Chronic inflammation GPPE
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
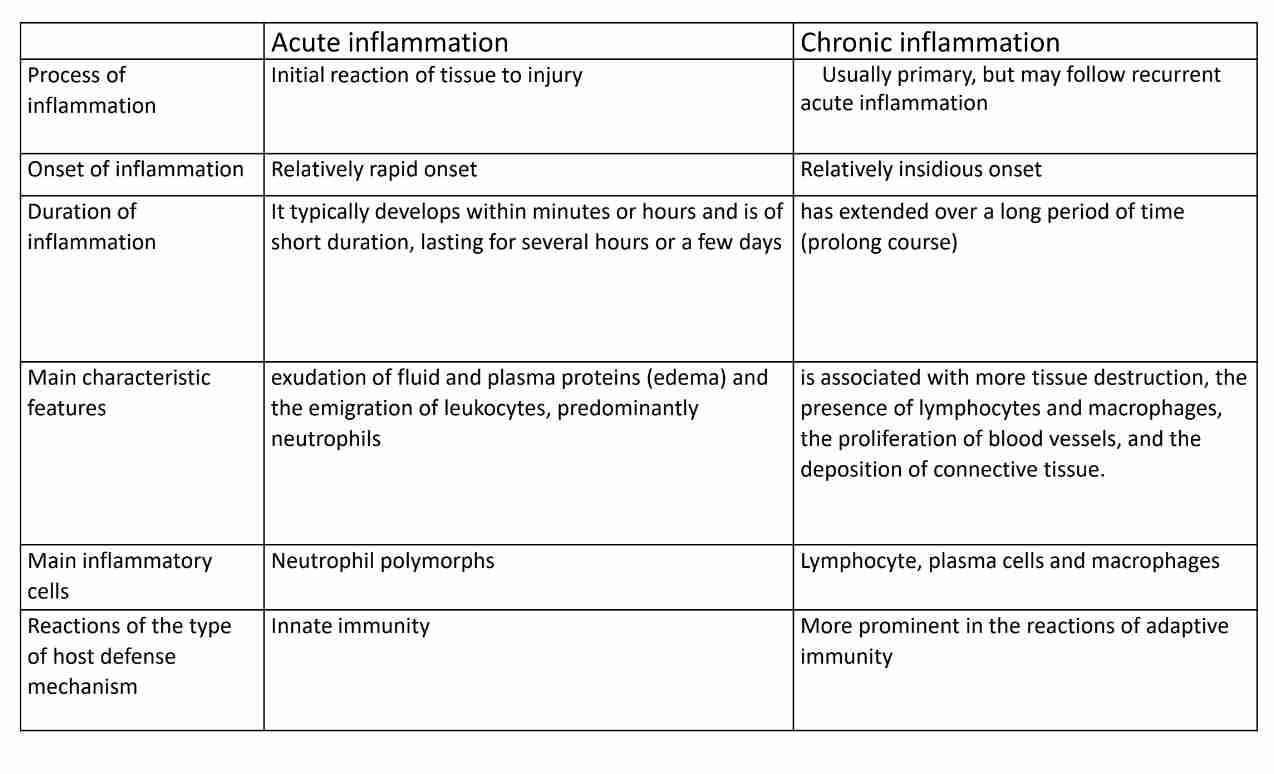
Chronic inflammation
Prolonged duration (weeks/months)
Coexist with repair
Pattern:
Chronic nonspecific inflammation
Granulomatous inflammation
Characteristics (Histological) features
Infiltration with MONONUCLEAR CELLS; macrophages, lymphocytes & plasma cells
Tissue destruction; persistent offending agent/inflammatory cells
Attempt healing by connective tissue replacement of damage tissue by proliferation of small blood vessels (angiogenesis) & fibrosis
Causes of chronic inflammation
Primary chronic inflammation
Inflammatory response has all Histological features of chronic inflammation from onset& no initial phase of acute Inflammation
Progression from acute Inflammation
Acute Inflammation progress to chronic inflammation is supportive type
Osteomyelitis (abscess in bone marrow cavity)
Recurrent episodes of acute inflammation
Recurrent cycle of acute inflammation & healing
Chronic cholecystitis with gall stones
Pattern of chronic inflammation
Chronic nonspecific inflammation
Granulomatous inflammation
Chronic nonspecific inflammation
Characteristics:
Cellular reaction with preponderance of mononuclear cells(macrophages, lymphocytes and plasma cells)
Proliferation of fibroblast & new vessels
Scaring & distortion of tissue
Cytokines derived from monocytes-macrophages active lymphocytes
Lymphocyte activation by macrophage : presented antigen results in formation of antibody by producing plasma cells
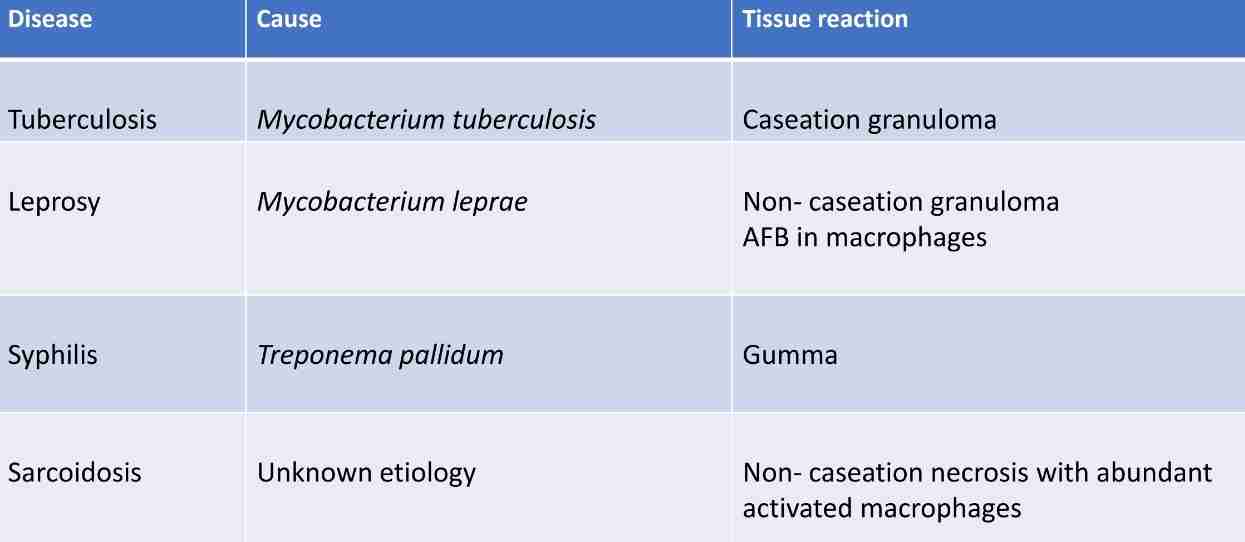
Granulomatous inflammation
Characteristics by granulomas: nodular collection of specialized macrophages (Epithelioid cells) & granulomas are usually surrounded by rim of lymphocytes
Caseous necrosis is often Characteristics (tuberculosis), resulting from killing of mycobacteria-laden macrophages by T lymphocytes & possibly by cytokines/sensitive macrophages
Langhans giant cell: has nuclei arranged in horse-shaped pattern
Tuberculosis
Conclusion