Savannah Lab Practical
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What are the components of an enzyme reaction (equation)?
Enzyme + Substrate → Substrate Complex → Products
What is an enzyme
Cataylst that speeds up a reaction
What is a substrate
Molecule enzyme acts on, binds to active site of enzyme
Do enzymes require an optimal PH for function?
Yes, enzymes require an optimal pH to function
3 things that cause enzymes to denature
ph, chemicals, temperature
how do you determine the optimum pH for an enzyme
Test the enzyme activity at various pH levels and graph the results
Can an enzyme be used multiple times
yes, reusable catalysts.
Can a substrate be used multple times
Yes, a substrate can be reused if sterilized to remove pathogens,
What is feedback inhibition
a regulatory mechanism which inhibits the enzyme's activity and prevents the overproduction of that product
What is the cell cycle
a sequence of ordered events that a cell goes through to grow and divide
What are the stages of the cell cycle
interphase (G1,S,G2)
and mitotic (M) phase.
What happens in G1
Cell growth
What happens in S phase
DNA replication
What happens in G2
The cell prepares for mitosis
What happens in prophase
chromsomes form, the nuclear envelope breaks down
what happens in metaphase
The chromosomes align at the cell's equator, forming the metaphase plate
what happens in anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell, ensuring each new daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes
What happens in telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms, spindle fibers break down
What happens in cytokinesis?
divides the cytoplasm into two separate daughter
How many divisions occur in mitosis
1
Mitosis starts with 1 ____cell and ends with 2 ___ cell
diploid
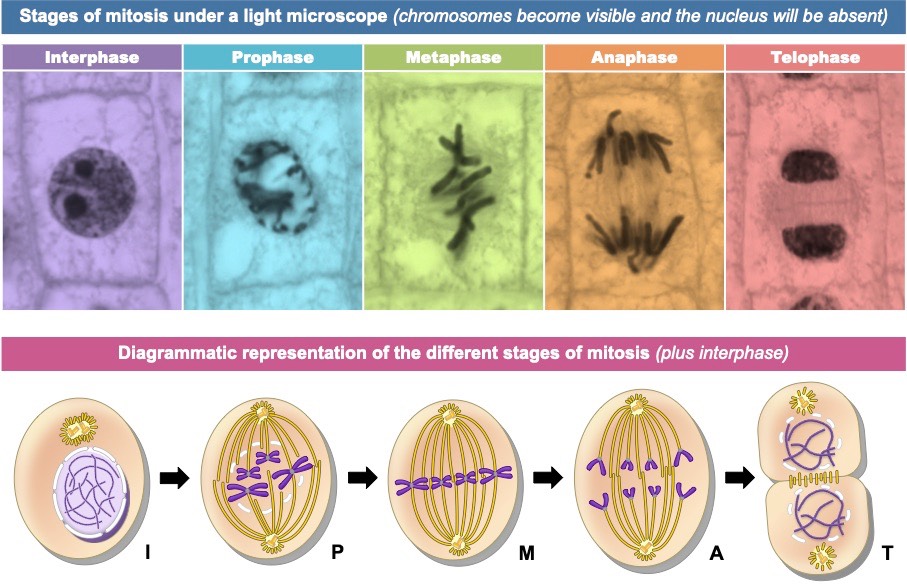
Mitosis in cells
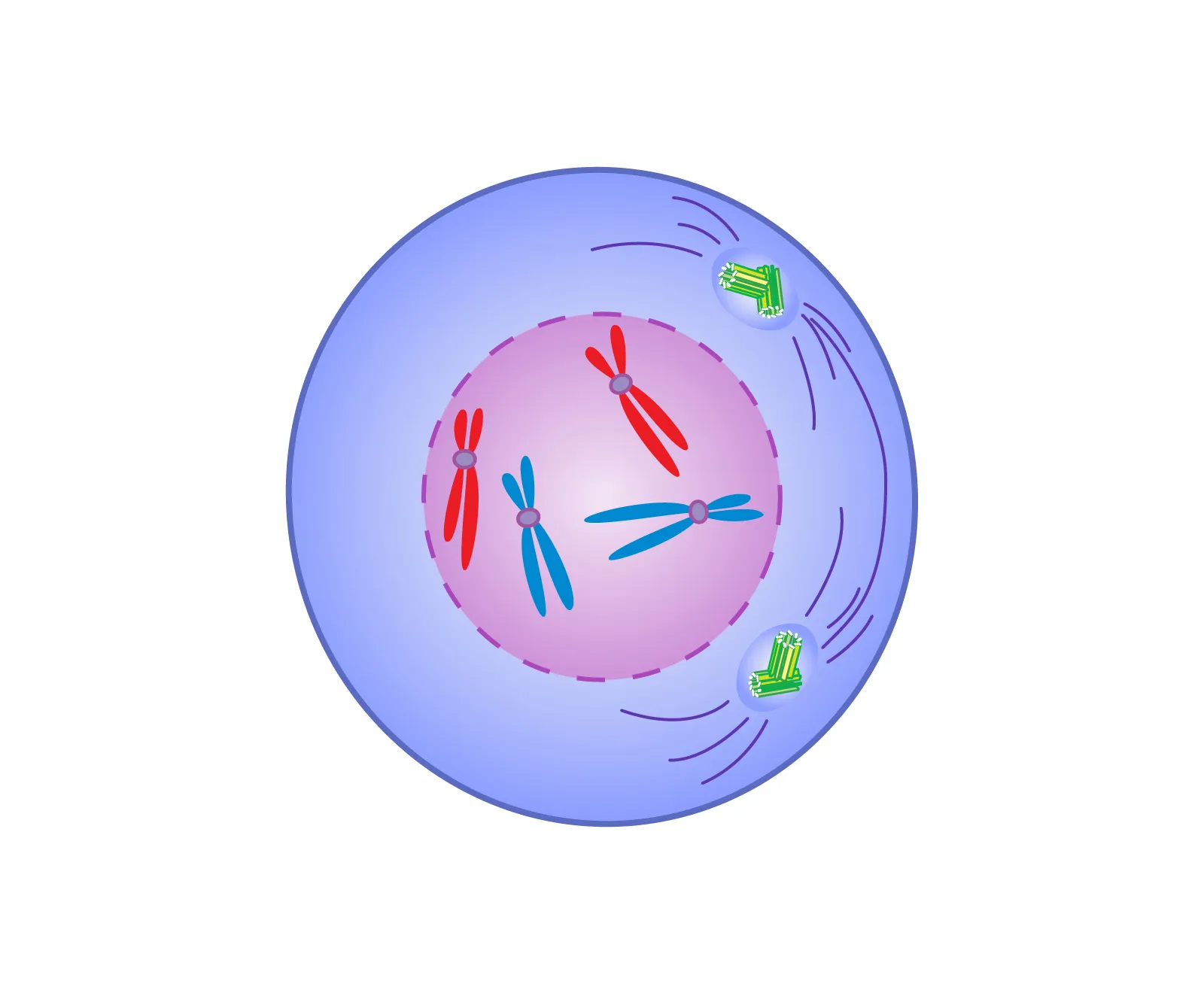
What stage is this
prophase
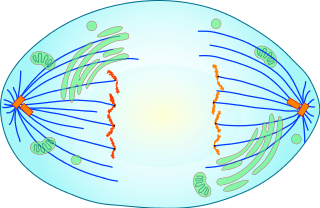
What stage is this
Anaphase
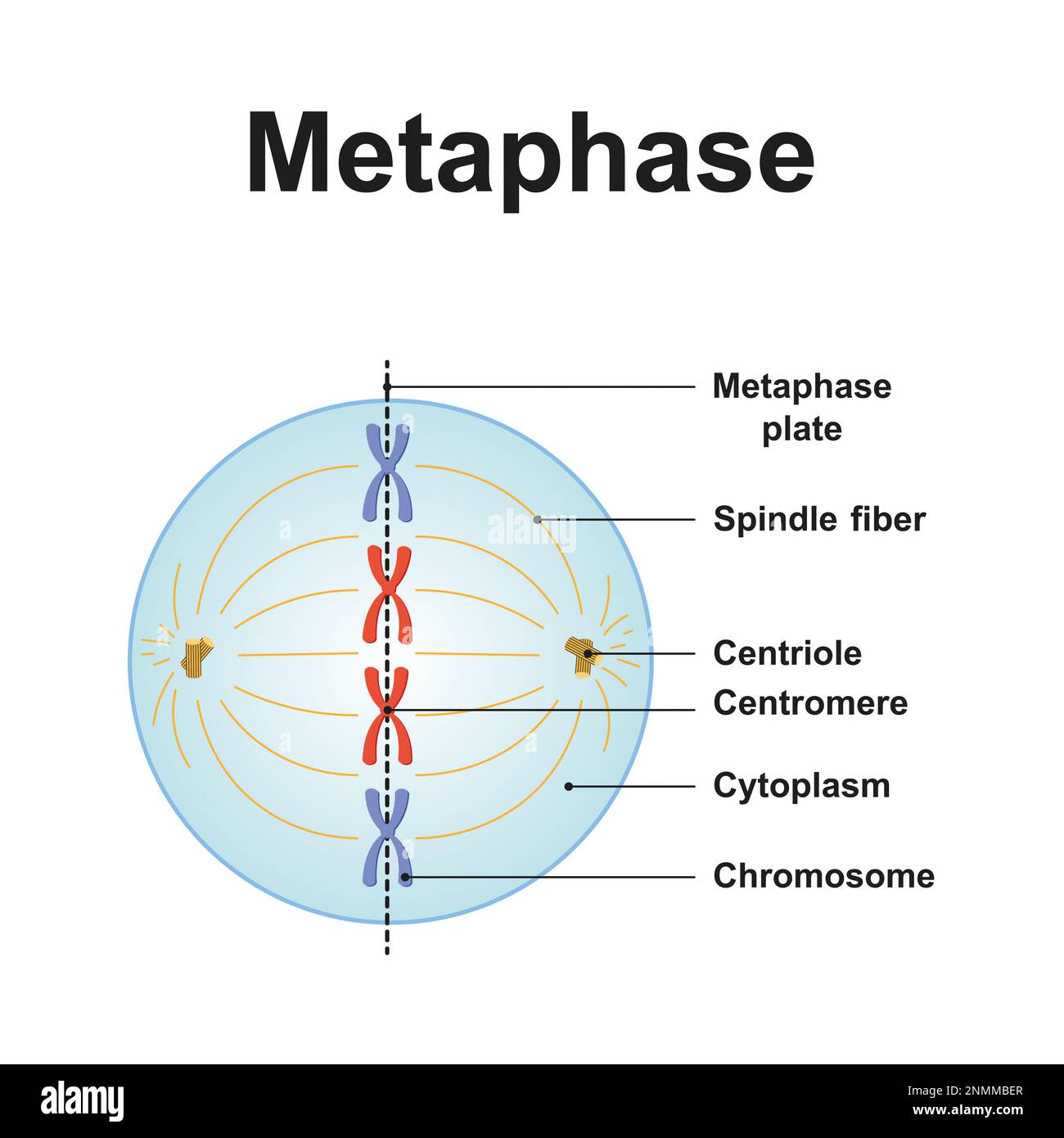
What stage is this
metaphase
What happens in prophase 1
homologous chromosomes pair up and condense, forming tetrads
What happens in metaphase 1
homologous chromosome pairs (tetrads) line up along the metaphase plate
What happens in anaphase 1
tetrads while the sister chromatids remain attached at their centromeres
What part of the cell cycle dose crossing over occur in?
prophase 1
what happens in telophase 1
The chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell, nuclear membrane reform around chromosomes.
What happens in cytokenesis 1
cytoplasm divides to form two haploid daughter cells
How many daughter cells are created after meiosis 1? And what kind of cells are they
2, haploid
What happens in prophase 2
forming a new spindle and breaking down the nuclear envelope
What happens in Metaphase 2
chromosomes align the metaphase plate) in the two haploid cells from meiosis
What happens in anaphase 2
the sister chromatids of each chromosome are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell by spindle fibers
What happens in telophase 2
nuclear envelopes reform around the chromosomes, chromosomes decondense back into chromatin, and the spindle fibers disappear
What happens in cytokenesis
division of the cytoplasm
How many daughter cells are created after meiosis 2
4 unique daughter cells
Are the daughter cells from meiosis 1 diploid or haploid
haploid
What are being created from meiosis 2
four genetically distinct haploid cells
Male gamete
sperm
female gamete
egg/ovum
Each organism has half genes from each parent
What does Domiant AA mean
The trait is expressed
What does recessive aa mean
The trait requires to copies to be expressed
2 examples of homozygous
AA,aa
Heterozygous example
Aa
Does an organism express a dominant trait or recessive trait if they are heterozygous
Dominant trait
What is the most major pigment in photosynthesis
chlorophyll
Why do plants appear green
green lights reflected, violet and blue light absorbed
Where does photosynthesis occour
chloro[last in plants
steps of light-dependent reactions
PS2: Electrons move into ETC, creating NADPH. Proton motive force forms ATP
O₂ goes into air, created ATP, NADPH, and oxygen
What happens in the calvin cycle
CO₂, atp, nadph create carbs
Products of the calvin cycle
nadph, atp carbs, glucose
In the lab experiment, what happened when Elodea was exposed to white light?
produced oxygen bubbles, and photosynthesis happened
in the lab experiment what happened when Elodea was exposed to green light
minimal photosynthesis occurs few or none oxygen bubles
in the lab experiment what happened when Elodea was exposed to darkness
it stopped photosynthesizing but continued cellular respiration, leading to a net production of carbon dioxide
What color did the elodea in the phenol red solution turn when blowing on it with a straw
yellow
Why did the phenol solution turn yellow
due to breath containing co2
What is phenol red
a pH indicator dye that changes color to indicate the acidity or alkalinity of a solution
Structure of DNA
Double helix, nucleotides
What dose A pair with nitrogenous bases
T
what does G pair with nitrogenous bases
C
What does A go to RNA bases
U
What does G go to RNA Bases
c
What holds bases together
Hydrogen bonds
What is RNA
Ribose sugar
What is DNA
dexyoribose sugar
Can you create an mRNA complement to a DNA template strand?
yes, through transcription
Can you create a complementary DNA strand as would occur in DNA replication
yes
transcription definition
Dna is copied into an mRNA strand that complements the DNA template
Where does transcription occur?
Nucleus
How does transcription occour
MRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the cytoplasm for translation on a ribsome
Translation definition
mRNA is coded into amino acids to create a polypeptide chain from the original DNA code.
mRNA contains codons that occur in
3s
TRNA contains
anticodons and carry the amino acids
What are the parts of tRNA
Amino acid receptor arm, Anticodon arm
Whatg organism did we extract DNA from
strawberry
What process is used to break up the cell membrane using dish soap
chemical lysis
How did we obtain genetic material
The cell membrane was degraded and we were able to obtain genetic info
What is causing the separation of pigments in gel electrophoresis?
an electric current pulling charged molecules through a gel matrix,
Do larger or smaller fragments move farther in gel electrophoresis?
smaller