Unit 3- part E- Diffusion of molecules
1/12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is meaning of diffusion?
the random movement of molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
What is kinetic theory?
A theory describing the movement of particles in solids, liquids and gases.
Explain how it is possible for you to spray air freshener in one corner of the room and and you can smell it in other parts of the room?
This occurs due to diffusion, where the air freshener molecules move randomly from the area of high concentration (near the spray) to areas of low concentration (the rest of the room), allowing the scent to spread.
How does the concentration gradient effect the rate of diffusion?
A concentration gradient affects the rate of diffusion by determining the direction and speed at which molecules move; a steeper gradient (larger difference in concentration) leads to a faster rate of diffusion, as molecules move from high to low concentration more rapidly.
How does the shape and the size of the molecule impact diffusion?
The shape and size of a molecule impact diffusion by influencing how easily it can pass through membranes or navigate through a medium; smaller and more streamlined molecules typically diffuse faster than larger or more complex ones.
How does temperature effect diffusion?
Temperature affects diffusion by increasing the kinetic energy of molecules; higher temperatures result in faster-moving molecules, which enhances the rate of diffusion as they collide and spread more rapidly.
How does distance effect the rate of diffusion?
Distance affects the rate of diffusion by determining how far molecules must travel to reach equilibrium; greater distances result in slower diffusion rates, as molecules take longer to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
How doe surface area effect the rate of diffusion?
When diffusion takes place through a semi-permeable membrane, such as a cell membrane, the greater the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion of molecules through the membrane.
What is the meaning of semi-permeable?
a membrane that will allow small molecules such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen to pass through it, but will not allow large molecules to pass through it.
What experiments can be used to demonstrate diffusion?
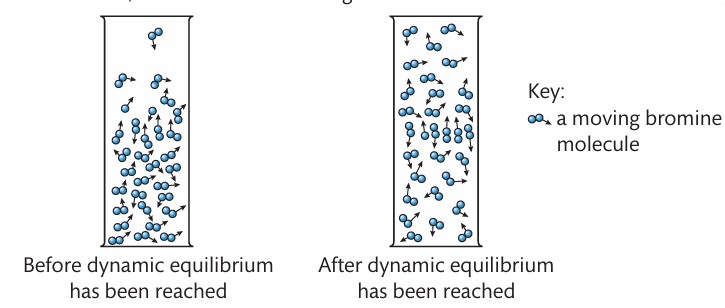
The diffusion of bromine in air
The diffusion of hydrogen chloride and ammonia gases
What is Brownian motion?
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium.
What is the meaning of absolute zero?
the lowest possible temperature, which is 0K on the kelvin temperature scale and -273°C on the Celsius temperature scale.
What is the meaning of dynamic equilibrium?
when two processes take place at the same rate so there is no further change in concentration of the substances involved