Chapter 3: Macromolecules
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all material covered in lectures as of 8/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are the six most common elements in biological molecules?
C, H, N, O, P, S
which type of bond involves electrons transferred to one atom forming cations and anions?
ionic
which type of bond involves equal sharing of electrons?
non-polar covalent
which type of bond involves unequal sharing of electrons?
polar covalent
Which bond involves electrostatic attraction between H and N/O
Hydrogen bond
Strength of hydrogen bonds is ___. Compared to other bonds, hydrogen bonds are the (strongest/weakest).
additive, weakest
What are amphipathic molecules?
molecules that have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties.
What are functional groups?
small reactive groups of atoms that give larger molecules specific chemical properties
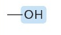
Which functional group?
Hydroxyl
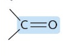
Which functional group?
Carbonyl
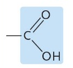
Which functional group?
carboxyl
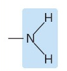
Which functional group?
Amino
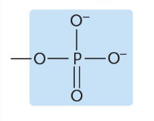
Which functional group?
Phosphate
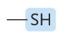
Which functional group?
sulfhydryl
Carbons that are linked to four different atoms or functional groups are asymmetric. They can take one of two positions, known as
isomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other
stereoisomers
isomers that have the same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms
structural isomers
process that forms monomers through the addition of water
hydrolysis
process that forms a polymer and produces water
dehydration synthesis
which major biological molecule is not considered a macromolecule?
lipids
carbs stored in plant cells as ___ and in animal cells as ___
starch, glycogen
general ratio of 1C:2H:1O
carbohydrates
what is the monomer for carbohydrates?
saccharide
What is the bond between monomers called in a disaccharide?
glycosidic bond
describe the three types of lipids
Neutral lipids - stored and used as an energy source (two types - oils and fats)
phospholipids - form cell membranes
steroids - serve as hormones that regulate cellular activities
What is a fatty acid?
contains a single hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end
triglycerides form by ___ between three-carbon glycerol (an ___) and three fatty acid side chains
dehydration synthesis, alcohol
what bond forms between a fatty acid and the glycerol to form a triglyceride? Where does it form?
An ester linkage, between the -COOH of the fatty acid and the -OH of the glycerol.
as chain length increases, fatty acids
become less water-soluble and more oily.
What is a monounsaturated fatty acid? What is a polyunsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with one double bond. a polyunsaturated acid has more than one double bond.
functions of triglycerides
energy reserves in animals, fatty tissue for mammals and birds, and waterproofing bird feathers
In a phospholipid, which end is polar and hydrophilic?
the end with the phosphate group
Steroids (structure)
based on a framework of four carbon rings
What is the most common type of steroid? Describe its structure.
Sterols. They have a single polar OH group linked to one end of the ring framework, and a complex nonpolar hydrocarbon chain at the other end
What type of molecule is cholesterol?
A sterol
How do sex hormones differ in structure?
Varying functional groups
What are the predominant molecules in cells?
Proteins
What is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
What are protein polymers called?
peptides/polypeptides/proteins
Describe the basic structure of an amino acid.
A central carbon attached to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen and a variable R group.
Do amino acids act as acids or bases?
They can act as either.
Primary structure of proteins
The unique sequence of amino acids forming a polypeptide
Secondary structure of proteins
twists and turns of the amino acid chain
Tertiary structure
folding of the amino acid chain into an overall 3D shape
Quaternary structure of proteins
formed from more than one polypeptide chain
alpha helix
twisted into a regular right-hand spiral
beta strand
zigzags in a flat plane, forming a sheet
What is denaturation?
Unfolding a protein from its active conformation
Chaperonins
guide proteins that bind temporarily with new proteins to direct their conformation toward the correct tertiary structure
What are functional domains?
subdivisions
monomer for nucleic acids
nucleotides
parts of a nucleotide
A nitrogenous base (formed from rinds of carbon and nitrogen atoms), a five carbon ring shaped sugar, and one to three phosphate groups
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
pyrimidines and purines
Pyrimidine structure, examples
one carbon-nitrogen ring. U, T, C
Purines structure, examples
two carbon-nitrogen rings. A, G
How do DNA nucleotides and RNA nucleotides differ?
DNA contains a deoxyribose sugar. DNA nitrogenous bases are A, T, G, C
RNA contains a ribose sugar. RNA nitrogenous bases are A, U, G, C
What bonds are between two nucleotides?
a phosphodiester bond
One nucleotide is linked to the next by a bridging phosphate group between the ___ carbon of one sugar and the ___ carbon of the next
5’, 3’
What are the sides of the ladder in a DNA molecule? What are the rungs of the ladder?
The sides of the ladder are the sugar-phosphate backbones. The rungs are nitrogenous bases
DNA base pairs
Adenine-Thymine, Guanine-Cytosine
ATP structure
adenine, ribose, three phosphates
ATP is formed by ___ and broken by ___
dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis