Aqa Alevel Biology - Enzymes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
enzymes work by
lowering the activation energy of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction
enzymes are
globular proteins
the amino acids involved in the active site can't be changed because
the active site has to be complementary to the substrate
in induced fit model states that
the enzyme is flexible and can mould around the shape of a substrate
how do enzymes work?
they put strains on the bonds in the substrate as the enzyme moulds to tell shape , which distorts bonds in the substrate
the lock and key model is disapproved by
the ability of other molecules to bind to the active site, which showed the enzymes shape is altered by the binding molecule/substrate
an increased temperature will ...
increase the molecules kinetic energy, so the molecules move around more and cause more frequent collisions, leading to more ESC being formed
too high of a temperature will
denature then enzyme
what does a change in pH do to amino acids
it alters the charge on amino acids, so the substrate can no longer bind with the active site
what does a change in pH do to bonds
it can cause bonds containing a H+ in the tertiary structure to change or break, changing the active site shape
only a large pH change can
break and change tertiary bonds so this is rare
a high concentration of enzymes will
lead to a proportionate rate if reaction increase
in a solution with a high concentration of enzymes the graph will level off because
the amount of substrate is the limiting factor so can't supply all the enzyme active sites
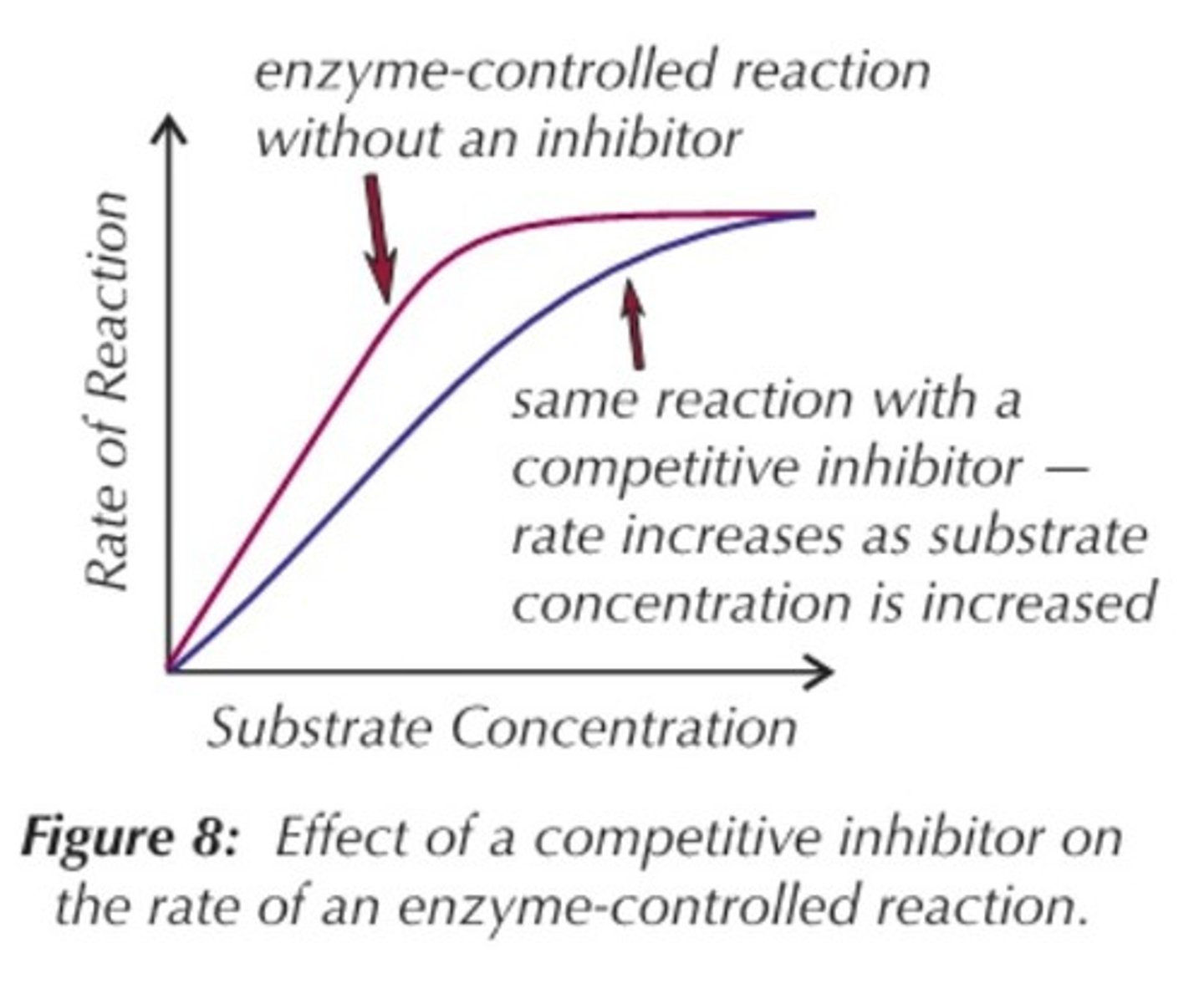
a competitive inhibitors shape is
similar to the substrate so they can compete for active sites but don't react.
Function of competitive inhibitor
-Competes for enzyme at the active site
-Interferes with active site of enzyme so the substrate cannot bind
competitive inhibitors aren't permanently bound to the active site so
eventually the substrate can move in and will inhabit all active sites
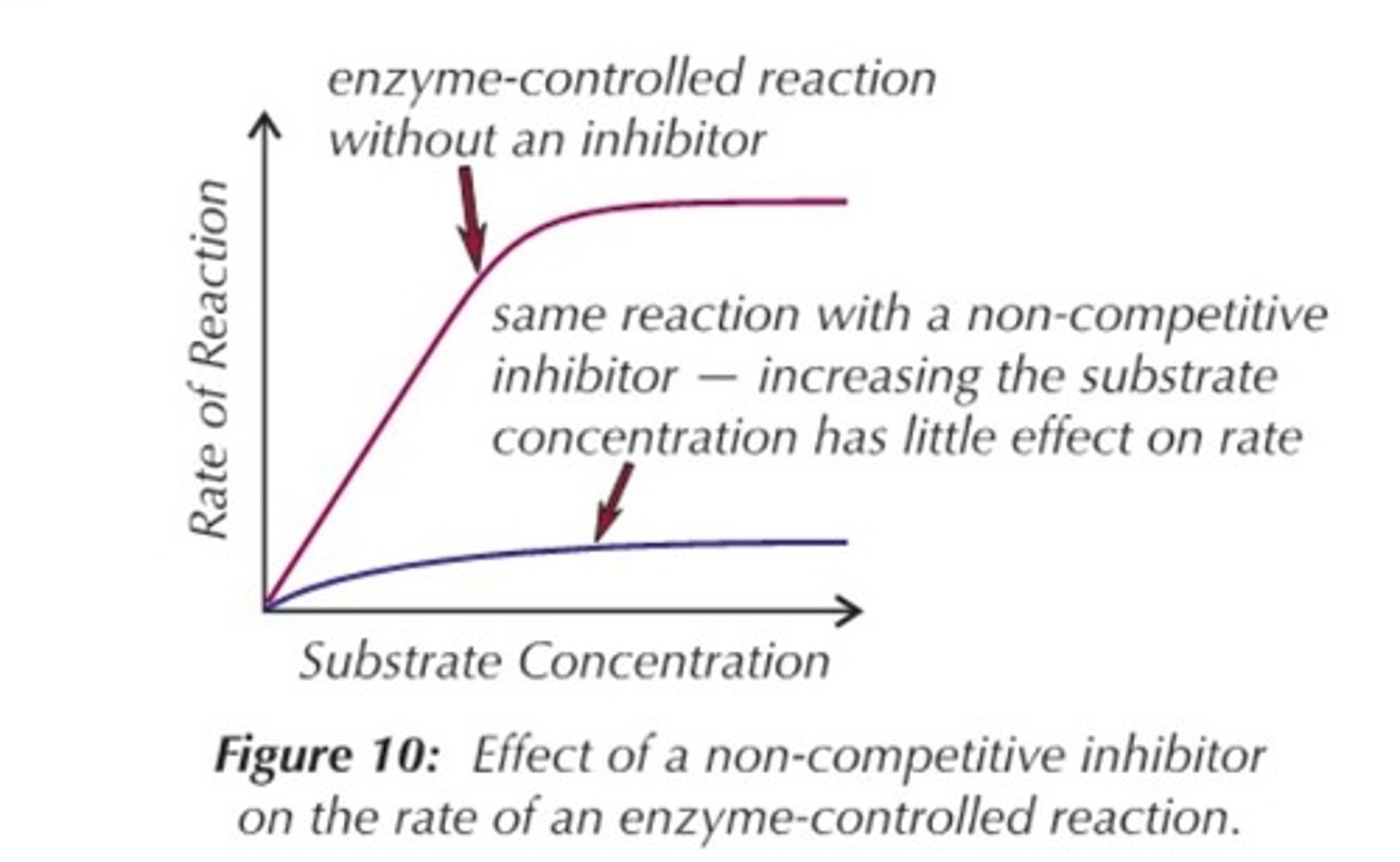
non-competitive inhibitors
join the enzyme at the binding site (allosteric site) , changes the shape of the enzyme and thus the active site so substrate can't bind

in non-competitive inhibitors, increasing the substrate won't increase the rate because
the effect of the inhibitor isn't reduced
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
activation energy (Ea)
the minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction
lock and key model
The model of the enzyme that shows the substrate fitting perfectly into the active site
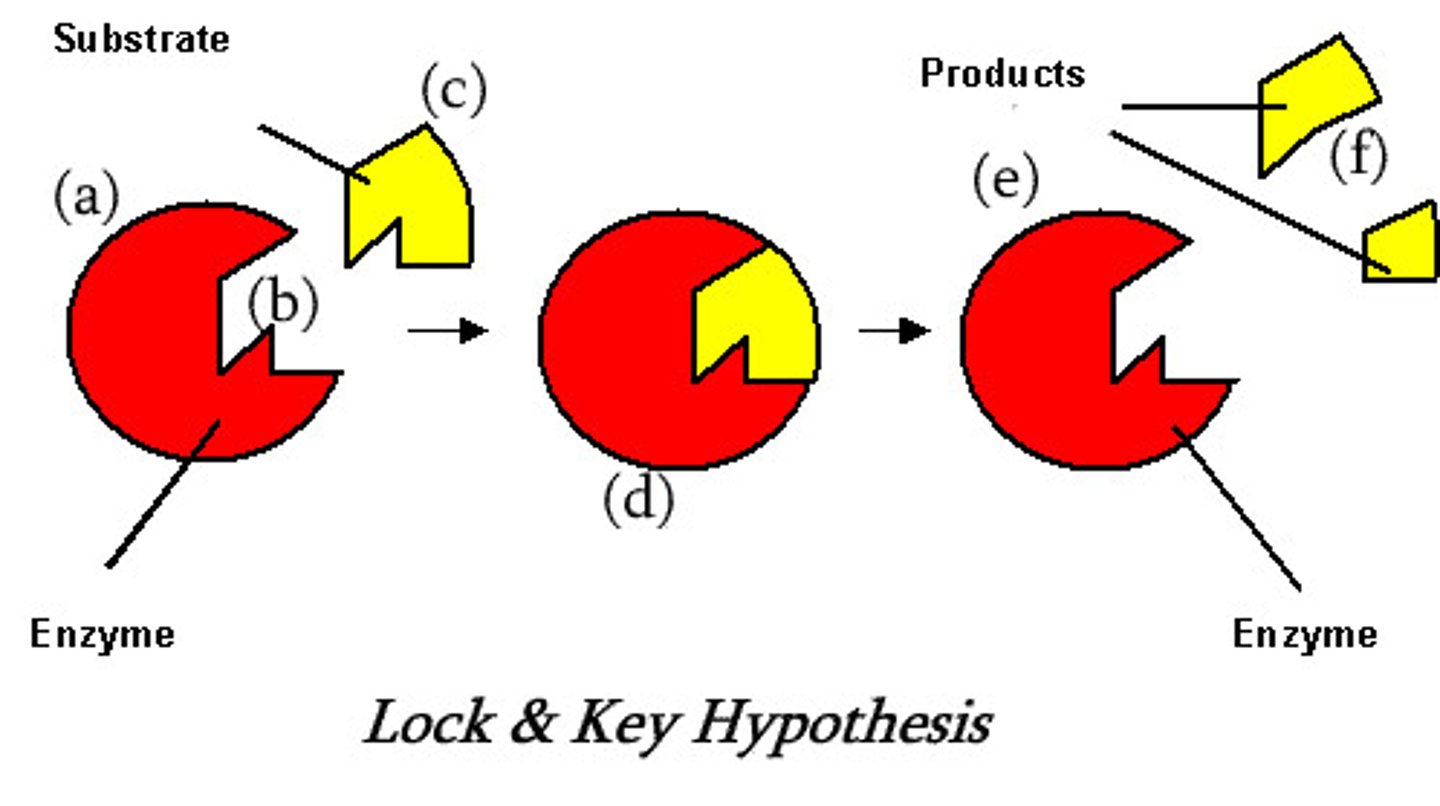
evidence for induced fit model
X-ray diffraction - observed changes in 3D structure
Factors that affect enzyme activity
Substrate & enzyme concentration, pH, temperature, inhibitors
optimum temperature
the maximum energy that can be supplied to the molecules before H and ionic bonds start to break
Effect of temperature on enzyme activity (above optimum)
-high kinetic energy
-causes AA in polypeptide chain to vibrate
-breaks H and ionic bonds between R groups
-tertiary structure is lost
-Active site no longer specific to substrate
-no esc form, enzyme is denatured
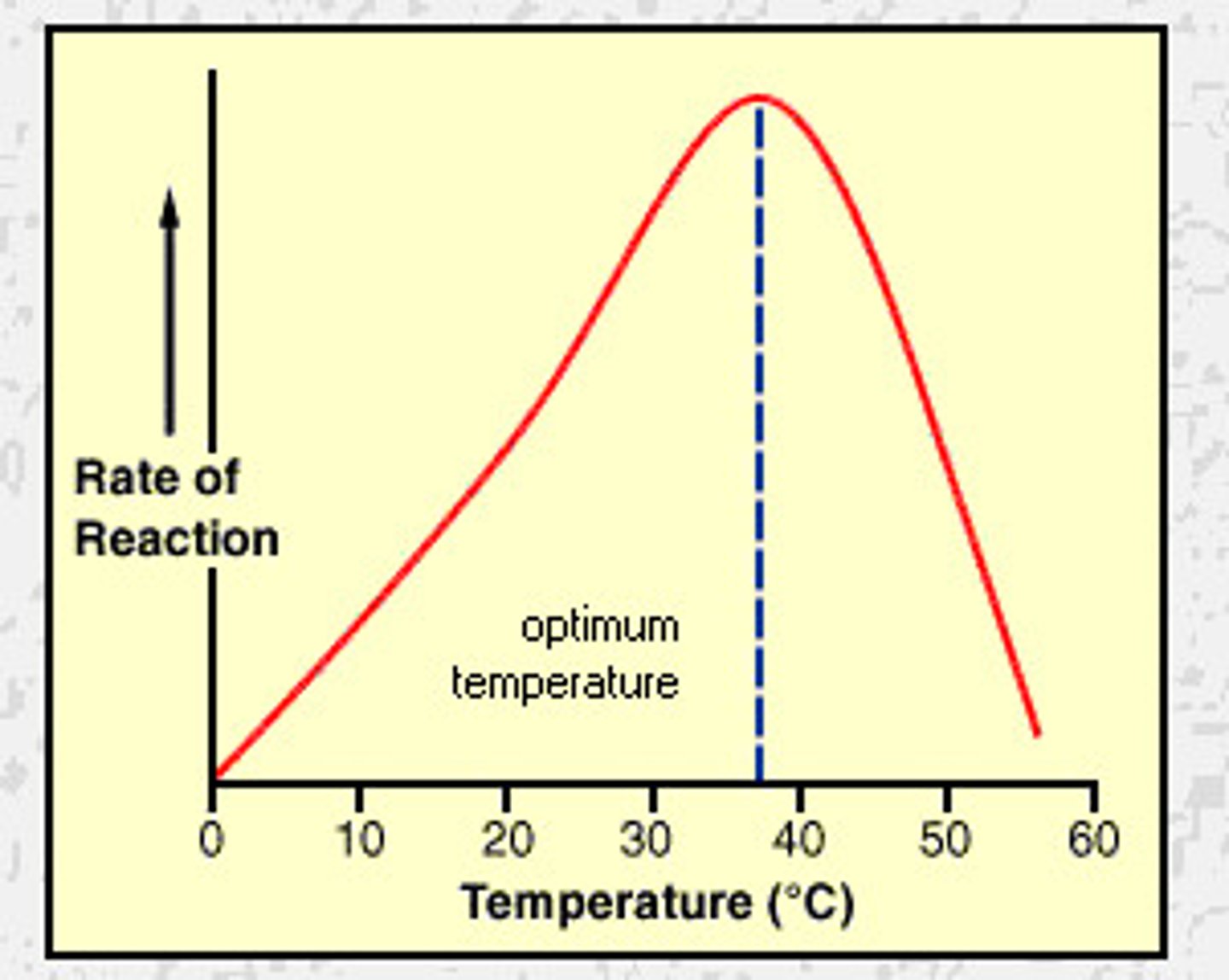
Effect of pH on enzyme activity
Enzyme activity decreases as pH alters from the optimum. Charge on R groups of AA are altered and ionic bonds in tertiary structure are broken. Active site changes, substrate no longer fits. No esc form. ROR decreases either side of the optimum and enzyme is denatured.

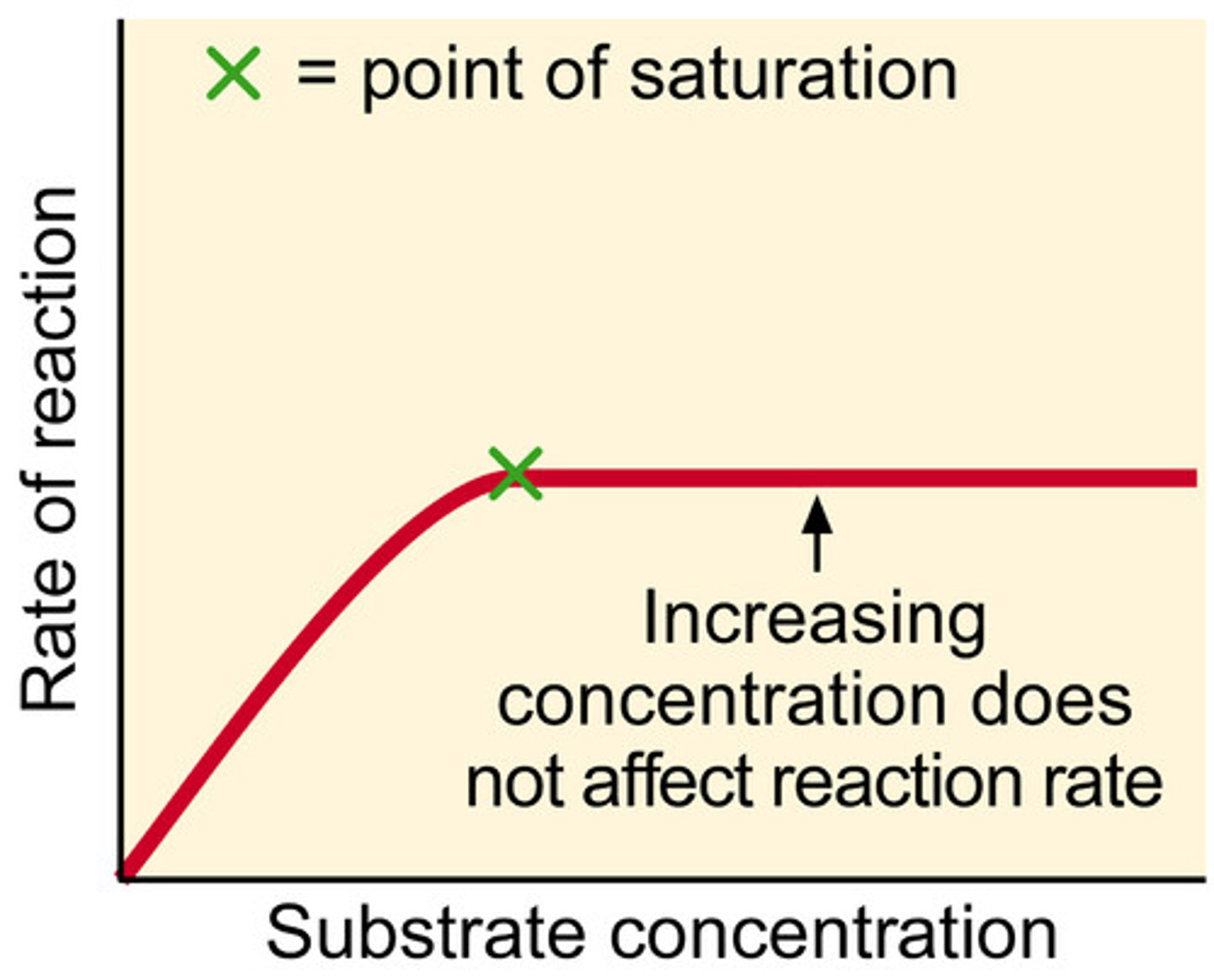
Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity
describe; as substrate conc inc, ROR inc, then levels off.
explain; ROR is low at low sub conc as not all of active sites are filled - limiting factor.
as sub conc inc, active sites are filled and ROR inc, due to more successful collisions. sun conc no longer a limiting factor.
at high levels of substrate, no rise in ROR as all active sites filled so no more esc till free. No. enzymes now limiting factor.
Graph of competitive inhibitor
Graph of non-competitive inhibitor
Immobilised enzymes
enzymes that are attached to an inert support system over which the substrate passes and is converted to the product
problems of commercially used enzymes
water soluble so hard to recover
some products can inhibit the enzyme activity (feedback inhibition)
Advantages of immobilised enzymes
-enzyme is easily removed
-can be packed into columns and used over a long period
-speedy separation of products reduces feedback inhibition
-thermal stability is increased allowing higher temps to be used
-^ increased ROR