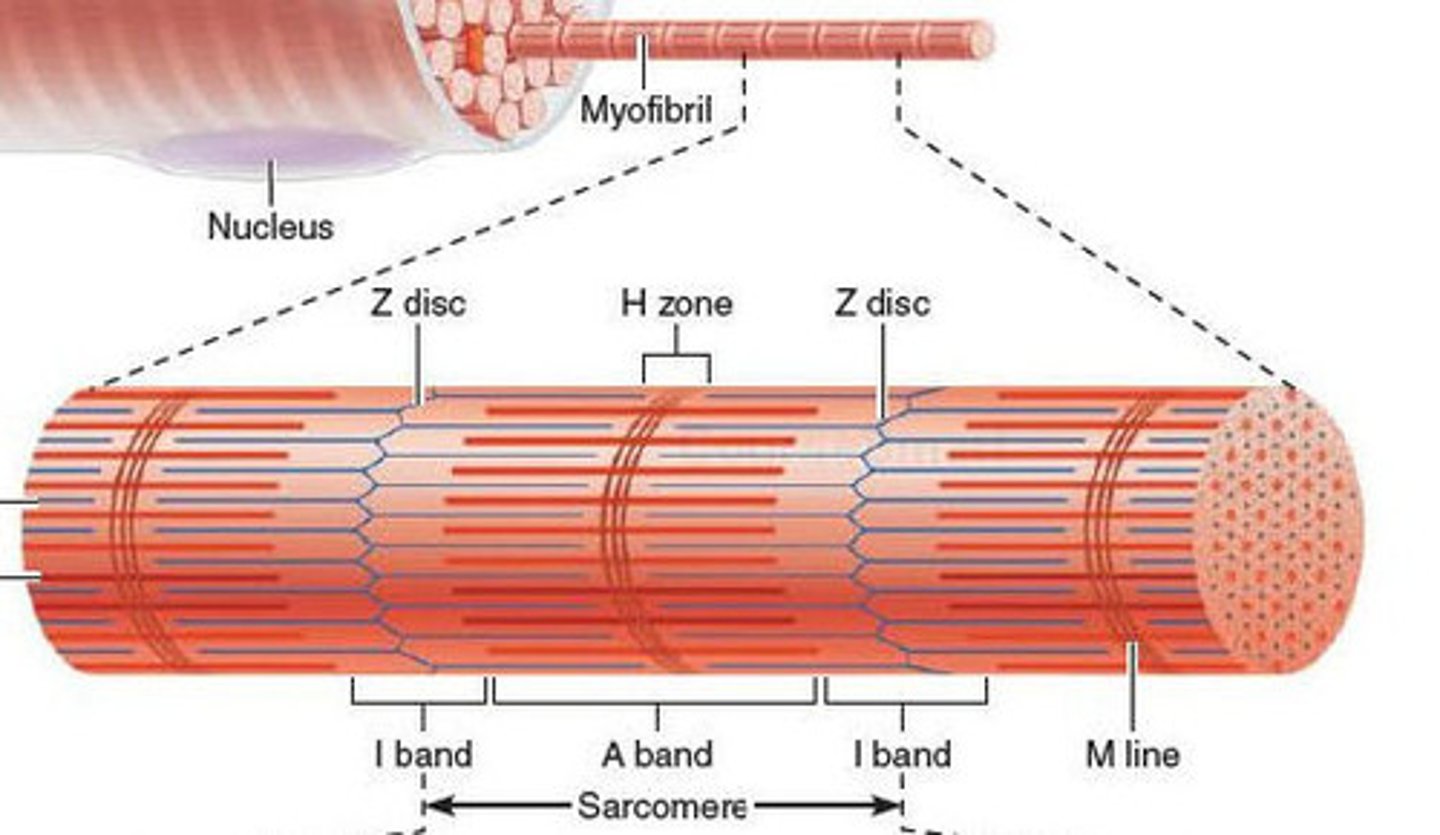
z disc
end of sarcomere, thin filaments anchored to it
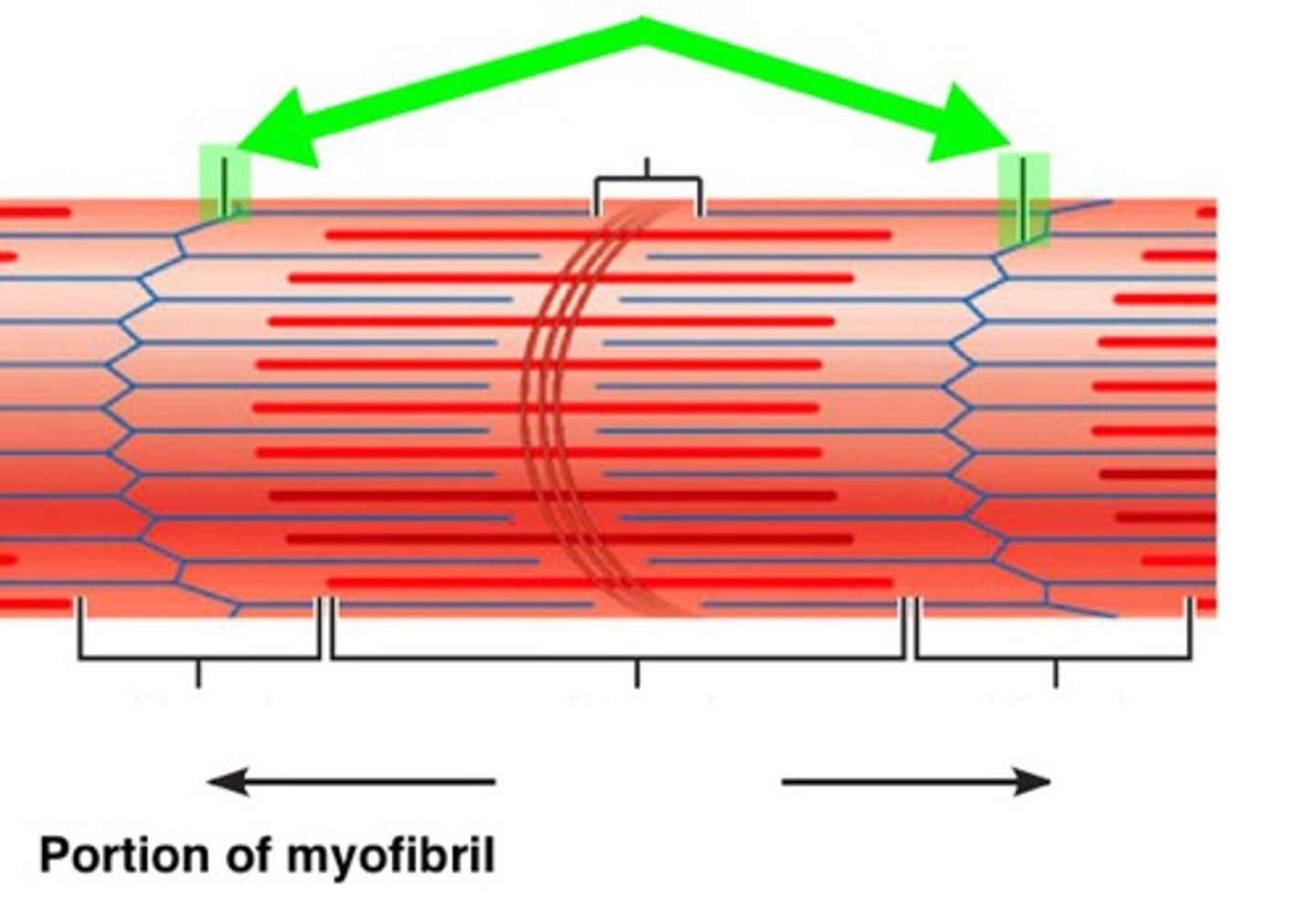
m line
anchors thick filaments down center of sarcomere
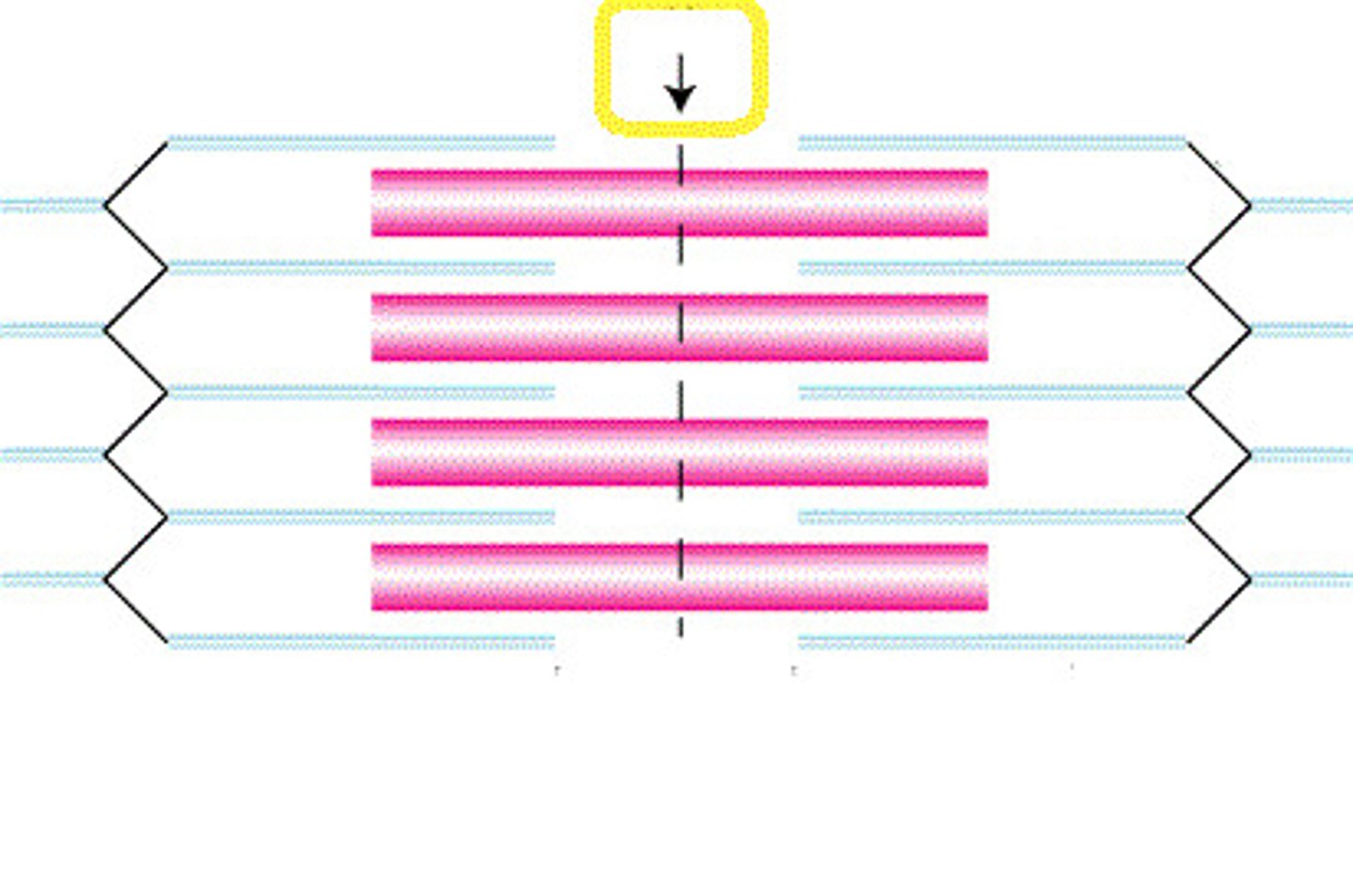
h zone
lighter region around m line contains only thick filaments
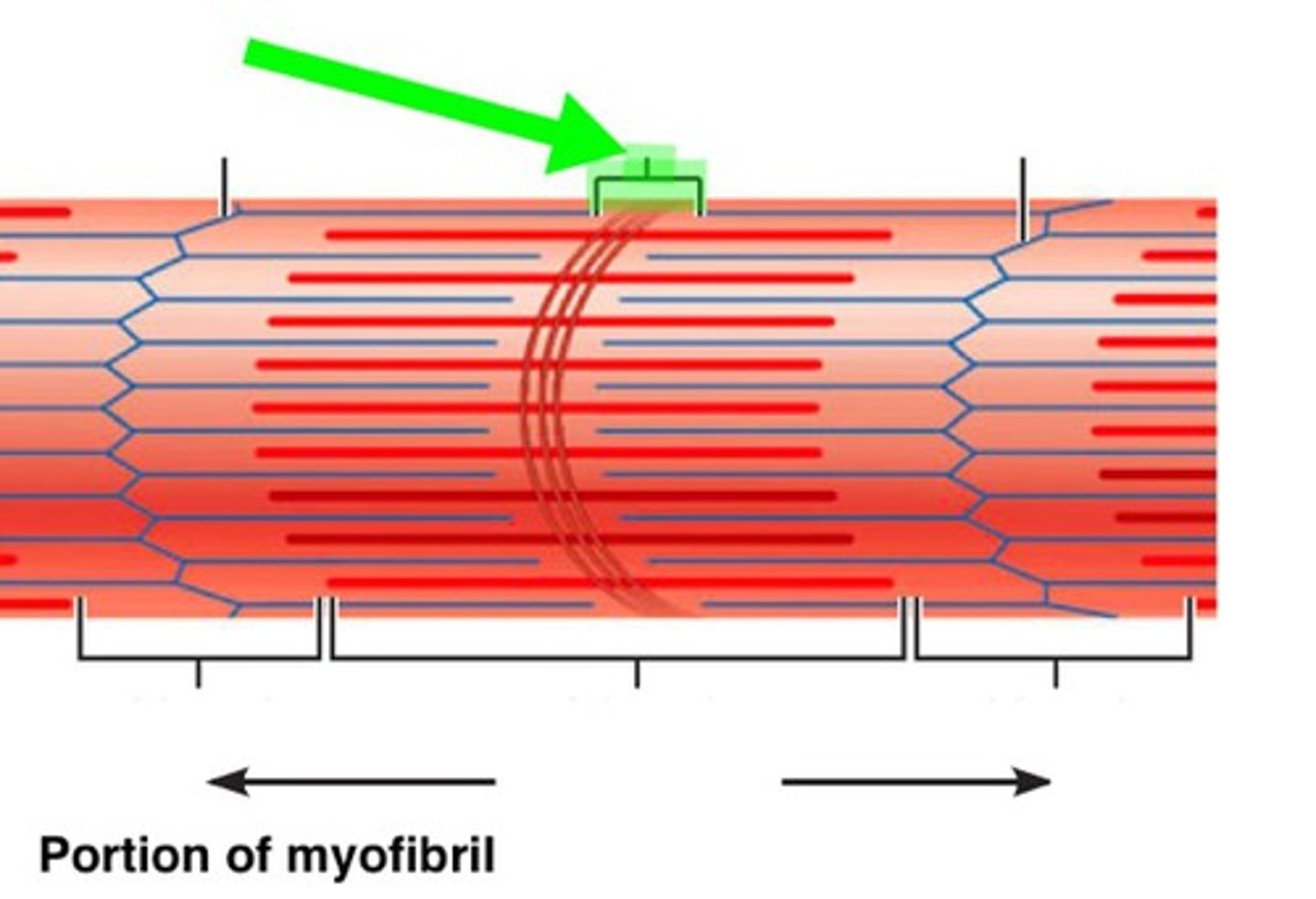
I band
light region at end with z disc in the middle contains only thin filaments
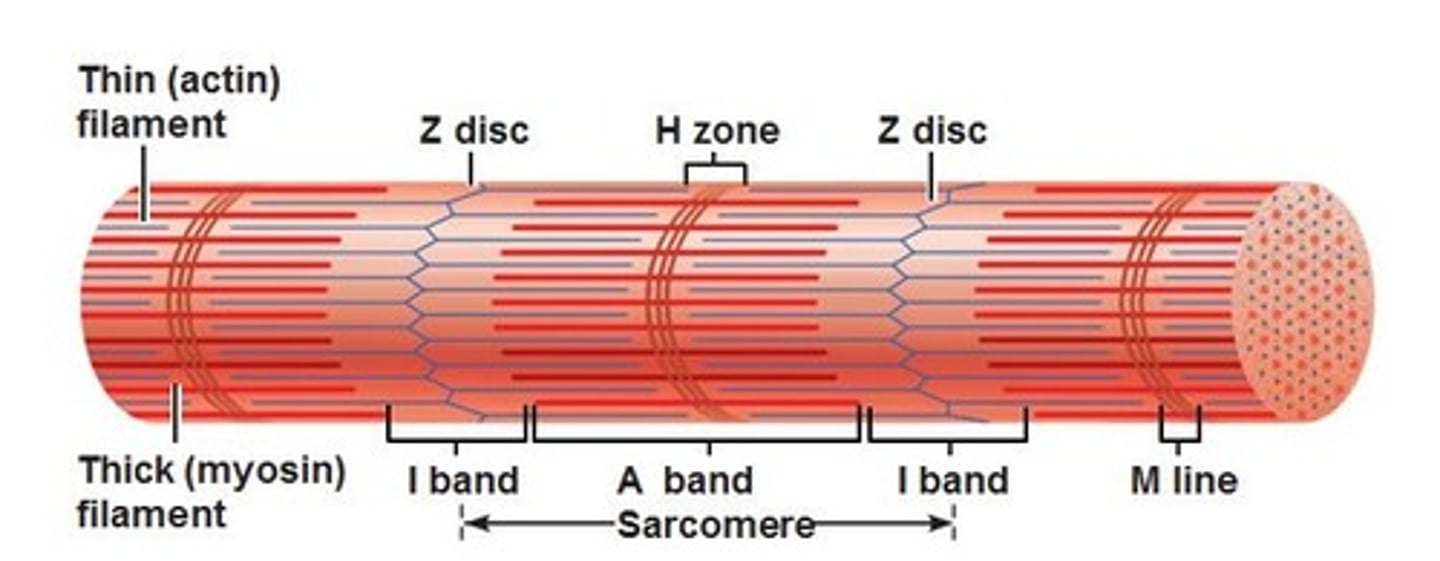
a band
anchors thick filaments down center of sarcomere
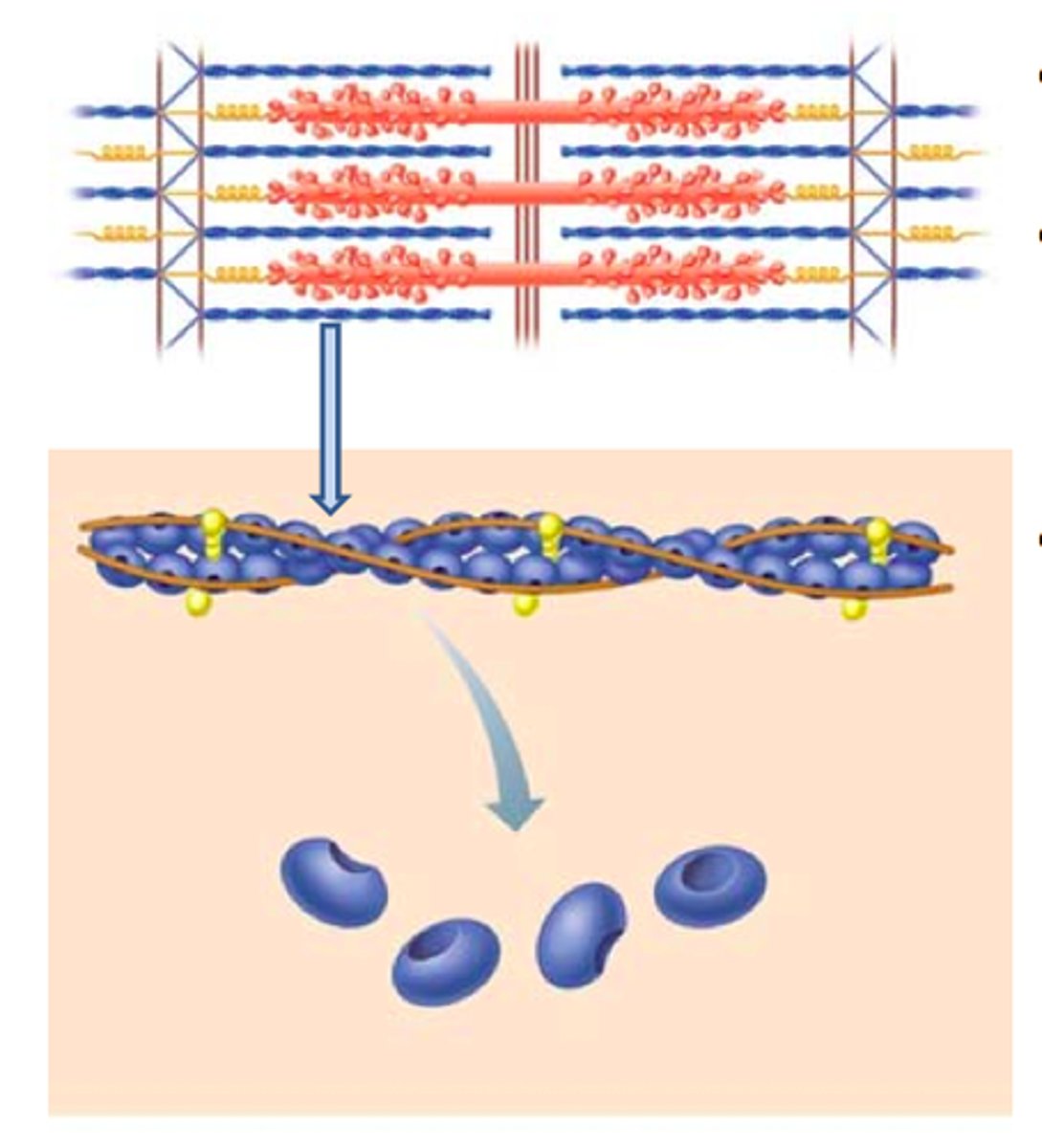
actin
A globular protein that links into chains, two of which twist helically about each other, forming microfilaments in muscle and other contractile elements in cells.
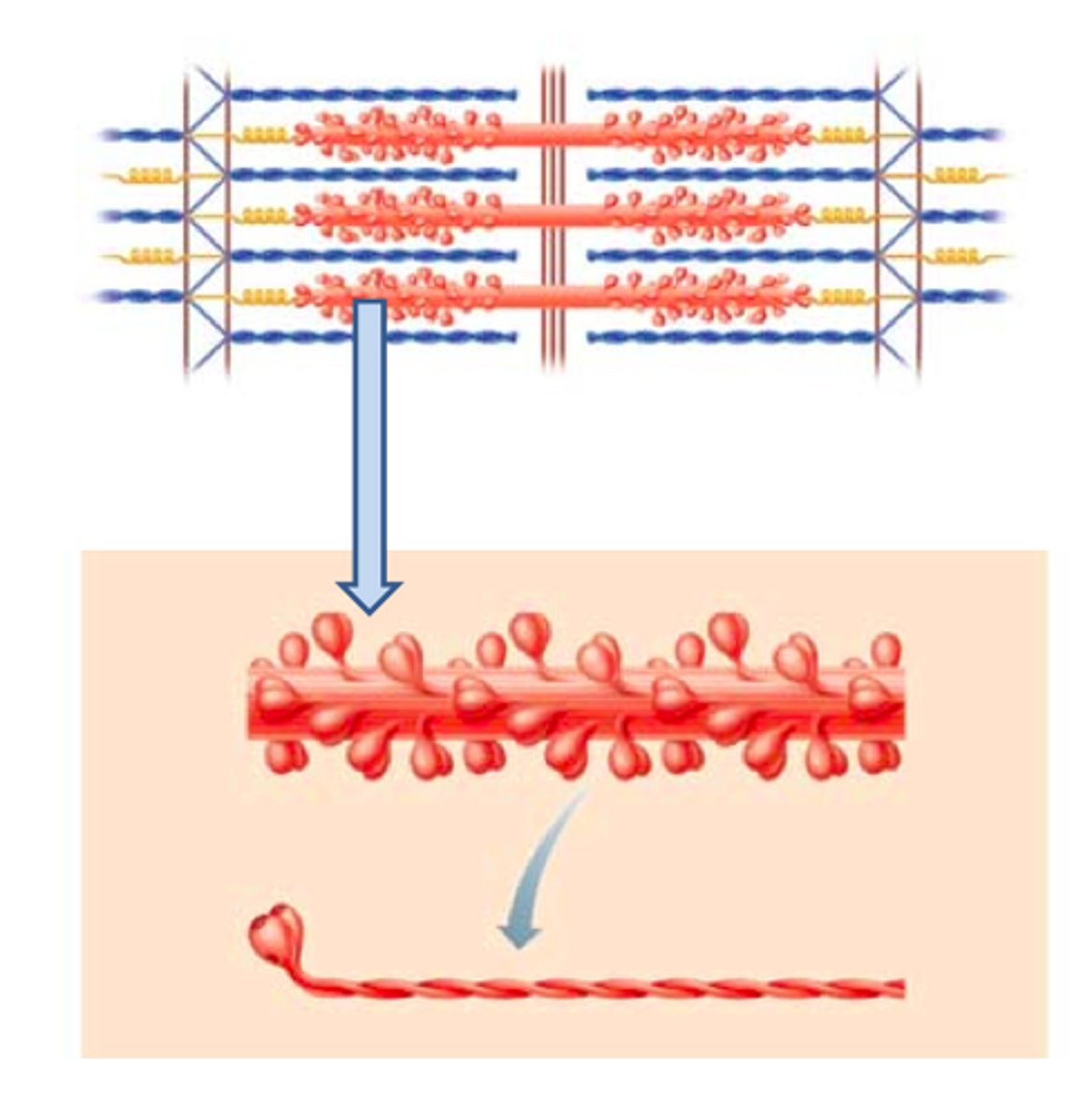
myosin
The contractile protein that makes up the thick filaments of muscle fibers
titin
a protein that positions the myosin filament to maintain equal spacing between actin filaments
troponin
A protein of muscle that together with tropomyosin forms a regulatory protein complex controlling the interaction of actin and myosin and that when combined with calcium ions permits muscular contraction
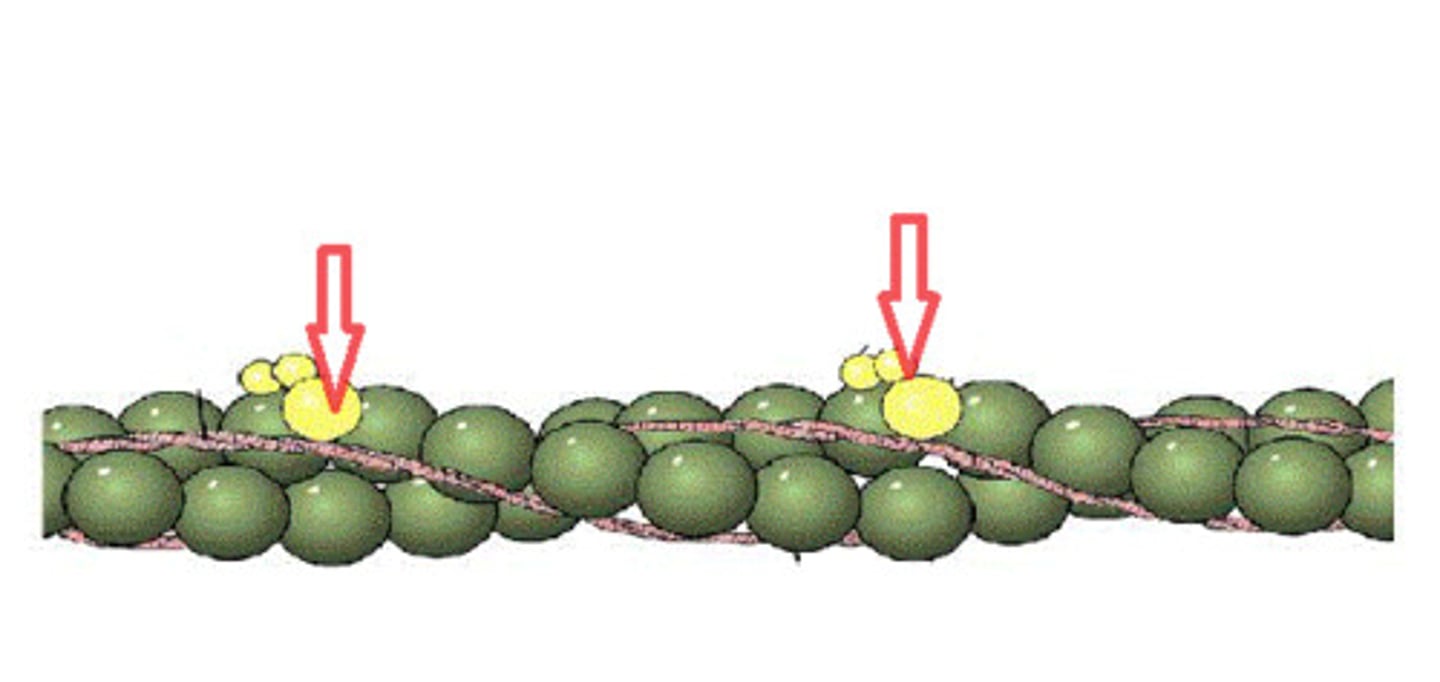
tropomyosin
covers myosin binding sites on the actin molecules
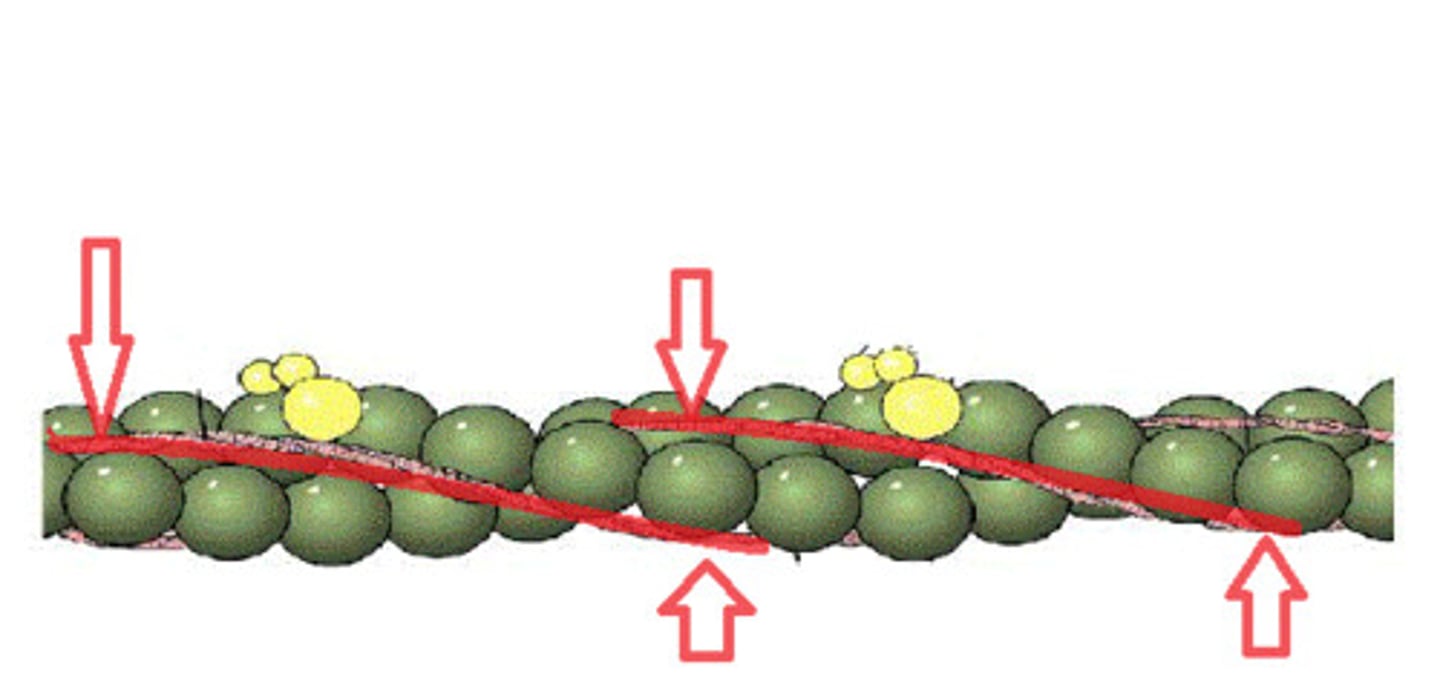
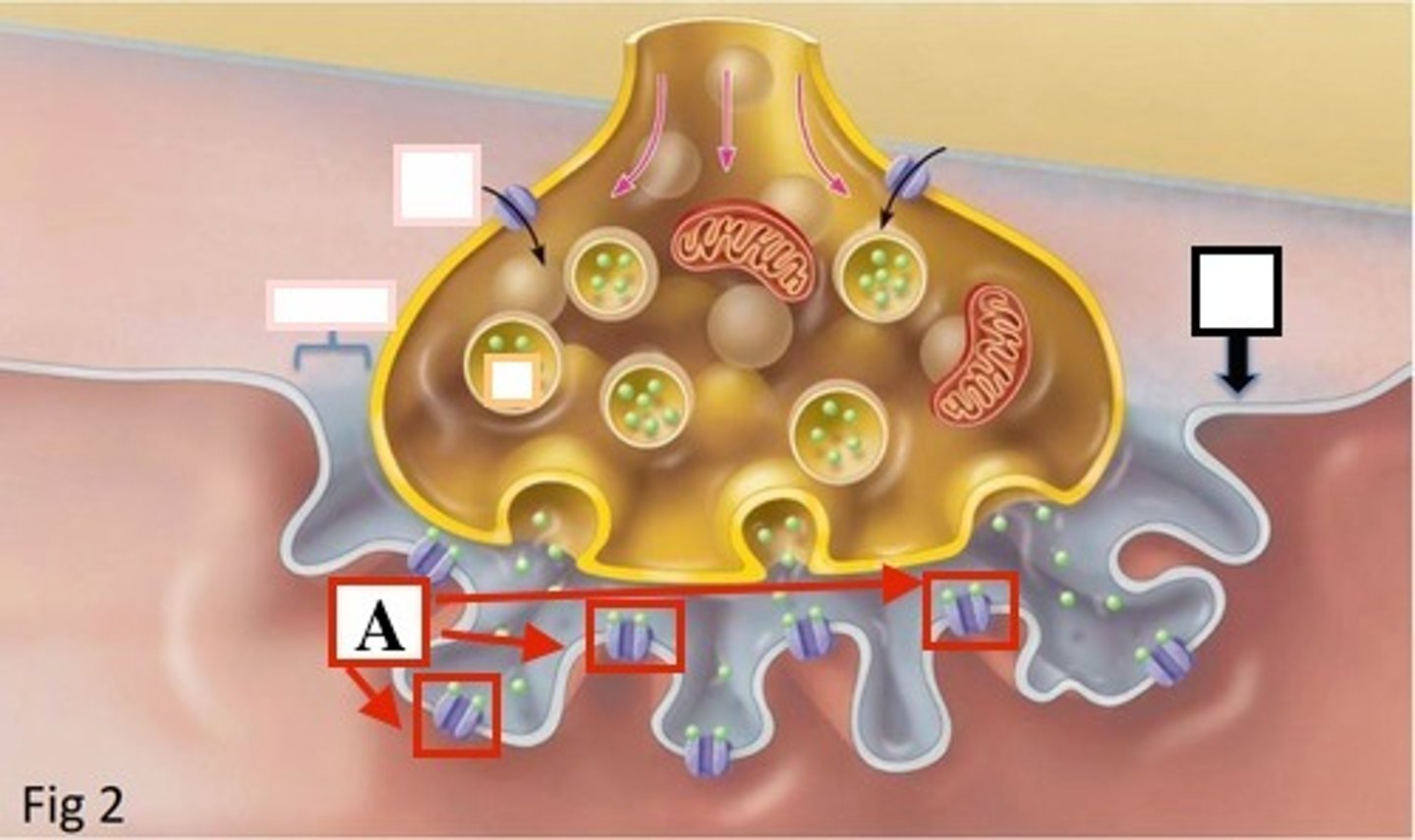
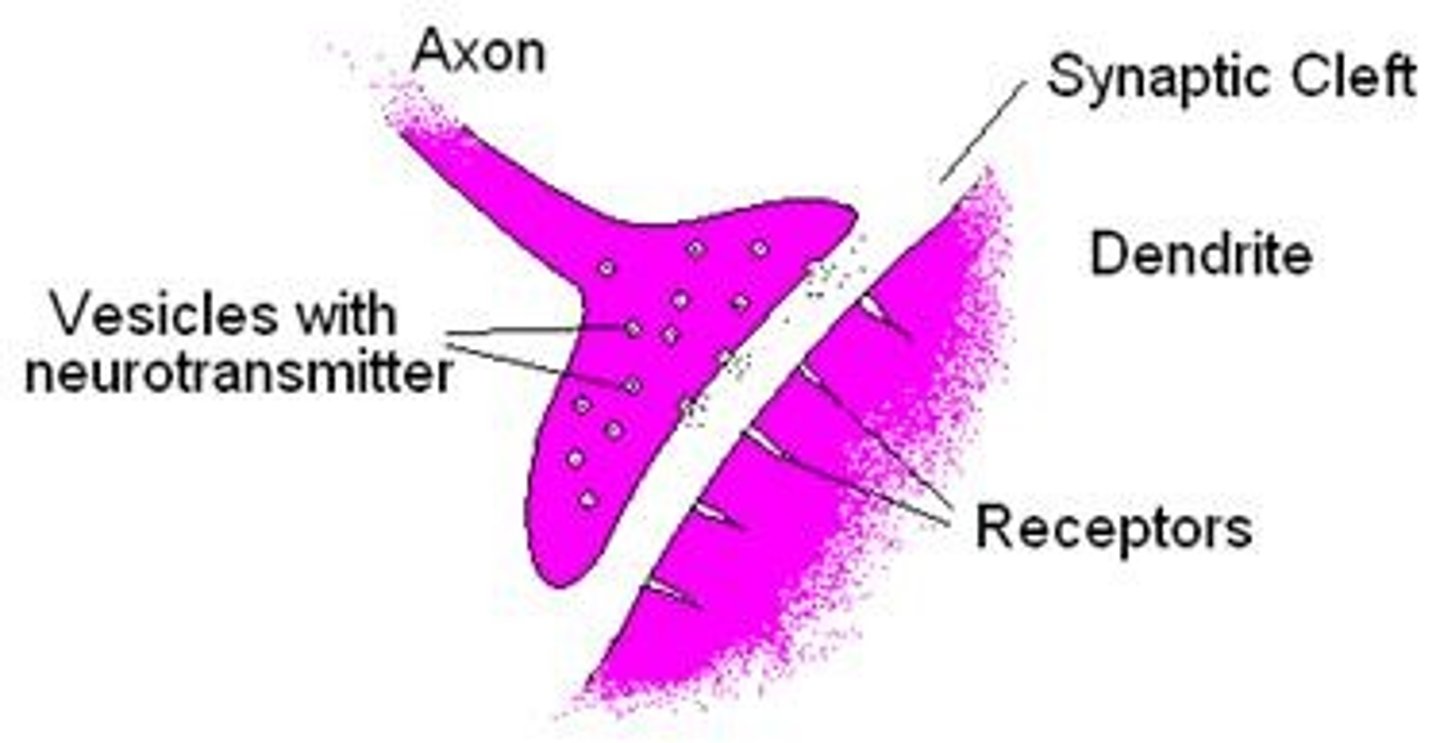
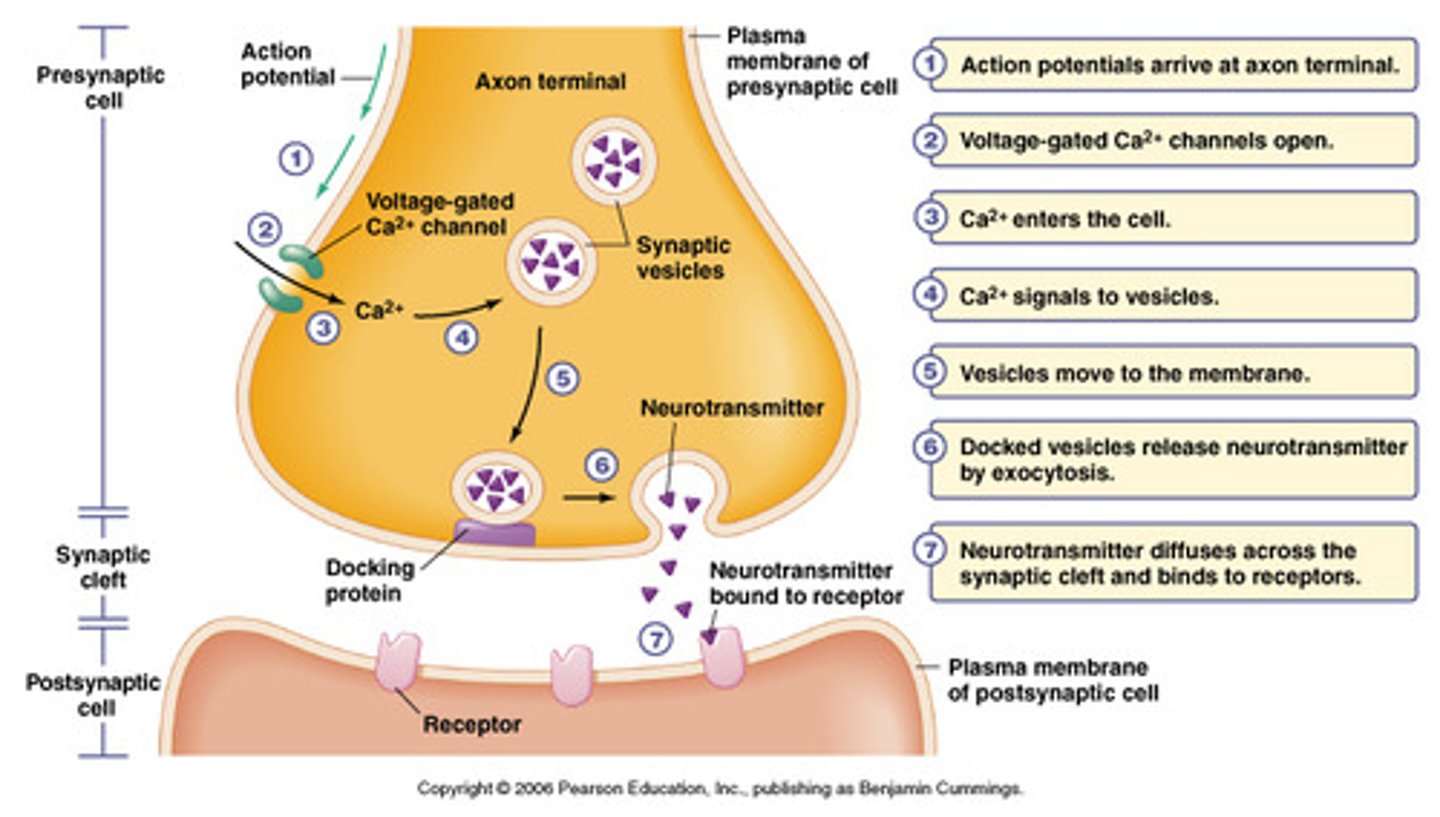
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
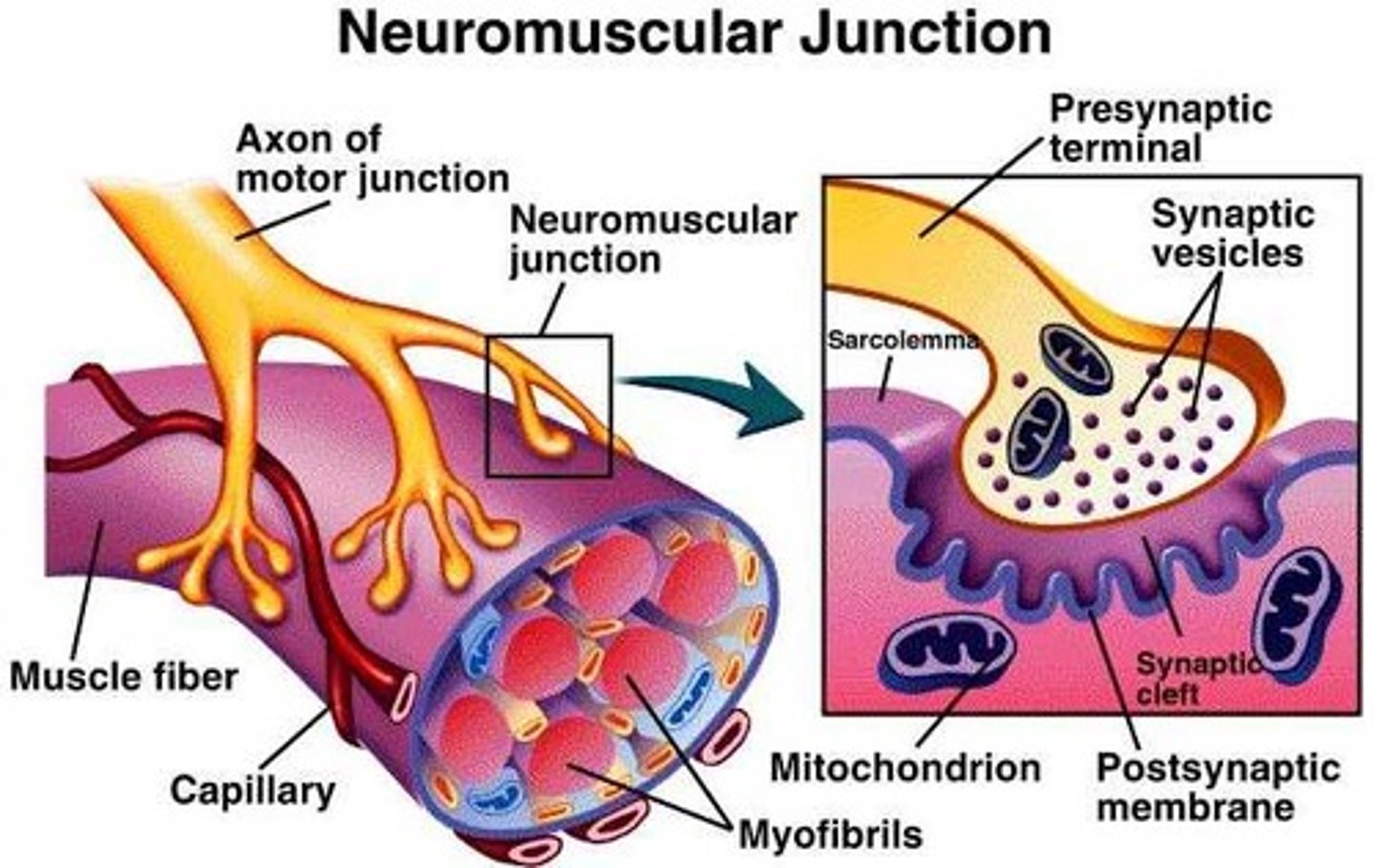
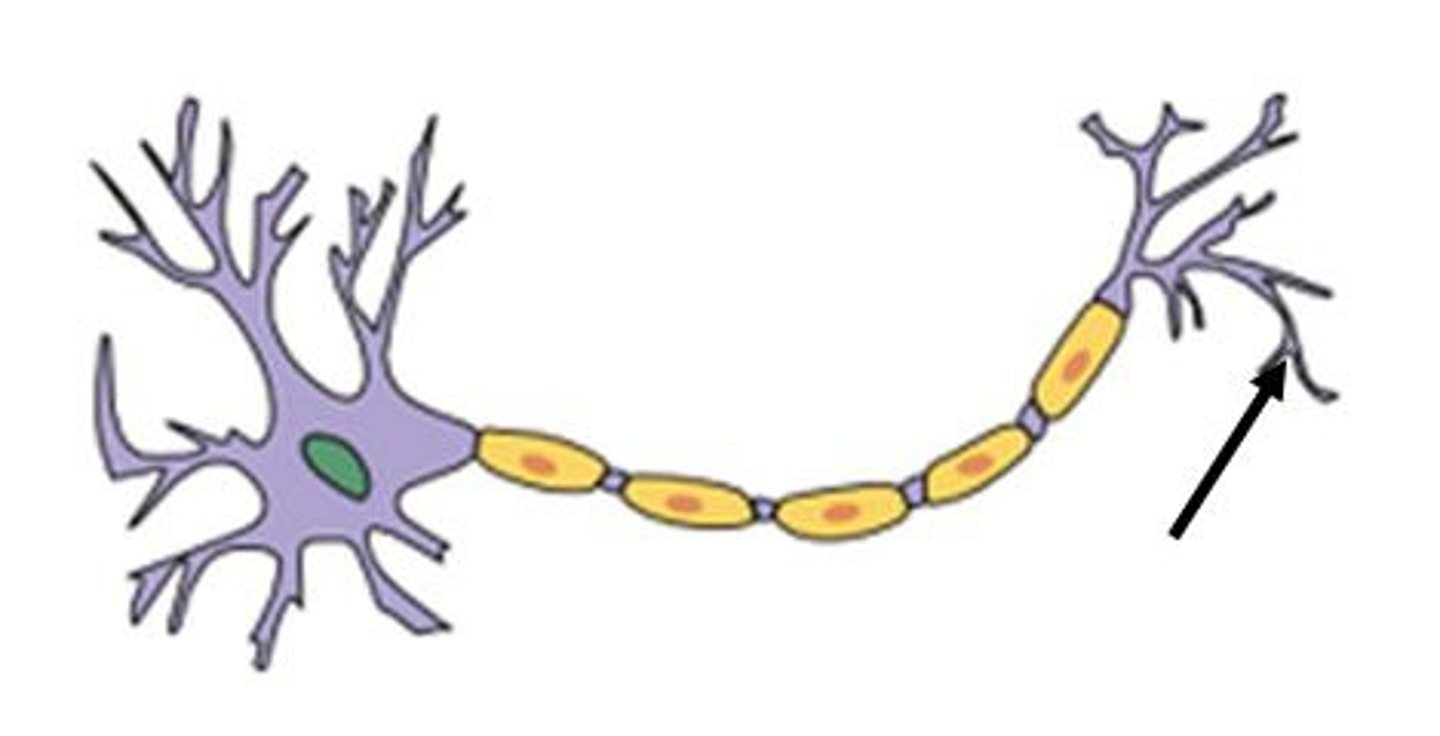
axon terminal
distal portion of a motor neuron, forms neuron side of neuromuscular junction
synaptic vesicle
located at tip of axon terminal contain neurotransmitter acetylcholine
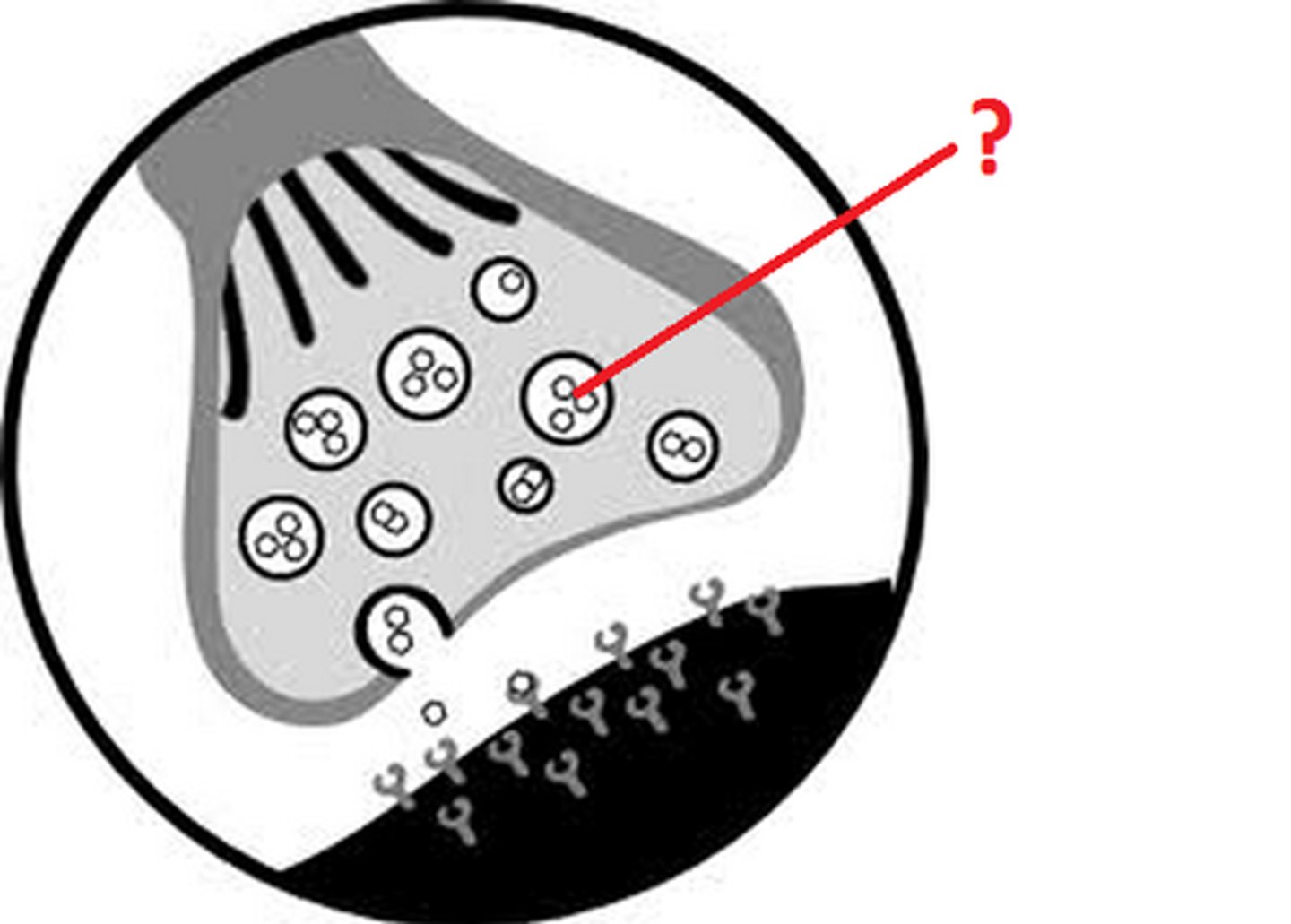
acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
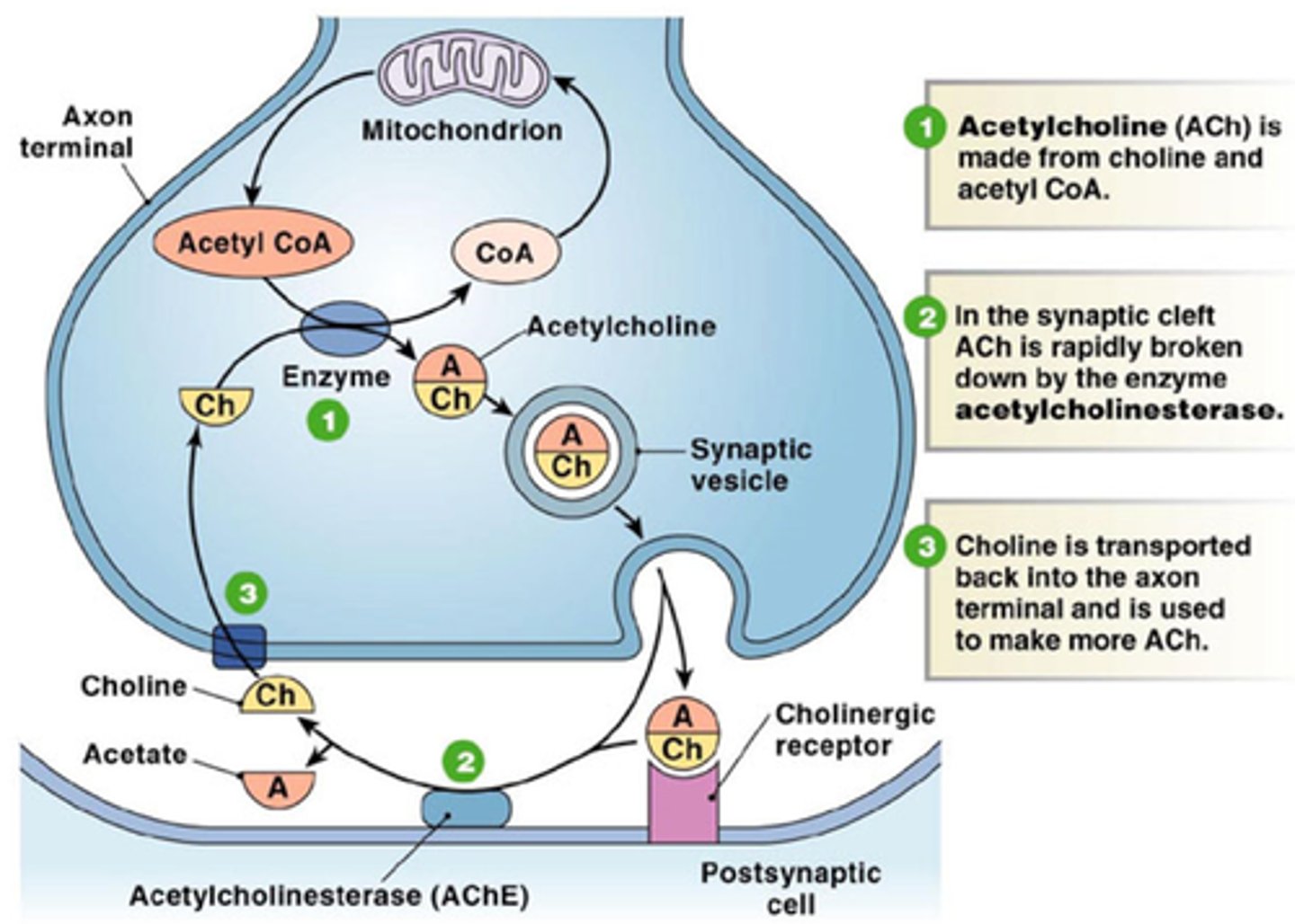
ach receptor
a transmembrane protein in the sarcolemma of the neuromuscular junction that binds to ACh
synaptic cleft
narrow space between axon terminal and motor end plate, contains the enzyme acetylcholinesterase which breaks down ACH
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Channels located in the membrane of T-tubules which open in response to an action potential and allow extracellular calcium to enter the cytosol
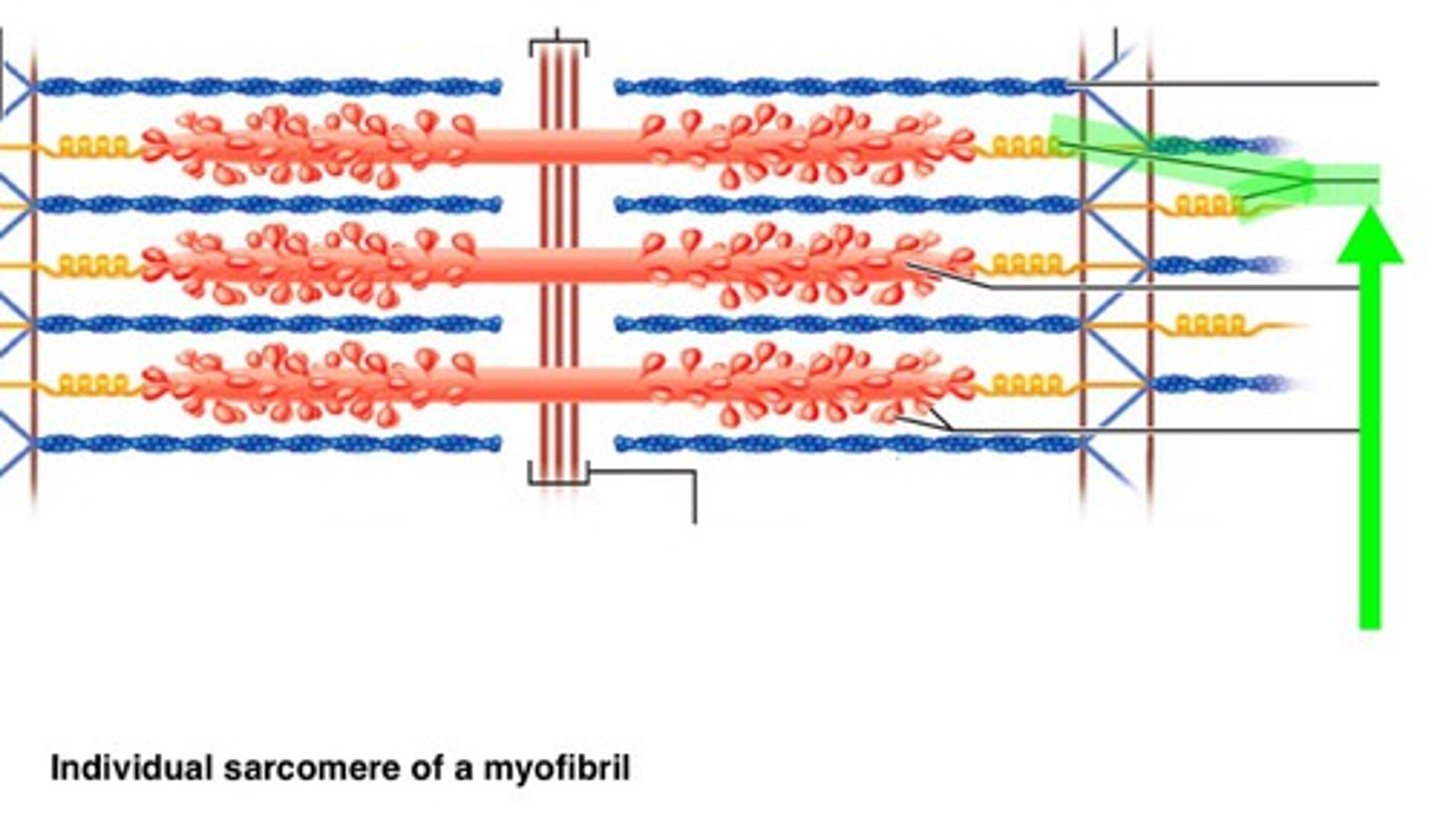
contracted sarcomere
myosin heads bind to actin, myosin head moves pulling actin, sarcomere shortens, z discs move closer together, I band narrows, h zone narrows/ disappears, a band stay the same
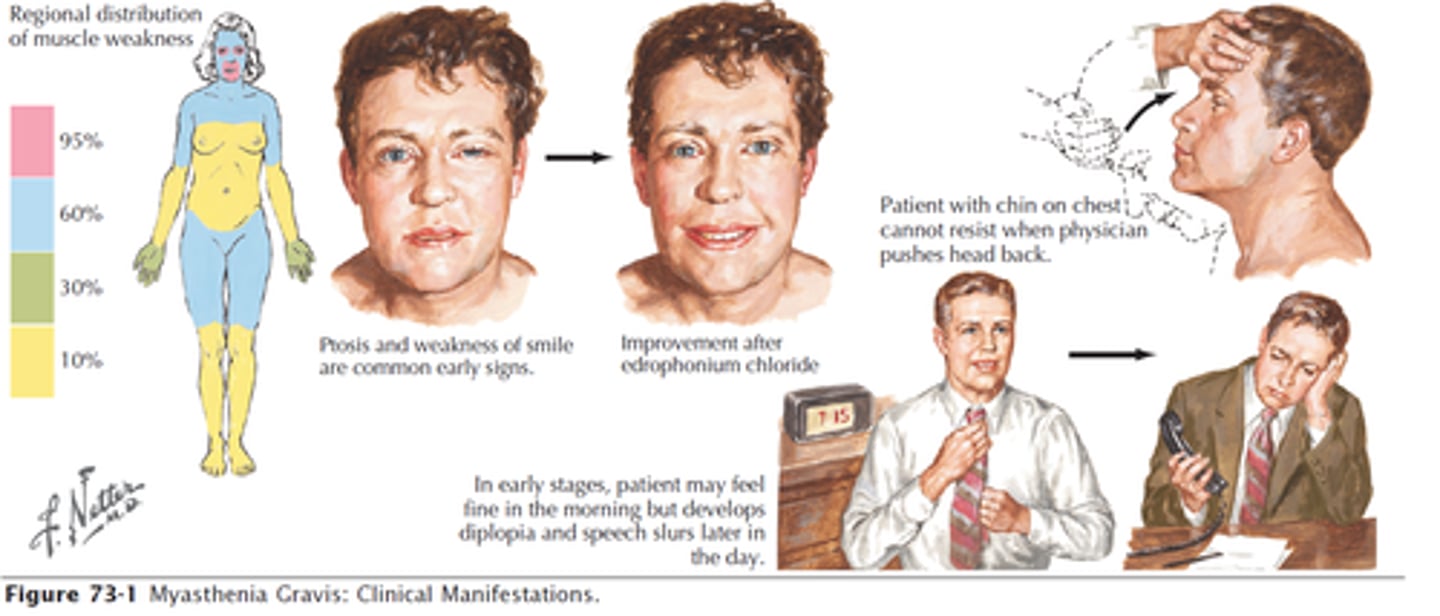
myasthenia
an autoimmune disease, antibodies damage or destroy the acetylcholine receptors at the motor end plate of a neuromuscular junction- serious muscle weaknesss, worsens with activity
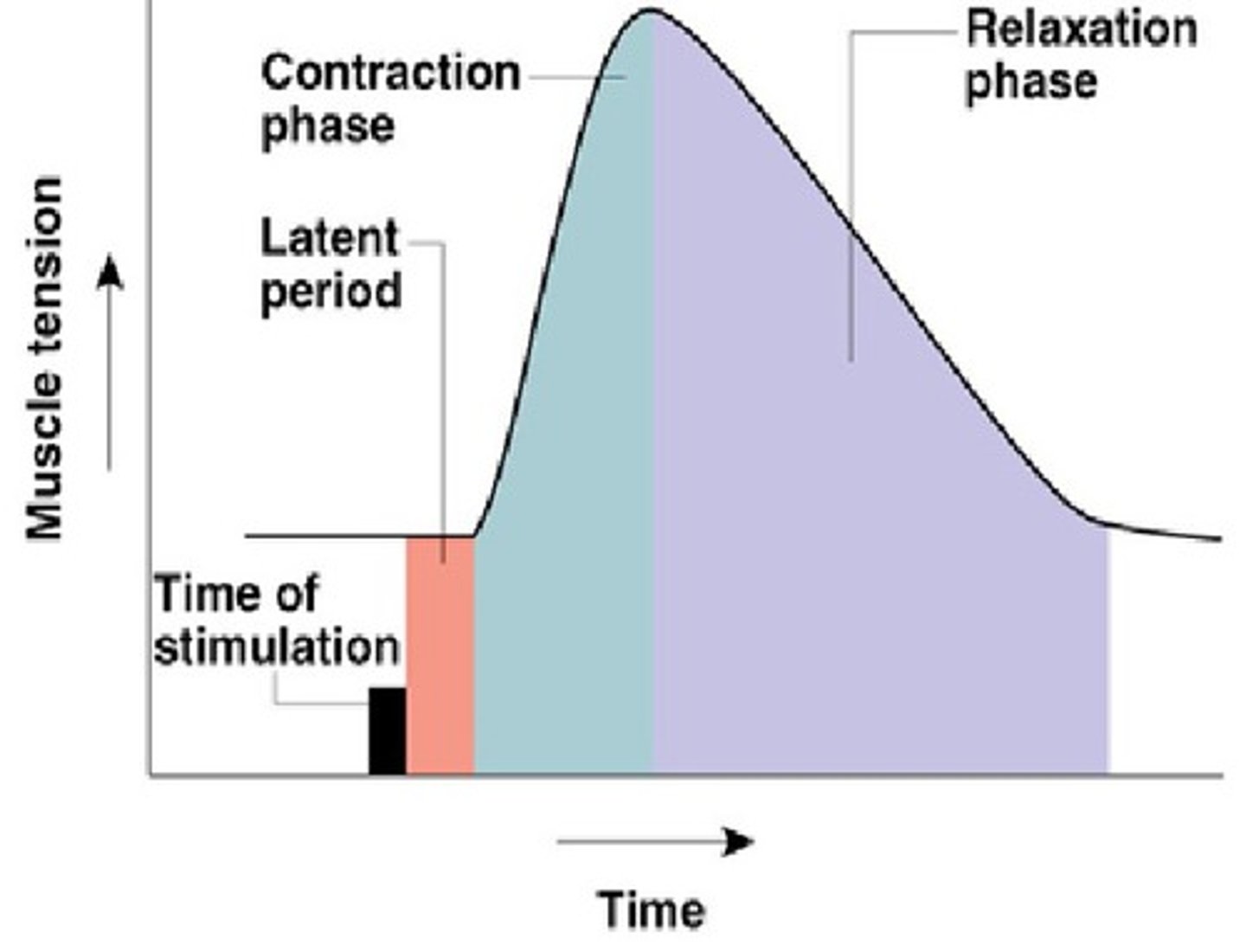
latent period
activation and excitation AP travels to entire muscle release of calcium
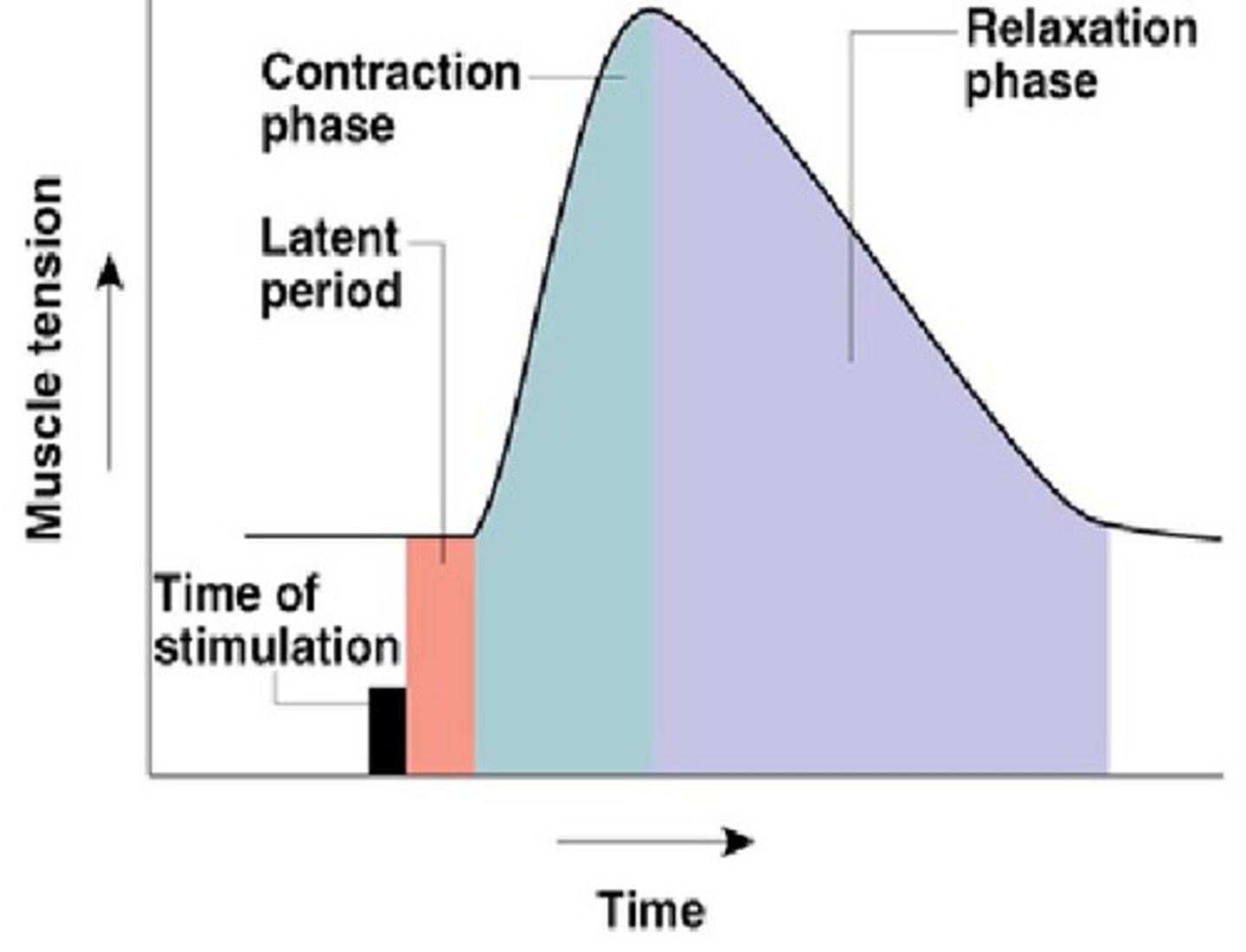
contraction period
cross bridge activity increase in muscle tension muscle shortening
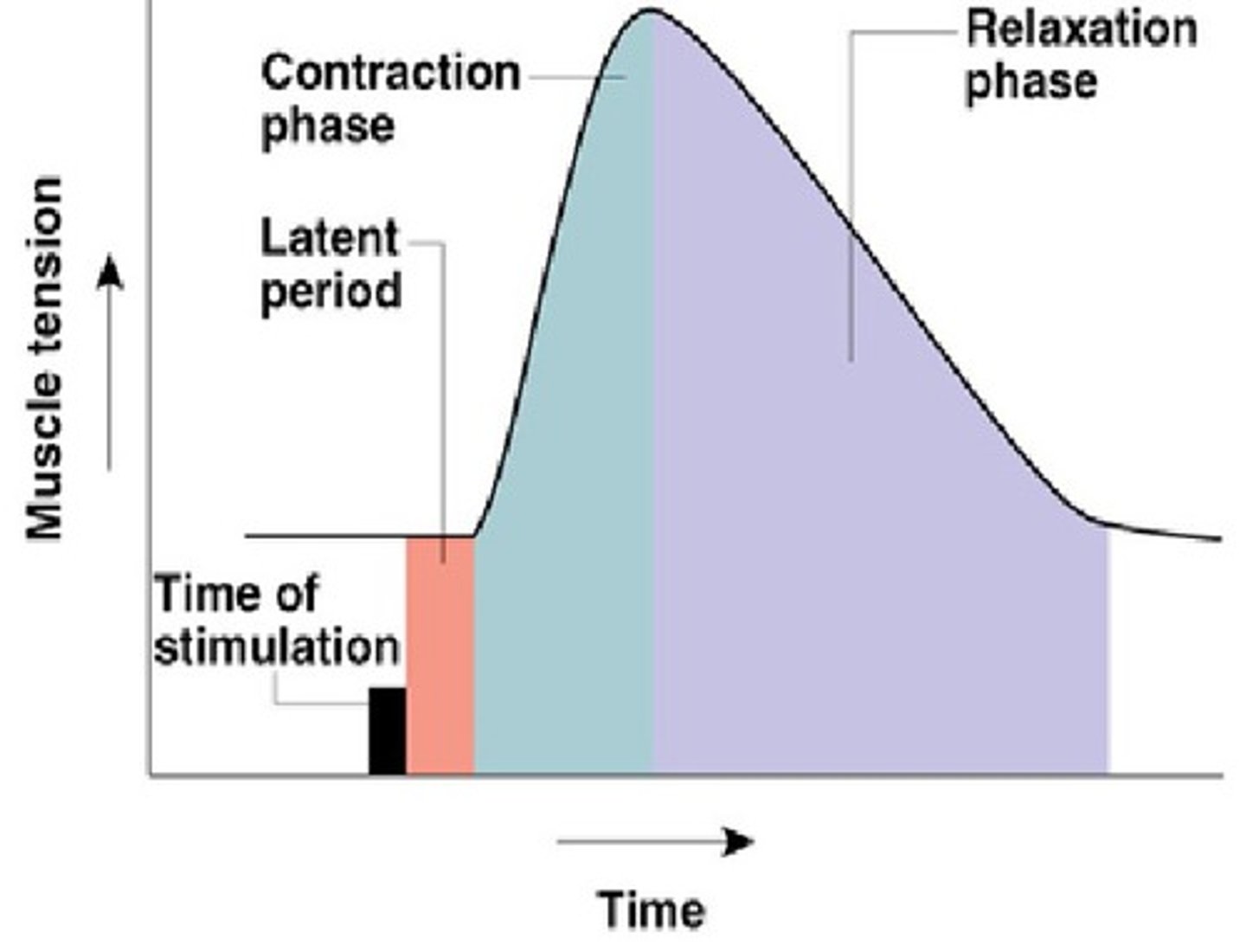
relaxation period
calcium returned to SR muscle tension decreases
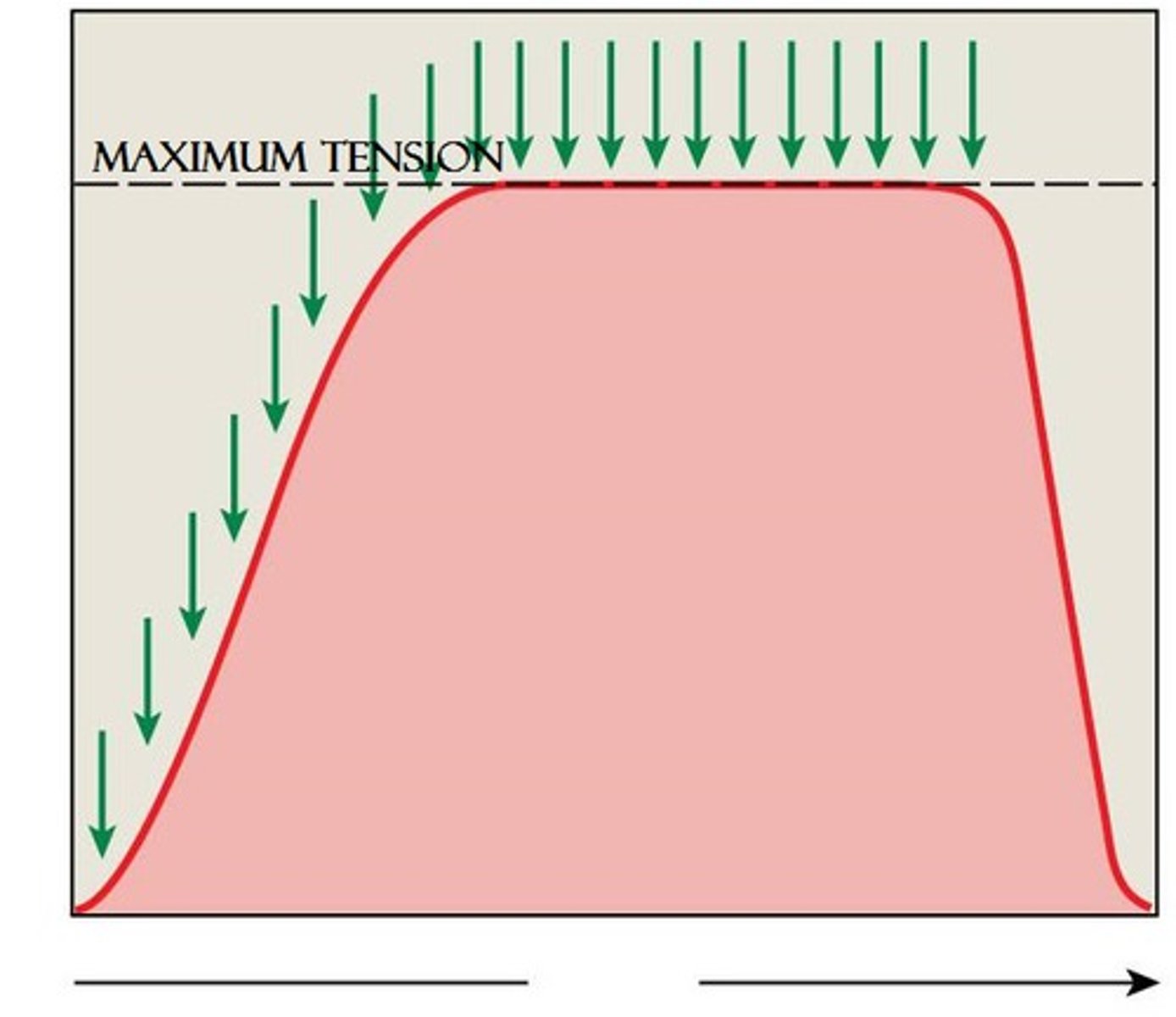
tetanus
a sustained muscular contraction resulting from a rapid series of nerve impulses
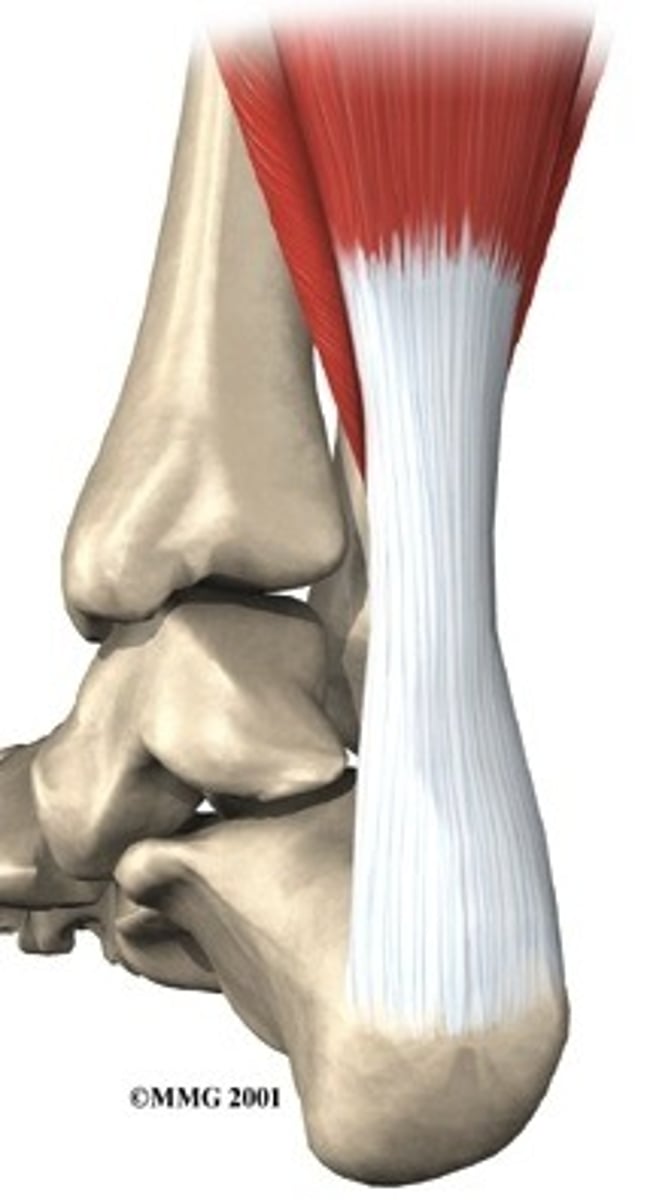
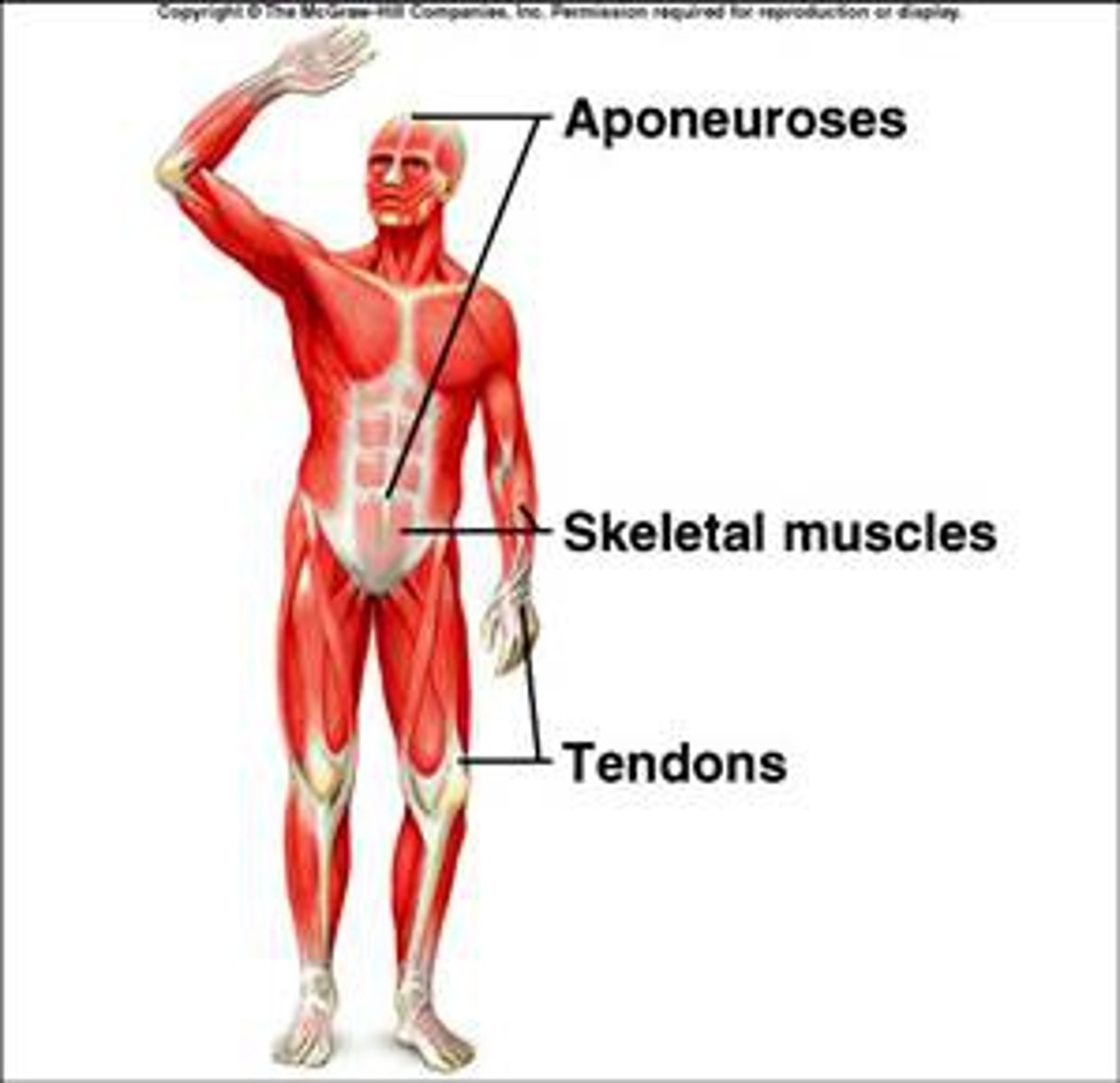
tendons/ aponeuroses
attach muscles to bones
fixed attachment
origin
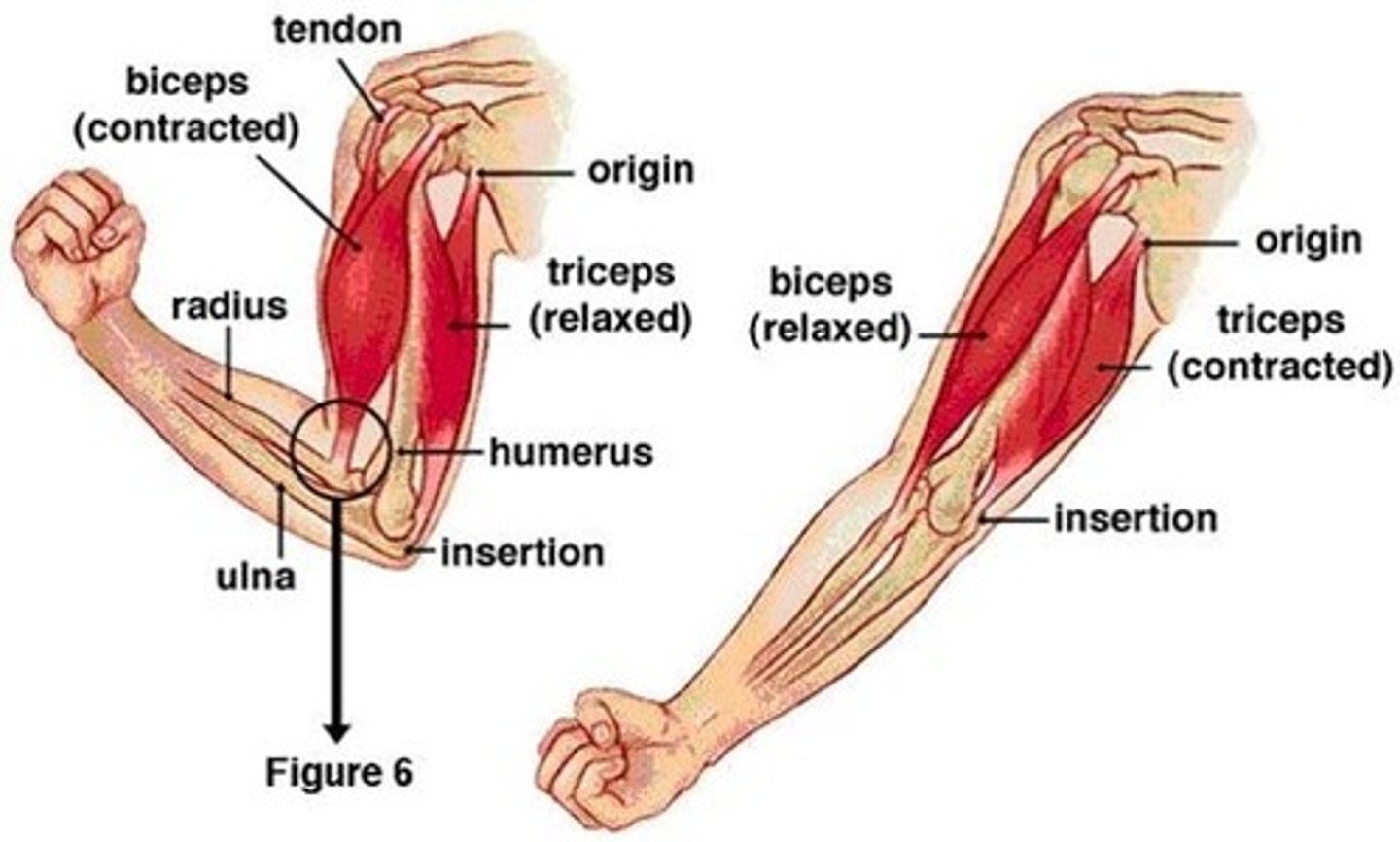
movable attachment
insertion
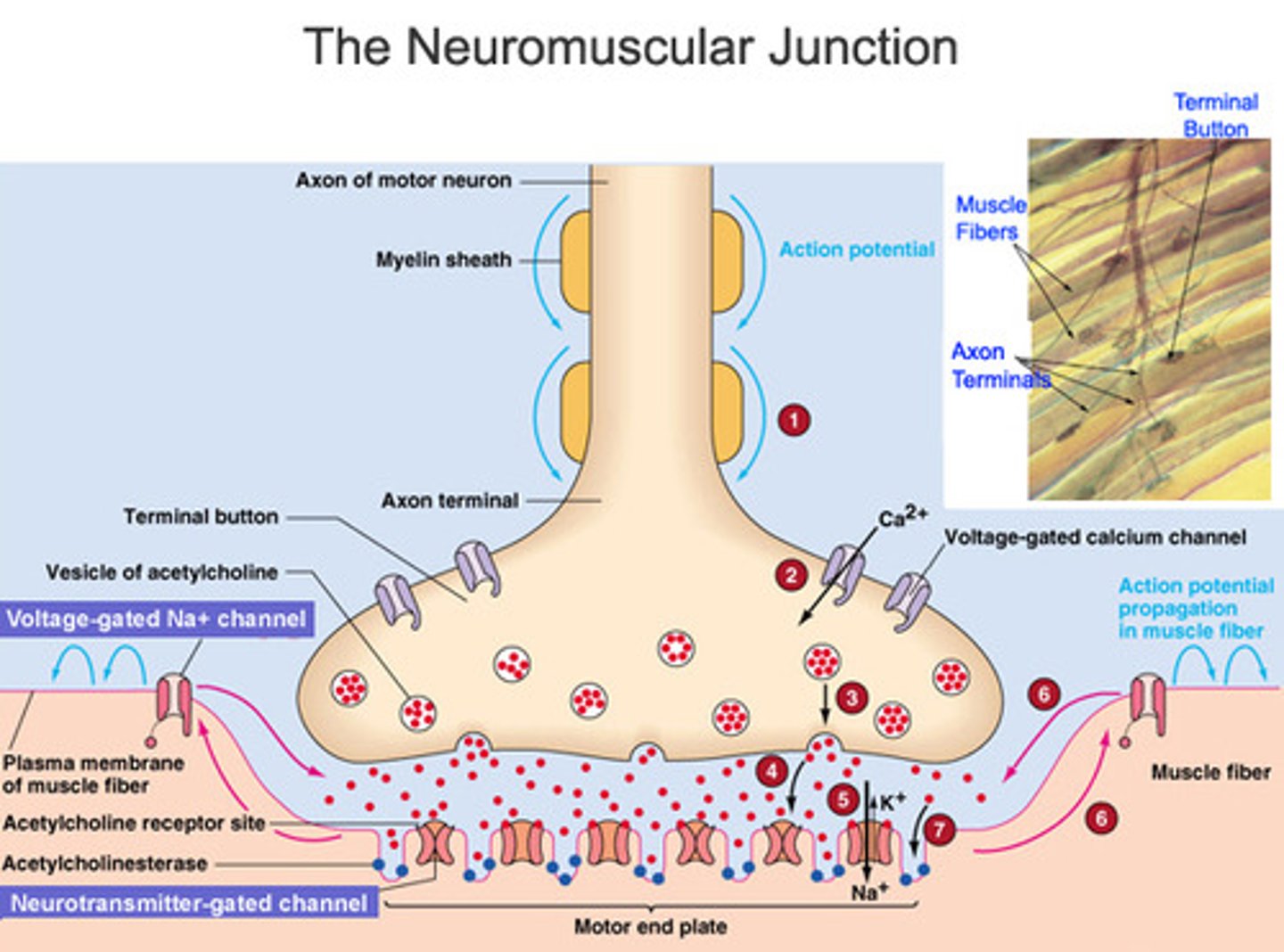
activation sequence step 1: depolarization and calcium ion release
An action potential from a motor neuron triggers the release of acetylcholine into the motor end plate
Acetylcholine initiates depolarisation within the sarcolemma, which is spread through the muscle fibre via T tubules
Depolarisation causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release stores of calcium ions (Ca2+)
Calcium ions play a pivotal role in initiating muscular contractions
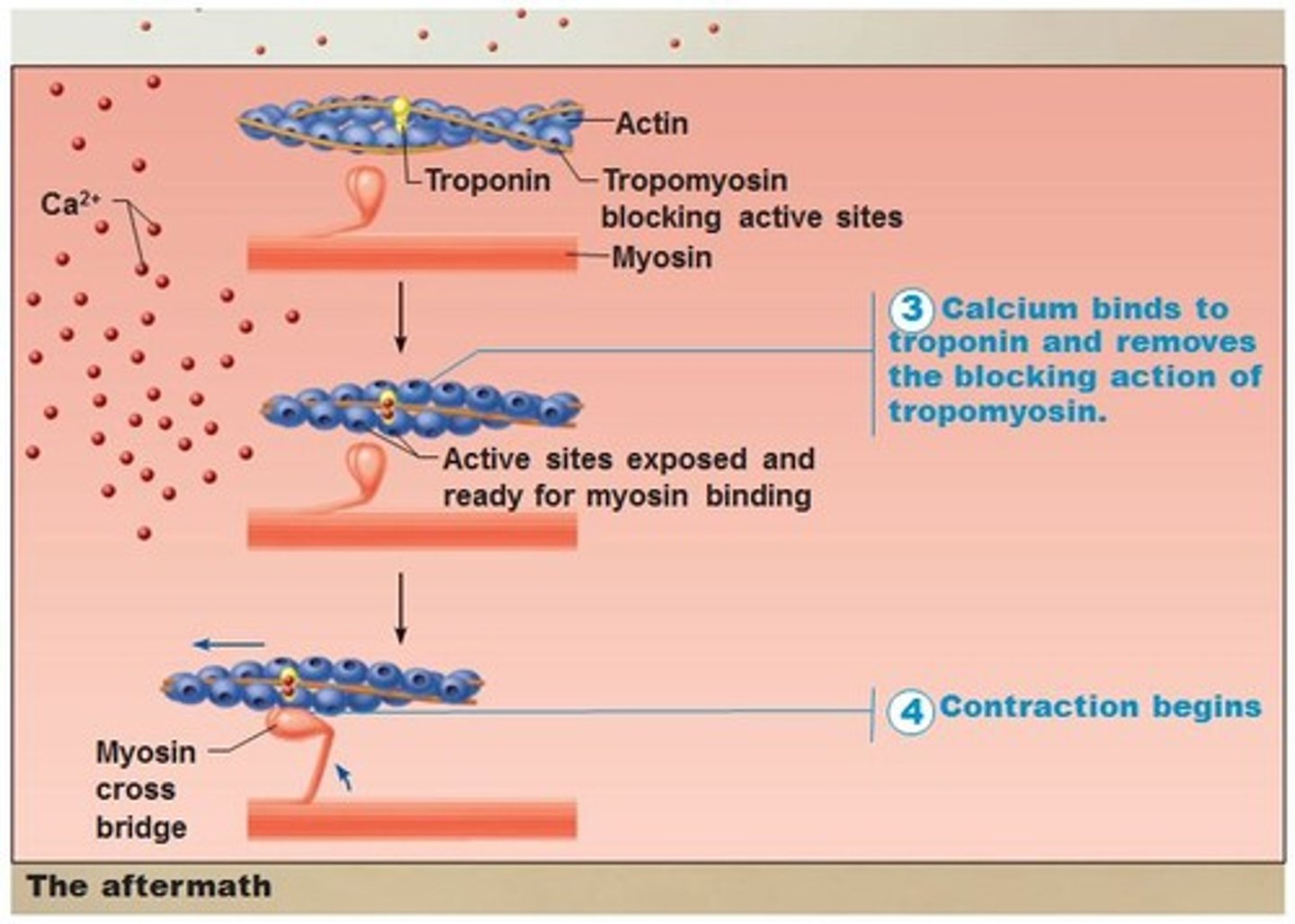
activation sequence step 2: Actin and Myosin Cross-Bridge Formation
On actin, the binding sites for the myosin heads are covered by a blocking complex (troponin and tropomyosin)
Calcium ions bind to troponin and reconfigure the complex, exposing the binding sites for the myosin heads
The myosin heads then form a cross-bridge with the actin filaments
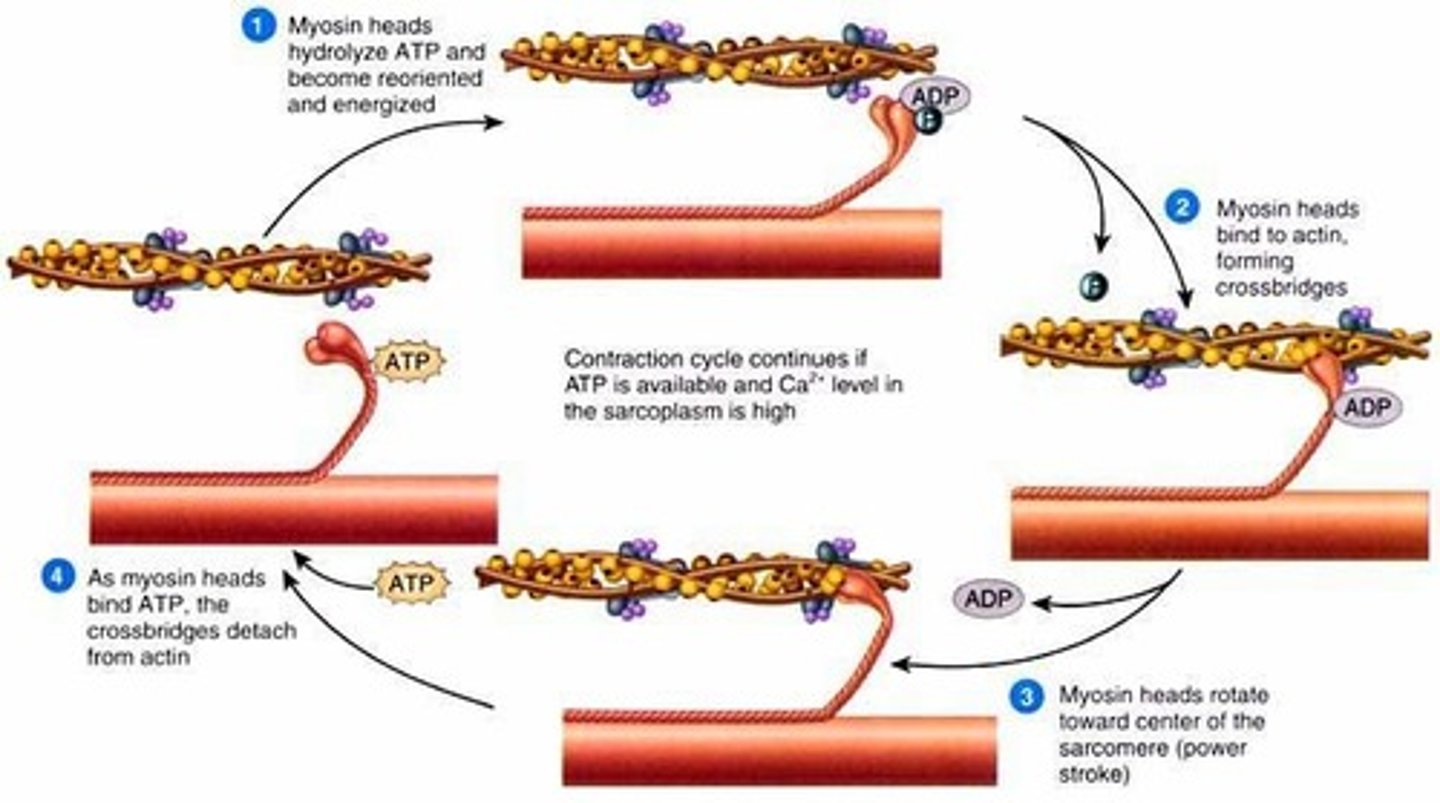
activation sequence step 3: Sliding Mechanism of Actin and Myosin
ATP binds to the myosin head, breaking the cross-bridge between actin and myosin
ATP hydrolysis causes the myosin heads to change position and swivel, moving them towards the next actin binding site
The myosin heads bind to the new actin sites and return to their original conformation
This reorientation drags the actin along the myosin in a sliding mechanism
The myosin heads move the actin filaments in a similar fashion to the way in which an oar propels a row boat
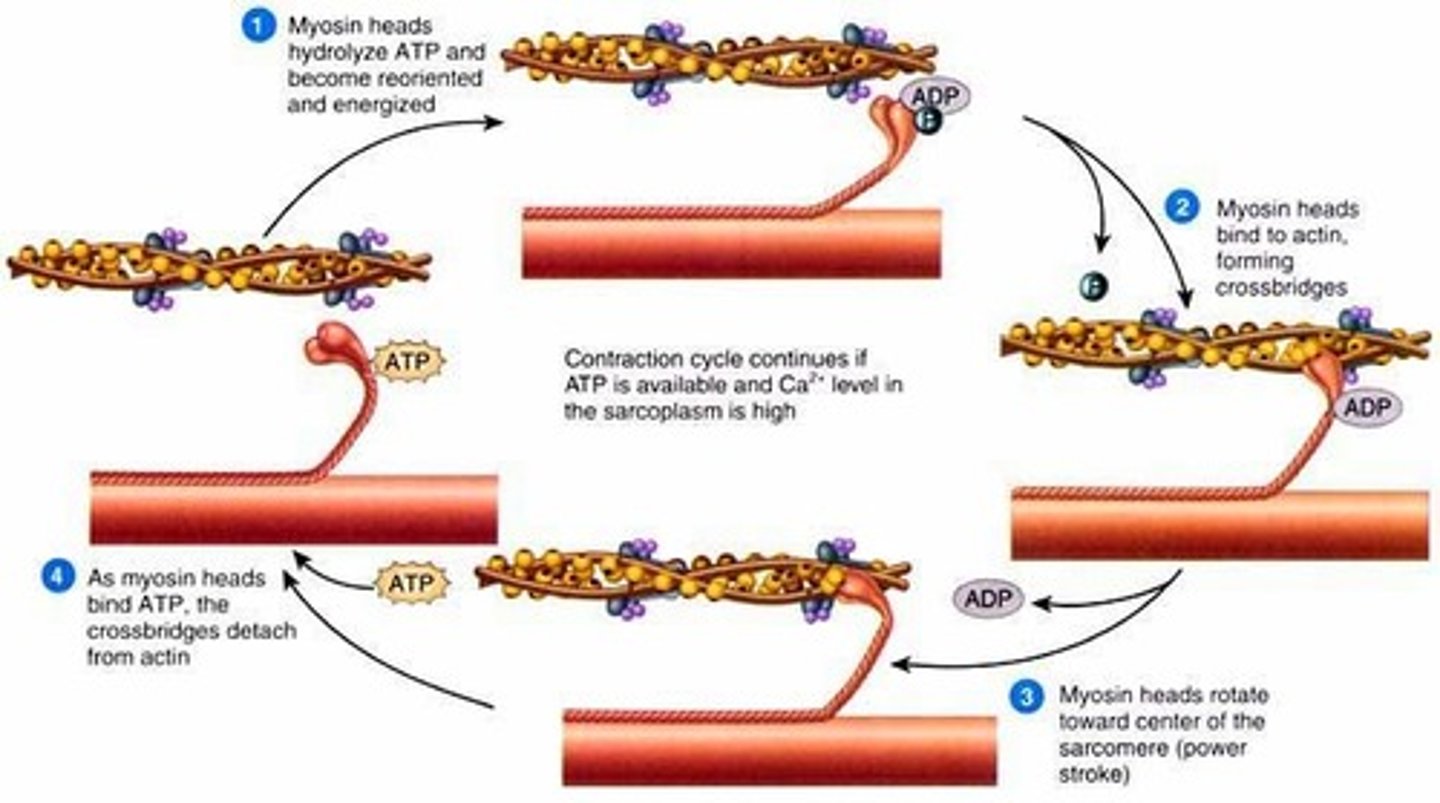
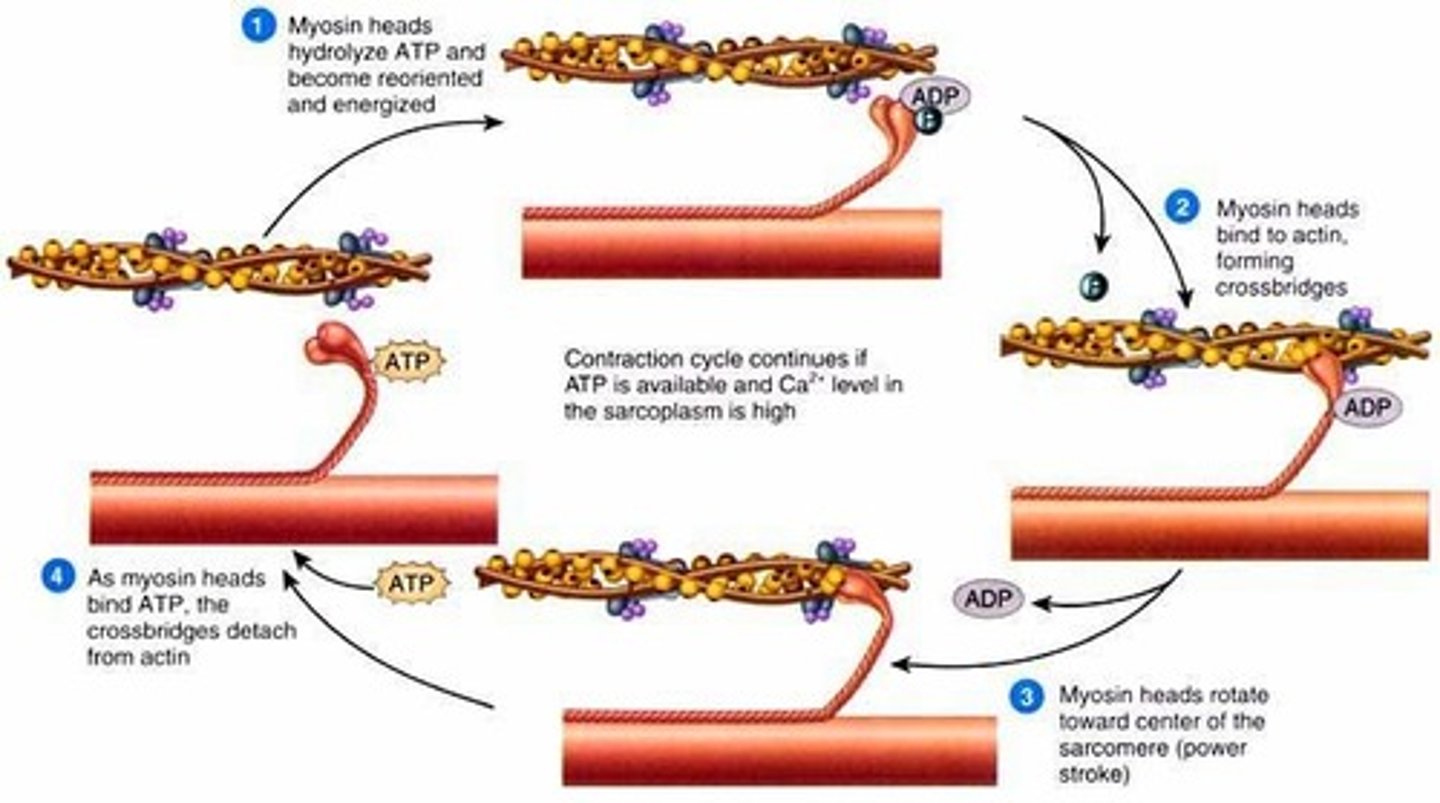
activation sequence step 4: Sarcomere Shortening
The repeated reorientation of the myosin heads drags the actin filaments along the length of the myosin
As actin filaments are anchored to Z lines, the dragging of actin pulls the Z lines closer together, shortening the sarcomere
As the individual sarcomeres become shorter in length, the muscle fibres as a whole contracts
excitation-contraction coupling
events that link the action potentials on the sarcolemma to activation of the myofilaments, thereby preparing them to contract
cross bridge cycle
repeated sequential interactions between myosin and actin filaments at cross-bridges that cause a muscle fiber to contract
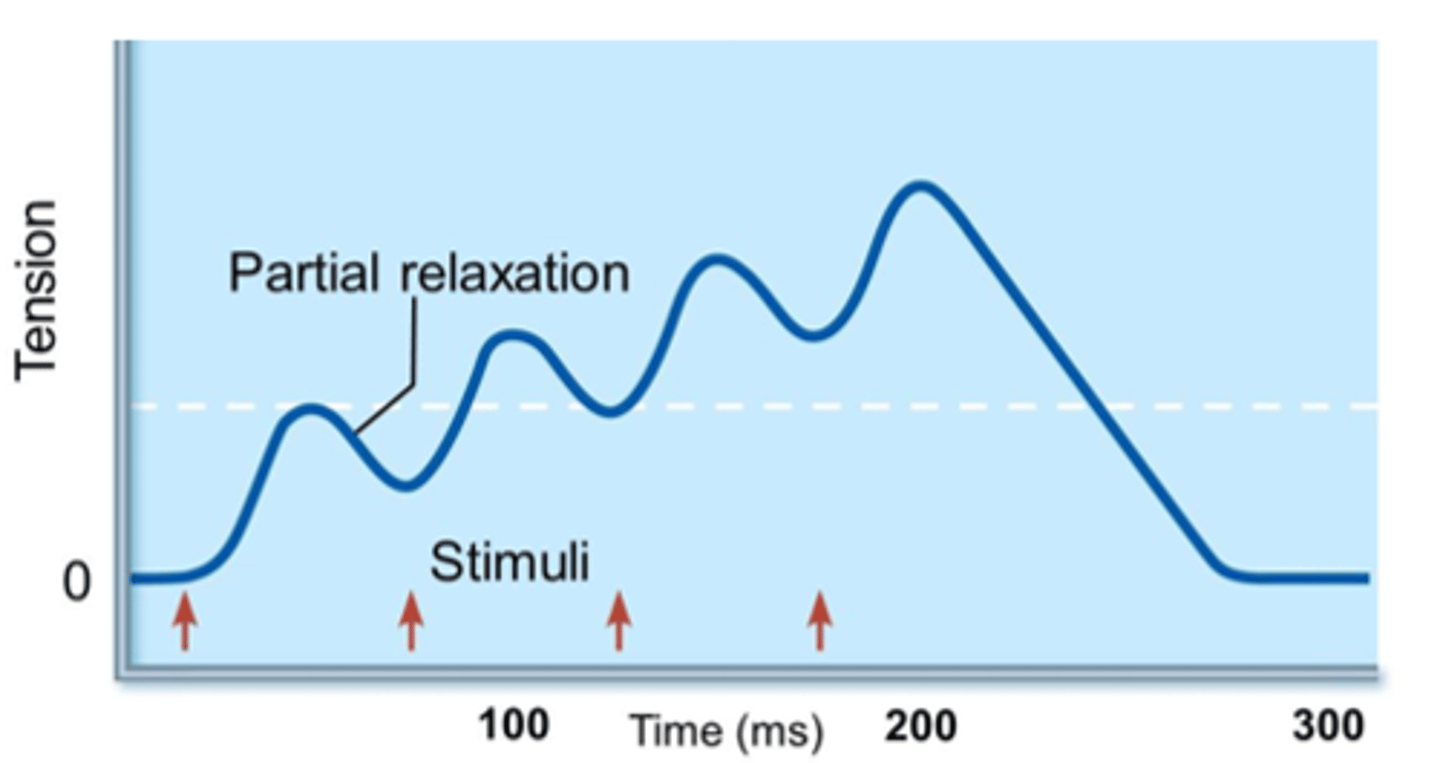
Wave summation (temporal summation)
If stimulus frequency set at about 20 per second
Relaxation is not completed between twitches
Contractile forces add up to produce higher tensions
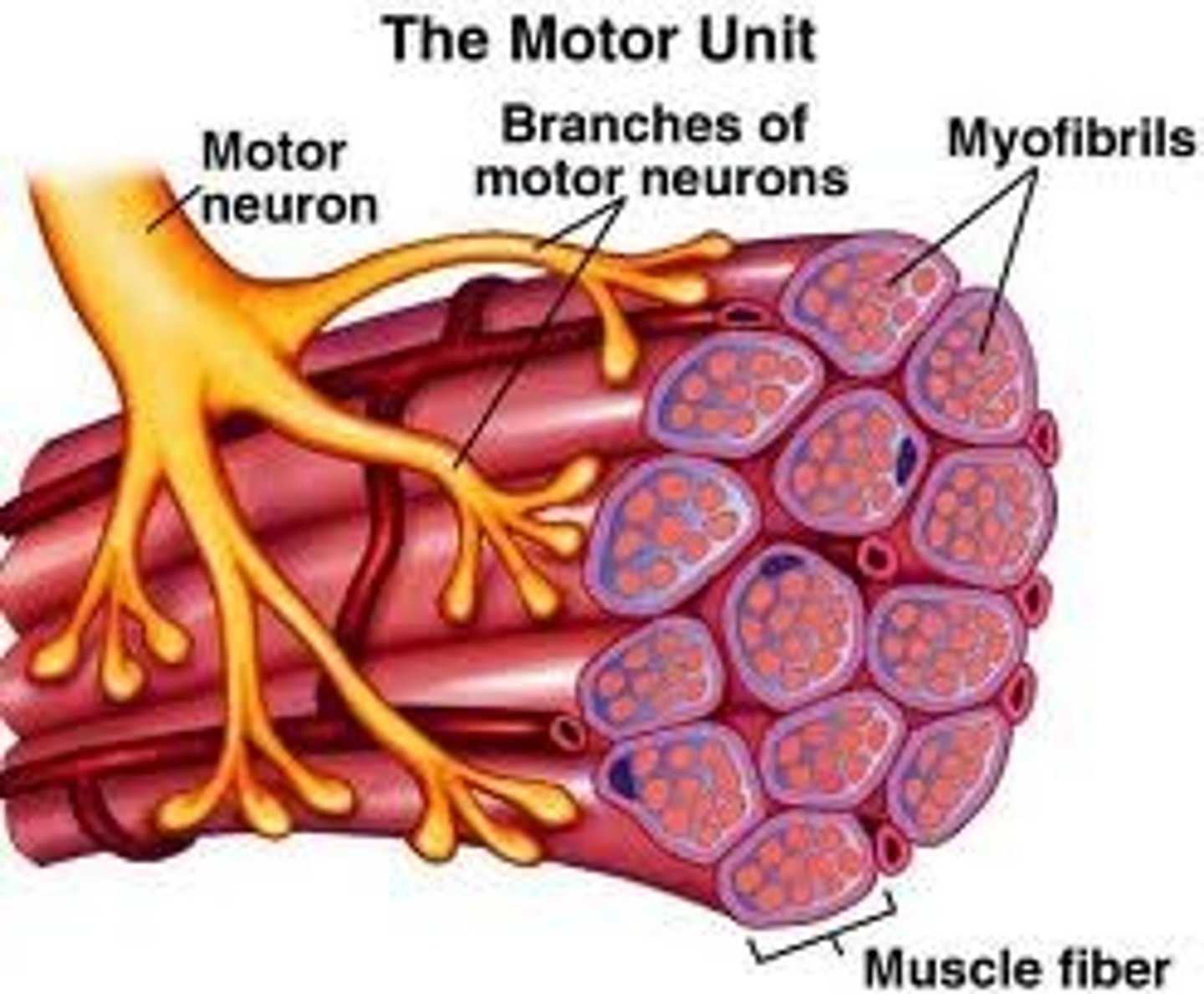
motor unit
motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
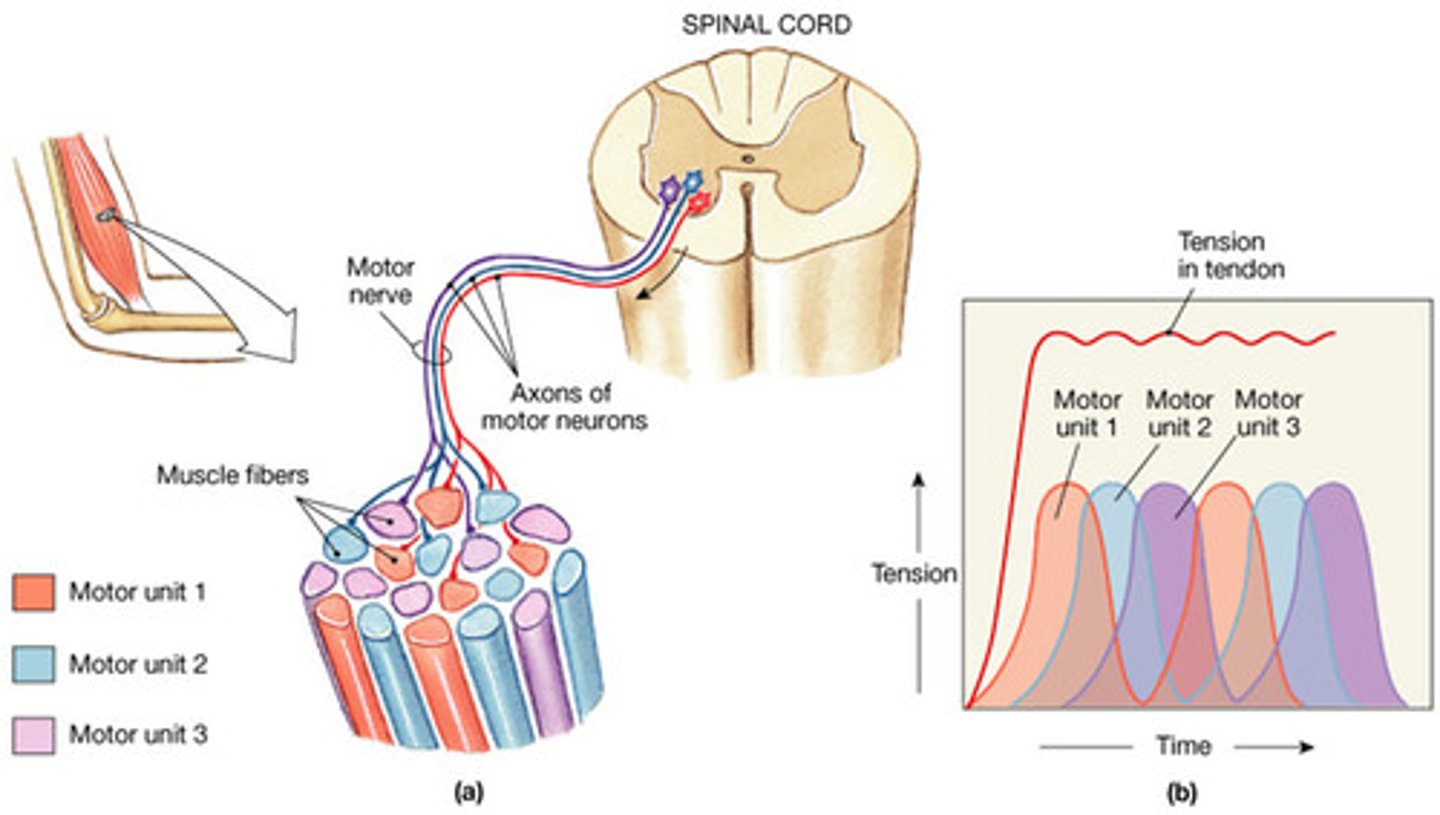
recruitment
increase the number of motor units that stimulate a muscle
threshold stimulus
membrane potential required to open voltage-gated channels
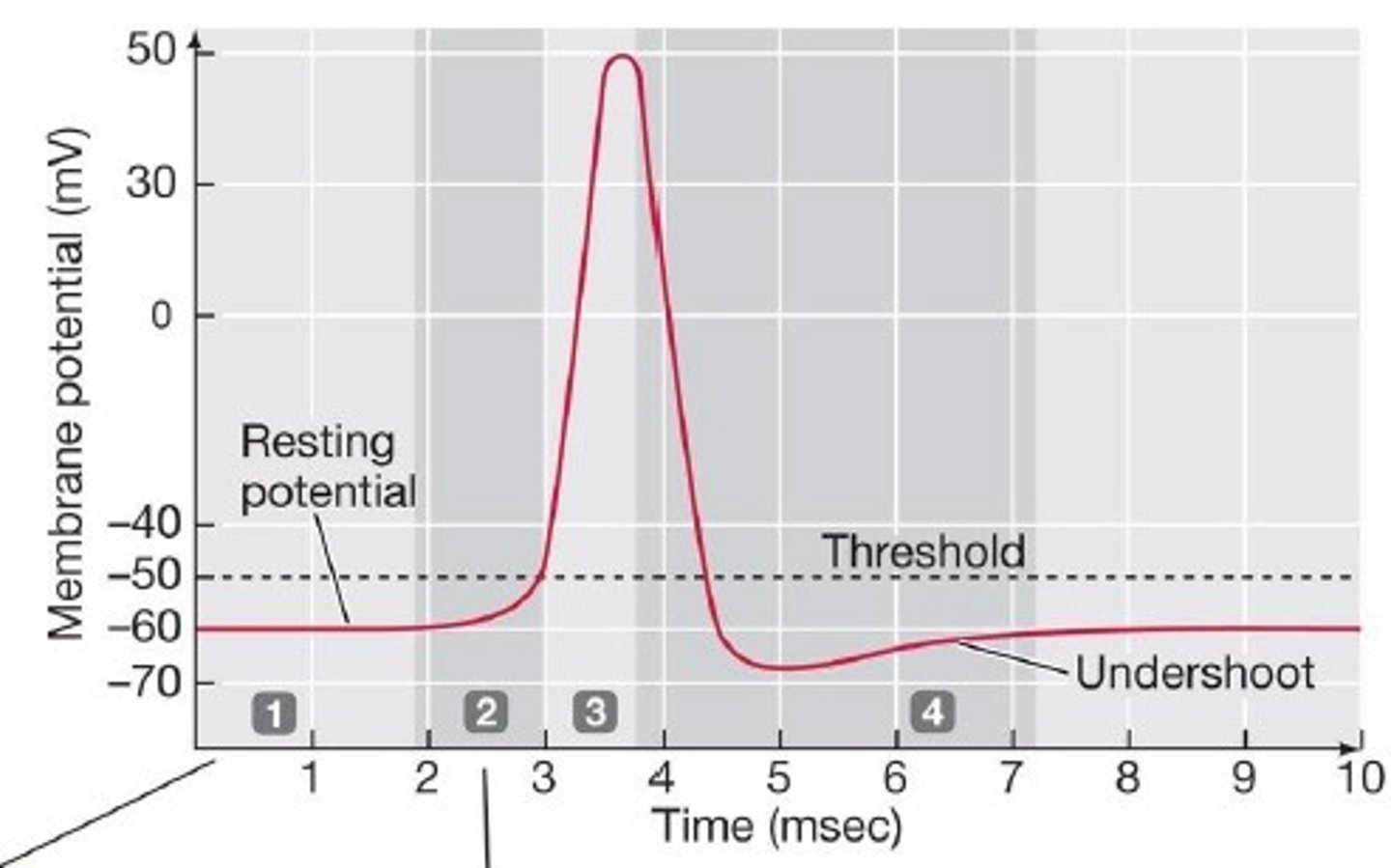
maximal stimulus
strongest stimulus to increase muscle tension (a stronger one will not result in further increase in tension; maximum frequency of neural stimulation or maximal recruitment)
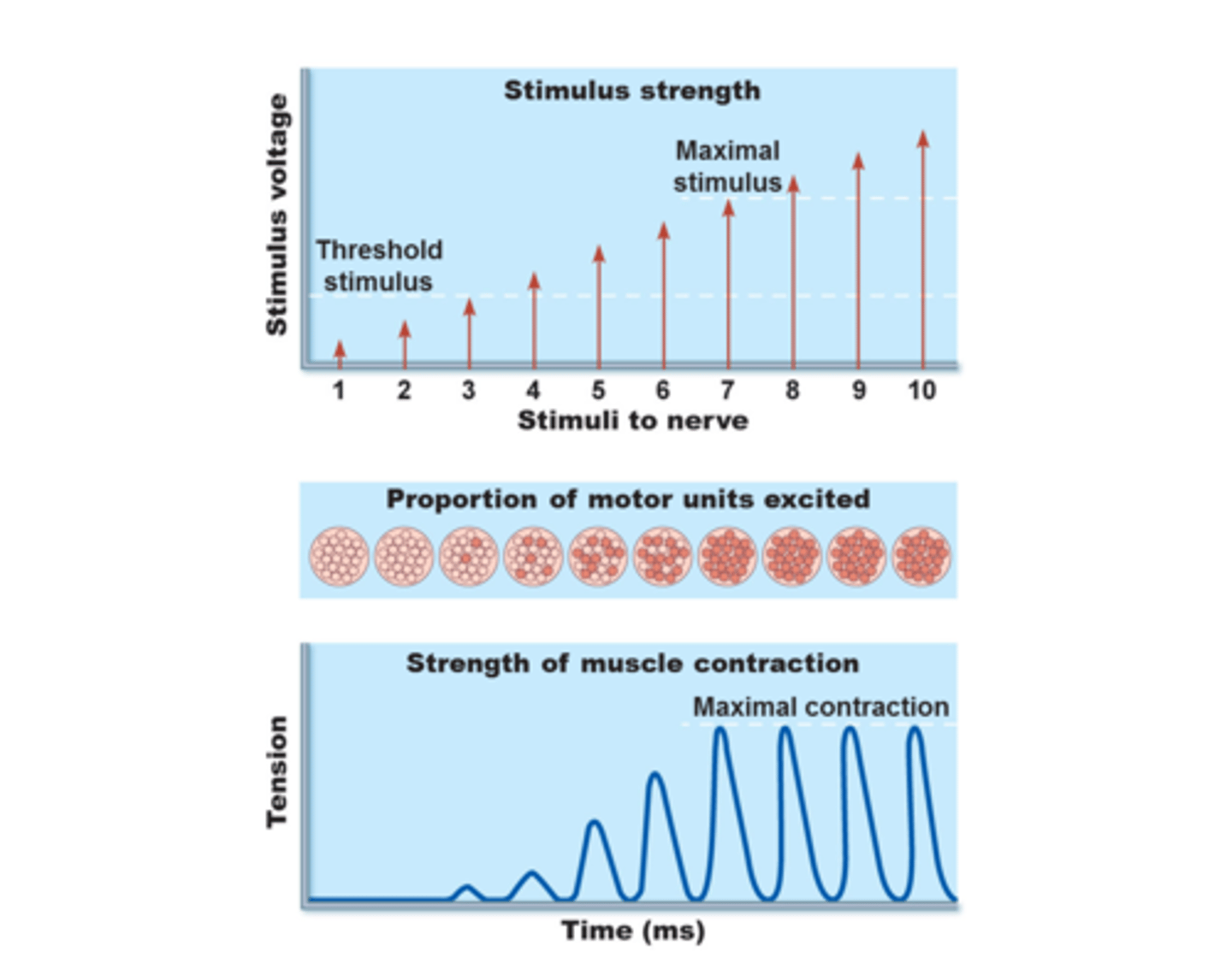
factors that affect force of muscle contraction (tension):
Stimulation frequency (# of action potentials produced by each motor unit)
Stimulus strength (# of motor units stimulated): recruitment
Length-tension relationship
Muscle mass

skeletal muscle functions:
produce movement, maintain posture, supporting and protecting soft tissue, controlling entrances of digestive and unrinary system, producing heat, reservoir for amino acids
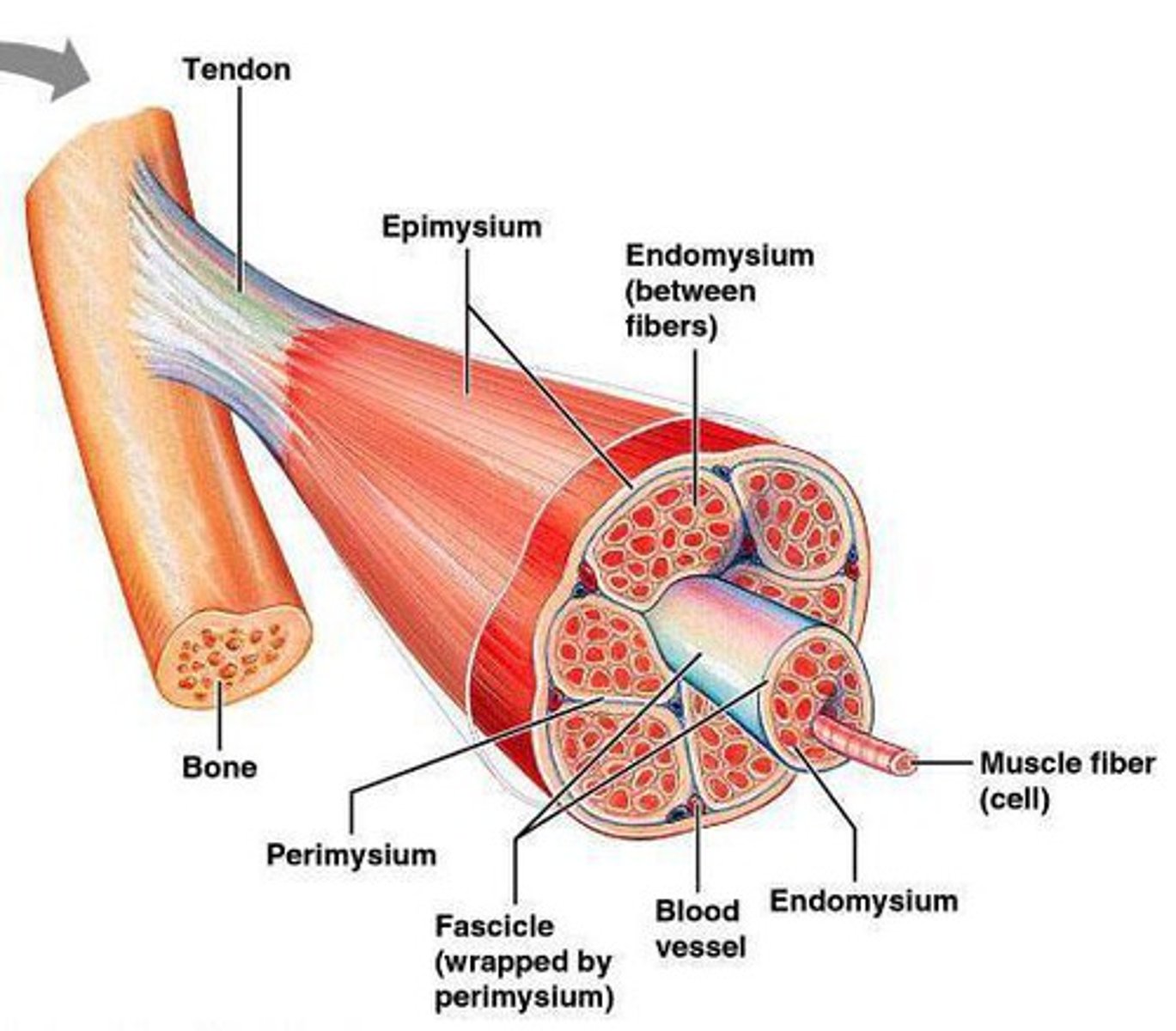
tendon
rope like bundle of dense regular connective tissue, attaches muscle to bone, if a tendon is a broad sheet it is called an aponeurosis