Lecture 2: Pressure-flow relationships
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Basic Principles of Circulatory Function
Under normal conditions, blood flow to most tissues is controlled according to tissue needs
Cardiac output (= heart rate x stroke volume) is the sum of all the local tissue blood flows
Arterial pressure is tightly regulated across wide changes in cardiac output and local tissue blood flows
Flow
The movement of substances or heat from one point to another, driven by energy gradients between those two points
Molecules
Concentration energy gradient
Heat
Temperature energy gradient
Gases
Partial Pressure gradient
Fluids
Hydrostatic pressure gradient
Ions
Concentration and voltage gradient
What is blood pressure?
pressure if a force
Blood pressure is a force exerted by the blood against the vessel all
Increased pressure pushing against vessel containing blood, that energy drives flow of blood
Blood flow
The blood pressure difference between two points in the circulation (P1-P2), and the resistance (based on Ohm’s law)
Blood flow equation
F = ∆P/R
Conductance equation
1/Resistance
Cardiac output (CO)
The total blood flow through the aorta.
∆P
The difference in mean blood pressure between the aorta and the right atrium
Total peripheral resistance (TPR)
The resistance of the entire systemic circulation
Laminar flow
Blood usually flows smoothly in ‘streamlines’ through vessels, with relatively little mixing in a radial direction
Turbulent flow
Blood flow can become disorderly, whirling in a radial (crosswise) direction form what are called ‘eddy currents’.
This usually only occurs in largest vessels, at highest flow rates, or around obstacles
Turbulence increases the resistance to blood flow compared to laminar flow
Poiseuille’s Law
Describes the effect of vessel radius on Flow under laminar conditions
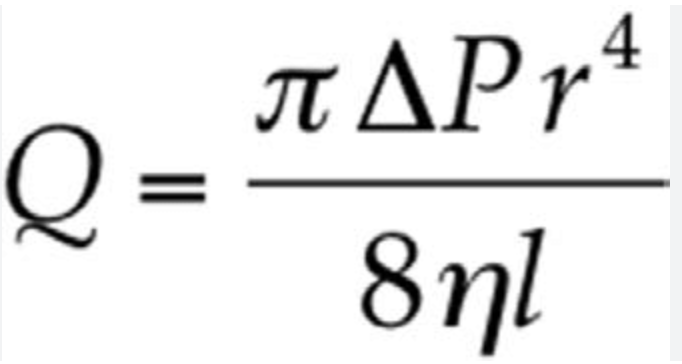
Anemia
Can occur during menstrual cycle, in response to blood loss, etc —> decrease in red blood cells
Polycythemia (excessive erythrocytosis)
Occurs at high elevation, in response to sleep apnea, in pulmonary diseases, etc —> excessive production of red blood cells
Isovolumic hemodilution
Removing blood and replacing it with saline