Chapter 4 - Tissues
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Tissue
a group or layer of cells that work together to perform a specific function
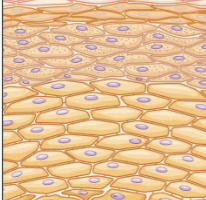
Epithelial tissue
also referred to as the “epithelium” the sheet of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body and lines, internal cavities and passageways from certain glands
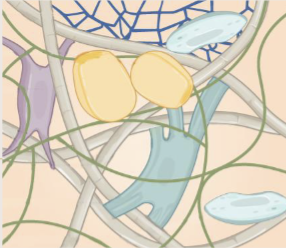
Connective tissue
binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in protection, support, and integration of all parts of the body
Histology
the study of the microscopic structure of tissues
Pathologist
a medical doctor who specializes in pathology
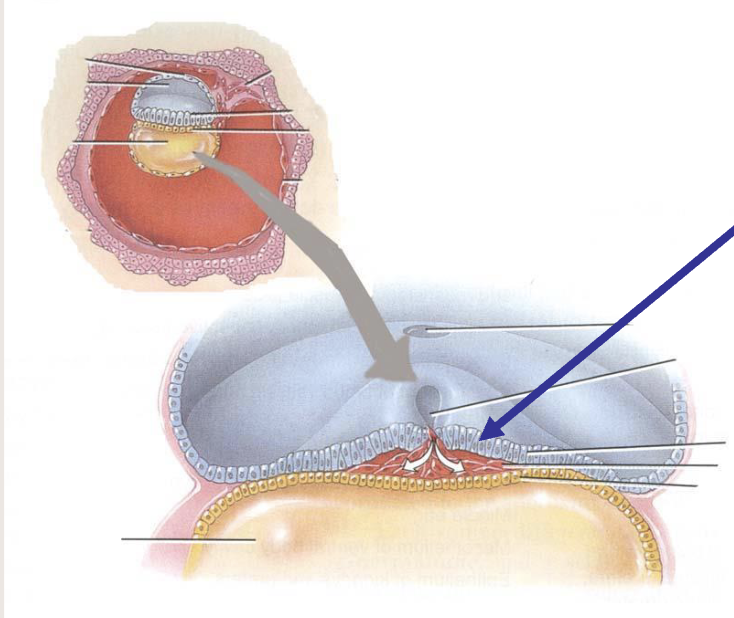
Ectoderm
develops into nervous tissues, epidermis of skin and other structures
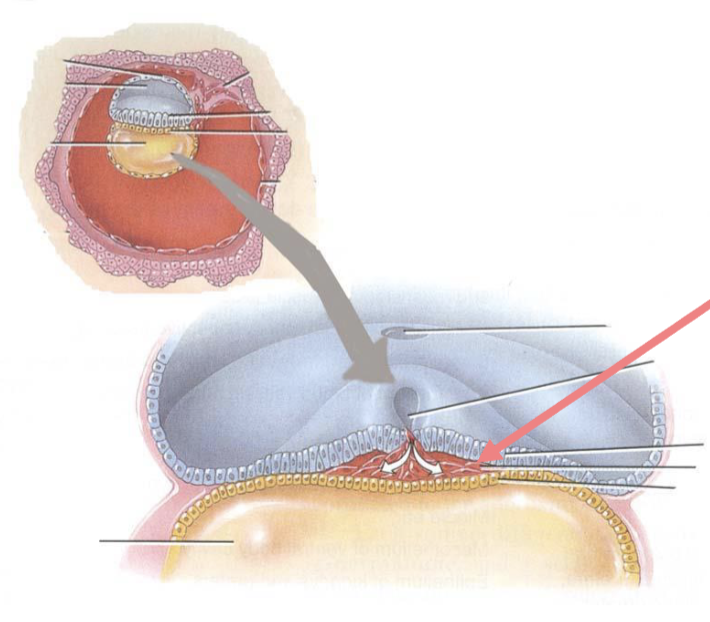
Mesoderm
gives rise to all connective tissues, most muscle tissues
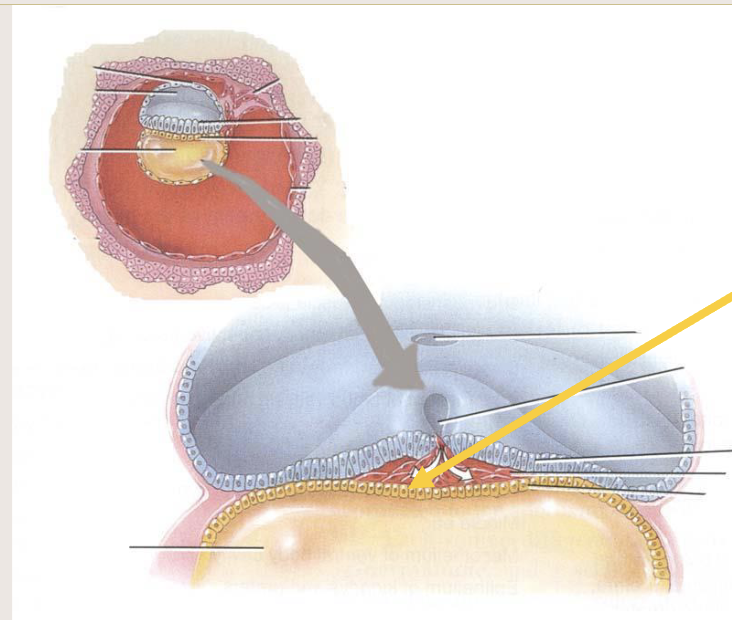
Endoderm
gives rises to epithelial linings of GI & respiratory tracts
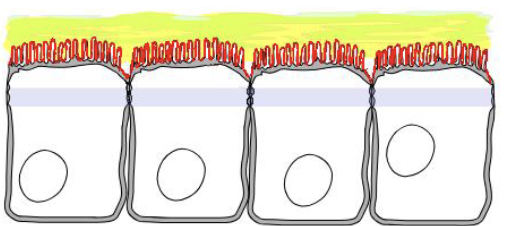
apical cell surface
lateral cell surface
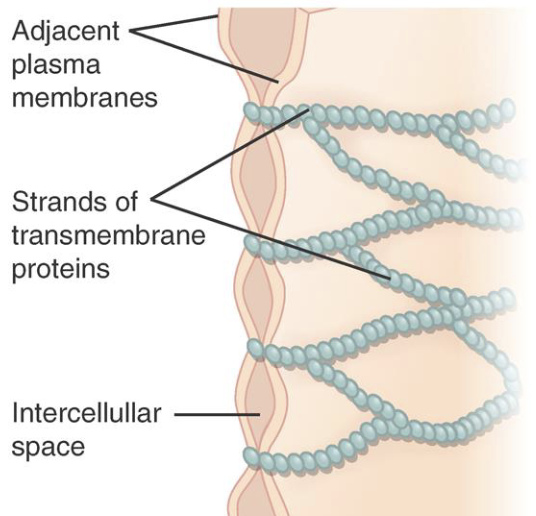
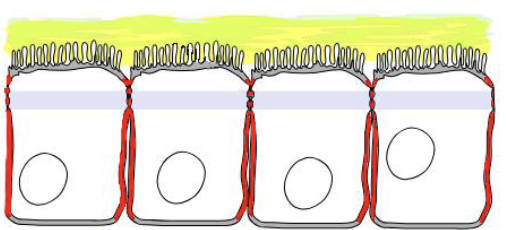
Tight junctions
retard passage of substances through epithelial membranes
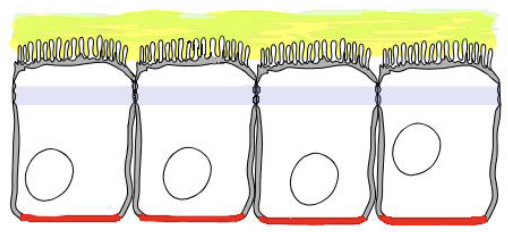
basal cell surface
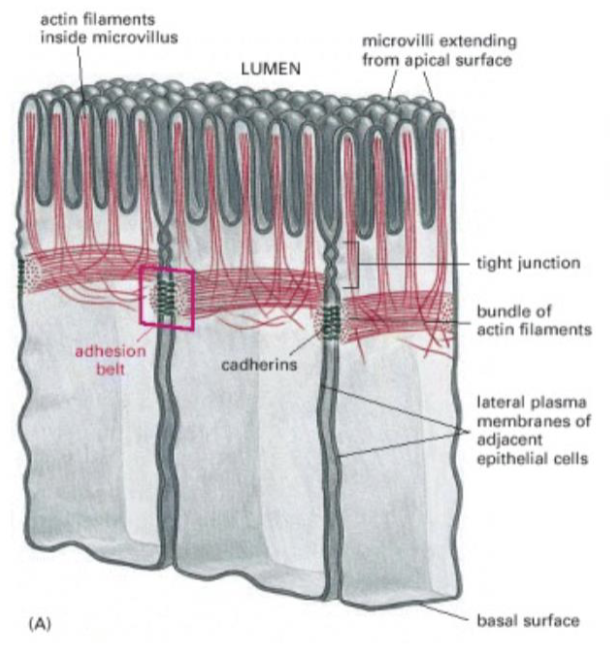
Adherens junctions
makes it possible for epithelia to bend and fold
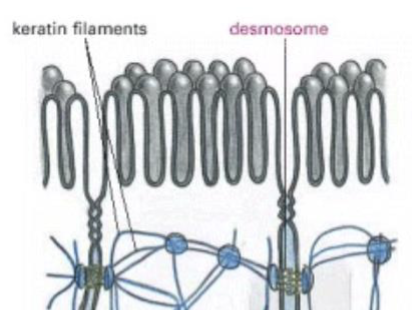
Desmosomes
anchor cells to neighboring cells
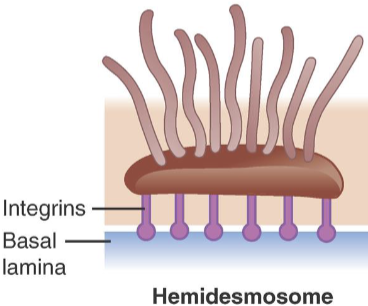
Hemidesmosomes
anchor cells to basement membrane
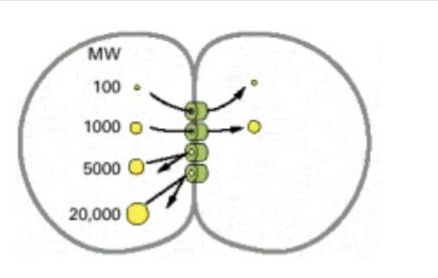
Gap junctions
connect cells and allow diffusion of ions in small molecules between those cells. It allows signals between sales to regular growth and cell differentiation.
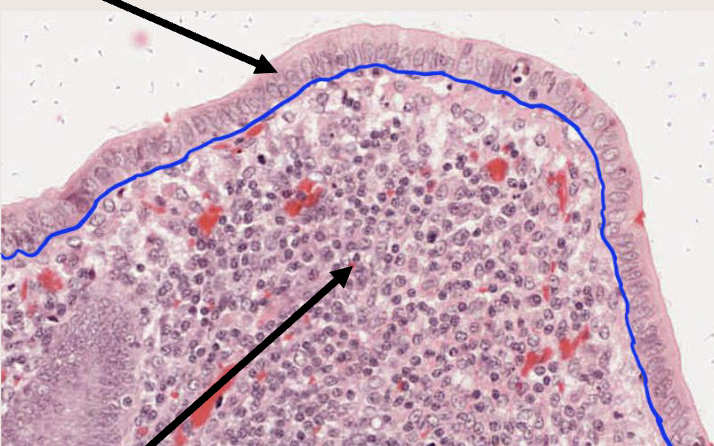
Basement membrane (the blue line thinger)
a thin layer that anchors epithelial tissue to the connective tissue underneath it
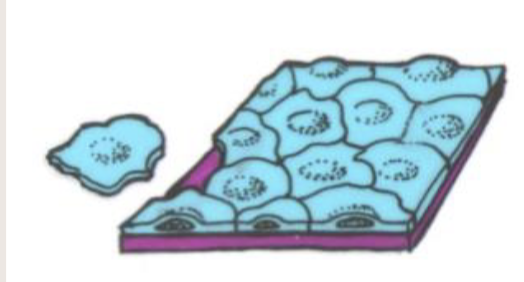
Simple squamous epithelium
a single layer of flat thin cells that allows for easy diffusion and infiltration
location: air sacs of lungs, lining of blood vessels
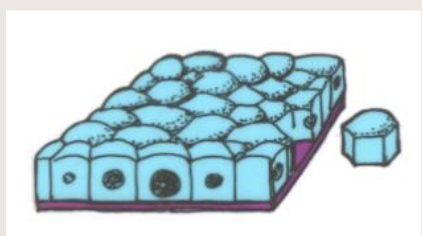
Simple cuboidal epithelium
a single layer of cube shaped cells that functions in secretion and absorption
locations: kidney tubules, glands, ducts
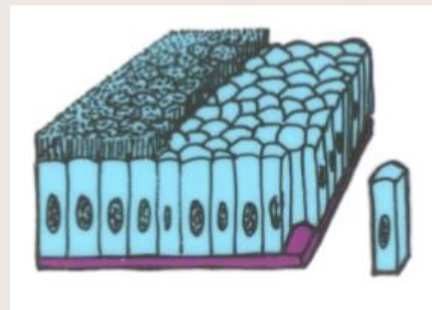
Simple columnar epithelium
a single layer of tall column like cell specialized for absorption(microvilli) and secretion.
location: lining of the stomach, intestines and uterus
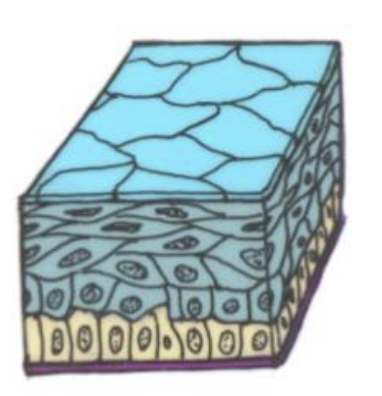
Stratified squamous epithelium
many layers of flat cells that protects against abrasion
ex: found in the skin (keratinized) and the mouth/esophagus (non-keratinized)
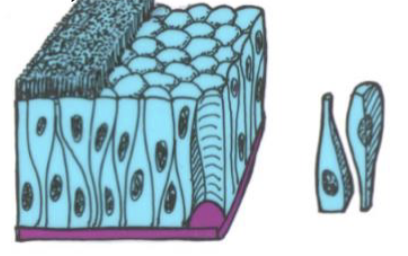
Transitional epithelium
layers of cells that stretch and chain shape; allows organs to expand
ex. Found in the bladder in the uterus.
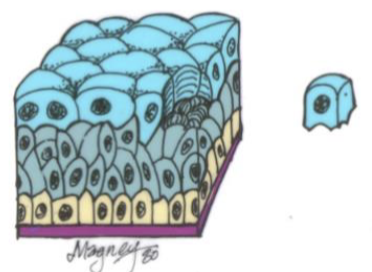
Pseudostraitified columnar epithelium
looks like multiple layers, but it's just one; often has Celia and goblet cells for moving mucus
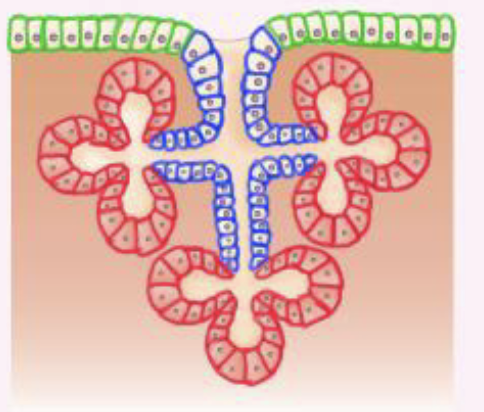
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances onto a surface or into ducts.
ex. Sweat glands, salivary glands, and oil glands
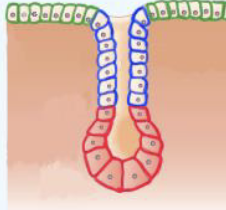
Acinar glands
rounded or sac-like glands
ex. Sebaceous (oil) glands.
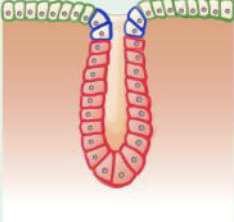
Tubular glands
tube-shaped glands
ex. Intestinal glands
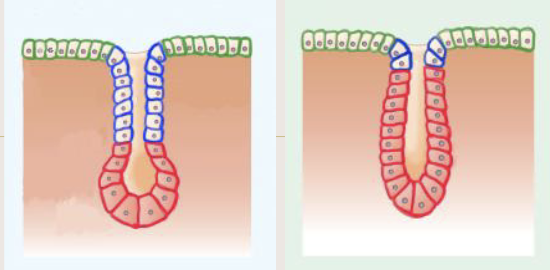
Tubuloacinar glands
has both tubular and acinar parts
ex. Pancreas
Simple gland
the duct that doesnt have branches
Compound gland
the duct that DOES have branches
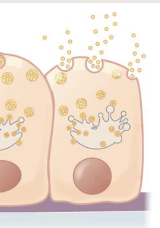
Merocrine glands
When the product is released by means of exocytosis
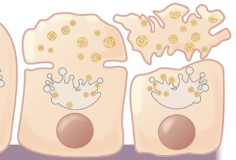
Apocrine glands
the apical part of the cell breaks off to become the secretion
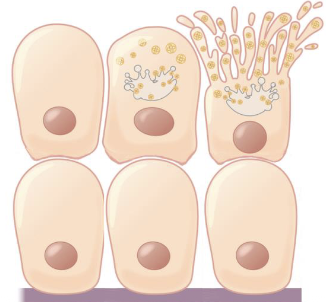
Holocrine glands
an entire cell burst and becomes the secretion. The cell that is sloughed off will be replaced by a new cell.
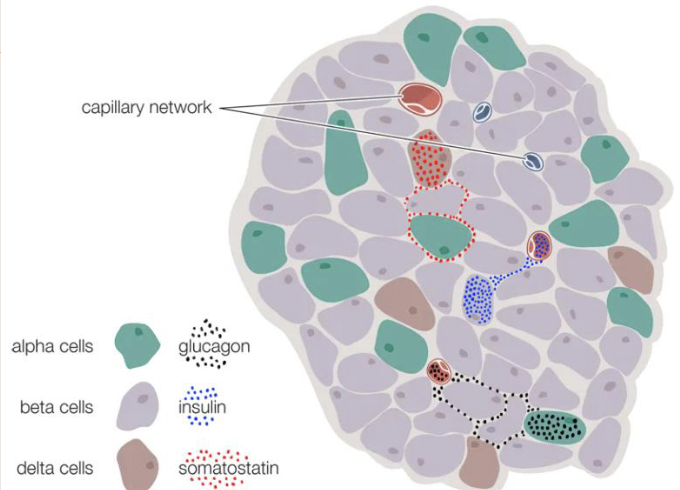
Endocrine glands
glands that secrete hormone directly into the bloodstream (the hormones enter the intersitial fluid)
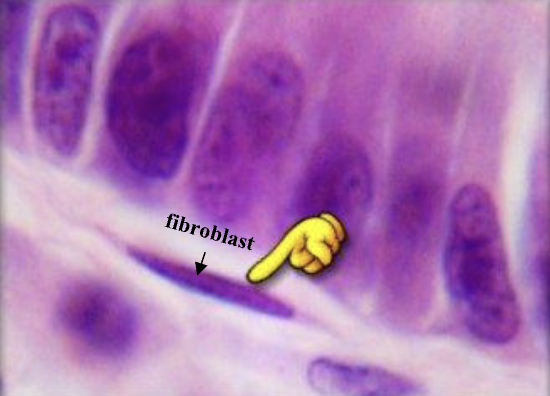
fibroblast
loose and dense connective tissue (CT)