lecture 1+2 (Financial Maths I: nominal+effective interest rates)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
log refresher

Cash Flow Example
E.g. A loan has 2 cash flows:
One at the start (loan principle)
One at the end (loan repayment)
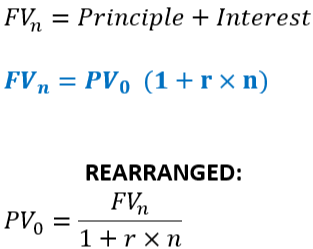
Simple Interest Formula FB
Don't forget if 9 months (t=9/12)
Rate of Return Calculation

Compound Interest Formula FB
The idea that interest is calculated periodically
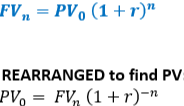
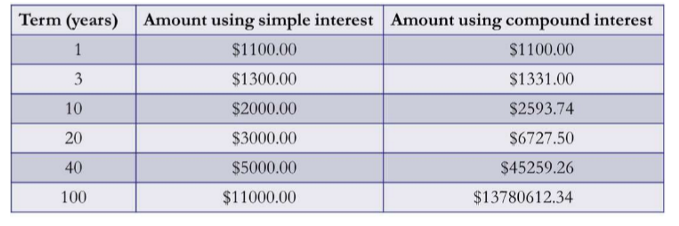
Comparison Between Simple and Compound Interest
For longer periods, the difference grows, shorter=not much difference
The difference will also be larger, when the interest rate is higher
Example:
5.2 Define Stated/Nominal Interest Rate
Nominal Rate: where the basis of quotation does not match the timing of cash flows STATE RATES MUST BE CHANGED INTO EFFECTIVE BEFORE CALCULATION
(e.g. 7.23% monthly, 7.26 quarterly)
5.2 Define Effective Interest Rate
Effective Rate= where the basis of quotation does match the timing of the cash flows. BASICALLY EFFECTIVE RATE APPLIES TO CASH FLOWS
(think of it as how it effects your pocket),
caters for compounding periods, (if you calculate 0.5% a month for a year)
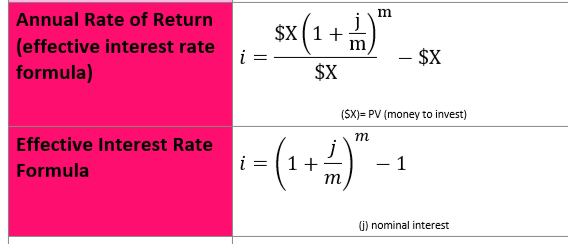
5.2 Converting Nominal to Effective Rare
think of (-1) as subtracting to find the cash flow made from the nominal interest. Answer is a percentage because finding the percentage of cash flow earnt. REMEMBER UNITS (pa or per month...)
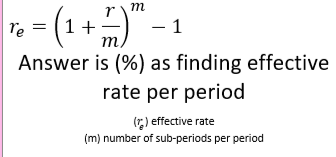
5.3 Effective Interest Rate Formula