BIOCH200 Biomolecules
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the four monomers?
amino acids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, lipids
What are the three polymers?
proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids
What are 3 examples of supra molecular assemblies?
ribosomes, chromatin, membranes
What is a monomer?
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
What are the defining characteristics of an amino acid structurally?
contains carboxylic acid group and amino group

What are the defining characteristics of a nucleotide structurally?
1-3 phosphates, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
What is a common characteristic between all lipids, because they lack structural similarity sometimes?
they don't like water
What is the ratio of carbon atoms to water molecules within a carbohydrate?
1:1
In solution, what form a carbohydrates usually found in?
ring structure
How many hydroxyl groups are there, relative to carbon atoms, in a carbohydrate?
carbons atoms - 1
What are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones?
an aldehyde or ketone with multiple hydroxyl groups attached
What functional groups do all linear carbohydrates contain?
carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone), hydroxyl
What does red represent?
oxygen
What does grey/black represent?
carbon
What does white represent?
hydrogen
What does blue represent?
nitrogen
What does yellow represent?
sulfur
What does orange represent?
phosphorus
What molecules contain sulphur?
amino acids
What molecules contain phosphorus?
nucleic acids
What is the structure of an alcohol?
R-OH
What is the structure of an aldehyde?
R-C=O-H
What is the structure of a ketone?
R-C=O-R
What is the structure of a carboxylic acid?
R-C=O-OH
What is the structure of a thiol?
R-SH
What is the structure of a primary amine?
RNH2
What is the structure of a secondary amine?
R-NH-R
What is the structure of a tertiary amine?
N bonded to 3 Rs
What is the structure of a hydroxyl group?
-OH
What is the structure of a carbonyl group?
C=O
What is the structure of a carboxylate group?
C=O-O
What is the structure of a sulfhydryl group?
-SH
What is the structure of an amino group?
NH2 or NH3+
What is the structure of a phosphate group?
PO4
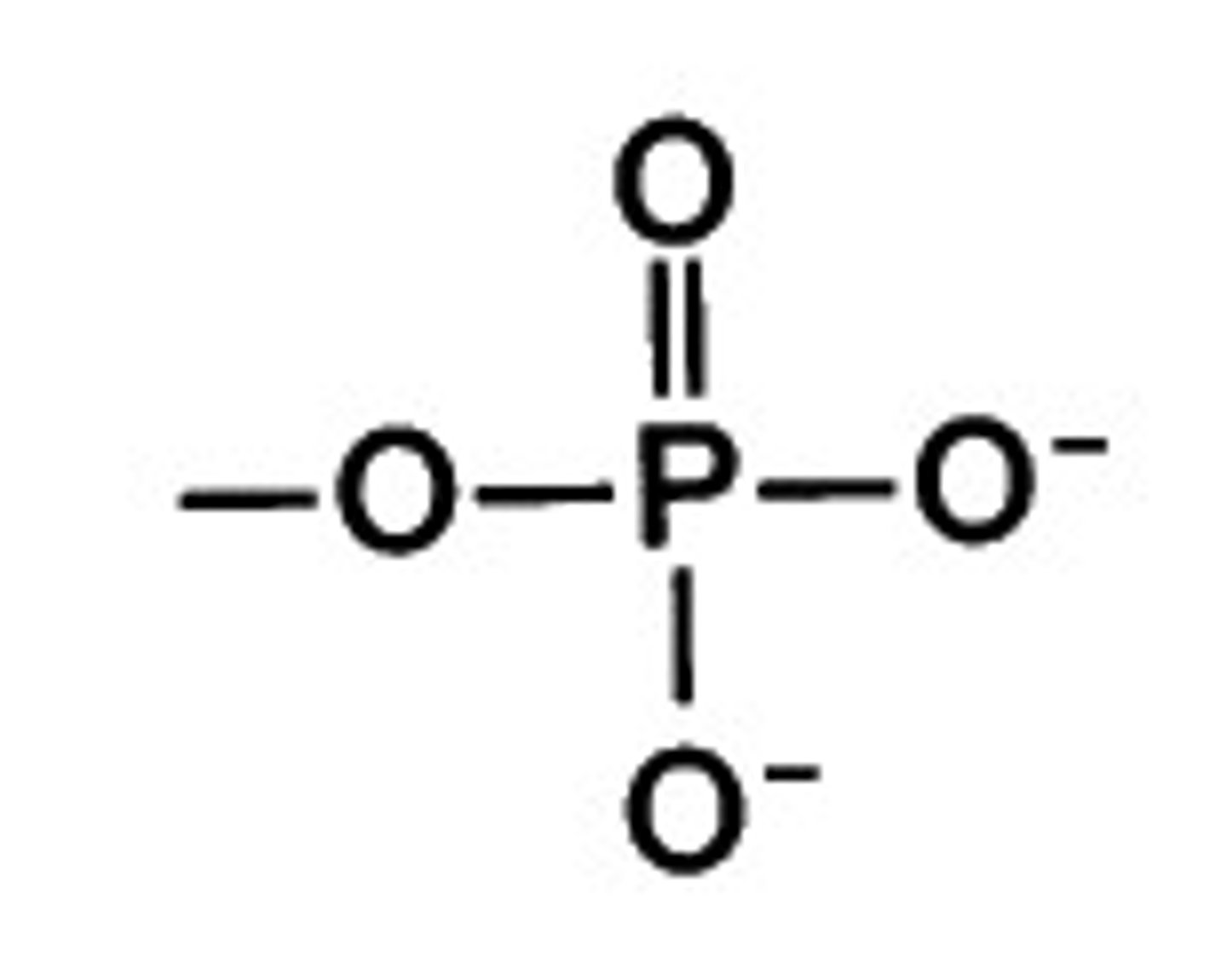
What is the structure of a phosphoryl group?
PO3
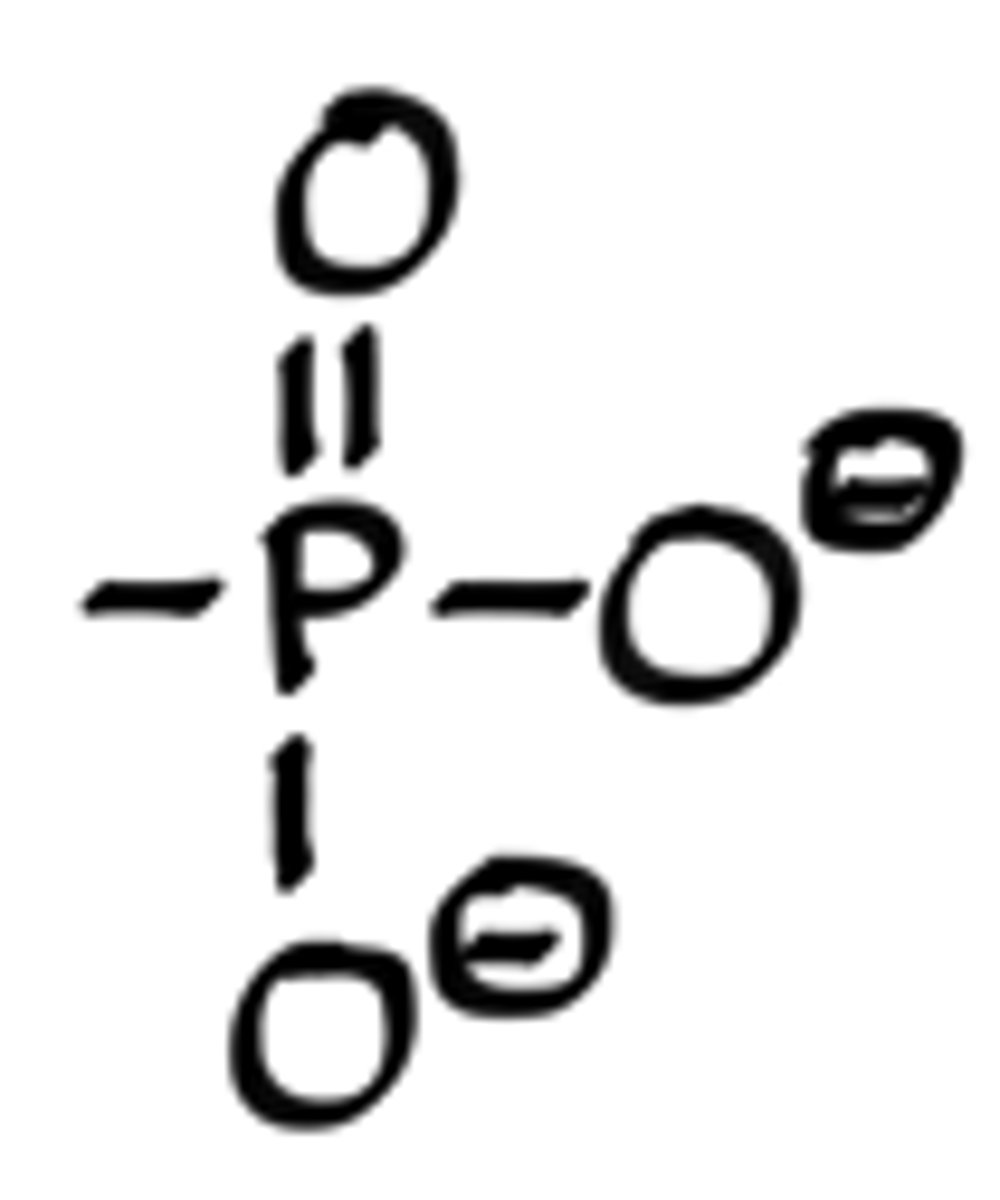
What is the structure of an ester?
-C-O-(C=O)-
What is the structure of an ether?
R-O-R
What is the structure of an amide?
-N-(C=O)-
What is an ester linkage?
-C-O-(C=O)-
What is an ether linkage?
-C-O-C-
What is an amide linkage?
-N-(C=O)-
What is a phosphate ester linkage?
-C-O-(P=O)-O-O
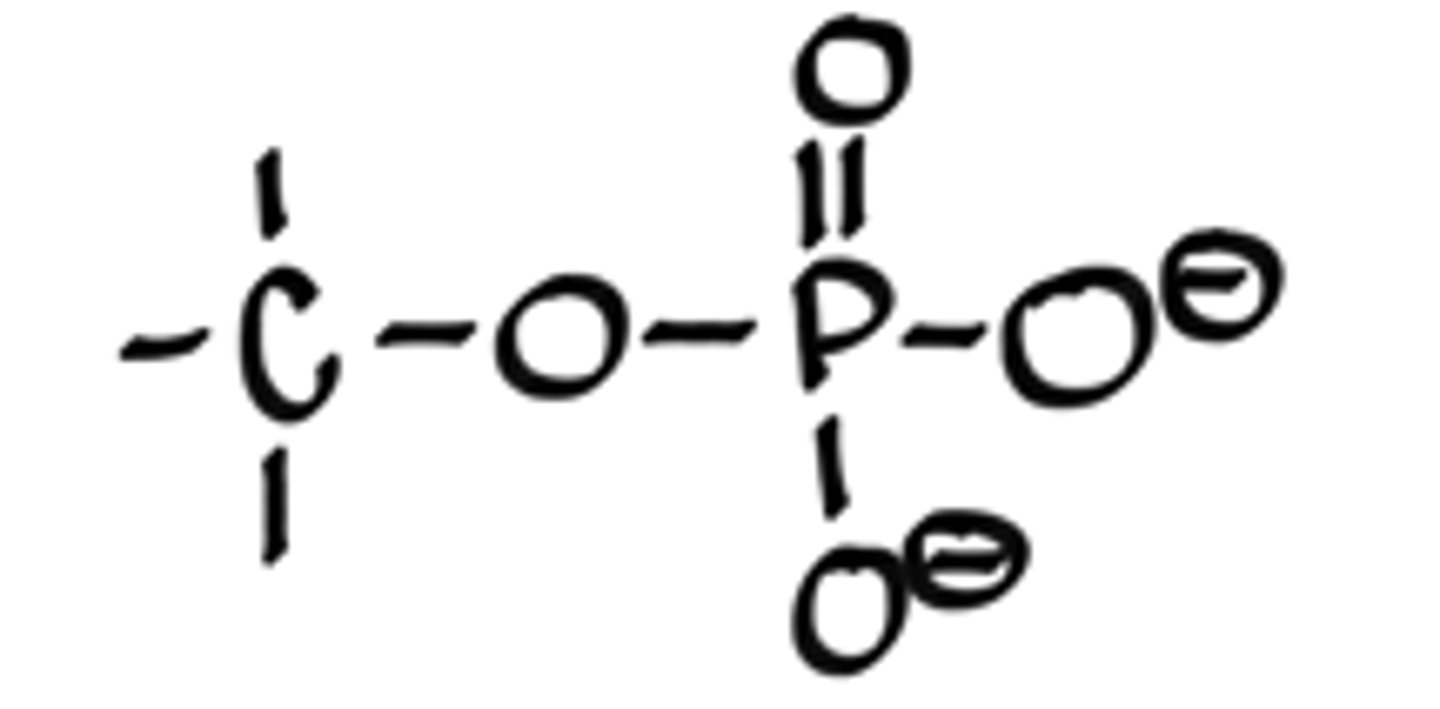
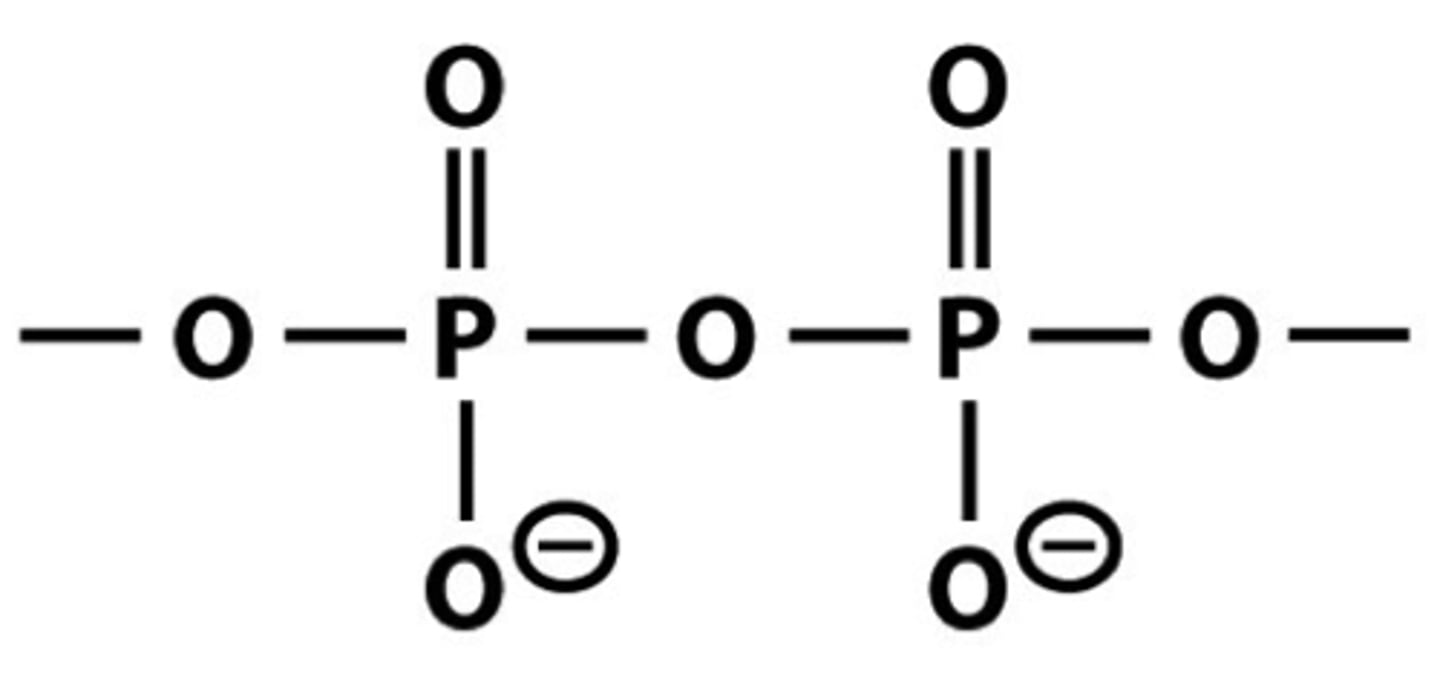
What is a phosphoanhydride linkage?
POP
What is the structure of a thioester?
R-(C=O)-SR
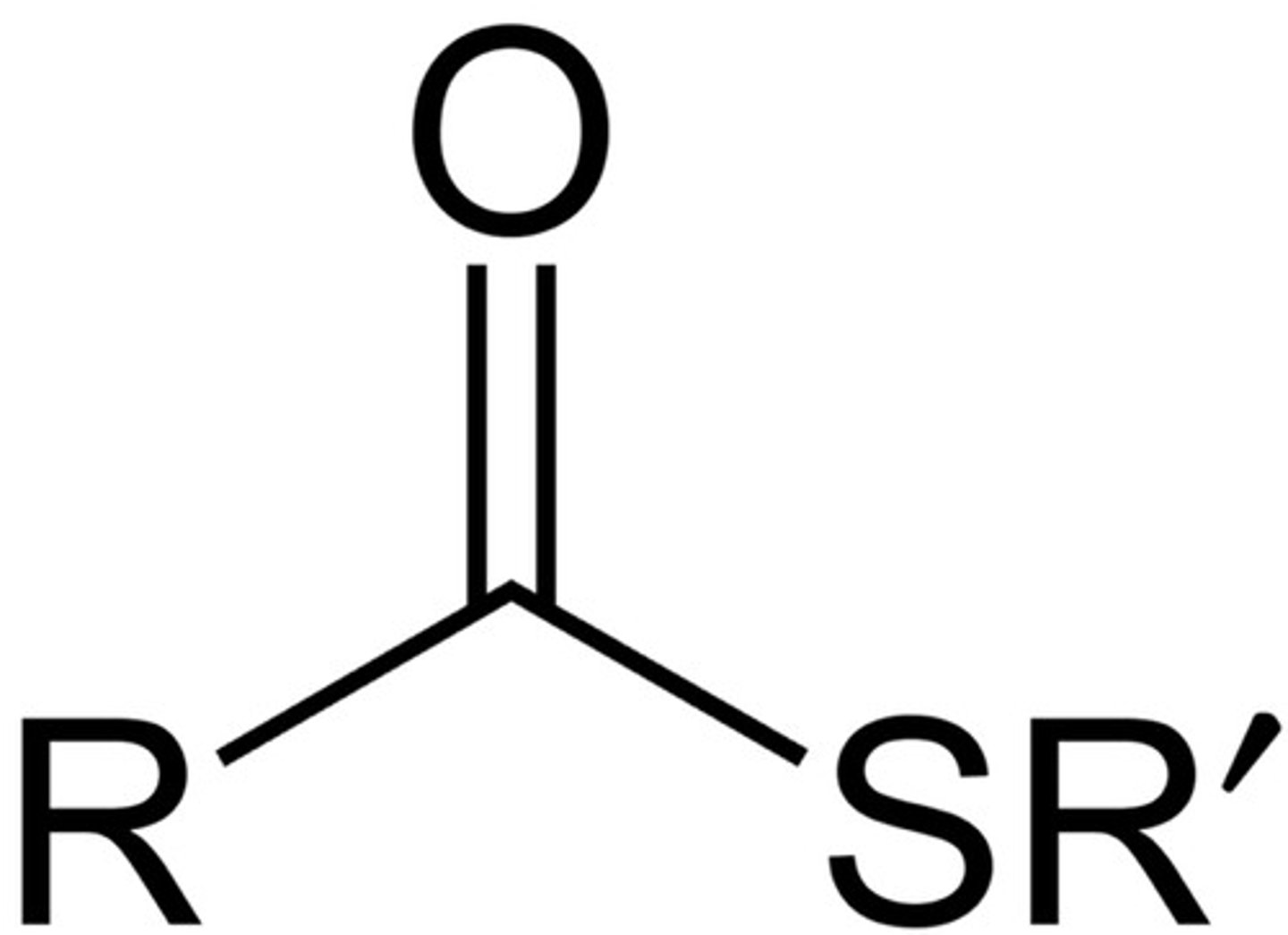
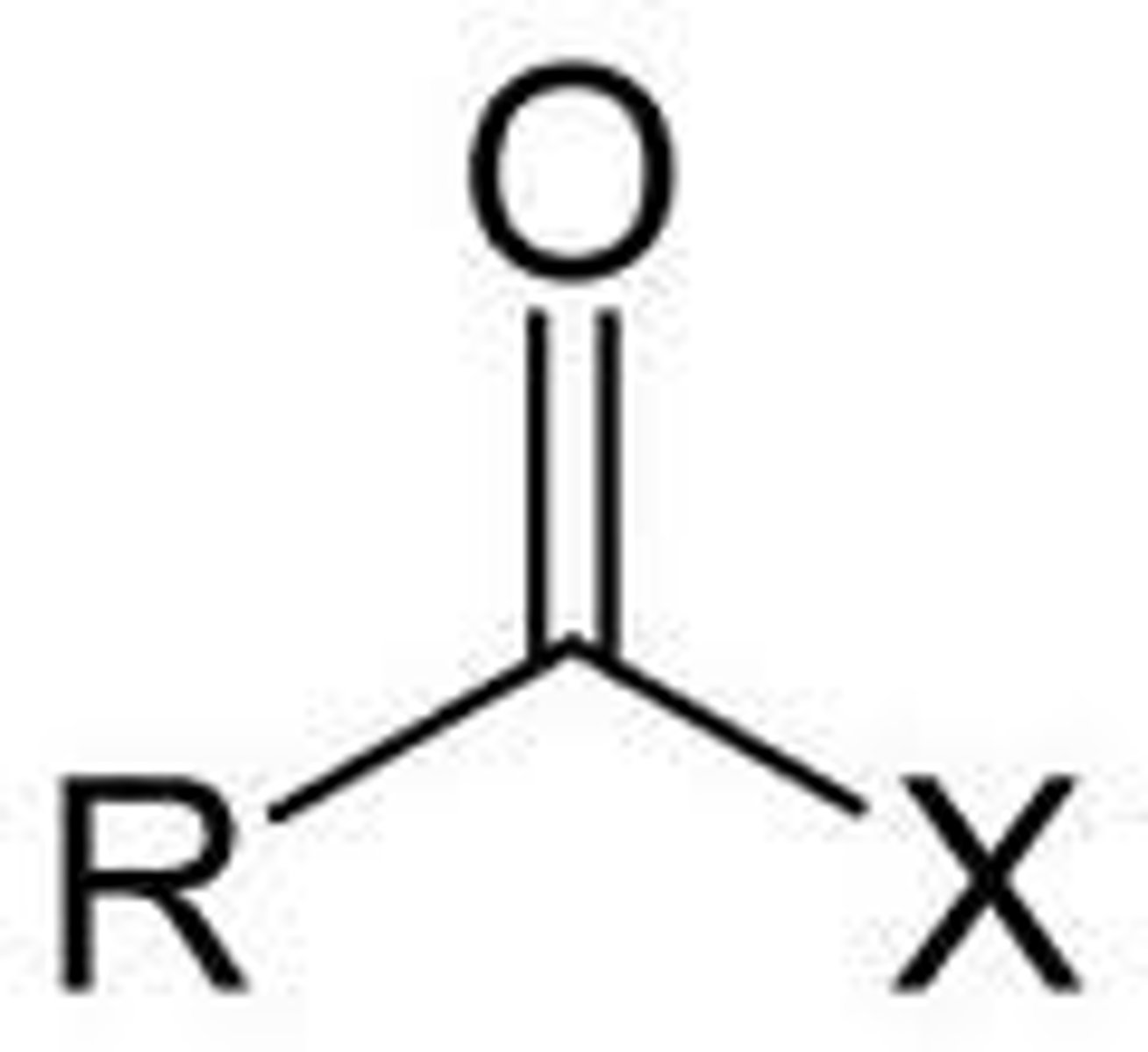
How is an acyl group formed?
removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from a carboxylic acid
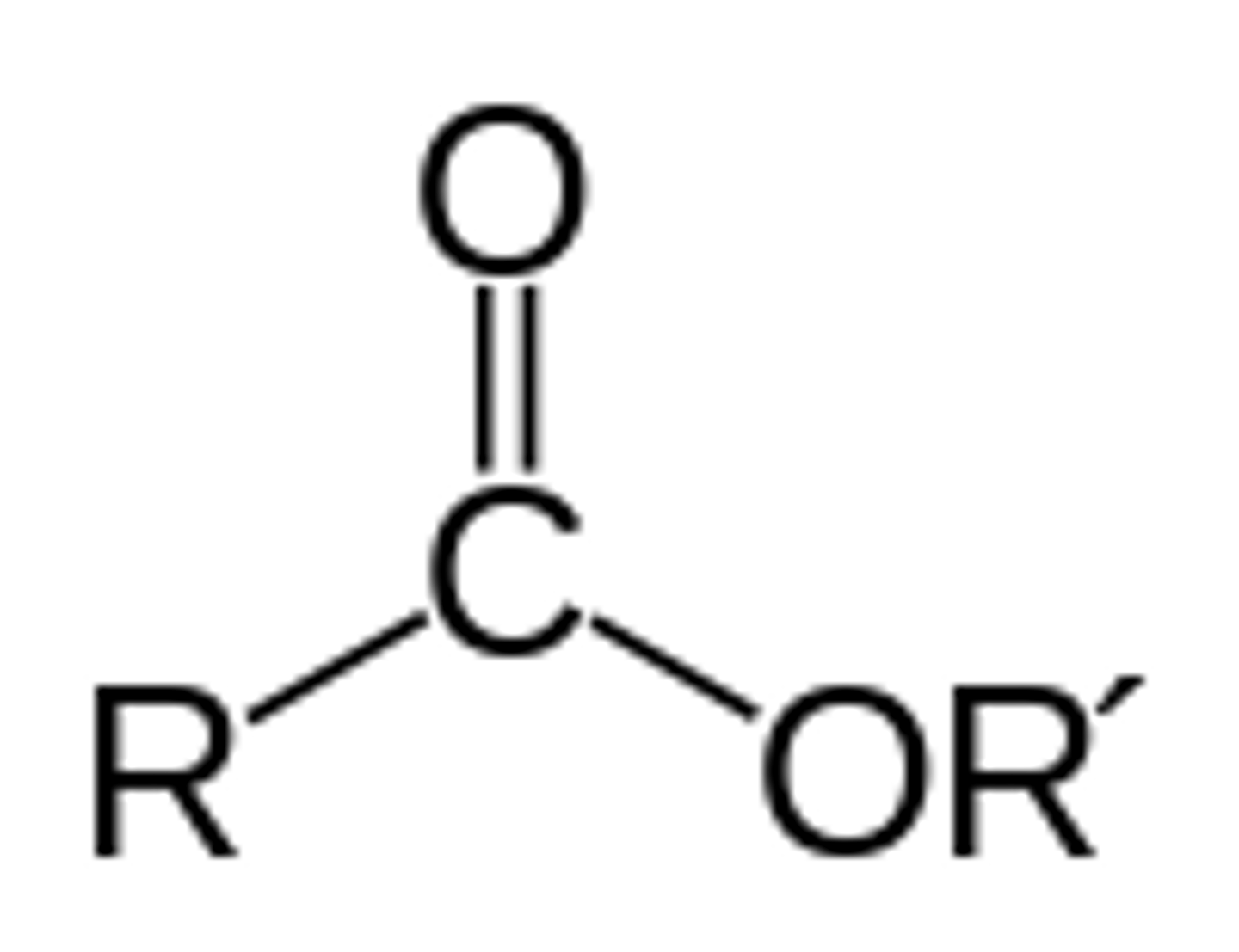
How is an ester linkage formed?
dehydration reaction that links a carboxyl group and hydroxyl group
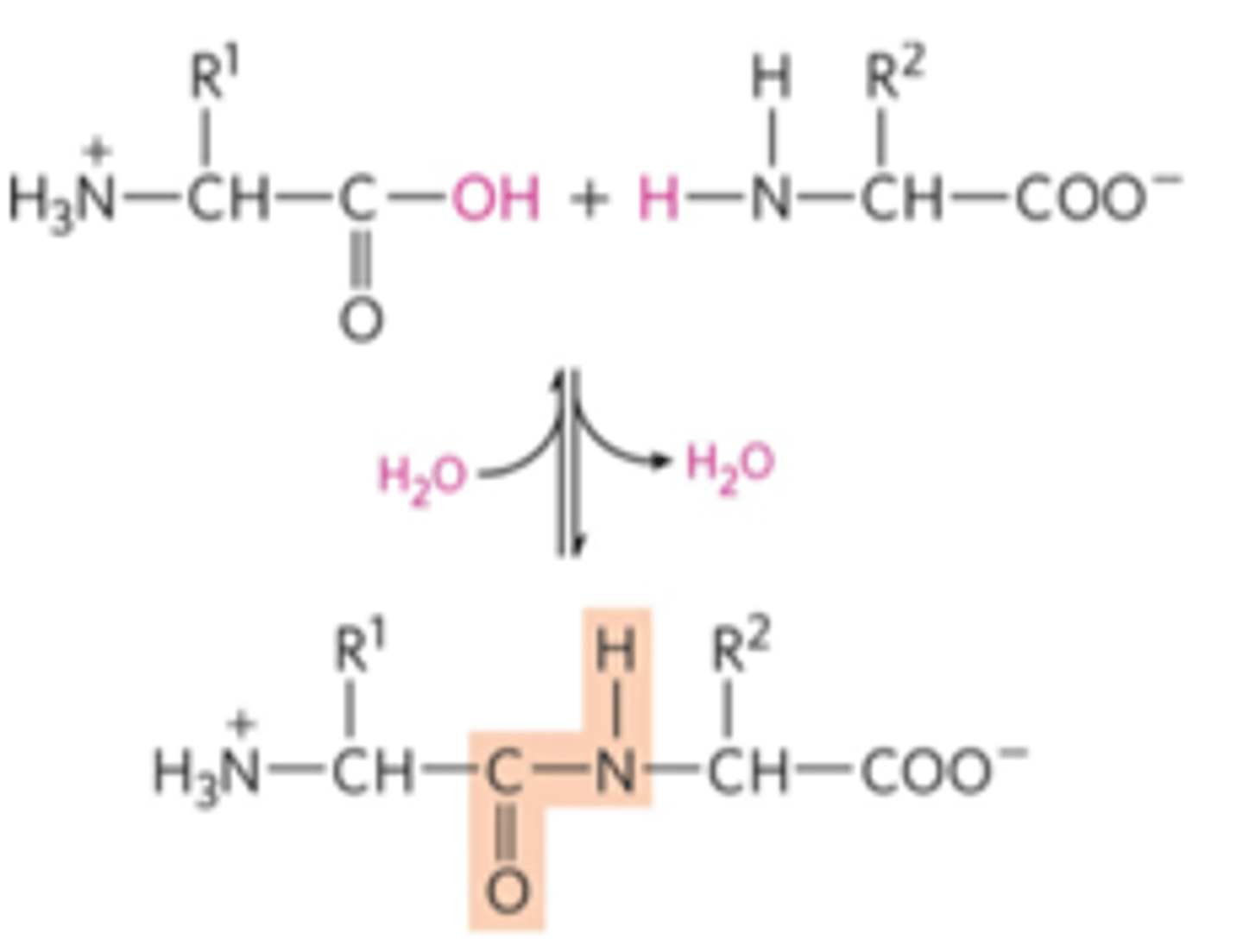
How is an amide linkage formed?
dehydration reaction that links a carboxyl group and an amino group
What is residue?
monomer that is part of a polymer
What does the directionality of polymers refer to?
all covalent bonds are in the same direction (like elephants holding tails in a line)
What is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
What links amino acids in a protein?
covalent peptide bonds
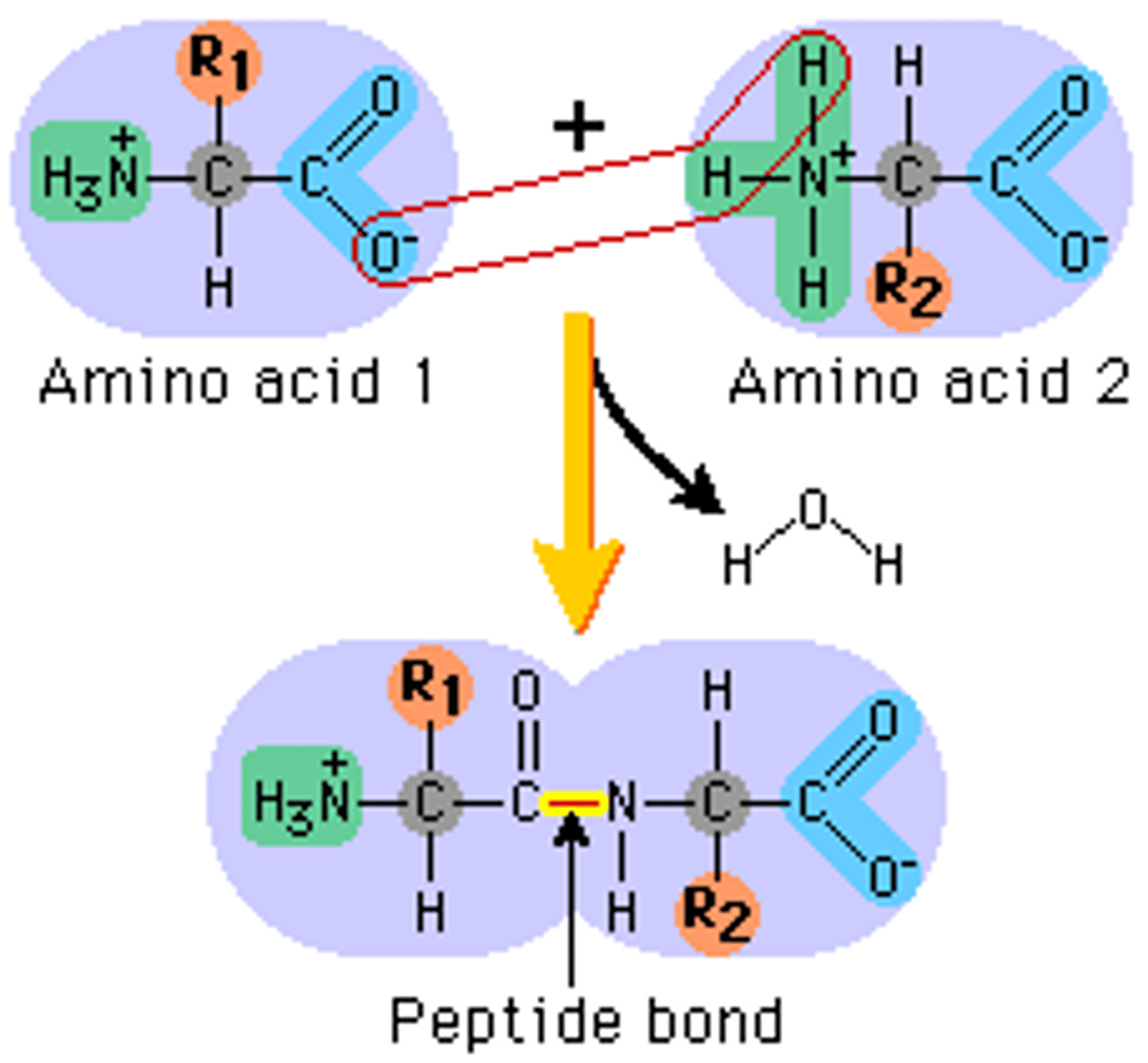
What is the monomer of nucleotides?
nucleic acids
What links nucleic acids in a nucleotide?
covalent phosphodiester bond
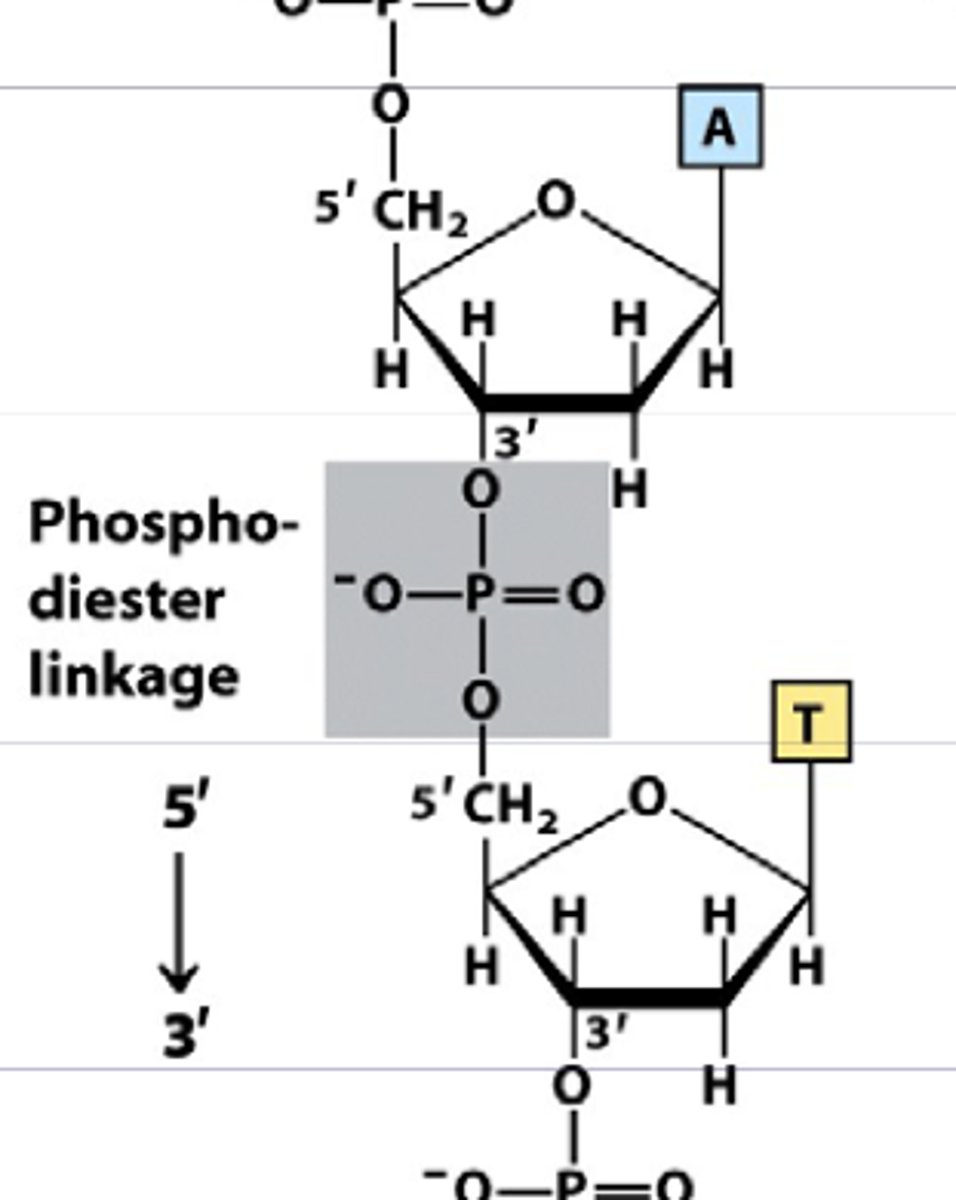
What link monosaccharides to form polysaccharides?
glycosidic bond
What creates a permanent dipole?
covalent bonds between atoms with different electronegativites
Rank: SONHC in terms of lowest to highest electronegativity?
HCSNO
What are the bond angles in water?
104.5
What are the requirements for a hydrogen donor?
hydrogen bonded to an electronegative atom (O, N, or S)
What are the requirements for a hydrogen acceptor?
a lone pair of electrons associated with an electronegative atom
How many hydrogen bonds does each water molecule form in ice?
4
How many hydrogen bonds does each water molecule form in water?
approx 3 but it fluctuates
In a hydrogen bond between two water molecules, what do the donor and acceptor act as?
donor- weak acid
acceptor- weak base
What are van Der Waals interactions?
dipole-dipole interactions between polar non-charged groups
What are London dispersion forces?
between non polar molecules, exhibited by all molecules
What is the hydrophobic effect?
the tendency of water to minimize its contacts with non polar substances, thereby inducing the substances to aggregate (involves London dispersion forces)
Rank the bonds from strongest to weakest.
covalent, ionic, hydrogen bond, van der waals
What groups can be hydrogen bond donors?
NH, OH, SH
What groups can be hydrogen bond acceptors?
O, N, or S with lone pair(s)
What does the hydrophobic effect do?
is entropically favourable for water