M1 - (MGT101) Principles of Management
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 1 : Introduction to Management: Theories and Practice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Terry and Rue:
•“Management is a process or form of work that involves the guidance and direction ”
Stoner:
•“Management is a process of planning, organizing, leading and controlling the efforts of organization members ”
Koontz, O’Donnell and Weihrich:
•“Management is the establishment of an environment for group effort,, with the least amount of such inputs as money, time, effort, discomfort and materials .”
Johnson and Stinson:
•“Management is the process of working with and through other people to accomplish organizational goals.”
Common Features
Management

PROCESS:
to achieve its overall goals to minimum cost and maximum profit
PERSON:
who are responsible and accountable for directing the workplace
9 M’s of Management
Manpower
Money
Materials
Machines
Methods/Procedure
Markets
Minutes/Time Management
Motivation/Morale
Measurement
BASIC MANAGERIAL FUNCTIONS
PLANNING
ORGANIZING
STAFFING
LEADING
MOTIVATING
CONTROLLING
PLANNING
the process of setting the objectives to be accomplished by an organization during time period
ORGANIZING
the process of grouping and assigning activities and authority to carry out the activities.
STAFFING
The process of filling positions with the most qualified people
LEADING
Managing and motivating others
MOTIVATING
getting people to contribute their maximum effort
CONTROLLING
The process of ensuring the achievement of an organization’s objectives.
Other Essential Processes:
Decision-Making
the process of choosing two or more alternatives
Planning
Organizing
Staffing
Motivating
Controlling
Other Essential Processes:
Communicating
the process of transferring or conveying ideas,
MANAGER
refers to a person responsible for the work performance
MANAGEMENT
to achieve organizational objectives through the functions of planning, organizing and staffing, leading and controlling.
Levels of Management
TOP
Chairman of the Board, CEO, President, Vice-President, COO (Chief Operating Officer), CFO (Chief Financial Officer), CIO (Chief Information Officer)
executive coaching, change management, leadership, delegations & empowerment, etc.
Levels of Management
MIDDLE
Director, Branch Manager, Department Chairperson, Chief of Surgery, Team Leader
problem solving, team building, talent development, performance management, etc.
Levels of Management
LOW LEVEL
Supervisor, Office
Manager, Crew
Chief
emotional intelligence & coaching for performance, etc.
Type of Managers:
Functional Managers
General Managers
Administrators
Entrepreneurs
Small Business Owner
Team Leader
Types of Managers:
FUNCTIONAL MANAGERS
They supervise the work of employees engaged
Types of Managers:
GENERAL MANAGERS
They are responsible for the work of several different groups
Types of Managers:
ADMINISTRATORS
They are typically a manager who works in a public (government) or non-profit organization, rather than in a business firm.
Types of Managers:
ENTREPRENEURS
•They are the persons who found and operate an innovative business.
•the entrepreneur develops the business into something bigger than can handle alone or with the help of only a few people,
that person becomes a general manager.
Types of Managers:
SMALL BUSINESS OWNER
•An individual who owns and operates a small business.
•Entrepreneurs are small business owners
BUT not all business owners are entrepreneurs.
Types of Managers:
TEAM LEADERS
A manager who coordinates the work of a small group of people, while acting as a facilitator and catalyst.
The Process of Management
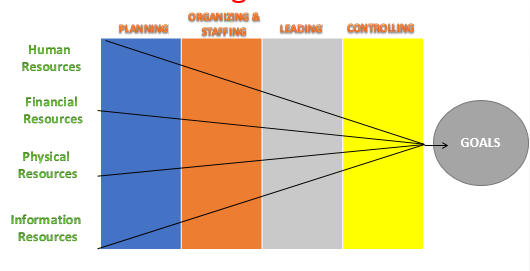
Resources Used by Managers
HUMAN RESOURCES
Are people needed to get the job done.
FINANCIAL RESOURCES
are the money the manager
PHYSICAL RESOURCES
a firm’s tangible goods and real estate, including raw materials,
INFORMATION RESOURCES
the data that the manager and the organization use to get the job done
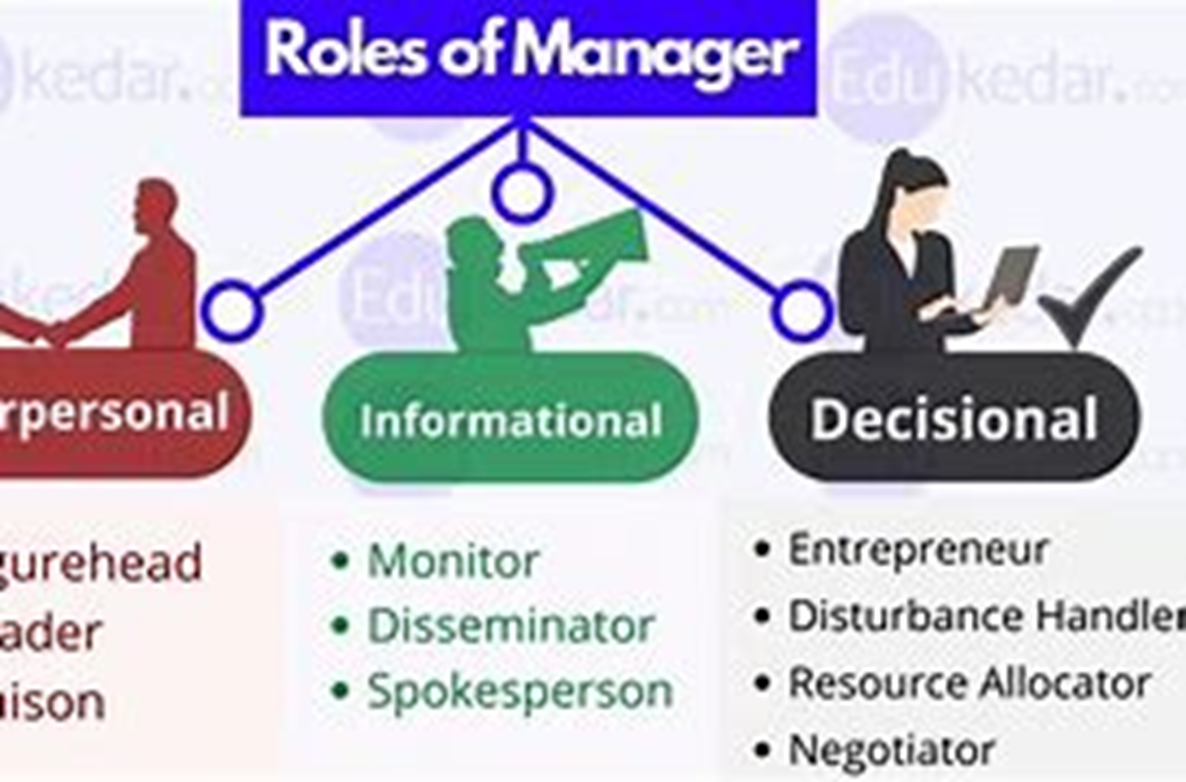
The Seventeen Managerial Roles
Planning
Strategic Planner
Operational Planner
The Seventeen Managerial Roles
Organizing & Staffing
Organizer
Liaison
Staffing Coordinator
Resource Allocator
Task Delegator
The Seventeen Managerial Roles
Controlling
Monitor
Disturbance Handler
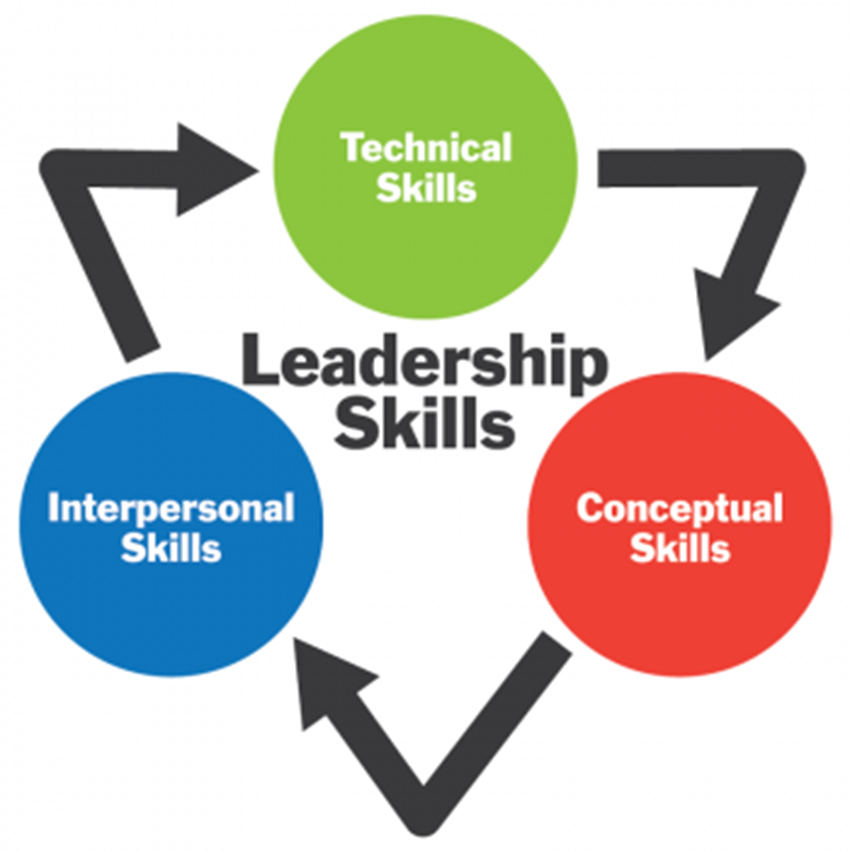
Five Key Managerial Skills
Technical Skills
understanding of and proficiency in a specific activity that involves methods, processes, procedures or techniques.
Five Key Managerial Skills
Interpersonal Skills
a manager’s ability to work effectively as a team member
Five Key Managerial Skills
Conceptual Skills
the ability to see the organization as a total entity
Five Key Managerial Skills
Diagnostic Skills
Ability to investigate a problem and then to decide on and implement a remedy.
Five Key Managerial Skills
Political Skills
The ability to obtain power and prevent others from taking it away.
Katz’ Managerial Role
Mintzberg’s Role of Manager
False
Managers are the same as a leaders in all aspects of their functions and responsibility
True
False
False
Being an efficient manager means you are able maximize all your resources to obtain your goal.
True
False
True
Being effective means you are able to obtain the oranization's goal.
True
False
True
Effectivity and efficiency are both necessary to become a successful manager.
True
False
planning and organizing
leading and controlling
Which among the following belong to top level managers ? – CEO of the group of company
Basic functions of manager include :
planning and organizing
leading and controlling
management is a process and requires resources
managing is through people
all levels of managerial position should acquire skills in basic functions
Which among the following statements are TRUE about management concept?
management is a process and requires resources
managing is through people
all levels of managerial position should acquire skills in basic functions
GLOBAL MANAGEMENT
• the rise of the “global village” and e-commerce,
• the trend of the world becoming one big market, and
• the rise of both megafirms and Internet-enabled minifirms worldwide.
INTRODUCTION
Globalization, the trend of the world economy toward becoming a more interdependent system, is reflected in three developments:
COUNTRY RANKING FOR COMPETITIVENESS 2019
Singapore
United States
Hong Kong SAR
Netherlands
Switzerland
Japan
Germany
Sweden
United Kingdom
Denmark
THE RISE OF THE “GLOBAL VILLAGE” AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE
Global village
The “shrinking” of time and space as air travel and the electronic media have made it easier for the people around the globe to communicate with one another
Global economy
The increasing tendency of the economies of the world to interact with one another as one market instead of many national markets
INTERNATIONAL MANAGEMENT
is management that oversees the conduct of operations in or with organizations in foreign countries
According to Hamilton Recruitment, you’ll be able to
- improve your communication skills,
- gain insights into other cultures,
- and experience personal growth,
Ethnocentric
managers believe that their native country, culture, language, and behavior are superior to all others.
Ethnocentric thinkers tend to believe that they can export the managers and practices of their home countries to anywhere in the world and that they will be more capable and reliable..
Polycentric
managers take the view that native managers in the foreign offices best understand native personnel and practices, and so the home office should leave them alone. Thus, the attitude of polycentric managers is nearly the opposite of that of ethnocentric managers..
GEOCENTRIC MANAGER
managers accept that there are differences and similarities between home and foreign personnel and practices and that they should use whatever techniques are most effective.
Ethnocentric manager
we know best
Polycentric Manager
they know best
Geocentric managers
What’s Best Is What’s Effective, Regardless of Origin”
WHY COMPANIES EXPAND
Lowest Risk & Investment,
Global Outsourcing → Importing → Exporting & Countertrading → Licensing & Franchising → Joint Ventures → Wholly Owned Subsidiaries
Highest Rank & Investment
FIGURE 3.1
The organization’s environment
The two main groups are internal and external stakeholders
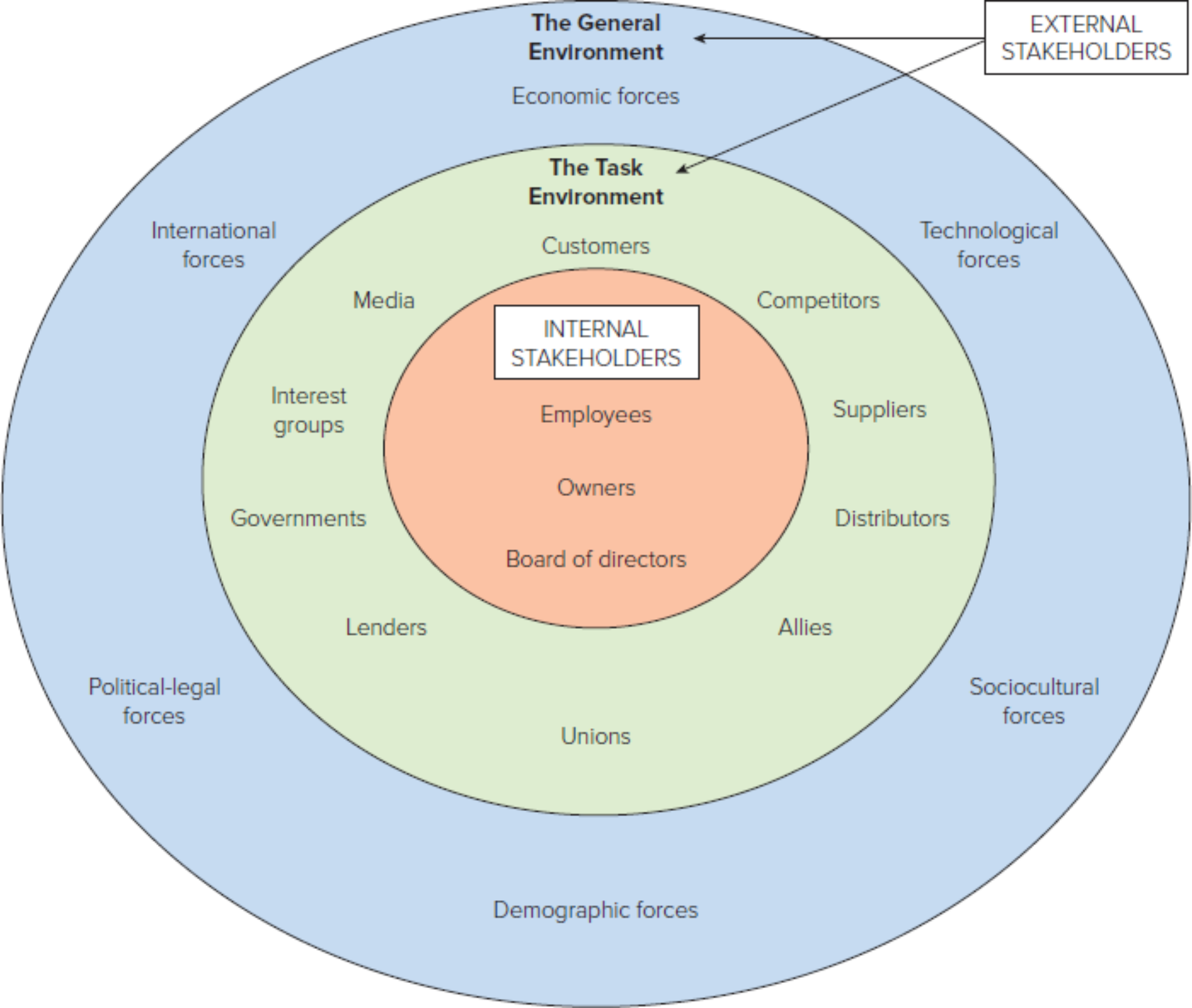
Internal Stakeholders
EMPLOYEE
OWNERS
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
•SOLE PPROPRIETOR
•PARTNERSHIP
•PRIVATE INVESTORS
•EMPLOYEE OWNERS
•SHAREGOLDERS
External Stakeholders
Task Environment
consists of 10 groups that interact with the organization
External Stakeholders
General Environment
macroenvironment—the set of broad, uncontrollable forces in the external environment that impact the organization
10 components of Task Environment
CUSTOMERS
SUPPLIERS
COMPETITORS
DISTRIBUTOR
STRATEGIC ALLIES
EMPLOYEE ORGANIZATION
LOCAL COMMUNITIES
FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
GOVERNMENT REGULATIONS
SPECIAL INTEREST GROUPS
General Environment
Economic Force
Unemployment
Interest rates
Trade balance
General Environment
Technological forces
technology and work arrangement
technology and automation
General Environment
Demographic Forces
age
gender
race
income, etc
General Environment
Politico-Legal Forces
laws and politics
General Environment
International Forces
changes in economy, politics, legal and global systems’ technology
ethical dilemma :
situation in which you have to decide whether to pursue a course of action that may benefit but that is unethical or even illegal
Ethics
Standards of right and wrong that
Values
deeply underlying beliefs and attitudes
value system : pattern of values within organization
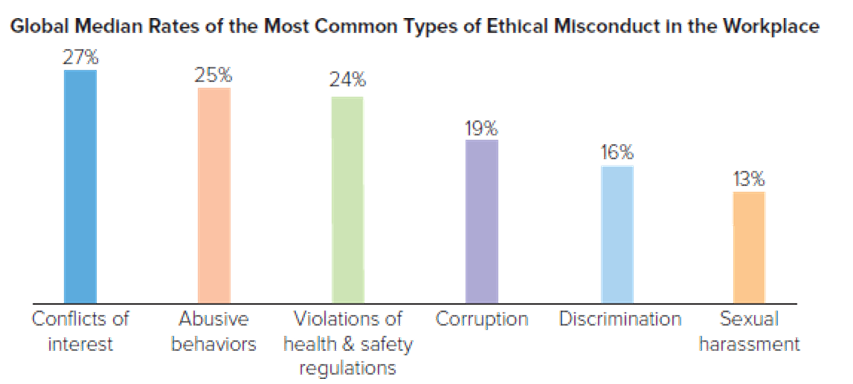
Fig 1.2 Survey results on workplace behavior considered ethical misconduct
Utilitarian
managers look for the greates good for the greatest number
Drawback : may damage workforce morales ,loss of employees with skills and experiences.
Individual Approach
guided by what will result in the individual’s best long term interest.
Moral-Rights
Respecting fundamental rights shared by everyone.
Justice Approach
guided by respect for impartial standards of fairness and equity

create strong ethical climate
screening propective employees
instituting ethics codes and training programs
rewarding ethical behavior
using multi-faceted approach!
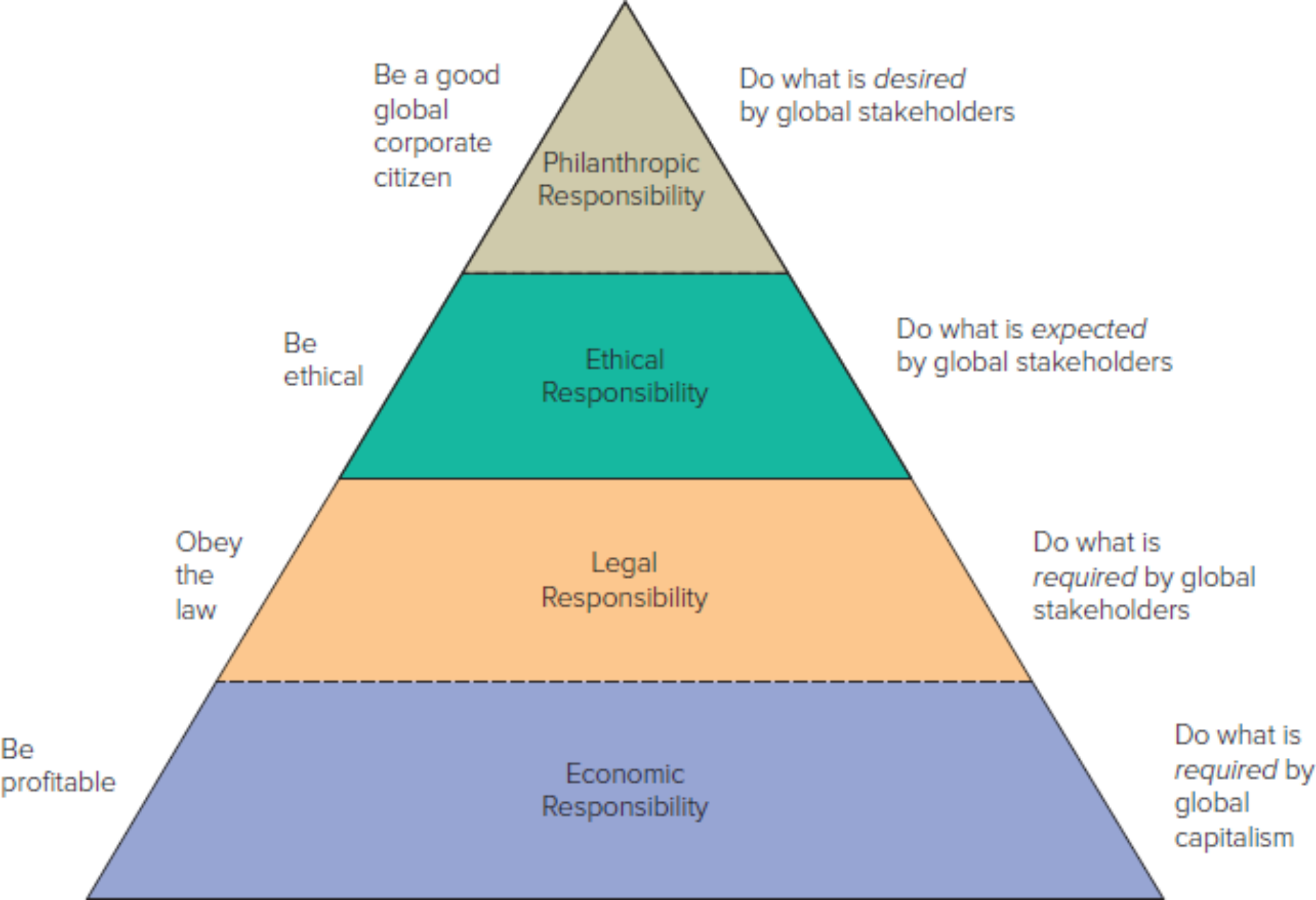
Fig 1.3 Carrol’s Global Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)